Submitted:
15 October 2025
Posted:
21 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The successful implementation of Business Intelligence (BI) technologies in public transport relies primarily on the Internet for connectivity to facilitate real-time data transfer and communication within the vehicle or system. This contributes to service quality, and due to a positive influence on the environment, it is a sustainable solution. Beyond chatbots and digital assistants, Business Intelligence (BI) technologies can change the face of urban transportation. Equipped with BI and advanced analytics, transport networks will be able to offer better, timely, more personalized services that will enable better decision-making, reduce operational costs, and enhance sustainability. The aim of the paper is to describe the application of Business Intelligence tools in process enhancement at public transport companies with a focus on urban transportation. Integration of such technologies allows new decision-support strategies to be created that will add to sustainable solutions with a positive environmental footprint. More specifically, it investigates how data mining and machine learning, supported by low-cost, open-source tools like Weka and KNIME, can upgrade the processes of transport service providers. The study also investigates the incentives and benefits for companies in charge of providing safe urban transportation through the adoption of these technologies. These tools will help the companies increase their efficiency by reducing operational costs and hence improve the quality of the services. Finally, the results and incentives of transport organizations are presented in order to create applications that can be the main tool for improving decision-making by company management and developing supportive strategies that will lead to sustainable development and efficient urban transport systems.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Research Context
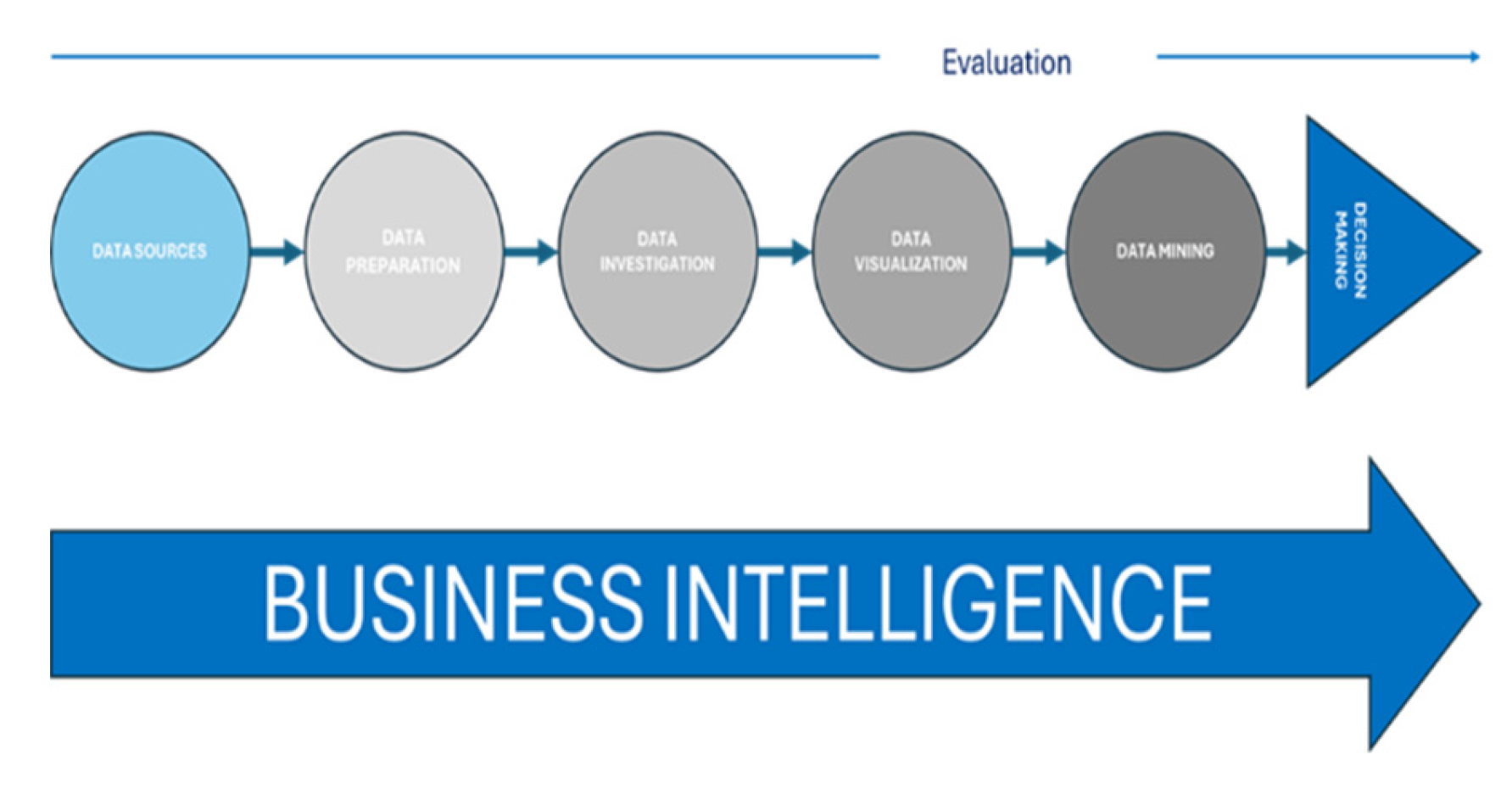
2.1. Business Intelligence: Overview and Implications
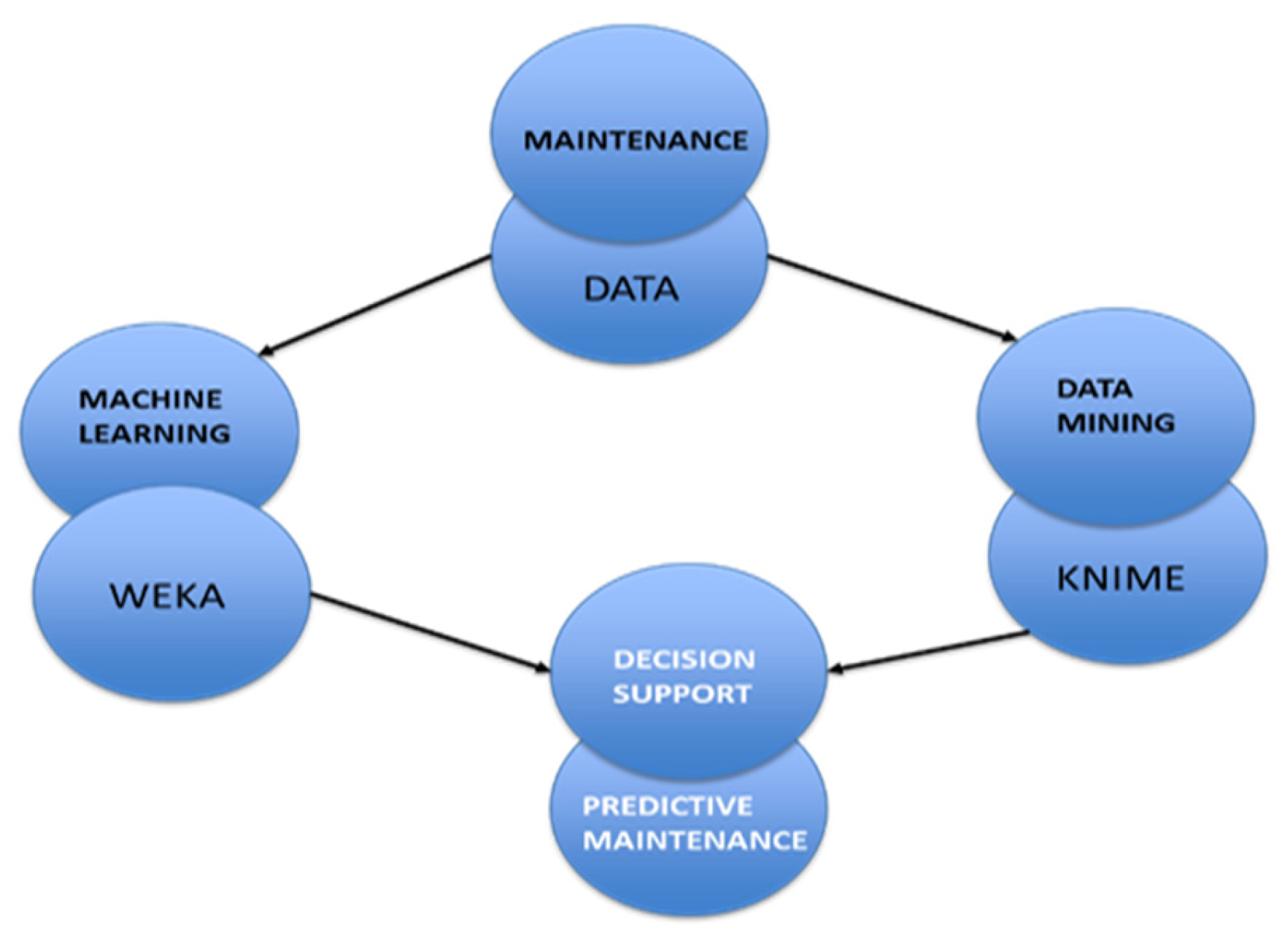
2.2. Smart Tools Business Intelligence
2.2.1. Machine Learning Tool – WEKA
2.2.2. Data Mining Tool – KNIME
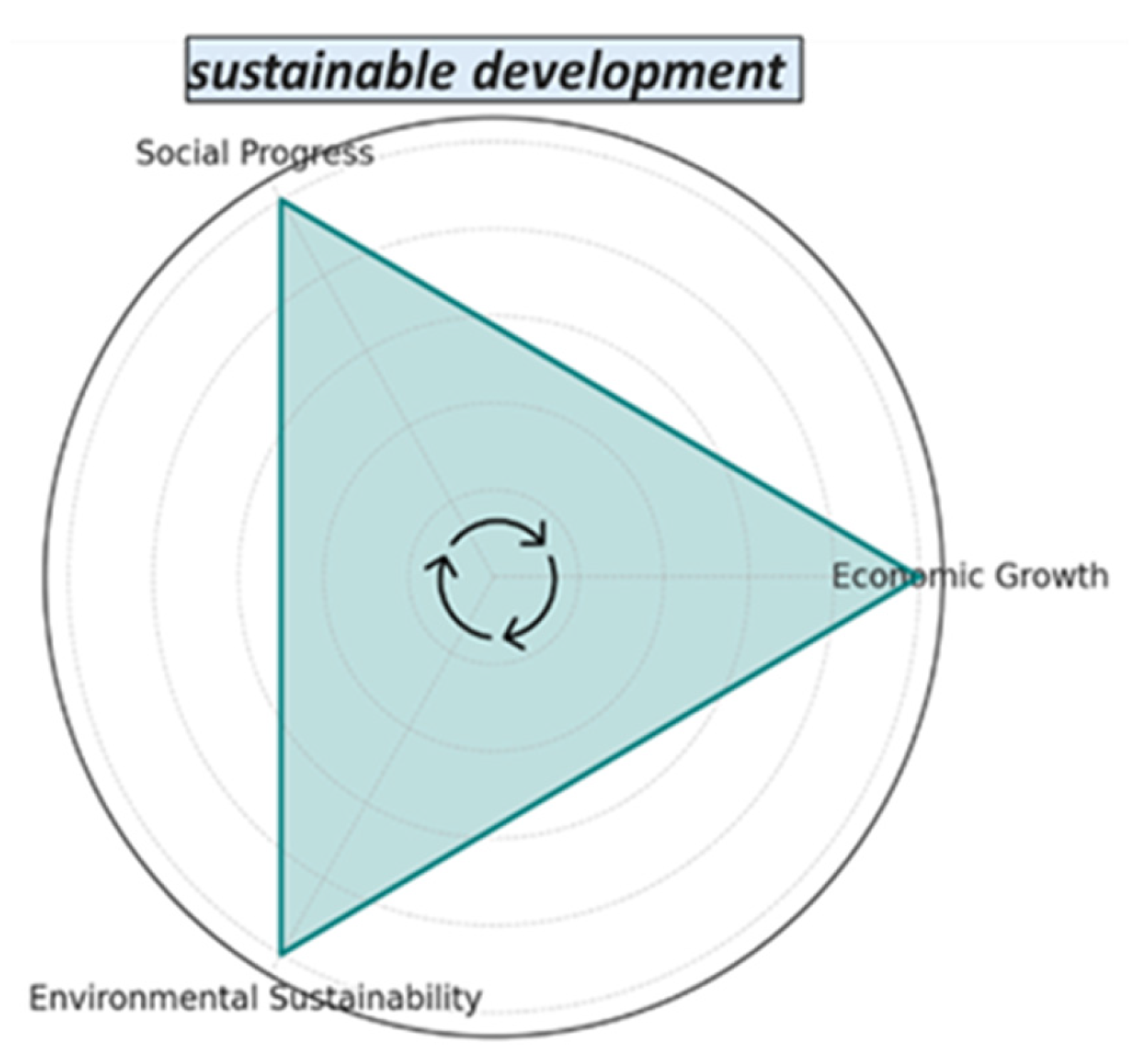
2.3. Sustainability
2.3.1. Definition of Sustainability
2.3.2. Principles of Sustainability
- Environmental integrity: It is about prudent conservation and use of planet processes and natural assets in a manner allowing future generations to access them.
