1. Introduction
According to the [
1], approximately 58% of the global population currently resides in urban areas, and this percentage is projected to increase to around 70% by 2050. Over the past decades, urbanization has accelerated to accommodate population growth and migration to large cities in search of development opportunities. Along with the development opportunities, the rapid increase in urbanization can lead to several negative impacts on the health of residents and the environment, manifested in various forms such as pollution, traffic congestion, climate change, and societal consequences [
2]. Given the challenges associated with the growth of urban populations, governmental bodies play a vital role in managing and improving the effects on both physical and mental health, addressing potential issues before they escalate.
Urbanization is a prolonged and intricate process marked by substantial shifts in socio-economic, ecological, and environmental factors, with the health impacts emerging as a key concern. Addressing these challenges has become increasingly complex, especially since the awareness of health issues, particularly mental health, in rapidly urbanizing countries like developing nations has not been given due priority. In many parts of the world, there are significant gaps in urban governance systems that aim to improve urban health and welfare. It can be said that urbanization is both an opportunity and a new challenge for human development across all human development indicators, including health indicators.
The relationship between urbanization and human health is a complex causal process that includes food, water, air, landscapes, waste, transport, housing infrastructure, energy, safety, security, and access to healthcare programs and services. Each factor interacts with the others. The common thread through all these factors is the relationship between economics, power, and human health, such as age, income, gender, race, and migration status. People with better economic conditions are more likely to access high-quality healthcare services. This is particularly common in developing countries. However, urbanization is uneven, especially depending on the region’s geographic, cultural, and historical context. Thus, a significant challenge for researchers is analyzing the prominent relationship between urbanization and human health. It becomes possible to assess the benefits and challenges related to new health issues in the context of ever-expanding urbanization, particularly in developing countries. This study conducts a bibliometric analysis of literature indexed in the Scopus database, focusing on how urban environmental tensions have impacted human health. These academic databases are known for curating the most influential scientific publications and providing data export features compatible with the analytical approach adopted in this research. The research answers four research questions (RQ):
What are the most common keywords in research examining the impact of urbanization on human health, specifically within rapidly growing urban environments?
Which scholars and regions have contributed the most to studies analyzing the effects of urbanization on the physical and mental health of populations in developing countries?
How have the interactions between urbanization and public health policies evolved, especially in the context of health challenges arising from rapid urban growth?
How have existing studies addressed regional variations and academic contributions related to health outcomes due to urbanization, and what new research topics have emerged in this field?
This research is organized into four main sections. The first section involves an extensive keyword search related to urbanization and health, adhering to established research guidelines. The data collected will be systematically displayed using tables, charts, and documents to answer the research questions. Subsequent sections will present an in-depth analysis and interpretation of the findings, addressing each research question. The final section will summarize the key insights from this analysis and critically evaluate how well the initial research objectives have been met.
2. Theoretical Foundations
2.1. Urban Environment
Determining the definition of an urban area is a challenging task, as there is no universally accepted or formal definition in many countries. Generally, metropolitan regions meet certain criteria, including a high concentration of people and buildings compared to surrounding rural regions, a more intricate economic and social structure, and a dominance of non-agricultural jobs. Urban areas, which include both cities and towns, possess unique physical, social, and economic attributes. Additionally, legal and institutional factors play a crucial role in urban classification, as aspects like land ownership, administrative regulations, and taxation policies have a significant impact on defining urban area [
3].
According to the International Council for Science [
4]. The urban environment encompasses the natural, constructed, and institutional factors that influence individuals’ physical, mental, and social health and well-being in cities and towns. Urbanization is the process through which the proportion of the population residing in urban areas grows, driven by three key factors: migration from rural to urban areas, natural population increase within urban settings, and the transformation of previously rural areas into urban ones. The most significant contributor to urban population growth is natural population increase, which accounts for about 60% of total growth [
5]. Nevertheless, rural-to-urban migration is the dominant force behind urbanization, with migration trends often driven by economic opportunities, social factors, and improved living conditions [
6].
The urban environment extends beyond merely the physical space-ecological and environmental contexts, socioeconomic structures, migration patterns, and political frameworks influence it. Governance structures, cultural identities, housing conditions, food security, education, health services, and access to clean water and sanitation are integral aspects of urban experience. These factors collectively impact the health and well-being of urban residents [
7]. Furthermore, urban life is shaped by the broader regional and national economies and international governance, all of which play pivotal roles in determining the health outcomes of urban populations. Additionally, exposure to pollutants, extreme weather events, and crime in urban environments further contribute to cities’ challenges in ensuring public health [
8].
In recent studies, the relationship between urban environments and public health has gained increasing attention. Research has shown that the urban environment influences physical health through environmental factors like air pollution and access to clean water and affects mental health through social determinants such as housing quality, social cohesion, and employment opportunities [
2]. As cities continue to expand, understanding these connections is essential to mitigating the adverse effects of urbanization on human health.
Urbanization is closely associated with economic growth, but its effects on health have changed over time and can differ widely across various urban settings. On the positive side, urbanization typically enhances access to advanced healthcare technologies, improved medical infrastructure, and highly skilled healthcare providers. Urban environments generally offer better educational opportunities, higher average incomes, and a wider range of healthcare services, all of which can contribute to better health outcomes, although this is not always the case [
9]. The concept of “economies of proximity,” which arises from high population density, can help lower the costs of essential services, such as clean water and social support systems [
7]. However, urban living also presents numerous challenges. Negative aspects include greater exposure to air pollution, the spread of infectious diseases, overcrowding, increased violence and crime, stressful work environments, social isolation, and lifestyle-related health risks like poor diets and physical inactivity. Additionally, as wealth becomes more concentrated in cities in developing countries, health inequalities between urban and rural areas are growing [
3].
Urban areas generally experience better health outcomes in several countries than rural regions. This health advantage is largely attributed to the implementation of various public health measures and interventions. These efforts have led to a reduction in the prevalence of infectious diseases in urban areas, though there are exceptions, such as outbreaks of diseases like dengue [
10]. However, with modern urbanization, there has been a notable increase in lifestyle-related non-communicable diseases (NCDs). The rising consumption of salt and energy-dense foods, combined with a decline in physical activity, higher tobacco usage, increased psychosocial stress, and greater social isolation, have all contributed to the growing prevalence of risk factors like hypertension and obesity. This has led to a higher incidence of conditions such as heart disease, stroke, certain types of cancer, and diabetes [
11]. The expanding global urban population is a major factor behind the anticipated 50% rise in global diabetes rates [
12]. Despite these concerns, mortality rates from chronic NCDs are typically lower in urban areas compared to rural regions, primarily due to better access to diagnostic services and treatment options.
Certain urban areas face specific challenges stemming from issues like migration, informal housing, food scarcity, job instability, prolonged and emerging conflicts, the re-emergence of infectious diseases, and extensive environmental damage. This is especially prevalent in countries where rapid and large-scale economic development has taken place. Many major cities are heavily dependent on fossil fuels for energy, which makes them significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, a leading cause of global warming [
13]. The effects of climate change will have wide-ranging consequences for urban health, including more frequent and severe heatwaves, flooding, worsening food security, the spread of specific infectious diseases, increased air pollution, and rising migration rates. These factors, both separately and together, have the potential to significantly harm the health and well-being of urban populations, often over long periods of time.
2.2. Human Health
The WHO (1948) states, “Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” [
14]. This definition incorporates the essential components that are central to understanding health and well-being in the context of urban environments. The term “health and well-being” is used throughout this study to emphasize that health is a multidimensional concept, extending far beyond the mere absence of illness. While the physical dimensions of health are undeniably important—encompassing indicators of disease, disability, and functional impairment the behavioral and social dimensions, including mental health issues, cognitive functioning, and emotional and social well-being, are equally crucial. These three interconnected aspects, physical health, mental health, and social functioning are mutually influential. Research that broadens the traditional definition of health beyond simply the presence or absence of disease is highly encouraged within this framework.
