Submitted:
28 October 2025
Posted:
30 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
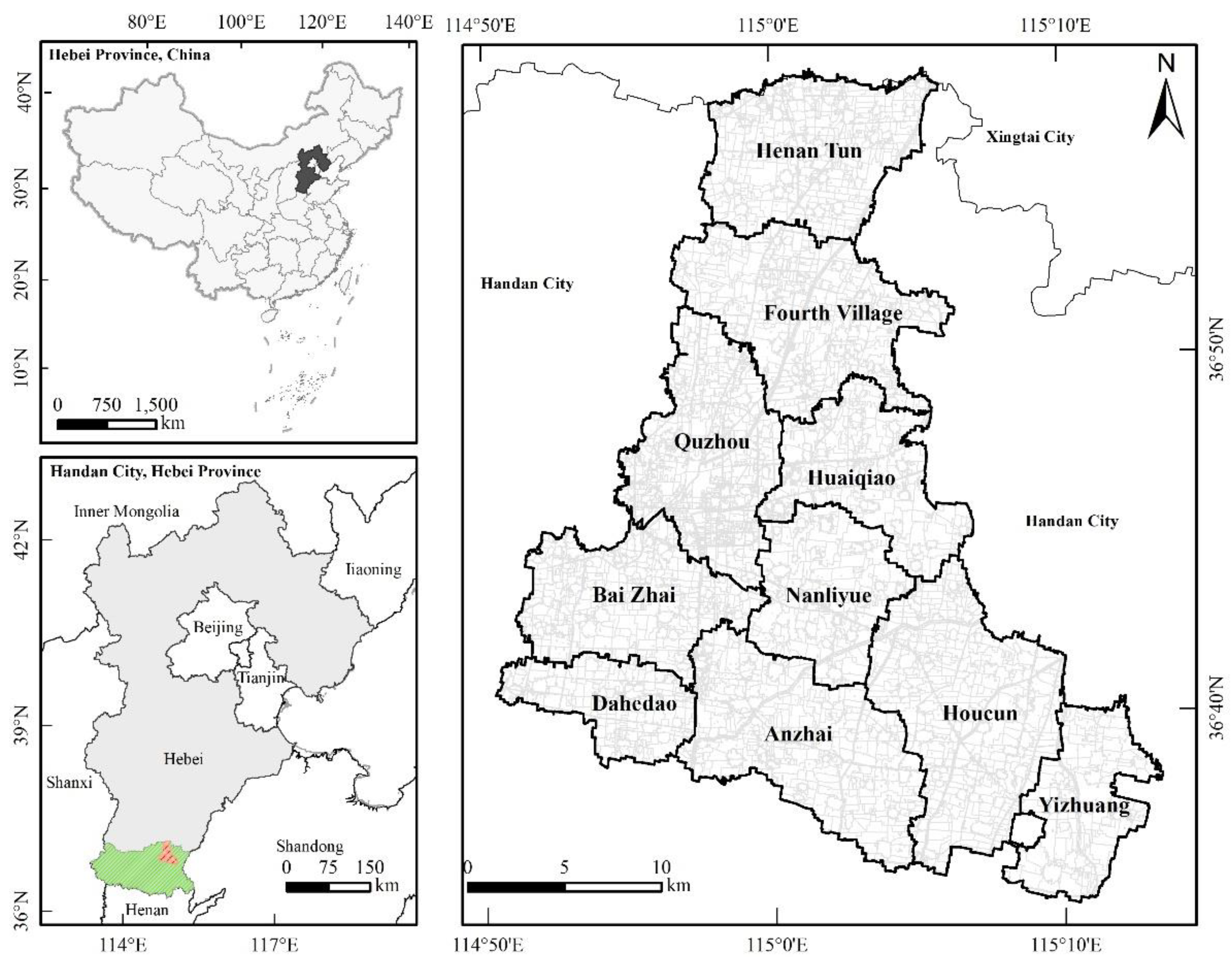
2.1. Study Area and Regional Context
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Data Preprocessing and Integration
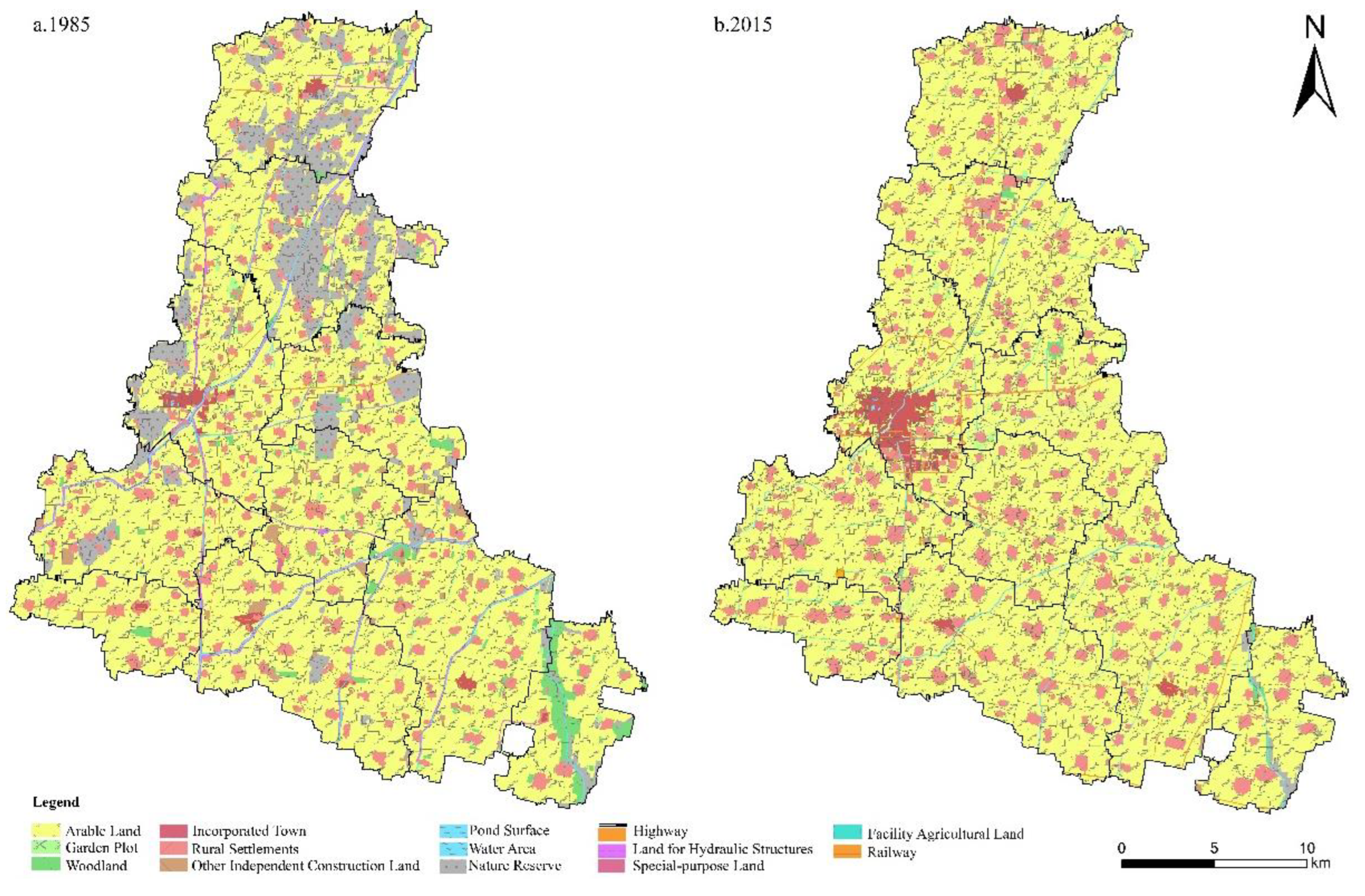
2.3.1. Remote Sensing Image Processing
2.3.2. Establishing a Rural Sexuality Assessment System
2.3.3. Data Quality and Uncertainty Control
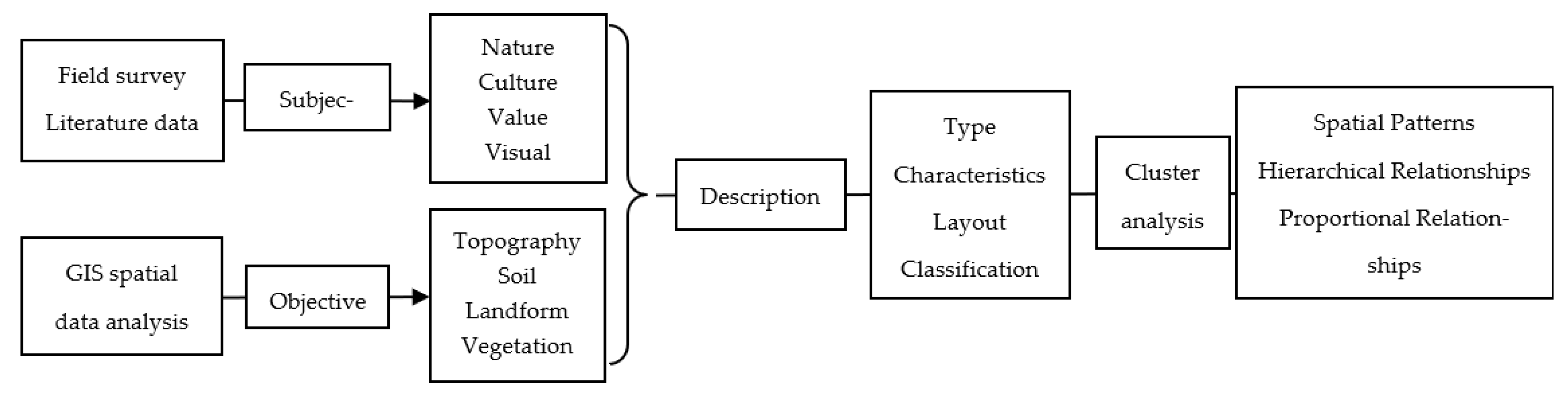
2.4. Research Framework and Methods
2.4.1. Overall Research Framework
2.4.2. Establishing a Rural Sexuality Evaluation System


2.4.3. Landscape Classification and Functional Evaluation
2.4.4. Analysis of Rural Spatial Form
3. Results
3.1. Rural Diagnosis and Analysis
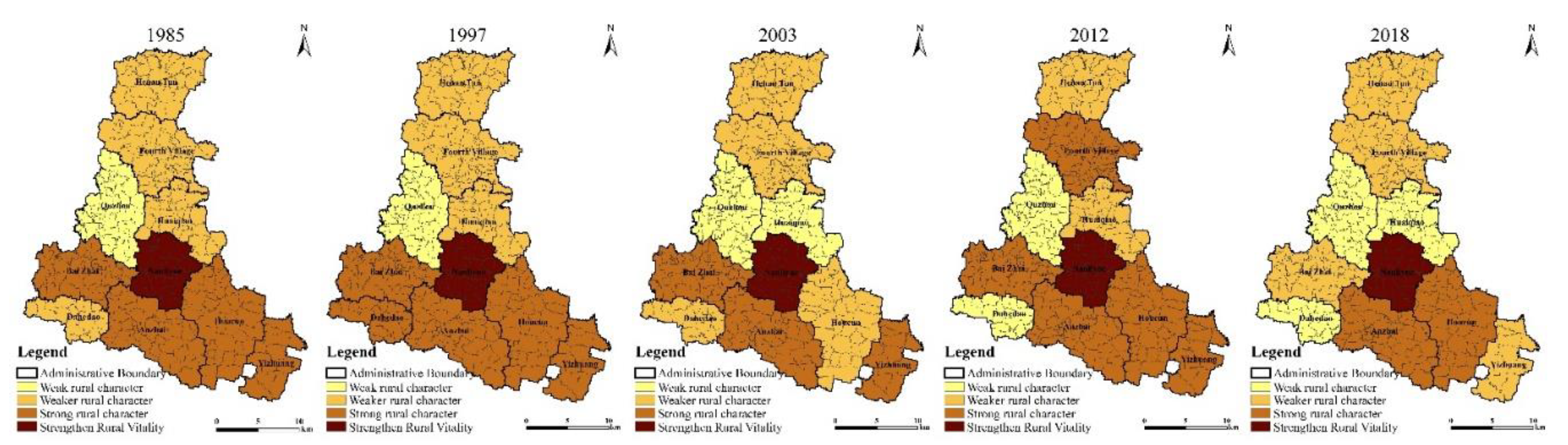
3.1.1. Time-Series Analysis of Rural Sexuality Index
