Submitted:
16 October 2025
Posted:
17 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Basis of Infrared Thermal Imaging
Infrared Imaging of the Peripheral Circulation
Discussion
- (i)
- they provide a straightforward, principled and mechanistic understanding of the functional consequences of lowered blood flow, and
- (ii)
- they are relatively inexpensive to implement: common cameras with software and interfaces to laptops or smartphones are available for £200-400.
- (iii)
- Unlike other methods inflammation can be observed separately via raised temperatures, although we recognise that this can be a confounder relative to the spatially lowered temperature caused by dysregulation of the microcirculation, adding a certain interpretational complexity.
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, C.; Teboul, J.L. (2023) Hemodynamic monitoring: current practice and new perspectives. In The sepsis codex (Sa, M.B., Hidalgo, J.; Perez-Fernandez, J., eds.). pp. 75–87, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
- Munoz, C.J.; Lucas, A.; Williams, A.T.; Cabrales, P. A Review on Microvascular Hemodynamics: The Control of Blood Flow Distribution and Tissue Oxygenation. Crit Care Clin 2020, 36, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana Jimenez, C.E.A. (2023) Sepsis and Microcirculation. In The sepsis codex (Sa, M.B., Hidalgo, J.; Perez-Fernandez, J., eds.). pp. 29–34, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
- Slovinski, A.P.; Hajjar, L.A.; Ince, C. Microcirculation in Cardiovascular Diseases. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2019, 33, 3458–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.Y.; Cringle, S.J.; Yu, P.K.; Balaratnasingam, C.; Mehnert, A.; Sarunic, M.V.; An, D.; Su, E.N. Retinal capillary perfusion: Spatial and temporal heterogeneity. Prog Retin Eye Res 2019, 70, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Zhao, H.; Pretorius, E. (2025) Assessment of the impacts of fibrinaloid microclots on the microcirculation and endothelial function, using laser speckle and laser Doppler imaging. Preprints, 2025062239. [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. On the utility of nailfold capillaroscopy in detecting the effects of fibrinaloid microclots in diseases involving blood stasis. Immune Discovery 2025, 1, 10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. (2023) Are fibrinaloid microclots a cause of autoimmunity in Long Covid and other post-infection diseases? Biochem J. 480, 1217-1240. [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.M.; Kruger, A.; Proal, A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. The occurrence of hyperactivated platelets and fibrinaloid microclots in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS). Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, C.F.; de Oliveira, M.I.R.; Stafford, P.; Peake, N.; Kane, B.; Higham, A.; Singh, D.; Jackson, N.; Davies, H.; Price, D.; Duncan, R.; Tattersall, N.; Barnes, A.; Smith, D.P. (2024) Increased fibrinaloid microclot counts in platelet-poor plasma are associated with Long COVID. medRxiv, 2024.2004.2004.24305318. [CrossRef]
- Grixti, J.M.; Theron, C.W.; Salcedo-Sora, J.E.; Pretorius, E.; Kell, D.B. Automated microscopic measurement of fibrinaloid microclots and their degradation by nattokinase, the main natto protease. J Exp Clin Appl Chin Med 2024, 5, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Khan, M.A.; Kane, B.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Pretorius, E. Possible role of fibrinaloid microclots in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS): focus on Long COVID. J Personalised Medicine 2024, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Pretorius, E. Fibrinaloid Microclots and Atrial Fibrillation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Khan, M.A.; Pretorius, E. Fibrinaloid microclots in Long COVID: assessing the actual evidence properly. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2024, 8, 102566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Proteomic evidence for amyloidogenic cross-seeding in fibrinaloid microclots. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25, 10809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Some potential roles of fibrin amyloid (‘fibrinaloid’) microclots in fibromyalgia syndrome. Int J Adv Med Clin Therapeut 2024, 2. [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E.; Zhao, H. A direct relationship between ‘blood stasis’ and fibrinaloid microclots in chronic, inflammatory and vascular diseases, and some traditional natural products approaches to treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Kell, D.B. A perspective on how fibrinaloid microclots and platelet pathology may be applied in clinical investigations. Semin Thromb Hemost 2024, 50, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, E.F.J.; Ammer, K. Infrared thermal imaging in medicine. Physiol Meas 2012, 33, R33–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Howell, K. Microvascular imaging: techniques and opportunities for clinical physiological measurements. Physiol Meas 2014, 35, R91–R141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tattersall, G.J. Infrared thermography: A non-invasive window into thermal physiology. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 2016, 202, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, E.; Gethin, G.; Flynn, L.; Watterson, D.; O’Connor, G.M. Enhanced thermal imaging of wound tissue for better clinical decision making. Physiol Meas 2017, 38, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrap, M.J.M.; Hempel de Ibarra, N.; Whitney, H.M.; Rands, S.A. Reporting of thermography parameters in biology: a systematic review of thermal imaging literature. R Soc Open Sci 2018, 5, 181281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.R.; Hamblin, M.R. Biological effects and medical applications of infrared radiation. J Photochem Photobiol B 2017, 170, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, L.; Brady, J.; Kincaid, C.M.; Torres, A.E.; Lim, H.W. The effects of infrared radiation on the human skin. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2023, 39, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzezinski, R.Y.; Rabin, N.; Lewis, N.; Peled, R.; Kerpel, A.; Tsur, A.M.; Gendelman, O.; Naftali-Shani, N.; Gringauz, I.; Amital, H.; Leibowitz, A.; Mayan, H.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Heller, E.; Shechtman, L.; Rogowski, O.; Shenhar-Tsarfaty, S.; Konen, E.; Marom, E.M.; Ironi, A.; Rahav, G.; Zimmer, Y.; Grossman, E.; Ovadia-Blechman, Z.; Leor, J.; Hoffer, O. Automated processing of thermal imaging to detect COVID-19. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 17489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.R.; Kuckelman, J.P.; McClellan, J.M.; Derickson, M.J.; Phillips, C.J.; Marko, S.T.; Smith, J.P.; Eckert, M.J.; Martin, M.J. Smartphone-based mobile thermal imaging technology to assess limb perfusion and tourniquet effectiveness under normal and blackout conditions. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2017, 83, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, E.Y.; Chandler, L.K.; Viviano, S.L.; Keith, J.D. Use of FLIR ONE Smartphone Thermography in Burn Wound Assessment. Ann Plast Surg 2018, 80, S236–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doremalen, R.F.M.; van Netten, J.J.; van Baal, J.G.; Vollenbroek-Hutten, M.M.R.; van der Heijden, F. Validation of low-cost smartphone-based thermal camera for diabetic foot assessment. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019, 149, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, O.; Brzezinski, R.Y.; Ganim, A.; Shalom, P.; Ovadia-Blechman, Z.; Ben-Baruch, L.; Lewis, N.; Peled, R.; Shimon, C.; Naftali-Shani, N.; Katz, E.; Zimmer, Y.; Rabin, N. (2024) Smartphone-based detection of COVID-19 and associated pneumonia using thermal imaging and a transfer learning algorithm. J Biophotonics, e202300486. [CrossRef]
- Hudson, T.; Hogue, E.; Mullner, D.; Herrera, F.; Scomacao, I. The Utility of Smartphone-Based Thermal Imaging in the Management and Monitoring of Microvascular Flap Procedures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann Plast Surg 2023, 90, S420–S425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, O.; Kustryn, T.; Nasinnyk, I.; Nevska, A.; Guzun, O.; Korol, A.; Pasyechnikova, N. Application of smartphone-based infrared thermography devices for ocular surface thermal imaging. Med Eng Phys 2024, 130, 104212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, V.; Staffa, E.; Pokorna, J.; Simo, A. Assessing detector stability and image quality of thermal cameras on smartphones for medical applications: a comparative study. Med Biol Eng Comput 2025, 63, 2707–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madian, I.M.; Sherif, W.I.; El Fahar, M.H.; Othman, W.N. The use of smartphone thermography to evaluate wound healing in second-degree burns. Burns 2025, 51, 107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Huang, R.; He, X.; Tang, L.; Ma, X. Advances in Machine Learning-Aided Thermal Imaging for Early Detection of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. Biosensors (Basel) 2024, 14, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterns, E.E.; Zee, B.; SenGupta, S.; Saunders, F.W. Thermography. Its relation to pathologic characteristics, vascularity, proliferation rate, and survival of patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Cancer 1996, 77, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagavathiappan, S.; Saravanan, T.; Philip, J.; Jayakumar, T.; Raj, B.; Karunanithi, R.; Panicker, T.M.R.; Korath, M.P.; Jagadeesan, K. Infrared thermal imaging for detection of peripheral vascular disorders. J Med Phys 2009, 34, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateb, B.; Yamamoto, V.; Yu, C.; Grundfest, W.; Gruen, J.P. Infrared thermal imaging: a review of the literature and case report. Neuroimage 2009, 47 Suppl 2, T154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, S.W.; Kim, K.; O’Donnell, M. Thermal strain imaging: a review. Interface Focus 2011, 1, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, B.B.; Bagavathiappan, S.; Jayakumar, T.; Philip, J. Medical applications of infrared thermography: A review. Infrared Phys Technol 2012, 55, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, S.; Gallese, V.; Merla, A. Thermal infrared imaging in psychophysiology: potentialities and limits. Psychophysiology 2014, 51, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Sánchez, E.; Vergara-Hernández, C.; Cibrián, R.M.; Salvador, R.; Sanchis, E.; Codoñer-Franch, P. Infrared thermal imaging in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014, 203, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardone, D.; Merla, A. New Frontiers for Applications of Thermal Infrared Imaging Devices: Computational Psychopshysiology in the Neurosciences. Sensors (Basel) 2017, 17, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LokeshBabu, D.S. Jeyakumar, S; Vasant, P.J.; Sathiyabarathi, M.; Manimaran, A.; Kumaresan, A.; Pushpadass, H.A.; Sivaram, M.; Ramesha, K.P.; Kataktalware, M.A.; Siddaramanna, *!!! REPLACE !!!*. Monitoring foot surface temperature using infrared thermal imaging for assessment of hoof health status in cattle: A review. J Therm Biol 2018, 78, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardasca, R.; Magalhaes, C.; Silva, P.; Abreu, P.; Mendes, J.; Restivo, M.T. Biomedical musculoskeletal applications of infrared thermal imaging on arm and forearm: A systematic review. J Therm Biol 2019, 82, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalidou, A.; Ali, N.; Sekulic, S.; Downe, S. Thermal imaging applications in neonatal care: a scoping review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Awale, R.N. Thermal Imaging - An Emerging Modality for Breast Cancer Detection: A Comprehensive Review. J Med Syst 2020, 44, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Formenti, D.; Cardone, D.; Filippini, C.; Merla, A. Regions of interest selection and thermal imaging data analysis in sports and exercise science: a narrative review. Physiol Meas 2021, 42, 08TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, G.; Capone, G.; Frize, M.; Zaffagnini, S.; Candrian, C.; Filardo, G. Infrared Thermography for the Evaluation of Inflammatory and Degenerative Joint Diseases: A Systematic Review. Cartilage 2021, 13, 1790S–1801S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesztyüs, D.; Brucher, S.; Kesztyüs, T. Use of infrared thermography in medical diagnostics: a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajakusumah, T.M.; Candrawinata, V.S.; Ho, J.P.; Herman, H.; Lukman, K.; Lesmana, R. The predictive value of infrared thermal imaging (IRT) for peripheral artery disease: A systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023, 102, e35639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesztyüs, D.; Brucher, S.; Wilson, C.; Kesztyüs, T. Use of Infrared Thermography in Medical Diagnosis, Screening, and Disease Monitoring: A Scoping Review. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 59, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridberg, M.; Bafor, A.; Iobst, C.A.; Laugesen, B.; Jepsen, J.F.; Rahbek, O.; Kold, S. The role of thermography in assessment of wounds. A scoping review. Injury 2024, 55, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persiya, J.; Sasithradevi, A. Thermal mapping the eye: A critical review of advances in infrared imaging for disease detection. J Therm Biol 2024, 121, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, M.N.; Ali, M.R.; Samsuzzaman Kabir, M.S.N.; Karim, M.R.; Ahmed, S.; Kyoung, H.; Kim, G.; Chung, S.O. Thermal imaging and computer vision technologies for the enhancement of pig husbandry: a review. J Anim Sci Technol 2024, 66, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, S.A.; Divall, P.; Thompson, J.P.; Charlton, M. Uses of infrared thermography in acute illness: a systematic review. Front Med (Lausanne) 2024, 11, 1412854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Jin, S.; Piao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, N.; Yao, H. Infrared thermography in clinical practice: a literature review. Eur J Med Res 2025, 30, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzari, S.; Pili, M.P.; Celik, E.; Lucchin, S.; Provenzi, L. Infrared Thermal Imaging (ITI), a Non-invasive Window Into Early Emotion Regulation: A Systematic Review. Dev Psychobiol 2025, 67, e70071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniga, M.; Sultana, A.; Alexandrescu, B.; Orzan, O. Towards an integrated imaging for melanoma diagnosis: A review of multispectral, hyperspectral, and thermal technologies with preliminary system development. Comput Biol Med 2025, 185, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.; Salih, S.; Turner, B.R.H.; Onida, S.; Davies, A.H. Thermal imaging as a diagnostic tool for superficial venous insufficiency - a systematic review. Phlebology 2025, 40, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verduzco-Mendoza, A.; Olmos-Hernández, A.; Bueno-Nava, A.; Villanueva-García, D.; Dominguez-Oliva, A.; Avila-Luna, A.; Mora-Medina, P.; Gálvez-Rosas, A.; Hernández-Ávalos, I.; Casas-Alvarado, A.; Garnica, M.A.; Mota-Rojas, D. Thermal imaging in biomedical research: a non-invasive technology for animal models. Front Vet Sci 2025, 12, 1544112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merla, A.; Romani, G.L.; Tangherlini, A.; Di Romualdo, S.; Proietti, M.; Rosato, E.; Aversa, A.; Salsano, F. Penile cutaneous temperature in systemic sclerosis: a thermal imaging study. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2007, 20, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, E.S.; Chekh, V.; Carranza, C.; Burge, M.R.; Edwards, A.; McGrew, E.; Zamora, G.; Soliz, P. Computational basis for risk stratification of peripheral neuropathy from thermal imaging. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2012, 2012, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhoff, M.D.; Wu, Y.; Huygen, F.J.; Schouten, A.C.; van der Helm, F.C.; Niehof, S.P. Reproducibility of axon reflex-related vasodilation assessed by dynamic thermal imaging in healthy subjects. Microvasc Res 2016, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnowski, M. Infrared thermal imaging in connective tissue diseases. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennert, J.; Wiesinger, I.; Beyer, L.P.; Schicho, A.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P.; Jung, E.M. Color coded perfusion analysis and microcirculation imaging with contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) for post-interventional success control following thermal ablative techniques of primary and secondary liver malignancies. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2019, 73, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.; Loughin, C.; Marino, D.; Leyva, F.; Dewey, C.; Umbaugh, S.; Lesser, M. Medical infrared thermal imaging of canine appendicular bone neoplasia. BMC Vet Res 2019, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perpetuini, D.; Filippini, C.; Zito, M.; Cardone, D.; Merla, A. Altered Microcirculation in Alzheimer’s Disease Assessed by Machine Learning Applied to Functional Thermal Imaging Data. Bioengineering (Basel) 2022, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, F. Thermal imaging today and its relevance to diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2010, 4, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, A.; Ismail, E.; Cardone, D.; Celletti, E.; Auriemma, M.; Sabatini, E.; Merla, A.; Amerio, P. Joint functional impairment and thermal alterations in patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A thermal imaging study. Microvasc Res 2015, 102, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinti, P.; Cardone, D.; Merla, A. Simultaneous fNIRS and thermal infrared imaging during cognitive task reveal autonomic correlates of prefrontal cortex activity. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 17471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perpetuini, D.; Cardone, D.; Bucco, R.; Zito, M.; Merla, A. Assessment of the Autonomic Response in Alzheimer’s Patients During the Execution of Memory Tasks: A Functional Thermal Imaging Study. Curr Alzheimer Res 2018, 15, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, G.A.; Singh, N.; Quiroga, E.; Tran, N.T. The Use of Smart Phone Thermal Imaging for Assessment of Peripheral Perfusion in Vascular Patients. Ann Vasc Surg 2018, 47, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Khan, A.Y.; Michael, S.G.; Tankha, P.; Tokuno, H. Use of Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging in the Electromyography Clinic: A Case Series. Cureus 2019, 11, e4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbroja, H.; Kowalski, M.; Lubkowska, A. The Effect of Dry Carbon Dioxide Bathing on Peripheral Blood Circulation Measured by Thermal Imaging among Patients with Risk Factors of PAD. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Qian, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Ren, L. Early diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on infrared thermal imaging technology. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2021, 37, e3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.F.; Nijboer, T.S.; Kleiss, S.F.; El Moumni, M.; Bokkers, R.P.H.; Schuurmann, R.C.L.; de Vries, J.P.M. Determination of Changes in Tissue Perfusion at Home with Hyperspectral and Thermal Imaging in the First Six Weeks after Endovascular Therapy in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaidachnyi, A.; Mayskov, D.; Fomin, A.; Zaletov, I.; Skripal, A. Separate extraction of human eccrine sweat gland activity and peripheral hemodynamics from high- and low-quality thermal imaging data. J Therm Biol 2022, 110, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergilio, M.M.; Gomes, G.; Aiello, L.M.; Fontana, M.; Aldred, A.; Ribeiro, J.A.S.; Gabbi, T.V.B.; Leonardi, G.R. Evaluation of skin using infrared thermal imaging for dermatology and aesthetic applications. J Cosmet Dermatol 2022, 21, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiss, S.F.; Ma, K.F.; El Moumni, M.; Ünlu, Ç.; Nijboer, T.S.; Schuurmann, R.C.L.; Bokkers, R.P.H.; de Vries, J.P.M. Detecting Changes in Tissue Perfusion With Hyperspectral Imaging and Thermal Imaging Following Endovascular Treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease. J Endovasc Ther 2023, 30, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakarinen, T.; Joutsen, A.; Oksala, N.; Vehkaoja, A. Assessment of chronic limb threatening ischemia using thermal imaging. J Therm Biol 2023, 112, 103467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabba, A.; Panasiti, M.S.; Scattolin, M.; Spitaleri, M.; Porciello, G.; Aglioti, S.M. The thermoception task: a thermal imaging-based procedure for measuring awareness of changes in peripheral body temperature. J Neurophysiol 2023, 130, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bergmann, J.H.M. Non-Contact Infrared Thermometers and Thermal Scanners for Human Body Temperature Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Sensors (Basel) 2023, 23, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanin, A.; Fekry, R.; Mostafa, M.; Kasem, S.; Eissa, A.; Mohamed, H.; Raafat, H. The use of thermal imaging for evaluation of peripheral tissue perfusion in surgical patients with septic shock. BMC Anesthesiol 2024, 24, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Ogi, A.; Villanueva-Garcia, D.; Hernandez-Avalos, I.; Casas-Alvarado, A.; Dominguez-Oliva, A.; Lendez, P.; Ghezzi, M. Thermal Imaging as a Method to Indirectly Assess Peripheral Vascular Integrity and Tissue Viability in Veterinary Medicine: Animal Models and Clinical Applications. Animals (Basel) 2024, 14, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Song, X.; He, J.; Liang, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, W. Thermal imaging-based core peripheral temperature difference measurement for neonatal monitoring in the NICU. Biomed Opt Express 2025, 16, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnawi, A.; Chhikara, P.; Tekchandani, R.; Kumar, N.; Alzahrani, B. Artificial intelligence-enabled Internet of Things-based system for COVID-19 screening using aerial thermal imaging. Future Gener Comput Syst 2021, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino Antunes, A.C.; Aldred, A.; Tirado Moreno, G.P.; de Souza Ribeiro, J.A.; Brandao, P.E.; Barone, G.T.; Conselheiro, J.A.; Goulart, A.C.; Desuo, I.C.; Gomes, G. Potential of using facial thermal imaging in patient triage of flu-like syndrome during the COVID-19 pandemic crisis. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0279930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Jimenez, M.A.; Loza-Gonzalez, V.M.; Kolosovas-Machuca, E.S.; Yanes-Lane, M.E.; Ramirez-GarciaLuna, A.S.; Ramirez-GarciaLuna, J.L. Diagnostic accuracy of infrared thermal imaging for detecting COVID-19 infection in minimally symptomatic patients. Eur J Clin Invest 2021, 51, e13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Filippini, C.; Cardone, D.; Merla, A. An Overview of Thermal Infrared Imaging-Based Screenings during Pandemic Emergencies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, R.X. Low-cost thermal imaging with machine learning for non-invasive diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of pneumonia. Infrared Phys Technol 2022, 123, 104201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksari, K.; Nguyen, T.; Hill, B.; Quang, T.; Perreault, J.; Gorti, V.; Malpani, R.; Blick, E.; Gonzalez Cano, T.; Shadgan, B.; Gandjbakhche, A.H. Review of the efficacy of infrared thermography for screening infectious diseases with applications to COVID-19. J Med Imaging (Bellingham) 2021, 8, 010901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesař, J.; Muzika, L.; Skála, J.; Kohlschütter, T.; Honner, M. Measurement and Processing of Thermographic Data of Passing Persons for Epidemiological Purposes. Sensors (Basel) 2023, 23, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutowski, M.; Klimkiewicz, J.; Rustecki, B.; Michalowski, A.; Paryz, K.; Lubas, A. Effect of Respiratory Failure on Peripheral and Organ Perfusion Markers in Severe COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Clin Med 2024, 13, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, C.M.; Moore, E.E.; Moore, H.B.; Neal, M.D.; Thomas, A.V.; Zackariya, N.; Zhao, J.; Zackariya, S.; Brenner, T.J.; Berquist, M.; Buckner, H.; Wiarda, G.; Fulkerson, D.; Huff, W.; Kwaan, H.C.; Lankowicz, G.; Laubscher, G.J.; Lourens, P.J.; Pretorius, E.; Kotze, M.J.; Moolla, M.S.; Sithole, S.; Maponga, T.G.; Kell, D.B.; Fox, M.; Gillespie, L.; Khan, R.Z.; Mamczak, C.N.; March, R.; Macias, R.; Bull, B.S.; Walsh, M.M. Immuno-thrombotic Complications of COVID-19: Implications for Timing of Surgery and Anticoagulation. Front Surg 2022, 9, 889999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobbelaar, L.M.; Venter, C.; Vlok, M.; Ngoepe, M.; Laubscher, G.J.; Lourens, P.J.; Steenkamp, J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 induces fibrin(ogen) resistant to fibrinolysis: implications for microclot formation in COVID-19. Biosci Rep 2021, 41, BSR20210611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobbelaar, L.M.; Kruger, A.; Venter, C.; Burger, E.M.; Laubscher, G.J.; Maponga, T.G.; Kotze, M.J.; Kwaan, H.C.; Miller, J.B.; Fulkerson, D.; Huff, W.; Chang, E.; Wiarda, G.; Bunch, C.M.; Walsh, M.M.; Raza, S.; Zamlut, M.; Moore, H.B.; Moore, E.E.; Neal, M.D.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Relative hypercoagulopathy of the SARS-CoV-2 Beta and Delta variants when compared to the less severe Omicron variants is related to TEG parameters, the extent of fibrin amyloid microclots, and the severity of clinical illness. Semin Thromb Haemost 2022, 48, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobler, C.; Maphumulo, S.C.; Grobbelaar, L.M.; Bredenkamp, J.; Laubscher, J.; Lourens, P.J.; Steenkamp, J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. COVID-19: The Rollercoaster of Fibrin(ogen), D-dimer, von Willebrand Factor, P-selectin and Their Interactions with Endothelial Cells, Platelets and Erythrocytes. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubscher, G.J.; Lourens, P.J.; Venter, C.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. TEG®, Microclot and Platelet Mapping for Guiding Early Management of Severe COVID-19 Coagulopathy. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Venter, C.; Laubscher, G.J.; Lourens, P.J.; Steenkamp, J.; Kell, D.B. Prevalence of readily detected amyloid blood clots in ‘unclotted’ Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19 plasma: A preliminary report. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2020, 19, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patroniti, N.; Bellani, G.; Maggioni, E.; Manfio, A.; Marcora, B.; Pesenti, A. Measurement of pulmonary edema in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 2005, 33, 2547–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.N.; Guo, H.P.; Wu, D.W. Comparison of quantitative computed tomography analysis and single-indicator thermodilution to measure pulmonary edema in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biomed Eng Online 2014, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteoli, S.; Finocchio, L.; Biagini, I.; Giacomelli, G.; Sodi, A.; Corvi, A.; Virgili, G.; Rizzo, S. A thermographic study on eyes affected by Age-related Macular Degeneration: Comparison among various forms of the pathology and analysis of risk factors. Infrared Ohys Technol 2016, 76, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidorf-Rosenblatt, H.; Landau-Part, D.; Moisseiev, J.; Alhalel, A.; Huna-Baron, R.; Skaat, A.; Pilus, S.; Levi, L.; Leshno, A. Ocular Surface Temperature Differences in Retinal Vascular Diseases. Retina 2022, 42, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulias-Cañizo, R.; Rodríguez-Malagón, M.E.; Botello-González, L.; Belden-Reyes, V.; Amparo, F.; Garza-Leon, M. Applications of Infrared Thermography in Ophthalmology. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Cardone, D.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Filippini, C.; Croce, P.; Zappasodi, F.; Rotunno, L.; Anzoletti, N.; Zito, M.; Merla, A. Autonomic impairment in Alzheimer’s disease is revealed by complexity analysis of functional thermal imaging signals during cognitive tasks. Physiol Meas 2019, 40, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Waal, G.M.; Engelbrecht, L.; Davis, T.; de Villiers, W.J.S.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Correlative Light-Electron Microscopy detects lipopolysaccharide and its association with fibrin fibres in Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 16798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobler, C.; van Tongeren, M.; Gettemans, J.; Kell, D.; Pretorius, E. Alzheimer-type dementia: a systems view provides a unifying explanation of its development. J Alz Dis 2023, 91, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Bester, J.; Kell, D.B. A bacterial component to Alzheimer-type dementia seen via a systems biology approach that links iron dysregulation and inflammagen shedding to disease. 2016, 53, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, E.; Bester, J.; Page, M.J.; Kell, D.B. The potential of LPS-binding protein to reverse amyloid formation in plasma fibrin of individuals with Alzheimer-type dementia. Frontiers Aging Neurosci 2018, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, L.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Iron Dysregulation and Dormant Microbes as Causative Agents for Impaired Blood Rheology and Pathological Clotting in Alzheimer’s Type Dementia. Front Neurosci 2018, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitoh, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ina, H.; Ofusa, Y.; Otagiri, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ono, K. Effects of lumbar sympathetic ganglion block for a patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J Anesth 2006, 20, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, A.; Horita, T.; Ohmuro, J.; Atsumi, T.; Ichikawa, K.; Tashiro, K.; Koike, T. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy in a patient with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 1999, 8, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de ASantos, C.M.; Quirino, P.G.C.; Rizzo, J.Â.; Medeiros, D.; de, A Ferreira, J.J.; Junior, M.A.C.V. Respiratory muscles’s thermographic analysis in asthmatic youth with and without bronchospasm induced by eucapnic voluntary hyperpnea. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2024, 44, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, O.P.; Boissevain, F.; Wittmann, H. Non-invasive measurement of the vascular dynamics of dermographism--comparative study in atopic and non-atopic subjects. J Dermatol 1991, 18, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, O.P.; Keller, J.; Boissevain, F. Abnormalities of cutaneous microcirculation in atopic eczematics. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1992, 176, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Miki, Y.; Kawatsu, T.; Matsuda, K. Thermographic venography in inflammatory lower leg nodules. Prog Clin Biol Res 1982, 107, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yahara, T.; Koga, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Deguchi, H.; Shirouzu, K. Relationship between microvessel density and thermographic hot areas in breast cancer. Surg Today 2003, 33, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, T.M.; Li, H.; Fisher, P.; Rosenblatt, R.; Dulaimy, K.; Li, S.; O’Hea, B.; Salvitti, M.; Geronimo, V.; Geronimo, C.; Jambawalikar, S.; Carvelli, P.; Weiss, R. Dynamic infrared imaging for the detection of malignancy. Phys Med Biol 2004, 49, 3105–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Little, R.F.; Vogel, A.; Aleman, K.; Wyvill, K.; Yarchoan, R.; Gandjbakhche, A.H. Quantitative assessment of tumor vasculature and response to therapy in kaposi’s sarcoma using functional noninvasive imaging. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2004, 3, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, O.A.; Ben-David, M.A.; Katz, E.; Zoltnik Kirshenabum, D.; Alezra, D.; Zimmer, Y.; Kelson, I.; Gannot, I. Thermal imaging as a tool for evaluating tumor treatment efficacy. J Biomed Opt 2018, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, C.; Vardasca, R.; Mendes, J. Recent use of medical infrared thermography in skin neoplasms. Skin Res Technol 2018, 24, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.M.; Vlok, M.; Proal, A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. (2024) Data-independent LC-MS/MS analysis of ME/CFS plasma reveals a dysregulated coagulation system, endothelial dysfunction, downregulation of complement machinery. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 23, 254. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, J.; He, X.; Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Fang, J.; Shao, X.; Fang, J. The difference in heat transport characteristics of the heart and lung meridians: A comparative study of COPD patients and healthy subjects. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, e23804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Jing, J.; Jiang, M.; Li, F. Difference of body surface temperature in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with different degree of airflow limitation. Heart Lung 2022, 52, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, H.; He, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, J.; Wu, Y.; Fang, J.; Shao, X.; Fang, J. Specificity for the correlation between the body surface and viscera in the pathological state of COPD: A prospective, controlled, and assessor-blinded trial. Front Physiol 2023, 14, 1051190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlmanns, S.; Reich-Schupke, S.; Schollemann, F.; Stucker, M.; Leonhardt, S.; Teichmann, D. Classification of chronic venous diseases based on skin temperature patterns. Physiol Meas 2021, 42, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávalos, M.P.A.; Brioschi, M.L.; da Rosa, S.E.; Brioschi, G.C.; Neves, E.B. (2023) Can Dual Infrared-Visual Thermography Provide a More Reliable Diagnosis of Perforator Veins and Reflux Severity? J Clin Med. 12. [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Cecchi, I.; Massara, C.; Rossi, D.; Radin, M.; Ladehesa, P.L.; Guinazu, F.; Rubini, E.; Foddai, S.G.; Alba, P.; Escudero, A.; Menegatti, E.; Roccatello, D. Thermography in systemic sclerosis patients and other rheumatic diseases: Diagnosis, disease activity assessment, and therapeutic monitoring. Autoimmun Rev 2020, 19, 102449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias de Lacerda, A.P.; Rodrigues de Andrade, P.; Kamonseki, D.H.; Parizotto, N.A.; Alves da Silva, A.S.; Bernardo de Medeiros, L.; de Almeida Ferreira, J.J. Accuracy of infrared thermography in detecting tendinopathy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport 2022, 58, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallathambi, N.; Bisaralli, R.; Naidu, S.P.; Mallikarjunaswamy, M.S.; Praveen, P.; Mamadapur, M. Clinical Application of Infrared Thermography in Rheumatic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Mediterr J Rheumatol 2025, 36, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, E.D.; Pilcher, M.F. Thermography in diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Br Med J 1973, 2, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, D.; Efsing, H.O.; Hallböök, T. (1977) Thermography. A noninvasive method for diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Arch Surg. 112, 600-604. [CrossRef]
- Aronen, H.J.; Suoranta, H.T.; Taavitsainen, M.J. (1981) Thermography in deep venous thrombosis of the leg. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 137, 1179-1182. [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, K.; Jacobsson, H.; Johnsson, H.; Löfsjögård-Nilsson, E. Thermography and plethysmography, a non-invasive alternative to venography in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. J Intern Med 1990, 228, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.R. Investigating deep venous thrombosis with infrared imaging. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 1998, 17, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Tang, Q.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, N. Effectiveness of digital infrared thermal imaging in detecting lower extremity deep venous thrombosis. Med Phys 2015, 42, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaydakov, M.E.; Diaz, J.A. Effectiveness of infrared thermography inthe diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis: anevidence-based review``. J Vasc Diagnost Intervent 2017, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhong, N.; Liu, G. Infrared thermal imaging and Doppler vessel pressurization ultrasonography to detect lower extremity deep vein thrombosis: Diagnostic accuracy study. Clin Respir J 2018, 12, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speeckaert, R.; Hoorens, I.; Lambert, J.; Speeckaert, M.; van Geel, N. Beyond visual inspection: The value of infrared thermography in skin diseases, a scoping review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2024, 38, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotter, H.; Kerbl, R.; Gallistl, S.; Nitsche, H.; Borkenstein, M. Rewarming index of the lower leg assessed by infrared thermography in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2003, 16, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejling, A.S.; Lange, K.H.; Frandsen, C.S.; Diemar, S.S.; Tarnow, L.; Faber, J.; Holst, J.J.; Hartmann, B.; Hilsted, L.; Kjaer, T.W.; Juhl, C.B.; Thorsteinsson, B.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, U. Infrared thermographic assessment of changes in skin temperature during hypoglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltheuner, L.; Kaltheuner, M.; Heinemann, L. Lipohypertrophic Skin Changes in Patients With Diabetes: Visualization by Infrared Images. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2018, 12, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.M.; Morris, D.E.; Robinson, L.; Randell, T.; Denvir, L.; Symonds, M.E.; Budge, H. Reduced brown adipose tissue-associated skin temperature following cold stimulation in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2021, 22, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivanandam, S.; Anburajan, M.; Venkatraman, B.; Menaka, M.; Sharath, D. Medical thermography: a diagnostic approach for type 2 diabetes based on non-contact infrared thermal imaging. Endocrine 2012, 42, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.C.M.; Castro, H.A.; Carvalho, L.C.; Chaves, É.C.L.; Ruela, L.O.; Iunes, D.H. Reliability of Infrared Thermography Images in the Analysis of the Plantar Surface Temperature in Diabetes Mellitus. J Chiropr Med 2018, 17, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreblanca González, J.; Gómez-Martín, B.; Hernández Encinas, A.; Martín-Vaquero, J.; Queiruga-Dios, A.; Martínez-Nova, A. The Use of Infrared Thermography to Develop and Assess a Wearable Sock and Monitor Foot Temperature in Diabetic Subjects. Sensors (Basel) 2021, 21, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Morquecho, R.; Guevara, E.; Ramirez-GarciaLuna, J.L.; Martinez-Jimenez, M.A.; Medina-Rangel, M.G.; Kolosovas-Machuca, E.S. Digital infrared thermography and machine learning for diabetic foot assessment: thermal patterns and classification. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2024, 23, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, E.; Oberholzer, H.M.; van der Spuy, W.J.; Swanepoel, A.C.; Soma, P. Qualitative scanning electron microscopy analysis of fibrin networks and platelet abnormalities in diabetes. Blood Coagul Fibrinol 2011, 22, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Bester, J.; Vermeulen, N.; Alummoottil, S.; Soma, P.; Buys, A.V.; Kell, D.B. Poorly controlled type 2 diabetes is accompanied by significant morphological and ultrastructural changes in both erythrocytes and in thrombin-generated fibrin: implications for diagnostics. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2015, 134, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Page, M.J.; Engelbrecht, L.; Ellis, G.C.; Kell, D.B. Substantial fibrin amyloidogenesis in type 2 diabetes assessed using amyloid-selective fluorescent stains. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2017, 16, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, P.; Felizardo, V.; Oliveira, D.; Couto, R.; Garcia, N.M. A review of thermal methods and technologies for diabetic foot assessment. Expert Rev Med Devices 2015, 12, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.; Ng, E.Y.K.; Tan, J.H.; Heng, M.L.; Tong, J.W.K.; Acharya, U.R. Computer aided diagnosis of diabetic foot using infrared thermography: A review. Comput Biol Med 2017, 91, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Contreras, D.A.; Peregrina-Barreto, H.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J. d. J.; Renero-Carrillo, F.J. Plantar Thermogram Database for the Study of Diabetic Foot Complications. Ieee Access 2019, 7, 161296–161307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliahmad, B.; Tint, A.N.; Poosapadi Arjunan, S.; Rani, P.; Kumar, D.K.; Miller, J.; Zajac, J.D.; Wang, G.; Ekinci, E.I. Is Thermal Imaging a Useful Predictor of the Healing Status of Diabetes-Related Foot Ulcers? A Pilot Study. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2019, 13, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilo, A.; Romsi, P.; Mäkelä, J. Infrared Thermography and Vascular Disorders in Diabetic Feet. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2020, 14, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Doremalen, R.F.M.; van Netten, J.J.; van Baal, J.G.; Vollenbroek-Hutten, M.M.R.; van der Heijden, F. Infrared 3D Thermography for Inflammation Detection in Diabetic Foot Disease: A Proof of Concept. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2020, 14, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faus Camarena, M.; Izquierdo-Renau, M.; Julian-Rochina, I.; Arrebola, M.; Miralles, M. Update on the Use of Infrared Thermography in the Early Detection of Diabetic Foot Complications: A Bibliographic Review. Sensors (Basel) 2023, 24, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodi, A.; Giambene, B.; Miranda, P.; Falaschi, G.; Corvi, A.; Menchini, U. Ocular surface temperature in diabetic retinopathy: a pilot study by infrared thermography. Eur J Ophthalmol 2009, 19, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, B.; Rao, A.P.; Murugesan, M.; Subramanian, S.; Sharath, D.; Manoharan, U.; Prodip, B.; Balasubramaniam, V. Ocular surface temperature measurement in diabetic retinopathy. Exp Eye Res 2021, 211, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.; Abrams, S.T.; Jenkins, R.; Lane, S.; Wang, G.; Toh, C.H. Microclots, as defined by amyloid-fibrinogen aggregates, predict risks of disseminated intravascular coagulation and mortality. Blood Adv 2024, 8, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. To what extent are the terminal stages of sepsis, septic shock, SIRS, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome actually driven by a toxic prion/amyloid form of fibrin? 2018, 44, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, N.; Nabavi, V.; Nuguri, V.; Hajsadeghi, F.; Flores, F.; Akhtar, M.; Kleis, S.; Hecht, H.; Naghavi, M.; Budoff, M. Low fingertip temperature rebound measured by digital thermal monitoring strongly correlates with the presence and extent of coronary artery disease diagnosed by 64-slice multi-detector computed tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2009, 25, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, K.M.; Ahmadi, N.; Wang, Z.; Jamieson, C.; Nasir, K.; Metcalfe, R.; Hecht, H.S.; Hartley, C.J.; Naghavi, M. Digital thermal monitoring of vascular function: a novel tool to improve cardiovascular risk assessment. Vasc Med 2009, 14, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, N.; McQuilkin, G.L.; Akhtar, M.W.; Hajsadeghi, F.; Kleis, S.J.; Hecht, H.; Naghavi, M.; Budoff, M. Reproducibility and variability of digital thermal monitoring of vascular reactivity. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2011, 31, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbach, A.M.; Ackerman, H.C.; Liu, W.M.; Meyer, J.M.; Littel, P.L.; Seamon, C.; Footman, E.; Chi, A.; Zorca, S.; Krajewski, M.L.; Cuttica, M.J.; Machado, R.F.; Cannon, R.O.; 3rd Kato, G.J. Infrared imaging of nitric oxide-mediated blood flow in human sickle cell disease. Microvasc Res 2012, 84, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schier, R.; Marcus, H.E.; Mansur, E.; Lei, X.; El-Zein, R.; Mehran, R.; Purugganan, R.; Heir, J.S.; Riedel, B.; Gottumukkala, V. Evaluation of digital thermal monitoring as a tool to assess perioperative vascular reactivity. J Atheroscler Thromb 2013, 20, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podtaev, S.; Stepanov, R.; Smirnova, E.; Loran, E. Wavelet-analysis of skin temperature oscillations during local heating for revealing endothelial dysfunction. Microvasc Res 2015, 97, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Yen, A.A.; Lin, A.W.; Tanaka, H.; Kleis, S. New Indices of Endothelial Function Measured by Digital Thermal Monitoring of Vascular Reactivity: Data from 6084 Patients Registry. Int