Submitted:
20 October 2025
Posted:
21 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Motivation
1.2. Research Challenges and Questions
1.3. Research Scope and Contributions
- Comprehensive Literature Survey: We conduct a broad review and categorization of existing energy-efficient routing techniques, distinguishing between conventional methods and AI-enhanced strategies, including machine learning, metaheuristic algorithms, and cross-layer optimization approaches. The surveyed protocols are systematically classified based on key performance attributes such as energy consumption, scalability, packet delivery ratio, latency, and protocol adaptability to IoT-specific constraints.
- Comparative Analysis: We present a detailed evaluation of the strengths, weaknesses, and application scenarios for traditional and AI-driven routing techniques, highlighting each technique's practical benefits and limitations.
- Research Gap/Challenges analysis led to future directions: Our analysis reveals several unresolved challenges, such as inefficient cluster head selection, energy bottlenecks in multi-hop routing, and limited real-time adaptability of routing algorithms in heterogeneous IoT environments. The paper recommends promising avenues for further exploration, including the development of energy-aware cluster formation mechanisms, lightweight and secure routing protocols for constrained devices, and the integration of AI models capable of self-learning and online optimization in dynamic WSN topologies.
1.4. Structure of This Paper
2. Summary of Existing Surveys
| Ref. | Type of Energy-Efficient Route optimization Techniques |
Clustering | AI-Driven Optimization |
Application Area |
Review Focused on | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | CL | MH | ML | DL | |||||
| [15] | ✓ | O | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | ✓ | WSN routing |
Comprehensive survey covering optimization strategies in routing, including trade-offs among cost, energy, and delay |
| [16] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | ✓ | O | WSN | Overview of different routing schemes and their performance in WSN, covering latency, scalability, and energy use trade-offs. |
| [17] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | ✓ | IoT applications |
Comprehensive review of energy-aware IoT routing protocols with a focus on efficiency, protocol types, performance, and research gaps |
| [18] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | ✓ | ✓ | WSN-IoT | Detailed exploration of optimal CH selection techniques for enhanced energy efficiency. |
| [19] | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | WSN-IoT | Application of Machine Learning in Localization for WSN-Assisted IoT with a Focus on Agricultural Monitoring. |
| [20] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | O | O | WSN | Comprehensive review of security threats and countermeasures in WSN routing, highlighting optimized secure communication. |
| [21] | O | ✓ | O | O | O | O | O | IoT applications |
Comprehensive cross-layer review focusing on secure and low-latency communication methods across access, network, and application layers. |
| [22] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | ✓ | O | MANETs | Detailed analysis of load balancing in energy-sensitive multipath routing protocols. |
| [23] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | ✓ | O | WSN | In-depth study of hierarchical routing protocols, focusing on energy conservation and extending network lifetime. |
| [24] | ✓ | O | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | ✓ | Energy- efficient WSN |
Comprehensive review of bio-inspired hybrids for enhancing energy efficiency and prolonging lifetime in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). |
| [25] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | ✓ | O | IoT systems |
Survey covering various WSN techniques, including routing, energy efficiency, and network scalability. |
| [26] | O | ✓ | O | O | O | O | O | Next-gen IoT networks |
Survey focusing on cross-layer secure communication with latency minimization in IoT. |
| [27] | ✓ | O | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | ✓ | WSN-IoT | Study on Protocol-Level Energy Optimization in Large-Scale Networks. |
| [28] | ✓ | O | O | O | O | ✓ | O | Query-driven WSNs | Exhaustive review of energy-efficient routing protocols employed in query-based Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). |
| [29] | ✓ | O | O | ✓ | O | ✓ | O | WSN-IoT | Bibliometric review using Web of Science dataset; maps publication trends, routing techniques, clustering and ML integration; compares protocols and identifies research trends. |
