Submitted:
04 December 2025
Posted:
05 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
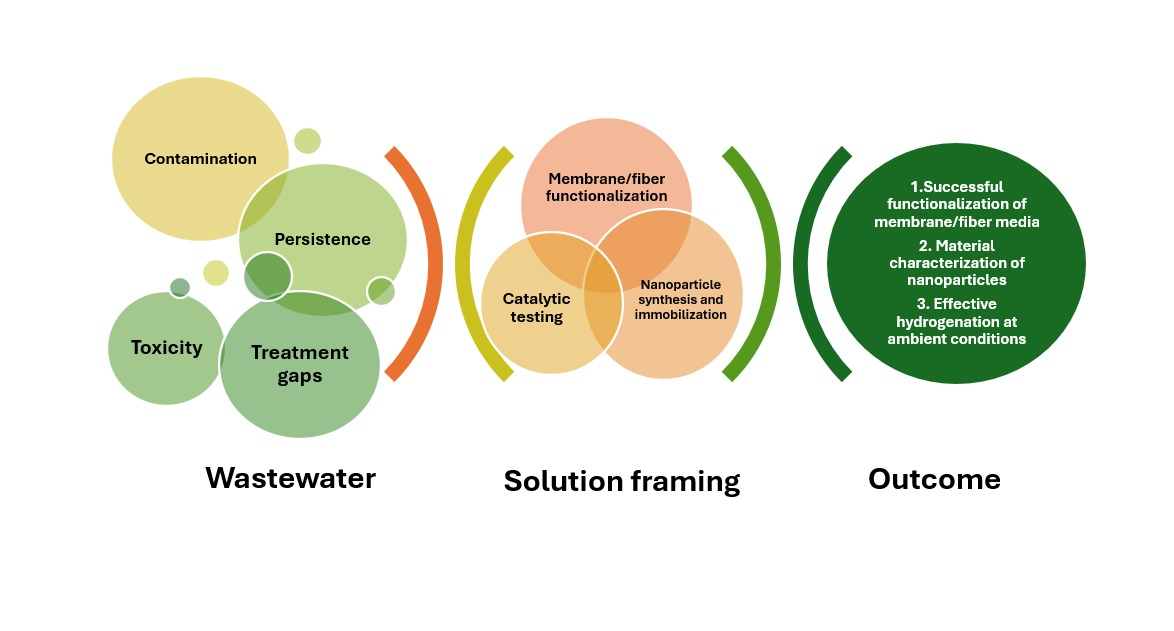
1. Introduction
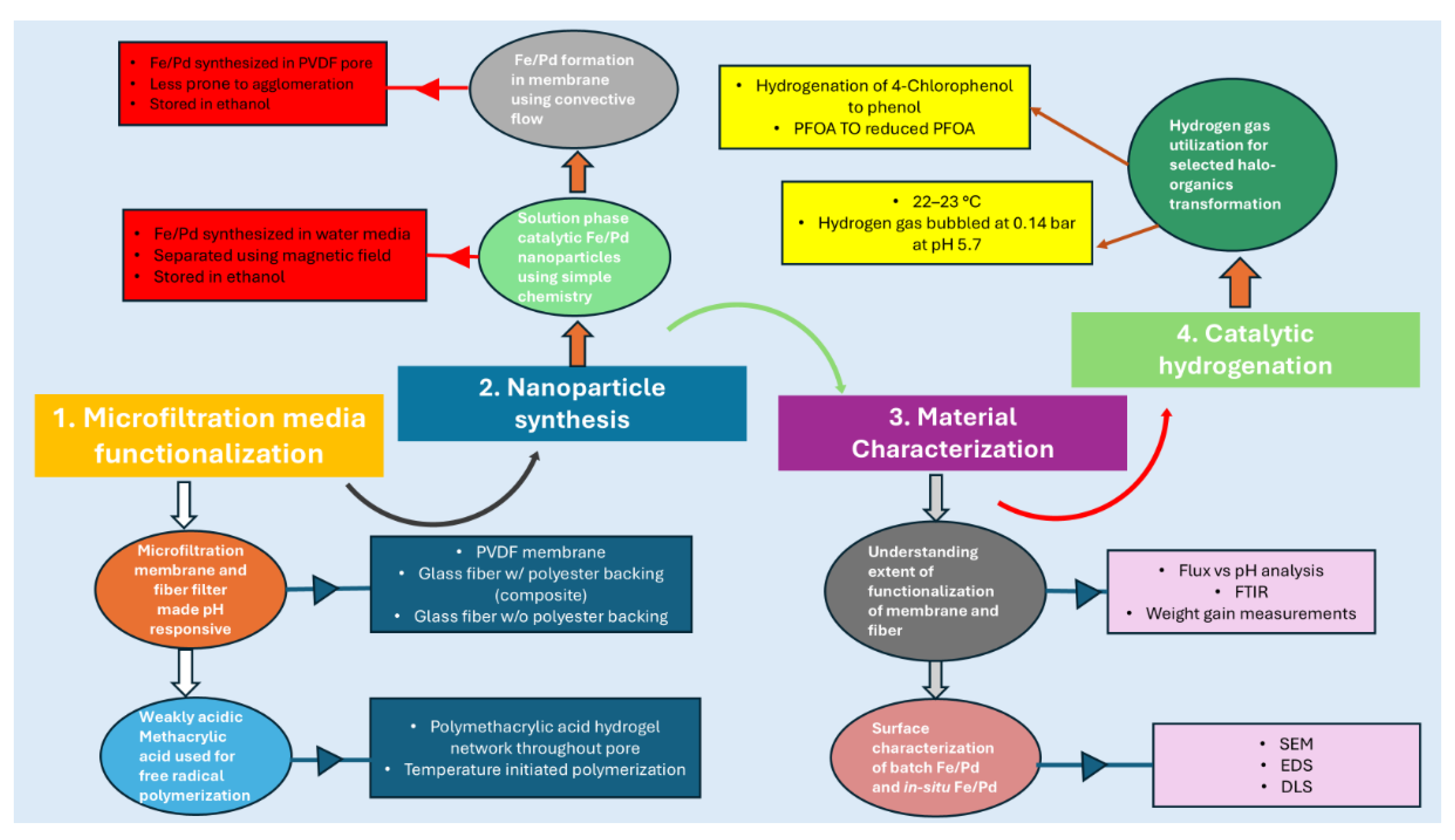
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Functionalization of PVDF Membranes and Fiber Filters
| Microfiltration Media | Functionalization | Catalyst Incorporation |
|---|---|---|
|
PMAA-PVDF650 | Fe/Pd PMAA-PVDF 650 |
|
PMAA-Fiber media
|
Not incorporated |
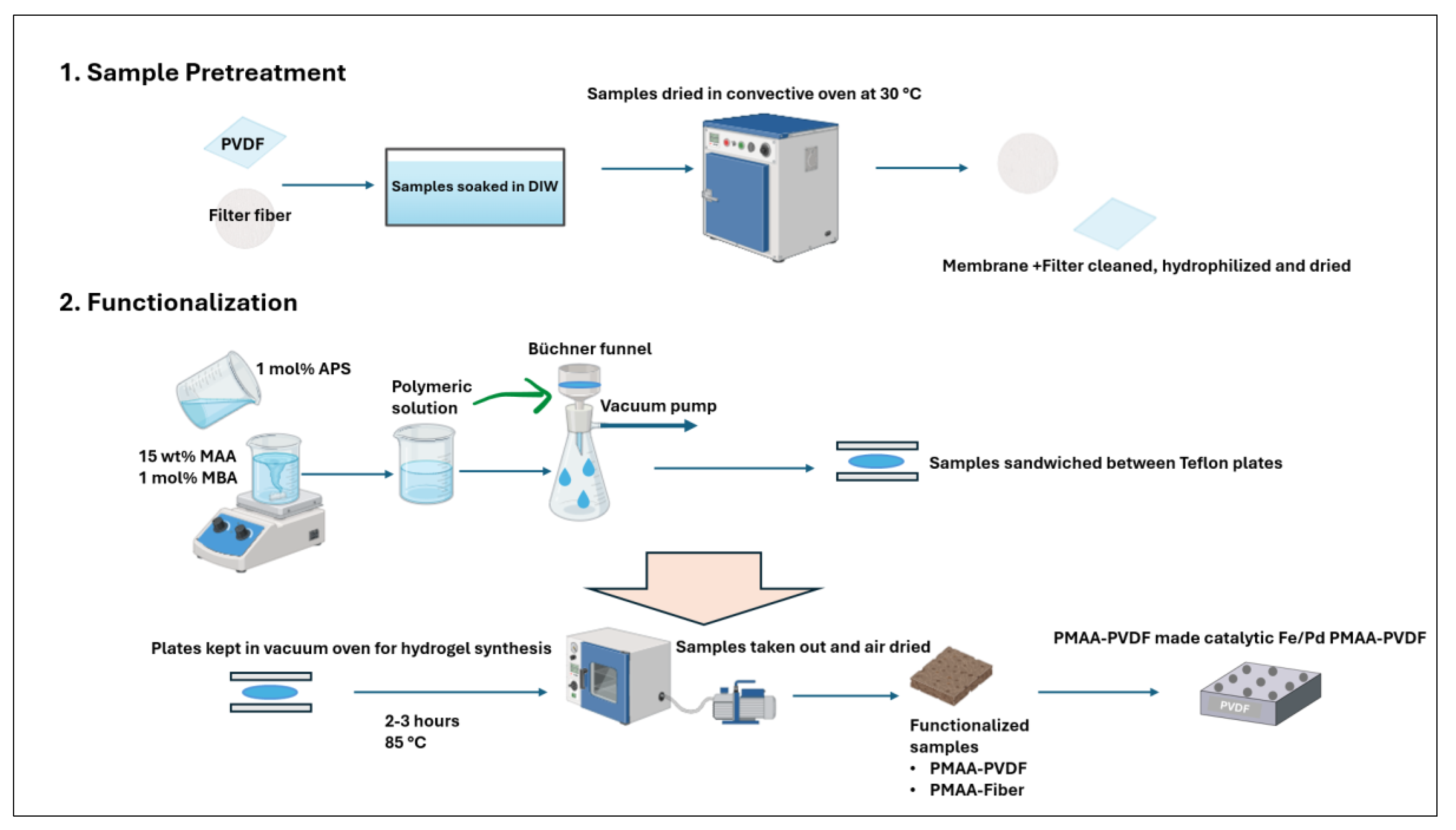
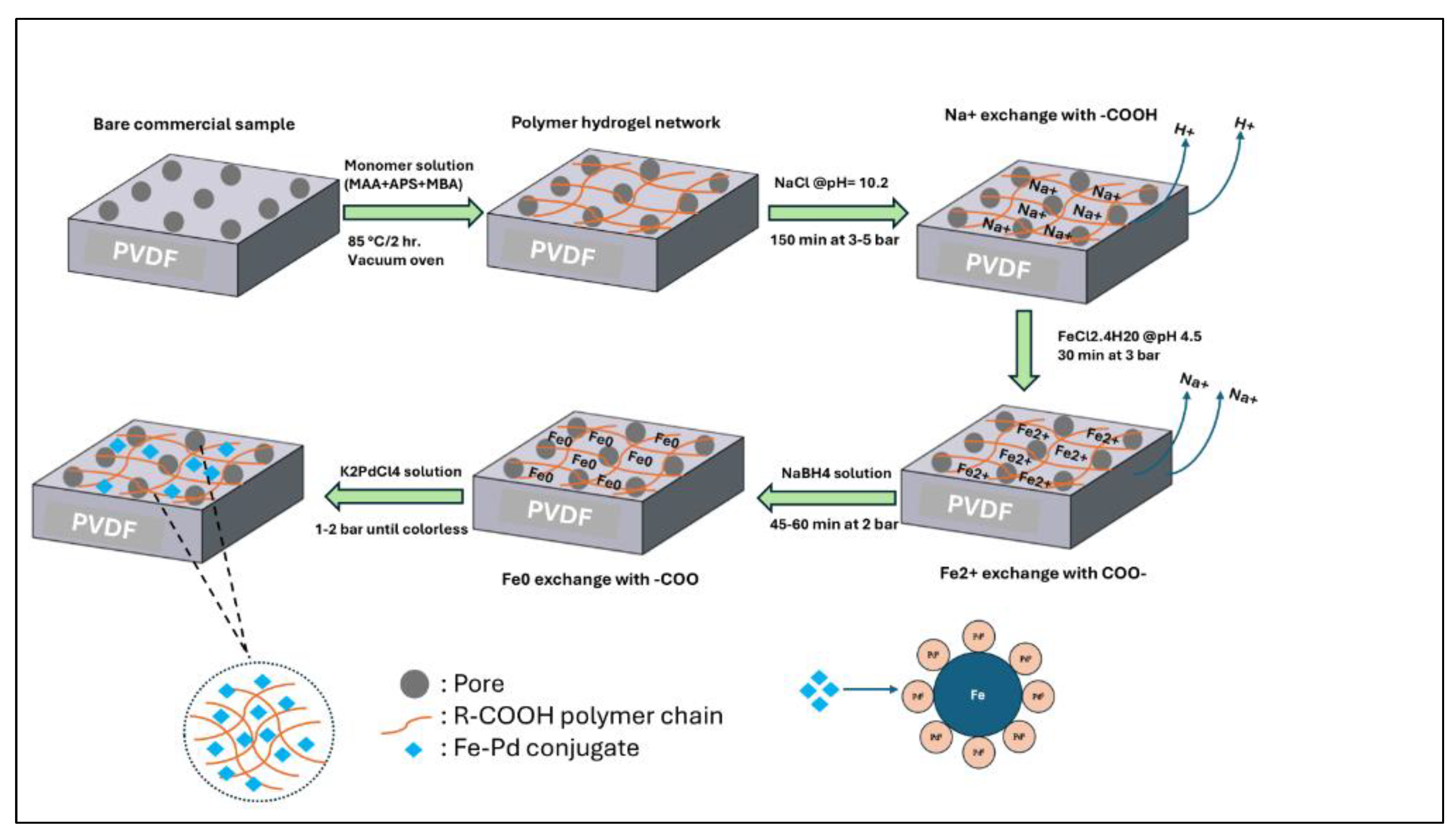
2.3. Synthesis of Fe/Pd Nanoparticles in Pore of PVDF Membranes
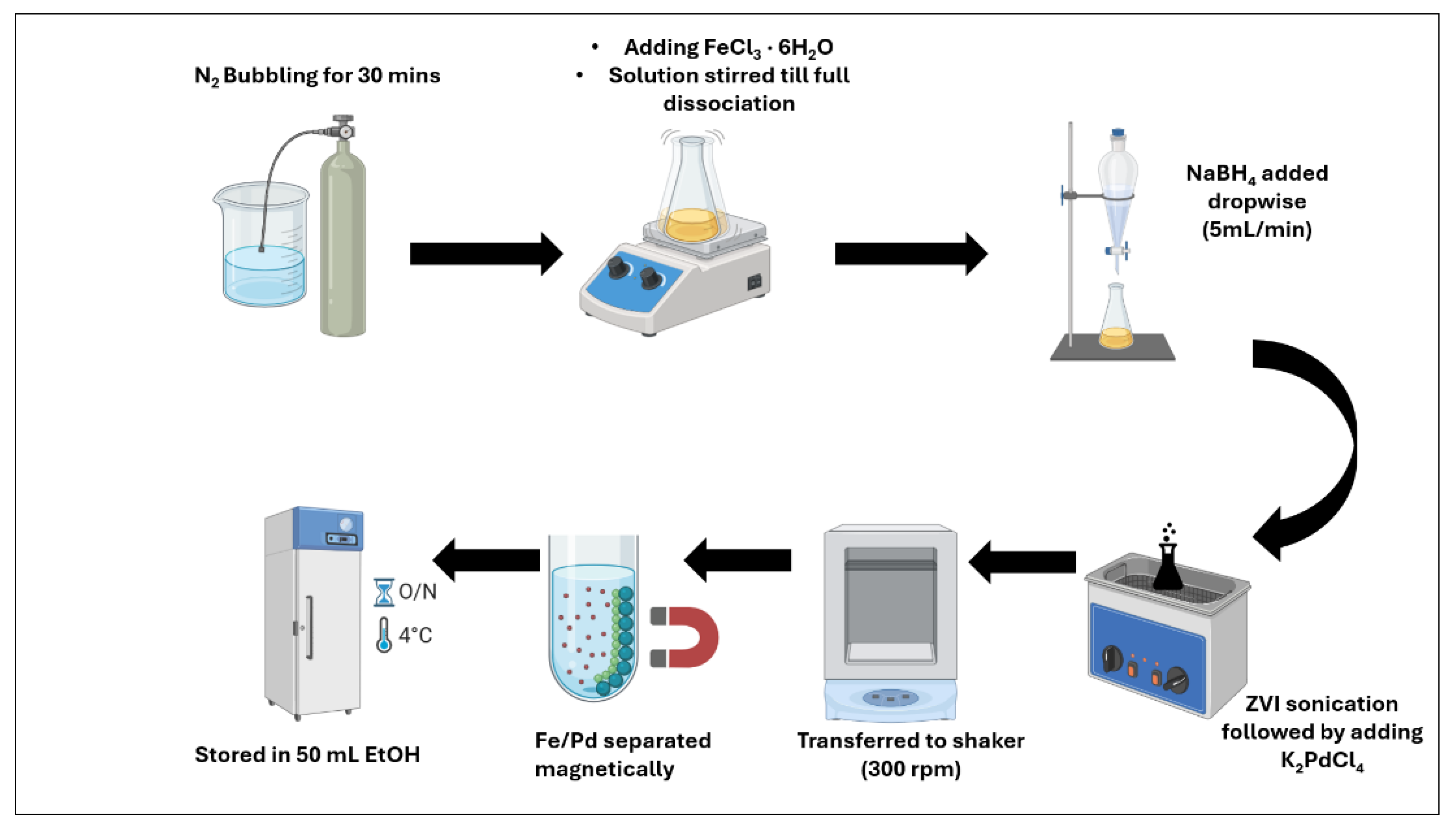
2.4. Synthesis of Fe/Pd Nanoparticles in Solution Phase
2.5. Material Characterization
2.5.1. Membrane and Filter Topography Analysis
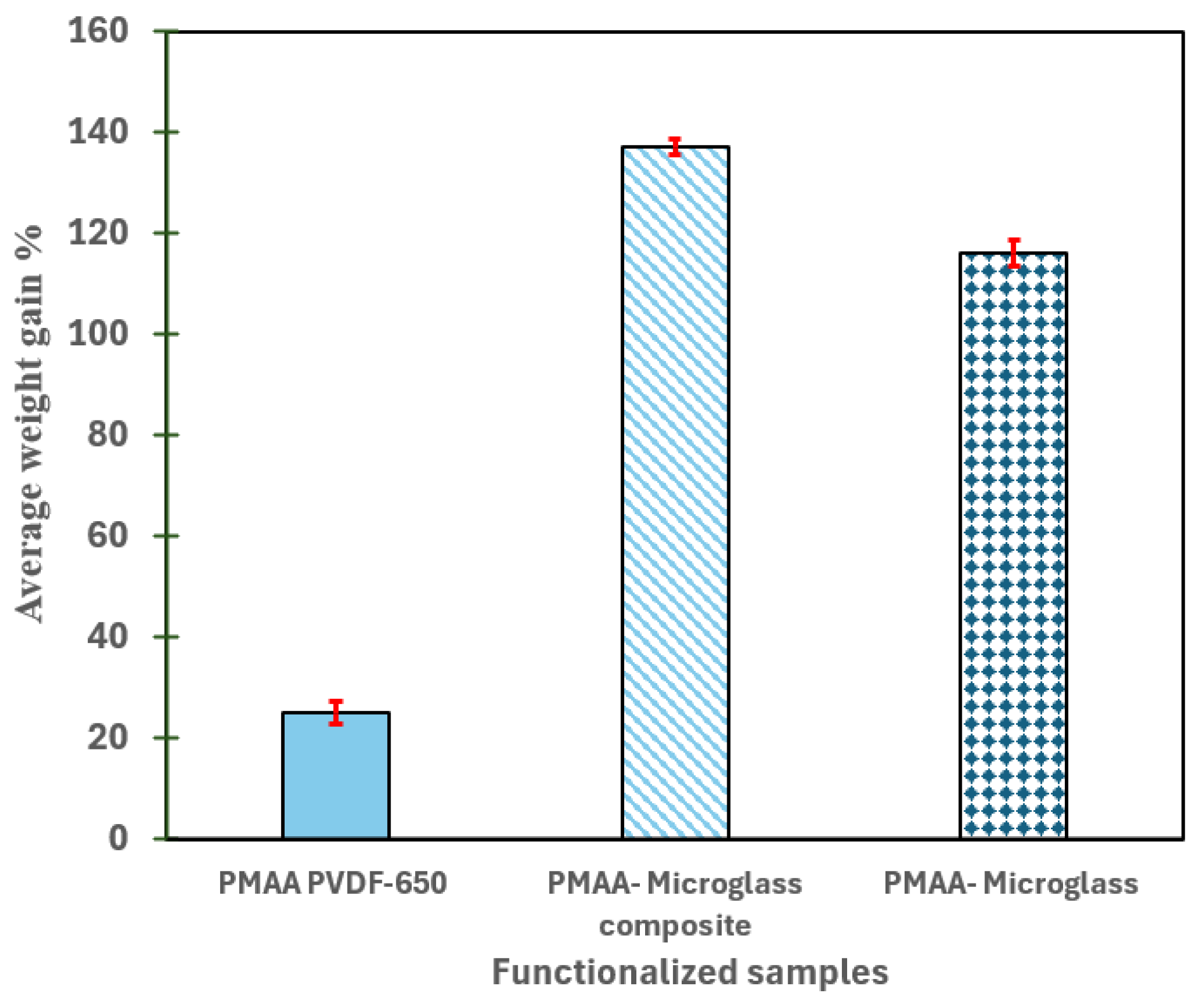
2.5.1. Weight Gain Measurements
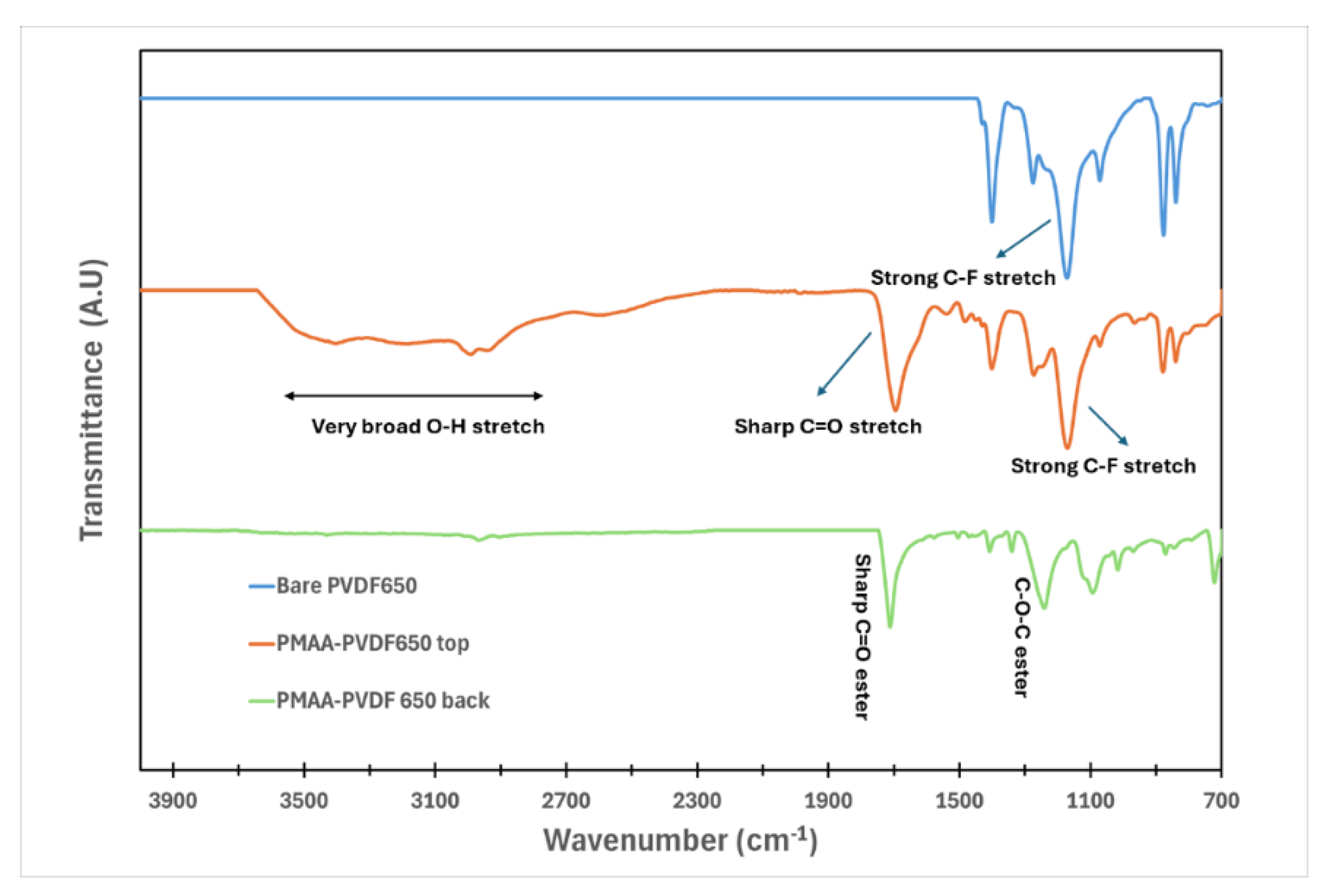
2.5.2. PMAA Incorporation onto Membranes
2.5.3. Characterization of Fe/Pd Catalytic Nanoparticles in Solution Phase
2.5.4. Morphology and Composition of Fe/Pd Nanoparticles Within the Membrane
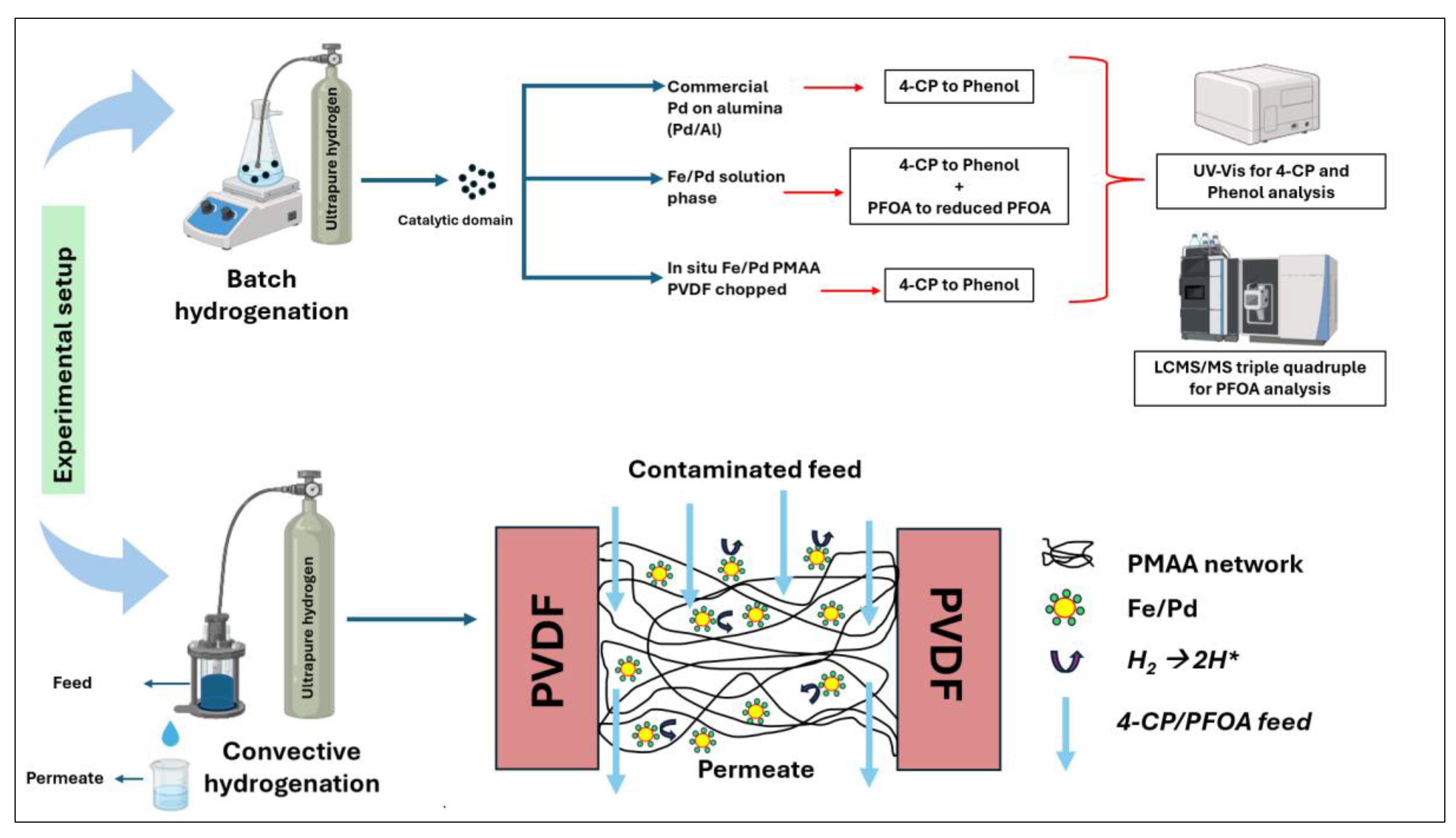
2.6. PFOA and 4-Chlorophenol (4-CP) Hydrogenation
3. Results
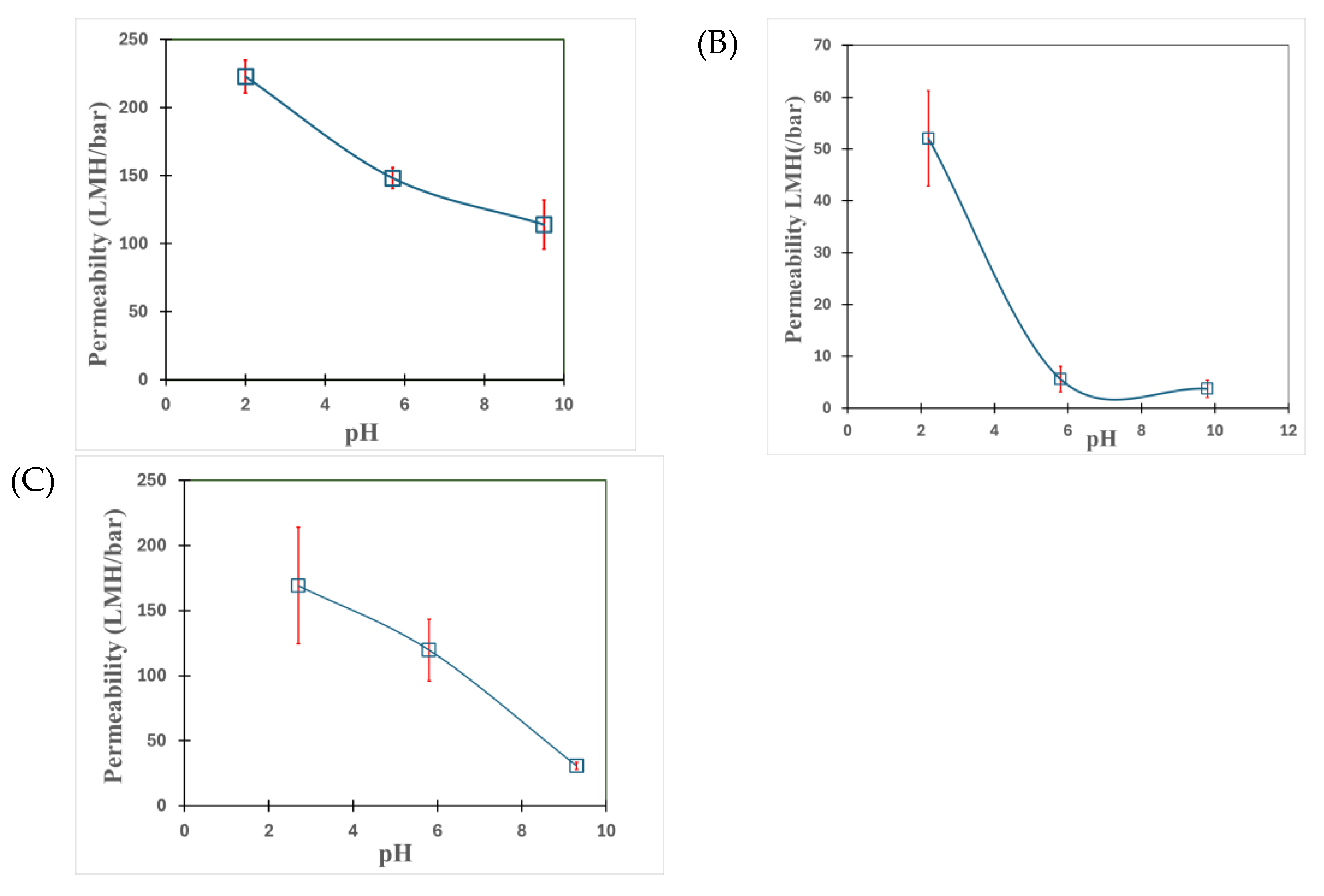
3.1. Understanding the Extent of Functionalization of Microfiltration Membrane and Fiber Media
3.2. Solution Phase Nanoparticles
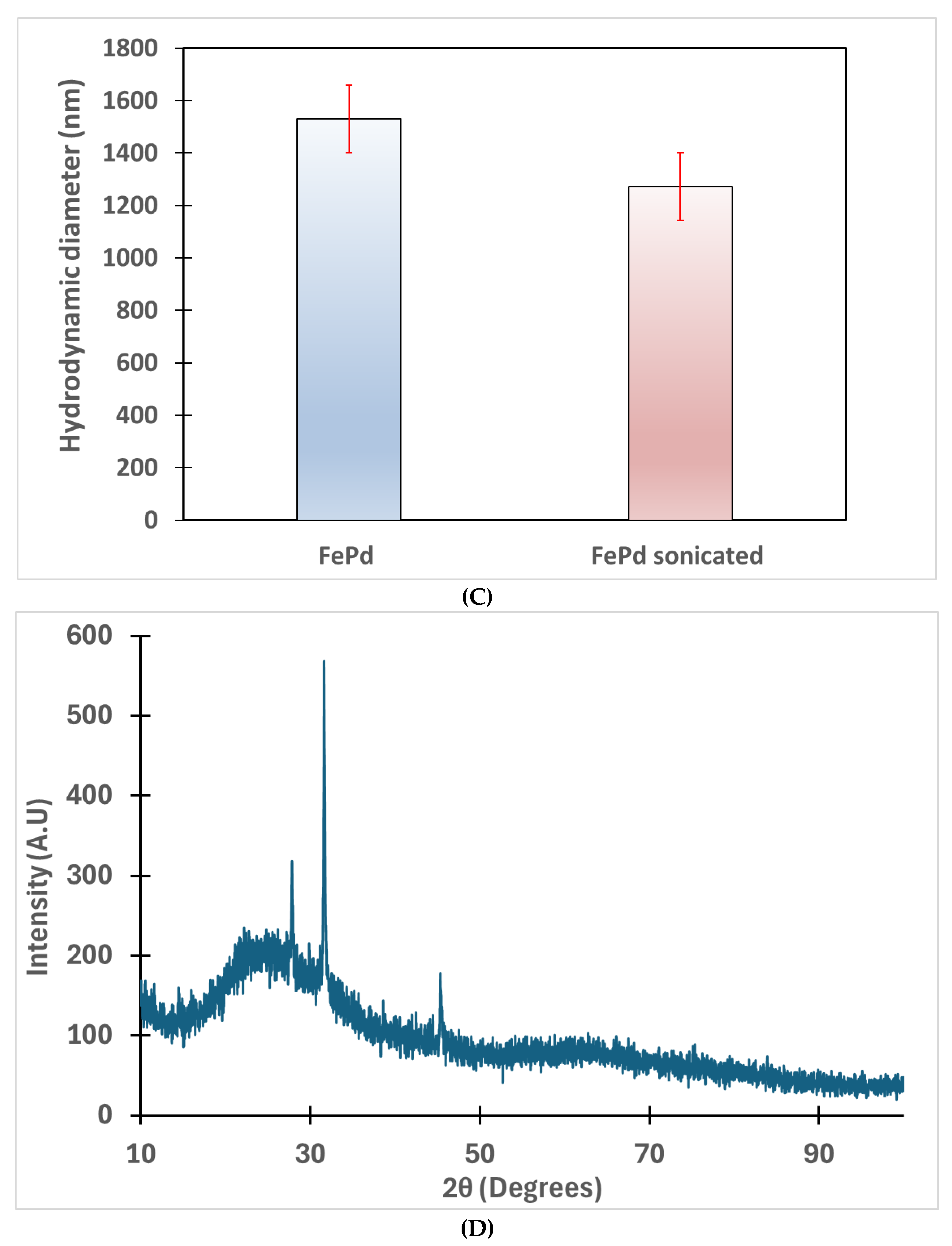
3.3. Fe/Pd In-Situ Nanoparticles Within Microfiltration Membrane Domain
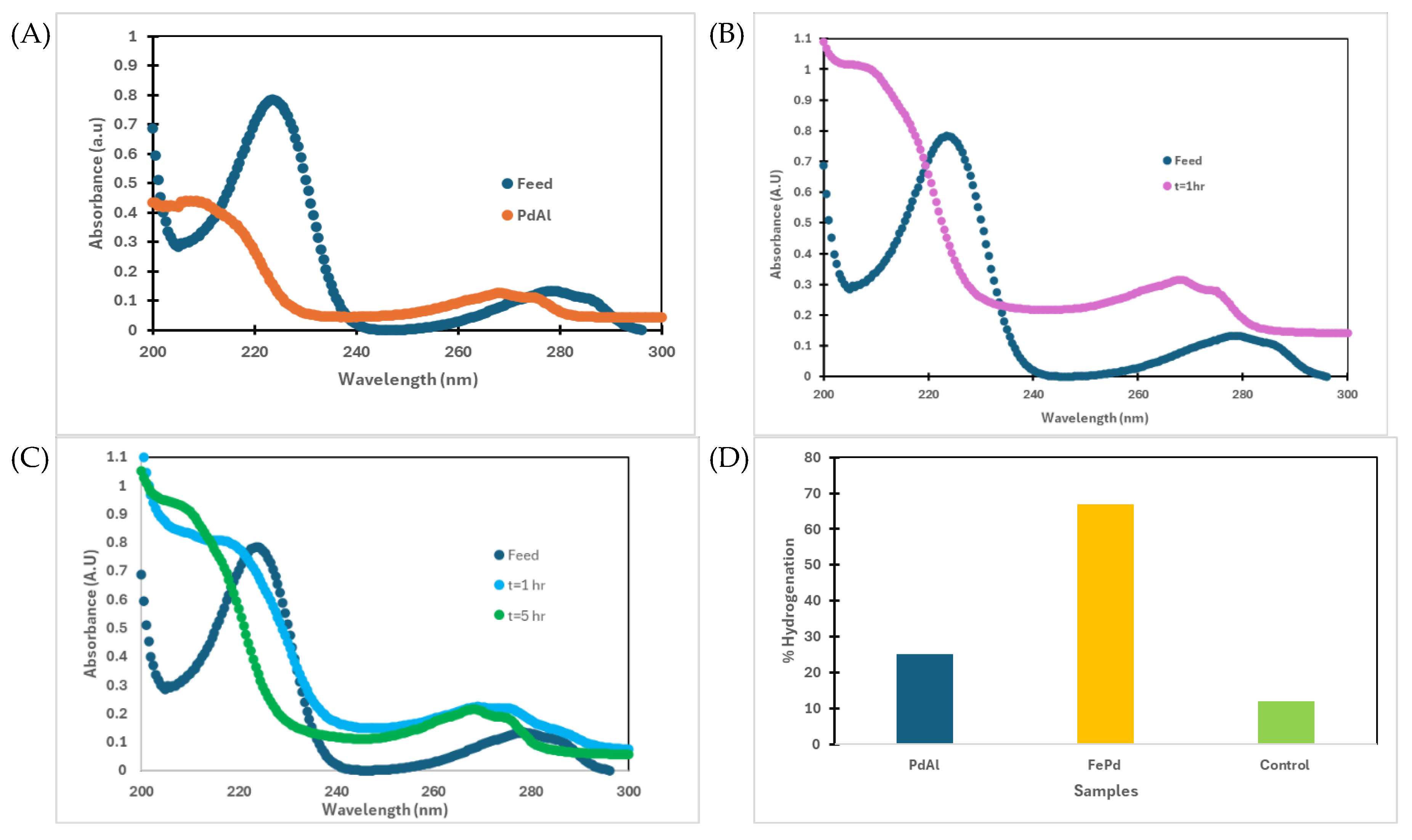
3.4. Halo Organics Degradation Studies in Batch and Convective Flow Mode
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| PFAS | Per/Polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFOA | Perfluoro-octanoic acid |
| PFOS | Perfluoro-octane sulfonic acid |
| PMAA | Poly methacrylic acid |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PE | Polyester |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EDX | Energy dispersive spectroscopy |