| Region | 1985 | 1997 | 2003 | 2012 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.4832 | 0.4363 | 0.4106 | 0.3955 | 0.2897 |
| Minimum Value | 0.3082 | 0.2353 | 0.2818 | 0.2635 | 0.1248 |
| Maximum Value | 0.7370 | 0.7550 | 0.7170 | 0.7288 | 0.5149 |
| Range | 0.4288 | 0.5197 | 0.4352 | 0.4653 | 0.3901 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.1162 | 0.1445 | 0.1148 | 0.1259 | 0.1118 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.2405 | 0.3312 | 0.2796 | 0.3183 | 0.3859 |
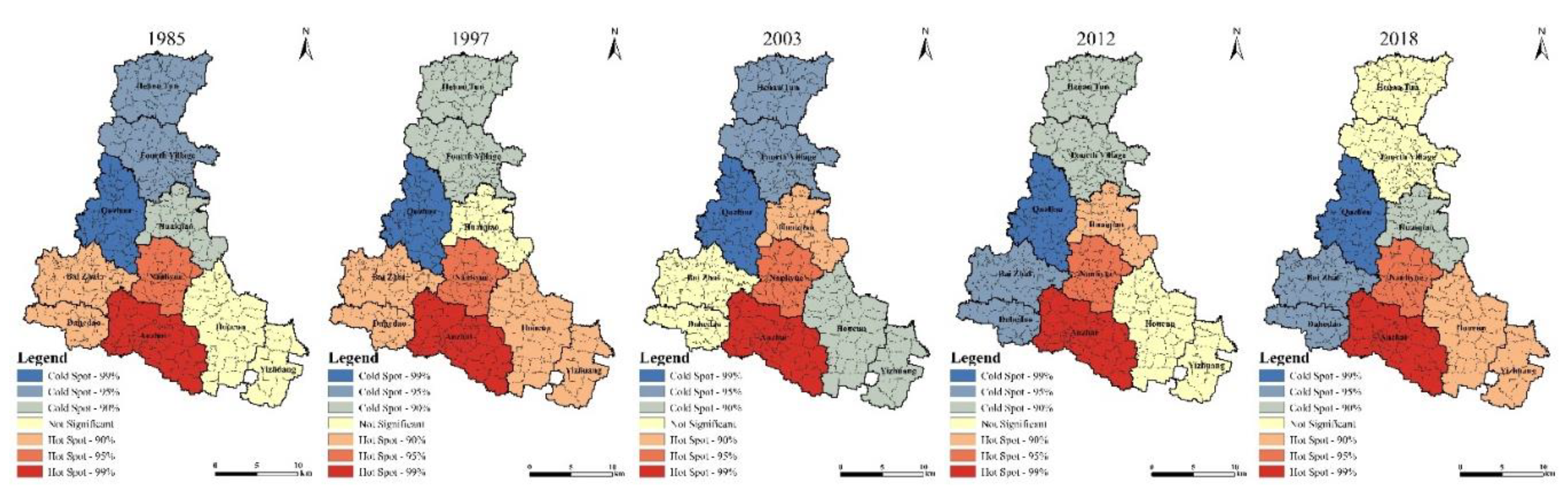
3.1.2. Spatial Differentiation Analysis of Rural Sexuality Index
3.2. Classification and Functional Evaluation of Rural Landscapes
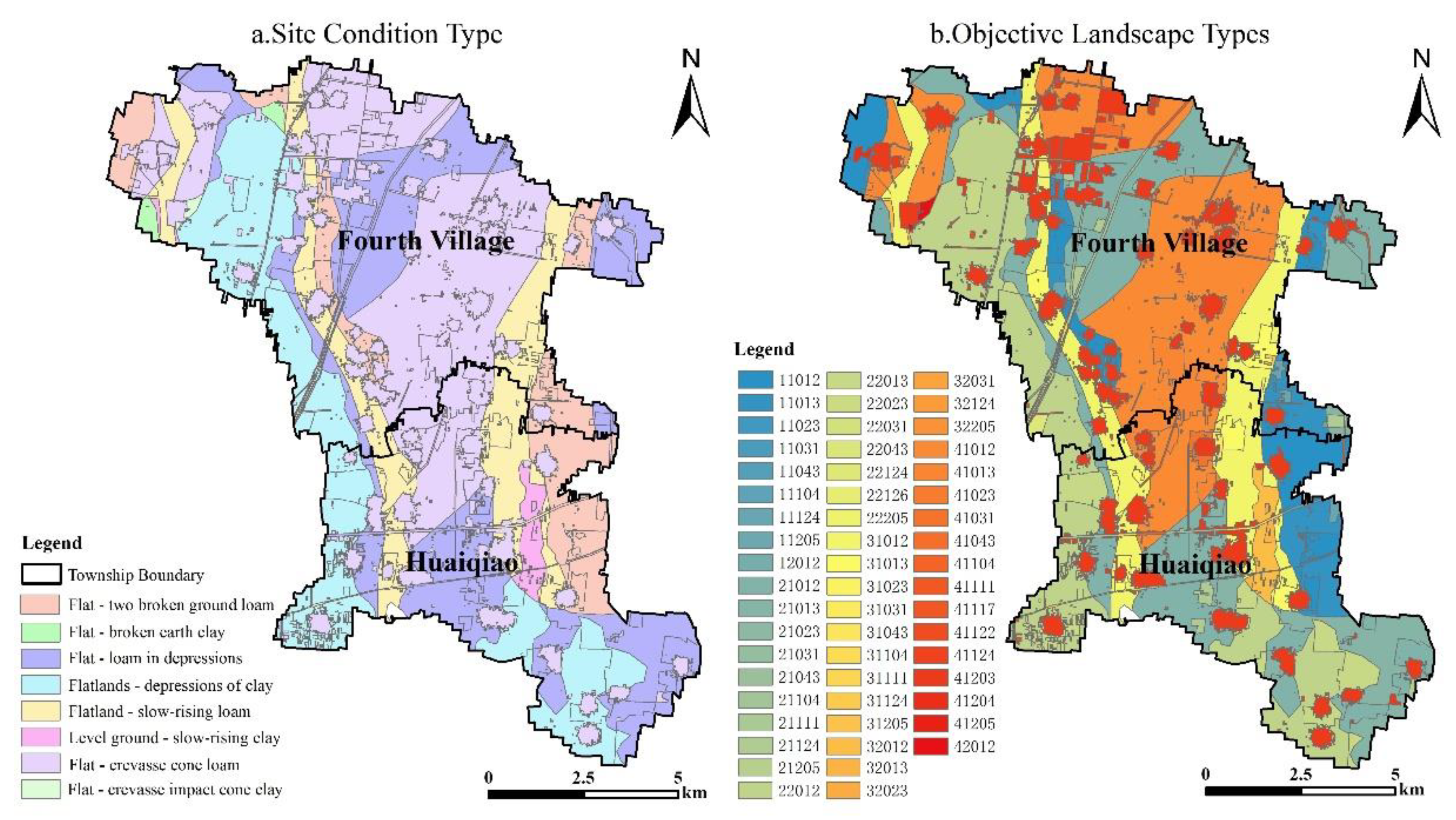
3.2.1. Results and Analysis of Subjective Landscape Classification
3.2.2. Objective Landscape Classification Results and Analysis
3.2.3. Integrative Analysis of Subjective and Objective Landscape Types