| Our Work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | IoT-based WSN | This survey offers a comprehensive review of routing techniques in IoT-based WSNs, encompassing network structure, cross-layer design, meta-heuristics, machine learning, and deep learning. It also highlights existing challenges in WSN-IoT routing and outlines future research opportunities and potential solutions. |
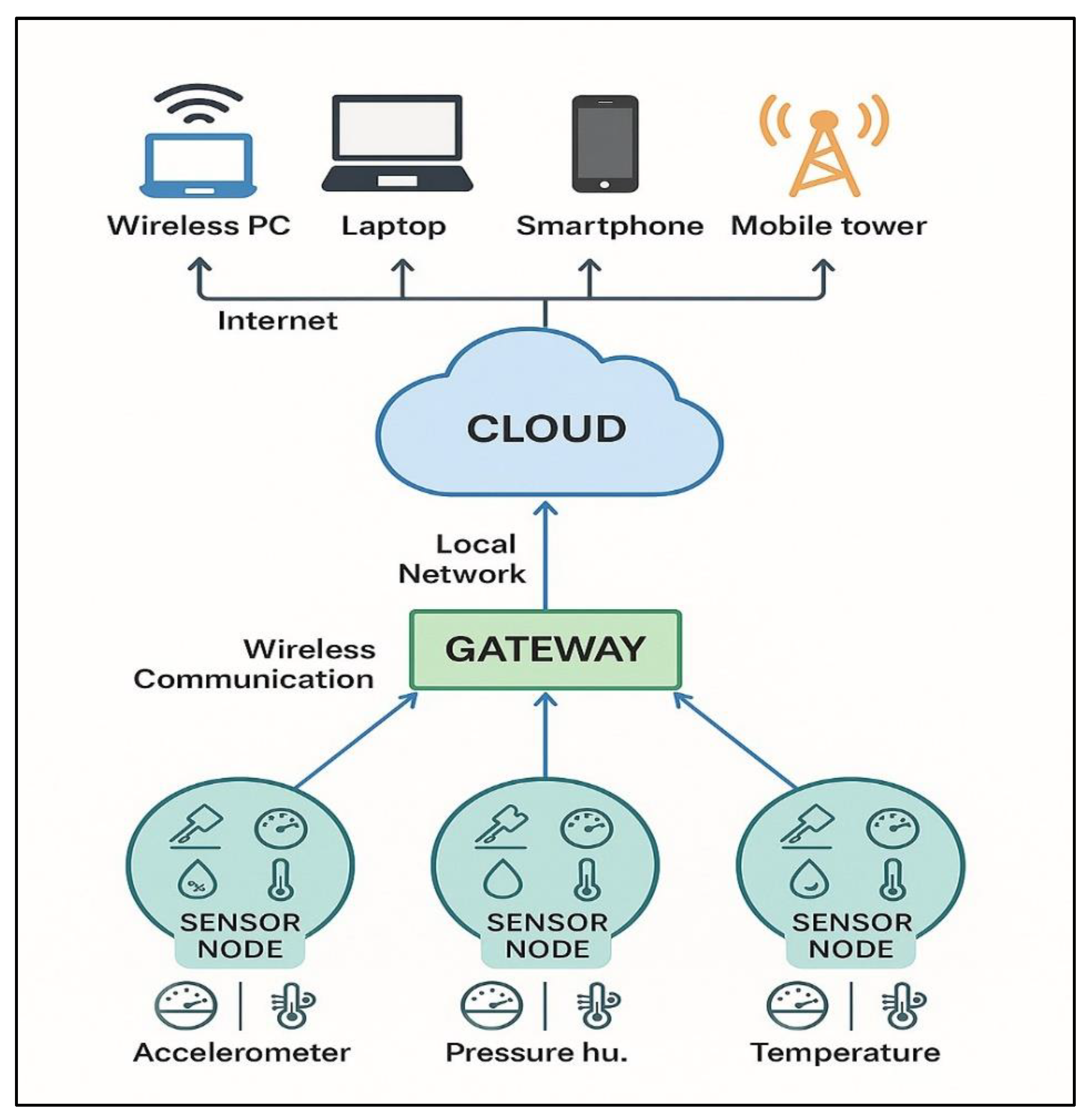
3. IoT-Based Wireless Sensor Networks
3.1. Background and Overview
| Communication Level |
Role | Routing involved |
Typical communication |
Technologies Used |
Data Operations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Perception Layer |
Sensing physical environment using sensor nodes | No | Sensor-to-gateway, Device-to-device (ZigBee, BLE, LoRa) | Sensors, RFID, Bluetooth, ZigBee, LoRa | Data collection and digital signal conversion |
|
Middleware Layer |
Data aggregation, protocol translation, and cloud interfacing |
Minimal/ No |
Gateway-to-cloud or Base station-to-server (IP-based protocols) | MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, Cloud services | Data filtering, coaching, load balancing, semantic processing |
|
Network Layer |
Routing and transmitting data across nodes to a sink/base station | Yes | Node-to-node, Cluster-to-sink (multi-hop routing protocols) |
Routing protocols (LEACH, AODV, RPL), Wireless standards (802.15.4) |
Path selection, energy-efficient forwarding, QoS maintenance |
|
Application Layer |
Presenting data to users or external systems through applications | No | User interface, API communication, cloud-to-app | Web/Mobile applications, Dashboards, REST APIs | Visualization, user notifications, and command actuation |
3.2. Applications and Challenges in IoT-Based WSN
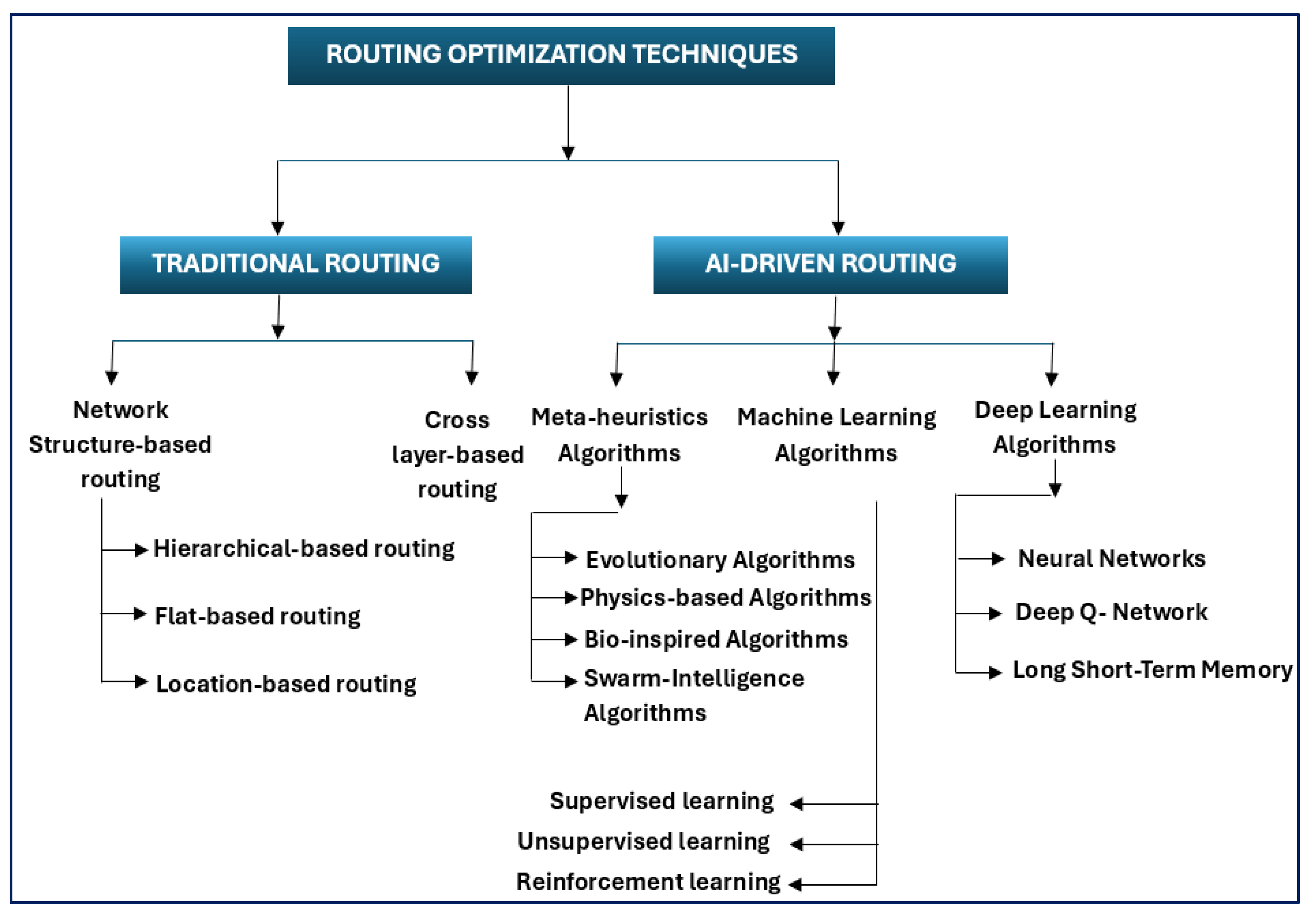
4. Routing Optimization for IoT-based WSN: A Classification of Literature Review
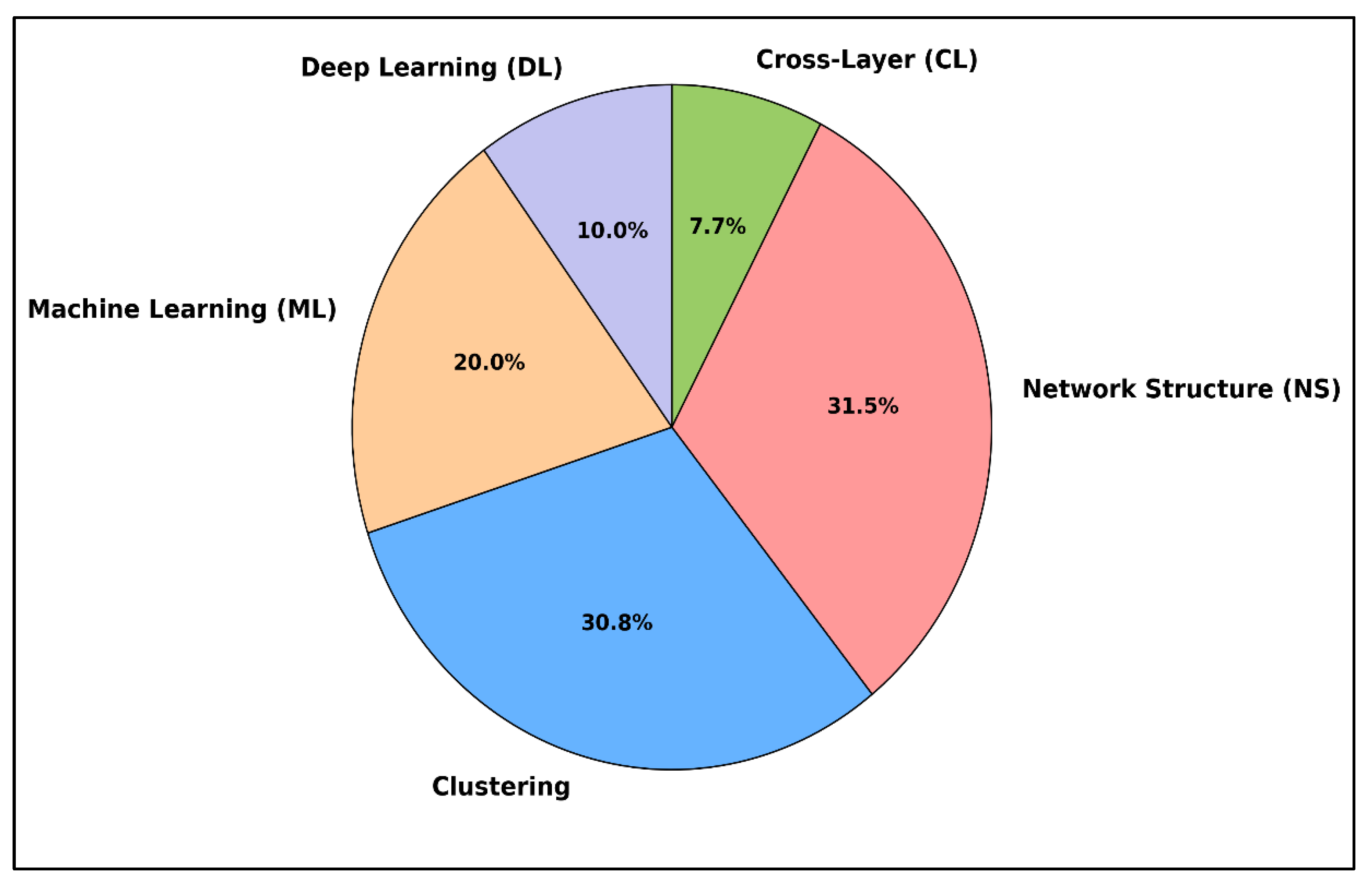
4.1. Traditional-Based Routing Techniques
4.1.1. Network Structure-Based Routing Techniques
4.1.2. Cross-Layer Design Approach
4.2. AI-Driven Routing Algorithms
4.2.1. Meta-Heuristics Routing Algorithms
4.2.2. Machine Learning-Based Routing Algorithms
4.2.3. Deep Learning-Based Routing Algorithms
| Ref. | AI Technique |
Energy Efficiency |
Network Delay |
Scalability | Link Prediction |
WSN/IoT Environment |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [114] | Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (Q-learning) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Dynamic | High computational overhead, slower in large/mobile networks |
| [115] | Dynamic Objective Selection with RL (DOS-RL) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Dynamic | Frequent policy updates raise costs and scalability issues as networks grow |
| [116] | Tabu Search + ACO Hybrid | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Static | Needs parameter tuning, cluster head depletion in topological changes |
| [117] | Swarm Intelligence (PSO, SI models) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Dynamic | Sensitive to initial values, synchronization overhead |
| [118] | Ant Colony Optimization (ACO Variant) |
✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Dynamic | Multi-agent overhead, increased coordination required |
| [119] | Genetic Algorithm Optimization | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Static | Iterative optimization slows for rapidly changing networks |
| [120] | Genetic Algorithm | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Static | Slow adaptation, routing overhead in dynamic scenarios |
| [121] | Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Dynamic | High computation needs, slow route updating |
| [122] | Quantum PSO + Fuzzy Logic | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Dynamic | Increased complexity with combined fuzzy/quantum models |
| [123] | Neuro-fuzzy Data Routing (NFDR) | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Dynamic | Degrades under rapid state changes |
| [124] | DRL + Graph Neural Network |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Dynamic | High cost for training and operation |
| [125] | AI-based Modular Framework | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Dynamic | Heavy overall demand for processing and data |
| [126] | CNN + BEA-SSA | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Static | Security/complex routing increases delay |
| [127] | RNN (Path Planning/Optimization) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Dynamic | Not optimal for all dynamic topologies (e.g., moving sink) |
