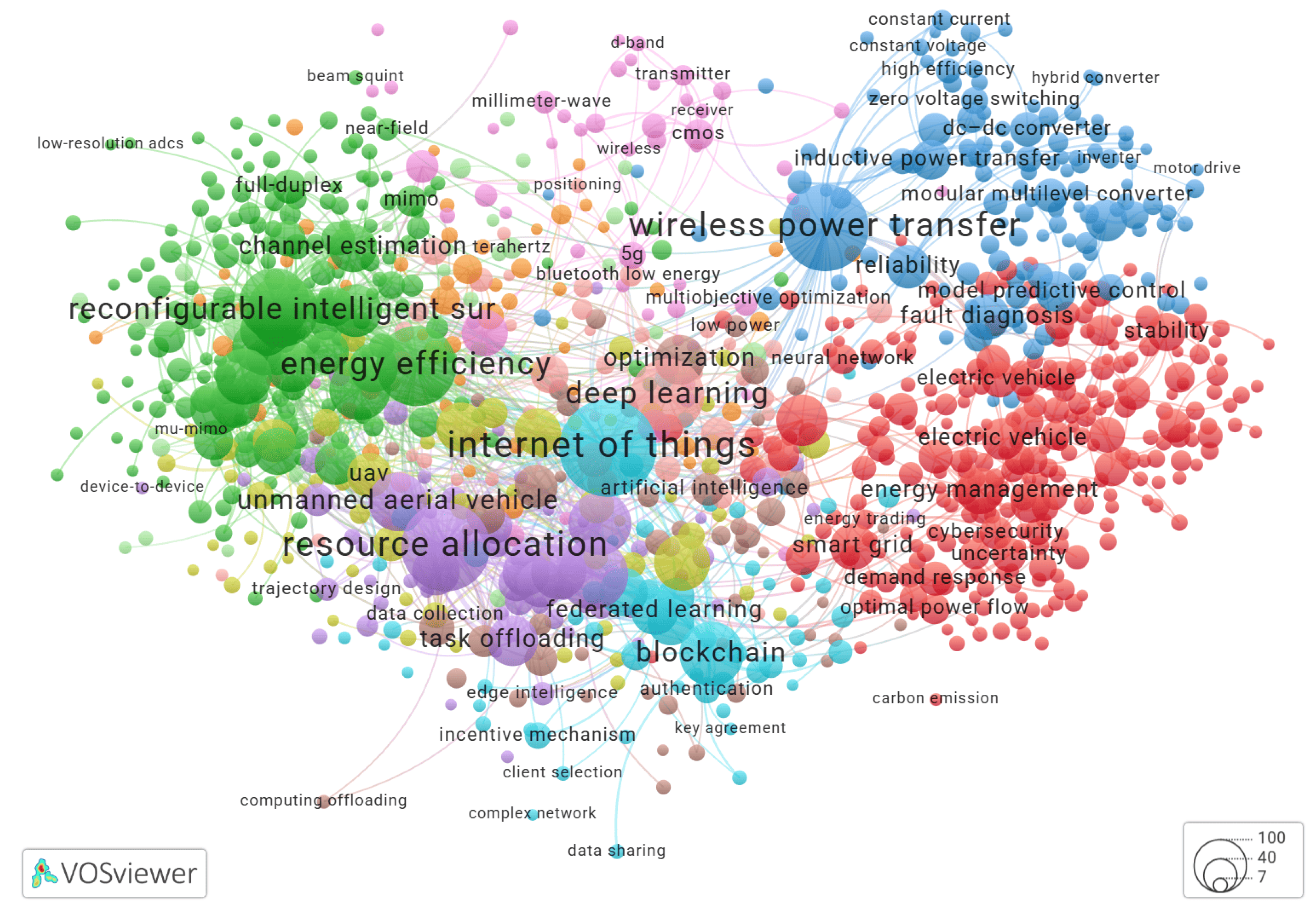
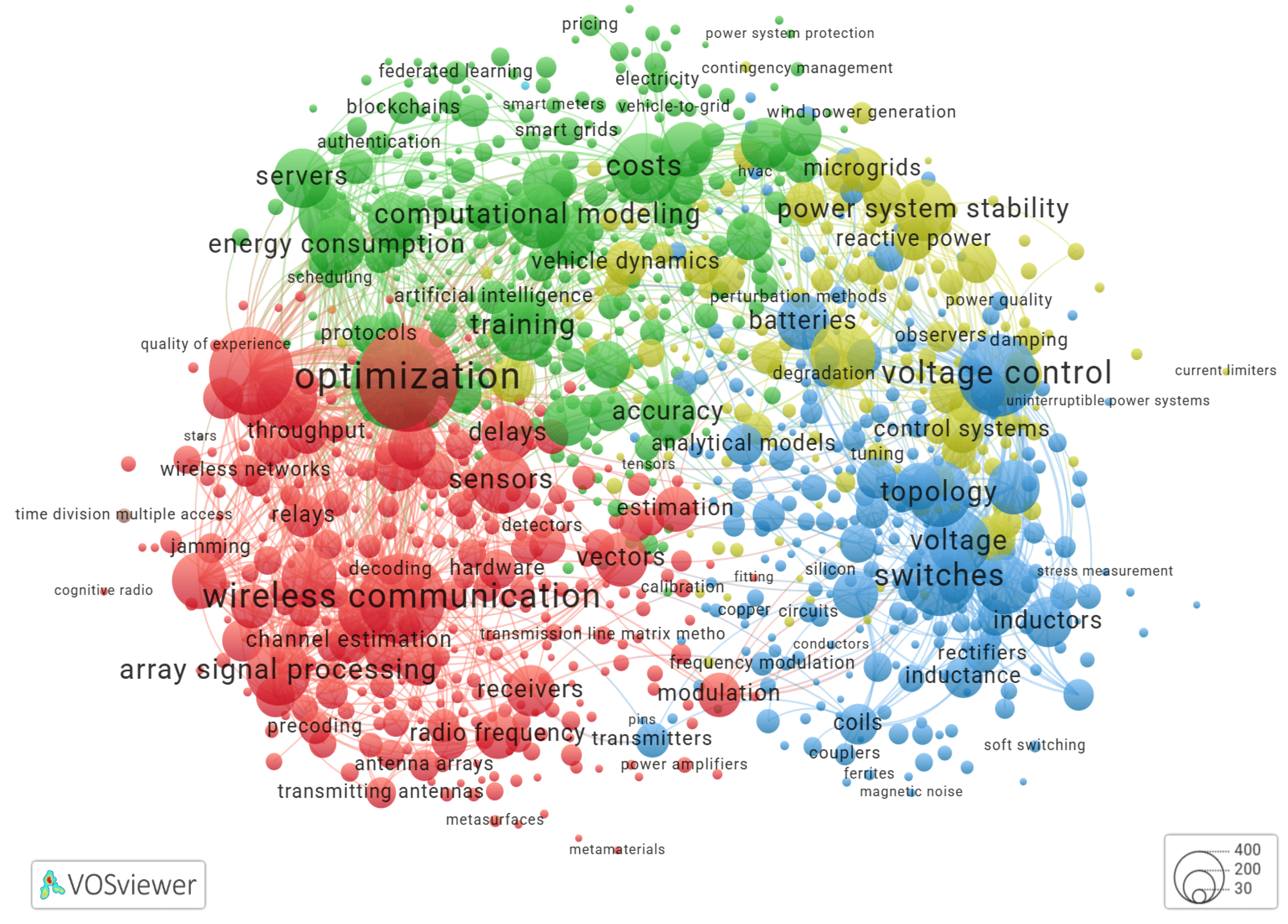
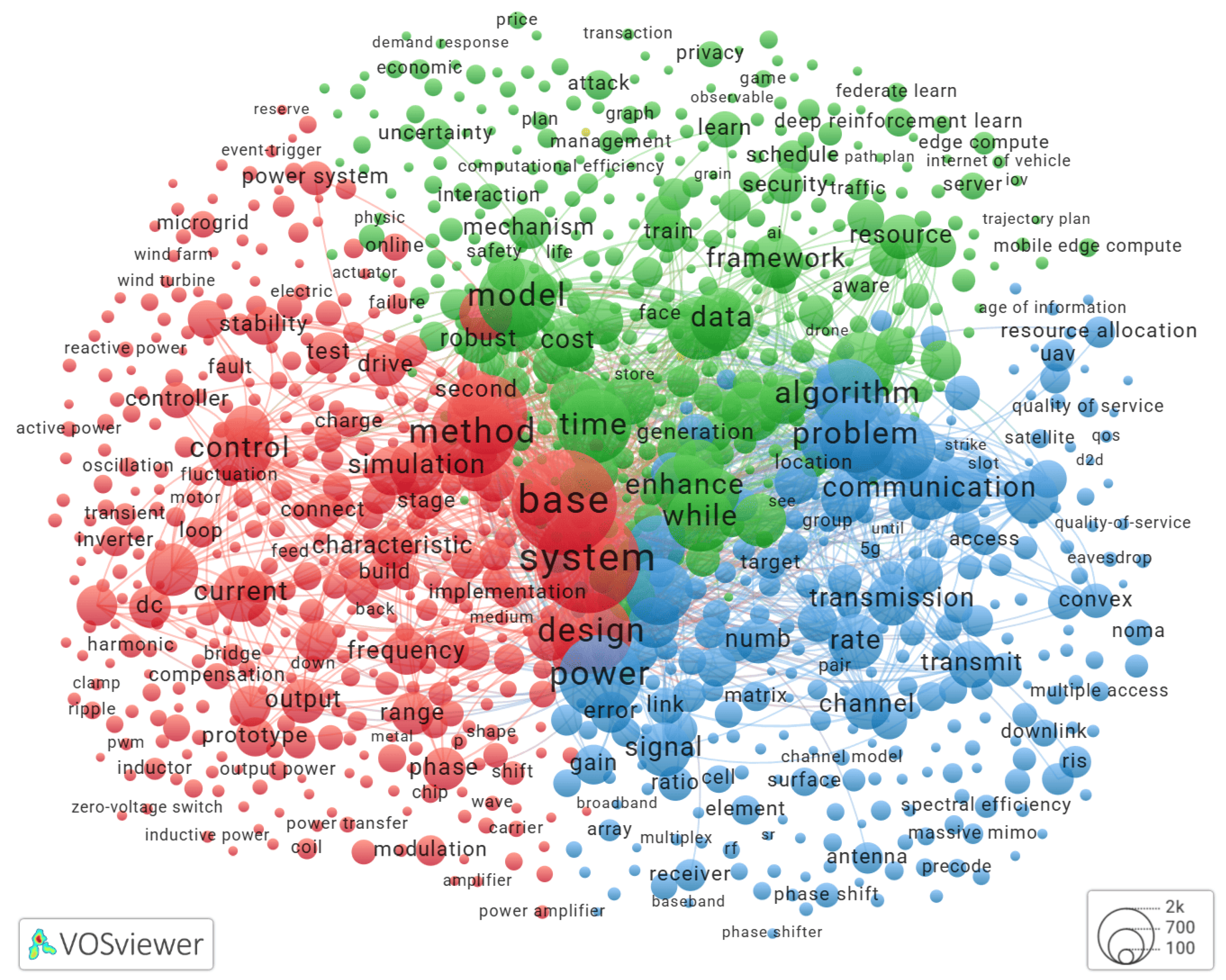
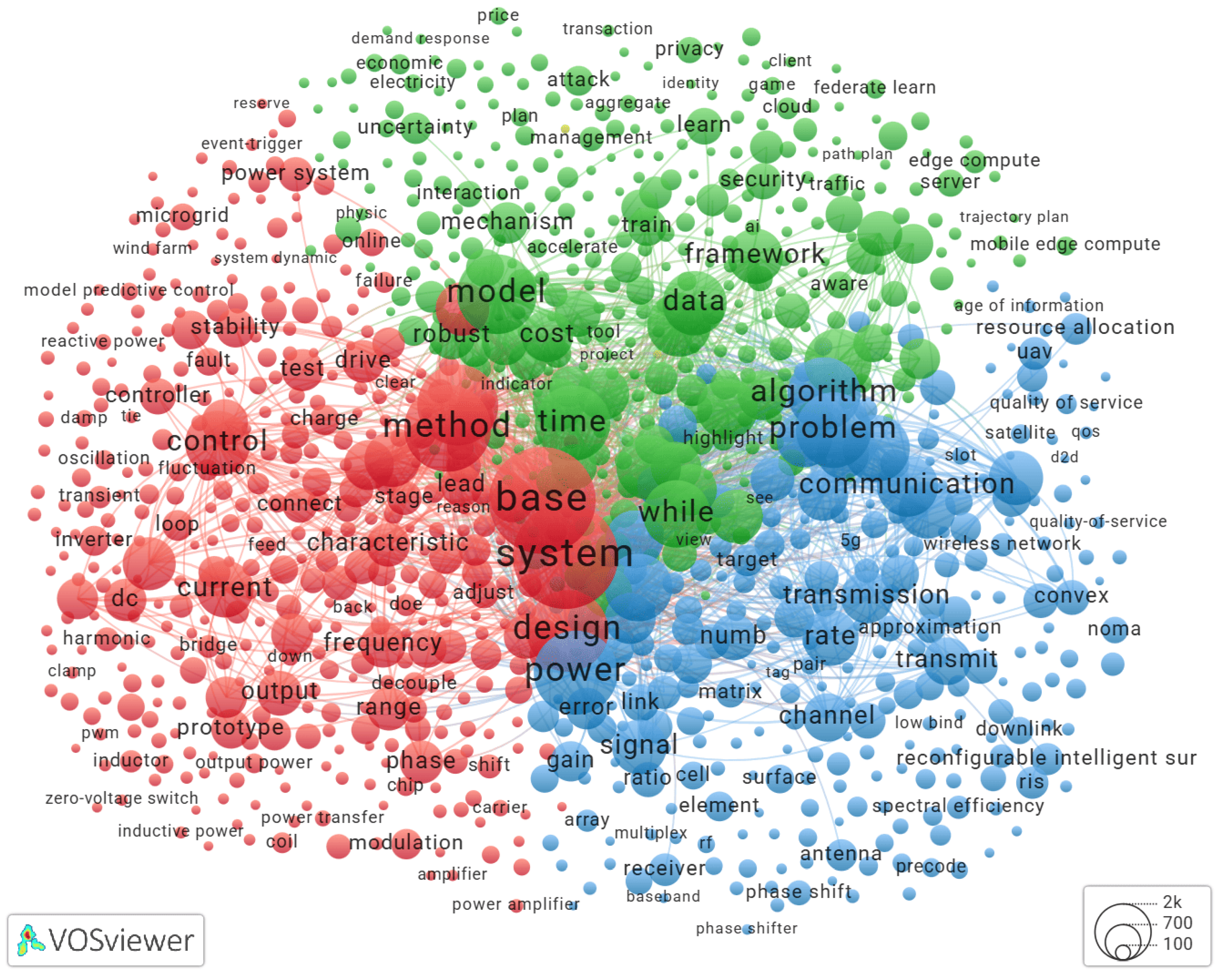
Brief Literature Review
This section discusses the significance of the research topic presented in this paper based on a review of the relevant literature. It examines various characteristics of previous studies and highlights the rationale for choosing the specific objective of this study, emphasizing its importance in the context of existing scientific works.
The following scholarly publications discuss methods for identifying themes and transferring knowledge between fields, often using thematic analysis and lexical approaches. They discuss the importance of identifying gaps in research in order to discover new and relevant research topics in the recipient field of knowledge.
The article [10.32996/ijllt.2022.5.12.6] discusses software developed for thematic analysis based on a manually created dictionary containing approximately 5,500 thematic words. It highlights the effectiveness of using dictionaries in text analysis, allowing words to relate to multiple themes. This methodology helps identify key themes by determining the most frequently occurring thematic words detected by the software.
