1. Introduction
In the standard model (SM), the time is the abstract concept even though the time that is relative is considered to be intertwined with the space according to the special and general relative theories based on the 4-D Minkowski space. Even the time can be so much curved along with the space so that the strange and complex shapes of the space-time are imagined theoretically [
1]. The universe is described as the space-time with the only time that is relative. This space-time is described on the, so called, 4-D Minkowski space. In the standard model, the future, present and past coexist geometrically even though we can move only toward the future time. In other words, only the time toward the positive time direction exists for our universe. Therefore, realistically, only the positive time has been observed [
2]. However, the space has both of the positive space direction and negative space direction. This time irreversibility [
2] that is one of the unsolved physics problems has been explained by using the entropy increase of the universe in terms of the second law of the thermodynamics.
In the present work, I introduce the 4-D Euclidean space with the absolute time axis (ct) in terms of the 3-dimensional quantized space model [
3,
4] in
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6. The relative time (ct
l) is defined just as the 4-D distance of the moving objects. Therefore, the observed time is the 4-D distance of the moving objects defined as the relative time in the present work. This relative time corresponds to the time in terms of the standard model including the special and general relative theories. In the present work, the absolute time is newly defined and introduced. The new absolute time is not entangled with the space in terms of the present 3-D quantized space model, but the relative time in the present work is entangled with the space as shown in terms of the special and general relative theories because the relative time is defined as the 4-D space-time distance of the moving objects.
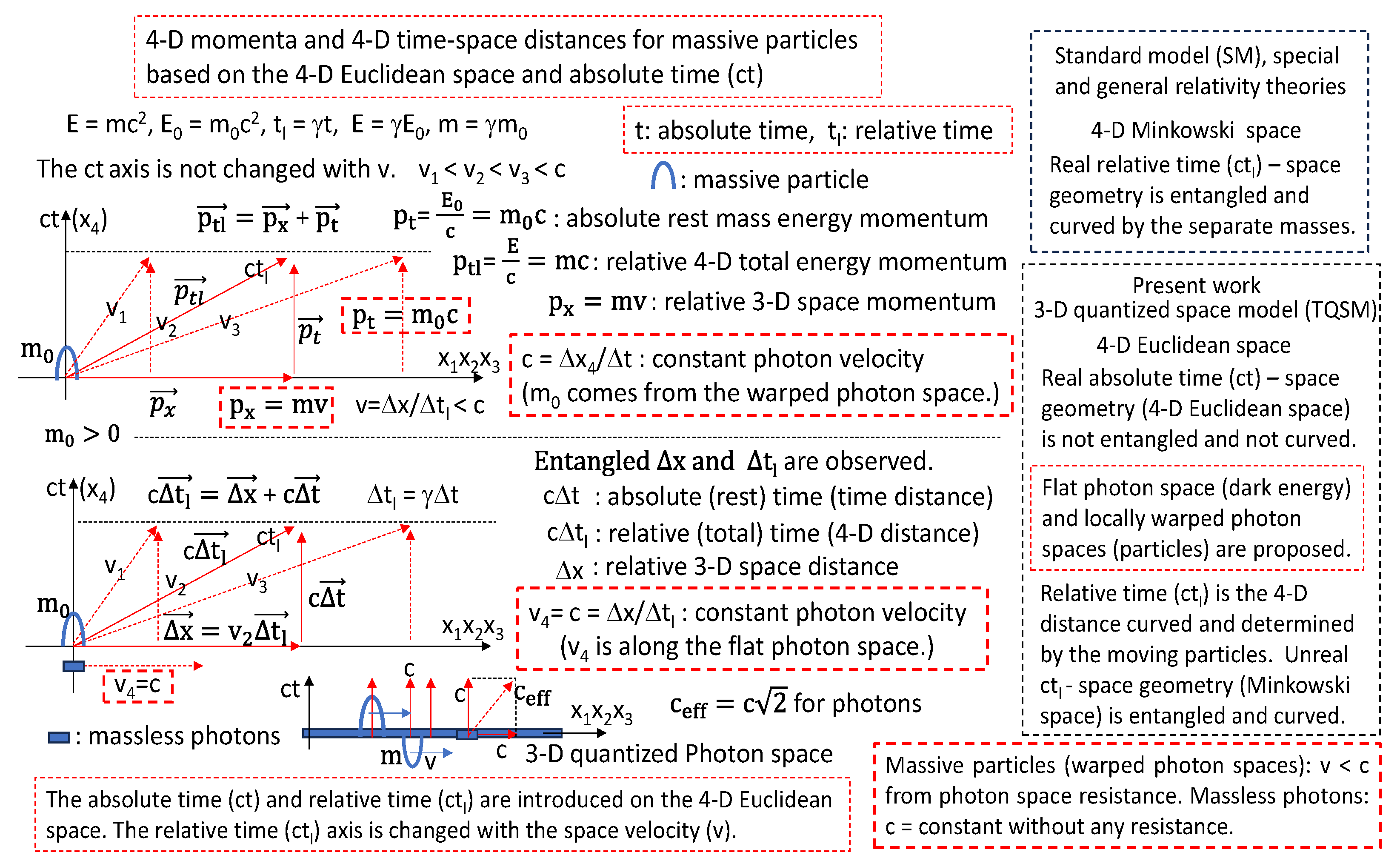
Figure 1.
The relative masses and relative time are defined on the 3-D quantized flat photon space.
Figure 1.
The relative masses and relative time are defined on the 3-D quantized flat photon space.
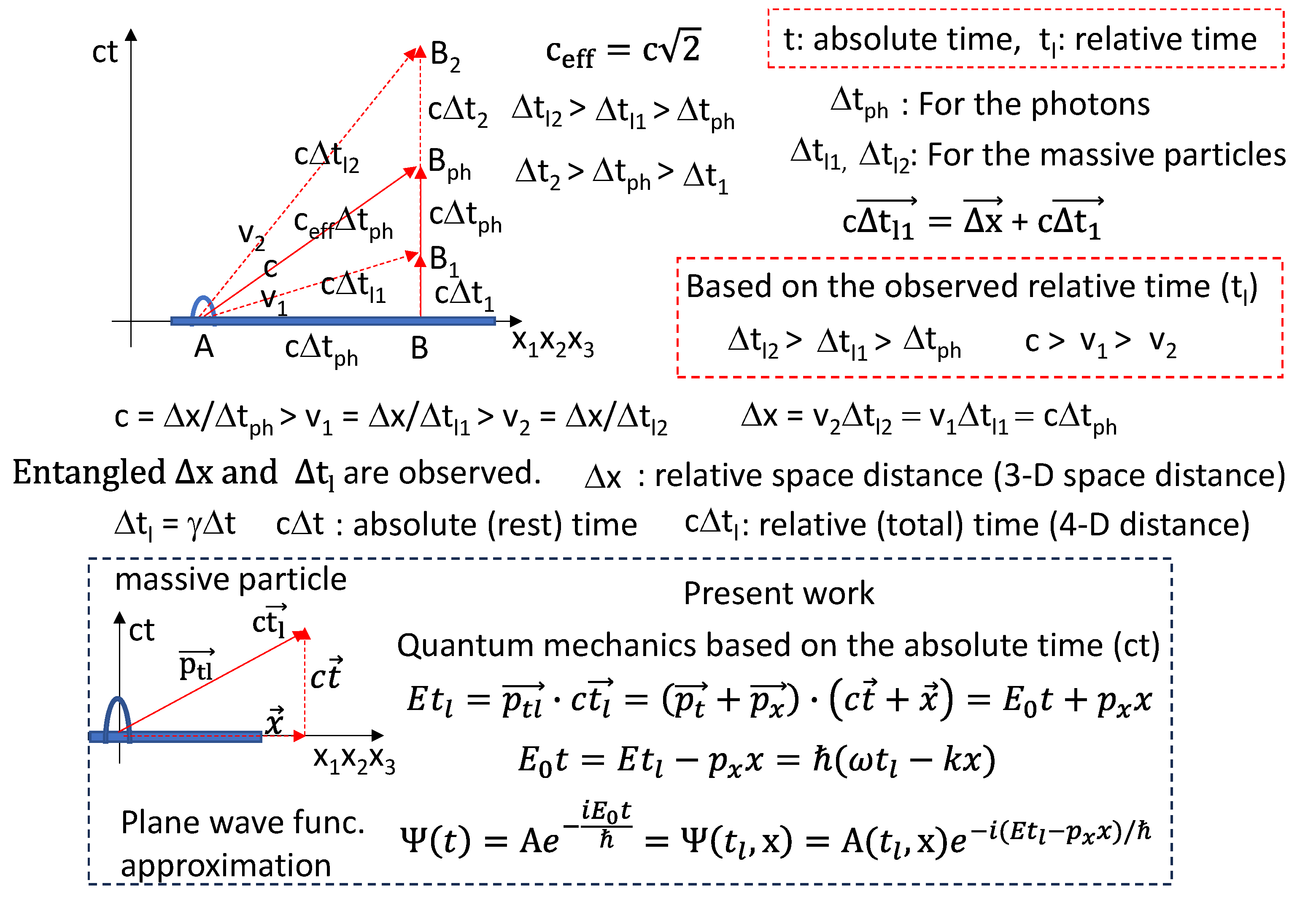
In the 3-D quantized space model, all massive objects in our universe have the same absolute times and all massive objects in our universe have their own relative times. The photons or gamma rays have the constant universal speed of c along the 3 space axes and along the absolute time axis. From these assumptions, it is thought that the universe is the photon space corresponding to the flat 3-D quantized space. This photon space (our whole universe) moves along the absolute time axis with the constant universal photon speed of c. Also, the photons on the universe move along the space axes with the constant universal speed of c. All massive objects in our universe have their own speeds slower than the constant photon speed of c along the space axes. From these speeds of the massive objects slower than the photons, all massive objects have the resistance when moving on the universe in Figures 1, 2, 3 and 4. Therefore, the massive objects and photons are proposed as the warped photon spaces and flat photon spaces, respectively.
