Submitted:
10 November 2025
Posted:
11 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Materials and AP Extract (APE)
2.3. Chromatographic Condition
2.4. Biological Sample Extraction Procedures
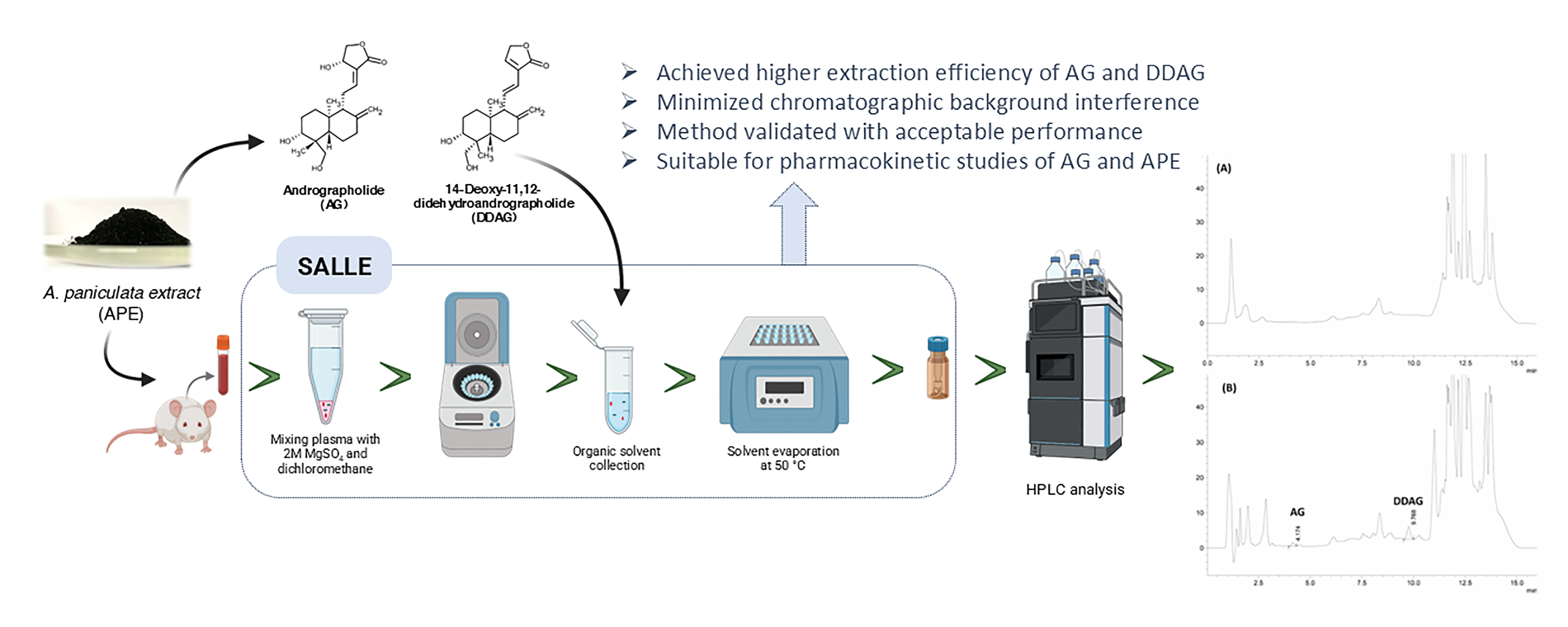
2.5. SALLE
2.6. SALLE-HPLC-DAD Method Validation
2.6.1. Selectivity and Specificity
2.6.2. Linearity and Range
2.6.3. Sensitivity
2.6.4. Matrix Effect
2.6.5. Precision and Accuracy
2.6.6. Stability
2.7. Method Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study
2.7.1. Animals
2.7.2. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chromatographic Conditions
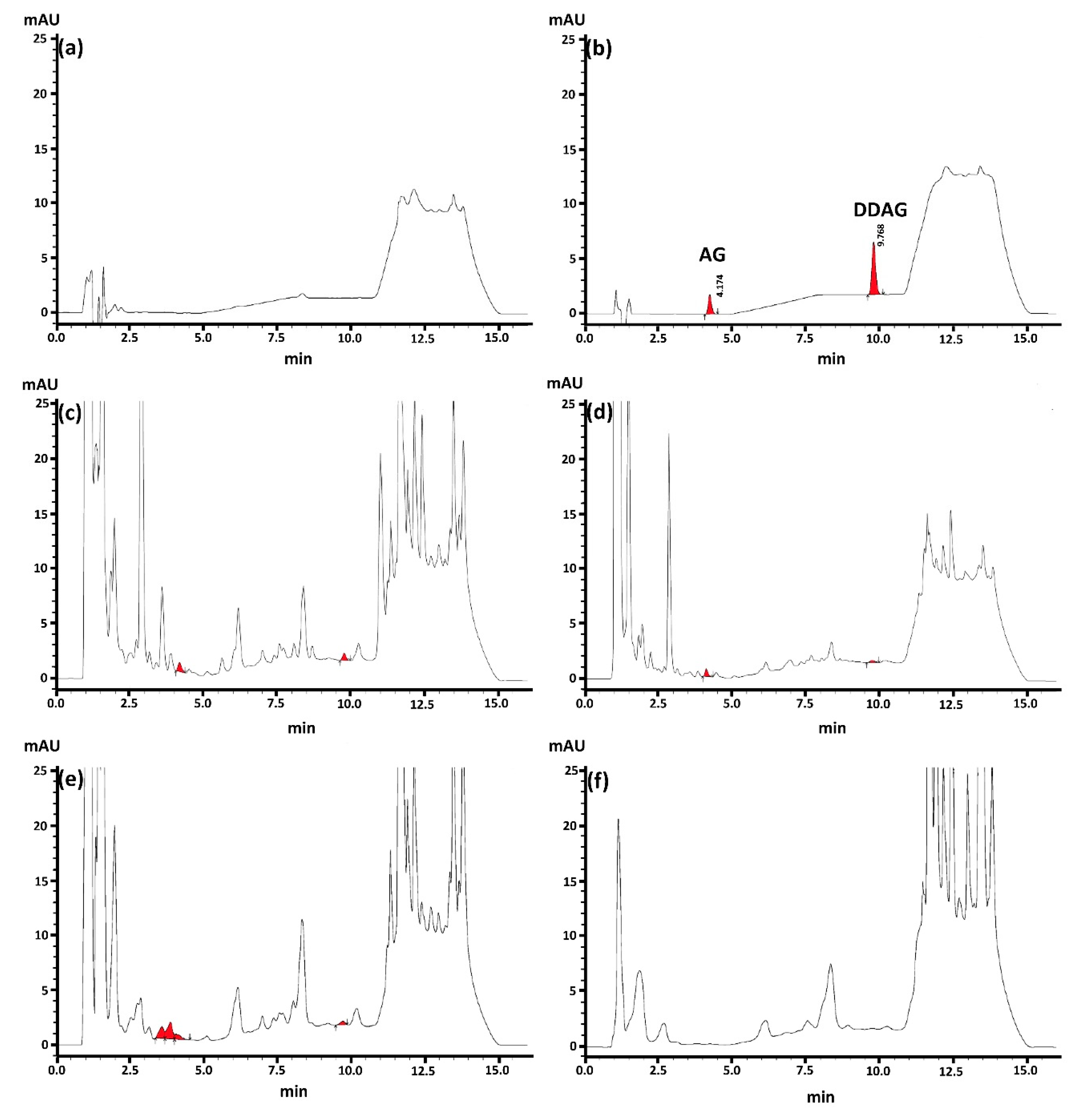
3.2. Biological Sample Preparations: Influences of Extraction Methods
3.2.1. PPT and LLE
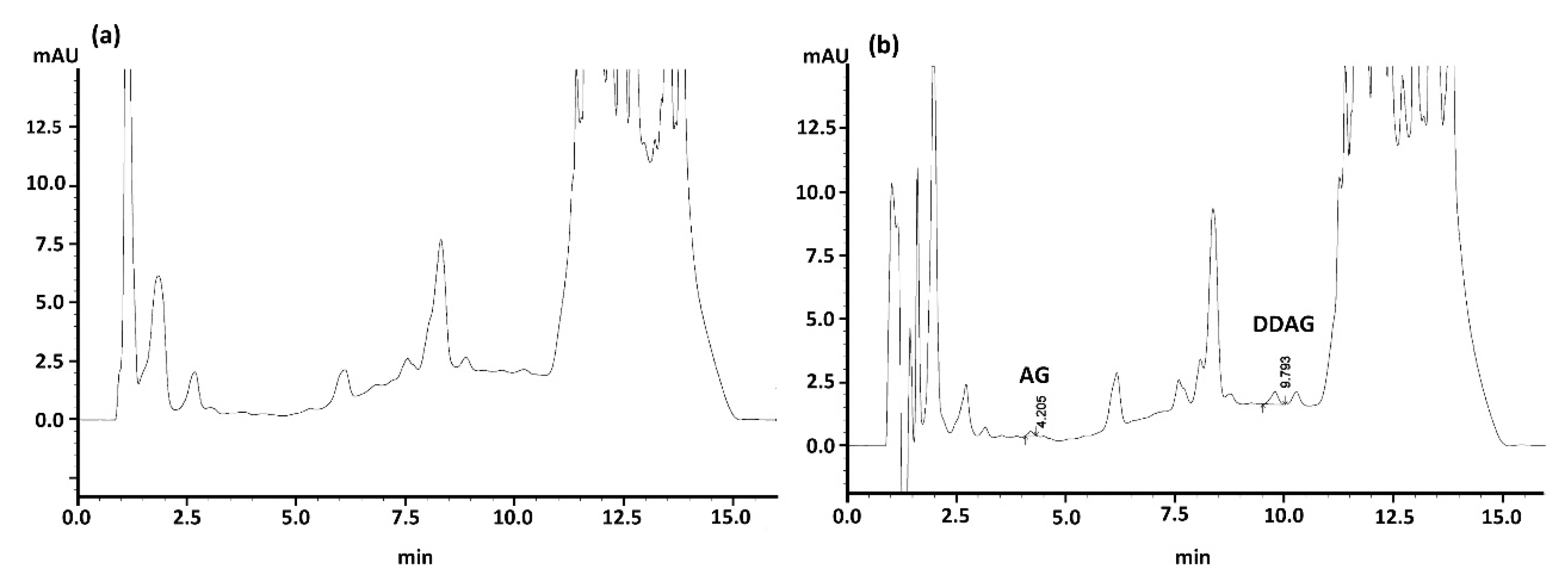
3.2.2. SALLE: Salt Effect
3.3. SALLE-HPLC-DAD Method Validation
3.3.1. Matrix Effect, Separation, and Specificity
3.3.2. Range and Linearity of Calibration Curve
3.3.3. Accuracy, Inter- and Intra-Day Precision
3.4. Sensitivity (LLOQ)
3.5. Sample Stability
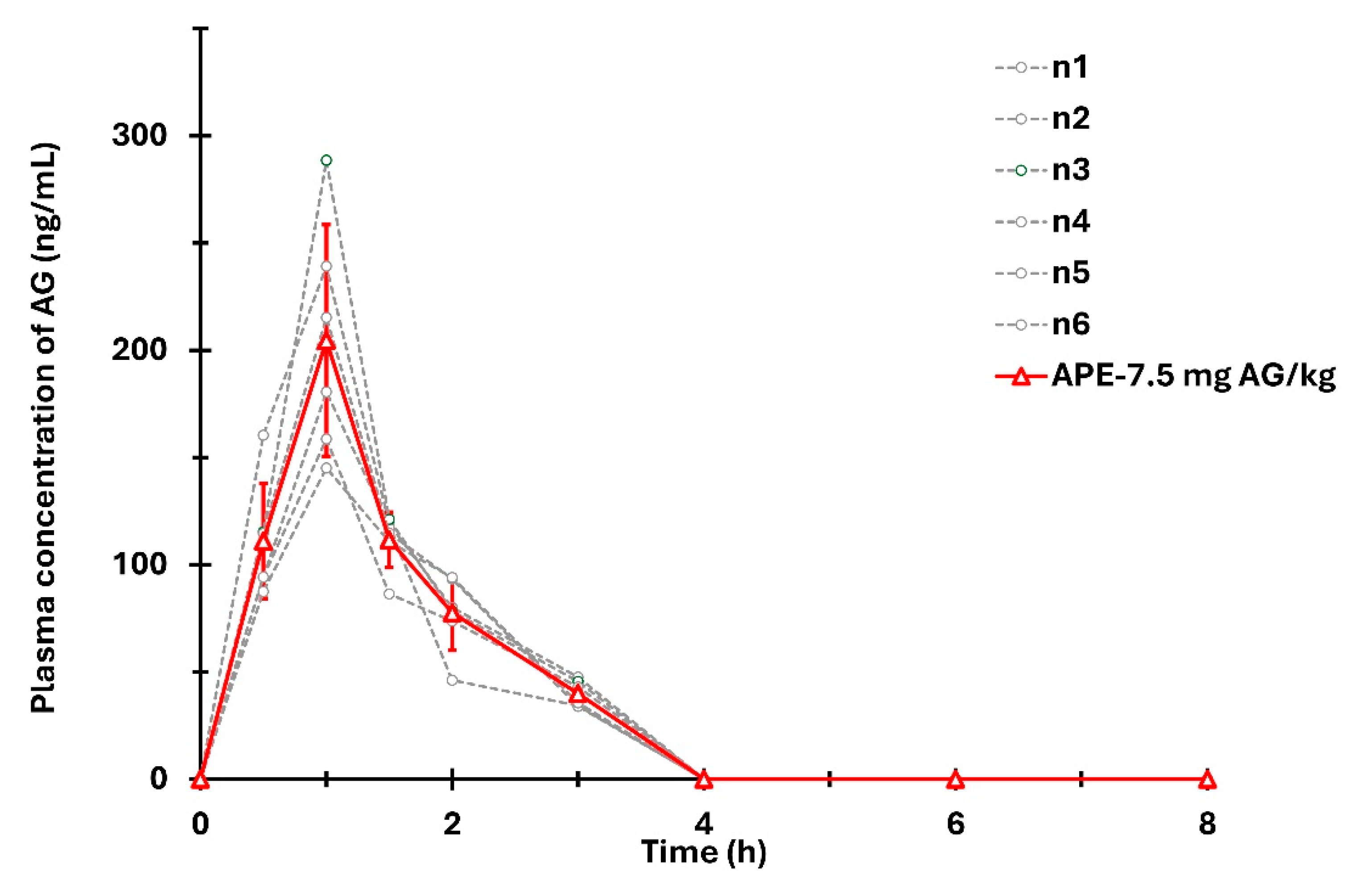
3.6. Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| AG | Andrographolide |
| AP | Andrographis paniculata |
| APE | AP extract |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BW | Body weight |
| Cmax | Maximum plasma concentration |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DDAG | 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide |
| EtOAc | Ethyl acetate |
| HPLC-DAD | high-performance liquid chromatography method coupled with diode array detection |
| LLE | liquid-liquid extraction |
| LLOQ | Lower limit of quantification |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MgSO4 | magnesium sulfate |
| MQC | Medium QC |
| Na2SO4 | sodium sulfate |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| PPT | protein precipitation |
| QC | Quality control |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| SALLE | salt-assisted liquid-liquid extraction |
| SPE | solid-phase extraction |
| T1/2 | Half-life |
| Tmax | Time to maximum concentration |
| ULOQ | Upper limit of quantification |
References
- Okhuarobo, A.; Falodun, J.E.; Erharuyi, O.; Imieje, V.; Falodun, A.; Langer, P. Harnessing the Medicinal Properties of Andrographis Paniculata for Diseases and beyond: A Review of Its Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thailand: National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) 2021 (Thai). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/thailand--national-list-of-essential-medicines-(nlem)-(thai) (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Low, M.; Khoo, C.S.; Münch, G.; Govindaraghavan, S.; Sucher, N.J. An in Vitro Study of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Standardised Andrographis Paniculata Extracts and Pure Andrographolide. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheeja, K.; Shihab, P. k.; Kuttan, G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Plant Andrographis Paniculata Nees. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2006, 28, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.L.; Wu, S.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ng, L.T. Antioxidant, Antioedema and Analgesic Activities of Andrographis Paniculata Extracts and Their Active Constituent Andrographolide. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmi, H.; Pamungkas, I.R.; Tumewu, L.; Hafid, A.F.; Widyawaruyanti, A. Analgesic and Antipyretic Activities of Ethyl Acetate Fraction Tablet of Andrographis Paniculata in Animal Models. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 8848797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Parai, D.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, S.K. Andrographolide: Antibacterial Activity against Common Bacteria of Human Health Concern and Possible Mechanism of Action. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2017, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rao, K.; Bhuvaneswari, Ch.; Giri, A.; Mangamoori, L.N. Phytochemical Analysis of Andrographis Paniculata Extract and Its Antimicrobial Activity. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyawaruyanti, A.; Asrory, M.; Ekasari, W.; Setiawan, D.; Radjaram, A.; Tumewu, L.; Hafid, A.F. In Vivo Antimalarial Activity of Andrographis Paniculata Tablets. Procedia Chem. 2014, 13, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, M.K.; Mishra, S.; Sonter, S.; Singh, P.K. Diterpenoids as Potential Anti-Malarial Compounds from Andrographis Paniculata. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Sarkar, C.; Saha, S.; Hossain, M.N.; Norouzi, R.; Mubarak, M.S.; Siyadatpanah, A.; Wilairatana, P.; Hossain, R.; Islam, M.T.; et al. Hepatoprotective Activity of Andrographolide Possibly through Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanna, M.; Bharathi, B.; Shivakumar, B.R.; Deepak, M.; Prashanth, D.; Prabakaran, D.; Vijayabhaskar, T.; Arun, B. Immunomodulatory Effects of Andrographis Paniculata Extract in Healthy Adults – An Open-Label Study. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2021, 12, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.R.; Hule, A. Evaluation of Immunomodulatory Activity of an Extract of Andrographolides from Andographis Paniculata. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiguna, S.P.; Panggabean, J.A.; Atikana, A.; Untari, F.; Izzati, F.; Bayu, A.; Rosyidah, A.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Putra, M.Y. Antiviral Activities of Andrographolide and Its Derivatives: Mechanism of Action and Delivery System. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-X.; Xue, H.-J.; Ye, W.-C.; Fang, B.-H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Yuan, S.-H.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.-Q. Activity of Andrographolide and Its Derivatives against Influenza Virus in Vivo and in Vitro. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.K.; Chen, R.; Lee, R.C.H.; Li, F.; Dai, K.; Zhou, G.-C.; Chu, J.J.H. Discovery of Novel Andrographolide Derivatives as Antiviral Inhibitors against Human Enterovirus A71. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa-ngiamsuntorn, K.; Suksatu, A.; Pewkliang, Y.; Thongsri, P.; Kanjanasirirat, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Charoensutthivarakul, S.; Wongtrakoongate, P.; Pitiporn, S.; Chaopreecha, J.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of Andrographis Paniculata Extract and Its Major Component Andrographolide in Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Cytotoxicity Evaluation in Major Organ Cell Representatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari Kishore, P.; Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy, M.; Kesava Reddy, M.; Gunasekar, D.; Caux, C.; Bodo, B. Flavonoids from Andrographis Lineata. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; My, N.T.T.; Cham, P.T.; Quang, T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Huong, T.T.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Diterpenoids and Flavonoids from Andrographis Paniculata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2020, 68, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.-P.; Kong, L.-R.; Cheng, C.; Lim, J.C.W.; Wong, W.S.F. Protective Role of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide, a Noncytotoxic Analogue of Andrographolide, in Allergic Airway Inflammation. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoopan, N.; Thisoda, P.; Rangkadilok, N.; Sahasitiwat, S.; Pholphana, N.; Ruchirawat, S.; Satayavivad, J. Cardiovascular Effects of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide and Andrographis Paniculata Extracts. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, M.; Misra, T.K.; Roy, D.N. In Vitro Anti-Biofilm Activity of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-J.; Rao, Y.K.; Chen, K.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chung, Y.-S.; Tzeng, Y.-M. Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata Attenuate High Glucose-Induced Fibrosis and Apoptosis in Murine Renal Mesangeal Cell Lines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Tan, B.K.H. Effects of 14-Deoxyandrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide on Nitric Oxide Production in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Pharmacopoeia Andrographis Herb. British Pharmacopoeia 2024; Medicine and Healthcare product Regulatory Agency (MHRA): London, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- FA THALAI. Thai Herbal Pharmacopoeia; Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health: Nonthaburi, 2021; pp. 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention. Powdered Andrographis. [CrossRef]
- Suo, X.-B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.-Q. HPLC Determination of Andrographolide in Rat Whole Blood: Study on the Pharmacokinetics of Andrographolide Incorporated in Liposomes and Tablets. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2007, 21, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songvut, P.; Pholphana, N.; Suriyo, T.; Rangkadilok, N.; Panomvana, D.; Puranajoti, P.; Satayavivad, J. A Validated LC-MS/MS Method for Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Presumptive Phase II Metabolic Pathways Following Oral Administration of Andrographis Paniculata Extract. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, J.; Jeličić, M.-L.; Amidžić Klarić, D.; Mornar, A. Green Solid-Phase (Micro)Extraction of Andrographolides’ from Human Plasma Samples Followed by UHPLC-DAD-QqQ-MS/MS Analysis. Separations 2023, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, R.G.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, H.; Fang, W.-J. Current Developments of Bioanalytical Sample Preparation Techniques in Pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; He, X.