Submitted:
01 December 2025
Posted:
01 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
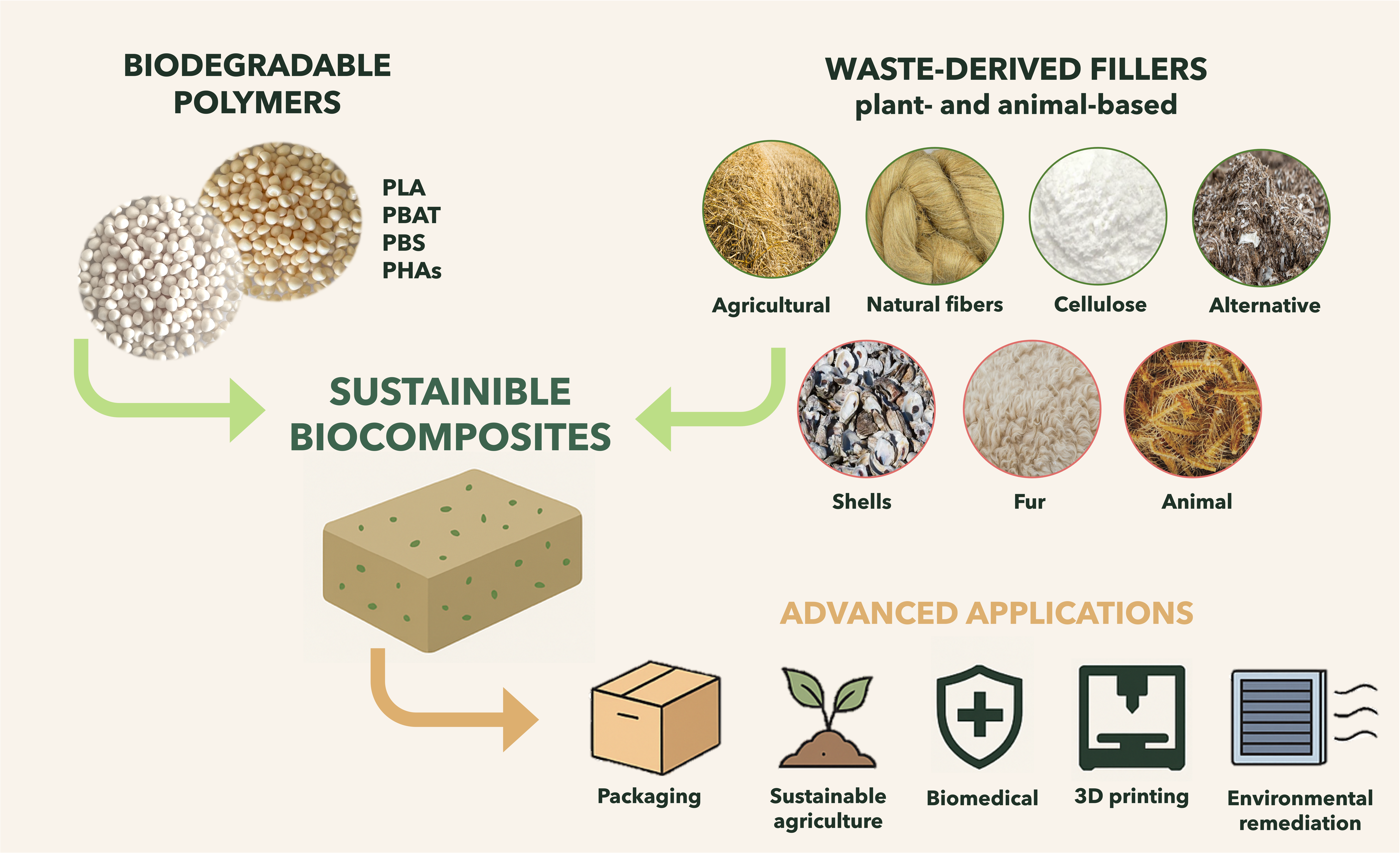
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Objective of the Review
- the types, characteristics, and pretreatments of natural fillers;
- the processing strategies employed across different polymer matrices;
- the resulting mechanical, thermal, morphological, functional, and degradation properties;
- the main applications and end-of-life scenarios;
- current challenges, limitations, and future research directions.
2. Biodegradable Polymeric Matrices for Biocomposites Production
3. Natural Waste Fillers in Biocomposites
3.1. Plant-Derived Organic Waste
3.1.1. Agricultural and Agrifood Waste
3.1.2. Natural Fibers
| Matrix | Filler | Sample Code | Area |
Type (*) |
Diameter [um] |
Length [mm] |
Density [g/cm3] |
Other Treatments |
Additive | Ref. |
| PLA | Abutilon indicum |
PLA/AI | Asia | D` | - | 2.5 | - | - | - | [96] |
| PLA | Agave |
PLA/AF | South America | - | - | - | - | - | - | [97] |
| PLA | Bamboo | PLA/BF | Asia | D | - | 2−6 | - | Chemical | - | [98] |
| PLA | Bamboo | PLA/BF | Asia | D | - | 2−6 | - | Chemical | - | [99] |
| PLA | Corn stalk | PLA/CS | Europe | D | - | 1−4 | - | - | - | [100] |
| PLA | Elephant grass | PLA/EG | Asia | D | 250 | 3 | - | Mercerization and Bleaching | - | [101] |
| PLA | Flax | PLA/CFY | Asia | C | 400 | 20 | - | - | - | [102] |
| PLA | Flax | PLA/Flax | Europe | D | - | - | - | - | - | [103] |
| PLA | Flax | PLA/FS | Europe | C | - | - | 1.47 | - | - | [104] |
| PLA | Flax | PLA/FS | Europe | D | 300−600 | 2−5 | - | - | Plasticizer | [105] |
| PLA | Hemp shives | PLA/HS | Europe | D | - | < 1 | 1.51 | - | - | [106] |
| PLA | Himalaya calamus falconeri |
PLA/THF | Asia | D | - | 3−5 | - | Mechanical extraction | - | [107] |
| PLA | Jute | PLA/Jute | Europe | D | - | - | - | - | - | [103] |
| PLA | Kenaf | PLA/KF | Asia | D | 250 | - | - | - | - | [108] |
| PLA | Kenaf | PLA/KF | Asia | D | 70−250 | - | - | - | - | [109] |
| PLA | Kenaf | PLA/KFA | Asia | D | - | - | - | Acetylation | Acetic anhydride |
[110] |
| PLA | Kenaf | PLA/LK | Asia | C | - | 175 | - | - | - | [111] |
| PLA | Kenaf (woven) |
PLA/WK | Asia | D | - | - | - | - | - | [112] |
| PLA | Pennisetum setaceum |
PLA/PS | Europe | D | 75 | 1−2 | - | - | - | [113] |
| PLA | Sisal | PLA/SF | Asia | D | - | 3−6 | 1,24 | Pretreatment | - | [114] |
| PLA | Sisal | PLA/SF | Asia | D | - | 3−8 | - | - | - | [115] |
| PLA | Sisal | PLA/SF | Africa | D | 239 | - | - | - | - | [116] |
| PLA | Sisal | PLA/MS | Africa | D | 239 | - | 1.42 | - | - | [117] |
| PCL | Date palm | PCL/DP | Asia | D | - | 10 | 0.9−1.2 | - | - | [118] |
| PCL | Hemp | PCL/HF | Europe | D | 22 | < 1 | - | - | - | [119] |
| PCL | Phoenix dactylifera L. |
PCL/DP | Asia | D | - | 10 | 0.92 | - | - | [120] |
| PBS | Curaua | PBS/C | South America | D | - | 10−40 | - | - | - | [121] |
| PBS | Hemp | PBS/HF | Europe | D | - | 30 | - | - | - | [122] |
| PHA | Pineapple leaf |
PHA/PLF | Asia | D | 300−450 | - | - | - | - | [81] |
| PHB | Sisal | PHB/SF | Asia | D | - | - | - | - | - | [123] |
| PHBV | Alfa | PHBV/AF | Africa | D | - | - | - | Chemical | - | [124] |
| PBAT | Croton lanjouwensis |
PBAT/CF | South America | D | - | - | 1.5 | - | - | [125] |
| PBAT | Malvastrum tomentosum | PBAT/MF | South America | D | - | - | 1.5 | - | - | [125] |
| PBAT | Trema micrantha |
PBAT/TF | South America | D | - | - | 1.5 | - | - | [125] |
| PBAT | Cannabis sativa |
PBAT/CS | Europe | D | < 32 | - | - | - | - | [126] |
| PBAT | Hemp | PBAT/HF | Asia | D | - | - | - | Surface alkylation |
Silane coupling agent |
[127] |
| PBAT | Kenaf | PBAT/KF | Asia | D | - | 1−5 | - | - | - | [128] |
| PBAT | Linum | PBAT/F | Europe | D | 1 | - | - | - | [129] | |
| Mater-Bi® | Agave | MB/AF | South America | D | - | 4−6 | - | - | - | [130] |

3.1.3. Cellulose and Derivatives
3.1.4. Alternative Plant-Derived Waste
3.2. Animal-Derived Waste
| Matrix | Filler | Sample Code | Area | Mechanical Treatment | Drying Temp. [°C] | Drying Time [h] |
Other Treatments |
Ref. |
| PLA | Eggshell | PLA/WE | N. America | Ground | 80 | 4 | - | [154] |
| PLA | Eggshell | PLA/ESP | Asia | Ground | - | - | - | [155] |
| PLA | Eggshell | PLA/WES | N. America | Ground | - | - | - | [156] |
| PLA | Fish gelatin | PLA/FG | Europe | - | 80 | 12 | [157] | |
| PLA | P. undulata shell | PLA/PUS | Asia | Ground | 100 / 60 | 24 / 48 | Calcination | [158] |
| PLA | Crab shells | PLA/CSP | Asia | Ground | 60 | 12 | HCl, NaOH | [159] |
| PLA | Anchovy fish bone | PLA/EE | Europe | Ground | 60 | 12 | - | [160] |
| PLA | Wool | PLA/WP | Europe | Ground | 60 | 12 | - | [161] |
| PHA | Oyster shell | PHA/OSP | Asia | Ground | - | - | - | [81] |