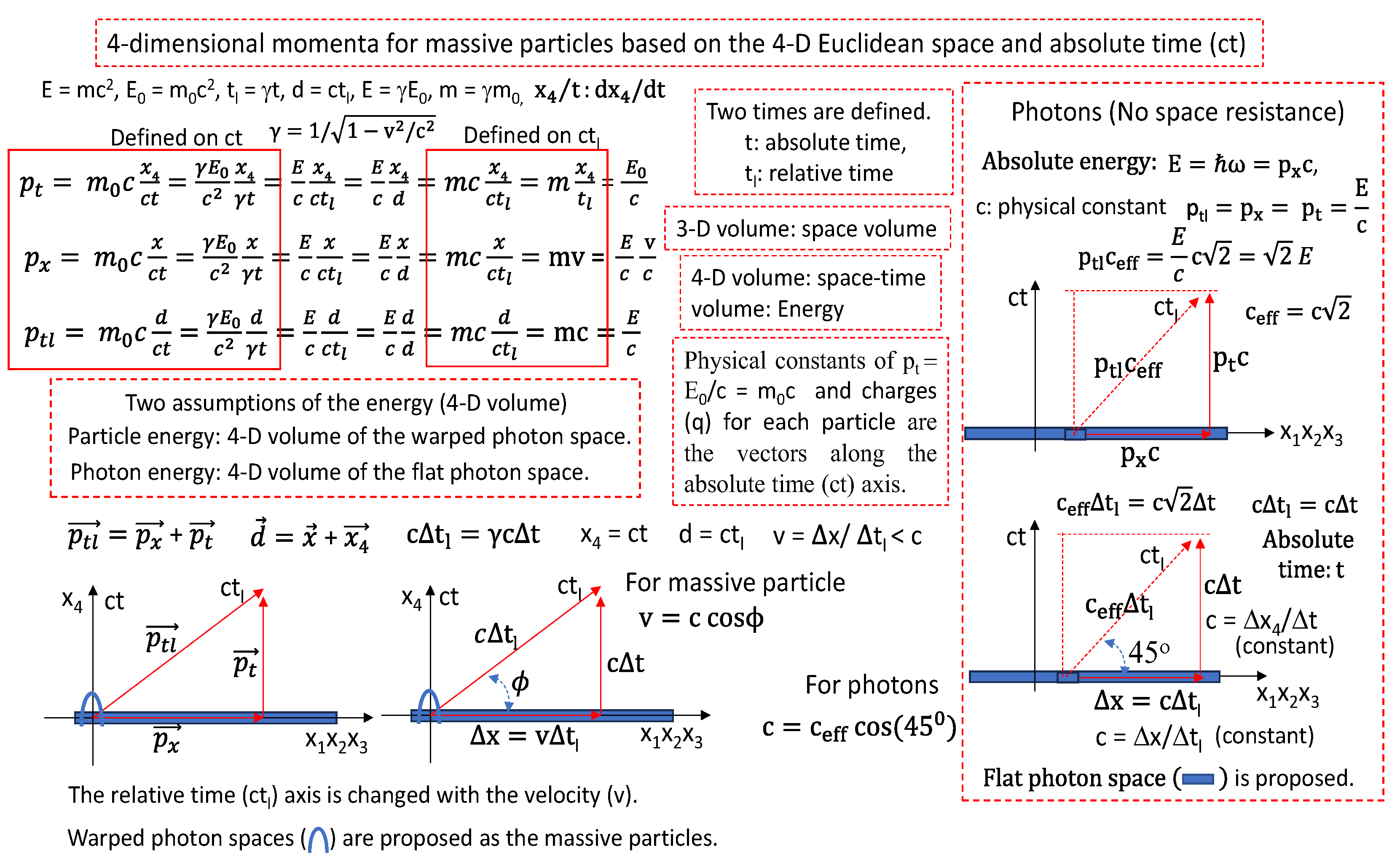
Figure 2.
The 4-D momentum vector and 4-D space distance vector on the 4-D Euclidean space are described in terms of the 3-D quantized space model.
Figure 2.
The 4-D momentum vector and 4-D space distance vector on the 4-D Euclidean space are described in terms of the 3-D quantized space model.
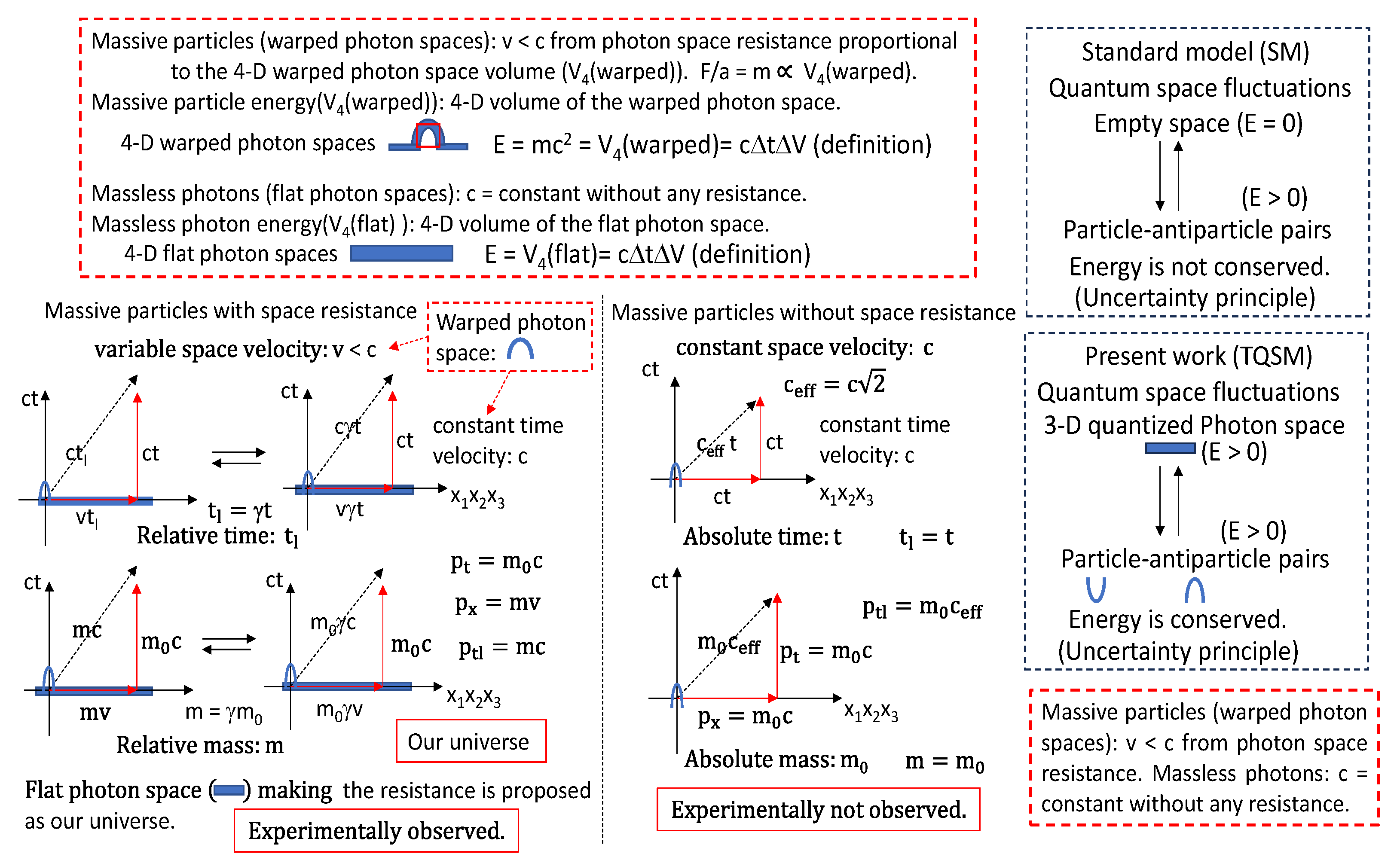
Figure 3.