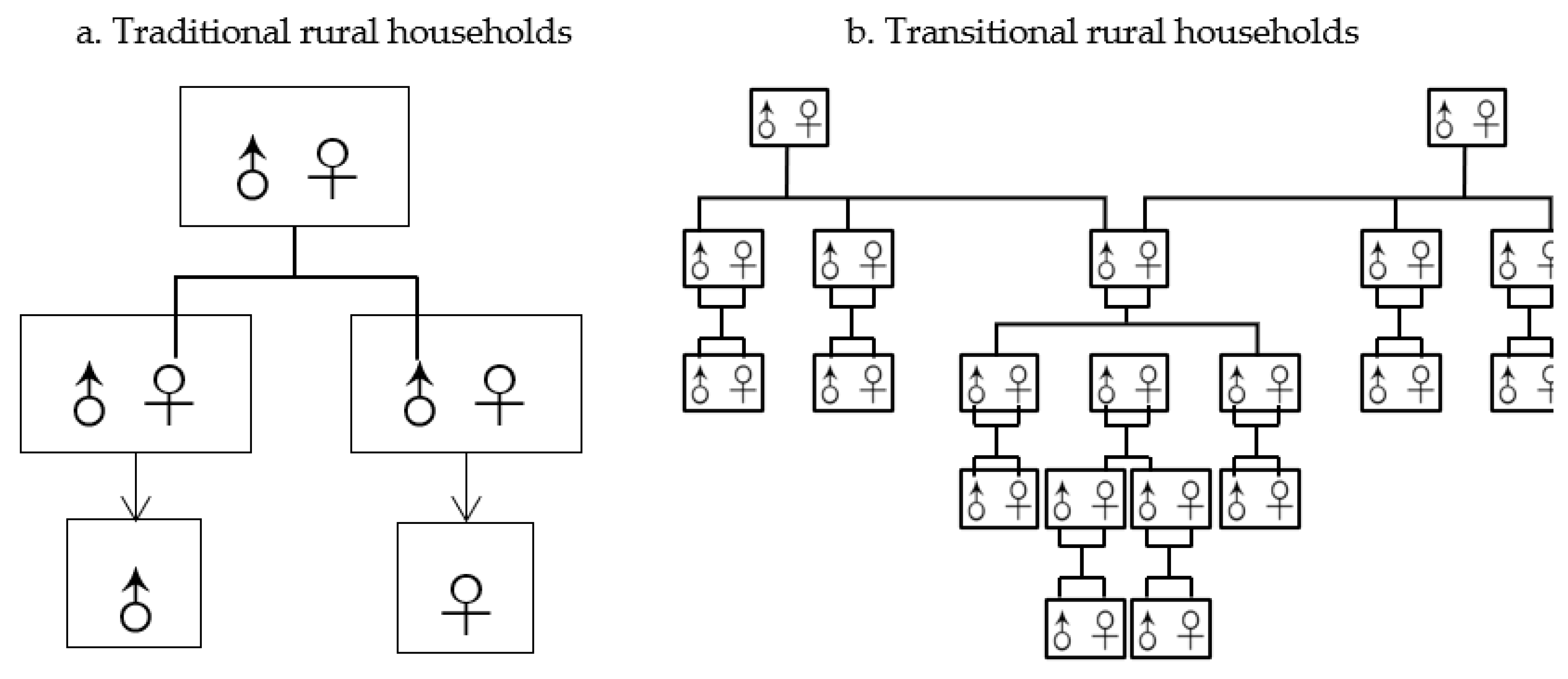
3.3. Analysis of the Spatial Structure and Functions of Rural Settlements
3.3.1. Time-Series Analysis of Rural Sexuality Index
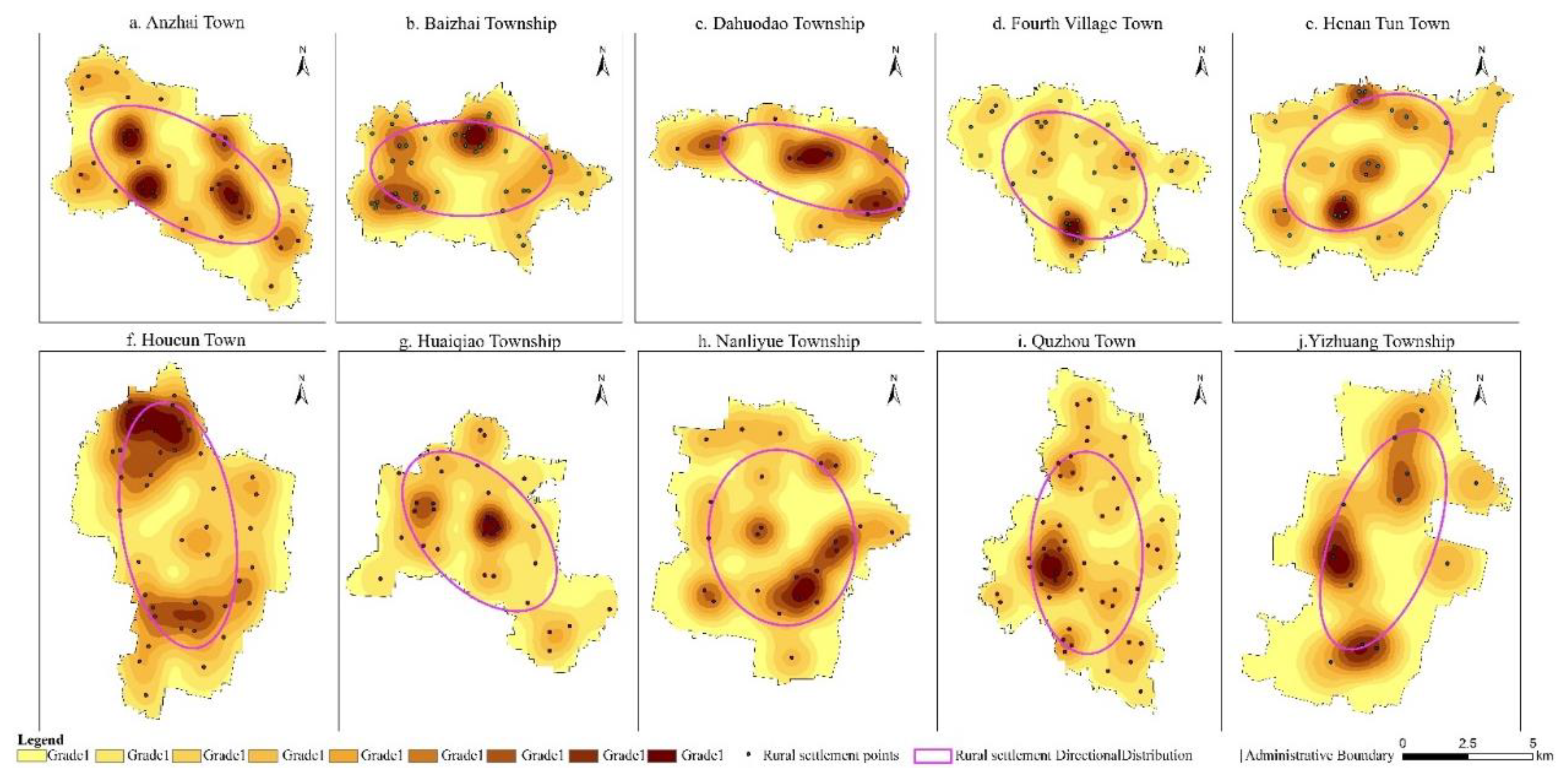
3.3.2. Time-Series Analysis of Rural Sexuality Index
3.3.3. External Drivers of the Evolution of Rural Spatial Structure and Function
3.4. Optimization Strategy for Rural Spatial and Landscape Based on “Diagnosis-Elements-Structure-Function”
3.4.1. Diagnosis: Existing Issues in Rural Spatial Planning
3.4.2. Core Elements: Identification of Key Components in Rural Spaces
3.4.3. Structure: Optimization of Rural Settlement Spatial Structure
3.4.4. Function: Strategies for Enhancing the Functional Role of Rural Spaces
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Relevance and Innovative Aspects of the Findings in Relation to Existing Research