| Mater-Bi® | Anchovy fish bone | MB/EE | Europe | Ground | 60 | 12 | - | [160] |
4. Processing, Properties Application and End of Life of the Natural Waste Based Biocomposites
4.1. Plant-Derived Organic Waste
4.1.1. Agricultural and Agrifood Waste
4.1.2. Natural Fibers
4.1.3. Cellulose and Derivatives
4.1.4. Alternative Organic Waste
4.2. Animal-Derived Organic Waste
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N. The Past, Present, and Future of Plastic Pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A. Plastic Pollution: When Do We Know Enough? J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, M.; Alam, I.; Mahbub, M.S. Plastic Pollution during COVID-19: Plastic Waste Directives and Its Long-Term Impact on the Environment. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastics the Fast Facts 2025 • Plastics Europe. Plast. Eur.
- Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Challenges and New Opportunities on Barrier Performance of Biodegradable Polymers for Sustainable Packaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 117, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaev, R.; Papež, N.; Allaham, M.M.; Holcman, V. Biodegradable Polymers: Properties, Applications, and Environmental Impact. Polymers 2025, 17, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olonisakin, K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Thimmanagari, M.; Misra, M. Recent Advances in Biodegradable Polymer Blends and Their Biocomposites: A Comprehensive Review. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 11656–11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latos-Brozio, M.; Rułka, K.; Masek, A. Review of Bio-Fillers Dedicated to Polymer Compositions. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e202500406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Megna, B. Structure-Property Relationship of PLA-Opuntia Ficus Indica Biocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 167, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Pitarresi, G. Lignocellulosic Fillers and Graphene Nanoplatelets as Hybrid Reinforcement for Polylactic Acid: Effect on Mechanical Properties and Degradability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 190, 108008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Citarrella, M.C.; Morreale, M. Green Composites Based on Mater-Bi® and Solanum Lycopersicum Plant Waste for 3D Printing Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarrella, M.C.; Scaffaro, R. Sustainable and Reusable 3D Fibrous Structures Based on PLA and Biomass Wastes for FOG (Fat, Oil, Greases) Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Gammino, M.; Citarrella, M.C.; Scaffaro, R. Photochemical Degradation of PLA-Based Green Composites Containing Waste Biomass from Posidonia Oceanica, Chamaerops Humilis and Ailanthus Altissima: A Comparative Study. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 234, 111204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F. Hydrolytic Degradation of PLA/Posidonia Oceanica Green Composites: A Simple Model Based on Starting Morpho-Chemical Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 213, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antor, R.I.; Bithi, A.M.; Nahin, A.M. Variation in Mechanical Properties of Polymer Composites With Reinforcements From Different Animal Origins—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2025, 2025, 4184239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholokhova, A.; Varžinskas, V.; Rutkaitė, R. Valorization of Agro-Waste in Bio-Based and Biodegradable Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive Review with Emphasis on Europe Perspective. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 16, 1537–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, Z.; Girdhar, M.; Anand, A.; Kumari, N.; Sood, B.; Malik, T.; Kumar, A.; Mohan, A. Trash to Treasure: Advancing Resource Efficiency Using Waste-Derived Fillers as Sustainable Reinforcing Agents in Bioplastics. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Mahur, B.K.; Izrayeel, A.M.D.; Ahuja, A.; Rastogi, V.K. Biomass Conversion of Agricultural Waste Residues for Different Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 73622–73647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, M.; Uddin, M.H.; Tania, I.S. Biocomposites Based on Natural Fibers and Polymers: A Review on Properties and Potential Applications. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2022, 41, 705–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and Mechanical Properties of PLA, and Their Functions in Widespread Applications — A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polylactic Acid: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Elsevier, 2008; pp. 433–450.