The massive particles and massless photons are defined as the 4-D warped photon spaces and 4-D flat photon spaces, respectively, with the energy definition.
Figure 3.
The massive particles and massless photons are defined as the 4-D warped photon spaces and 4-D flat photon spaces, respectively, with the energy definition.
Figure 4.
The 4-D momenta for the massive particles are defined on the absolute time (ct) based on the 4-D Euclidean space.
Figure 4.
The 4-D momenta for the massive particles are defined on the absolute time (ct) based on the 4-D Euclidean space.
Based on the 4-D Euclidean space and absolute time, the massive particles and massless photons are explained by analyzing the 4-D momenta in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. The flat 3-D quantized photon space with the quantized time width of cΔt
q in
Figure 5 is proposed for our universe. The present model is called as the 3-D quantized space model (TQSM). In
Figure 1, the massive particles and massless photons are moving with the time momenta of p
t = m
0c and p
γ = E
γ/c, respectively, along the absolute time axis of ct. The mass of m
0 is called as the rest mass because of the zero-space momentum (p
x). The rest masses and time momenta of the massive particles are not changed. And the time momenta of the massless photons are not changed. This means that the photons and particles are moving with the constant photon velocity of c without the resistance along the absolute time axis. For the space momentum of p
x, the massive particles and massless photons behave differently. The space momenta of the massive particles are changing. In other words, the massive particles are moving with the velocity of v slower than the photon velocity of c. In this case the rest masses of the massive particles become the relativistic masses of m = γm
0 larger than the rest masses. Therefore, the space momenta of p
x = mv are different from the time momenta of p
t = m
oc. This indicates that the space is filled of something that makes the resistance against the moving particles. The photons have the space momenta of p
x = E
γ/c the same as the time momenta of p
t = E
γ/c. The photons can move with the constant velocity of c without any resistance along the space axis. This indicates that our universe is the flat 3-D quantized photon space in
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3.
Also, time dilation effects are discussed in the present work. The absolute time (ct) is not dilated because of the constant speed (c) of the universe along the absolute time axis. But the 4-D moving distance of the objects is defined as the relative time (ctl). The 4-D moving distance (d = (c2Δt2 + Δx2)0.5 = (cΔtl)2 should be changed depending on the moving velocity (v = Δx/Δtl) of the objects in the 4-D Euclidean space. Please note that the axis (4-D moving direction) of the relative time is changed following the velocities of the objects. This tells that the relative time (4-D moving distance) of cΔtl should be entangled with the space of Δx. When the velocity (v) of the object is zero, the relative time axis of the object is the same as the absolute time axis of the object. However, the absolute time of ct is not entangled with the space of Δx. Also, the absolute time axis of the universe has the fixed direction applied to whole universe including all objects. This indicates that the relative time of one object is time-dilated or time-contracted from the relative time of another object because the relative time of the objects is increased or decreased by the relative factor of γ = (1-v2/c2)-0.5 depending on the moving velocities of the objects. But the absolute time of the moving objects is fixed and the same to all objects.
We have the earth standard time of ct
e. This earth standard time is measured on the mechanical clock. In the present work, it is assumed, for the simplicity, that the earth is moving much slower than the photons with the speed of c [
5]. Under this assumption, the earth standard time of ct
e is proposed as the absolute time (ct) of all objects, as the first approximation. When the objects with the translational velocities of v move fast, the time dilation effects of the relative times in terms of the earth standard time are discussed.
Also, it is, for the first time, proposed that the living objects experiencing the fast internal vibrations could have the time dilation effects. In fact, the DNA molecule and cell vibrations of the human body have been reported to have the frequency units of kHz, Giga Hz and Tera Hz [
6,
7,
8,
9]. These fast vibrations inducing the living activities can cause the time dilation effects in terms of the earth standard times. These vibrations of the living body increase the relative time of the living body because the 4-D moving distance is increased by these vibrations. It is discussed that there is the relation between the living activities and the time dilation effects. The more time dilations mean the more living activities of the more fast vibrations during the additional dilated times, while the earth standard time of the mechanical clock is fixed and the same to everybody. For example, an advanced person has the much longer time dilation to work more than the normal average persons.
2. 3-D quantized space model (TQSM) and absolute time (ct)
The 4
th axis is the absolute time axis of ct in
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. The photon speed along the absolute time axis is the universal constant of c. The rest mass (m
0) of the massive particle is the constant when the particle moves along the absolute time axis with v = 0. The time momentum (p
t) along the absolute time axis is p
t = m
0c. The massive particle has the constant speed of c along the absolute time axis. This tells that the rest mass of the particle has the character of the photon. The massless photon has the constant speed of c along the absolute time axis. There is no resistance when the particles and photons move along the absolute axis.
The 3-D space with the 3 space axes is proposed. The photon speed along the space axis is the universal constant of c. The rest mass (m0) of the massive particle is changed to the relativistic mass of m = γm0 along the space axis when the particle moves with the non-zero speed of v. The time momentum (pt) along the absolute time axis is, always, m0c. The massive particle has the speed of v slower than the photon speed of c along the space axis. The space momentum of the massive particle is px = mv. The massive particle has the resistance along the space axis but the photon does not. This tells that the massive particle and photon have the different characters of the photon because of the space resistance of the massive particle.
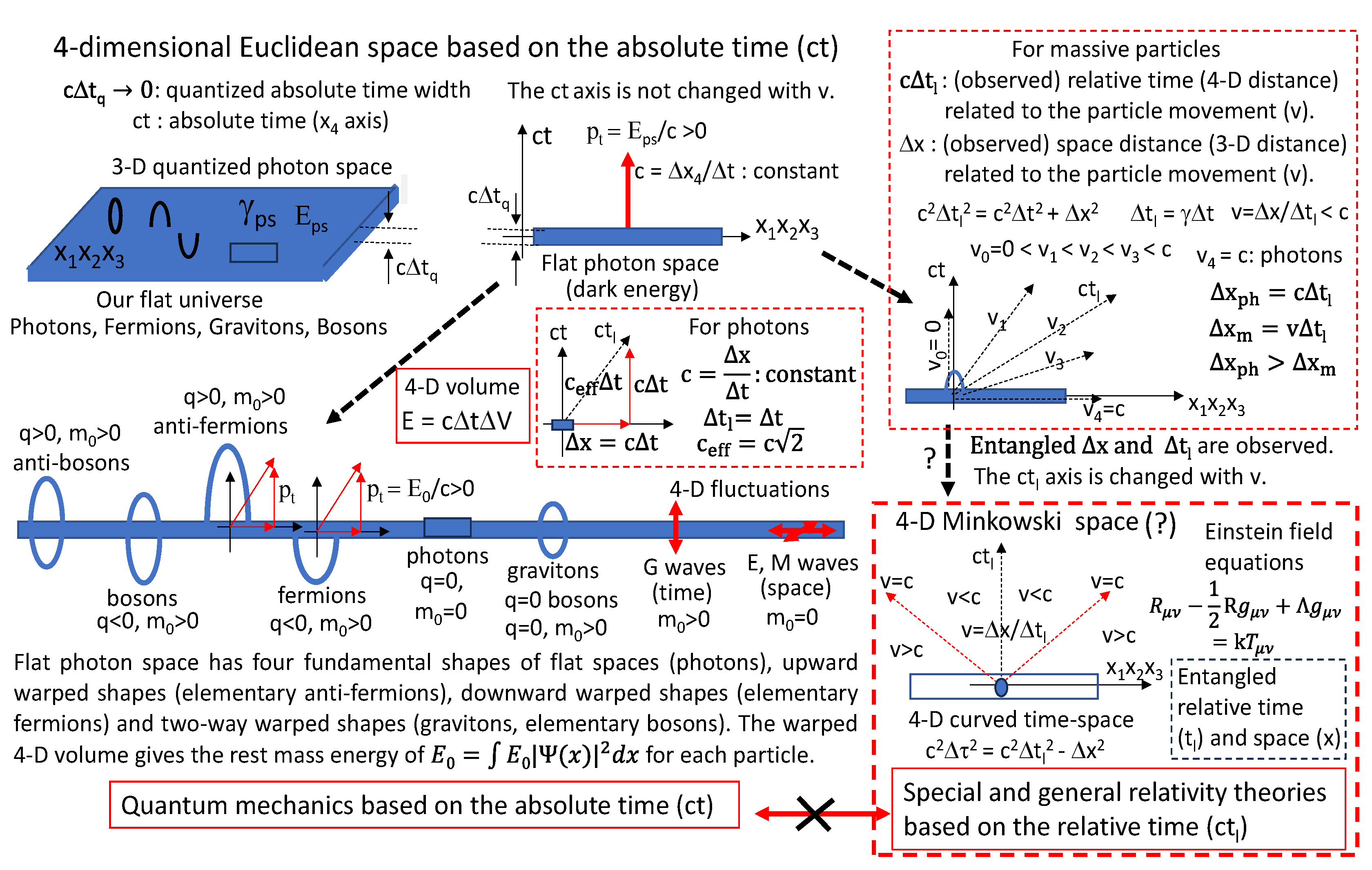
Figure 5.