4.2. Research Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
5.1. Key Research Findings
5.1.1. The Evolution Of Rurality Exhibits Pronounced Spatiotemporal Differentiation and Structured Characteristics
5.1.2. Developing an Integrated Objective–Subjective Framework for Rural Landscape Classification and Functional Assessment
5.1.3. Revealing Morphological Types and Evolutionary Drivers of Rural Settlement Spatial Structures
5.1.4. Proposing Rural Spatial Restructuring and Landscape Optimization Strategies Based on the DESF Model
5.2. Key Innovations and Contributions
5.2.1. Theoretical Contributions
5.2.2. Methodological Innovations
5.2.3. Practical Applications and Value
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long Hualou, Tu Shuangshuang. On Rural Reconstruction. Geographical Journal, 2017, 72(04): 563-576.
- Li Hongbo, Zhang Xiaolin. Progress and Recent Trends in Rural Settlement Geography Research Abroad. Human Geography, 2012, 27(04): 103-108.
- Ge Dazhuan, Long Hualou. On Rural Spatial Governance and the Integration of Urban-Rural Development. Geographical Journal, 2020, 75(06): 1272-1286.
- Guan Weihua, Wu Xiaoni, Li Huanlan, et al. Patterns and Evolution Mechanisms of Regional Urbanization in China Since the Reform and Opening-Up. Geographical Science, 2025, 45(02): 265-277.
- Zhang Yingnan, Long Hualou, Ma Li, et al. Research Progress on Urban-Rural Relations and Its Implications for Rural Revitalization. Geographical Research, 2019, 38(03): 578-594.
- Zheng Xiaoyu, Liu Yansui. The Scientific Connotation, Formation Mechanism, and Regulatory Strategies of “Rural Diseases” in China in the New Era. Human Geography, 2018, 33(02): 100-106.