| [128] | Neural Network LEACH Variant | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Static | Higher computational needs, heavier model |
| [129] | Greedy Discrete PSO (GMDPSO) | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Dynamic | Adapts to mobiles, but slow when updating routes |
| [130] | Nature/Swarm-Inspired | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Dynamic | Retracted; overhead; lacks robust validation |
| [131] | Multi-Intel. Biomedical Routing | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Static | Specific to biomedical routing; generalizability lacking |
| [132] | DRL with Graph Structure (GTD3-NET) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Dynamic | Resource-intensive, not yet validated in the field |
5. Open Research Problems and Future Directions
5.1. Open Research Problems
- (i)
- Limited Adaptivity and Scalability in Traditional and Hybrid Routing Protocols
- (ii)
- Inadequate Security, Robustness, and Fault Tolerance
- (iii)
- High Overhead and Complexity in Bio-Inspired Cluster-Based Protocols
- (iv)
- Lack of Multi-Objective Optimization and Real-World Validation
- (v)
- Energy Hole and Network Fairness
5.2. Future Research Directions
- (i)
- Advance Adaptive Routing with Context-Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning
- (ii)
- Integrate Lightweight AI-Driven Security Features and Predictive Fault Detection
- (iii)
- Hybridize Bio-Inspired Optimization with Lightweight Machine Learning for Cluster Management
- (iv)
- Develop Multi-Objective, Explainable AI-Based Routing Frameworks and Promote Real-World Validation
- (v)
- Edge Computing Integration
6. Conclusion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony |
| ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| AODV | Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector |
| ASFO | Adaptive Swarm Firefly Optimization |
| BEA-SSA | Bald Eagle Assisted Sparrow Search Algorithm |
| BFO | Bacterial Foraging Optimization |
| CBRP | Cluster-Based Routing Protocol |
| CLEERDTS | Cross-Layer Energy-Efficient Reliable Data Transmission System |
| CL-IoT | Cross-layer Internet of Things Protocol |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CSA | Cuckoo Search Algorithm |
| CWSN-eSCPM | Cross-layer Wireless Sensor Network—Enhanced Service and Congestion Prediction Management |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| DVRP | Distance Vector Routing Protocol |
| ECCM | Event-Cluster-based Cross-layer Management |
| EAR | Energy-Aware Routing |
| EER-RL | Energy-Efficient Routing with Reinforcement Learning |
| FDRL | Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| FMCB-ER | Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Clustering and Bio-inspired Energy-Efficient Routing |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GAPSO | Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization |
| GEAR | Geographic and Energy Aware Routing |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| GSA | Gravitational Search Algorithm |
| HEED | Hybrid Energy-Efficient Distributed |
| HSEERP | Hierarchical Secured Energy Efficient Routing Protocol |
| LEACH | Low-Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy |
| LSP | Link State Protocol |
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MH | Metaheuristics |
| MPNN | Message Passing Neural Network |
| NICC | Nature-Inspired Cross-layer Clustering |
| PEGASIS | Power-Efficient Gathering in Sensor Information System |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| QPSO | Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization |
| REERP | Region-based Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol |
| RPL | Routing Protocol for Low Power and Lossy Networks |
| RPP-RNN | Rank-Based Path Planning with Recurrent Neural Network |
| RSSI | Received Signal Strength Indicator |
| SNN | Spiking Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
References
- Akkaya, K. and M. Younis, A survey on routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. Ad hoc networks, 2005. 3(3): p. 325-349.
- Al-Karaki, J.N. and A.E. Kamal, Routing techniques in wireless sensor networks: a survey. IEEE wireless communications, 2004. 11(6): p. 6-28. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-Y., et al., Internet of Things (IoT) based design of a secure and lightweight body area network (BAN) healthcare system. Sensors, 2017. 17(12): p. 2919. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.E., A.I. Saleh, M. Abdelrazzak, and A.S. Samra, Survey on wireless sensor network applications and energy efficient routing protocols. Wireless Personal Communications, 2018. 101(2): p. 1019-1055. [CrossRef]