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Z. A Simple UPLC/MS-MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Lenvatinib and Telmisartan in Rat Plasma, and Its Application to Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interaction Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.; Wagrowski-Diehl, D.M.; Lu, Z.; Mazzeo, J.R. Systematic and Comprehensive Strategy for Reducing Matrix Effects in LC/MS/MS Analyses. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, C.I.C.; Santos, J.L.M.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Zagatto, E.A.G. Liquid–Liquid Extraction in Flow Analysis: A Critical Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 652, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; O. Saboe, P.; S. Kruger, J.; D. Tan, E.C.; W. Dempsey, J.; G. Linger, J.; Nogué, V.S. i; M. Karp, E.; T. Beckham, G. Liquid–Liquid Extraction for in Situ Carboxylic Acid Recovery via Continuous Membrane-Based Emulsion Separations. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 9398–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholds, I.; Pugajeva, I.; Perkons, I.; Bartkevics, V. The Application of Phospholipid Removal Columns and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry for Quantification of Multi-Class Antibiotics in Aquaculture Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michopoulos, F.; Edge, A.M.; Hui, Y.-T.; Liddicoat, T.; Theodoridis, G.; Wilson, I.D. Extraction Methods for the Removal of Phospholipids and Other Endogenous Material from a Biological Fluid. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhanova, I.I.; Dikunets, M.A.; Viryus, E.D.; Rodchenkov, G.M. Magnetic Separation as a New Method for the Extraction of Small Molecules from Biological Fluids of Humans. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 66, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namera, A.; Saito, T. Spin Column Extraction as A New Sample Preparation Method in Bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietecha-Posłuszny, R.; Garbacik, A.; Woźniakiewicz, M.; Moos, A.; Wieczorek, M.; Kościelniak, P. Application of Microextraction by Packed Sorbent to Isolation of Psychotropic Drugs from Human Serum. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jian, W.; Fu, Y. Basic Sample Preparation Techniques in LC-MS Bioanalysis. In Sample Preparation in LC-MS Bioanalysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2019; pp. 1–30 ISBN 978-1-119-27431-5.
- Cristale, J.; Becker, R.W.; Tornisielo, V.L.; Dantas, R.F.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Onanong, S.; Snow, D.D. Comparison of Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction to Polymeric Solid Phase Extraction for Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Neonicotinoids Insecticides and Metabolites in Wastewater: Occurrence and Aquatic Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.S.T.; Ladner, Y.; Amin, N. ’Cho C.; Perrin, C. Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction (SALLE): Principle, Optimization, and Applications in Blood Sample Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 257, 116720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Weng, N. Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for Bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 1583–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, A.M.; Zultanski, S.L.; Waldman, J.H.