- Economic Balance: It involves developing economies satisfying humans’ wants and requirements in a manner that does not exhaust planet assets.
2.3.2.1. Unsustainable Practices and Consequences
- Food Insecurity: Degraded lands will not produce enough food provisions.
- Climate Displacement: Climate change will displace millions and destroy livelihoods.
- Resource Conflicts: Inadequacies in such key requirements, including water and arable lands, can ignite discord.
2.3.2.2. Sustainability in Action
2.4. Smart Public Transport: Sustainable and Ecological Cities
3. Problems and Solutions for Urban Transportation Using Smart Tools ΒΙ
3.1. Problems Facing the Public Transport Organizations
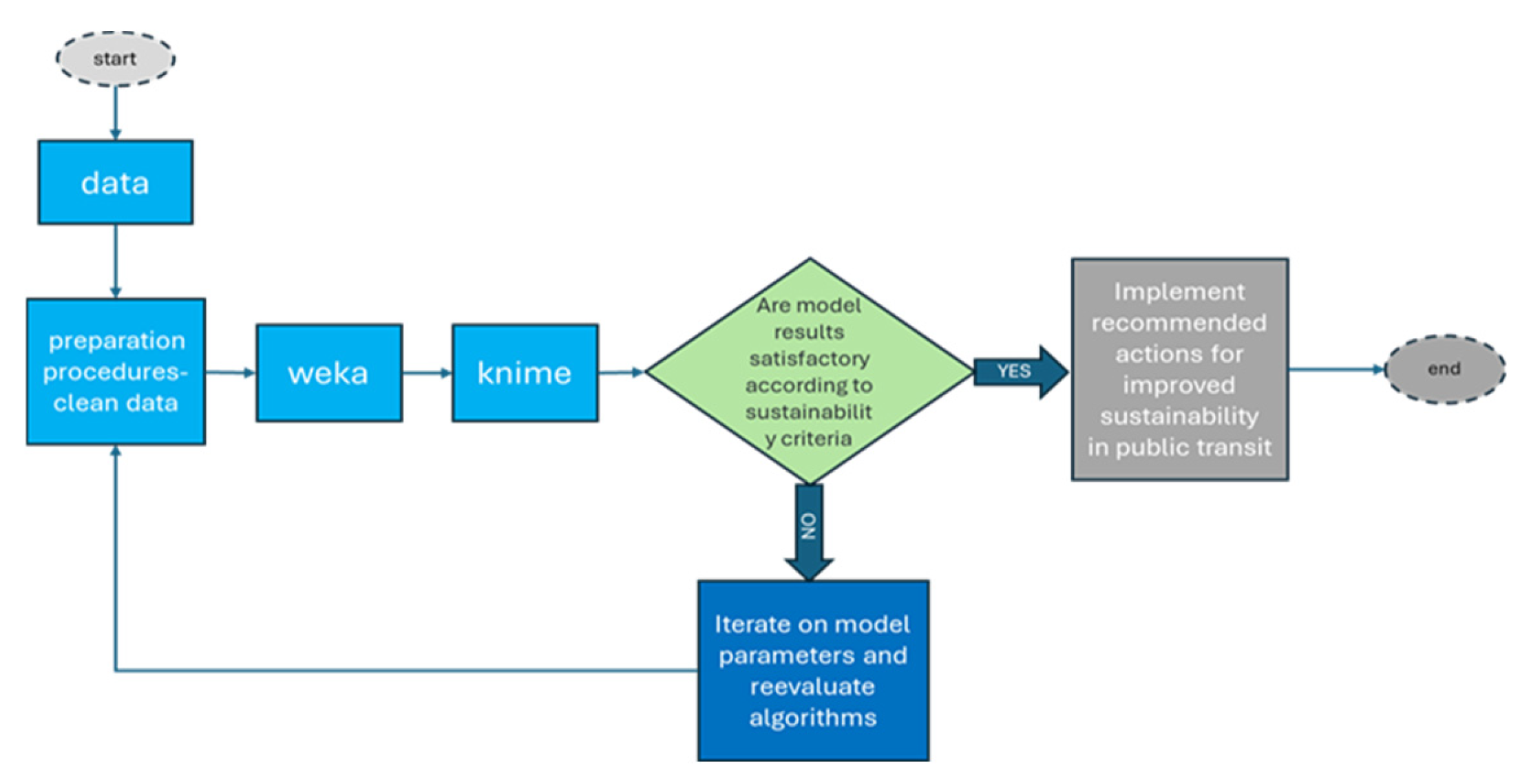
3.2. Using KNIME and WEKA for Environment Friendly Transportation Solutions for the City
4. Analysis and Potential Directions
4.1. Discourse
4.2. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, N. Evaluating sustainable urban transport systems: A Review study for the identification of smart mobility indicators. Transactions on Transport Sciences 2021, 12, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavlutova, I.; Atstaja, D.; Grasis, J.; Kuzmina, J.; Uvarova, I.; Roga, D. Urban Transportation Concept and Sustainable Urban Mobility in Smart Cities: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, E.P.; Hinnig, M.P.F.; Costa, E.M.; Marques, J.S.; Bastos, R.C.; Yigitcanlar, T. Sustainable development of smart cities: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 2017, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-Hong Kuo, Janny M.Y. Leung, Yimo Yan a. Public transport for smart cities: Recent innovations and future challenges. European Journal of Operational Research 2023, 306, 1001–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Smart public transportation systems: A review of the literature. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2020, 120, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J. Generating a vision for smart sustainable cities of the future: A scholarly backcasting approach. European Journal of Futures Research 2019, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chiang, R.H.L.; Storey, V.C. Business Intelligence and Analytics: From Big Data to Big Impact. MIS Quarterly 2012, 36, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, Z.A. On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities. Cities 2019, 89, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Byrd, T.A. Big data analytics: Understanding its capabilities and potential benefits for healthcare organizations. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2018, 126, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröger, C.; Niedermann, F.; Mitschang, B. (2012) Data Mining-driven Manufacturing Process Optimization. Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, 4-6 July 2012, Corpus ID: 14461305.