- Heinzelman, W.B., Application-specific protocol architectures for wireless networks. 2000, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- Younis, O. and S. Fahmy, HEED: a hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on mobile computing, 2004. 3(4): p. 366-379. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K., M. Singh, and D.K. Singh, Routing protocols in wireless sensor networks–a survey. International Journal of Computer Science & Engineering Survey (IJCSES), 2010. 1(2): p. 63-83.
- Almufti, S.M., et al., Overview of metaheuristic algorithms. Polaris Global Journal of Scholarly Research and Trends, 2023. 2(2): p. 10-32.
- Joshi, P. and A.S. Raghuvanshi, Hybrid approaches to address various challenges in wireless sensor network for IoT applications: opportunities and open problems. International Journal of Computer Networks and Applications, 2021. 8(3): p. 151-187. [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, B. and S.C. Pushpan, A review on swarm intelligence based routing approaches. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov, 2019. 9(3): p. 182-195.
- Priyadarshi, R., Energy-Efficient Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Meta-heuristic and Artificial Intelligence-based Approach: A Comprehensive Review. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2024. 31(4). [CrossRef]
- Al-Karaki, J.N., A.E. Kamal, and R. Ul-Mustafa. On the optimal clustering in mobile ad hoc networks. in First IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, 2004. CCNC 2004. 2004. IEEE.
- Priyadarshi, R., Exploring machine learning solutions for overcoming challenges in IoT-based wireless sensor network routing: a comprehensive review. Wireless Networks, 2024. 30(4): p. 2647-2673. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.S., J. Mathew, and A.V. Vasilakos, Security and fault tolerance in Internet of things. 2019: Springer.
- Al Aghbari, Z., et al., Routing in wireless sensor networks using optimization techniques: A survey. Wireless Personal Communications, 2020. 111(4): p. 2407-2434. [CrossRef]
- Agarkar, P.T., M.D. Chawan, P.T. Karule, and P.R. Hajare, A comprehensive survey on routing schemes and challenges in wireless sensor networks (WSN). International Journal of Computer Networks and Applications (IJCNA), 2020. 7(6): p. 193-207. [CrossRef]
- Poornima, M., H. Vimala, and J. Shreyas, Holistic survey on energy aware routing techniques for IoT applications. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2023. 213: p. 103584.
- Ramya, R. and T. Brindha, A comprehensive review on optimal cluster head selection in WSN-IOT. Advances in Engineering Software, 2022. 171: p. 103170. [CrossRef]
- Singh, H., et al., Localization in WSN-Assisted IoT Networks Using Machine Learning Techniques for Smart Agriculture. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2025. 38(5): p. e6004. [CrossRef]
- Nag, A., et al. A Survey on Wireless Sensor Network Routing Performance Optimizing and Security Techniques. in International Conference on Frontiers in Computing and Systems. 2023. Springer.
- Martalò, M., G. Pettorru, and L. Atzori, A cross-layer survey on secure and low-latency communications in next-generation IoT. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2024. 21(4): p. 4669-4685. [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N. and S. Veenadhari, A Comprehensive Survey of Load Balancing Techniques in Multipath Energy-Consuming Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad hoc Networks in MANET. Indian Journal of Data Communication and Networking (IJDCN), 2024. 4(4): p. 5-10. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A., S. Anwar, M.I. Pramanik, and M.F. Rahman. A survey on energy efficient routing techniques in wireless sensor network. in 2013 15th International Conference on Advanced Communications Technology (ICACT). 2013. IEEE.
- Yadav, R., I. Sreedevi, and D. Gupta, Bio-inspired hybrid optimization algorithms for energy efficient wireless sensor networks: a comprehensive review. Electronics, 2022. 11(10): p. 1545. [CrossRef]
- Gulati, K., et al., A review paper on wireless sensor network techniques in Internet of Things (IoT). Materials Today: Proceedings, 2022. 51: p. 161-165. [CrossRef]
- Moslehi, M.M., Exploring coverage and security challenges in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 2025: p. 111096. [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, G., S. Rani, and A. Sharma. Optimizing Routing Protocols for Energy Efficiency in Large-Scale WSN-IoT Deployments. in 2024 Global Conference on Communications and Information Technologies (GCCIT). 2024. IEEE.