| FT-IR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| TCE | Trichloroethylene |
| PCB | Polychlorinated biphenyl |
References
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; Balaram, V.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Lu, Z.; Crini, G. Worldwide cases of water pollution by emerging contaminants: A re-view. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2311–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, V.; Ullberg, M.; McCleaf, P.; Wålinder, M.; Köhler, S.J.; Ahrens, L. The Price of Really Clean Water: Combining Nanofiltration with Granular Activated Carbon and Anion Exchange Resins for the Removal of Per- And Polyfluoralkyl Substances (PFASs) in Drinking Water Production. ACS ES&T Water 2021, 1, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, R.A.; Mullin, E.J.; Spink, D.C. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Analytical Techniques, Environmental Fate, and Health Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyllenhammar, I.; Benskin, J.P.; Sandblom, O.; Berger, U.; Ahrens, L.; Lignell, S.; Wiberg, K.; Glynn, A. Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) in Children’s Serum and Contribution from PFAA-Contaminated Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11447–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, M.; Capozzi, S.L.; Miller, P.; McLaughlin, K.R.; Medina, S.S.; Byrne, S.; Zheng, G.; Salamova, A. PFAS in drinking water and serum of the people of a southeast Alaska community: A pilot study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelsen, M.; Weber, R.; Panglisch, S. Minimizing the environmental impact of PFAS by using specialized coagulants for the treatment of PFAS polluted waters and for the decontamination of firefighting equipment. Emerg. Contam. 2021, 7, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadik, A.; Akintunde, O.O.; Habibi, H.R.; Achari, G. PFAS in water environments: Recent progress and challenges in monitoring, toxicity, treatment technologies, and post-treatment toxicity. Environ. Syst. Res. 2025, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances-pfas.