Human health is closely linked to the built environment and air pollution through opportunities for physical activity that promote good health and exposure to air pollution, which leads to poor health outcomes. A primary focus in urban planning literature is to improve urban design and planning to reduce car dependency and create more opportunities for physical activity. This literature often implies That air pollution should be reduced, though not always directly addressed. A separate body of literature from scientific and technological fields tackles air pollution more directly. Improvements in fuel standards, automobile emissions regulations, the rise of electric vehicles, and increasing tree planting to absorb air pollution or act as buffer zones are key examples discussed in this work. This second group of literature is especially relevant for current car-dependent residential areas. Due to historical factors, many suburban areas in cities will remain reliant on cars for the foreseeable future. Urban planners and public officials are collaborating with research communities to seek sustainable solutions to the emerging link between urban air pollution, and their impacts on human health. The global growth of urban populations is a key driver behind the projected 50% increase in global diabetes rates, as F. Wild, (2024) highlighted. Despite this, mortality rates from chronic NCDs tend to be lower in urban areas than in rural areas due to better access to diagnostic and treatment facilities, including advanced technologies and specialized care.
Certain urban settings encounter unique difficulties related to population migration, informal housing, food scarcity, employment instability, prolonged and emerging conflicts, the resurgence of infectious diseases, and significant environmental decline. These issues are particularly prevalent in regions where economic growth has been rapid and expansive. A significant number of major cities remain heavily dependent on non-renewable energy sources, particularly fossil fuels, making them substantial contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, which are a leading factor in the acceleration of global warming [
13]. Climate change is expected to impact urban health in numerous ways, including a rise in the frequency and intensity of heatwaves, flooding, food insecurity, the spread of certain infectious diseases, worsened air quality, and increased migration flows. A 2022 study on the urban heat island effect highlighted that elevated temperatures during extreme heat events exacerbate cardiovascular and respiratory conditions, and contribute to mental health issues, such as anxiety and fatigue [
16]. Collectively and individually, these factors pose significant threats to the health and well-being of urban populations, often with long-term consequences.
2.3. Bibliometrics in Urban Environment
The origins of bibliometric analysis can be traced back to the 18th century, with early contributions from Frömmichen, whose pioneering work established the foundation for developing this research methodology [
17]. Bibliometrics, which utilizes quantitative methods to evaluate academic literature, is inherently interdisciplinary, incorporating elements from statistics, sociology, and computer science [
18]. This approach plays a vital role in enhancing our understanding of various research domains by providing insights into specific areas of study and identifying key contributors [
19]. Bibliometric methods rely on statistical analysis of scholarly publications to offer valuable insights into academic productivity and emerging research trends. Rooted in scientometric practices, bibliometric techniques help assess scientific contributions, fostering a deeper understanding of scholarly literature, its impact, and its evolving patterns [
20]. Citation counts, often considered a more valuable metric than the sheer volume of publications, measure a researcher’s influence in their field [
18]. Traditionally, bibliometric methods have been most prevalent in natural and life sciences, where research output is primarily gauged through peer-reviewed journal articles and citation trends [
21].
Moreover, bibliometric analysis has highlighted both positive and negative effects on editorial decisions and publication strategies adopted by researchers [
22]. In the context of urban health and environmental studies, bibliometrics provides a comprehensive way to map out the growth of research in this area, identify emerging trends, and assess the influence of key scholars. Through systematic citation analysis, bibliometrics enables a deeper understanding of how urban environments and health studies have evolved, helping researchers and policymakers navigate the expanding body of literature in this critical field. This broader application of bibliometric techniques in fields like urban health studies reflects a shift towards more nuanced, data-driven approaches to understanding the intersection of environmental factors and human well-being. As the focus on urbanization and its health impacts grows, the role of bibliometrics becomes even more pivotal in shaping future research agendas and public health strategies.
In the field of urban health research, bibliometric studies have highlighted a significant increase in scholarly publications over the past few decades. Tools such as VOSviewer, Pajek, and Sci2 have facilitated comprehensive data processing and analysis, allowing researchers to map trends and identify emerging topics in this dynamic field. Specialized areas within urban health, such as the effects of air pollution, urban heat islands (UHI), and the role of green spaces in improving well-being, have gained increasing attention, with related literature experiencing notable growth in recent years. Analyzing the general trends in urban health research over time helps reveal key developments and new research themes crucial for theoretical advancement and future studies. These bibliometric analyses often rely on extensive academic databases for data collection, utilizing tools like VOSviewer to conduct in-depth analysis. Alternative tools like Publish or Perish, SPSS, and Excel are also used for specific analytical tasks, demonstrating the versatility of bibliometric methods in studying the relationship between urban environments and human health.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Source and Study Selection
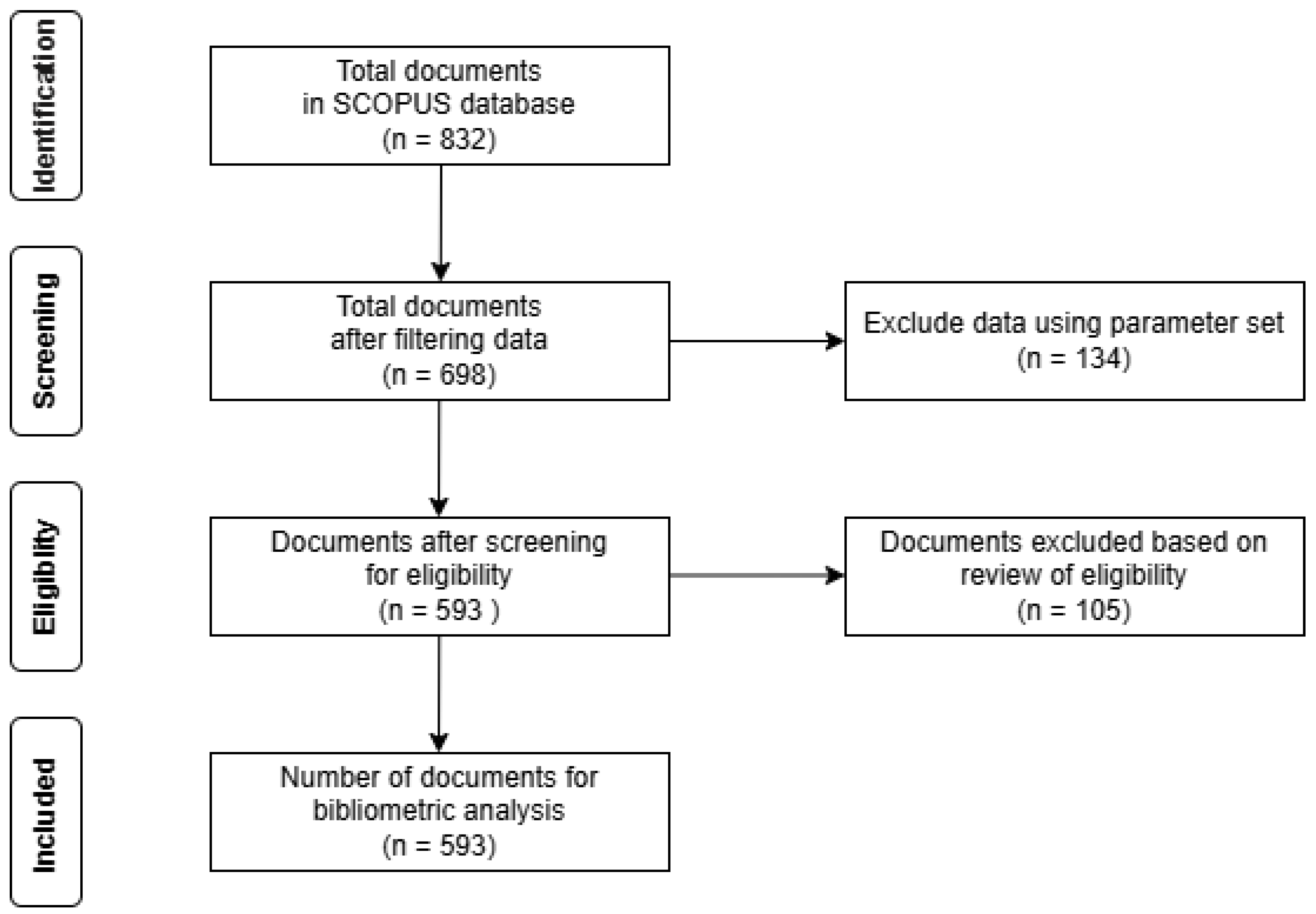
This study employed a comprehensive bibliometric approach to analyze academic articles retrieved from the Scopus database systematically. A precise and well-targeted search strategy, utilizing carefully selected thematic terms closely aligned with the research objectives, was crafted to capture relevant scholarly literature focused on “Urban Environment” and “Human Health.” The search strategy and data extraction process are visually represented in the PRISMA diagram shown in
Figure 1. The data analyzed in this study was updated as of April 2025, covering a broad range of articles from 1967 to 2025. The structured query for the Scopus database was formulated as follows: (TITLE-ABS-KEY “Urban Environment” OR “Urbanization” AND “Human Health” OR “Public Health”) AND PUBYEAR < 2025. This search resulted in a total of 832 articles being retrieved from Scopus. After rigorous filtering, 698 documents were selected for the next screening stage. The eligibility of these documents was then reviewed, resulting in the exclusion of 105 papers based on specific criteria, including relevance and content alignment with the research objectives. Finally, the remaining 593 documents were deemed eligible for bibliometric analysis, providing a rich data set for further exploration. This research represents a thorough investigation into the global evolution of urban health research, tracing its development over nearly six decades. By using bibliometric methods, this study aims to shed light on the growth of urban health research, the emergence of key topics, and the contributions of leading scholars in this field.