- Bekal, P., P. Kumar, P.R. Mane, and G. Prabhu, A comprehensive review of energy efficient routing protocols for query driven wireless sensor networks. F1000Research, 2024. 12: p. 644.
- Kumar, P., et al. Exploring Energy-Efficient Routing in IoT-based WSNs: A WoS Bibliometric-based Review. in 2025 8th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC). 2025. IEEE.
- Alam, T., A reliable communication framework and its use in internet of things (IoT). Authorea Preprints, 2023.
- Uviase, O. and G. Kotonya, IoT architectural framework: connection and integration framework for IoT systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.04780, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M. and D. Udaya, A Survey on Sensor Networks. International Journal of Embedded and Software Computing IJESC, DOI, 2014. 10(2014.125).
- Yick, J., B. Mukherjee, and D. Ghosal, Wireless sensor network survey. Computer networks, 2008. 52(12): p. 2292-2330.
- Zanella, A., et al., Internet of things for smart cities. IEEE Internet of Things journal, 2014. 1(1): p. 22-32.
- Marios, K., C. Konstantinos, N. Sotiris, and R. José. Passive target tracking: Application with mobile devices using an indoors WSN Future Internet testbed. in 2011 International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems and Workshops (DCOSS). 2011. IEEE.
- Centenaro, M., L. Vangelista, A. Zanella, and M. Zorzi, Long-range communications in unlicensed bands: The rising stars in the IoT and smart city scenarios. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2016. 23(5): p. 60-67. [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, O.A., Energy Efficient and Load-Balanced Routing Schemes for In-Network Data Aggregation in Wireless Sensor Networks. 2017, University of Malaya (Malaysia).
- Pantazis, N.A., S.A. Nikolidakis, and D.D. Vergados, Energy-efficient routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications surveys & tutorials, 2012. 15(2): p. 551-591. [CrossRef]
- Al-Fuqaha, A., et al., Internet of things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE communications surveys & tutorials, 2015. 17(4): p. 2347-2376. [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P., A survey on Internet of Things architectures. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2018. 30(3): p. 291-319.
- Ojha, A. and B. Gupta, Evolving landscape of wireless sensor networks: a survey of trends, timelines, and future perspectives. Discover Applied Sciences, 2025. 7(8): p. 825. [CrossRef]
- Al-Healy, A.A. and Q. Ibrahim, WSN Routing Protocols: A Clear and Comprehensive Review. 2025.
- Tawfeek, M.A., et al., Improving energy efficiency and routing reliability in wireless sensor networks using modified ant colony optimization. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2025. 2025(1): p. 22. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.S., T. Dag, and T. Gucluoglu, Optimizing Mobile Base Station Placement for Prolonging Wireless Sensor Network Lifetime in IoT Applications. Applied Sciences, 2025. 15(3): p. 1421. [CrossRef]
- Al-Healy, A.A. and Q. Ibrahim, Evaluation Metrics and Optimization Strategies for Routing Protocols in Resource-Constrained Wireless Sensor Networks. 2025.
- Botta, A., W. De Donato, V. Persico, and A. Pescapé, Integration of cloud computing and internet of things: a survey. Future generation computer systems, 2016. 56: p. 684-700. [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, M., Applications of graphene-based materials in sensors. 2020, MDPI. p. 3196. [CrossRef]
- Salam, A., Internet of things in agricultural innovation and security, in Internet of Things for Sustainable Community Development: Wireless Communications, Sensing, and Systems. 2024, Springer. p. 71-112.
- Sanchez, L., et al., SmartSantander: IoT experimentation over a smart city testbed. Computer networks, 2014. 61: p. 217-238. [CrossRef]
- Nur, S., The role of digital health technologies and sensors in revolutionizing wearable health monitoring systems. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science and Technology, 2024. 12(6): p. 69-80. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J., R. Runge, and M. Snyder, Wearables and the medical revolution. Personalized medicine, 2018. 15(5): p. 429-448. [CrossRef]
- Wan, J., J. Yang, Z. Wang, and Q. Hua, Artificial intelligence for cloud-assisted smart factory. IEEE Access, 2018. 6: p. 55419-55430. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y., X. Xu, E. Klotz, and S.T. Newman, Intelligent manufacturing in the context of industry 4.0: a review. Engineering, 2017. 3(5): p. 616-630. [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M., et al., Recent advances in internet of things solutions for early warning systems: A review. Sensors, 2022. 22(6): p. 2124. [CrossRef]
- 김시관, Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks. 2017.
- Sukjaimuk, R., Q.N. Nguyen, and T. Sato, A smart congestion control mechanism for the green IoT sensor-enabled information-centric networking. Sensors, 2018. 18(9): p. 2889. [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S., S. Zeadally, H. Fahim, and B. He, Medical sensors and their integration in wireless body area networks for pervasive healthcare delivery: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022. 22(5): p. 3860-3877. [CrossRef]
- Lin, J., et al., A survey on internet of things: Architecture, enabling technologies, security and privacy, and applications. IEEE internet of things journal, 2017. 4(5): p. 1125-1142. [CrossRef]
- Humayed, A., J. Lin, F. Li, and B. Luo, Cyber-physical systems security—A survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017. 4(6): p. 1802-1831.
- Lahane, S.R. and K. Jariwala. Network structured based routing techniques in wireless sensor network. in 2018 3rd International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT). 2018. IEEE.
- Sabri, A. and K. Al-Shqeerat, Hierarchical cluster-based routing protocols for wireless sensor networks–a survey. IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, 2014. 11(1): p. 93-105.
- Patil, R. and V.V. Kohir, Energy efficient flat and hierarchical routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR–JECE), 2016. 11(6): p. 24-32.
- Boussoufa-Lahlah, S., F. Semchedine, and L. Bouallouche-Medjkoune, Geographic routing protocols for Vehicular Ad hoc NETworks (VANETs): A survey. Vehicular communications, 2018. 11: p. 20-31. [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, C., G.N. Sharma, and K.R. Singh. Improved energy lifetime of integrated LEACH protocol for wireless sensor network. in 2021 International Conference on Disruptive Technologies for Multi-Disciplinary Research and Applications (CENTCON). 2021. IEEE.
- Ramadhan, F. and R. Munadi. Modified combined leach and pegasis routing protocol for energy efficiency in iot network. in 2021 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication (iSemantic). 2021. IEEE.
- Chen, S., Y. Chen, Y. Huang, and W. Wei. Optimization of LEACH routing protocol algorithm. in 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Power, Electronics and Computer Applications (ICPECA). 2023. IEEE.
