Submitted:
11 November 2025
Posted:
12 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Immunohistochemistry
3.2. Statistical Analysis
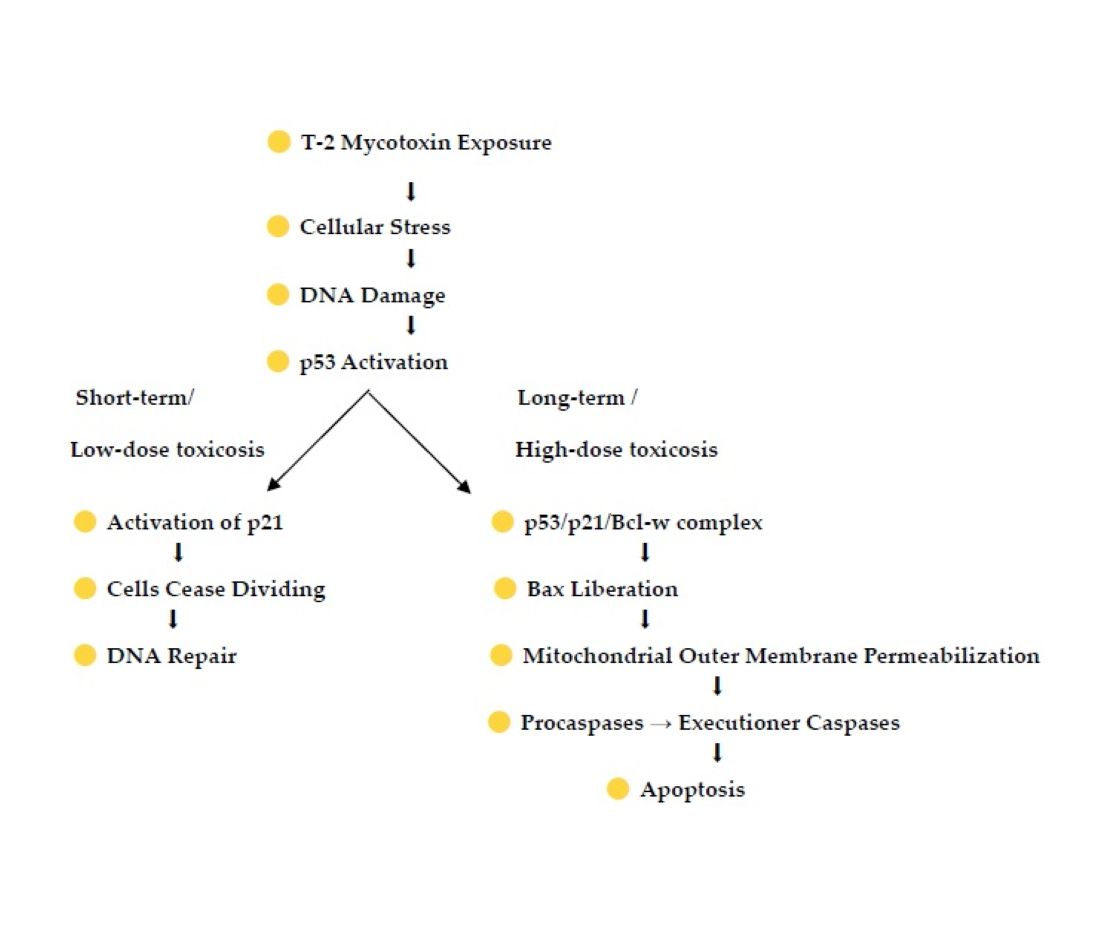
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| MAPK | Mitogen activated protein kinase |
| CDK inhibitor 21 | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, also known as p21waf1/cip1 or P21/CDKN1A |
| CIP/Kip | CDK interacting protein/Kinase inhibitory protein |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PCT | Proximal convoluted tubuls |
| DCT | Distal convoluted tubuls |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TRP53 | transformation-related protein 53 |
| Bcl | B-cell lymphoma |
| Bcl Xl | B-cell lymphoma-extra large |
| Bcl-w | BCL-2-like protein 2 |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
References
- Meneely, J.; Greer, B.; Kolawole, O.; Elliott, C. T-2, and HT-2 Toxins: Toxicity, Occurrence and Analysis: A Review. Toxins (Basel) 2023, 15, 8, 481. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, T. An update on T2-toxins: metabolism, immunotoxicity mechanism and human assessment exposure of intestinal microbiota. Heliyon 2022, 8, 8. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, M.; Negi, B.; Kaushik, N.; Adhikari, A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Choi, E.H. T-2 mycotoxin: toxicological effects and decontamination strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33933-33952. [CrossRef]
- Janik, E.; Niemcewicz, M.; Podogrocki, M.; Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Bijak, M. T-2 Toxin—The Most Toxic Trichothecene Mycotoxin: Metabolism, Toxicity, and Decontamination Strategies. Molecules 2021, 26, 6868. [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M; Ishii, K.; Ueno, Y. Metabolism of Trichothecene Mycotoxins: I. Microsomal Deacetylation of T-2 Toxin in Animal Tissues. JB 1977, 82, 6, 1591–1598.