- Abdelsamad, A.M.; Saeidi, N.; Mackenzie, K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for rapid removal of PFOA: Impact of surface functional groups on adsorption efficiency and adsorbent regeneration. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aedan, Y.; Altaee, A.; Shon, H.K. Performance of pressure stimuli-responsive nanofiltration and cellulose acetate forward osmosis membranes for PFOA contaminated wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yu, J.; Yuan, J.; Lu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, A.; Xiao, W.; Tang, L. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment and their removal by advanced oxidation processes. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2025, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, F.L.; Stoica, C.; Iftode, C.; Pirvu, F.; Petre, V.A.; Paun, I.; Pascu, L.F.; Vasile, G.G.; Nita-Lazar, M. Bacterial Biodegradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorosulfonic Acid (PFOS) Using Pure Pseudomonas Strains. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ruiz, B.; Ribao, P.; Diban, N.; Rivero, M.J.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) using a composite TiO2-rGO catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 344, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, A.L.; Juve, J.-M.A.; Bai, L.; Christensen, C.S.Q.; Ahrens, L.; Cousins, I.T.; Ateia, M.; Wei, Z. Best Practices for Experimental Design, Testing, and Reporting of Aqueous PFAS-Degrading Technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 8939–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninayake, D.M. Comparison of currently available PFAS remediation technologies in water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugbe, E.O.