Our universe is the flat photon space. The particles are proposed by using the fundamental shapes of the warped photon space. The quantum mechanics is based on the absolute time (ct) and the relative theory is based on the relative time (ctl).
Figure 5.
Our universe is the flat photon space. The particles are proposed by using the fundamental shapes of the warped photon space. The quantum mechanics is based on the absolute time (ct) and the relative theory is based on the relative time (ctl).
Figure 6.
The plan wave function is displayed on the absolute time (ct). The moving relative times of the particles and photons are compared.
Figure 6.
The plan wave function is displayed on the absolute time (ct). The moving relative times of the particles and photons are compared.
Therefore, it is proposed that the massive particles are the warped shapes of the 3-D quantized flat photon space along the space axis in
Figure 5. Our universe is the 3-D quantized flat photon space which are made up of photons with all kinds of frequencies. The photons have the constant speed of c when the photons are moving on the flat photon space. But the particles with the warped shapes of the flat photon space have the variable speed of v slower than the photon speed of c because of the resistance.
In
Figure 2, the 4-D momenta are described based on the 4-D Euclidean space. The relative time of ct
l is the 4-D distance. The absolute time of ct is the 4
th axis of the 4-D Euclidean space. The absolute time axis is perpendicular to the three space axes. This means that the absolute time is not entangled with the space in our universe. By the definition of the velocity (v = Δx/Δt
l), the 4-D space distance (the relative time) is depending on the particle velocities by the factor of γ = (1-v
2/c
2)
-0.5. Now I think that our universe is the 3-D flat photon space along the space axes with the quantized quantum time width of cΔt
q in
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. Also, the gamma rays are the 3-D flat photon space. The gamma rays can move with the photon speed along the space axes without the resistance. But the particles are moving with the resistance along the space axes. It is possible for the particles to have the resistance if the particles are the warped shapes of the flat photon space along the absolute time axis. Then it is proposed in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 that the rest mass energies of the massive particles are defined as the 4-D volumes of the warped shapes.
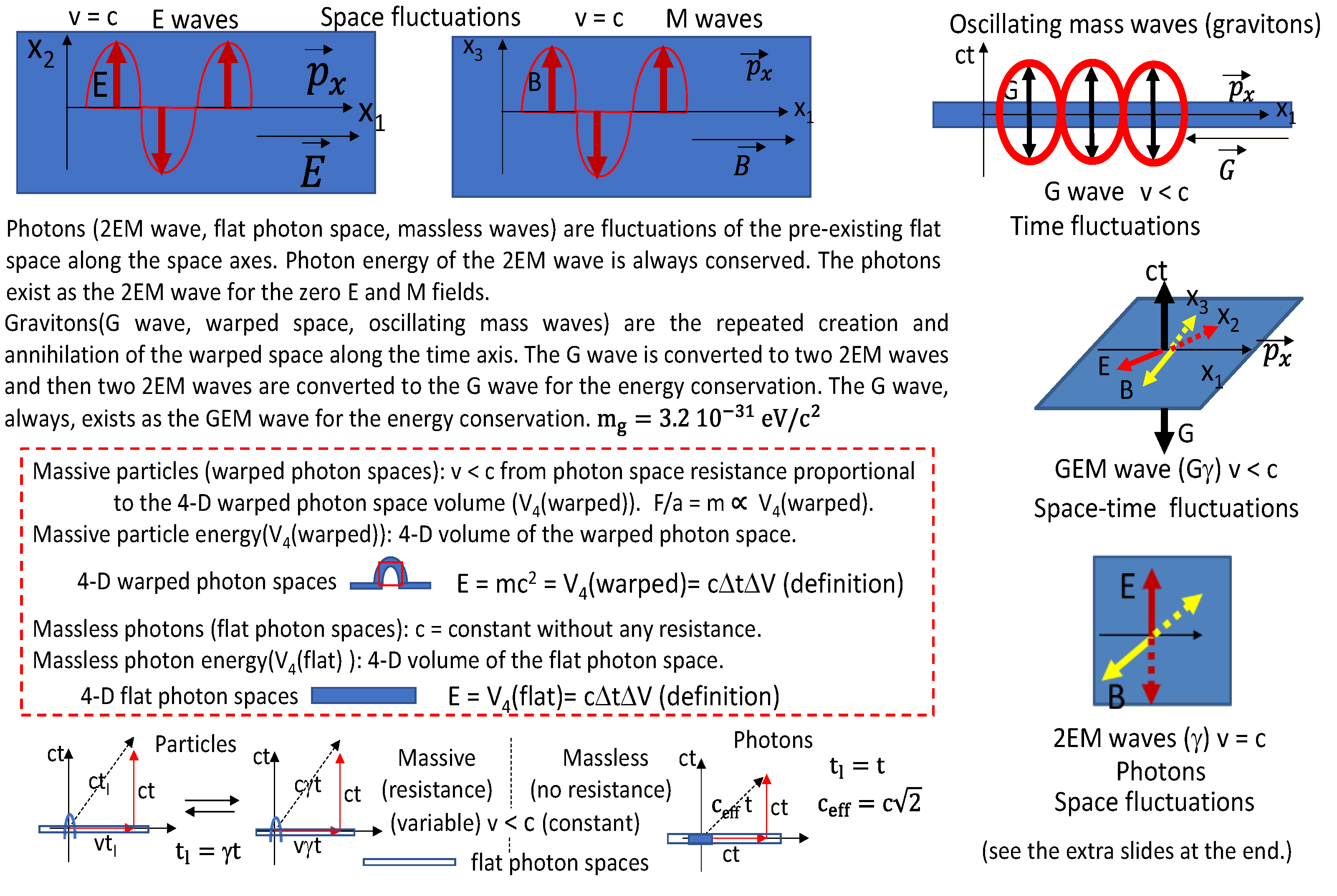
Figure 7.
The electric and magnetic waves are originated from the space fluctuations along the space axes and the gravitational waves are defined as the time fluctuations along the absolute time axis. The photons are the 2EM waves.
Figure 7.
The electric and magnetic waves are originated from the space fluctuations along the space axes and the gravitational waves are defined as the time fluctuations along the absolute time axis. The photons are the 2EM waves.