- Vellela, S.S. and R. Balamanigandan, Optimized clustering routing framework to maintain the optimal energy status in the wsn mobile cloud environment. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2024. 83(3): p. 7919-7938. [CrossRef]
- Dogra, R., S. Rani, and G. Gianini, REERP: a region-based energy-efficient routing protocol for IoT wireless sensor networks. Energies, 2023. 16(17): p. 6248. [CrossRef]
- Parween, S., S.Z. Hussain, M.A. Hussain, and A. Pradesh, A survey on issues and possible solutions of cross-layer design in Internet of Things. Int. J. Comput. Networks Appl, 2021. 8(4): p. 311.
- Parween, S. and S.Z. Hussain, A review on cross-layer design approach in WSN by different techniques. Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst, 2020. 5(4): p. 741-754. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W., J. Kim, and J. Lee, Cross-Layer MAC/Routing Protocol for Reliability Improvement of the Internet of Things. Sensors, 2022. 22(23): p. 9429.
- Hosahalli, D. and K. G. Srinivas, Cross-layer routing protocol for event-driven M2M communication in IoT-assisted Smart City Planning and Management: CWSN-eSCPM. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 2020. 10(1): p. 1-12.
- Mahajan, H.B. and A. Badarla, Cross-layer protocol for WSN-assisted IoT smart farming applications using nature inspired algorithm. Wireless Personal Communications, 2021. 121(4): p. 3125-3149. [CrossRef]
- Panchal, M., R. Upadhyay, and P.D. Vyavahare. Cross-layer based energy efficient reliable data transmission system for IoT networks. in 2022 IEEE 11th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT). 2022. IEEE.
- Sun, Z., et al., An energy-efficient cross-layer-sensing clustering method based on intelligent fog computing in WSNs. IEEE Access, 2019. 7: p. 144165-144177. [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, K., A HSEERP—Hierarchical secured energy efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2024. 17(1): p. 163-175. [CrossRef]
- Prince, B., P. Kumar, and S.K. Singh, Multi-level clustering and Prediction based energy efficient routing protocol to eliminate Hotspot problem in Wireless Sensor Networks. Scientific reports, 2025. 15(1): p. 1122. [CrossRef]
- Moussa, N., S. Khemiri-Kallel, and A. El Belrhiti El Alaoui, Fog-assisted hierarchical data routing strategy for IoT-enabled WSN: Forest fire detection. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2022. 15(5): p. 2307-2325. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadoon, M.E., A. Jedidi, and H. Al-Raweshidy, Dual-tier cluster-based routing in mobile wireless sensor network for IoT application. IEEE Access, 2023. 11: p. 4079-4094. [CrossRef]
- Cherappa, V., et al., Energy-efficient clustering and routing using ASFO and a cross-layer-based expedient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 2023. 23(5): p. 2788. [CrossRef]
- Sarwesh, P. and A. Mathew, Cross layer design with weighted sum approach for extending device sustainability in smart cities. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022. 77: p. 103478. [CrossRef]
- Renaldo Maximus, A. and S. Balaji, Energy-Efficient Fuzzy Logic With Barnacle Mating Optimization-Based Clustering and Hybrid Optimized Cross-Layer Routing in Wireless Sensor Network. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2025. 38(5): p. e6132. [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, H.B., A. Badarla, and A.A. Junnarkar, CL-IoT: cross-layer Internet of Things protocol for intelligent manufacturing of smart farming. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2021. 12(7): p. 7777-7791. [CrossRef]
- Tandon, A. and P. Srivastava, Location based secure energy efficient cross layer routing protocols for IOT enabling technologies. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE) ISSN, 2019: p. 2278-3075.
- Pham, T.H. and B. Raahemi, Bio-inspired feature selection algorithms with their applications: a systematic literature review. IEEE Access, 2023. 11: p. 43733-43758. [CrossRef]
- Qubbaj, N., A.A. Taleb, and W. Salameh. Review on LEACH protocol. in 2020 11th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS). 2020. IEEE.
- Senthil, G., A. Raaza, and N. Kumar, Internet of things energy efficient cluster-based routing using hybrid particle swarm optimization for wireless sensor network. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 122(3): p. 2603-2619. [CrossRef]
- Han, H., J. Tang, and Z. Jing, Wireless sensor network routing optimization based on improved ant colony algorithm in the Internet of Things. Heliyon, 2024. 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M., et al., A hybrid delay aware clustered routing approach using aquila optimizer and firefly algorithm in internet of things. Mathematics, 2022. 10(22): p. 4331. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, K. and V. Anand, A Grey-Wolf based Optimized Clustering approach to improve QoS in wireless sensor networks for IoT applications. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2021. 14(4): p. 1943-1962. [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, G. and K. Prasad, Energy optimization routing for hierarchical cluster based WSN using artificial bee colony. Measurement: sensors, 2023. 29: p. 100848. [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D., et al., CUCKOO-ANN Based Novel Energy-Efficient Optimization Technique for IoT Sensor Node Modelling. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2022. 2022(1): p. 8660245. [CrossRef]
- Mohanadevi, C. and S. Selvakumar, A qos-aware, hybrid particle swarm optimization-cuckoo search clustering based multipath routing in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 127(3): p. 1985-2001. [CrossRef]
- Agbulu, G.P., G.J.R. Kumar, V.A. Juliet, and S.A. Hassan, PECDF-CMRP: a power-efficient compressive data fusion and cluster-based multi-hop relay-assisted routing protocol for IoT sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 127(4): p. 2955-2977. [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, T., et al., A novel hybrid optimization for cluster-based routing protocol in information-centric wireless sensor networks for IoT based mobile edge computing. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 127(1): p. 39-62. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D. and S. Saxena, Hierarchical WSN protocol with fuzzy multi-criteria clustering and bio-inspired energy-efficient routing (FMCB-ER). Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022. 81(24): p. 35083-35116. [CrossRef]
- Giri, A., S. Dutta, and S. Neogy, An optimized fuzzy clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 126(3): p. 2731-2751. [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, G. and M. Kiran, Improved harmony search algorithm for multihop routing in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Computer and Systems Sciences International, 2022. 61(6): p. 1058-1075. [CrossRef]
- Gurupriya, M. and A. Sumathi, HOFT-MP: a multipath routing algorithm using hybrid optimal fault tolerant system for WSNs using optimization techniques. Neural Processing Letters, 2022. 54(6): p. 5099-5124. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.S. and P.T. Rao, An optimal emperor penguin optimization based enhanced flower pollination algorithm in WSN for fault diagnosis and prolong network lifespan. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 127(3): p. 2003-2020. [CrossRef]
- Jeevanantham, S. and B. Rebekka, Energy-aware neuro-fuzzy routing model for WSN based-IoT. Telecommunication Systems, 2022. 81(3): p. 441-459. [CrossRef]
- Sood, T. and K. Sharma, A Novelistic GSA and CSA Based Optimization for Energy-Efficient Routing Using Multiple Sinks in HWSNs Under Critical Scenarios. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 127(1): p. 1-37. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.P. and B. Saha, Load balanced clustering scheme using hybrid metaheuristic technique for mobile sink based wireless sensor networks. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022. 13(11): p. 5283-5294. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. and G. Wan, An enhanced ACO-based mobile sink path determination for data gathering in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2022. 2022(1): p. 100. [CrossRef]
- Norouzi Shad, M., M. Maadani, and M. Nesari Moghadam, GAPSO-SVM: an IDSS-based energy-aware clustering routing algorithm for IoT perception layer. Wireless Personal Communications, 2022. 126(3): p. 2249-2268. [CrossRef]
- Singh, H., M. Bala, and S.S. Bamber, Augmenting network lifetime for heterogenous WSN assisted IoT using mobile agent. Wireless Networks, 2020. 26(8): p. 5965-5979. [CrossRef]
- Amin, R., et al., A survey on machine learning techniques for routing optimization in SDN. IEEE Access, 2021. 9: p. 104582-104611. [CrossRef]
- Mammeri, Z., Reinforcement learning based routing in networks: Review and classification of approaches. Ieee Access, 2019. 7: p. 55916-55950. [CrossRef]
- Serra, A. and R. Tagliaferri, Unsupervised Learning: Clustering. 2019.