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Shevlin, M.; Peng, F. General Principles and Strategies for Salting-Out Informed by the Hofmeister Series. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Kim, E.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. Salting-out Assisted Liquid/Liquid Extraction with Acetonitrile: A New High Throughput Sample Preparation Technique for Good Laboratory Practice Bioanalysis Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2009, 23, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rodila, R.; Gage, E.; Hautman, M.; Fan, L.; King, L.L.; Wu, H.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. High-Throughput Salting-out Assisted Liquid/Liquid Extraction with Acetonitrile for the Simultaneous Determination of Simvastatin and Simvastatin Acid in Human Plasma with Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 661, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- nternational Council for Harmonisation’s (ICH) ICH Harmonised Guideline: Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis (M10); European Medicines Agency, 2023.
- International Council for Harmonisation’s (ICH) ICH Q2(R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures; European Medicines Agency, 2024.
- 〈621〉 CHROMATOGRAPHY. [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, H.P.; Thapa, P.; Van Schepdael, A. Simple HPLC-UV Method for the Quantification of Metformin in Human Plasma with One Step Protein Precipitation. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Eissa, M.S.; Ahmed, H.M. Simple Protein Precipitation Extraction Technique Followed by Validated Chromatographic Method for Linezolid Analysis in Real Human Plasma Samples to Study Its Pharmacokinetics. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1043, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.; Adkar, S.S.; Prabhudesai, A.V.; Viswanathan, C.V. Selective Extraction of Phospholipids from Egg Yolk. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevc, G.; Löbbecke, L.; Nagel, N.; Vierl, U. Phospholipid-Alcohol Interactions: Effects of Chain-Length and Headgroup Variations. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1996, 109, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, L.; Fontes, A.L.; Salsinha, S.; Machado, M.; Correia, I.; Gomes, A.M.; Pintado, M.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M. Suitable Simple and Fast Methods for Selective Isolation of Phospholipids as a Tool for Their Analysis. ELECTROPHORESIS 2018, 39, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, Gh.; Mirzaeei, Sh.; Kiani, A. Determination of Acyclovir in Human Serum by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Using Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Its Application in Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 816, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shaik, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Nhkata, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, C.; Kim, S.-H.; Lü, J. Preparation of Penta-O-Galloyl-β-d-Glucose from Tannic Acid and Plasma Pharmacokinetic Analyses by Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Reverse-Phase HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fast, D.M. Systematic Evaluation of Supported Liquid Extraction in Reducing Matrix Effect and Improving Extraction Efficiency in LC–MS/MS Based Bioanalysis for 10 Model Pharmaceutical Compounds. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 891–892, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špadina, M.; Dufrêche, J.-F.; Pellet-Rostaing, S.; Marčelja, S.; Zemb, T. Molecular Forces in Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2021, 37, 10637–10656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.M.; Perović, J.M.; Nikolić, R.S.; Cakić, M.D. Salting-out Extraction of Catechol and Hydroquinone from Aqueous Solutions and Urine Samples. Facta Univ. - Ser. Phys. Chem. Technol. 2003, 2, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Celano, R.; Campone, L.; Rastrelli, L.; Piccinelli, A.L. Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for the Rapid and Simple Simultaneous Analysis of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids and Related N-Oxides in Honey and Pollen. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 108, 104457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Nishinari, K. Effects of the Lyotropic Series Salts on the Gelation of Konjac Glucomannan in Aqueous Solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Sodeinde, K.O.; Adediran, A.A.; Nishinari, K.; Olatunji, O.S.; Ayanda, O.S. Effects of Lyotropic Series Salts on the Functional Properties of Bambaragroundnut (Voandzeia Subterranean) Protein Isolate. Food Res. 2022, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Timasheff, S.N. On the Role of Surface Tension in the Stabilization of Globular Proteins. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 1996, 5, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, M.; Kazemzadeh, Y.; Martyushev, D.A.; Dai, Z.; Riazi, M. Effect of Chemicals on the Phase and Viscosity Behavior of Water in Oil Emulsions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, A.; Koba, M.; Kośliński, P.; Siódmiak, J. Comparison of LC-MS and LC-DAD Methods of Detecting Abused Piperazine Designer Drugs. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomlim, L.; Jirayupong, N.; Plubrukarn, A. Heat-Accelerated Degradation of Solid-State Andrographolide. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2003, 51, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fang, L.-H.; Du, G.-H. Andrographolide. Nat. Small Mol. Drugs Plants 2018, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanaya, T.; Chuangrattanawan, C.; Chootip, K.; Pekthong, D.; Plubrukarn, A. Fates of Diterpene Lactones in Storage Andrographis Paniculata Extracts. Phytochem. Anal. PCA 2025, 36, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, N.A.; Sapi’i, N.A.; Jiunn Hieng, A.L.; Ab Latif, N.; Amran, S.I.; Hasham, R.; Jemon, K. In Vitro and in Silico Evaluation of Andrographis Paniculata Ethanolic Crude Extracts on Fatty Acid Synthase Expression on Breast Cancer Cells. BioMedicine 14, 60–73. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Xiang, S. Pharmacological Effects and Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Dehydroandrographolide. Mediators Inflamm. 2025, 2025, 4123997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panossian, A.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Mamikonyan, G.; Abrahamian, H.; Hambardzumyan, E.; Gabrielian, E.; Goukasova, G.; Wikman, G.; Wagner, H. Pharmacokinetic and Oral Bioavailability of Andrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata Fixed Combination Kan Jang in Rats and Human. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2000, 7, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, T.G.; Mi, Z. The Structural Basis of Camptothecin Interactions with Human Serum Albumin: Impact on Drug Stability. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Yao, H.-T.; Chen, H.-W.; Lii, C.-K. Bioavailability of the Diterpenoid 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide in Rats and up-Regulation of Hepatic Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme and Drug Transporter Expression. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 61, 152841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, F. Regio-Selective PEGylation of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide and Their Biological Evaluation. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5909–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellampillai, B.; Pawar, A.P. Improved Bioavailability of Orally Administered Andrographolide from pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 35, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, R.; Ahmed, S.K.M.; Sarkar, L.; Sen, T.; Karmakar, S. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Tissue Distribution of Andrographolide in Rat by a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, V.; Karlsson, M.O. Impact of Omission or Replacement of Data below the Limit of Quantification on Parameter Estimates in a Two-Compartment Model. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.; Veigure, R.; Couchman, L.; S Barker, C.I.; Standing, J.F.; Takkis, K.; Evard, H.; Johnston, A.; Herodes, K.; Leito, I.; et al. Utilization of Data below the Analytical Limit of Quantitation in Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Modeling: Promoting Interdisciplinary Debate. Bioanalysis 2018, 10, 1229–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusko, W.J. Use of Pharmacokinetic Data Below Lower Limit of Quantitation Values. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2628–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Sheng, H.-H.; Feng, N.-P.; Wei, H.; Wang, Z.-T.; Wang, C.-H. Preparation of Andrographolide-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Their In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations: Characteristics, Release, Absorption, Transports, Pharmacokinetics, and Antihyperlipidemic Activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 4414–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Wang, T.; Tang, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Z.; Cai, Z.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Poor Oral Bioavailability of a Promising Anticancer Agent Andrographolide Is Due to Extensive Metabolism and Efflux by P-Glycoprotein. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5007–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, R.; Ahmed, S.K.M.; Sarkar, L.; Sen, T.; Karmakar, S. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Tissue Distribution of Andrographolide in Rat by a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipduangta, P.; Chansakaow, S.; Tansakul, P.; Meungjai, R.; Dilokthornsakul, P. Polymer Matrix and Manufacturing Methods in Solid Dispersion System for Enhancing Andrographolide Solubility and Absorption: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpitchanarong, C.