It should be noted that the approaches currently used to analyze scientific and technical texts and search for connections between different fields of knowledge have long been used by linguists, albeit not at such a computerized level. An illustration of this can be found in the work [10.1016/0304-422X(94)90011-6]. In this work, language is viewed as a window into the world of the mind. Language is also a window into the world of culture. By analyzing texts, one can study the interaction between human cognition and culture. By analyzing texts, one can describe the cognitive similarities and differences between people that form the basis of culture. Such analysis allows us to identify similarities and differences between cultures, as well as changes within cultures. This article explores the relative advantages of using content analysis and cartographic analysis to extract and analyze cultural characteristics based on a set of texts.
As an example of contemporary research, consider the article [10.1371/journal.pone.0329302], which analyzes the importance of interdisciplinary exchange in the development of science and the problems of tracking knowledge flows in interdisciplinary fields. It presents a new network analysis framework that uses citation data to study the dynamics of knowledge transfer. By applying dynamic community detection to evolving citation networks, this framework identifies research areas and maps interdisciplinary integration, revealing gaps in knowledge. This work aims to support strategies for synthesizing ideas.
The bibliometric and scientometric approaches to the issue under consideration have a long history, as demonstrated by the following publications. Interdisciplinarity can manifest itself in the use of concepts from different disciplines by individual scientists. The paper [10.1007/s11192-009-0121-z] focuses on how the convergence of ideas contributes to new discoveries. It uses science maps to identify potential interdisciplinary connections, analyzed using contextual analysis of co-citations.
Scientists acquire and transfer knowledge daily, though many flows of this knowledge are often unobserved. The review [10.1007/s11024-024-09542-2] examines the application of bibliometric methods in studying these flows, highlighting that traditional bibliometrics has primarily focused on formal knowledge through citation data and is now shifting towards informal knowledge within social networks. However, studies on interpersonal knowledge flows remain limited. The review emphasizes the untapped potential of bibliometric methods and proposes directions for future methodological advancements.
Comment: “network analysis framework that uses citation data” can be modified to “network analysis using controlled vocabulary terms.”
Knowledge transfer can also occur through the implementation of achievements in rapidly developing areas of research into a specific subject area. Here are some examples of such works.
The [10.2118/226792-MS] article discusses the transformative impact of advanced digital technologies, including big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation, on petroleum engineering. It emphasizes the importance of integrating traditional domain knowledge with digitalization, identifying this combination as crucial for success. The interaction between deep domain expertise and data-driven approaches enhances established engineering practices, leading to improved operational efficiency and promoting sustainable growth. Key technologies highlighted include AI-based modeling, machine learning for predictive maintenance, and real-time data visualization platforms.
The oil and petrochemical industries face pressures to enhance efficiency, minimize environmental impacts, and respond to evolving market dynamics. The [10.36713/epra24128] study employs a thorough literature review to explore the development of Process System Engineering (PSE) from traditional optimization methods to the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) through hybrid modeling approaches. It considers empirical data from diverse regions, including the United States, Iran, and China, bolstered by quantitative market analytics and performance metrics. Findings indicate that the integration of machine learning (ML) with PSE can effectively address the limitations present in purely data-driven or non-physics-based methodologies by leveraging physics-informed technologies.
Pressure–volume–temperature (PVT) properties of crude oil are considered the most important properties in petroleum engineering applications as they are virtually used in every reservoir and production engineering calculation. Determination of these properties in the laboratory is the most accurate way to obtain a representative value, at the same time, it is very expensive. However, in the absence of such facilities, other approaches such as analytical solutions and empirical correlations are used to estimate the PVT properties. The study [10.1115/1.4050579] demonstrates the combined use of two machine learning (ML) technique, viz., functional network (FN) coupled with particle swarm optimization (PSO) in predicting the black oil PVT properties such as bubble point pressure (Pb), oil formation volume factor at Pb, and oil viscosity at Pb. This study also proposes new mathematical models derived from the coupled FN-PSO model to estimate these properties.
Many oil and gas companies are exploring opportunities in the renewable energy market, particularly in subsea large-scale hydrogen storage systems, which play a crucial role in the global energy transition. Companies leverage their subsea oil and gas expertise to create these hydrogen storage solutions and emphasize the importance of efficient knowledge transfer to integrate new stakeholders into the development process [10.1002/iis2.13076].