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mehejabin, F.; Momtahin, A.; Tasannum, N.; Faria, N.T.; Mofijur, M.; Hoang, A.T.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Mahlia, T. Strategies to improve membrane performance in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Vogler, R.J.; Al Hasnine, S.M.A.; Hernández, S.; Malekzadeh, N.; Hoelen, T.P.; Hatakeyama, E.S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Mercury Removal from Wastewater Using Cysteamine Functionalized Membranes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22255–22267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman-Leach, M.; Bukowski, J.; Horn, E.; Thompson, S.; Chwatko, M.; Bhattacharyya, D. Tunable retention and recovery via pore-to-particle interactions in amine functionalized micro- and ultrafiltration Membranes: Towards scalable viral vector purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Yuan, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Polymeric nanocomposite membranes for water treatment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Pazirofteh, M.; Dehghani, M.; Asghari, M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Valderrama, C.; Cortina, J.-L. Application of ZnO nanostructures in ceramic and polymeric membranes for water and wastewater technologies: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The Future of Seawater Desalination: Energy, Technology, and the Environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, eaab0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, Z.Z.; Zaidi, N.S.; Syafiuddin, A.; Yong, E.L.; Boopathy, R.; Kueh, A.B.H.; Prastyo, D.D. Shifting from Conventional to Organic Filter Media in Wastewater Biofiltration Treatment: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Urban, M.W. Recent advances and challenges in designing stimuli-responsive polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Isner, A.; Waldrop, K.; Saad, A.; Takigawa, D.; Bhattacharyya, D. Development of bench and full-scale temperature and pH responsive functionalized PVDF membranes with tunable properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 457, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hernández, S.; Wan, H.; Ormsbee, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Role of membrane pore polymerization conditions for pH responsive behavior, catalytic metal nanoparticle synthesis, and PCB degradation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Mills, R.; Wan, H.; Ormsbee, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Thermoresponsive PNIPAm–PMMA-Functionalized PVDF Membranes with Reactive Fe–Pd Nanoparticles for PCB Degradation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 16614–16625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, A.C.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Z. Water treatment via non-membrane inorganic nanoparticles/cellulose composites. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.-X.; Chen, Q.; Shao, R.-R.; Sun, H.-H.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, D.-H. Encapsulating lipase on the surface of magnetic ZIF-8 nanosphers with mesoporous SiO2 nano-membrane for enhancing catalytic performance. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mao, Z.; Qu, R.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Luo, X.; Shi, M.; Mao, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, B. Electrochemical hydrogenation of oxidized contaminants for water purification without supporting electrolyte. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Tang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Jin, Z.; Li, P.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, H.; Yu, G. Intermetallic Single-Atom Alloy In–Pd Bimetallene for Neutral Electrosynthesis of Ammonia from Nitrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 13957–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Sun, J.