- Islam, Z.; Nagase, M.; Yoshizawa, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Sakato, N. T-2 toxin induces thymic apoptosis in vivo in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1998, 148, 2, 205-214. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Wu, G.; He, Q.; Tang, H.; Wang Y. The toxicity of acute exposure to T-2 toxin evaluated by the metabonomics technique. Mol Biosyst 2015, 11, 882–891. [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.P. Effects of T-2 mycotoxin on gastrointestinal tissues: A Review of in vivo and in vitro models. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 1989, 18, 374–387. [CrossRef]
- Lafarge-Frayssinet, C.; Chakor, K.; Lafont, P.; Frayssinet, C. Transplacental transfer of T2-toxin: pathological effect. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 1990, 10, 64– 68.
- Song, C.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Neurotoxic mechanisms of mycotoxins: Focus on aflatoxin B1 and T-2 toxin. Environ Pollut 2024, 356, 124359. [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Das Gupta, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Velkov, T.; Shen, J. T-2 toxin and its cardiotoxicity: New insights on the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. FCT 2022, 167, 113262. [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Magun, B.; Wood, L. Lung inflammation caused by inhaled toxicants: a review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016, 11, 1, 1391-1401. [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Han, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, Q. T-2 Toxin Induces Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Cytoprotective Autophagy in Chicken Hepatocytes. Toxins 2020, 12, 90. [CrossRef]
- Nayakwad, S.; Ramu, R.; Sharma, A. K.; Gupta, V. K.; Rajukumar, K.; Kumar, V.; Shirahatti, P. S.; Rashmi L.; Basalingappa, K. M. Toxicopathological studies on the effects of T-2 mycotoxin and their interaction in juvenile goats. PLOS One 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, N.D.; Prawez, S. Immunopathological effects of experimental T-2 mycotoxicosis in Wistar rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2020, 40, 772–790.
- Chrustek, A.; Twarużek, M.; Zastempowska, E.; GrajewskAnnales, J. Ann Univ Pedagog Crac Stud Naturae 2016, 1: 105–114. ISSN 2543-8832.
- Sancho-Martínez, S.M.; López-Novoa, J.M.; López-Hernández, F.J. Pathophysiological role of different tubular epithelial cell death modes in acute kidney injury. Clin Kidney J 2015, 8, 5, 548-559. [CrossRef]
- Molitoris, B. A. Therapeutic translation in acute kidney injury: the epithelial/endothelial axis. J Clin Invest 2014, 124, 6, 2355- 2363. doi.org/10.1172/JCI72269.