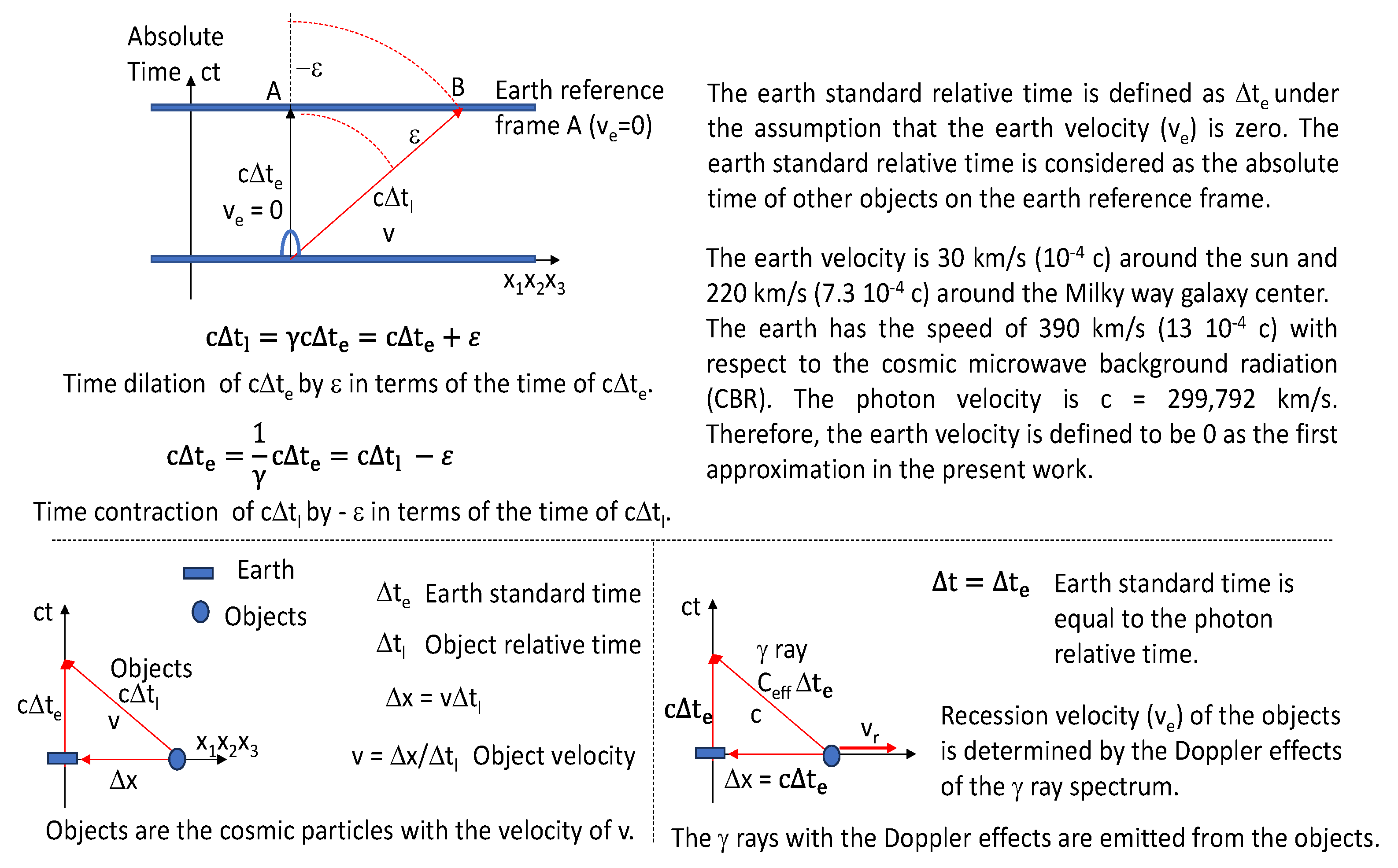
Figure 8.
The relative time dilation is explained on the earth reference frame. The cosmic rays and gamma rays coming from the distant stars are described.
Figure 8.
The relative time dilation is explained on the earth reference frame. The cosmic rays and gamma rays coming from the distant stars are described.
In
Figure 4, the 4-D momenta are described based on the absolute time of ct. Two assumptions are proposed. The particle energy is the 4-D volume of the warped photon space. The photon energy is the 4-D volume of the flat photon space in
Figure 4. Then, in
Figure 5 the flat photon space has four fundamental shapes of flat spaces (photons), upward warped shapes (elementary anti-fermions), downward warped shapes (elementary fermions) and two-way warped shapes (gravitons, elementary bosons). The warped 4-D volume gives the rest mass energy of
for each particle in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6. Quantum mechanics is originated from the warped 4-D volume based on the absolute time (ct) based on the 4-D Euclidean space. But the special and general relativities are based on the relative time of ct
l based on the 4-D Minkowski space in
Figure 5. It is thought from
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 that the difference of the fundamental times between the quantum mechanics and special and general relativities is the major reason why the quantum mechanics and special and general relativity theories cannot be unified in terms of the standard model (SM). In
Figure 6, the plan wave function is shown based on the absolute time of ct.
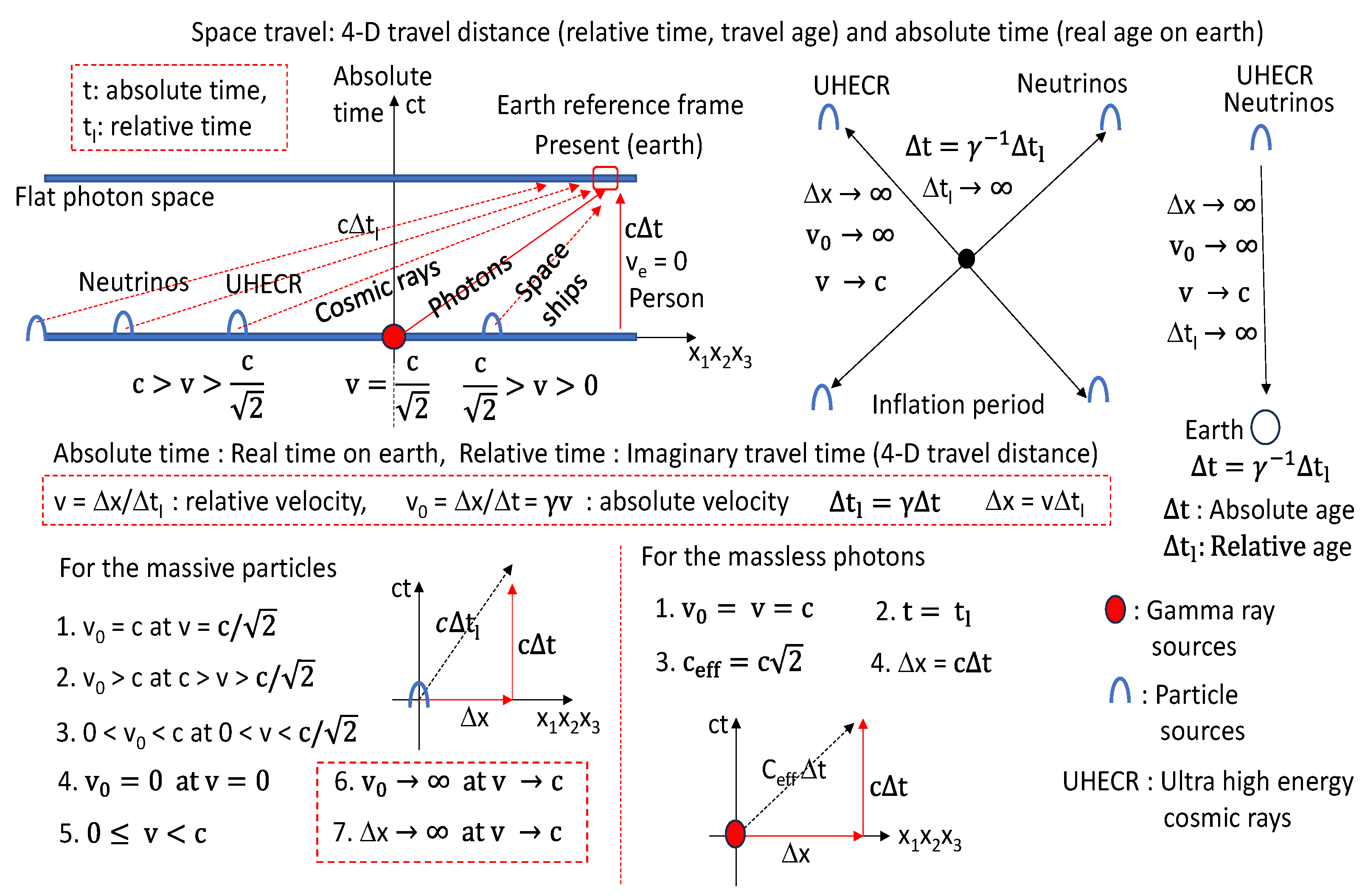
Figure 9.
The relative times of the particles and photons coming from the far distance to the earth are compared. UHECR could be explained by the relative time dilation effect.
Figure 9.
The relative times of the particles and photons coming from the far distance to the earth are compared. UHECR could be explained by the relative time dilation effect.
In the present work, the dark energy is the 3-D quantized flat photon space because our universe is the flat photon space. Therefore, the universe acceleration could be explained by using the flat photon space expansion including the neutrino effects. In
Figure 7, it is proposed that the electric waves and magnetic waves are the space fluctuations because the photons are the electromagnetic waves that are originated from the flat photon spaces. Then the time fluctuations make the gravitational waves which are related with the gravitons. The space-time fluctuations are the GEM waves (gravito-electromagnetic waves). Then the gamma rays are the 2EM waves.