Scopus is a leading academic database extensively utilized in literature reviews due to its comprehensive coverage and high reliability across various disciplines. This platform is essential for conducting thorough searches of scholarly works and is integral to academic research globally [
23]. Scopus was chosen as the primary data source for aggregation and analysis for this study due to its robust and expansive coverage, particularly in urban health and environmental studies. Unlike other databases, Scopus provides in-depth access to theoretical frameworks and practical studies, offering a comprehensive repository of academic papers and citation data [
24]. As the largest and most comprehensive database, Scopus allows for a broader view of urban health-related research, capturing relevant studies across various disciplines that impact human health in urban environments. Using a single, highly reputable database such as Scopus minimizes potential biases from relying on multiple data sources. It ensures that the research findings are consistent and representative [
25]. This approach enables an in-depth examination of the evolution of urban health research, providing valuable insights into trends and emerging themes in the field.
3.2. Data Analysis and Visualization
This study employed advanced analytical tools, including VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) and RStudio (version 4.4.0), integrated with specialized bibliometric packages to conduct a comprehensive bibliometric analysis. VOSviewer generated keyword maps based on co-occurrence data, helping visualize emerging trends and connections in urban health research. At the same time, RStudio facilitated the quantitative analysis of bibliometric data. A total of 593 relevant articles were selected for inclusion in this study. These articles, sourced exclusively from Scopus, were imported into RStudio for further analysis. During the bibliometric process, merging synonymous terms and keyword variations was essential to ensure consistency and accuracy in the results, preventing data fragmentation during visualization and providing more reliable insights.
4. Result
4.1. The Trends of Annual Articles Publication
Research on urban environments and human health has seen significant growth in the past few decades, as reflected in the number of documents published and the number of citations (
Figure 2). Initially, between 1967 and 1999, the number of publications remained low, with only a few documents published yearly. Specifically, in 1967, there was just 1 document with 12 citations, and in 1970, there were two documents with 20 citations. The trend of low publication and citation numbers continued in the subsequent years, with the most notable year being 1999, which had 1 document and a remarkable 353 citations. This indicates that while publications were limited, the ones that were published had a significant impact at the time. From 2000 to 2009, the number of publications began to rise more steadily, with the number of documents increasing yearly. In 2000, there was 1 document with 451 citations, and by 2009, 6 documents were published, attracting 480 citations. This period marks the beginning of more focused research on urban health, as cities worldwide were undergoing rapid urbanization. The publications from this decade laid the groundwork for future studies, though citation numbers remained relatively modest, with six documents published in 2009 and 480 citations.
The fundamental shift in publication and citation volume occurred between 2010 and 2020, as the focus on urban health and its relation to environmental factors became increasingly important. For instance 2010, 13 documents were published with a high citation count of 1746. Over the next decade, the number of publications rose sharply, with 61 papers published in 2020, leading to 2269 citations. This spike reflects the growing recognition of urban health as an important area of research, particularly as cities face mounting challenges related to pollution, public health, and climate change. The citation numbers also mirrored this growth, indicating that the research was gaining substantial recognition and influence in the academic community. In 2021, 59 documents were published with 1530 citations, followed by another year of high publication in 2022 with 61 papers and 1168 citations. However, there was a noticeable decline in citations in 2023, with 59 documents published and only 678 citations. This could suggest that while the volume of publications continued to rise, some newer studies had not yet gained the same level of recognition and citation as earlier works. As of 2024, 60 documents have been published, but the total citations for this year dropped significantly to 181. This decline in citations could be attributed to the recent nature of these publications, which might not have had enough time to accumulate citations and may indicate a shift towards more focused or specialized topics that take time to integrate into broader academic discourse.
Overall, the growth in both publications and citations over the years indicates the increasing importance of urban health research. The rise in publications and citations after 2010 underscores the growing recognition of urban health issues in the context of rapid urbanization, climate change, and environmental stressors. Future research in this area will likely continue to expand, particularly as cities worldwide grapple with the health challenges posed by environmental factors and urbanization.
4.2. Analysis of Countries Involved in Research
Of the 593 articles selected from Scopus, research articles from 91 countries were analyzed.
Table 1 lists the Top 10 countries with the highest publication rates from 1967 to 2024. The country with the highest publication rate is China, with 134 articles published. China also leads in total citations, with 7822 total, highlighting its significant contribution to urban health and environmental research. Despite having fewer articles than China, the United States ranks second in citations, with 6393 citations from 126 articles. The United States also ranks first in total link strength (TLS), with 4166 total links to other articles, which indicates a strong network of interconnections in the research.
Next, Australia stands in third place, with 49 articles and 1852 citations, along with 2108 TLS, demonstrating its important role in contributing to the academic discourse on urban health, albeit with fewer articles than the top two countries. The United Kingdom follows Australia, with 53 articles and 2474 citations, contributing to a robust body of research on urban environments and health, with 1592 TLS. India ranks fifth, with 38 articles and 1011 citations, while Pakistan contributes 19 articles and 560 citations, indicating a smaller but growing presence in the field. These countries, despite having fewer publications, continue to make notable contributions to the understanding of urban health in the context of developing countries. Other notable countries include Spain and Brazil, with 23 articles each and 1220 and 381 citations, respectively. Spain has higher TLS (1032) than Brazil (579), reflecting a stronger network of interrelated research in urban health. Canada and Italy have published 21 and 23 articles, respectively. Canada shows a relatively more substantial research influence, with 1054 citations and 521 TLS. Italy’s contributions are more limited, with 854 citations and 378 TLS, indicating a less interconnected body of research in comparison.