- Södergård, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of Lactic Acid Based Polymers and Their Correlation with Composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Sacligil, D.; Carreau, P.J.; Kamal, M.R.; Heuzey, M.-C. Poly (Lactic Acid) Blends: Processing, Properties and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 307–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasprilla, A.J.R.; Martinez, G.A.R.; Lunelli, B.H.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly-Lactic Acid Synthesis for Application in Biomedical Devices — A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhvi, M.S.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Gokhale, D.V. Polylactic Acid: Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonchaeng, U.; Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Auras, R.; Selke, S.; Rubino, M.; Lim, L.-T. Poly(Lactic Acid) Mass Transfer Properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 85–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudane, J.; Nottelet, B.; Mouton, J.; Garric, X.; Van Den Berghe, H. Poly(ε-Caprolactone)-Based Graft Copolymers: Synthesis Methods and Applications in the Biomedical Field: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachan, R.; Warkar, S.G.; Purwar, R. An Overview on Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Polycaprolactone Copolymers, Blends & Composites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2023, 62, 327–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, E.H.; Harb, S.V.; Beatrice, C.A.G.; Shimomura, K.M.B.; Passador, F.R.; Costa, L.C.; Pessan, L.A. Polycaprolactone Usage in Additive Manufacturing Strategies for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 1479–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.-H. Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Its Copolymers: Research, Development and Industrialization. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiqah, S.A.; Khalina, A.; Harmaen, A.S.; Tawakkal, I.A.; Zaman, K.; Asim, M.; Nurrazi, M.N.; Lee, C.H. A Review on Properties and Application of Bio-Based Poly(Butylene Succinate). Polymers 2021, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Tan, B.; Soule, J.L.; Sobkowicz, M.J. Enzymatic Degradation of Poly (Butylene Succinate-Co-Hexamethylene Succinate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 155, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Aversa, C.; Ayyoob, M.; Gisario, A.; Hamad, K.; Mehrpouya, M.; Vahabi, H. Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS): Materials, Processing, and Industrial Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 132, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Defersha, F.; Yang, S. Expanding Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) and Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) Applications: A Review on Modifications and Effects. Polymers 2021, 13, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, M.E.; Grigorescu, R.M.; Iancu, L.; Ion, R.-M.; Zaharia, C.; Andrei, E.R. Methods of Synthesis, Properties and Biomedical Applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates: A Review. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, C.; Fai Tsang, Y.; Andrew Lin, K.-Y. Towards Sustainable Production of Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate: Non-Biological Catalytic Syntheses of Biomass-Derived Constituents. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202401070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denial, Mahata; Karthikeyan, S.; Godse, R.; Gupta, V.K. Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Polyester Synthesis Process and Product Development. Polym. Sci. Ser. C 2021, 63, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.V.; Cividanes, L.S.; Gouveia, R.F.; Lona, L.M.F. An Overview on Properties and Applications of Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate)–PBAT Based Composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, E7–E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Xiangbin, Z.; Xianbo, H. An Overview on Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Poly(Butylene-Adipate-Co-Terephthalate)–PBAT. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, S. A Review on Introduction and Applications of Starch and Its Biodegradable Polymers. Int. J. Environ. 2015, 4, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyana, Z.N.; Jumaidin, R.; Selamat, M.Z.; Ghazali, I.; Julmohammad, N.; Huda, N.; Ilyas, R.A. Physical Properties of Thermoplastic Starch Derived from Natural Resources and Its Blends: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Policastro, G.; Panico, A.; Fabbricino, M. Improving Biological Production of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) Co-Polymer: A Critical Review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 479–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and Its Blends with Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS): A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Manik, K.H.; Nath, A.; Shohag, J.R.; Mim, J.J.; Hossain, N. Recent Advances in Sustainable Natural Fiber Composites: Environmental Benefits, Applications, and Future Prospects. Mater. Today Sustain. 2025, 32, 101220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttegowda, M. Eco-Friendly Composites: Exploring the Potential of Natural Fiber Reinforcement. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, A.; Idström, A.; Mincheva, R.; Nakayama, K.; Evenäs, L.; Raquez, J.-M.; Lo Re, G. Reactive Melt Crosslinking of Cellulose Nanocrystals/Poly(ε-Caprolactone) for Heat-Shrinkable Network. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 163, 107166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, A.; Ruda, M.; Gioia, C.; Sessini, V.; Roulin, T.; Carrick, C.; Verendel, J.; Lo Re, G. Lignin Valorization in Thermoplastic Biomaterials: From Reactive Melt Processing to Recyclable and Biodegradable Packaging. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restaino, O.F.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Mirpoor, S.F.; Cammarota, M.; Hejazi, S.; Mariniello, L.; Schiraldi, C.; Porta, R. Sustainable Exploitation of Posidonia Oceanica Sea Balls (Egagropili): A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragassa, C.; Pesic, A.; Mattiello, S.; Pavlovic, A.; Santulli, C. Exploring the Potential of Posidonia Oceanica Fibers in Eco-Friendly Composite Materials: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrappa, D.R.K.; Kamath, M.S.S. The Egg Shell as a Filler in Composite Materials - a Review. J. Mech. Energy Eng. 2020, 4, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, İ.; Sever, K. Production and Characterization of Agricultural Waste Natural Fiber-Filled Polylactic Acid Composites. Polym. Bull. 2025, 82, 4051–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komal, U.K.; Lila, M.K.; Singh, I. PLA/Banana Fiber Based Sustainable Biocomposites: A Manufacturing Perspective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 180, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fico, D.; Rizzo, D.; De Carolis, V.; Esposito Corcione, C. Bio-Composite Filaments Based on Poly(Lactic Acid) and Cocoa Bean Shell Waste for Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF): Production, Characterization and 3D Printing. Materials 2024, 17, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.H.M. de; Jesus, R.M. de; Santana, G.M.; Khan, S.; Silva, E.F.M.S.; Cruz, I.S. da; Santos, I. de S.; dos Anjos, P.N.M. The Development of Biocomposite Filaments for 3D Printing by Utilizing a Polylactic Acid (PLA) Polymer Matrix Reinforced with Cocoa Husk Cellulose Fibers. Polymers 2024, 16, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, J.E.; Castillo, M.; López de Dicastillo, C.; Muñoz-Shugulí, C.; Lira, M.; Guarda, A.; Rodríguez-Mercado, F.J.; Galotto, M.J. Development of Active Biocomposite Films Based on Poly(Lactic Acid) and Wine by-Product: Effect of Grape Pomace Content and Extrusion Temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Bonacchi, D.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A. Analysis, Development, and Scaling-Up of Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) Biocomposites with Hazelnuts Shell Powder (HSP). Polymers 2021, 13, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balart, J. f.; García-Sanoguera, D.; Balart, R.; Boronat, T.; Sánchez-Nacher, L. Manufacturing and Properties of Biobased Thermoplastic Composites from Poly(Lactid Acid) and Hazelnut Shell Wastes. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Gulino, E.F.; Citarrella, M.C.; Maio, A. Green Composites Based on Hedysarum Coronarium with Outstanding FDM Printability and Mechanical Performance. Polymers 2022, 14, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.M.B.; Middea, A.; Neumann, R.; Thiré, R.M. da S.M.; Pereira, J.F.; de Freitas, S.C.; Penteado, M.S.; Lima, A.M.; Minguita, A.P. da S.; Mattos, M. da C.; et al. Biocomposites of PLA and Mango Seed Waste: Potential Material for Food Packaging and a Technological Alternative to Reduce Environmental Impact. Starch - Stärke 2021, 73, 2000118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fico, D.; Rizzo, D.; De Carolis, V.; Montagna, F.; Palumbo, E.; Corcione, C.E. Development and Characterization of Sustainable PLA/Olive Wood Waste Composites for Rehabilitation Applications Using Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). J. Build. Eng. 2022, 56, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Alaimo, G.; Morreale, M. Green Composites Based on PLA and Agricultural or Marine Waste Prepared by FDM. Polymers 2021, 13, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Lamattina, G.; Gargano, F.; Liguori, G. Opuntia Ficus-Indica Fruit by-Products as Fillers for PLA-Based Biocomposites: A Comparison between Glochids and Peel. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 12243–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambudi, N.S.; Lin, W.Y.; Harun, N.Y.; Mutiari, D. Modification of Poly(Lactic Acid) with Orange Peel Powder as Biodegradable Composite. Polymers 2022, 14, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Tsou, C.-H. Fabrication, Characterization, and Application of Biocomposites from Poly(Lactic Acid) with Renewable Rice Husk as Reinforcement. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mu, W.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, K.; Chen, L.; Ying, J.; et al. Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Micro-Nano Rice Husk/Polylactic Acid Filaments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheghi-Oskooee, R.; Morsali, P.; Mohammadi-Roshandeh, J.; Hemmati, F. Tailoring Interfacial Adhesion and Mechanical Performance of Biocomposites Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)/Rice Straw by Using Maleic Anhydride through Reactive Extrusion Process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampeerapappun, P.; O-Charoen, N.; Dhamvithee, P.; Jansri, E. Biocomposite Based on Polylactic Acid and Rice Straw for Food Packaging Products. Polymers 2024, 16, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Dong, L.; Lei, W.; Shi, J. Rice Straw Powder/Polylactic Acid Biocomposites for Three-Dimensional Printing. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2020, 29, 2633366X20967360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, T.; Saravanakumar, S.S.; Balavairavan, B.; Senthamaraikannan, P. Development and Characterization of a Polylactic Acid/Sesame Husk Powder–Based Biocomposite Film for Packaging Application. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 15, 2845–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Caturla, J.; Montanes, N.; Quiles-Carrillo, L.; Balart, R.; Garcia-Garcia, D.; Dominici, F.; Puglia, D.; Torre, L. Development of Biodegradable PLA Composites and Tangerine Peel Flour with Improved Toughness Containing a Natural-Based Terpenoid. Express Polym. Lett. 2023, 17, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, E.; Cetin, M.S.; Kizilirmak Esmer, O.; Karahan Toprakci, H.A. Effects of Tomato Peel Extract on Morphological, Chemical, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid). Iran. Polym. J. 2023, 32, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, N.; Maccaferri, E.; Benelli, T.; Bovo, M.; Torreggiani, D.; Campari, E.G.; Tassinari, P.; Giorgini, L.; Mazzocchetti, L. Valorization of Agro-Wastes as Fillers in PLA-Based Biocomposites for Increasing Sustainability in Fused Deposition Modeling Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2024, 17, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, N.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Bovo, M.; Gazzotti, S.; Torreggiani, D.; Tassinari, P.; Giorgini, L. A New Biocomposite Material Based on Wheat Waste and Suitable for 3D Printing Applications. Macromol. Symp. 2022, 405, 2100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A.; Sulyman, M.; Przybysz, M.; Saeb, M.R.; Klein, M.; Formela, K. On the Correlation of Lignocellulosic Filler Composition with the Performance Properties of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Based Biocomposites. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Monte, C.; Arrighetti, L.; Ricci, L.; Civello, A.; Bronco, S. Agro-Waste Bean Fibers as Reinforce Materials for Polycaprolactone Composites. Compounds 2023, 3, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, M.C.; Rodriguez-Uribe, A.; Thimmanagari, M.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Sustainable Biocomposites from Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Apple Pomace: A Study on Compatibilization Performance. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 3775–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.P.; Beatrice, C.A.G.; Backes, E.H.; Costa, L.C. Enhancing Sustainability and Biodegradability of Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS) Composite Filaments Reinforced with Cocoa Bean Shell Residues. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 13650–13662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liminana, P.; Garcia-Sanoguera, D.; Quiles-Carrillo, L.; Balart, R.; Montanes, N. Development and Characterization of Environmentally Friendly Composites from Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS) and Almond Shell Flour with Different Compatibilizers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 144, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasimowski, E.; Grochowicz, M.; Szajnecki, Ł. Preparation and Spectroscopic, Thermal, and Mechanical Characterization of Biocomposites of Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Onion Peels or Durum Wheat Bran. Materials 2023, 16, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, K.P.; Pal, A.K.; Pesaranhajiabbas, E.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Injection Moulded Composites from High Biomass Filled Biodegradable Plastic: Properties and Performance Evaluation for Single-Use Applications. Compos. Part C Open Access 2023, 11, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Wu, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-S. Preparation, Characterization, and Functionality of Bio-Based Polyhydroxyalkanoate and Renewable Natural Fiber with Waste Oyster Shell Composites. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 4817–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S. Preparation and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Bioplastic-Based Green Renewable Composites from Rice Husk. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Safont, E.L.; Aldureid, A.; Lagarón, J.M.; Gámez-Pérez, J.; Cabedo, L. Biocomposites of Different Lignocellulosic Wastes for Sustainable Food Packaging Applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 145, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, K.C.; Silva, D.A.K.; Coelho, L.A.F.; Pezzin, S.H.; Pezzin, A.P.T. Soil Biodegradation of PHBV/Peach Palm Particles Biocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qiao, X.; Sun, K. Environmental-Friendly Corn Stover/Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Biocomposites. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Techawinyutham, L.; Techawinyutham, W.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S. Lignocellulose Based Biofiller Reinforced Biopolymer Composites from Fruit Peel Wastes as Natural Pigment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, X.; Peng, F.; Lu, F. Biodegradable, Colorless, and Odorless PLA/PBAT Bioplastics Incorporated with Corn Stover. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 8870–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez García, A.; Martínez García, A.; Ferrándiz Bou, S. Study of the Influence of the Almond Shell Variety on the Mechanical Properties of Starch-Based Polymer Biocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-García, A.; Martínez-García, A.; Ferrándiz-Bou, S. Influence of Almond Shell Content and Particle Size on Mechanical Properties of Starch-Based Biocomposites. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 5823–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titone, V.; Rapisarda, M.; Pulvirenti, L.; Napoli, E.; Impallomeni, G.; Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Rizzarelli, P. Sustainable Biocomposites Based on Mater-Bi and Grape Pomace for a Circular Economy: Performance Evaluation and Degradation in Soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 231, 111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceraulo, M.; La Mantia, F.P.; Mistretta, M.C.; Titone, V. The Use of Waste Hazelnut Shells as a Reinforcement in the Development of Green Biocomposites. Polymers 2022, 14, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffaro, R.; Citarrella, M.C.; Gulino, E.F.; Morreale, M. Hedysarum Coronarium-Based Green Composites Prepared by Compression Molding and Fused Deposition Modeling. Materials 2022, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Citarrella, M.C.; Gulino, E.F. Opuntia Ficus Indica Based Green Composites for NPK Fertilizer Controlled Release Produced by Compression Molding and Fused Deposition Modeling. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 159, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Gulino, E.F.; Citarrella, M.C. Multifunctional 3D-Printed Composites Based on Biopolymeric Matrices and Tomato Plant (Solanum Lycopersicum) Waste for Contextual Fertilizer Release and Cu(II) Ions Removal. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Dominici, F.; Luzi, F.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C.; Torre, L.; Puglia, D. Effect of Almond Shell Waste on Physicochemical Properties of Polyester-Based Biocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hassan, E.A.M.; Memon, H.; Elagib, T.H.H.; Abad AllaIdris, F. Characterization of Natural Composites Fabricated from Abutilon-Fiber-Reinforced Poly (Lactic Acid). Processes 2019, 7, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Velarde, V.; Diaz-Vidal, T.; Cisneros-López, E.O.; Robledo-Ortiz, J.R.; López-Naranjo, E.J.; Ortega-Gudiño, P.; Rosales-Rivera, L.C. Mechanical and Physicochemical Properties of 3D-Printed Agave Fibers/Poly(Lactic) Acid Biocomposites. Materials 2021, 14, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, G.S.; Debnath, K.; Mahapatra, R.N. Mechanical, Thermal, Morphological, and Fibre Characteristics During Injection Moulding of Green Composites. Fibers Polym. 2024, 25, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.S.; Debnath, K.; Mahapatra, R.N. Recycling and Degradation Behaviour of the Bamboo Fibre Reinforced Green Composite Fabricated by Injection Moulding. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, e00865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łączny, D.; Macko, M.; Moraczewski, K.; Szczepański, Z.; Trafarski, A. Influence of the Size of the Fiber Filler of Corn Stalks in the Polylactide Matrix Composite on the Mechanical and Thermomechanical Properties. Materials 2021, 14, 7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunti, R.; Ratna Prasad, A. v.; Gupta, A. v. s. s. k. s. Mechanical and Degradation Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composites: Jute, Sisal, and Elephant Grass. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Barbé, A.; Guillou, E.; Castro, M. 3D Printing of Continuous Flax Fibre Reinforced Biocomposites for Structural Applications. Mater. Des. 2019, 180, 107884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morreale, M.; Mistretta, M.C.; Fiore, V. Creep Behavior of Poly(Lactic Acid) Based Biocomposites. Materials 2017, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Neitzel, B.; MohammadKarimi, S.; Puch, F. Investigation on the Influence of Process Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of Extruded Bio-Based and Biodegradable Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Sheets. Polymers 2023, 15, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuydt, D.; Balthazar, M.; Hendrickx, K.; Six, W.; Ferraris, E.; Desplentere, F.; Ivens, J.; Van Vuure, A.W. Production and Characterization of Bamboo and Flax Fiber Reinforced Polylactic Acid Filaments for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, L.; Carroccio, S.C.; Ambrogi, V.; Podda, E.; Filippone, G.; Salzano de Luna, M. Degradation Kinetics of PLA/Hemp Biocomposites: Tradeoff between Nucleating Action and pro-Hydrolytic Effect of Natural Fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 257, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhriyal, M.; Rakesh, P.K. Processing and Characterization of Novel Himalayacalamus Falconeri Fiber Reinforced Biodegradable Composites. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 21245–21260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, F.S.; Hameed Sultan, M.T.; Safri, S.N.A.; Jawaid, M.; Abu Talib, Abd.R.; Basri, A.A.; Md Shah, A.U. Fatigue and Impact Properties of 3D Printed PLA Reinforced with Kenaf Particles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussuf, A.A.; Massoumi, I.; Hassan, A. Comparison of Polylactic Acid/Kenaf and Polylactic Acid/Rise Husk Composites: The Influence of the Natural Fibers on the Mechanical, Thermal and Biodegradability Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Tai Yin Tze, W. The Improvement of Mechanical Properties, Thermal Stability, and Water Absorption Resistance of an Eco-Friendly PLA/Kenaf Biocomposite Using Acetylation. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ’Atiqah Abdul Azam, F.; Tharazi, I.; Bakar Sulong, A.; Che Omar, R.; Muhamad, N. Mechanical Durability and Degradation Characteristics of Long Kenaf-Reinforced PLA Composites Fabricated Using an Eco-Friendly Method. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 57, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, M.A.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Zainudin, E.S. Mechanical, Thermal and Morphological Properties of Woven Kenaf Fiber Reinforced Polylactic Acid (PLA) Composites. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-García, P.; Marrero, M.D.; Benítez, A.N. Disintegration and Marine Biodegradability of Biocomposite Using Pennisetum Setaceum Fiber and PLA as Matrix. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 230, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Gairola, S.; Singh, I. Sustainable Polymers and Sisal Fibers Based Green Composites: A Detailed Characterization and Analysis. Express Polym. Lett. 2023, 17, 992–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, S.; Singh, I. Processing of PLA/Sisal Fiber Biocomposites Using Direct- and Extrusion-Injection Molding. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouh, Z.; Molnar, K.; Boussu, F.; Cherkaoui, O.; El Moznine, R. Mechanical and Thermal Characterization of Sisal Fiber Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouh, Z.; Molnár, K.; Hajba, S.; Boussu, F.; Cherkaoui, O.; El Moznine, R. Elaboration and Characterization of Biocomposite Based on Polylactic Acid and Moroccan Sisal Fiber as Reinforcement. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 3812–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, A.; Chacko, N.G.; Dhakal, H.N.; Khan, S.H.; Sarker, F.; Zhang, Z. Valorisation of Agricultural Residue Bio-Mass Date Palm Fibre in Dry-Blended Polycaprolactone (PCL) Bio-Composites for Sustainable Packaging Applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 15, 5805–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.N.; Ismail, S.O.; Zhang, Z.; Barber, A.; Welsh, E.; Maigret, J.-E.; Beaugrand, J. Development of Sustainable Biodegradable Lignocellulosic Hemp Fiber/Polycaprolactone Biocomposites for Light Weight Applications. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 113, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.; Bourmaud, A.; Berzin, F.; Almansour, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shah, D.U.; Beaugrand, J. Mechanical Properties of Leaf Sheath Date Palm Fibre Waste Biomass Reinforced Polycaprolactone (PCL) Biocomposites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 126, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frollini, E.; Bartolucci, N.; Sisti, L.; Celli, A. Biocomposites Based on Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Curaua: Mechanical and Morphological Properties. Polym. Test. 2015, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.N.; Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Papadopoulou, E.; Athanassiadou, E.; Reinders, M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Development and Study of Fully Biodegradable Composite Materials Based on Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Hemp Fibers or Hemp Shives. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagazzo, A.; Moliner, C.; Bosio, B.; Botter, R.; Arato, E. Evaluation of the Mechanical and Thermal Properties Decay of PHBV/Sisal and PLA/Sisal Biocomposites at Different Recycle Steps. Polymers 2019, 11, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammiche, D.; Boukerrou, A.; Grohens, Y.; Guermazi, N.; Arrakhiz, F.E. Mechanical Properties and Biodegradation of Biocomposites Based on Poly (Hydroxybutyrate-Co-Valerate) and Alfa Fibers. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.V.; Pinheiro, I.F.; Mariano, M.; Cividanes, L.S.; Costa, J.C.M.; Nascimento, N.R.; Kimura, S.P.R.; Neto, J.C.M.; Lona, L.M.F. Environmentally Friendly Polymer Composites Based on PBAT Reinforced with Natural Fibers from the Amazon Forest. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsaf, H.; Singh, S.; Pereira, J.; Poças, F. Multifunctional Properties of PBAT with Hemp (Cannabis Sativa) Micronised Fibres for Food Packaging: Cast Films and Coated Paper. Coatings 2023, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Zhang, L.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhou, K.; Lu, W. Mechanical Properties and Tensile Model of Hemp-Fiber-Reinforced Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) Composite. Materials 2022, 15, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.M.; Choo, J.E.; Park, T.H.; Hwang, S.W. The Effect of Isocyanate on the Properties of Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate)/Kenaf Fiber Composites. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 10799–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badouard, C.; Traon, F.; Denoual, C.; Mayer-Laigle, C.; Paës, G.; Bourmaud, A. Exploring Mechanical Properties of Fully Compostable Flax Reinforced Composite Filaments for 3D Printing Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 135, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fonseca, A.A.; Reynoso-Llamas, C.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R.; Rodrigue, D.; Martín del Campo, A.S. Recycling of Biodegradable Biobased Polymer/Agave Fiber Biocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2025, 46, 4059–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, R.; Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Gulino, E.F.; Lo Re, G.; Jonoobi, M. Processing-Structure-Property Relationships of Electrospun PLA-PEO Membranes Reinforced with Enzymatic Cellulose Nanofibers. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessini, V.; Latty, H.; Milazzo, M.; Mirkhalaf, M.; Lo Re, G. Experiments and Computational Modelling Combined to Shed Light on the Reinforcement Mechanism in Reactive Extruded Pulp Fibres/Starch Biocomposites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbakoba, V.C.; Hlangothi, P.; Andrew, J.; John, M.J. Mechanical and Shape Memory Properties of 3D-Printed Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC)-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Bionanocomposites for Potential 4D Applications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikhosana, S.T.; Gumede, T.P.; Malebo, N.J.; Ogundeji, A.O.; Motloung, B. The Influence of Cellulose Content on the Morphology, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Eucomis Autumnalis Cellulose Biocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ding, K.; Ji, T.; Sun, H.; Chi, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, M.; Cai, L.; Xia, C. Design of Sustainable 3D Printable Polylactic Acid Composites with High Lignin Content. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Garofalo, G.; Baiamonte, M.; Molinari, G.; Lazzeri, A.; La Mantia, F.P.; Botta, L. Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA)/Micro-Fibrillated Cellulose (MFC) Biocomposites for Film Blowing Applications. Cellulose 2025, 32, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.G.; Barbosa, R.F.S.; Rosa, D.S. Nanocellulose from Industrial and Agricultural Waste for Further Use in PLA Composites. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1851–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Orti, C.; Navas-Martos, F.J.; Rodríguez-Liébana, J.A.; La Rubia, M.D.; Jurado-Contreras, S. Development of PLA–Waste Paper Biocomposites with High Cellulose Content. Polymers 2024, 16, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, W.S.; Yeu, Y.L.; Chung, P.P.; Soon, K.H. Extraction and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) from Durian Rind for Biocomposite Application. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 6544–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Deng, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Z.; Yang, R.; Wu, D. Preparation and Research of PCL/Cellulose Composites: Cellulose Derived from Agricultural Wastes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, G.; Bras, J.; Follain, N.; Belbekhouche, S.; Marais, S.; Dufresne, A. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bio-Nanocomposites Reinforced by Luffa Cylindrica Cellulose Nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, L.; Titone, V.; Teresi, R.; Scarlata, M.C.; Lo Re, G.; La Mantia, F.P.; Lopresti, F. Biocomposite PBAT/Lignin Blown Films with Enhanced Photo-Stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, L.; Titone, V.; Mistretta, M.C.; La Mantia, F.P.; Modica, A.; Bruno, M.; Sottile, F.; Lopresti, F. PBAT Based Composites Reinforced with Microcrystalline Cellulose Obtained from Softwood Almond Shells. Polymers 2021, 13, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, R.H.; Taha, T.H.; Elnouby, M.; Desouky, E.A.E.; Alhudhaibi, A.M.; Moustafa, M.; Elsherif, M.A.; Yahia, M.; Abu-Saied, M.A. Environmentally Green Film Blends: Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)/Cellulose Acetate (CA)/Potato Peel Starch as an Alternative to Petroleum Plastics. Cellulose 2024, 31, 6155–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarena-Bononad, P.; Freitas, P.A.V.; Chiralt, A.; Vargas, M. Use of Cellulose Fibres from Posidonia Oceanica to Obtain Chitosan Biocomposites and Poly(Lactic Acid) Laminates. Polysaccharides 2025, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Lopresti, F.; Botta, L. PLA Based Biocomposites Reinforced with Posidonia Oceanica Leaves. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 139, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barandiaran, A.; Lascano, D.; Montanes, N.; Balart, R.; Selles, M.A.; Moreno, V. Improvement of the Ductility of Environmentally Friendly Poly(Lactide) Composites with Posidonia Oceanica Wastes Plasticized with an Ester of Cinnamic Acid. Polymers 2023, 15, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffaro, R.; Citarrella, M.C. Stable and Reusable Electrospun Bio-Composite Fibrous Membranes Based on PLA and Natural Fillers for Air Filtration Applications. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 42, e01146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicácio, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Dantas, L.; Siqueira, D.; Ries, A.; Wellen, R. Biocomposites Based on Poly(Lactic Acid)/Aloe Vera/Priplast. Effects of UVA Radiation on the Crystallization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 34, 3097–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Lopresti, F. Physical Properties of Green Composites Based on Poly-Lactic Acid or Mater-Bi® Filled with Posidonia Oceanica Leaves. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.K.; Damare, N.A.; Hazarika, D.; Bhagabati, P.; Kalamdhad, A.; Katiyar, V. Biodegradation and Characterization Study of Compostable PLA Bioplastic Containing Algae Biomass as Potential Degradation Accelerator. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdi, A.G.; de Souza, A.G.; Rocha, D.B.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Alves, R.M.V.; dos Santos Rosa, D. Biodegradable Films Functionalized with Moringa Oleifera Applied in Food Packaging. Iran. Polym. J. 2021, 30, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Morais, D.D.S.; Braz, C.J.F.; Haag, K.; Wellen, R.M.R.; Canedo, E.L.; de Carvalho, L.H.; Koschek, K. Impact of the Natural Filler Babassu on the Processing and Properties of PBAT/PHB Films. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 124, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, D.; Soleimani, M. Bio-Based White Eggshell as a Value-Added Filler in Poly(Lactic Acid) Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, B.; Naresh, S.; Reddy, K.O.; Madhukar, K.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Rajulu, A.V. Tensile and Thermal Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Eggshell Powder Composite Films. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2014, 19, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, N.G.; Cree, D.E. Mechanical Properties of Poly (Lactic Acid) Composites Reinforced with CaCO3 Eggshell Based Fillers. MRS Adv. 2017, 2, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.V.; Cunha, A.B.; Andrade, M.A.; Vilarinho, F.; Machado, A.V.; Castro, M.C.R. Blown Film of PLA for Packaging with Green Tea and Fish Industrial Residues: An Insight on Their Properties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 43, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Wu, D.-Y.; Wang, S.-S. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Bio-Based Polyester Composites Derived from Renewable Distillers Grains and Shellfish. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ye, X.; Zhong, J.; Lin, Z.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, W.; Wei, Y.; Dong, X. Recycling of Waste Crab Shells into Reinforced Poly (Lactic Acid) Biocomposites for 3D Printing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 122974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffaro, R.; Citarrella, M.C.; Catania, A.; Settanni, L. Green Composites Based on Biodegradable Polymers and Anchovy (Engraulis Encrasicolus) Waste Suitable for 3D Printing Applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 230, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Gulino, E.F.; Citarrella, M.C. Sandwich-Structured Bimodal Polymeric Fiber/Waste Wool Fiber Bio-Composite Membrane for High-Performance and Eco-Friendly Air Filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2026, 380, 135543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Matrix | Filler | Sample Code | Area | Mechanical Treatment | Drying Temp. [°C] | Drying Time [h] |
Other Treatments |