- Rahim, A.; Hamizah, F.; Noor, N.M.; Abdullah, H.; Annanurov, B. Cost Minimization of Aircraft Critical Components for Planning and Maintenance Requirements. International Journal of Integrated Engineering 2020, 12, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayzid, S.M.; Mohamed, Y.; Al-Hussein, M. Prediction of Maintenance Cost for Road Construction Equipment: A Case Study. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering 2016, 43, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathas, Ilias; Papoutsidakis, Michail; Drosos, Christos. Business Intelligence and Machine Learning Methods for Predictive Maintenance in Greek railways. Open Journal of Applied Sciences. 2021, 11, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, A.; Maritati, V.; Galiano, A.; Birardi, V.; Pellicani, L. ESB Platform Integrating Knime Data Mining Tool Oriented on Industry 4.0 Based on Artificial Neural Network Predictive Maintenance. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence & Applications 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüttenberg, H.; Bartelheimer, C.; Beverungen, D. (2018) Designing Predictive Maintenance for Agricultural Machines. 26th European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2018), Portsmouth, Research Papers 153. https://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2018_rp/153.
- Rahmaoui, O.; Souali, K.; Ouzzif, M. Towards a Documents Processing Tool usIng Traceability Information Retrieval and Content Recognition through\ Machine Learning in a Big Data Context. Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal 2020, 5, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.; Nik Ibrahim, N.N.L.; Wan Abdul Karim Ghani, W.A.; Sani, N.S.; Hon, L.L. (2022). A hybrid P-graph and WEKA approach in decision-making: Waste conversion technologies selection. Tamkang University Press. [CrossRef]
- Shulajkovska, M.; Smerkol, M.; Noveski, G.; Gams, M. Enhancing Urban Sustainability: Developing an Open-Source AI Framework for Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 2670–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taques, Fernando & Chasco, Coro & Taques, Flávio. Integrating big data with KNIME as an alternative without programming code: an application to the PATSTAT patent database. Journal of Geographical Systems 2024, 1–31. [CrossRef]
- Mary, S.S.C.; Arun, C.J. (2024). Data Mining and Business Intelligence Trends. In: Poulose, J., Sharma, V., Maheshkar, C. (eds) Data-Driven Decision Making. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Du, Juan; Wang, Wenxin; Gao, Ray; hu, Min; Jiang, Haili. Sustainable Operations: A Systematic Operational Performance Evaluation Framework for Public–Private Partnership Transportation Infrastructure Projects. Sustainability. 2023, 15, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, Syed Muhammad. (2016). METHODS OF DATA COLLECTION. in book: Basic Guidelines for Research: An Introductory Approach for All Disciplines (pp.201-275) Edition: FirstChapter: 9Publisher: Book Zone Publication, Chittagong-4203, Bangladesh.