Figure 3 illustrates the global landscape of scientific collaboration and research production, showing the interconnectedness between countries involved in urban health research. The map highlights key research hubs, with the United States and China forming the most significant collaborative links. These two countries are the primary contributors to urban health, with numerous collaborations with other nations, especially in Europe and Australia. The visualization also indicates growing research connections between India, Brazil, and Pakistan, where there has been an increasing output of studies on urban health. The map provides an overview of the international nature of urban health research, emphasizing the essential role of cross-border collaborations in advancing the knowledge necessary to address global urban health challenges. This figure highlights the significant role of international partnerships in tackling the complexities of urbanization and its impact on public health, underscoring the collaborative efforts that shape the development of urban health research worldwide.
4.3. Institute Distribution of Literature
After reviewing the list of the most productive institutions in urban health research, it is evident that certain universities and organizations have made significant contributions to the field. The University of California emerged as the leading institution, with 24 articles published. Following closely behind, Queensland University of Technology (QUT) published 21 articles, while Tongji University and the University of Belgrade each published 19 articles. University College London and Aristotle University of Thessaloniki contributed 18 articles each. The University of Nottingham, Beijing, and Beijing Normal University ranked with 17 articles, highlighting the diverse global engagement in this field. Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia also contributed significantly with 11 articles showcasing the growing research output from Southeast Asia. These institutions reflect a broad, international collaboration in urban health, with significant contributions from universities across different continents, indicating the global nature of research in this area.
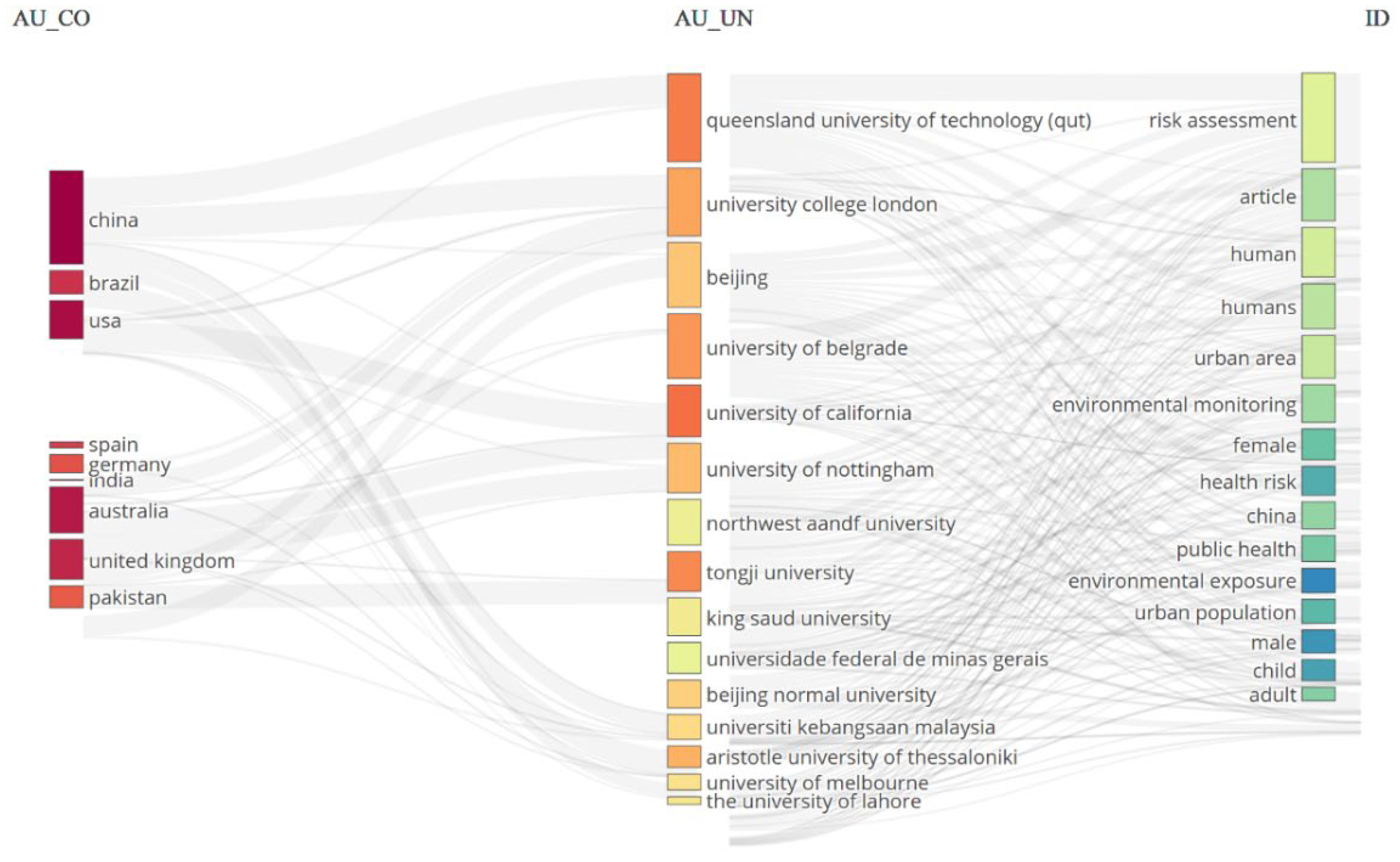
Figure 4 presents a three-field plot illustrating the relationship between institutions, countries, and research keywords in urban health research. This visualization was created using R-Studio software (Version 4.1.3) and bibliometric libraries from the Scopus Database. The plot emphasizes institutions’ prominent role in shaping the discourse and research output related to urban health. The plot reveals key patterns in how universities and research institutions collaborate across various countries and focus on specific topics within urban health. The institutions on the plot, such as Queensland University of Technology (QUT), University College London, and Tongji University, are at the forefront of this field. These universities are deeply involved in urban health research, with their publications covering key areas such as risk assessment, human health, environmental exposure, and urban areas. The map shows strong collaborations between institutions in China, Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Queensland University of Technology (QUT), based in Australia, is prominently linked to keywords like “risk assessment” and “article”, highlighting its leadership in evaluating health risks in urban environments. Similarly, University College London and Beijing Normal University are deeply involved in studies focusing on the human aspect of urban health, with research concentrated on humans, urban populations, and environmental monitoring.
China and the USA emerged as the dominant countries, contributing substantially to the overall research output. Institutions from both countries, such as Beijing Normal University and the University of California, have the highest publications and exhibit extensive collaborations with other global institutions. These institutions also contribute to primary keywords in urban health, such as “public health”, “environmental exposure”, and “health risk”. Notably, the connection between China and its institutions like Tongji University and Beijing Normal University underscores the growing research capacity in China, particularly in areas related to environmental exposure and public health. The analysis highlights the significant role of international collaborations in advancing the urban health agenda. Institutions in developed countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom collaborate with those in developing countries like China, India, and Pakistan. This cross-border research exchange demonstrates the global commitment to addressing urban health challenges.