- Woods, M. Rural. London and New York: Routledge, 2011.
- Ge Dazhuan, Lu Yuqi, Sun Pan. On Rural Spatial Governance and the Rural Revitalization Strategy. Geographical Journal, 2022, 77(04): 777-794.
- Li Feng, Zhang Yibin. Ecological Asset Management and Ecosystem Restoration: Supporting High-Quality Green Development. Yuejiang Journal, 2023, 15(05): 28-34+167-168.
- Bai Zhongke, Zhou Wei, Wang Jinman, et al. A Discussion on the Overall Protection, Systematic Restoration, and Comprehensive Management of Territorial Space. China Land Science, 2019, 33(02): 1-11.
- Fu Bojie. Key Points to Grasp in Ecological Restoration of Territorial Space. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 36(01): 64-69.
- Zhuang Shaoqin. Spatial Planning Logic in the New Era. China Land, 2019, (01): 4-8.
- Martin D, M. Ecological Restoration Should Be Redefined for the Twenty-First Century. Restoration Ecology, 2017, 25(5): 668-673. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y X, Fu B J, Zhao W W, et al. A Solution to the Conflicts of Multiple Planning Boundaries: Landscape Functional Zoning in a Resource-Based City in China. Habitat International, 2018, 77: 43-55.
- Wu B, Tian F, Zhang M, et al. Cloud Services with Big Data Provide a Solution for Monitoring and Tracking Sustainable Development Goals. Geography and Sustainability, 2020, 1: 25-32. [CrossRef]
- Wang Yong, Zhou Xue, Li Guangbin. Evaluation and Characteristics of Rurality in Different Types of Traditional Villages in Southern Jiangsu—Based on a Survey of 12 Traditional Villages in Suzhou. Geographical Research, 2019, 38(06): 1311-1321.
- Zhang Yibin, Feng Li. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Urban Ecological Asset Utilization Efficiency from a “Technology-Scale-Structure” Perspective. 2025, 14, 1837.
- Hong Buting, Ren Ping. Ecological Suitability Evaluation of Rural Settlement Land Based on the Minimum Cumulative Resistance Model: A Case Study of Dujiangyan City. Yangtze River Basin Resources and Environment, 2019, 28(06): 1386-1396.
- Wang Yuncai, Chen Zhaofang, Cheng Yuning. Construction of a Representation System for Rural Landscape Characteristics and Personality in the New Era. Landscape Architecture, 2021, 28(07): 107-113.
- Jiang Juanli, Yang Qingyuan, Zhang Zhongxun, et al. Research Progress and Prospects of Agricultural Landscape. Economic Geography, 2021, 41(06): 223-231.
- Zhang Yibin, Hao Jinmin, Huang An, et al. Research on Rural Landscape Classification Combining Perceptual Elements and Remote Sensing Data. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(16): 297-308.
- Lü Guiju, Liu Daliang. Evaluation of Rural Landscape Personality Traits in the Central Shandong Mountainous Area. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2020, 36(02): 85-90.
- Zhang Yibin, Li Feng, Shi Yuyang, et al. Progress in Ecological Asset Research Based on Scientometric Analysis. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2022, 27(12): 59-77.
- Jing Juan, Wang Yanglin, Peng Jian. Landscape Diversity and Rural Industrial Structure. Journal of Peking University (Natural Science Edition), 2003, (04): 556-564.
- Long Hualou, Liu Yansui, Zou Jian. Rural Development Types and Rurality Evaluation in the Eastern Coastal Region of China. Geographical Journal, 2009, 64(04): 426-434.
- Shi Yuyang, Zhang Yibin, Hao Jinmin. Research on Rural Development Types and Rurality Evaluation in County Areas of Hebei Province Under the Background of Rural Revitalization. China Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 2021, 42(04): 18-28.
- Zhang Rongtian, Zhang Xiaolin, Li Chuanwu. Research on the Evolution and Mechanism of Rural Spatial Patterns in Jiangsu Province Based on County Scale. Human Geography, 2013, 28(02): 91-97.
- Jiang Juanli, Yang Qingyuan, Zhang Zhongxun, et al. Research Progress and Prospects of Agricultural Landscape. Economic Geography, 2021, 41(06): 223-231.
- Li Zhenpeng, Liu Liming, Xie Hualin. A Study on Methods of Rural Landscape Classification—A Case Study of Baijiacun Village in Haidian District, Beijing. Resource Science, 2005, (02): 167-173.
- Zeng Li, Lü Guangyao, An Ning. Research on Rural Landscape Reproduction Under the Context of Art Intervention. Human Geography, 2022, 37(04): 53-64.
- Zhang Yibin, Huang An, Zu Jian, et al. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Built-up Land Utilization Intensity in China and Its Driving Mechanisms. Journal of Peking University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 56(05): 893-906.
- Jin Xiaobin, Ye Chao, Yue Wenze, et al. Urban-Rural Integration Development in New Era China: Challenges and Pathways. Journal of Natural Resources, 2024, 39(01): 1-28.
- Ji Zhengxin, Xu Yueqing, Lu Longhui, et al. Research Progress and Prospects on Rural Settlement Spatial Optimization. China Land Science, 2021, 35(06): 95-104.
- Feng Yingbin, Long Hualou. Research Progress and Prospects of Rural Settlement Spatial Reconstruction in Mountainous Areas of China. Progress in Geographical Sciences, 2020, 39(05): 866-879.