Coupling Agent | Ref. |
| PLA | Artichoke plants | PLA/AP | Europe | Ground and sieved | 60 | 12 | - | - | [51] |
| PLA | Banana | PLA/BF | Asia | - | 90 | 6 | - | - | [52] |
| PLA | Cocoa Bean Shell | PLA/CBSW | Europe | Milled and sieved | 60 | 24 | - | - | [53] |
| PLA | Cocoa Husk | PLA/CH | South America | Knife mill and sieved | 60 | 12 | - | - | [54] |
| PLA | Grape Pomace |
PLA/GP | Europe | Milled and sieved | 48 | 72 | - | - | [55] |
| PLA | Hazelnut Shell | PLA/HSF | - | UC mill and sieved | 60 | 24 | - | - | [56] |
| PLA | Hazelnuts Shell | PLA/HSF | Europe | Milled and sieved | 60 | 16 | - | - | [57] |
| PLA | Hedysarum coronarium | PLA/HC | Europe | Ground and sieved | 90 | ~16 on | - | - | [58] |
| PLA | Mango Seed | PLA/MS | South America | Milled and sieved | 52 | 24 | - | - | [59] |
| PLA | Olive Wood | PLA/OW | Europe | UC mill and sieved | 60 | - | - | - | [60] |
| PLA | Opuntia Ficus Indica |
PLA/OFI | Europe | Ground and sieved | 90 | ~16 on | - | - | [61] |
| PLA | Opuntia Ficus-Indica |
PLA/OFI | Europe | HS mill and sieved | 70 | ~16 on | - | - | [62] |
| PLA | Orange Peel | PLA/OPP | Europe | Ground and sieved | 60 | 18 | - | - | [63] |
| PLA | Rice husk | PLA/RH | Asia | Ground and sieved | 90 | 12 | - | yes | [64] |
| PLA | Rice husk | PLA/MNRH | Asia | - | - | - | Alkaline treatment |
- | [65] |
| PLA | Rice Straw | PLA/RS | Asia | Milled and sieved | 105 | 12 | - | yes | [66] |
| PLA | Rice Straw | PLA/RS | Asia | Knife mill and sieved | 80 | 6 | - | yes | [67] |
| PLA | Rice straw | PLA/RSP | Asia | Ground and sieved | 60 | 12 | - | - | [68] |
| PLA | Sesame Husk | PLA/SSHP | Asia | Milled and sieved | 50 | 36 | - | - | [69] |
| PLA | Tangerines | PLA/TPF | Europe | UC mill and sieved | 40 | 48 | - | yes | [70] |
| PLA | Tomato Peel | PLA/THP | Europe | Milled and sieved | 60 | 8 | Alkaline extraction |
- | [71] |
| PLA | Wheat Middling |
PLA/WM | Europe | Milled and sieved | 75 | 1 | - | - | [72] |
| PLA | Wheat Wastes | PLA/WW | Europe | - | - | - | - | - | [73] |
| PCL | Date Seed | PCL/DS | Europe | Ground and sieved | - | - | - | - | [74] |
| PCL | Olive Stones | PCL/OS | Europe | Ground and sieved | - | - | - | [74] | |
| PCL | Waste Bean | PCL/WaB | Europe | - | 50 | ~16 on | - | - | [75] |
| PCL | Wheat Bran | PCL/WhB | Europe | Ground and sieved | - | - | - | - | [74] |
| PBS | Apple Pomace |
PBS/AP | Asia | Milled and sieved | 80 | 12 | - | yes | [76] |
| PBS | Cocoa bean shells | PBS/CBS | South America | Ground and sieved | 80 | 16 | - | -- | [77] |
| PBS | Almond Shell Flour | PBS/ESF | Europe | Milled and sieved | 50 | 24 | - | yes | [78] |
| PBS | Onion Peels | PBS/OP | Europe | Knife mill and sieved | 60 | 24 | - | - | [79] |
| PBSA | Almond Shell | PBSA/AS | North America | Ground and sieved | 68 | 48 | - | yes | [80] |
| PHA | Pineapple leaf | PHA/PL | Asia | Ground and sieved | - | - | Alkaline treatment |
- | [81] |
| PHA | Rice Husk | PHA/RH | Asia | Ground and sieved | 105 | 24 | - | - | [82] |
| PHB | Almond shell | PHB/AS | Europe | Ground and sieved | 60 | 24 | - | - | [83] |
| PHB | Rice Husk | PHB/RH | Europe | UC mill | 60 | 24 | - | - | [83] |
| PHB | Seagrass | PHB/SG | Europe | UC mill | 60 | 24 | - | - | [83] |
| PHBV | Peach Palm | PHBV/PP | South America | Ground and sieved | 60 | 48 | - | - | [84] |
| PBAT | Corn stover | PBAT/CS | Asia | Ground and sieved | 80 | 12 | - | - | [85] |
| PBAT | Mangosteen | PBAT/M | Asia | Ground and sieved | 80 | 2 | - | - | [86] |
| PLA/PBAT | Corn Stover | PLA/PBAT/CS | Asia | - | 50 | - | - | [87] | |
| Mater-Bi® | Almond Shell | MB/AS | Europe | Milled and sieved | 105 | 24 | - | - | [88] |
| Mater-Bi® | Almond Shell | MB/AS | Europe | Milled and sieved | 102 | 24 | - | - | [89] |
| Mater-Bi® | Grape Pomace |
MB/GP | Europe | Milled and sieved | 80 | ~16 on | - | - | [90] |
| Mater-Bi® | Hazelnut Shells | MB/HS | Europe | - | 60 | 4 | - | - | [91] |
| Mater-Bi® | Hedysarum coronarium | MB/HC | Europe | Ground and sieved | 60 | ~16 on | - | - | [92] |
| Mater-Bi® | Opuntia Ficus Indica |
MB/OFI | Europe | Ground and sieved | 90 | ~16 on | - | - | [93] |
| Mater-Bi® | Tomato Plant | MB/TP | Europe | Ground and sieved | 40 | ~16 on | - | - | [94] |
| Inzea® | Almond Shell | Inz/AS | - | HS mill and sieved | - | - | - | - | [95] |
| Matrix | Cellulose Type | Sample Code | Area | Mechanical Treatment | Drying Temp. [°C] | Drying Time [h] |
Other Treatments |
Additive | Ref. |
| PLA | Nanocrystal (eucalyptus) |
PLA/CNC | Africa | Freeze-dried | - | - | - | - | [133] |
| PLA | Eucomis autumnalis |
PLA/EA | Africa | Ground and sieved | - | - | Sodium chloride |
- | [134] |
| PLA | Lignin (corn cob) |
PLA/Lignin | Asia | - | 80 | 12 | - | Plasticizer | [135] |
| PLA | Micro-fibrillated | PLA/MFC | Europe | - | - | - | - | - | [136] |
| PLA | Nanocellulose (agro-industrial) | PLA/NCs | South America | - | - | - | Bleaching | - | [137] |
| PLA | Waste Paper | PLA/WP | Europe | UC mill and sieved | 60 | 24 | Fatty acid ester | - | [138] |
| PCL | Microcrystalline (durian rind) | PCL/MCC | Asia | Ground and sieved | 100 | 24 | Alkaline and bleaching | - | [139] |
| PCL | Cellulose (agricultural) |
PCL/CNC | Asia | Ground and sieved | - | - | - | - | [140] |
| PCL | Nanocrystal (luffa cylindrica) |
PCL/MLW | South America | - | - | - | Acid and bleaching | Compatibilizer | [141] |
| PBAT | Lignin (black liquor) |
PBAT/lignin | Europe | - | 80 | 12 | - | - | [142] |
| PBAT | Microcrystalline (almond shells) | PBAT/as-MCC | Europe | Ground and sieved | 80 | 4 | - | - | [143] |
| PVA | Cellulose acetate (potato peel) | PVA-CA/Starch | Asia | Ground and sieved | - | - | - | - | [144] |
| PVA | Nanofibrils (coconut) |
CCNF/PVA | Asia | - | - | - | Alkaline and bleaching | - | [145] |
| Matrix | Filler | Sample Code | Area | Mechanical Treatment | Drying Temp. [°C] | Drying Time [h] | Additive | Ref. |
| PLA | Posidonia Oceanica leaves |
PLA/PO | Europe | Ground and sieved | 80 | 12 | - | [146] |
| PLA | Egagropili | PLA/POS | Europe | Crushed | 65 | 12 | DCP, Plasticizer |
[147] |
| PLA | Posidonia Oceanica leaves |
PLA/POL | Europe | Ground and sieved | 60 | 12 | - | [148] |
| PLA | Aloe Vera | PLA/AV | S. America | - | 60 | 16 | - | [149] |
| PLA | Posidonia Oceanica leaves |
PLA10A | Europe | Ground and sieved | 90 | 12 | - | [150] |
| PLA | Duneleila Tertiolecta Algae |
PLA/AB | Asia | - | - | - | - | [151] |
| PBAT | Moringa oleifera |
PBAT/MO | S. America | Ground and sieved | 60 | 24 | - | [152] |
| PBAT/PHB | Babassu | PBAT/PHB/BS | Europe | Ground and sieved | 60 | 20 | - | [153] |
| Sample Code | Processing | Key Results | Application | End of Life | Ref. |
| PLA/AP | MC + Hot process | ↑ Elastic modulus | Variety of Fields | - | [51] |
| PLA/BF | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Flexure and tensile strength |
- | - | [52] |
| PLA/CBSW | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Rigidity and load resistance |
3D printing filament | - | [53] |
| PLA/CH | MC+ 3D printing | ↑ Tensile strength | 3D printing filament | - | [54] |
| PLA/GP | MC + Film blowing | ↑ Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity |
Packaging | - | [55] |
| PLA/HSF | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Flexural modulus and sustainability | Building industry | - | [56] |
| PLA/HSF | MC + Inject. mould. | Easily scalable | - | - | [57] |
| PLA/HC | MC + Compress. mould. MC + 3D printing |
↑ Elastic modulus Excellent printability |
- Automotive |
- - |
[58] |
| PLA/MS | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Barrier properties | Packaging | - | [59] |
| PLA/OW | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Porosity | Non-structural | - | [60] |
| PLA/OFI | MC + 3D printing | Good processability | 3D printing filament | - | [61] |
| PLA/OFI | MC + Compress. mould. | ↑ Stiffness | Packaging | [62] | |
| PLA/OPP | Solvent casting | ↑ Biodegradation | - | Soil burial | [63] |
| PLA/RH | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Tensile strength and improved adhesion |
3D printing filament | - | [64] |
| PLA/MNRH | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Mechanical and thermal properties | Automotive | - | [65] |
| PLA/RS | MC + Compress. mould. | Improve interfacial Adhesion |
- | - | [66] |
| PLA/RS | MC + Inject. mould. | - | - | [67] | |
| PLA/RSP | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Flexure and tensile strength | 3D printing filament | Soil burial | [68] |
| PLA/SSHP | Solvent casting | ↑ Tensile and thermal properties | Packaging | Soil degradation | [69] |
| PLA/TPF | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Biodegradation | - | Compost soil | [70] |
| PLA/THP | Solvent casting + compress. mould. |
↑ Tensile strength | Packaging | - | [71] |
| PLA/WM | MC + 3D printing | Good filler dispersion | 3D printing filament | - | [72] |
| PLA/WW | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Sustainability | 3D printing filament | - | [73] |
| PCL/DS | MC + Hot process | ↑Modulus and thermal stability |
Packaging | - | [74] |