4.4. Most Influential Source Title
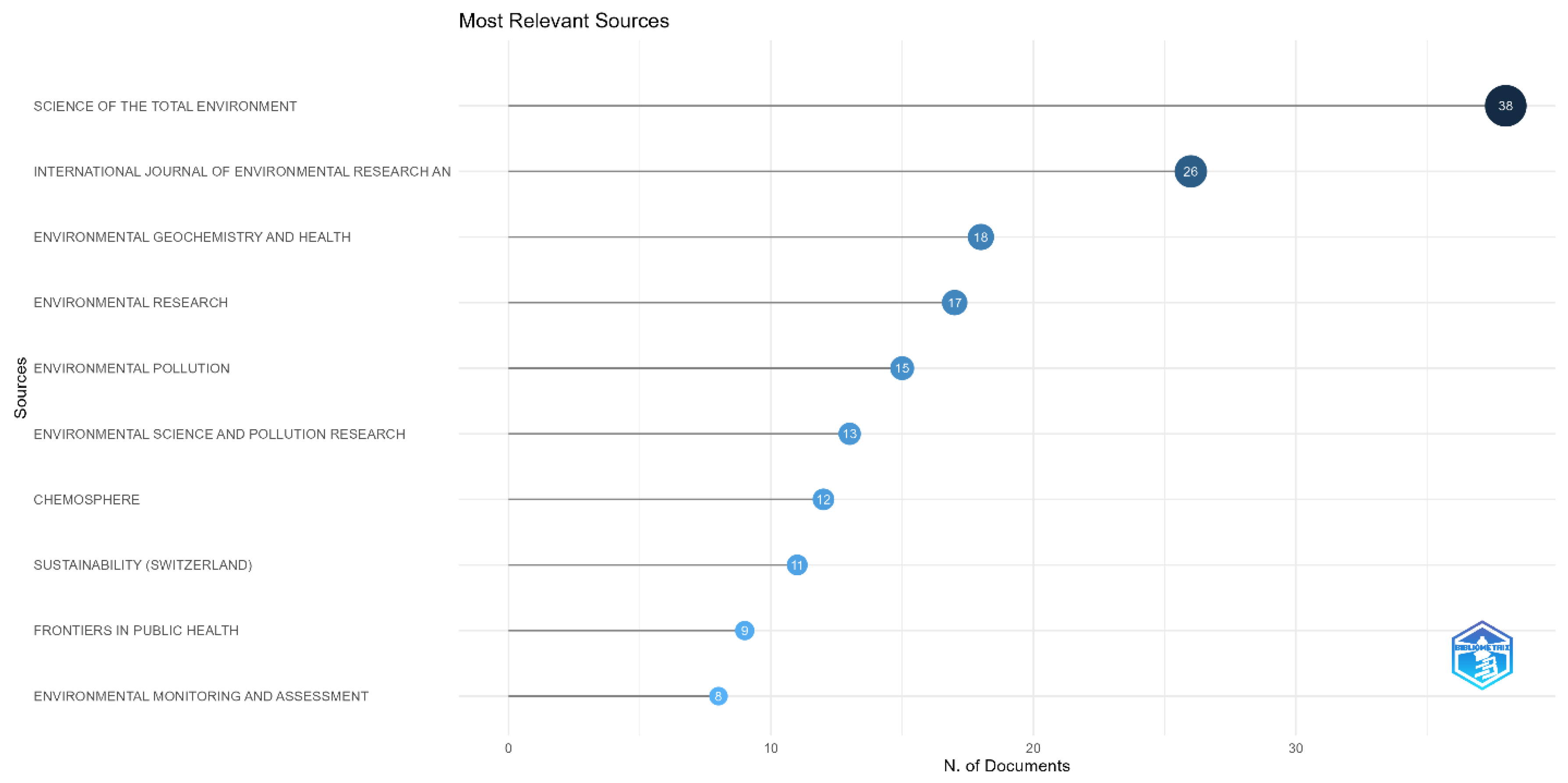
Table 2 shows that “Science of the Total Environment” is the leading journal in urban health and environmental research, with the highest Quality score of 38 (
Figure 5) and an impressive total of 3801 citations. This journal significantly impacts the field, as reflected in its H-Index of 399, indicating high productivity and citation frequency across a range of articles. The second-ranked journal is the “International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health”, which has 26 articles published and 716 citations. Despite having fewer total citations than “Science of the Total Environment”, it remains a significant source of research in this area, with a notable H-Index of 299. The third position is occupied by “Environmental Pollution”, a prominent journal with 15 articles and 905 citations, reflecting its contribution to environmental health and urban pollution research. This journal also has a strong H-Index of 328, further solidifying its standing within the academic community. Notably, the journal “Environmental Geochemistry and Health” with 18 articles and 501 citations, contributes significantly to urban health research, particularly concerning environmental impact studies. Yet, it lags behind the top three in total citations.
4.5. Publication per Author and Co-Authorship Network
In terms of authorship, 2613 authors contributed to the 593 documents evaluated. This contains the primary writers and their co-authors with at least six papers per author and a Scopus database collection of total citations. According to
Table 3, “LIU Y” stands out as one of the most productive authors, with a total of 10 articles published. LIU Y has garnered 407 citations, significantly impacting the field. Despite the high number of citations, the H-Index of LIU Y is 15, suggesting a balanced contribution to the field regarding productivity and influence. Another prominent author, “WANG Y”, published 7 articles and received 444 citations. However, their H-Index is relatively lower at 3, suggesting that while their articles have been cited many times, the number of articles with high citation impact is fewer than other authors. This could indicate that WANG Y may have authored a few highly influential papers but has fewer sustained citations across all published works. “CASSELL EJ” also contributed to the research with 10 articles published, but with a lower citation count of 60 and an H-Index of 21. This suggests that CASSELL EJ has maintained a consistent level of academic output, and their work has received a moderate citation level, contributing steadily to the body of knowledge in this field.
Figure 6.
Author’s Production over time.
Figure 6.
Author’s Production over time.
4.6. Most Cited Publications of Articles
It is necessary to analyze the extracted articles to determine the most cited documents and their focus areas, particularly on the Scopus database, one of the most significant sources covering most scientific fields. Just 10 of the 593 retrieved articles were mentioned at least 377 times by Scopus Core, as shown in
Table 4.