- Gad-Elrab, A.A. Modern business intelligence: Big data analytics and artificial intelligence for creating the data-driven value. E-Business-Higher Education and Intelligence Applications 2021, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farayola, Oluwatoyin; Olatoye, Funmilola; Chinwe, Nnabugwu; Daraojimba, Chibuike. BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE TRANSFORMATION THROUGH AI AND DATA ANALYTICS. Engineering Science & Technology Journal. 2023, 4, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Shetty, A.; Jain, A.; Dhanare, R.K. (2021). A Comparative Analysis on Various Business Intelligence (BI), Data Science and Data Analytics Tools. In 2021 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI) (pp. 1- 11). IEEE. Available at: https://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICCCI50826.2021.9402226. [CrossRef]
- Olszak, C.M.; Zurada, J.; Cetindamar, D. Business intelligence & big data for innovative and sustainable development of organizations. Information Systems Management 2021, 38, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, R.; Ivanova, M.; Peycheva, T.; Nikolov, Y. (2021). Modelling in support of decision making in business intelligence. In Integration Challenges for Analytics, Business Intelligence, and Data Mining (pp. 115-144). IGI Global. [online] 2021, pp. 61-76. Available at: https://dx.doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-5781-5.ch006.
- Asha Kiranmai, S.; Jaya Laxmi, A. Data Mining for Classification of Power Quality Problems Using WEKA and the Effect of Attributes on Classification Accuracy. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems 2018, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, E.G.; Kulkarni, R.B. Article: Weka Powerful Tool in Data Mining. IJCA Proceedings on National Seminar on Recent Trends in Data RTDM 2016, 2, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Feltrin, L. KNIME an Open Source Solution for Predictive Analytics in the Geosciences [Software and Data Sets]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine 2015, 3, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagla, B.; Wiswedel, B.; Coppée, J.-Y. Extending KNIME for Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2907–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlman, T. , & Farrington, J. What is Sustainability? Sustainability 2010, 2, 3436–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, Meetika, (2012). A Study on Sustainability and Sustainable Development: Detailed Explanation of the Terms and Its Evolution, Concept and Meaning Including Discussion on How to Enable Sustainable Development. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3652024 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3652024. [CrossRef]
- European Union https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=LEGISSUM:sustainable_development.
- Cairns,Jr, John. (2001). Ethics in environmental politics and sustainable use of the planet. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics. 1. 10.3354/esep001038. [CrossRef]
- Timo Busch, Carolin Weber, and Theresa Sophie Rötzel, (2024) Sustainability Transformation or Utopia? The Role of Organizational Practices for Resolving Tensions. Proceedings. [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Barrera, M.E.; Alfaro-Aucca, C.; Pacheco-Mendoza, J.; et al. Bibliometric analysis of prominent topics in global scientific production on sustainable development goals in Scopus (2013–2022). Discov Sustain 2025, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Desul, S.; Santos, C.A.G.; et al. A bibliometric analysis of sustainable development goals (SDGs): a review of progress, challenges, and opportunities. Environ Dev Sustain 2024, 26, 11101–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirone, M. The formation of a field: sustainability science and its leading journals. Scientometrics 2024, 129, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfirević, N.; Malešević Perović, L.; Mihaljević Kosor, M. Productivity and Impact of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)-Related Academic Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Jining, D.; Shoukat, K.; Shoukat, M.U.; Nawaz, S.A. A Human–Machine Interaction Mechanism: Additive Manufacturing for Industry 5. 0—Design and Management. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Desul, S.; Santos, C.A.G.; et al. A bibliometric analysis of sustainable development goals (SDGs): a review of progress, challenges, and opportunities. Environ Dev Sustain 2024, 26, 11101–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirone, M. The formation of a field: sustainability science and its leading journals. Scientometrics 2024, 129, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Rallings, A.M.; Espinoza, V.; Luo, P.; Duan, W.; Peng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Viers, J.H. (2021). Flowing from East to West: A bibliometric analysis of recent advances in environmental flow science in China. Ecological Indicators. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, Aayesha & Idrisi, Dr. M. Smart and Sustainable Public Transportation - A Need of Developing Countries. International Journal of Networked and Distributed Computing 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Wasif, Mumtaz & Sano, Nadeem. (2025). Smart City Development and AI: Revolutionizing Urban Infrastructure Optimization for Efficient Transportation Planning.