- Mutombo, V.K., S. Lee, J. Lee, and J. Hong, EER-RL: Energy-Efficient Routing Based on Reinforcement Learning. Mobile Information Systems, 2021. 2021(1): p. 5589145. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N., et al., Energy-efficient and QoS-aware data routing in node fault prediction based IoT networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023. 20(4): p. 4585-4599. [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S., et al., Congestion prediction for smart sustainable cities using IoT and machine learning approaches. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021. 64: p. 102500. [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, M. and Y. Lim, Reinforcement learning-based dynamic routing using mobile sink for data collection in WSNs and IoT applications. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2021. 194: p. 103223. [CrossRef]
- Soltani, P., M. Eskandarpour, A. Ahmadizad, and H. Soleimani, Energy-Efficient Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:2508.14679, 2025.
- Godfrey, D., et al., An energy-efficient routing protocol with reinforcement learning in software-defined wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 2023. 23(20): p. 8435. [CrossRef]
- Li, M. and J. Ai, Energy-Aware Clustering in the Internet of Things using Tabu Search and Ant Colony Optimization Algorithms. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science & Applications, 2023. 14(12). [CrossRef]
- Shin, C. and M. Lee, Swarm-intelligence-centric routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 2020. 20(18): p. 5164. [CrossRef]
- Razooqi, Y.S. and M. Al-Asfoor, Enhanced Ant Colony Optimization for Routing in WSNs An Energy Aware Approach. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering & Systems, 2021. 14(6).
- Al-agar, M.A.N.O., et al., Reduce Energy Consumption and Increase Lifetime via Genetic Algorithm over Wireless Communication Networks. Journal of Intelligent Systems & Internet of Things, 2025. 14(2).
- Norouzi, A. and A.H. Zaim, Genetic algorithm application in optimization of wireless sensor networks. The Scientific World Journal, 2014. 2014(1): p. 286575. [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S., A. Al Qahtani, and A.S.M. Al-Shahrani, Particle Swarm Optimization for Wireless Sensor Network Lifespan Maximization. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research, 2024. 14(2): p. 13665-13670. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H., X. Fan, and C. Wang, Energy efficient clustering and routing protocol based on quantum particle swarm optimization and fuzzy logic for wireless sensor networks. Scientific reports, 2024. 14(1): p. 18595. [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, S.S.S. and T. Deepa, Energy-efficient data routing using neuro-fuzzy based data routing mechanism for IoT-enabled WSNs. Scientific Reports, 2024. 14(1): p. 30081. [CrossRef]
- Pushpa, G., R.A. Babu, S. Subashree, and S. Senthilkumar, Optimizing coverage in wireless sensor networks using deep reinforcement learning with graph neural networks. Scientific Reports, 2025. 15(1): p. 16681. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R., R.R. Kumar, R. Ranjan, and P.V. Kumar, AI-based routing algorithms improve energy efficiency, latency, and data reliability in wireless sensor networks. Scientific Reports, 2025. 15(1): p. 22292. [CrossRef]
- Gurumoorthy, S., P. Subhash, R. Pérez de Prado, and M. Wozniak, Optimal cluster head selection in WSN with convolutional neural network-based energy level prediction. Sensors, 2022. 22(24): p. 9921. [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, K.V., S. Kavipriya, and K. Vijayalakshmi, Enhanced mobile sink path optimization using RPP-RNN algorithm for energy efficient data acquisition in WSNs. WIRELESS NETWORKS, 2025. 31(2): p. 1705-1717. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.H., et al., An efficient neural network LEACH protocol to extended lifetime of wireless sensor networks. Scientific Reports, 2024. 14(1): p. 26943. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J., F. Liu, J. Cao, and L. Wang, Discrete particle swarm optimization routing protocol for wireless sensor networks with multiple mobile sinks. Sensors, 2016. 16(7): p. 1081. [CrossRef]
- Bangotra, D.K., et al., [Retracted] Energy-Efficient and Secure Opportunistic Routing Protocol for WSN: Performance Analysis with Nature-Inspired Algorithms and Its Application in Biomedical Applications. BioMed research international, 2022. 2022(1): p. 1976694. [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, H., A.F.d. Santos, L.H. Azevedo, and L. Corrêa. https://www. sciencedirect. com/science/article/pii/S2212440325006418. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology, 2025. 139(5): p. e131.
- Lu, Y., et al., GTD3-NET: A deep reinforcement learning-based routing optimization algorithm for wireless networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2025. 18(1): p. 23. [CrossRef]
- Snigdh, I. and D. Gosain, Analysis of scalability for routing protocols in wireless sensor networks. Optik, 2016. 127(5): p. 2535-2538. [CrossRef]
- Hassn, B.M., Securing the Connected World: A Review Paper of IoT Security Architecture, Challenges, and Emerging Solutions. Journal of Al-Qadisiyah for Computer Science and Mathematics, 2025. 17(2): p. 215–228-215–228. [CrossRef]
- Vaddadi, S.A. and S.E.V.S. Pillai. Fault-Tolerant Routing Strategies in Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks. in 2024 International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Communication Systems (ICICACS). 2024. IEEE.
- Karpurasundharapondian, P. and M. Selvi, A comprehensive survey on optimization techniques for efficient cluster based routing in WSN. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2024. 17(5): p. 3080-3093. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., W.H. Chan, E.L.M. Su, and Q. Diao, Multi-objective optimization for smart cities: a systematic review of algorithms, challenges, and future directions. PeerJ Computer Science, 2025. 11: p. e3042. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D. and V. Kushwaha, An Exploratory Study of Optimization Techniques for Congestion Control in Wireless Sensor Networks. Adhoc & Sensor Wireless Networks, 2024. 58.