4.7. Social Network Analysis: Co-Occurrence Network of Keywords
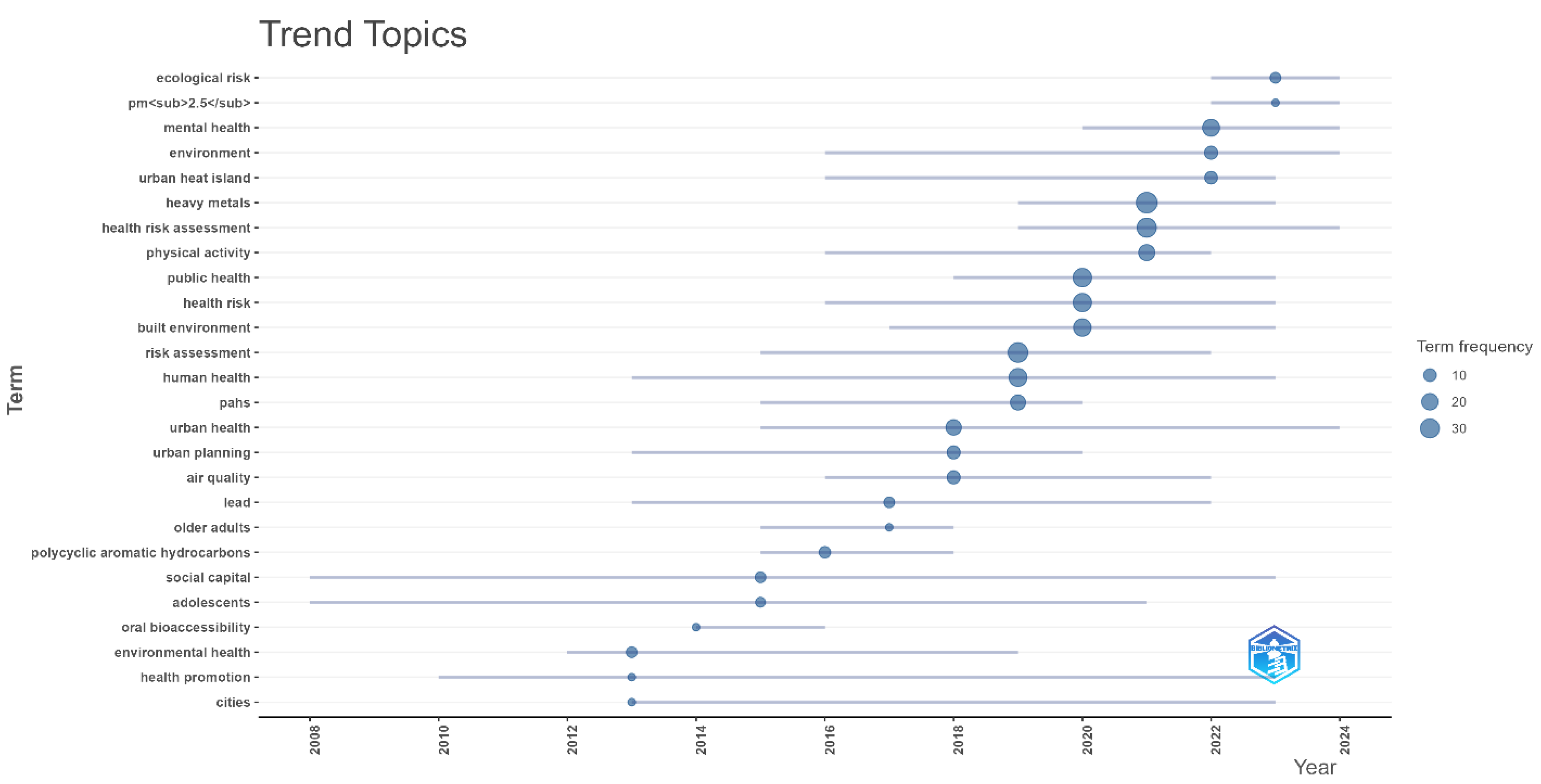
Figure 7 presents a Trend Topics chart, visualizing the frequency of specific terms used in urban health research over time. The chart demonstrates how specific topics have gained traction in the field, particularly urban environments and human health. From the chart, it is evident that issues such as “urban heat island”, “health risk”, “health assessment”, and “human health” have steadily increased in frequency, especially from 2015 onwards. These terms indicate a growing focus on understanding how urban environments, with factors like heat islands and health risks, impact public well-being. For instance, the term “urban heat island” shows significant growth in usage, reflecting an increased concern with climate change and its effect on urban populations. Another noticeable trend is the prominence of terms like “air quality” and “public health”, which spiked notably around 2020. These frequency shifts correspond to global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, which brought issues related to air pollution, health risk assessments, and overall public health to the forefront of urban research agendas.
The term “risk assessment” shows steady growth over time, indicating an increasing emphasis on evaluating the health risks posed by urban environments, including exposure to pollutants and extreme weather conditions. Additionally, terms related to “environmental health” and “physical activity” have been gaining attention, highlighting the growing recognition of the importance of designing urban spaces that promote healthy lifestyles. A slight increase in terms like “adolescents”, “older adults” and “health promotion” suggests a growing focus on specific population groups and their vulnerability to urban environmental factors, such as air pollution and inadequate access to green spaces. The terms “urban health” and “urban planning” surged from 2019 onwards, reflecting the broader academic trend of integrating urban design with health outcomes. Researchers are increasingly focusing on how urban planning and the built environment influence the health of residents, particularly in rapidly growing cities.
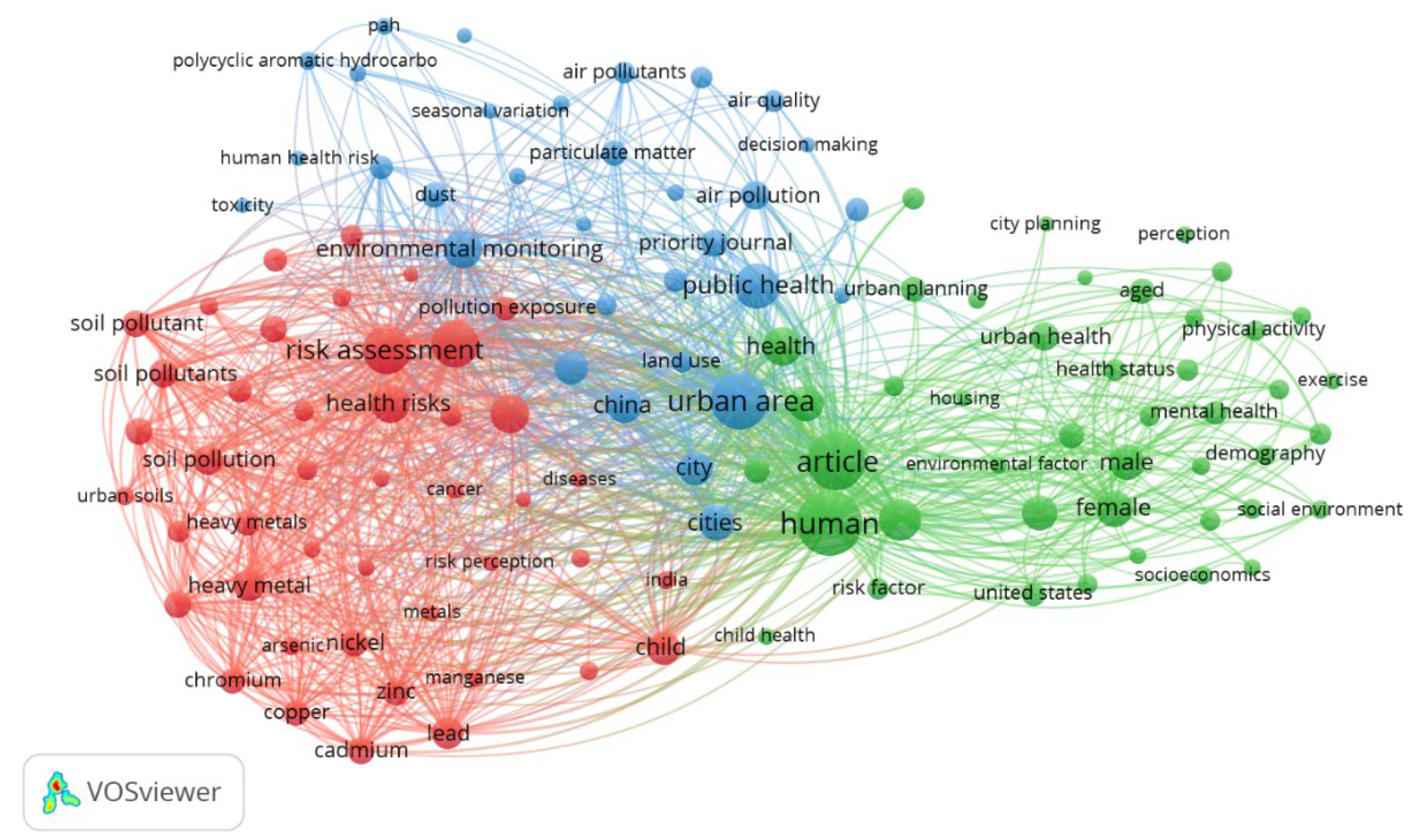
VOSviewer checked a total of 2658 keywords that appeared at least once; however, with the simultaneous keyword analysis, articles asked for at least 20 occurrences of each keyword and collected 122 related keywords, as shown in
Table 5,
Figure 8.