- Tang, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J.; Dong, Z. P53 in kidney injury and repair: Mechanism and therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol Ther 2019, 195, 5-12. [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Djokovic, B.; Jankovic, M.G.; Harrell, C. R.; Fellabaum, C.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: a balance on the knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity. J Biomed Sci 2019, 26, 25. [CrossRef]
- Melchini, A.; Traka, M. Biological Profile of Erucin: A New Promising Anticancer Agent from Cruciferous Vegetables. Toxins 2010, 2, 593-612. [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, J.M.; Gifford, C.C.; Tang, J.; Higgins, P.J.; Samarakoon, R. Emerging role of tumor suppressor p53 in acute and chronic kidney diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 2022, 9, 79, 9, 474. [CrossRef]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ 2022, 29, 946–960. [CrossRef]
- Shinozuka, J.; Li, G.; Kiatipattanasakul, W.; Uetsuka, K.; Nakayama, H.; Doi, K. T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis in lymphoid organs of mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 1997, 49, 5, 387–392. [CrossRef]
- Hussar, P. Apoptosis Regulators Bcl-2 and Caspase-3. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 1624-1636. [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 2007, 35(4), 455–516. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shaikh, Z. A. Cadmium induces cell cycle arrest in rat kidney epithelial cells in G2/M phase. Toxicology 2006, 224, 1–2, 56-65. [CrossRef]
- Surget, S.; Khoury, M.P.; Bourdon, J.C. Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: a clinical perspective. OncoTargets Ther 2013, 7, 57–68. [CrossRef]
- Hernández Borrero, L.J.; El-Deiry, W.S. Tumor suppressor p53: Biology, signaling pathways, and therapeutic targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2021, 1876, 1, 188556. [CrossRef]
- Bykov, V.J.; Eriksson, S.E.; Bianchi, J.; Wiman, K.G. "Targeting mutant p53 for efficient cancer therapy". Nat Rev Cancer 2018, 2, 89–102. [CrossRef]
- Capuozzo, M.; Santorsola, M.; Bocchetti, M.; Perri, F.; Cascella, M.; Granata, V.; Celotto, V.; Gualillo, O.; Cossu, A.; Nasti, G.; Caraglia, M.; Ottaiano, A. p53: From Fundamental Biology to Clinical Applications in Cancer. Biology 2022. 11. 1325. [CrossRef]
- Vaseva, A. V.; Moll, U. M. The mitochondrial p53 pathway. BBA – Bioenergetics 2008, 1787, 5, 414-420. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. M.; Jung, C.-H.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S.-G.; Jong, Park, K.; Um, H.-D. The p53/p21 Complex Regulates Cancer Cell Invasion and Apoptosis by Targeting Bcl-2 Family Proteins. Cancer Res I 2017, 77, 11, 3092–3100. [CrossRef]
- Karimian, A.; Ahmadi, Y.; Yousefi, B. Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair 2016, 42, 63-71. [CrossRef]
- O’Brate, A.; Giannakakou, P. The importance of p53 location: nuclear or cytoplasmic zip code? Drug Resist Updat 2003, 6, 6, 313-322. [CrossRef]
- Abella, N.; Brun, S.; Calvo, M.; Tapia, O.; Weber, J.D.; Berciano, M.T.; Lafarga, M., Bachs, O.; Agell, N. Nucleolar disruption ensures nuclear accumulation of p21 upon DNA damage. Traffic 2010, 11, 6, 743-55. [CrossRef]
- Hussar, P.; Blagoevska, K.; Dovenska, M.; Pendovski, L.; Popovska-Percinic, F. Apoptosis in Kidneys Exposed to T-2 Mycotoxin: Immunolocalization of p53 and p21. In Sciendo, 16, 1-2. Proceedings of the Latvian Academy of Sciences. Section B. Natural, Exact, and Applied Sciences, 79: The International Scientific Conference on Medicine, University of Latvia (UL), UL House of Science, Riga, 25.04.2025.