- HC, H.K. and B. TG, DeepLight-RPL: Context-aware Adaptive RPL with Lightweight Deep Learning for Improving the QoS in Industrial IoT Application Scenarios. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering & Systems, 2025. 18(5).
- Wang, J., et al., Smart fault detection, classification, and localization in distribution networks: AI-driven approaches and emerging technologies. IEEE Access, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Rajput, M. and R. Yadav, Machine and Deep Learning Driven Energy Efficient Clustering in IOT-WSNs: A Review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Alsalamah, H.A. and W.N. Ismail, A Swarm-Based Multi-Objective Framework for Lightweight and Real-Time IoT Intrusion Detection. Mathematics, 2025. 13(15): p. 2522. [CrossRef]
- Rancea, A., I. Anghel, and T. Cioara, Edge computing in healthcare: Innovations, opportunities, and challenges. Future internet, 2024. 16(9): p. 329. [CrossRef]
| Ref. | Network Structure | Cross-Layer Optimization | Cluster Head Selection |
Energy Efficient | Multi-hop Routing | Mobility Support | Scalability | Research Gaps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [64] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Does not resolve issues such as cluster head failure, scalability in large WSNs, inefficiencies in random cluster creation, security vulnerabilities, and adaptation to dynamic network conditions. |
| [65] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Leaves gaps in real-time adaptivity, context-awareness, efficient data aggregation, and secure routing in highly mobile or variable IoT environments. |
| [66] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Does not address advanced machine learning integration, security enhancement, or cluster-head election reliability under dynamic loads. |
| [67] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Lacks mechanisms for security, handling intense mobility, and robust cross-layer integration needed for IoT/cloud deployments at scale. |
| [68] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | it does not fully address security, mobility, or energy balancing for nodes experiencing uneven traffic loads. |
| [71] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Limited attention to energy consumption minimization and security integration in real-world IoT deployments. |
| [72] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Needs further study in terms of energy efficiency, privacy, and data integrity under city-scale stress tests. |
| [73] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Gaps remain in generic applicability, integration of security features, and adaptation for unpredictable event patterns. |
| [74] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Lacks scalability, validation, and built-in adaptive defences against network attacks. |
| [75] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | research gaps persist in end-to-end security, practical real-time event responsiveness, and field deployment studies. |
| [76] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Leaves open challenges in lightweight cryptography, scalability, intra-cluster attacks, and context-aware adaptation. |
| [77] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Fails to integrate cross-layer optimizations and dynamic mobility handling for non-uniform event patterns. |
| [78] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Research still lacks real-world scalability tests, robust security features, and integration of AI for dynamic event response. |
| [79] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Gaps persist in achieving seamless energy balance during rapid node movements, secure data aggregation, and adaptive hierarchical architectures. |
| [80] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Real-world adaptability, collaborative energy scheduling, and robust, lightweight security are still underdeveloped. |
| [81] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Leaves gaps in fine-grained energy management, privacy engineering, and validation for city-scale networks. |
| [82] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Missing adaptive real-time mobility, next-gen security, and high-scale empirical deployment data. |
| [83] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Lacks comprehensive multi-objective balancing and deployment across other verticals (limited scope) |
| [84] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Fails to ensure lightweight, scalable privacy protocols are effective across diverse IoT hardware. |
| Ref. | Core technique |
Contribution | CH selection basis | Routing/data handling | Key features |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [93] | Hybrid PSO + Cuckoo search | QoS-aware clustering with multipath routing | Energy + QoS fitness | Clustered, multipath | QoS supported; static sink | The data transmission process can be optimized using a swarm intelligence algorithm. |
| [94] | Compressive data fusion + clustering | Relay-assisted compressive fusion | Weighted unequal clustering | Multi-hop relay clustering | Energy saving; static sink | Relay nodes are selected based on energy and path loss. Optimization methods could enhance relay selection by energy, distance, and traffic. |
| [95] | Hybrid optimization for ICWSNs | Information-centric clustering with edge | Energy + distance | Clustered, edge-assisted | Edge-enabled; static sink | Six factors were considered for optimal CH selection. Coordination among them is crucial; multi-attribute approaches are required. |
| [96] | Fuzzy multi-criteria + bio-inspired routing | Adaptive fuzzy CH selection | Energy + distance + rank | Clustered, multi-hop | Robust clustering | The use of bio-inspired algorithms instead of Fuzzy rules may optimize the selection of CHs in a better way. |
| [97] | Optimized fuzzy clustering | Uncertainty-aware CH election | Energy + distance (fuzzy rules) | Clustered | Improved energy balance | The use of bio-inspired algorithms instead of Fuzzy rules may optimize the selection of CHs in a better way. |
| [98] | Improved Harmony Search | Throughput-optimized clustering | Energy + distance | Multi-hop clustered | Throughput focus | The network can be clustered to improve energy efficiency further. |
| [99] | Hybrid fault-tolerant multipath | Fault-resilient multipath routing | Energy + reliability | Clustered, multipath | Fault tolerance | Using deep neural networks is resource-consuming, leading to computational complexity and overhead on resource-constrained sensors. |
| [100] | Emperor penguin optimization + enhanced flower pollination | Joint fault diagnosis + CH routing | Energy + behavior indicators | Clustered, multipath | Fault detection | CHs with high energy usage form multiple routes, potentially increasing CH energy consumption |
| [101] | Neuro-fuzzy routing | QoS-aware clustering | Learned fuzzy rules | Clustered | QoS supported | Using neural networks may cause additional computational overhead on the resource-constrained sensors. |
| [102] | Hybrid GSA + CSA | Multi-sink optimization | Energy + delay | Clustered, multi-sink | Multi-sink supported | Swarm optimization guarantees better CH election than weightage-based fitness functions. |
| [103] | Hybrid ABC + DE | Load-balanced clustering for mobile sinks | Avg. energy + delay | Clustered | Mobile sink supported | Mobile sink movement needs location and clock synchronization, inducing routing overhead. |
| [104] | Enhanced ACO | Cluster + mobile sink path optimization | CH + pheromone reinforcement | Clustered, mobile sink | Latency optimized | CHs can be selected using swarm intelligence algorithms for better optimization. |
| [105] | GAPSO + SVM | IDSS-based clustering for IoT layer | Energy + location (SVM aided) | Clustered | Localization aided | Multi-hop communication can provide more energy efficiency. |
| [106] | Mobile agent-assisted clustering | Lifetime extension for heterogeneous WSNs | Heterogeneous energy tiers | Clustered, agent forwarding | Reliability focus | Mobile agents have bloating issues problem |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