5. Discussions
Based on the results presented in the previous section, this section presents an in-depth discussion of key findings, explores their important implications and contributions, and highlights the study’s limitations.
Firstly, for urban health research in the context of global sustainability goals, the exponential growth of urban health research since 2010 demonstrates a fundamental shift in global academic and policy priorities. This trajectory strongly aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly sustainable cities and communities (SDG11), which emphasizes inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable urbanization. The increase in publications and citations reflects an expanding scientific response to pressing urban challenges such as climate change, environmental stressors, and rapid demographic transitions. This finding confirms the evolution of urban health into an interdisciplinary field, requiring systemic approaches that integrate environmental science, public health, and urban planning [
36]. Next, in terms of institutional and geographical dimensions, the distribution of research leadership reveals important imbalances. Institutions from developed nations such as the University of California and Queensland University of Technology dominate publication outputs, while emerging institutions from China and Southeast Asia are increasingly visible. This pattern highlights both progress and persistent gaps, for example, although knowledge production is becoming more geographically diverse, substantial disparities remain in Africa and Latin America, potentially limiting context-specific evidence for policymaking [
37,
38]. From a sustainability perspective, strengthening institutional capacity in the Global South is crucial for achieving SDG 11 equitably.
Regarding national contributions and collaboration networks, China and the United States dominate both the quantity and impact of publications, supported by extensive collaboration networks. While this concentration demonstrates strong institutional capacity, it raises concerns about dependency and knowledge asymmetry. Compared with McMichael (2000) earlier observations on the challenges of urbanization in developing countries, recent trends indicate growing participation from India and Brazil, though still limited. International collaborations remain essential to ensure that evidence-based practices reach low- and middle-income countries, where urban health risks are most acute. When it comes to influential sources and thematic maturity, high-impact journals such as Science of the Total Environment and International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health play a central role in shaping the discourse. Their prominence underscores scientific consensus on the critical links between the urban environment and human health, providing policymakers with credible evidence to design interventions such as green infrastructure, emissions regulations, and climate adaptation strategies. The dominance of urban heat island studies and environmental contamination research further highlights the centrality of climate resilience and environmental quality in achieving SDG 11 targets.
For authorship and co-authorship networks, knowledge production is concentrated among a relatively small group of highly productive authors, including Liu Y and Wang Y (
Table 3), whose work exerts significant influence. This concentration suggests a strong intellectual core, while co-authorship patterns reflect the collaborative, interdisciplinary nature of the field. These findings echo Rydin et al.s’ (2012) call for systemic approaches and align with Vardoulakis et al.’s (2016) emphasis on international collaboration. From a policy standpoint, expanding networks to include scholars from the Global South will be vital for translating evidence into locally relevant, equitable urban health solutions. As for keyword co-occurrence and thematic evolution, the co-occurrence analysis demonstrates how research themes have evolved from basic environmental exposure studies to clusters emphasizing health risks, environmental factors, and public health. This shift is consistent with global recognition of the need for integrated approaches to urban planning and health promotion. In relation to McMichael’s (2000) focus on infectious disease and rapid urbanization, current scholarship emphasizes climate resilience, environmental justice, and population-specific vulnerabilities. Practically, embedding risk assessment into urban design, expanding green infrastructure, and promoting cross-sectoral collaboration are increasingly viewed as necessary for sustainable urban futures.
This study makes several theoretical and practical contributions. Firstly, it systematically maps six decades of global scholarship, demonstrating the interdisciplinary maturity of urban health research to some degree. Secondly, it identifies persistent gaps, including the underexplored intersection of urban design and mental health, and geographic imbalances in research production. Thirdly, it provides a conceptual bridge between knowledge generation and cultural transformation, emphasizing the role of environmental literacy and/or high-value culture. In light of the Culture Tower (Khuc, 2023; Khuc et al., 2024), the Mindsponge-Mindspongeconomics system (Khuc, 2022; Vuong, 2023) and the SM3D knowledge management system (Vuong et al., 2022), our study suggests a clearer pathway from improving environmental knowledge and/or environmental literacy (Khuc et al., 2023) to facilitating individual and collective actions that contribute to sustainable urban systems. To be more specific, Nature Quotient (Vuong & Nguyen, 2025), for example, could be used to measure and monitor the progress of environmental culture transformation. This perspective advances theory by linking bibliometric evidence with sustainability culture, offering a novel approach to embedding SDG 11 into urban lifestyles.
For rapidly urbanizing nations such as Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia, the findings underline the importance of proactive strategies. Evidence from influential studies [
28,
31] demonstrates that urban design- through active transport, green spaces, and mixed-use planning-directly affects population health. Policies should therefore move from reactive health interventions to integrated urban planning that reduces environmental hazards and promotes social equity. Strengthening collaboration networks with developed countries while investing in local capacity building will be essential to adapt global evidence to local contexts. Beyond policies, the study highlights the necessity of cultural change. Developing environmental culture and eco-surplus culture requires embedding sustainability into everyday practices of urban residents. By leveraging the Culture Tower, education systems, community organizations, and urban planners can cultivate environmental literacy and translate it into sustainable behavior. This transformation not only supports SDG 11 but also enhances social cohesion, resilience, and long-term well-being in rapidly urbanizing contexts.
While offering comprehensive insights, this study has some limitations. Declining recent citations for newer publications might not indicate lesser impact but natural academic discourse integration lags, as specialized topics require adoption time. Bibliometric focus on citation counts may underrepresent immediate influence of recent research. Dominance of specific countries and institutions, while reflecting established capacities, could introduce bias in global research priority representation, potentially underemphasizing local urban health issues critical to rapidly urbanizing developing regions less extensively published in international databases. These factors suggest that while the study effectively charts major trends, nuanced interpretation is necessary regarding emerging areas and underrepresented geographical contexts.
6. Conclusions
This paper aims to advance the understanding of the evolving field of urban health and its relationship with urban environments through a structured bibliometric analysis of scholarly sources indexed in Scopus. Specifically, this comprehensive bibliometric study systematically analyzed 593 urban health research documents published between 1967 and 2024, sourced from the Scopus database. Employing advanced bibliometric tools such as R-Studio and VOSviewer, the research mapped publication trends, identified key contributing countries, institutions, and authors, highlighted influential publication sources, and elucidated the thematic evolution through keyword co-occurrence analysis. This methodical approach allowed for a robust understanding of the landscape and trajectory of urban health scholarship. The study reveals a fundamental shift and exponential growth in urban health research, particularly since 2010. This surge underscores the escalating recognition of urban health issues amidst rapid urbanization, climate change, and environmental stressors. Key findings indicate the dominance of China and the United States in both publication output and collaborative networks, alongside the significant contributions of institutions like the University of California, Queensland University of Technology, and Tongji University. Influential journals such as Science of the Total Environment and International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health play a pivotal role in shaping academic discourse. Thematic analysis demonstrates an evolution from basic environmental exposure studies to a broader focus on health risks, environmental factors, and public health, with terms like urban heat island, air quality, and risk assessment gaining prominence, especially post-2015. The top-cited articles further highlight critical areas, including the impact of urban heat islands, heavy metal pollution, and the influence of the built environment on health.
These findings offer significant implications for green, clean, and civilized urban development, particularly in alignment with SDG 11 on sustainable cities and communities. The research strongly advocates for a paradigm shift from reactive health interventions to integrated urban planning that champions green infrastructure, active transport, and mixed-use designs to mitigate environmental hazards and foster social equity. Crucially, achieving sustainable urban futures necessitates a profound cultural transformation. By leveraging frameworks such as the Culture Tower and metrics like the Nature Quotient, cities can actively cultivate environmental literacy among residents. This approach aims to embed sustainability into daily practices, promoting an eco-surplus culture that enhances social cohesion, resilience, and long-term well-being in rapidly urbanizing countries. Strengthening international collaboration, particularly with developing countries, is essential to adapt global evidence to local contexts and address acute urban health risks.