- Yu Zhaowu, Xiao Lishan, Chen Xiji, et al. Spatial Restructuring and Land Consolidation of Urban-Rural Settlements in Mountainous Areas Based on Ecological Niche Perspective. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2018, 28(2): 131-151.
| Sensor | Spatial Resolution (metres) | Time Coverage | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat TM/ETM+/OLI | 30 | 2000, 2010, 2015 | Long-term Land Use/Land Cover Change Detection |
| Sentinel-2 | 10–20 | 2017–2020 | Fine-scale landscape classification and vegetation index analysis |
| GF-1 PMS | 2(Full colour)、8(Multispectral) | 2015 | Interpretation of Village-Level Spatial Patterns |
| DEM | 30 | 2000, 2010, 2015 | Terrain and Gradient Analysis |
| Evaluation Dimension | Core Indicators | Data Sources | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Population density, agricultural population proportion | Statistical yearbooks, field surveys, etc. | Quantify rural population structure characteristics |
| Economic | Primary industry share of GDP, per capita agricultural income | Statistical yearbooks, agricultural statistical ledgers, etc. | Analyze the impact of economic structure on rurality |
| Spatial | Per capita arable land area, settlement density | Land use maps, statistical yearbooks, etc. | Examine settlement spatial structure characteristics |
| Functional | Productive, living, ecological, and cultural functions | Remote sensing images, questionnaires, etc. | Support multidimensional interactions of rural multifunctionality |
| Year | Moran's I | P-value | Z-score | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | 0.0092 | 0.7414 | 0.3301 | 0.1330 |
| 1997 | 0.0738 | 0.6124 | 0.5067 | 0.1332 |
| 2003 | -0.2605 | 0.5859 | -0.5449 | 0.0752 |
| 2012 | -0.0792 | 0.5096 | 0.1135 | 0.0792 |
| 2015 | 0.1948 | 0.4212 | 0.8043 | 0.1446 |
| Category | Imagery Landscape Elements |
|---|---|
| Living
Landscape Elements |
Dew, morning mist, cooking smoke, fishing, rice jar, cock crow, bird song, tomb, fallen leaves, woodcutter, rural elders, elderly man, farmer, mountain visitor, fisherman, old fisherman, old man, village child, agricultural laborer, shepherd boy, carrying hoe, weeding, farming, reclaiming wasteland, grazing, joint plowing, butterfly, dragonfly, dog, cow, sheep, wasp, swallow, calf, firefly, ox, crow |
| Production
Landscape Elements |
Vegetable garden,rural field, farmland, wheat field, field ridge, open field, hemp, crops, bean seedlings, buckwheat flower, rapeseed flower, rice seedling, wheat, vegetable bed, Malabar spinach, rice, Chinese cabbage |
| Ecological
Landscape Elements |
Woodland, chrysanthemum, weeds, courtyard tree, solitary pine, mulberry tree, poplar, elm, willow, peach tree, plum tree, apricot flower, green grass, mugwort, orchid, tender grass shoots, old tree, apricot tree, pond, pond, slope |
| Infrastructure Landscape Elements | Village outer wall, threshing ground, house, narrow road, courtyard, small garden, simple house, fence, thatched cottage, yard, well, stove, firewood door, ancient temple, bird's nest, stone bridge, thatched house, slope road, gate tower, farmyard, granary, water pavilion, cowshed, chicken coop, thatched hall, thatched pavilion, small earthen fort,door, fence, roller,well sweep,plow tool |
| Landscape Zone | Key Components | Definition and Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Rural Settlement Landscape Zone | Villages, designated towns, special-purpose land, and mining land | Predominantly consisting of rural settlements, primarily providing residential spaces for village populations and ancillary facilities under specific environmental and specialized production conditions |
| Rural Facility Landscape Zone | Rural roads, urban-rural highways, and agricultural facility land | Provides service-oriented facilities for rural agricultural production and landscape amenities with recreational and tourism functions for urban populations |
| Rural Ecological Landscape Zone | Ecological woodlands, grasslands, river surfaces, pond surfaces, ditches, hydraulic structures, saline-alkaline lands, and sandy lands | Plays a significant role in ecological environment protection, with crucial ecological regulatory functions including regional water conservation, humidity regulation, air purification, and biodiversity conservation |
| Rural Production Landscape Zone | Dry farmland, irrigated farmland, orchards, and economic forests | Subject to primary artificial inputs by local residents to obtain direct economic output value, while providing agricultural products, industrial raw materials, and other agricultural commodities |
| Landscape Group | Landscape Zone | Code | Landscape Type | Perceptual Landscape Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural
Ecological Landscape Group |
Ecological Landscape Zone | 22031 | Depression Clay Ecological Forest Landscape | Woodland, chrysanthemum, weeds, courtyard trees, solitary pine, mulberry tree, poplar, elm, willow, peach tree, plum tree, apricot blossom, green grass, mugwort, orchid,, old tree, apricot tree, pond, pond, spring, river, pond... |
| 22043 | Depression Clay Wasteland Landscape | |||
| 22124 | Depression Clay Saline-Alkali Landscape | |||
| 22126 | Depression Clay Sandy Landscape | |||
| 21111 | River Water Surface Landscape | |||
| 31111 | Lake Water Surface Landscape | |||
| 22205 | Depression Clay Rural Ecotourism Landscape | |||
| Production Landscape Zone | 41111 | Aquaculture Water Surface Landscape | ||
| 41117 | Ditch Landscape | |||
| 11012 | Slope Loam Irrigated Farmland Landscape | |||
| 11013 | Slope Loam Dry Farmland Landscape | |||
| Rural
Production Landscape Group |
Production Landscape Zone | 41111 | Aquaculture Water Surface Landscape | Vegetable garden, wheat field, field ridge, crops, rice seedling, vegetable bed, threshing ground, well, stove, firewood door, stone bridge, gate tower, farmyard, cowshed, chicken coop, roller,ancient temple, bird's nest, shepherd boy, carrying hoe, weeding, farming, reclaiming wasteland, grazing, joint plowing... |
| 41117 | Ditch Landscape | |||
| 11012 | Slope Loam Irrigated Farmland Landscape | |||
| 11013 | Slope Loam Dry Farmland Landscape | |||
| 11023 | Slope Loam Orchard Landscape | |||
| 41122 | Agricultural Facility Landscape | |||
| Facility Landscape Zone | 41122 | Agricultural Facility Landscape | ||
| 41204 | Rural Industrial Landscape | |||
| Rural