| PCL/OS | MC+ Hot process | ↑Modulus and thermal stability |
- | - | [74] |
| PCL/WaB | MC + Compress. mould. | ↑Modulus and thermal stability |
Industrial | - | [75] |
| PCL/WhB | MC + Hot process | Plasticization effect | Industrial | - | [74] |
| PBS/AP | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Impact and tensile strength | - | - | [76] |
| PBS/CBS | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Modulus | Packaging | - | [77] |
| PBS/ESF | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Disintegration rate | 3D printing filament | Disintegration in soil |
[78] |
| PBS/OP | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Ductile properties (with compatibilizers) |
Automotive | - | [79] |
| PBSA/AS | MC + Inject. mould | ↑Mechanical properties (with compatibilizers) | Packaging | - | [80] |
| PHA/PL | MC + Hot process | ↑Biodegradation | Packaging | - | [81] |
| PHA/RH | MC + Hot process | ↑Biodegradation | - | - | [82] |
| PHB/AS | MC + Hot process | ↑Permeability | Packaging | Disintegration | [83] |
| PHB/RH | MC + Hot process | ↑Mechanical properties | Packaging | Disintegration | [83] |
| PHB/SG | MC + Hot process | ↑Mechanical properties | Packaging | Disintegration | [83] |
| PHBV/PP | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Biodegradation | Packaging | Soil burial | [84] |
| PBAT/CS | MC + Compress. mould. | ↑ Stiffness | Packaging | - | [85] |
| PBAT/M | MC + Compress. mould. | ↑ Thermal stability | Packaging | - | [86] |
| PLA/PBAT/CS | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical properties | Packaging | Soil burial | [87] |
| MB/AS | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Biodegradation | Packaging | Soil burial | [88] |
| MB/AS | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical properties | Packaging | - | [89] |
| MB/GP | MC + Compress. mould. | Good fertilizer release | 3D printing filament | - | [90] |
| MB/HS | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑ Ductility | - | - | [91] |
| MB/HC | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Rigidity | - | - | [92] |
| MB/OFI | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Fertilizer release | - | - | [93] |
| MB/TP | MC + 3D printing | ↑Mechanical properties | 3D printing filament | - | [94] |
| Inz/AS | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical properties | - | Compost soil | [95] |
| Sample Code | Processing | Key Results | Application | End of Life | Ref. |
| PLA/AI | MC + Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | Industrial | - | [96] |
| PLA/AF | MC + 3D printing | ↑Impact tensile | 3D printing filament | Compost in soil | [97] |
| PLA/BF | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical and Thermal Properties | Variety of fields | - | [98] |
| PLA/BF | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Recycling | Variety of fields | - | [99] |
| PLA/CS | MC+ Inject. mould. | Low interfacial adhesion | - | - | [100] |
| PLA/EG | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties and Bio | - | Soil degradation | [101] |
| PLA/CFY | Extr. coating + 3D printing | ↑Mechanical Properties | 3D printing filament | - | [102] |
| PLA/Flax | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Tensile strength | - | - | [103] |
| PLA/FS | Direct Extr. process | ↑Impact and tensile modulus | Automotive | - | [104] |
| PLA/FS | Direct Extr. process | ↑ l/d ratio at low rotational speed | 3D printing filament | - | [105] |
| PLA/HS | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Biodegradation | - | Soil degradation | [106] |
| PLA/THF | Direct Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical and Thermal Properties | Non-structural | - | [107] |
| PLA/Jute | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Resistence creep | - | - | [103] |
| PLA/KF | MC + 3D printing | ↑Toughness | 3D printing filament | - | [108] |
| PLA/KF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | Soil burial | [109] |
| PLA/KFA | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical and water resistance | - | - | [110] |
| PLA/LK | MC + Hot process | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [111] |
| PLA/WK | MC+ Hot process | ↑Mechanical Properties | Automotive | - | [112] |
| PLA/PS | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Biodegradation | - | Compost in soil | [113] |
| PLA/SF | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical and Thermal Properties | Non-structural | - | [114] |
| PLA/SF | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Impact and tensile modulus | - | - | [115] |
| PLA/SF | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [116] |
| PLA/MS | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [117] |
| PCL/DP | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [118] |
| PCL/HF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | Packaging | - | [119] |
| PCL/DP | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑ Flexure and tensile strength | - | - | [120] |
| PBS/C | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | Packaging | - | [121] |
| PBS/HF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Sustainability | - | Enzymatic hydrolysis and soil burial | [122] |
| PHA/PLF | MC+ Hot pression | ↑Biodegradation | 3D printing filament | Soil burial | [81] |
| PHB/SF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Recycling | - | - | [123] |
| PHBV/AF | MC+ Inject. mould. | ↑Mechanical properties (with Alkali treatment) | - | Aqueous environment |
[124] |
| PBAT/CF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [125] |
| PBAT/MF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [125] |
| PBAT/TF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Mechanical Properties | - | - | [125] |
| PBAT/CS | Solvent casting | ↑ Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity | Packaging | - | [126] |
| PBAT/HF | Open blending + Hot press | ↑Biodegradation | - | Soil burial | [127] |
| PBAT/KF | MC+ Hot process | ↑Mechanical properties (with compatibilizers) | - | - | [128] |
| PBAT/F | MC + 3D printing | ↑Stiffness and strength | 3D printing filament | - | [129] |
| MB/AF | MC+ Compress. mould. | ↑Recycling | - | Compost in soil | [130] |
| Sample Code | Processing | Key Results | Application | End of Life | Ref. |
| PLA/CNC | MC+ 3D printing | ↑ Mechanical, shape memory |
4D applications | - | [133] |
| PLA/EA | MC + Compress Mould. | No significant changes | 3D printing filament | - | [134] |
| PLA/Lignin | MC + 3D printing | ↑ Elongation and toughness |
Biomedical | - | [135] |
| PLA/MFC | MC + Film Blowing | ↑ Mechanical | Packaging | - | [136] |
| PLA/NCs | MC + Compress Mould. | ↑ Mechanical | Packaging | - | [137] |
| PLA/WP | Melt compounding | ↑ Mechanical, sustainability |
Packaging | - | [138] |
| PCL/MCC | Melt compounding | ↑ Mechanical, biodegradability |
- | Soil degradation | [139] |
| PCL/CNC | Solution casting | ↑ Tensile Strength | - | - | [140] |
| PCL/MLW | Solution casting | ↑ Modulus | - | - | [141] |
| PBAT/lignin | MC + Film Blowing | ↑ Modulus, photo degradation |
Packaging | - | [142] |
| PBAT/as-MCC | MC + Compress Mould | ↑ Modulus | - | - | [143] |
| PVA-CA/Starch | Solution casting | ↑ Mechanical, biodegradability |
- | Enzymatic degradation | [144] |
| CCNF/PVA | Solution casting | ↑ Mechanical | Packaging | - | [145] |
| Sample Code | Processing | Key Results | Application | End of Life | Ref. |
| PLA/PO | Compression molding | ↑ Sustainability | - | - | [146] |
| PLA/POS | Injection molding | ↑ Ductility, Sustainability | - | - | [147] |
| PLA/POL | Electrospinning | ↑ Mechanical, Sustainability | Air filtration | - | [148] |
| PLA/AV | Injection molding | ↑ UV resistance | - | - | [149] |
| PLA10A | Compression molding | ↑ Sustainability | - | - | [150] |
| PLA/AB | Extrusion | ↑ Degradation, Sustainability | - | Compostability, soil degradation | [151] |
| PBAT/MO | Wire Extension (film) | ↑ Fruit shelf life | Packaging | - | [152] |
| PBAT/PHB/BS | Wire Extension (film) | ↑ Mechanical, Sustainability | Packaging and mulch films |
- | [153] |
| Sample Code | Processing | Key Results | Application | End of Life | Ref. |
| PLA/WE | Injection molding | ↑ Tensile modulus | - | - | [154] |
| PLA/ESP | Film Casting | ↑ Mechanical, sustainability | Packaging | - | [155] |
| PLA/WES | Injection molding | No significant changes | - | - | [156] |
| PLA/FG | Film Blowing | ↑ Oxy barrier, antioxidant | Packaging | Compostability | [157] |
| PLA/PUS | Compression Molding | ↑ Mechanical, sustainability | Packaging, utensils | Soil degradation | [158] |
| PLA/CSP | 3D Printing | ↑ Mechanical | Biomedical | - | [159] |
| PLA/EE | 3D Printing | ↑ Mechanical, ↑ processability, sustainability | Packaging | - | [160] |
| PLA/WP | Solution Blow Spinning | ↑ Mechanical, sustainability | Air filtration | - | [161] |
| PHA/OSP | Compression Molding | ↑ Mechanical, sustainability | Packaging, utensils | Soil degradation | [81] |
| MB/EE | 3D Printing | ↑ Mechanical, sustainability | Packaging | - | [160] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