-F.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Jiang, G. Critical Review of Pd-Catalyzed Reduction Process for Treatment of Waterborne Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3079–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Electrocatalytic hydro-dehalogenation of halogenated organic pollutants from wastewater: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P.; Reinhard, M.; Schneider, W.F.; Schüth, C.; Shapley, J.R.; Strathmann, T.J.; Werth, C.J. Critical Review of Pd-Based Catalytic Treatment of Priority Contaminants in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3655–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.; Takahashi, H.; Morikawa, M. Organic syntheses by means of noble metal compounds XVII. Reaction of π-allylpalladium chloride with nucleophiles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1965, 6, 4387–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, X.; Yao, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.-H. Porous carbon-confined palladium nanoclusters for selective dehydrogenation of formic acid and hexavalent chromium reduction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 104, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.M.; Rusho, M.A.; Muniyandy, E.; Diab, M.; Abilkasimov, A.; Madaminov, B.; Atamuratova, Z.; Smerat, A.; Issa, S.K.; Arabi, A.I.A.; et al. Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles facilitated by Artemisia absinthium extract as an effective nanocatalyst for Heck–Mizoroki coupling reactions. J. Organomet. Chem. 2025, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.; Gutierrez, A.M.; Bukowski, J.; Bhattacharyya, D. Microfiltration Membrane Pore Functionalization with Primary and Quaternary Amines for PFAS Remediation: Capture, Regeneration, and Reuse. Molecules 2024, 29, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, M.E.; Thum, M.D.; Weise, N.K.; Daniels, G.C. PFAS removal from water using quaternary amine functionalized porous polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Joseph, S.; Aluru, N.R. Effect of Cross-Linking on the Diffusion of Water, Ions, and Small Molecules in Hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Islam, S.; Briot, N.J.; Schnobrich, M.; Pacholik, L.; Ormsbee, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Pd/Fe nanoparticle integrated PMAA-PVDF membranes for chloro-organic remediation from synthetic and site groundwater. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koto, N.; Soegijono, B. Effect of Rice Husk Ash Filler of Resistance Against of High-Speed Projectile Impact on Polyester-Fiberglass Double Panel Composites. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1191, 012058. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, C.; Liang, S.; Chu, L.-Y.; Crittenden, J. PVDF blended PVDF-g-PMAA pH-responsive membrane: Effect of additives and solvents on membrane properties and performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, B.; Zhu, X. High-Flux pH-Responsive Ultrafiltration Membrane for Efficient Nanoparticle Fractionation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56575–56583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, J.; Ademovic, Z.; Ameringer, T.; Klee, D.; Moeller, M. Comparison of Coatings from Reactive Star Shaped PEG-stat-PPG Prepolymers and Grafted Linear PEG for Biological and Medical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalousha, M.; Manciulea, A.; Cumberland, S.; Kendall, K.; Lead, J.R. Aggregation and surface properties of iron oxide nanoparticles: Influence of ph and natural organic matter. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, D.; Ori, G. Reversible assembly of nanoparticles: Theory, strategies and computational simulations. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 14385–14432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Briot, N.J.; Saad, A.; Ormsbee, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Pore functionalized PVDF membranes with in-situ synthesized metal nanoparticles: Material characterization, and toxic organic degradation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, N.D.; Smuleac, V.; Stevens, C.; Bhattacharyya, D. Iron-Based Nanoparticles for Toxic Organic Degradation: Silica Platform and Green Synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 9581–9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detisch, M.J.; Balk, T.J.; Bezold, M.; Bhattacharyya, D. Nanoporous metal–polymer composite membranes for organics separations and catalysis. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 2629–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, J.; Sultan, M.A.; Sarma, R.; Wilson, S.; Meeks, N.; Kim, D.Y.; Hastings, J.T.; Bhattacharyya, D. Rhodopseudomonas palustris-based conversion of organic acids to hydrogen using plasmonic nanoparticles and near-infrared light. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41218–41227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Sultan, M.A.; Kim, D.Y.; Meeks, N.; Hastings, J.T.; Bhattacharyya, D. Effect of silica-core gold-shell nanoparticles on the kinetics of biohydrogen production and pollutant hydrogenation via organic acid photofermentation over enhanced near-infrared illumination. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 7821–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Elias, W.C.; Heck, K.N.; Luo, Y.-H.; Lai, Y.S.; Jin, Y.; Gu, H.; Donoso, J.; Senftle, T.P.; Zhou, C. Hydrodefluorination of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in the H2-Based Membrane Catalyst-Film Reactor with Platinum Group Metal Nanoparticles: Pathways and Optimal Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16699–16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