Production optimization is vital for closed-loop reservoir management, focusing on maximizing economic benefits through optimal development schemes. Traditional methods often operate in isolation, neglecting knowledge from past optimizations, leading to a high number of simulations that can be computationally expensive. The paper [10.2118/219732-PA] introduces a competitive knowledge transfer method designed to utilize insights from previously solved tasks to improve production optimization outcomes.
The transfer of knowledge between broader and specialized fields is essential for sustainable technological development. Bibliometric studies addressing this knowledge transfer can offer comprehensive insights into the issue.
The article [10.1007/s13132-025-02814-6] discusses that knowledge transfer has been identified as one of the key factors for innovation and business success in the knowledge economy, and how networks are strategic tools that can contribute to this. Performance analysis, scientific mapping, and dynamic network analysis were performed using VOSviewer and SciMat software. This study identifies the most influential participants in this field, presents the evolution of the research direction, describes thematic clusters, and outlines a research program.
The study [10.1007/s10961-019-09774-5] examines the field of technology transfer (TT) in academic research, noting its significant growth and increasing scientific interest in recent years. Using a bibliometric approach, the study examines current issues and their interrelationships in order to identify influential topics and suggest directions for future research. It analyzes the co-authorship network to assess the existing literature, determines the current state of research in the field of TT, and identifies five main areas of research along with related topics.
Organizations rely on external sources to acquire knowledge, especially in the context of university-industry (U-I) knowledge transfer. This topic is becoming increasingly important as U-I collaboration fosters the innovation that companies need to remain competitive. The purpose of the article [10.1108/VJIKMS-07-2024-0270] was to examine this topic in detail by conducting a bibliometric systematic review of the literature with a focus on knowledge transfer, collaboration, interaction, and interdependence of new research areas.
Despite the importance of knowledge transfer for successful cross-border acquisitions, contemporary literature does not pay sufficient attention to knowledge management in the acquired company. The study [10.1108/JKM-04-2024-0494] is the first to examine the dynamics of knowledge transfer after an acquisition, focusing on knowledge integration, learning capacity, and knowledge reverse transfer. The authors aim to analyze existing research on these topics and suggest directions for future research in the field of cross-border acquisitions.
Research in the field of knowledge transfer (KT) has attracted considerable attention from scholars over the past decade, although bibliometric and visualization studies remain limited. The study [10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3061576] analyzes key trends in the KT literature using data from the Scopus database, offering a comprehensive overview of KT trends and trajectories through visual diagrams. This approach aims to help researchers and practitioners understand current trends and identify future research directions.
The identification of existing research gaps is crucial for knowledge transfer between fields, particularly for identifying bottlenecks in the receiving field. This issue is discussed in various publications that address different aspects of the problem.
Growing interest in research on energy service companies (ESCOs) has led to an increase in publications over the past decade. Despite this growth, there is still no comprehensive mapping of global research in the field of ESCOs. The purpose of the article [10.1016/j.esr.2024.101516] is to analyze trends in ESCO research, assess the current state of the field, and identify existing gaps in research. This objective is achieved through a systematic literature review and qualitative analysis of recently published articles using bibliometric analysis, co-citation analysis, and keyword analysis to identify recent trends in global ESCO research.
The literature on life cycle assessment (LCA) of lithium-ion batteries (LIB) for transportation applications includes life cycle inventory data relevant to stationary energy storage systems (ESS). However, it does not address the unique characteristics of stationary systems, such as system material balance, operating profiles, and specific end-of-life (EOL) requirements. The literature review [10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00120] examines existing studies on grid-scale stationary LIB ESS and identifies significant gaps in research related to comprehensive environmental impacts.
The following review [10.1016/j.egyai.2025.100514] examines in detail how reinforcement learning algorithms offer advantages such as fast convergence and stability, particularly relevant to energy management optimization in hybrid electric vehicles. It highlights that deep reinforcement learning outperforms other methods in managing complex energy tasks due to its ability to navigate high-dimensional state spaces. However, challenges remain, such as computational complexity and generalization to different driving conditions.
Comment. To fill the gap in research on electric vehicles, future studies should examine findings from other fields where similar issues have been explored in greater depth, for example, in the development of large language models, and apply this knowledge to the specific field of electric vehicle research.