Living Landscape Group |
Settlement Landscape Zone | 41104 | Breach Alluvial Cone Rural Road Landscape | Courtyard, fence, thatched cottage, dew, morning mist, cooking smoke, fishing, rice jar, cock crow, bird song, tomb, rural elders, farmer, village child, agricultural laborer, shepherd boy, carrying hoe, weeding, farming, reclaiming wasteland, grazing, joint plowing... |
| 41203 | Rural Settlement Landscape |
| Xiangongzhuang Village | Xiaodiba Village | Disituan Village | Gong Village | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population (persons) | 636 | 820 | 697 | 740 |
| Land Use (ha) | 6.56 | 8.12 | 8.07 | 8.37 |
| Conservation Rationale | The original village morphological structure remains intact with a sound economic foundation, positioning it as a critical tourism resource through systematic planning and design. | Characterized by large population agglomeration, intensive land use, robust economic base under collective management, and pristine environment, qualifying it as a representative model village. | Clear industrial development orientation with extensive agricultural cultivation areas under county-university collaborative production model, exhibiting distinct industrial and landscape characteristics. | Possesses adequate population scale, intensive land utilization, diverse industrial development, and high richness of surrounding agricultural landscapes. |
| Renovation Measures | Renovation and upgrading as a spatially significant tourism resource cluster in the region | Renovation and development as a tourism-oriented village to establish a regional model | Implement ecological agriculture-focused development strategy to deepen county-university win-win collaboration | Ecological environment remediation combined with agritourism and tertiary industry development for rural economic advancement |
| Township | Village | Population (persons) |
Land Use (ha) | Per Capita (㎡/person) |
Intervention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disituan Town | Bujie Village | 3130 | 16.09 | 51.42 | Develop as Central Village |
| Chengzhai Village | 2555 | 9.19 | 35.99 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Dabadi Village | 1786 | 19.35 | 108.37 | Relocate to Surrounding Villages | |
| Dazhongzhai Village | 2365 | 14.84 | 62.73 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Deng Village | 1097 | 6.93 | 63.21 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Wudituan Village | 2324 | 18.87 | 81.19 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Dongliushangzhai Village | 1720 | 16.74 | 97.29 | Develop as Central Village | |
| Dongwei Village | 1185 | 13.62 | 114.91 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Guolizhuang Village | 1786 | 14.62 | 81.85 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Longwangmiao Village | 990 | 11.14 | 112.54 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Shen Village | 976 | 8.65 | 88.65 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Sun Village | 430 | 4.49 | 104.4 | Relocate to Surrounding Villages | |
| Zheng Village | 1113 | 8.80 | 79.04 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Huaiqiao Township | Guozhuang Village | 1940 | 22.45 | 115.70 | Integrate to Form Central Village |
| Houguanzhai Village | 1373 | 14.38 | 104.68 | Develop as Central Village | |
| Jinzhuang Village | 1070 | 9.34 | 87.18 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Liuguotun Village | 1822 | 18.20 | 98.97 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Liuwangzhuang Village | 1994 | 22.18 | 111.22 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Qianguanzhai Village | 1237 | 12.25 | 98.97 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Yanglizhuang Village | 1834 | 12.13 | 66.13 | Preserve and Renovate |
| Township | Village | Population (persons) |
Land Use (ha) | Per Capita (㎡/person) |
Intervention Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disituan Town | Beilongtang Village | 749 | 37.86 | 505.83 | Develop as Central Village |
| Liutuan Village | 512 | 46.34 | 904.74 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Disituan Village | 154 | 75.66 | 4927.57 | Relocate to Surrounding Villages | |
| Jiaozhuang Village | 103 | 96.49 | 9364.75 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Matuan Village | 898 | 51.67 | 575.37 | Relocate to Central Village | |
| Quzhou County Farm | 556 | 153.91 | 2770.19 | Preserve and Renovate | |
| Huaiqiao Township | Qiaobao Village | 567 | 31.46 | Integrate and Upgrade | Integrate and Upgrade |
| Xizhangtou Village | 508 | 32.06 | 630.93 | Integrate and Upgrade |
| Electric Bicycles | Electric Tricycles | Motorcycles | Agricultural Tricycles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| 10 min | 1.6 | 1.6 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
| Target Layer | Criterion Layer | Weight | Indicator | Weight | Composite Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Village
Suitability A |
Production
Conditions B1 |
0.48 | C11 Farmland Fragmentation Degree (patches/km²) | 0.53 | 0.25 |
| C12 Trunk and Township Road Density (m/km²) | 0.05 | 0.02 | |||
| C13 Field Road Density (m/km²) | 0.04 | 0.02 | |||
| C14 Grain Yield per Hectare (kg/hm²) | 0.08 | 0.04 | |||
| C15 Settlement Density (units/km²) | 0.16 | 0.08 | |||
| C16 Cultivated Land Proportion (%) | 0.13 | 0.06 | |||
| C17 Motor-Pumped Well Density (units/km²) | 0.02 | 0.01 | |||
| Ecological
Conditions B2 |
0.11 | C21 River and Ditch Density (m/km²) | 0.75 | 0.08 | |
| C22 Forest Network Density (m/km²) | 0.25 | 0.03 | |||
| Living
Conditions B3 |
0.41 | C31 Settlement Population Size (persons) | 0.50 | 0.21 | |
| C32 Per Capita Net Income (CNY) | 0.05 | 0.02 | |||
| C33 Distance to Nearest Township (km) | 0.07 | 0.03 | |||
| C34 Transport Accessibility (km) | 0.22 | 0.09 | |||
| C35 Construction Land Area (hm²) | 0.16 | 0.06 |
| Zoning Category | Villages |
|---|---|
| Priority Development Zone | Huaiqiao Village, Disituan Village |
| Key Development Zone | Wangzhuang Village, Xingyuan Village, Xiaodiba Village, Xianggongzhuang Village, Shizhai Village |
| Guided Development Zone | Deng Village, Fuzhuang Village, Guolizhuang Village, Lizhuang Village, Xinanzhai Village, Kushuibao Village |
| Restricted Development Zone | Yanglizhuang Village, Jinzhuang Village, Wudituan Village, Chengzhai Village |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