3. Relative time dilations in terms of the TQSM model
In
Figure 8, the earth standard time (t
e) is the earth relative standard time (t
le). In other words, t
e = t
le. The earth velocity (v
e) is assumed to be much slower than the photon velocity (c). In other words,
Figure 10.
The relative time dilations and relative momentum increase are explained by using the flat photon space which are our universe.
Figure 10.
The relative time dilations and relative momentum increase are explained by using the flat photon space which are our universe.
v
e << c. Under this assumption of v
e = 0 in
Figure 8, the earth relative standard time is the earth absolute time. All of the moving particles have their own relative times (cΔt
l) depending on their own velocities (v). Then the earth standard time (t
e) can be considered as the absolute time (ct) of the moving particles. Always cΔt > cΔt
e and cΔt
l = γcΔt
e = cΔt
e + ε. Therefore, always the time dilation of cΔt
e by ε takes place in terms of the time of cΔt
e in
Figure 8. And always the time contraction of cΔt
l by -ε takes place in terms of the time of cΔt
l in
Figure 8. The cosmic particles with the very long relative time can arrive at the earth from the distant stars in
Figure 9. The recession velocities of the stars can be measured by using the well-known Doppler effects of the photon spectra. The earth velocity is 30 km/s (10
-4 c) around the sun and 220 km/s (7.3 10
-4 c) around the Milky way galaxy center. The earth has the speed of 390 km/s (13 10
-4 c) with respect to the cosmic microwave background radiation (CBR) [
5]. The photon velocity is c = 299,792 km/s. Therefore, the earth velocity is defined to be 0 as the first approximation in the present work in
Figure 8.
In
Figure 9, the neutrinos and particles with the high velocities close to the photon velocity of c can be produced during the inflation period. Those particles could be observed as the ultra-high energy cosmic rays (UHECR) at the earth at the present time. The time dillation effects in
Figure 9 can explain the origin of the ultra-high energy cosmic rays. Also, the absolute time velocities and relative time velocities are compared. The absolute time ages (Δt) are the biological ages of the living objects and correspond to the half lives of the cosmic rays. The relative time ages of Δt
l are the time dilated ages corresponding to the 4-D space-time moving distances. In fact, all of objects leaving the same universe at the same absolute times have the same absolute time ages of Δt but the different realtive time ages of Δt
l in
Figure 9. The cosmic rays make the succesful space travels with the velocity close to the photon velocity of c. Therefore, we, the human, can make the succesful space travels with the relative time dillation effects if the space ship can have the velocity close to the photon velocity of c. The space travels of the human could not be impossible because the biological ages of the human are the absilute time ages of Δt much younger than the relative time ages of Δt
l. In other words, Δt
l = γΔt. Observation of the relative time dilations supports the assumption that our universe is the 3-D quantized flat photon space. In
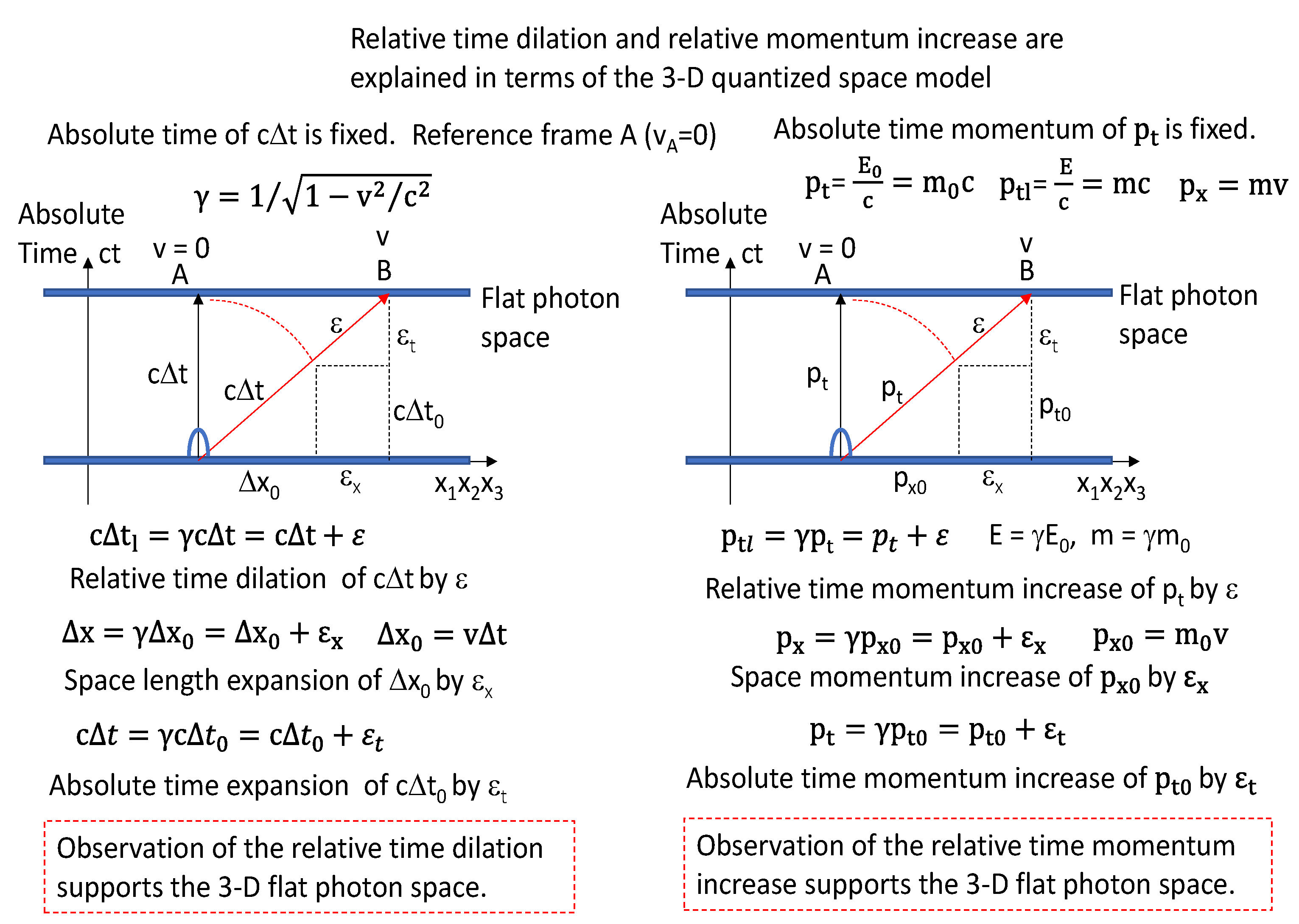
Figure 10, the relative time dilation and relative momentum increase are explained in terms of the 3-D quantized space model. Δt
l = γΔt and p
tl = γp
t. The relative time dilation is closely related to the fixed absolute time of cΔt. Also, the relative momentum increase is closely related to the fixed absolute time momentum of p
t. In
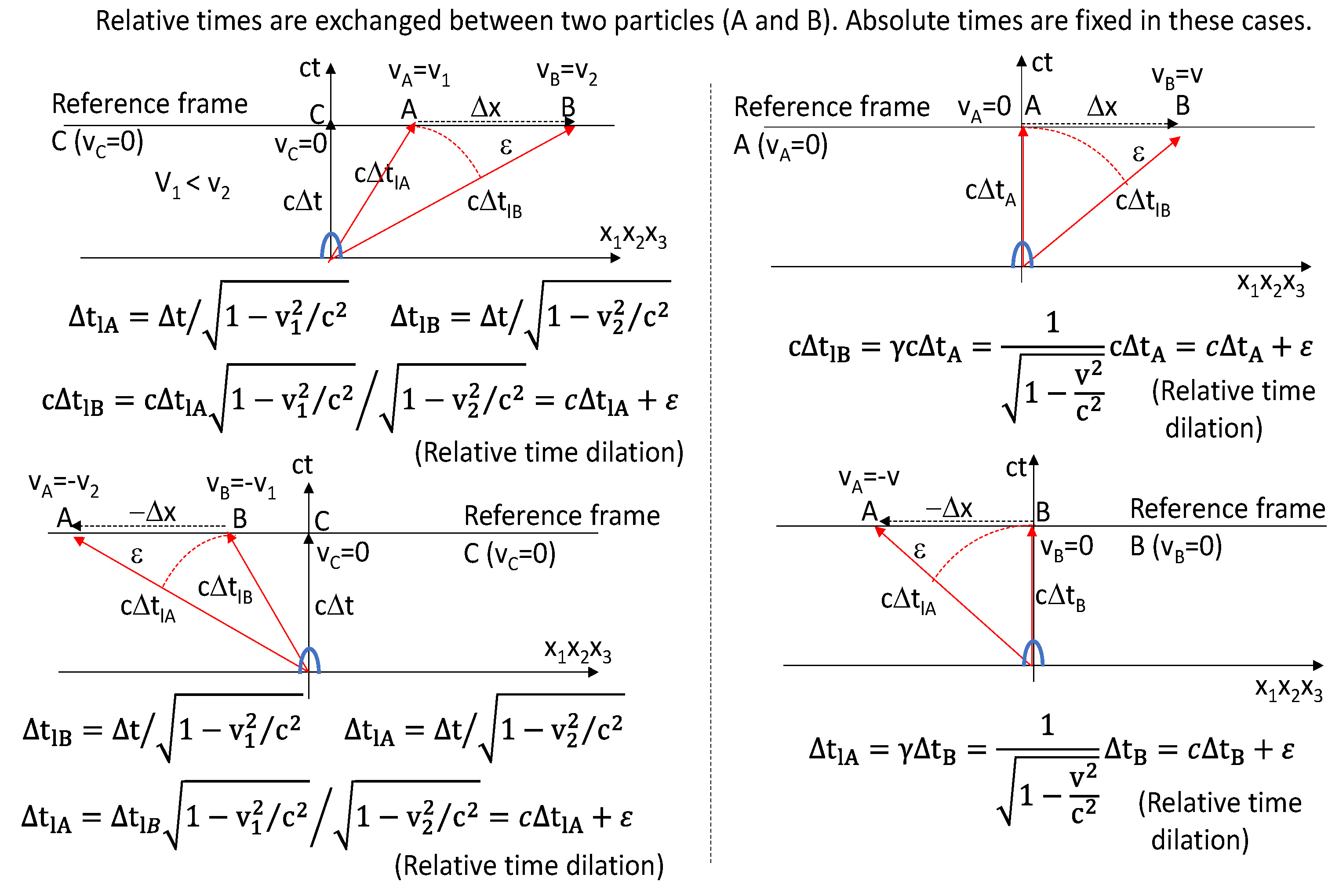
Figure 11, the relative times are exchanged between two particles of A and B. The absolute times are fixed in these cases.