- E, IKUGBE & T., HASSAN & MATHEW, ANIH. (2025). AN APPRAISAL OF THE IMPACTS OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY ON SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT. International Journal of African Innovation and Multidisciplinary Research. [CrossRef]
- Sezer, Nurettin & Batur, Irfan & Arı, Ibrahim. (2016). Green Mobility Application (GMAP). [CrossRef]
- Torre-Bastida, A.I.; Del Ser, J.; Laña, I.; Ilardia, M.; Bilbao, M.N.; Campos-Cordobés, S. Big Data for transportation and mobility: recent advances, trends and challenges. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 12, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwandi,; Pratomo, Soni; Febri, Cynthia; Indarti, Sri; ., Taufiqurrachman; Sari, Avid. PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS FOR SUSTAINABLE URBAN DEVELOPMENT: LESSONS FROM INDONESIAN CITIES. VISIONER Jurnal Pemerintahan Daerah di Indonesia. 2024, 16, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverry, Juan & Ibañez, Ana & Moya, Andres & Hillón, Luis. The Economics of TransMilenio, a Mass Transit System for Bogota. Journal of LACEA Economia 2004, 5. [CrossRef]
- Chin, Hoong & Foong, Kok. (2006). Issues in transportation planning - the Singapore Experience. [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, A. The Impact of Vehicle Ownership on Carbon Emissions in the Transportation Sector. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhu, L.Q.; Chen, H.R.; Kong, X.R.; Pan, F.; Yang, H. “Forecasting of Emission Co-reduction of Greenhouse Gases and Pollutants for the Road Transport Sector in Lanzhou Based on the LEAP Model. ” Huan Jing Ke Xue 2022, 43, 3386–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Bo & Sun, Yefei & Chen, Qingxiang & Wang, Zhaohua, (2018) “Determinants analysis of carbon dioxide emissions in passenger and freight transportation sectors in China,” Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, Elsevier, vol. 47(C), pages 127-132. [CrossRef]
- Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. Development of a road transport emission inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area: Effects of important parameters. The Science of the total environment 2014, 505C, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdzik, B.; Wolniak, R.; Nagaj, R.; Žuromskaitė-Nagaj, B.; Grebski, W.W. The Influence of the Global Energy Crisis on Energy Efficiency: A Comprehensive Analysis. Energies 2024, 17, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.; Osman, A.I.; Chen, Z.; et al. Social, environmental, and economic consequences of integrating renewable energies in the electricity sector: a review. Environ Chem Lett 2023, 21, 1381–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, Tugce, and Jeremy J. Michalek. ”Effects of Regional Temperature on Electric Vehicle Efficiency, Range, and Emissions in the United States.”. Environmental Science & Technology 2015, 49, 3974–3980. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Zhihong, Yi Wang, Bo Liu, Bin Zhao, and Yangsheng Jiang. “Fuel Consumption and Transportation Emissions Evaluation of Mixed Traffic Flow with Connected Automated Vehicles and Human-Driven Vehicles on Expressway.”. Energy 2021, 230, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Fang, J.; Liu, C. The effects of transportation infrastructure on urban carbon emissions. Applied Energy 2017, 196, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y. Influencing Factors and Decoupling Elasticity of China’s Transportation Carbon Emissions. Energies 2018, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddoha, M.; Kashem, M.A.; Nasir, T. A Review of Transportation 5.0: Advancing Sustainable Mobility Through Intelligent Technology and Renewable Energy. Future Transportation 2025, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adão, B.; Narajabad, B.; Temzelides, T. Renewable technology adoption costs and economic growth. Energy Economics 2024, 129, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demartini, M.; Ferrari, M.; Govindan, K.; Tonelli, F. The transition to electric vehicles and a net zero economy: A model based on circular economy, stakeholder theory, and system thinking approach. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 410, 137031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.; Reed, J.; Sunderland, T. Bridging funding gaps for climate and sustainable development: Pitfalls, progress and potential of private finance. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Peláez, R.; Ochoa-Brust, A.; Rivera, S.; Félix, V.G.; Ostos, R.; Brito, H.; Félix, R.A.; Mena, L.J. Role of Digital Transformation for Achieving Sustainability: Mediated Role of Stakeholders, Key Capabilities, and Technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikci, Y.; Kabadurmus, O. Barriers to the adoption of the mobility-as-a-service concept: The case of Istanbul, a large emerging metropolis. Transport Policy 2022, 129, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaere, H.; Basu, S.; Macharis, C.; et al. Barriers and opportunities for developing, implementing, and operating inclusive digital mobility services. European Transport Research Review 2024, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforiadis, A.; Tsavdari, D.; Mizaras, V.; Ayfantopoulou, G. Identifying Barriers and Expectations in MaaS: Users’ and Stakeholders’ Perspective. Future Transportation 2023, 3, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelti, F.; Allouhi, A.; Tabet Aoul, K.A. Transition Paths towards a Sustainable Transportation System: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıyık, C.; Abareshi, A.; Paz, A.; Arce Ruiz, R.; Battarra, R.; Rogers, C.D.F.; Lizarraga, C. Smart mobility adoption: A review of the literature. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 2021, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathuri, Naveena. IoT-Enabled Cross-Platform Applications for Real-Time Logistics Monitoring. International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science. Engineering and Information Technology. 2024, 10, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.W.; Saad, S.; Ammad, S.; Rasheed, K.; Jamal, Q. Smart Infrastructure and AI. In AI. In AI in Material Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 193–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan, Karthika. (2023). Robotic Process Automation: Streamlining Operations and Revolutionizing Traditional Banking Processes. Journal of Artificial Intelligence & Cloud Computing. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Bejinaru, Ruxandra; Marian-Vladut, Toma. Enhancing Business Operations Through Microlearning, BPM and RPA. Proceedings of the International Conference on Business Excellence. 2024, 18, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhosseinian, Ashkan & Khalifeh, Ahmad. (2012). Cloud Computing and Sustainability: Energy Efficiency Aspects. [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Bower, A. Cyber security and the disaster resilience framework”. International Journal of Disaster Resilience in the Built Environment 2020, 11, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Reskilling and Upskilling the Future-ready Workforce for Industry 4. 0 and Beyond. Inf Syst Front 2024, 26, 1697–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| The Impact of Business Intelligence on Public Transportation | |
| Sphere of influence |
Description |
| Optimization & Traffic Management | GPS & traffic data analysis for efficient routes, fuel & emissions reduction |
| Energy Consumption Reduction | Identifying efficient vehicles, transitioning to electric transport & consumption analysis. |
| Demand Management During Peak Hours | Demand forecasting, schedule adjustments, congestion reduction & fuel savings. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Vehicle data analysis to predict failures, reduce costs & enhance reliability. |
| Waste Minimization & Recycling | Tracking & managing transport waste, promoting reuse & recycling. |
| Enhancing Public Transport | Passenger pattern analysis, service improvement, reduced private car dependency & emissions. |
| Economic benefits | |
| Component | Description |
| Economically Viable Solutions | Open-source BI tools (KNIME, WEKA) enable cost-effective transport operations. |
| Data Analysis Capability | Allows analysis of large datasets without high financial investment. |
| Adherence to Aims | Supports goals by reducing reliance on expensive proprietary software. |
| Enhanced Decision-Making | Improve decision-making while keeping operating costs low |
| Economic & Monetary Benefits | Simplifies financial incentives for business and investment. |
| Future Technological Strategies [73,74,75,76,77,78,79] | |
| Key Technological Strategy | Description |
| Phygital Experience Platform | IoT-enabled platform for real-time passenger engagement. |
| Data and AI Hub | Central AI hub to optimize data architecture and AI-driven processes. |
| Process Optimization | Uses BPM & RPA to enhance efficiency and streamline operations. |
| Standardization of Enterprise Systems | Replace outdated systems with cloud solutions for efficiency and sustainability. |
| Operational Resilience | Strengthens cybersecurity, disaster recovery, and business continuity. |
| Talent Development | Upskilling programs to support digital innovation and adaptability. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