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Nattapulwat, N.; Opanasopit, P.; Patrojanasophon, P. Development and Optimization of Andrographis Paniculata Extract-Loaded Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System Using Experimental Design Model. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramanick, D.; Rani, K.N.; Singh, V.K.; Basist, P.; Khan, R.; Al-Tamimi, J.H.; Noman, O.M.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Alhalmi, A. Enhancement of Cognitive Function by Andrographolide-Loaded Lactose β-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Optimization, and Behavioural Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Salt types and concentrations |
Extraction Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| AG | DDAG | |
| Control (no salt addition) | 50.66±4.44 | 56.03±4.32 |
| NaCl, 1M | 81.75±4.81* | 69.31±1.64* |
| NaCl, 2M | 86.52±5.59* | 93.41±6.33* |
| Na2SO4,1M | 0.00±0.00* | 7.24±2.41* |
| Na2SO4, 2M | N/A | N/A |
| MgSO4, 1M | 82.64±2.68* | 81.70±1.28* |
| MgSO4, 2M | 93.75±0.56* | 95.39±2.95* |
| Parameters | AG | DDAG |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity factor | 3.05 ± 0.01 | 8.33 ± 0.02 |
| Resolution | 16.46 ± 0.41 | 25.49 ± 0.11 |
| Tailing factor | 1.17 ± 0.06 | 1.23 ± 0.01 |
| Column efficiency | 6702 ± 147 | 29631 ± 252 |
| Analytical method | Actives | Linearity range (ng/mL) | R2 | LOD (ng/mL) |
LOQ (ng/mL) |
EE (%) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SALLE-HPLC-DAD * | AG | 125 – 2000 | 0.9973 ± 0.0029 | 60.3 ± 13.6 | 70.3 ± 28.9 | 93 – 94 | - |
| DDAG | 125 – 2000 | 0.9974 ± 0.0023 | 201.1 ± 45.5 | 234.3 ± 96.3 | 92 – 98 | ||
| LLE-HPLC-DAD | AG | 53 − 530000 | 0.996 | 15 | 53 | 65 – 72 | [28] |
| DDAG | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| PPT-HPLC-MS/MS | AG | 0.98 – 1000 | >0.99 | - | 0.98 | 78 – 81 | [29] |
| DDAG | 0.98 – 1000 | >0.99 | - | 0.98 | 81 – 89 | ||
| SPE-HPLC-MS/MS | AG | 4000 – 12000 | 0.9989 | 40 | 150 | 97 – 99 | [30] |
| DDAG | 4000 – 12000 | 0.9987 | 20 | 60 | 92 – 95 |
| Concentration (ng/mL) |
AG | DDAG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy* (% Recovery) |
Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy*(% Recovery) | |||
| Inter-day | Intra-day | Inter-day | Intra-day | |||
| 125 | 9.5 | 5.1 | 91.8 ± 4.7 | 9.9 | 2.0 | 103.1 ± 10.7 |
| 1000 | 5.6 | 2.0 | 99.2 ± 2.0 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 99.3 ± 8.6 |
| 2000 | 8.6 | 2.6 | 91.4 ± 2.4 | 5.2 | 4.7 | 102.3 ± 5.0 |
| Storage time and condition | Percentage remaining (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| AG | DDAG | |
| Control (0 h) | 102.83 ± 6.70 | 95.48 ± 3.40 |
| 4 h Bench-top | 67.44 ± 6.72 | 88.20 ± 9.50 |
| 24 h auto-sampler | 99.94 ± 6.70 | 96.70 ± 4.73 |
| Freeze-thaw (3 cycles) | 90.64 ± 5.81 | 83.99 ± 2.01 |
| 14 days at -20 °C | 106.74 ± 6.83 | 94.57 ± 6.58 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Tmax (h) | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 219.0 ± 46.5 |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 309.5 ± 4.8 |
| T1/2 (h) | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