Figure 11.
The relative times are exchanged between two particles. The reference frames are exchanged between the right two figures.
Figure 11.
The relative times are exchanged between two particles. The reference frames are exchanged between the right two figures.
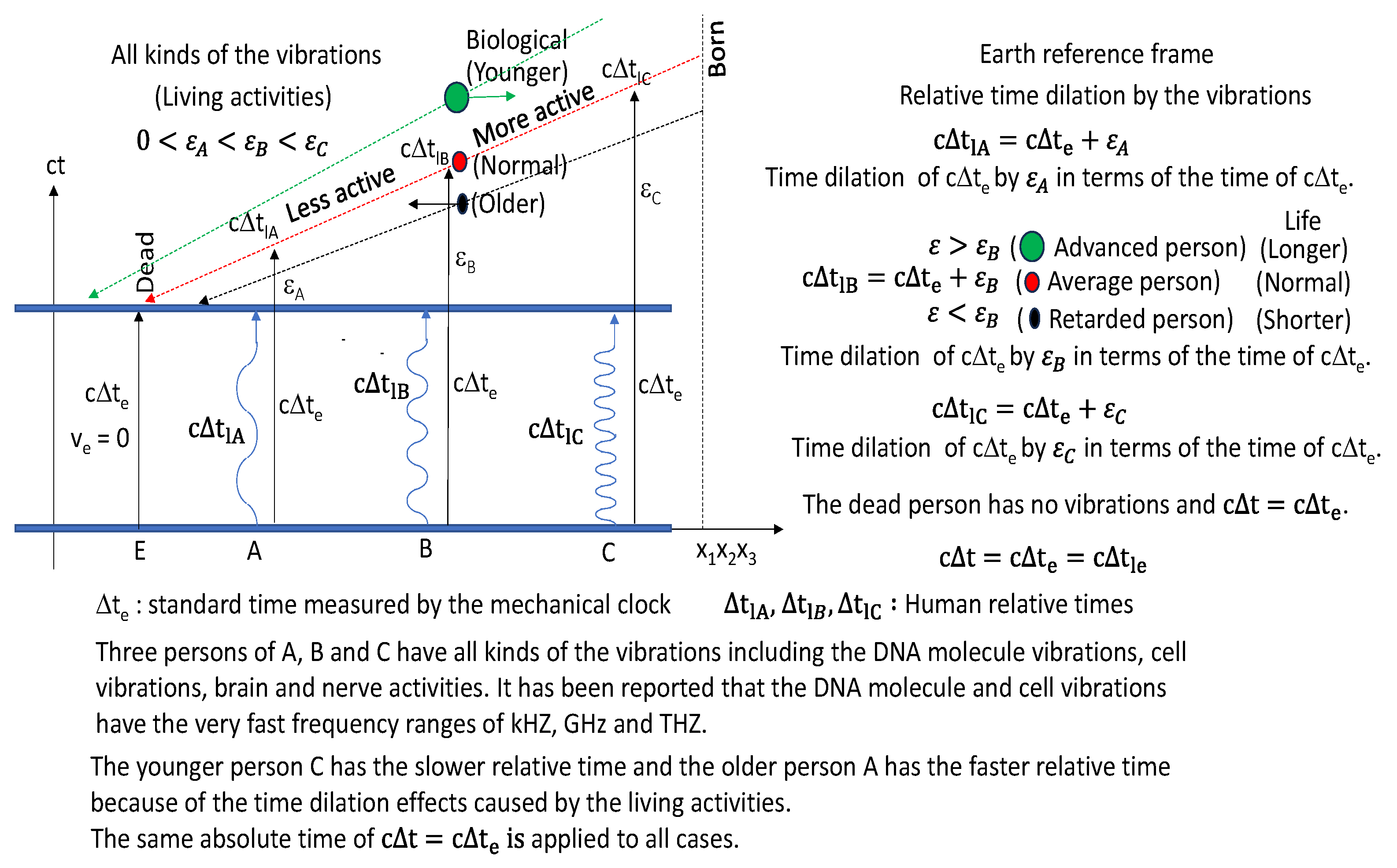
In
Figure 12, the time dilations take place because of the high frequency vibrations of the absolute times with the very high frequency ranges of KHz, GHz and THz which all organs, all cells and all DNA molecules of the living objects have [
6,
7,
8,
9]. If there are no vibrations, there are no time dilation. The absolute time is the earth standard time in
Figure 12. If the objects on the earth are vibrating, the time of the objects will make the time dilations. I will apply this concept to the living persons. Three persons of A, B and C have all kinds of the vibrations including the brain and nerve activities. The younger person C has the slower relative time and the older person A has the faster relative time because of the time dilation effects caused by the living activities. The same absolute time of
applied to all cases. The time of Δt
lB is the real time of an average person in
Figure 12 even though the mechanical clock shows the time of Δt
e. The average person feels like his time flows slow when the average person sees the time (Δt
e) of the mechanical clock. Then, when the person B works very hard and have more activities, the person B feels like his time flows slower than the time of the person A and faster than the time of the person C when the three persons see the time (Δt
e) of the mechanical clock. For example, when the time of the mechanical clock indicates 6 hours, the persons A, B and C feel like 7 hours, 8 hours and 9 hours. The very hard-working persons, very active athletes, very fast-growing babies, and very hard-studying researchers etc. causing the very active living activities of the brains and internal bodies have the more time dilations which mean the much slower times [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. As a matter of fact, we feel the perceptual time dilations during the everyday lives. For example, when we are at the child age like the elementary kids, we feel a day and a year longer than when we are at the old age like the grandparents. These kinds of the time dilations can be explained in the present work by introducing, for the first time, the absolute time (ct) and relative time (ct
l).
Figure 12.
The fast vibrations of the living activities including the DNA molecules and cells of the body could cause the relative time dilations. These relative times that we feel are different from the absolute times measured by the mechanical clock. Our ages are measured by the clock times. Also, our lives can be closely related with the relative time dilation effects of our body.
Figure 12.
The fast vibrations of the living activities including the DNA molecules and cells of the body could cause the relative time dilations. These relative times that we feel are different from the absolute times measured by the mechanical clock. Our ages are measured by the clock times. Also, our lives can be closely related with the relative time dilation effects of our body.