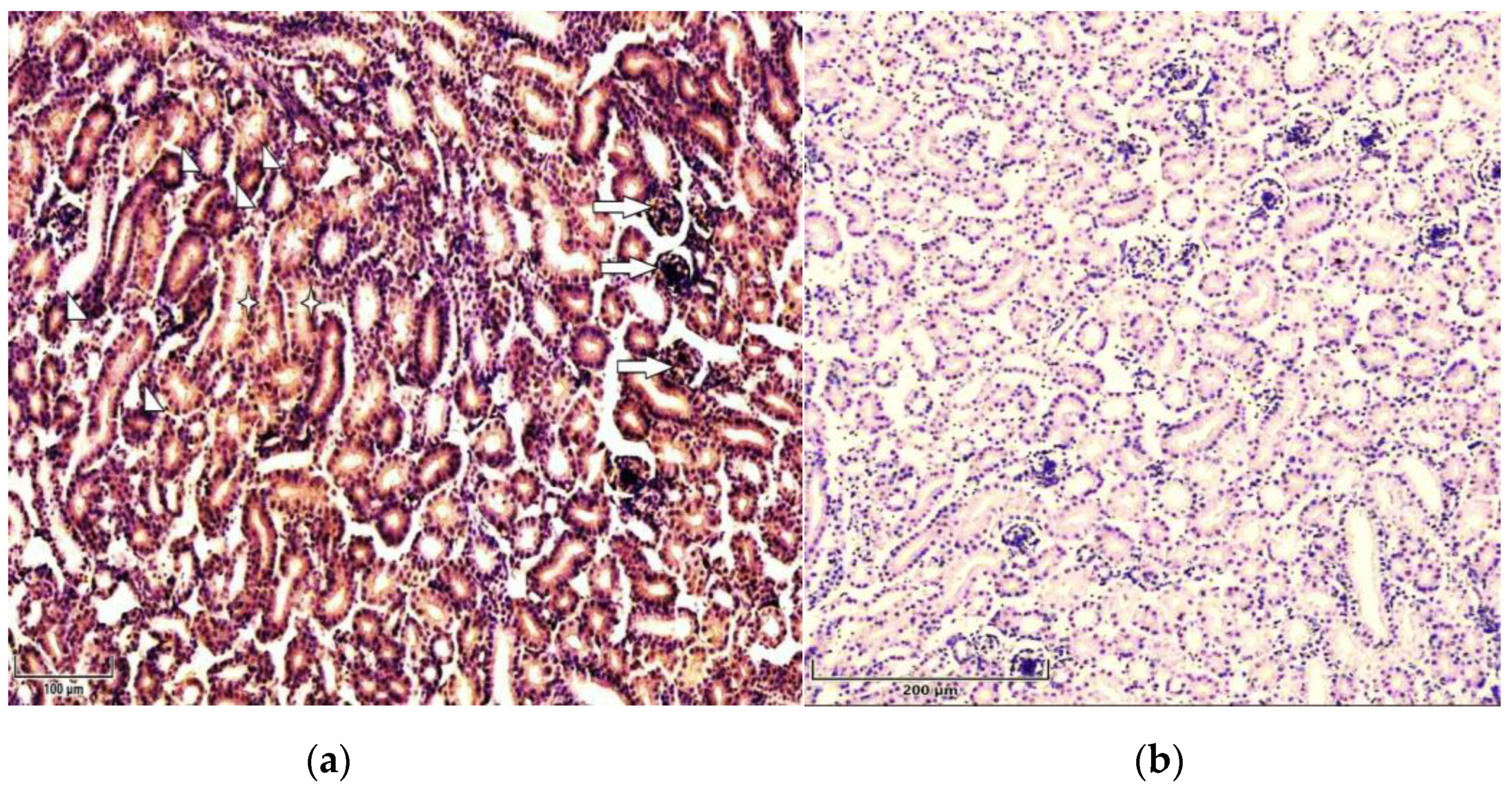
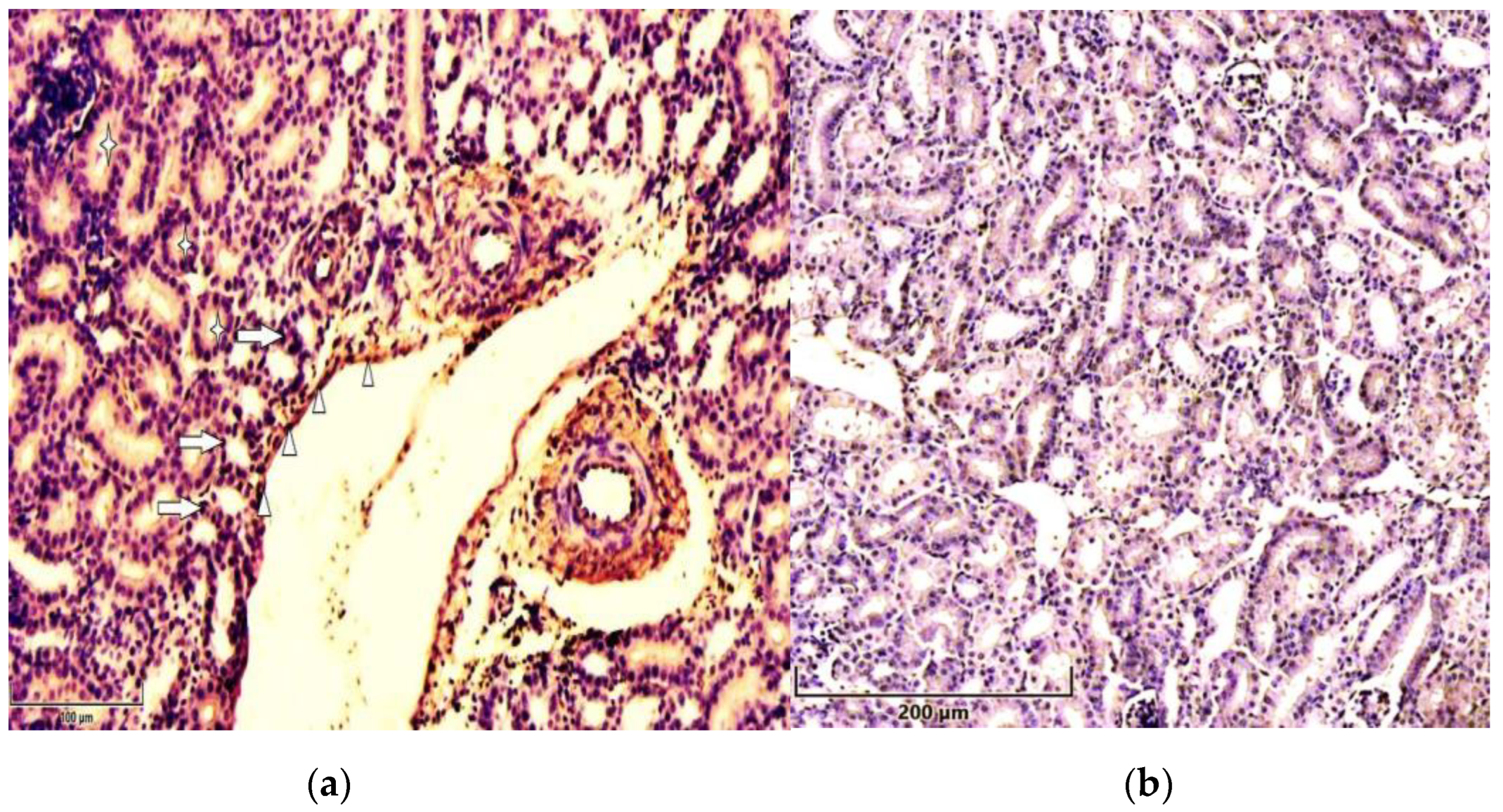
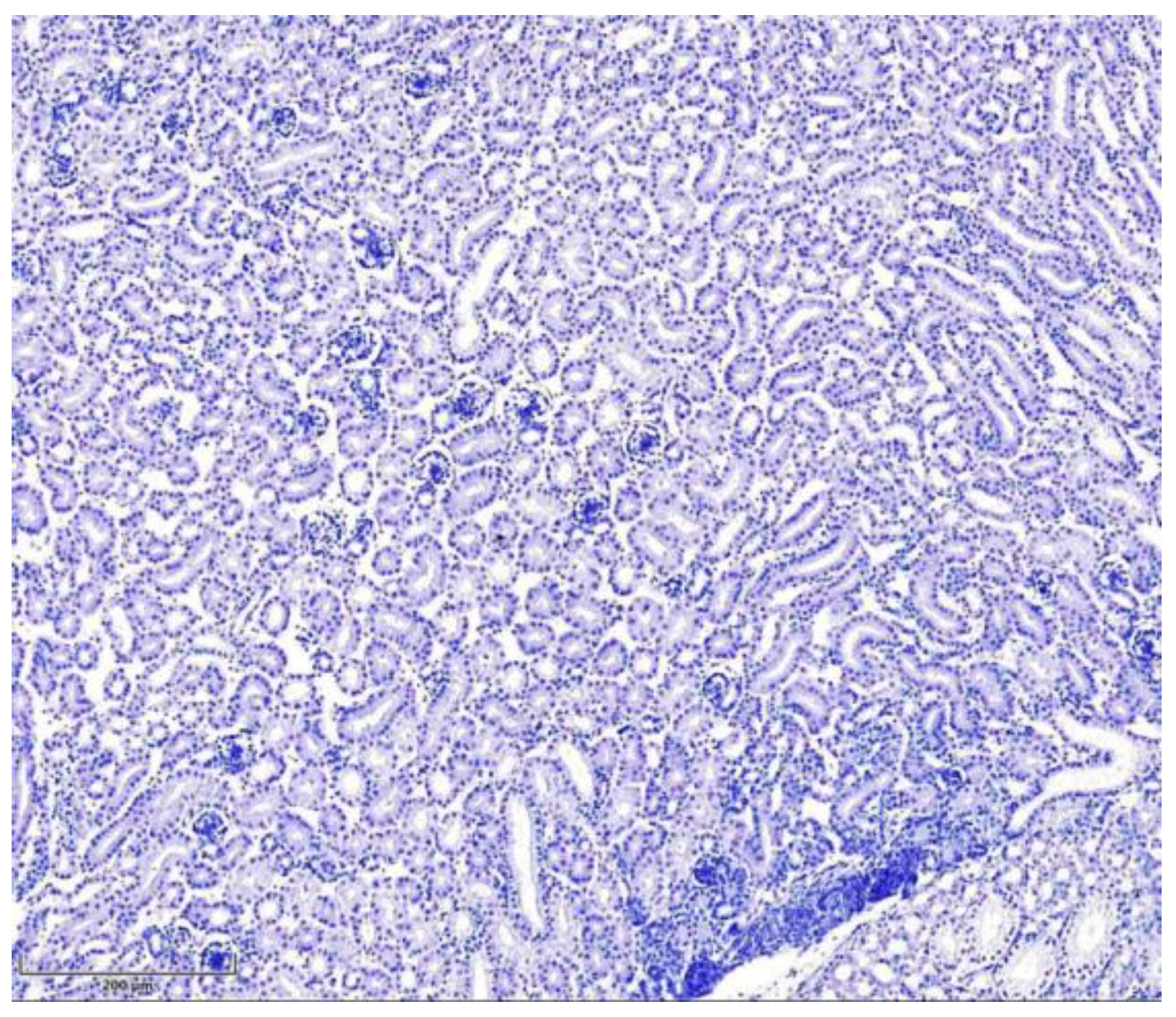
| Antibody | p53* | p21* | ||
| Chicken’s group | T-2 toxin group | Control group | T-2 toxin group | Control group |
|
Proximal convoluted tubules |
+++ | + | ++ | + |
|
Distal convoluted tubules |
++ | + | ++ | + |
| Endothelium | ++ | + | ++ | + |
| Glomerulus | ++ | + | +/++ | + |
| Protein |
Mean intensity T-2 toxin group |
SD T-2 toxin group |
Mean intensity Control group |
SD Control group |
Paired t-test p-value 1 |
| p53 | 2.25 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.0154 |
| p21 | 1.88 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.00 2 | 0.0060 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





