Submitted:
25 October 2025
Posted:
27 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Nrf2 Signaling Pathways and Regulation: Key Players and Mechanisms of Nrf2 Activation and Suppression
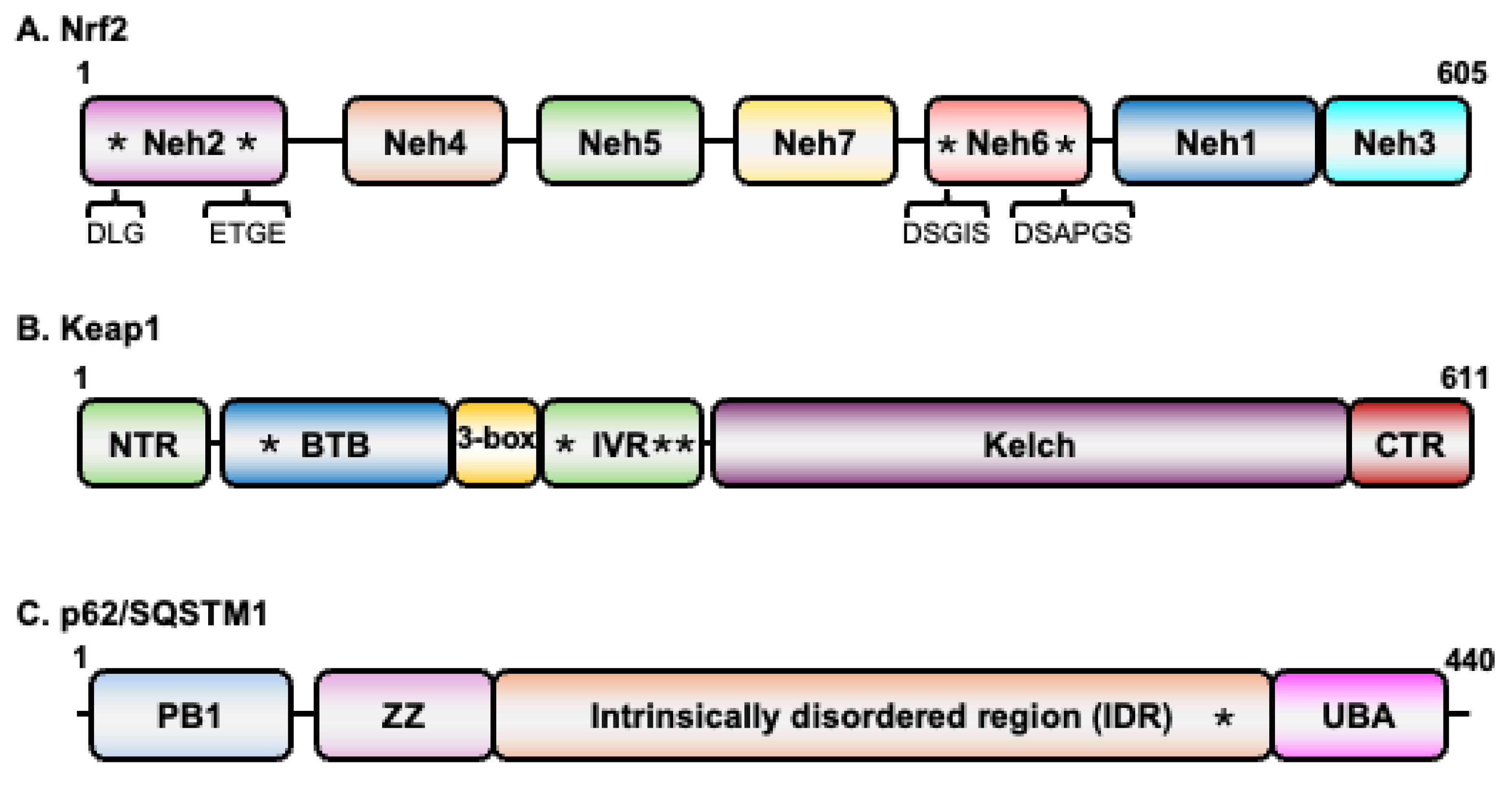
2.1. Nrf2
2.2. Keap1
2.3. p62/SQSTM1
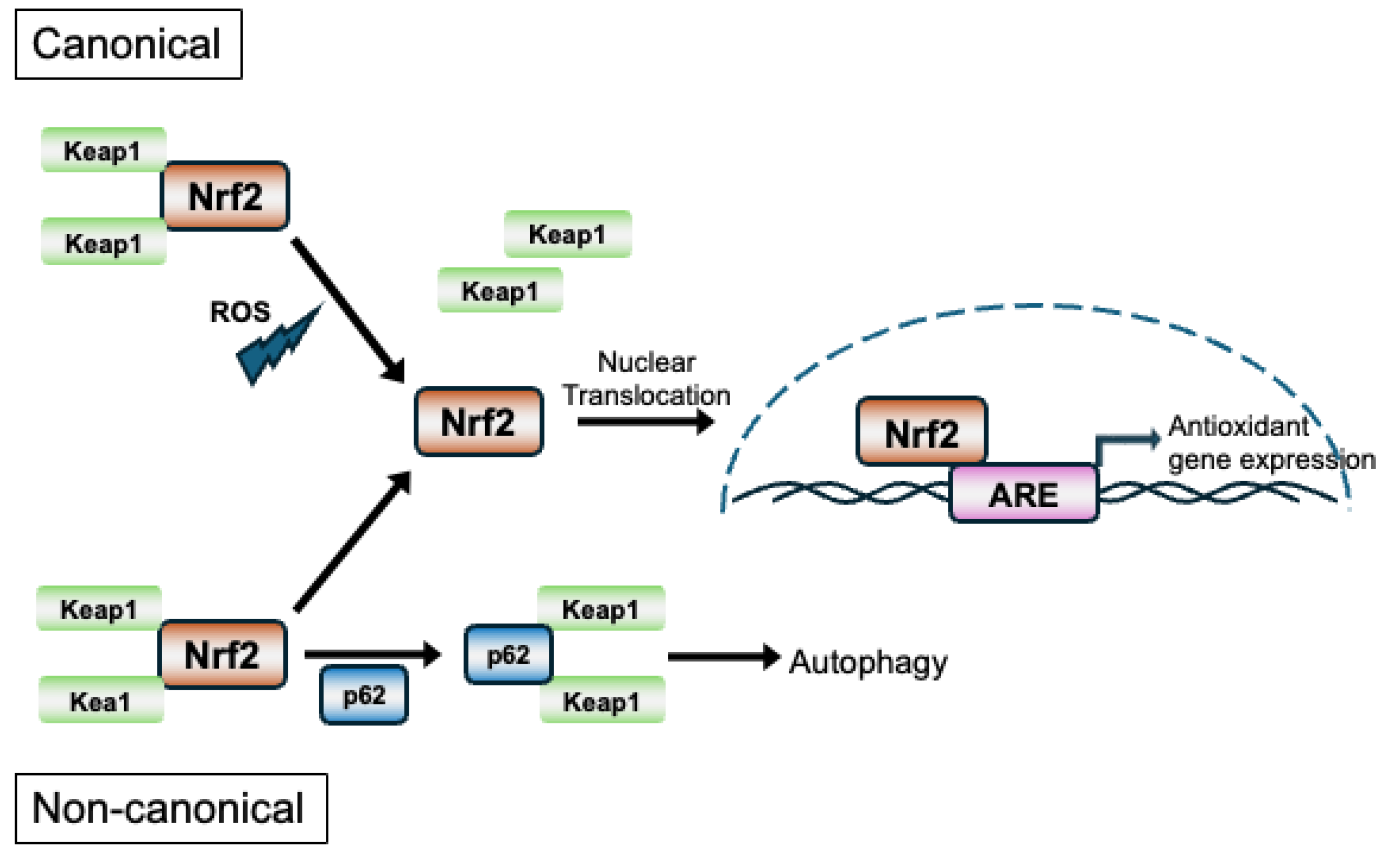
2.4. Mechanisms of Nrf2 Activation and Its Regulation
3. Nrf2 in Antiviral Immunity
4. Nrf2 in Proviral Roles
5. Therapeutic Targeting of Nrf2 in Viral Infections
6. Outstanding Questions and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kayesh, M.E.H.; Kohara, M.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K. Effects of oxidative stress on viral infections: an overview. Npj Viruses 2025, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, H.K.; Pereira, M.; Rajavelu, I.; Jayaraman, V.; Krishna, K.; Wang, T.; Bei, K.; Rajasekaran, J.J. Oxidative stress: fundamentals and advances in quantification techniques. Front Chem 2024, 12, 1470458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, J.M.; Gao, B.; Hybertson, B.M. The Complex Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Nrf2 Pathways: A Review. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Kurokawa, H.; Waguri, S.; Taguchi, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Ichimura, Y.; Sou, Y.-S.; Ueno, I.; Sakamoto, A.; Tong, K.I.; et al. The selective autophagy substrate p62 activates the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 through inactivation of Keap1. Nature Cell Biology 2010, 12, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Ohzeki, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Naito, S.; Ohtsuru, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Kuroiwa, Y. Stimulation of in vitro angiogenesis by hydrogen peroxide and the relation with ETS-1 in endothelial cells. Life Sci 1999, 64, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D. Thirty years of NRF2: advances and therapeutic challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2025, 24, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 2014, 39, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Xie, L.; Portbury, A.L.; Kumar, S.; Lockyer, P.; Li, X.; Patterson, C. NADPH oxidase-generated reactive oxygen species are required for stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha-stimulated angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2014, 34, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herengt, A.; Thyrsted, J.; Holm, C.K. NRF2 in Viral Infection. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.R.; Crook, A.A.; Pattnaik, A.; Torres-Gerena, A.D.; Khalimonchuk, O.; Powers, R.; Franco, R.; Pattnaik, A.K. Redox Regulation and Metabolic Dependency of Zika Virus Replication: Inhibition by Nrf2-Antioxidant Response and NAD(H) Antimetabolites. J Virol 2023, 97, e0136322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Gomez, M.; Kwak, M.K.; Dolan, P.M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Talalay, P.; Kensler, T.W. Sensitivity to carcinogenesis is increased and chemoprotective efficacy of enzyme inducers is lost in nrf2 transcription factor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 3410–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.K.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Sutter, T.R.; Kensler, T.W. Role of transcription factor Nrf2 in the induction of hepatic phase 2 and antioxidative enzymes in vivo by the cancer chemoprotective agent, 3H-1, 2-dimethiole-3-thione. Mol Med 2001, 7, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuishi, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Kawatani, Y.; Shibata, T.; Nukiwa, T.; Aburatani, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Motohashi, H. Nrf2 redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways in metabolic reprogramming. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vomund, S.; Schafer, A.; Parnham, M.J.; Brune, B.; von Knethen, A. Nrf2, the Master Regulator of Anti-Oxidative Responses. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhan, A.; Dodson, M.; Shakya, A.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, K.; et al. NRF2 controls iron homeostasis and ferroptosis through HERC2 and VAMP8. Sci Adv 2023, 9, eade9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, P.; Chan, K.; Asunis, I.; Cao, A.; Kan, Y.W. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91, 9926–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Igarashi, K.; Hayashi, N.; Nishizawa, M.; Yamamoto, M. Cloning and characterization of a novel erythroid cell-derived CNC family transcription factor heterodimerizing with the small Maf family proteins. Mol Cell Biol 1995, 15, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Keap1-dependent proteasomal degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 contributes to the negative regulation of antioxidant response element-driven gene expression. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 21592–21600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinan, S.B.; Gordan, J.D.; Jin, J.; Harper, J.W.; Diehl, J.A. The Keap1-BTB protein is an adaptor that bridges Nrf2 to a Cul3-based E3 ligase: oxidative stress sensing by a Cul3-Keap1 ligase. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 8477–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Ishii, T.; O’Connor, T.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 regulates both cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling and degradation of Nrf2 in response to electrophiles. Genes Cells 2003, 8, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, M.; Xiong, Y. BTB protein Keap1 targets antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 for ubiquitination by the Cullin 3-Roc1 ligase. Mol Cell Biol 2005, 25, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Gu, T.; Gao, X.; Song, Z.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y. African swine fever virus enhances viral replication by increasing intracellular reduced glutathione levels, which suppresses stress granule formation. Vet Res 2024, 55, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Menegatto, M.B.; Ferraz, A.C.; Lima, R.L.S.; Guimaraes, P.H.; Ola-Olu, O.S.; Machado-Junior, P.A.; Carvalho Malta, W.; de Fatima Silva Moraes, T.; Silva Bezerra, F.; de Mello Silva, B.; et al. Vaccinia virus modulates the redox environment by inhibiting reactive oxygen and nitrogen species with increased activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 29771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjyshi, O.; Flaherty, S.; Veettil, M.V.; Johnson, K.E.; Chandran, B.; Bottero, V. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces Nrf2 activation in latently infected endothelial cells through SQSTM1 phosphorylation and interaction with polyubiquitinated Keap1. J Virol 2015, 89, 2268–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjyshi, O.; Bottero, V.; Veettil, M.V.; Dutta, S.; Singh, V.V.; Chikoti, L.; Chandran, B. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces Nrf2 during de novo infection of endothelial cells to create a microenvironment conducive to infection. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, P.; Sorrell, F.J.; Bullock, A.N. Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med 2015, 88, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, K.I.; Katoh, Y.; Kusunoki, H.; Itoh, K.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, M. Keap1 recruits Neh2 through binding to ETGE and DLG motifs: characterization of the two-site molecular recognition model. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 2887–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, H.; Katsuoka, F.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Small Maf proteins serve as transcriptional cofactors for keratinocyte differentiation in the Keap1-Nrf2 regulatory pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 6379–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, Y.; Itoh, K.; Yoshida, E.; Miyagishi, M.; Fukamizu, A.; Yamamoto, M. Two domains of Nrf2 cooperatively bind CBP, a CREB binding protein, and synergistically activate transcription. Genes Cells 2001, 6, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nioi, P.; Nguyen, T.; Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B. The carboxy-terminal Neh3 domain of Nrf2 is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 2005, 25, 10895–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Thomas, N.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Redox-regulated turnover of Nrf2 is determined by at least two separate protein domains, the redox-sensitive Neh2 degron and the redox-insensitive Neh6 degron. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 31556–31567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Geng, M.; Gao, P.; Wu, X.; Hai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Hayes, J.D.; et al. RXRalpha inhibits the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the Neh7 domain of NRF2. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleasby, A.; Yon, J.; Day, P.J.; Richardson, C.; Tickle, I.J.; Williams, P.A.; Callahan, J.F.; Carr, R.; Concha, N.; Kerns, J.K.; et al. Structure of the BTB domain of Keap1 and its interaction with the triterpenoid antagonist CDDO. PLoS One 2014, 9, e98896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, P.; Cooper, C.D.O.; Krojer, T.; Murray, J.W.; Pike, A.C.W.; Chaikuad, A.; Keates, T.; Thangaratnarajah, C.; Hojzan, V.; Marsden, B.D.; et al. Structural basis for Cul3 protein assembly with the BTB-Kelch family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 7803–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.C.; Li, X.; Henzl, M.T.; Beamer, L.J.; Hannink, M. Structure of the Keap1:Nrf2 interface provides mechanistic insight into Nrf2 signaling. EMBO J 2006, 25, 3605–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, B.; Tong, K.I.; Ohta, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Scharlock, M.; Ohtsuji, M.; Kang, M.I.; Kobayashi, A.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamamoto, M. Structural basis for defects of Keap1 activity provoked by its point mutations in lung cancer. Mol Cell 2006, 21, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.I.; Padmanabhan, B.; Kobayashi, A.; Shang, C.; Hirotsu, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamamoto, M. Different electrostatic potentials define ETGE and DLG motifs as hinge and latch in oxidative stress response. Mol Cell Biol 2007, 27, 7511–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukutomi, T.; Takagi, K.; Mizushima, T.; Ohuchi, N.; Yamamoto, M. Kinetic, thermodynamic, and structural characterizations of the association between Nrf2-DLGex degron and Keap1. Mol Cell Biol 2014, 34, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; Wang, X.J.; Zhao, F.; Villeneuve, N.F.; Wu, T.; Jiang, T.; Sun, Z.; White, E.; Zhang, D.D. A noncanonical mechanism of Nrf2 activation by autophagy deficiency: direct interaction between Keap1 and p62. Mol Cell Biol 2010, 30, 3275–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuragi, Y.; Ichimura, Y.; Komatsu, M. Regulation of the Keap1–Nrf2 pathway by p62/SQSTM1. Current Opinion in Toxicology 2016, 1, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, L.; Yamamoto, M. The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Hannink, M. Distinct cysteine residues in Keap1 are required for Keap1-dependent ubiquitination of Nrf2 and for stabilization of Nrf2 by chemopreventive agents and oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23, 8137–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatbonton-Schwager, T.; Yagishita, Y.; Joshi, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Srinivasan, H.; Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. A Point Mutation at C151 of Keap1 of Mice Abrogates NRF2 Signaling, Cytoprotection in Vitro, and Hepatoprotection in Vivo by Bardoxolone Methyl (CDDO-Me). Mol Pharmacol 2023, 104, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: a Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol Rev 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, C.; Lastres-Becker, I.; Demirdogen, B.C.; Costa, V.M.; Daiber, A.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R.; Kalyoncu, S.; Arioz, B.I.; Genc, S.; et al. Biomarkers of NRF2 signalling: Current status and future challenges. Redox Biol 2024, 72, 103134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushmore, T.H.; Morton, M.R.; Pickett, C.B. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem 1991, 266, 11632–11639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo de la Vega, M.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzammil, K.; Sabah Ghnim, Z.; Saeed Gataa, I.; Fawzi Al-Hussainy, A.; Ali Soud, N.; Adil, M.; Ali Shallan, M.; Yasamineh, S. NRF2-mediated regulation of lipid pathways in viral infection. Mol Aspects Med 2024, 97, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Chowdhry, S.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Sutherland, C. Dual regulation of transcription factor Nrf2 by Keap1 and by the combined actions of beta-TrCP and GSK-3. Biochem Soc Trans 2015, 43, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Yan, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Barati, M.T.; Wintergerst, K.A.; Pan, K.; et al. Elevating CXCR7 Improves Angiogenic Function of EPCs via Akt/GSK-3beta/Fyn-Mediated Nrf2 Activation in Diabetic Limb Ischemia. Circ Res 2017, 120, e7–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, J.W.; Jaiswal, A.K. Antioxidant-induced phosphorylation of tyrosine 486 leads to rapid nuclear export of Bach1 that allows Nrf2 to bind to the antioxidant response element and activate defensive gene expression. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaravelli, N.; Tian, B.; Ivanciuc, T.; Mautemps, N.; Brasier, A.R.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. Respiratory syncytial virus infection down-regulates antioxidant enzyme expression by triggering deacetylation-proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med 2015, 88, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaravelli, N.; Ansar, M.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. Respiratory syncytial virus induces NRF2 degradation through a promyelocytic leukemia protein - ring finger protein 4 dependent pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 113, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, R.; Zou, W.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Jin, M. The Influenza Virus H5N1 Infection Can Induce ROS Production for Viral Replication and Host Cell Death in A549 Cells Modulated by Human Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase (SOD1) Overexpression. Viruses 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmider, B.; Messier, E.M.; Janssen, W.J.; Nahreini, P.; Wang, J.; Hartshorn, K.L.; Mason, R.J. Nrf2 protects human alveolar epithelial cells against injury induced by influenza A virus. Respir Res 2012, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yageta, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Masuko, H.; Ano, S.; Yamadori, T.; Itoh, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hizawa, N. Role of Nrf2 in host defense against influenza virus in cigarette smoke-exposed mice. J Virol 2011, 85, 4679–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J. Dual role of HO-1 in mediating antiviral immune responses and mitigating excessive inflammatory damage during influenza virus infection. iScience 2025, 28, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.P.; Wang, Q.W.; Su, Y.; Gu, L.M.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.X.; Chen, C.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, G.F.; Li, K.S. Emodin Inhibition of Influenza A Virus Replication and Influenza Viral Pneumonia via the Nrf2, TLR4, p38/JNK and NF-kappaB Pathways. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, F.H.; Shehata, M.; Elgaher, W.A.M.; Lacour, A.; Kurmasheva, N.; Begnini, F.; Kiib, A.E.; Dahlmann, J.; Chen, C.; Pavlou, A.; et al. NRF2 activators inhibit influenza A virus replication by interfering with nucleo-cytoplasmic export of viral RNPs in an NRF2-independent manner. PLoS Pathog 2023, 19, e1011506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, B.; Hsieh, C.F.; Lin, T.J.; Hu, P.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Tseng, S.N.; Horng, J.T.; Hsieh, P.W. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Itaconic Acid Derivatives as Potential Anti-Influenza Agents. J Med Chem 2019, 62, 2390–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ci, X. Role of Nrf2 and Its Activators in Respiratory Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 7090534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesic, M.J.; Simmons, S.O.; Bauer, R.; Jaspers, I. Nrf2 expression modifies influenza A entry and replication in nasal epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2011, 51, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, M.; Amatore, D.; Checconi, P.; Zevini, A.; Fraternale, A.; Magnani, M.; Hiscott, J.; De Chiara, G.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L. Influenza Virus Down-Modulates G6PD Expression and Activity to Induce Oxidative Stress and Promote Its Replication. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 804976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zevini, A.; Ferrari, M.; Olagnier, D.; Hiscott, J. Dengue virus infection and Nrf2 regulation of oxidative stress. Curr Opin Virol 2020, 43, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.B.; Muthuraman, K.R.; Mariappan, V.; Belur, S.S.; Lokesh, S.; Rajendiran, S. Oxidative stress response in the pathogenesis of dengue virus virulence, disease prognosis and therapeutics: an update. Arch Virol 2019, 164, 2895–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, N.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, D.; An, J. Inhibitory effect of glutathione on oxidative liver injury induced by dengue virus serotype 2 infections in mice. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagnier, D.; Peri, S.; Steel, C.; van Montfoort, N.; Chiang, C.; Beljanski, V.; Slifker, M.; He, Z.; Nichols, C.N.; Lin, R.; et al. Cellular oxidative stress response controls the antiviral and apoptotic programs in dengue virus-infected dendritic cells. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Chen, C.L.; Tsai, T.T.; Tsai, C.C.; Wu, Y.W.; Ou, Y.D.; Chu, Y.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Yu, C.Y.; et al. Activation of Nrf2 by the dengue virus causes an increase in CLEC5A, which enhances TNF-alpha production by mononuclear phagocytes. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 32000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Falgout, B.; Takeda, K.; Yamada, K.M.; Dhawan, S. Nrf2-dependent induction of innate host defense via heme oxygenase-1 inhibits Zika virus replication. Virology 2017, 503, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskou, M.; Fotooh Abadi, L.; Gain, C.; Wong, M.; Sharma, E.; Kombe Kombe, A.J.; Nanduri, R.; Kelesidis, T. The Role of the NRF2 Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Viral Respiratory Infections. Pathogens 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosakote, Y.M.; Liu, T.; Castro, S.M.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. Respiratory syncytial virus induces oxidative stress by modulating antioxidant enzymes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2009, 41, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.A.; Leon, M.A.; Cespedes, P.F.; Gomez, R.S.; Canedo-Marroquin, G.; Riquelme, S.A.; Salazar-Echegarai, F.J.; Blancou, P.; Simon, T.; Anegon, I.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulates Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Replication and Lung Pathogenesis during Infection. J Immunol 2017, 199, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casola, A.; Burger, N.; Liu, T.; Jamaluddin, M.; Brasier, A.R.; Garofalo, R.P. Oxidant tone regulates RANTES gene expression in airway epithelial cells infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Role in viral-induced interferon regulatory factor activation. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 19715–19722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, M.; Kato, T.; Seko, Y.; Minamino-Muta, E.; Tanada, Y.; Kimura, T.; Ono, K. Cobalt protoporphyrin promotes heme oxygenase 1 expression and ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in long-term fasting mice. Int J Cardiol 2024, 404, 131972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhu, T.N.; Huang, S.H. Respiratory syncytial virus infection up-regulates TLR7 expression by inducing oxidative stress via the Nrf2/ARE pathway in A549 cells. Arch Virol 2018, 163, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.Y.; Imani, F.; Miller-DeGraff, L.; Walters, D.; Melendi, G.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Polack, F.P.; Kleeberger, S.R. Antiviral activity of Nrf2 in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009, 179, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Haas de Mello, A.; Morris, D.R.; Jones-Hall, Y.L.; Ivanciuc, T.; Sattler, R.A.; Paessler, S.; Menachery, V.D.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A. SARS-CoV-2 Inhibits NRF2-Mediated Antioxidant Responses in Airway Epithelial Cells and in the Lung of a Murine Model of Infection. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0037823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledinos-Anton, N.; Fernandez-Gines, R.; Manda, G.; Cuadrado, A. Activators and Inhibitors of NRF2: A Review of Their Potential for Clinical Development. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 2019, 9372182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Du, J.; Yang, S.; Zheng, B.; Shen, J.; Huang, J.; Cao, L.; Huang, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a sensitizes cells to ferroptosis via Keap1-NRF2 axis. Redox Biol 2023, 63, 102752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Anichini, G.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L.; Gori Savellini, G. Dysregulation of intracellular redox homeostasis by the SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 protein. Virol J 2023, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, S.; Byrnes, S.; Cochrane, C.; Roche, M.; Estes, J.D.; Selemidis, S.; Angelovich, T.A.; Churchill, M.J. The role of oxidative stress in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Brain Behav Immun Health 2021, 13, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Ivanova, O.N.