A person, in general, has a translational speed much slower than the photon speed of c. Therefore, the translational time dilation effect of the person is negligible on the earth. But the internal vibrations of every organ, every cell and all DNA molecules have the very high frequencies of the kHz, GHz and THz units and can be increased by the external activities such as the running, exercise and deep thinking [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. In
Figure 12, it is proposed that the advanced persons with the more living activities enhancing the internal vibrations have the more relative time dilations and live the longer lives. The difference between the perceptual times and mechanical clock times we are feeling in the real daily lives is explained by the time dilation effects due to the fast vibrations of the DNA molecules and cells, in the present work. Therefore, the further research on how to enhance the internal vibrations is needed. The many researches have been made on the difference between the perceptual time and the real clock time [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. It has been reported that the perceptual time is slower than the mechanical clock time. In the present work, it is proposed that this difference is originated from the relative time dilation effects due to the fast vibrations of the DNA molecules and cells in the body.
4. Summary
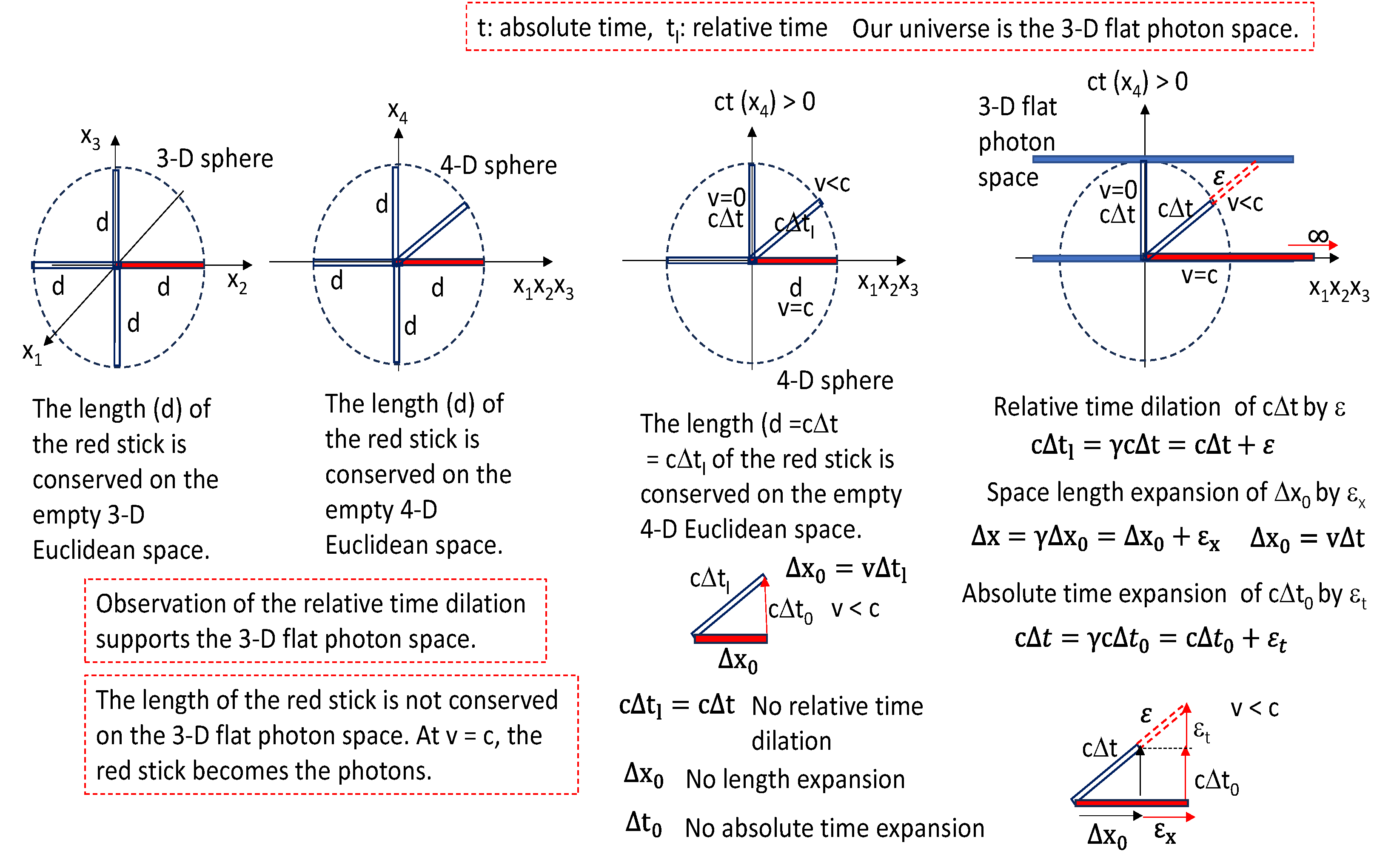
In
Figure 13, the 3-D Euclidean space is applied to explain our universe. The relative time dilation has been observed. The relative time dilation is proved easily by using the 3-D flat photon space. Our universe is proposed as the 3-D quantized space which is the 3-D flat photon space. The space length is expanded, too, depending on the particle velocity of v. The fixed absolute time axis of ct is the 4
th axis and the variable relative time axis of ct
l is the 4-D space-time moving distance axis of the particles. Because the 4-D red stick is the 4-D vector, the 4-D stick length is separated into the space component along the space axis and absolute time component along the absolute time axis. Then the 4-D red stick length is conserved when changing the vector direction in the empty 4-D Euclidean space. This indicates that there is no relative time dilation or relative time expansion. But the relative time dilation has been observed as Δt
l = γΔt. When the 4-D stick length is increased from cΔt to γcΔt
l, the 3-D quantized flat space is introduced as our universe. Because the red stick becomes the photons when v is equal to the photon velocity of c, the 3-D quantized space is considered as the 3-D quantized flat photon space. The photons are the 3-D flat space. The massive particles are the warped forms of the 3-D quantized photon space in the present work. And the energy is defined as the 4-D volume of the massive particles and photons.
Figure 13.
The 4-D length of the red stick is fixed between the empty 4-D Euclidean space. But the 4-D length, defined as the relative time on the flat photon space, of the red stick is varying depending on the velocity of v. This varying relative time (cΔt) causes the time dilation in terms of the absolute time (cΔt). Observation of the relative time dilations support the assumption that our universe is the 3-D quantized flat photon space.
Figure 13.
The 4-D length of the red stick is fixed between the empty 4-D Euclidean space. But the 4-D length, defined as the relative time on the flat photon space, of the red stick is varying depending on the velocity of v. This varying relative time (cΔt) causes the time dilation in terms of the absolute time (cΔt). Observation of the relative time dilations support the assumption that our universe is the 3-D quantized flat photon space.
The relative time dilation effects have been observed from many cases like, for example, the GPS time correction system and the cosmic muon decay. In the present work, the relative time dilations depending on the particle velocities are simply explained by comparing the absolute times and relative times based on the 4-D Euclidean space with the 3-D quantized flat photon space. It is assumed that our universe is the 3-D quantized flat space. Also, the relative time momentum increase is proved. The space length expansion and space momentum increase are proved easily in the present work. Observation of the relative time dilations (Δt
l=γΔt) and relative time momentum increase (E=γE
0) in
Figure 10 supports the assumption that our universe is the 3-D quantized flat photon space in terms of the TQSM model.
In the present work, the 4-D Euclidean space is used for our universe. The 4th (x4) axis is defined as the absolute time axis of ct and the 3-D x1x2x3 space is named as the 3-D quantized space which corresponds to the 3-D quantized flat photon space. The 4-D momenta are analyzed by using the absolute time. Because the relative time vector is the 4-D moving distance vector, the relative time is entangled with the x1x2x3 space and the absolute time (ct) but the absolute time is not entangled with the x1x2x3 space.
The wave functions of the particles are established based on the absolute time of ct but the special and general relative theories are based on the relative time of ctl. This is the reason why the quantum theory and special and general relative theories have not been unified. But in the present work, the gravitational waves are defined as the fluctuations along the absolute time axis of ct. And the wave functions in the quantum mechanics are displayed based on the absolute times of ct. Therefore, the quantum mechanics and gravitational theory can be united by using the same absolute times of ct and the same 4-D Euclidean space in the present work.
Also, in the present work, it is concluded that the fast vibrations of the DNA molecules and cells inside the body could make the relative time dilation effects. Because the fast vibrations of the DNA molecules and cells with the frequency ranges of KHz, GHz and THz [
7,
8,
9] are the living activities, the infants could have relatively the most active and faster vibrations and the old people would have relatively the less active and slower vibrations. This indicates that the infants would have the more time dilation effects and the old people would have the less time dilation effects. And, it is expected that the very active people with the more time dilation effects at the same ages would live the longer lives. The difference between the perceptual times and mechanical clock times we are feeling in the real daily lives [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16] is explained by the time dilation effects due to the fast vibrations of the DNA molecules and cells, in the present work. The systematic further researches are required.