Future research should continue to address persistent gaps, notably the underexplored intersection of urban design and mental health. There is also a critical need to strengthen institutional capacity in the Global South to reduce existing geographic imbalances and ensure the generation of context-specific evidence for policymaking. Methodologically, future studies could explore more nuanced interpretations of research impact beyond traditional citation counts, accounting for the natural integration lag of newer, specialized topics. Further exploration into the practical application and measurement of environmental culture transformation using tools like the Culture Tower and/or Nature Quotient would provide valuable insights for fostering sustainable urban lifestyles. This continued focus will ensure that urban health research remains dynamic and responsive to global challenges, guiding the creation of healthier, more sustainable urban environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Methodology, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Validation, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Formal analysis, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Resources, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Data curation, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Writing—original draft, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Writing—review and editing, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T; Project administration, V.Q.K. and T.T.H.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets utilized in the present investigation can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SDGs |
Sustainable Development Goals |
| PRISMA |
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| TLS |
Total link strength |
| SM3D |
Serendipity Mindsponge Discipline knowledge management system |
References
- Anestis, G.; Stathakis, D. Chapter 17 - Urbanization trends from global to the local scale. In; Petropoulos, G.P., Chalkias, C.B.T.-G.I.S., Eds.; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 357–375. ISBN 978-0-443-13605-4.
- Krefis, A.C.; Augustin, M.; Schlünzen, K.H.; Oßenbrügge, J.; Augustin, J. How Does the Urban Environment Affect Health and Well-Being ? A Systematic Review. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat World Cities Report.
- ICSU Science Plan on Health and Wellbeing in the Changing Urban Environment: A Systems Approach.
- Preston, S.H. Urban Growth in Developing Countries: A Demographic Reappraisal. Popul. Dev. Rev. 1979, 5, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
TRB & IM Does the Built Environment Influence Physical Activity?: Examining the Evidence - Special Report 282; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, 2005.
- Satterthwaite, D.; Sverdlik, A.; Brown, D. Revealing and Responding to Multiple Health Risks in Informal Settlements in Sub-Saharan African Cities. J. Urban Health 2019, 96, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO WHO Health Promotion Team. Healthy Cities Effective Approach to a Changing World.
- Bloom, D.E.; Canning, D.; Fink, G. Urbanization and the Wealth of Nations. Science (80-. ). 2008, 319, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Poel, E.; O’Donnell, O.; Van Doorslaer, E. Urbanization and the spread of diseases of affluence in China. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2009, 7, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.A.; Popkin, B.M. Globalization, Urbanization and Nutritional Change in the Developing World. eJADE Electron. J. Agric. Dev. Econ. 2004, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-rodriguez, R. Science Plan. Urbanization and Global Environmental Change. 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, D. The WHO definition of “health”. Stud. Hastings Cent. 1973, 1, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, F. Development in Sub-Saharan Africa New Micro-Level Evidence on Education, Geography and Trade, 2024.
- Jiang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, E.; Cohen, N.; Ohtori, M.; Sun, A.; Dill, S.-E.; Singh, M.K.; She, X.; Medina, A.; et al. Perinatal Mental Health Problems in Rural China: The Role of Social Factors. Front. Psychiatry, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel Cortés Vargas Medir la producción científica de los investigadores universitarios: la bibliometría y sus límites. Rev. la Educ. Super. 2007, XXXVI, 43–65.
- Bonilla, C.A.; Merigó, J.M.; Torres-Abad, C. Economics in Latin America: a bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.J.M.; Fernandes, C.I.; Ratten, V. A co-citation bibliometric analysis of strategic management research. Scientometrics 2016, 109, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glänzel, W.; Moed, H.F. Opinion paper: thoughts and facts on bibliometric indicators. Scientometrics 2013, 96, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildgaard, L.; Schneider, J.W.; Larsen, B. A review of the characteristics of 108 author-level bibliometric indicators. Scientometrics 2014, 101, 125–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guz, A.N.; Rushchitsky, J.J. Scopus: A system for the evaluation of scientific journals. Int. Appl. Mech. 2009, 45, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadegani, A.A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections : Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, S.; Jones, P.; Kailer, N.; Weinmann, A.; Chaparro-banegas, N. Digital Transformation: An Overview of the Current State of the Art of Research. SAGE Open 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Song, G.; Zhen, X.; Yuan, D.; Kalkstein, A.J.; Li, F.; et al. The urban heat island and its impact on heat waves and human health in Shanghai. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-rueda, D.; Nazelle, A. De; Tainio, M. The health risks and benefits of cycling in urban environments compared with car use : health impact assessment study. BMJ 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, A.J. The urban environment and health in a world of increasing globalization: issues for developing countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-S.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Yu, S. Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban park soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.D.; Engelke, P.O. The Built Environment and Human Activity Patterns : Exploring the Impacts of Urban Form on Public Health. J. Plan. Lit. 2001, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Hirabayashi, S.; Doyle, M.; McGovern, M.; Pasher, J. Air pollution removal by urban forests in Canada and its effect on air quality and human health. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, M.-J.; Kang, Y.; Wang, H.-S.; Leung, A.O.W.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban surface dust of Guangzhou, China: Status, sources and human health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4519–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.E. The relationship of urban design to human health and condition. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-T.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.-C.; Wu, M.-H.; Yu, G. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban soils of the megacity Shanghai: Occurrence, source apportionment and potential human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydin, Y.; Bleahu, A.; Davies, M.; Dávila, J.D.; Friel, S.; De Grandis, G.; Groce, N.; Hallal, P.C.; Hamilton, I.; Howden-Chapman, P.; et al. Shaping cities for health: Complexity and the planning of urban environments in the 21st century. Lancet 2012, 379, 2079–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Sharifi, A.; Aina, Y.A.; Ahmad, S.; Mora, L.; Filho, W.L.; Abubakar, I.R. Charting sustainable urban development through a systematic review of SDG11. Nat. Cities 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Desul, S.; Santos, C.A.G.; Mishra, S.K.; Kamal, A.H.M.; Goswami, S.; Kalumba, A.M.; Biswal, R.; da Silva, R.M.; dos Santos, C.A.C.; et al. A bibliometric analysis of sustainable development goals (SDGs): a review of progress, challenges, and opportunities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 11101–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Dear, K.; Wilkinson, P. Challenges and Opportunities for Urban Environmental Health and Sustainability: the HEALTHY-POLIS initiative. Environ. Heal. 2016, 15, S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuc, V.Q. Culture Tower. SSRN 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuc, V.Q.; Tran, M.; Thinh, N.A.; Lich, H.K.; Dang, T.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Tran, D.T. Closing nature connectedness to foster environmental culture: investigating urban residents’ utilization and contribution to parks in Vietnam. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuc, V.Q. Mindspongeconomics. SSRN 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.H. Mindsponge Theory; Sciendo, 2023.
- Vuong, Q.H.; Le, T.T.; La, V.P.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Ho, M.T.; Van Khuc, Q.; Nguyen, M.H. Covid-19 vaccines production and societal immunization under the serendipity-mindsponge-3D knowledge management theory and conceptual framework. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuc, Q.; Tran, M.; Nguyen, T.; Thinh, N.A.; Dang, T.; Tuyen, D.T.; Pham, P.; Dat, L.Q. Improving Energy Literacy to Facilitate Energy Transition and Nurture Environmental Culture in Vietnam. Urban Sci. 2023, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.; Nguyen, M. On Nature Quotient. Pacific Conserv. Biol. 2025, 31, PC2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).