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Starodubova, E.S.; Bartosch, B.; Isaguliants, M.G. Oxidative Stress during HIV Infection: Mechanisms and Consequences. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016, 8910396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, N.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A. Oxidative stress in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Cell Mol Life Sci 1997, 53, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritis, M. Endothelial dysfunction in HIV infection: experimental and clinical evidence on the role of oxidative stress. Annals of Research Hospitals 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrantonio, R.; Cervelli, M.; Pietropaoli, S.; Mariottini, P.; Colasanti, M.; Persichini, T. HIV-Tat Induces the Nrf2/ARE Pathway through NMDA Receptor-Elicited Spermine Oxidase Activation in Human Neuroblastoma Cells. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0149802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staitieh, B.S.; Ding, L.; Neveu, W.A.; Spearman, P.; Guidot, D.M.; Fan, X. HIV-1 decreases Nrf2/ARE activity and phagocytic function in alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 2017, 102, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lu, X.; Yin, W.; Fu, H.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, L.; Liu, F.; Jin, C.; Tian, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Activation of NRF2 blocks HIV replication and apoptosis in macrophages. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Smirnova, O.A.; Ivanova, O.N.; Masalova, O.V.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Isaguliants, M.G. Hepatitis C virus proteins activate NRF2/ARE pathway by distinct ROS-dependent and independent mechanisms in HUH7 cells. PLoS One 2011, 6, e24957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Ebinuma, H.; Nakamoto, N.; Sakasegawa, N.; Murakami, Y.; Chu, P.S.; Usui, S.; Ishibashi, Y.; Wakayama, Y.; Taniki, N.; et al. Prominent steatosis with hypermetabolism of the cell line permissive for years of infection with hepatitis C virus. PLoS One 2014, 9, e94460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, R.; Ploen, D.; Spengler, C.; Elgner, F.; Ren, H.; Bunten, S.; Hildt, E. HCV-induced oxidative stress by inhibition of Nrf2 triggers autophagy and favors release of viral particles. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 110, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.Y.K.; Ou, J.J. Autophagy in HCV Replication and Protein Trafficking. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Yepes, M.; Himmelsbach, K.; Schaedler, S.; Ploen, D.; Krause, J.; Ludwig, L.; Weiss, T.; Klingel, K.; Hildt, E. Hepatitis C virus impairs the induction of cytoprotective Nrf2 target genes by delocalization of small Maf proteins. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 8941–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaedler, S.; Krause, J.; Himmelsbach, K.; Carvajal-Yepes, M.; Lieder, F.; Klingel, K.; Nassal, M.; Weiss, T.S.; Werner, S.; Hildt, E. Hepatitis B virus induces expression of antioxidant response element-regulated genes by activation of Nrf2. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 41074–41086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, J.; Kubo, T.; Nagano, H.; Tsuda, R.; Ogi, T.; Nakashima, K.; Suzuki, T. Effect of Nrf2 Activators in Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Cells Under Oxidative Stress. Mar Drugs 2025, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Fang, M.; He, Z.; Cui, D.; Jia, S.; Lin, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, W. Hepatitis B virus stimulates G6PD expression through HBx-mediated Nrf2 activation. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyler, E.; Franke, V.; Menegatti, J.; Kocks, C.; Boltengagen, A.; Praktiknjo, S.; Walch-Ruckheim, B.; Bosse, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Grasser, F.; et al. Single-cell RNA-sequencing of herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells connects NRF2 activation to an antiviral program. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Upregulation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) represses the replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virol J 2022, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, Y.S.; Li, W.; Kwon, E.B.; Chung, H.S.; Go, Y.; Choi, J.G. Ginsenoside Rg5, a potent agonist of Nrf2, inhibits HSV-1 infection-induced neuroinflammation by inhibiting oxidative stress and NF-kappaB activation. J Ginseng Res 2024, 48, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seelige, R.; Saddawi-Konefka, R.; Adams, N.M.; Picarda, G.; Sun, J.C.; Benedict, C.A.; Bui, J.D. Interleukin-17D and Nrf2 mediate initial innate immune cell recruitment and restrict MCMV infection. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Koh, K.; Kim, Y.E.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, S. Upregulation of Nrf2 expression by human cytomegalovirus infection protects host cells from oxidative stress. J Gen Virol 2013, 94, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagnier, D.; Brandtoft, A.M.; Gunderstofte, C.; Villadsen, N.L.; Krapp, C.; Thielke, A.L.; Laustsen, A.; Peri, S.; Hansen, A.L.; Bonefeld, L.; et al. Nrf2 negatively regulates STING indicating a link between antiviral sensing and metabolic reprogramming. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmasheva, N.; Said, A.; Wong, B.; Kinderman, P.; Han, X.; Rahimic, A.H.F.; Kress, A.; Carter-Timofte, M.E.; Holm, E.; van der Horst, D.; et al. Octyl itaconate enhances VSVDelta51 oncolytic virotherapy by multitarget inhibition of antiviral and inflammatory pathways. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaguliants, M.; Smirnova, O.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kilpelainen, A.; Kuzmenko, Y.; Petkov, S.; Latanova, A.; Krotova, O.; Engstrom, G.; Karpov, V.; et al. Oxidative stress induced by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase modulates the enzyme’s performance in gene immunization. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2013, 9, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullinan, S.B.; Zhang, D.; Hannink, M.; Arvisais, E.; Kaufman, R.J.; Diehl, J.A. Nrf2 is a direct PERK substrate and effector of PERK-dependent cell survival. Mol Cell Biol 2003, 23, 7198–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Mizushima, T.; Takagi, K.; Hirose, Y.; Nagahashi, M.; Iso, T.; Fukutomi, T.; et al. p62/Sqstm1 promotes malignancy of HCV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma through Nrf2-dependent metabolic reprogramming. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Doo, E.; Coux, O.; Goldberg, A.L.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Is both a Substrate and a Potential Inhibitor of the Proteasome Complex. Journal of Virology 1999, 73, 7231–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapochnik, D.; Raimondi, A.R.; Medina, V.; Naipauer, J.; Mesri, E.A.; Coso, O. A major role for Nrf2 transcription factors in cell transformation by KSHV encoded oncogenes. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 890825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T.; McKercher, S.R.; Lipton, S.A. Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs. Free Radic Biol Med 2013, 65, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olagnier, D.; Farahani, E.; Thyrsted, J.; Blay-Cadanet, J.; Herengt, A.; Idorn, M.; Hait, A.; Hernaez, B.; Knudsen, A.; Iversen, M.B.; et al. SARS-CoV2-mediated suppression of NRF2-signaling reveals potent antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity of 4-octyl-itaconate and dimethyl fumarate. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noah, T.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Glista-Baker, E.; Muller, L.; Bauer, R.N.; Meyer, M.; Murphy, P.C.; Jones, S.; Letang, B.; et al. Effect of broccoli sprouts on nasal response to live attenuated influenza virus in smokers: a randomized, double-blind study. PLoS One 2014, 9, e98671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.K.; Yim, N.H.; Lee, M.M.; Han, C.H.; Ma, J.Y. Broccoli Leaves Attenuate Influenza A Virus Infection by Interfering With Hemagglutinin and Inhibiting Viral Attachment. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 899181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yageta, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Ano, S.; Ohtsuka, S.; Matsuyama, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hizawa, N. Carbocisteine reduces virus-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice exposed to cigarette smoke. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2014, 50, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J.L.; Tate, M.D.; MacKenzie-Kludas, C.J.; Pinar, A.; Zeng, W.; Stutz, A.; Latz, E.; Brown, L.E.; Mansell, A. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by IAV virulence protein PB1-F2 contributes to severe pathophysiology and disease. PLoS Pathog 2013, 9, e1003392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Gu, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, H.; Li, W.; Wang, G.; Li, K. Inhibition of curcumin on influenza A virus infection and influenzal pneumonia via oxidative stress, TLR2/4, p38/JNK MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 2018, 54, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Zang, G.; Chen, T.; Lu, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G. Curcumin Inhibits Replication of Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 3 by Affecting Viral Inclusion Body Formation. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021, 1807293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Wen, H.W.; Ou, J.L.; Chiou, S.S.; Chen, J.M.; Wong, M.L.; Hsu, W.L. Inhibition of enveloped viruses infectivity by curcumin. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, N.N.; Mahmud, S.; Ark, S.M.A.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Hasan, M.K. Bakuchiol, a natural constituent and its pharmacological benefits. F1000Res 2023, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.; Arakaki, Y.; Esumi, T.; Kohnomi, S.; Yamamoto, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, E.; Konishi, S.; Kido, H.; Kuzuhara, T. Bakuchiol Is a Phenolic Isoprenoid with Novel Enantiomer-selective Anti-influenza A Virus Activity Involving Nrf2 Activation. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 28001–28017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoyama, D.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Beamer, L.J.; Kong, A.N.; Hu, L. Optimization of fluorescently labeled Nrf2 peptide probes and the development of a fluorescence polarization assay for the discovery of inhibitors of Keap1-Nrf2 interaction. J Biomol Screen 2012, 17, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.; Schaap, M.; Pfister, H.; Wells, G. Peptide inhibitors of the Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction with improved binding and cellular activity. Org Biomol Chem 2013, 11, 3553–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.G.; Jain, A.D.; Speltz, T.E.; Moore, T.W. Non-electrophilic modulators of the canonical Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2015, 25, 2261–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Poulsen, C.; Narayanan, D.; Chan, C.B.; Chen, X.; Montes, B.R.; Tran, K.T.; Mukminova, E.; Lin, C.; Gajhede, M.; et al. Structure-Guided Conformational Restriction Leading to High-Affinity, Selective, and Cell-Active Tetrahydroisoquinoline-Based Noncovalent Keap1-Nrf2 Inhibitors. J Med Chem 2024, 67, 18828–18864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, K.T.; Pallesen, J.S.; Solbak, S.M.O.; Narayanan, D.; Baig, A.; Zang, J.; Aguayo-Orozco, A.; Carmona, R.M.C.; Garcia, A.D.; Bach, A. A Comparative Assessment Study of Known Small-Molecule Keap1-Nrf2 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors: Chemical Synthesis, Binding Properties, and Cellular Activity. J Med Chem 2019, 62, 8028–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.; Qin, Y.; Cadot, M.E.H.; Barraja, P.; Bach, A. Advances in developing noncovalent small molecules targeting Keap1. Drug Discov Today 2023, 28, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qu, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, C.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, Z. Synthesis and pharmacodynamic evaluation of naphthalene derivatives against influenza A virus in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Med Chem 2023, 259, 115660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Villeneuve, N.F.; Jiang, T.; Wu, T.; Lau, A.; Toppin, H.A.; Zhang, D.D. Brusatol enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy by inhibiting the Nrf2-mediated defense mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Ye, W.; Huang, C.; Yu, D.; Chen, H.; Deng, T.; Zhang, F.; Lou, B.; Zhang, J.; Shi, K.; et al. Brusatol Enhances the Chemotherapy Efficacy of Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer via the Nrf2 Signalling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018, 2360427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, C.; Mori, N. ML385, a selective inhibitor of Nrf2, demonstrates efficacy in the treatment of adult T-cell leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2025, 66, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