J Vasc Med 2016, 2016, 1348028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 170. Karunathilake, I. M. D., Maduwantha1, H. P. E. R. S. Y., Jayasinghe, S. and De Silva, A. C. (2017) A System to Assess Endothelial Dysfunction by combining Peripheral Arterial Tonometry with Digital Thermal Monitoring. Proc Int Conf Inust Inf Syst, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.; Gourley, D.; Naghavi, M.; Klies, S.; Tanaka, H. Digital thermal monitoring techniques to assess vascular reactivity following finger and brachial occlusions. J Clin Hypertens 2021, 23, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, C.M.; Gonçalves, L.; Seiça, R. Methods to evaluate vascular function: a crucial approach towards predictive, preventive, and personalised medicine. EPMA J 2022, 13, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Montalvo, S.I.; Cruz-Dominguez, M.D.P.; Martinez-Godinez, M.L.A.; Calderon-Aranda, E.; Martinez-Bencomo, M.A.; Diaz, G.M.; Cruz-Segura, A.; Miliar-Garcia, A. Infrared thermography for normal endothelial function screening. Gac Med Mex 2024, 160, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.; Joffe, D.; Lloyd-Jones, G.; Khan, M.A.; Šalamon, Š.; Laubscher, G.J.; Putrino, D.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. (2025) Vascular pathogenesis in acute and long covid: current insights and therapeutic outlook Semin Throm Hemost. 51, 256-271. [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.K.; Ng, Y.K.; Tan, Y.K. Qualitative study of sexual functioning in couples with erectile dysfunction: prospective evaluation of the thermography diagnostic system. J Reprod Med 2009, 54, 698–705. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Diao, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Sun, D.; Kong, F.; Fu, Q. Establishing a Thermal Imaging Technology (IRT) Based System for Evaluating Rat Erectile Function. Sex Med 2022, 10, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisostomo-Wynne, T.; Hertz, A.; Maloney, T.; Walter, J.; Caras, R.J. Use of thermographic imaging for the evaluation of erectile dysfunction and Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res 2024, 36, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümpel, C., Cordeiro de Souza , A., Ribeiro, J. S., Shirata, H. M., de Oliveira, J. and Filho, C. B. (2016) Diagnosis of fibromyalgia: diagnostic feasibility and accuracy of thermography. ABCS Health Sci. 48, e023225. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ferrándiz, M.E.; Casas-Barragán, A.; Tapia-Haro, R.M.; Rus, A.; Molina, F.; Correa-Rodríguez, M. Evaluation of sympathetic adrenergic branch of cutaneous neural control throughout thermography and its relationship to nitric oxide levels in patients with fibromyalgia. J Therm Biol 2021, 95, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas-Barragán, A.; Molina, F.; Tapia-Haro, R.M.; García-Ríos, M.C.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Aguilar-Ferrándiz, M.E. Association of core body temperature and peripheral blood flow of the hands with pain intensity, pressure pain hypersensitivity, central sensitization, and fibromyalgia symptoms. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2021, 12, 2040622321997253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Barragán, A.; Molina, F.; Tapia-Haro, R.M.; Martínez-Martos, J.M.; Ramírez-Expósito, M.J.; Rus, A.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Aguilar-Ferrándiz, M.E. (2024) Different Correlation Patterns Between Circulating Amino Acids and Body Temperature in Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Mol Sci, 25. [CrossRef]
- Strangi, T.; Lombardi, G.; Braccili, M.P.; Lo Sterzo, E.; Lalli, A.; Pennesi, A. Peripheral vascular hyperreactivity in arterial hypertension. Int J Cardiol 1989, 25 Suppl 1, S57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, J.; Mariamichael, A. A preliminary study for the assessment of hypertension using static and dynamic IR thermograms. Biomed Tech (Berl) 2018, 63, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.; Pena, C.; Nugent, K. (2025) Skin microcirculation and hypertension: is there a connection? J Bras Nefrol. 47, e202440192. [CrossRef]
- Salgado, D.R.; Ortiz, J.A.; Favory, R.; Creteur, J.; Vincent, J.L.; De Backer, D. Microcirculatory abnormalities in patients with severe influenza A (H1N1) infection. Can J Anaesth 2010, 57, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwajda-Białasik, J.; Mościcka, P.; Jawień, A.; Szewczyk, M. Infrared thermography to prognose the venous leg ulcer healing process-preliminary results of a 12-week, prospective observational study. Wound Repair Regen 2020, 28, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monshipouri, M.; Aliahmad, B.; Ogrin, R.; Elder, K.; Anderson, J.; Polus, B.; Kumar, D. Thermal imaging potential and limitations to predict healing of venous leg ulcers. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelechi, T.J.; Prentice, M.; Mueller, M.; Madisetti, M. Infrared Thermometry and Thermography in Detecting Skin Temperature Variations to Predict Venous Leg Ulcer Reulceration: A Case Report. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs 2024, 51, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- das Neves, P.F.M.; Quaresma, J.A.S.; Queiroz, M.A.F.; Silva, C.C.; Maia, E.V.; OliveiraJ.S. d. S., das Neves, C.M.A., Mendonça, S. d. S., Falcão, A.S.C., Melo, G.S., Santos, I.B.F., de Sousa, J.R., dos Santos, E.J.M., da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F., Vallinoto, A.C.R.; Falcão, L.F.M. Imbalance of Peripheral Temperature, Sympathovagal, and Cytokine Profile in Long COVID. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhuang, S.; Gu, Z. Evaluation of ocular surface temperature in post-COVID-19 patients with different degrees of fever via infrared thermal imaging. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Laubscher, G.J.; Pretorius, E. A central role for amyloid fibrin microclots in long COVID/PASC: origins and therapeutic implications. Biochem J 2022, 479, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.; Vlok, M.; Turner, S.; Venter, C.; Laubscher, G.J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Proteomics of fibrin amyloid microclots in Long COVID/ Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) shows many entrapped pro-inflammatory molecules that may also contribute to a failed fibrinolytic system. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022, 21, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Vlok, M.; Venter, C.; Bezuidenhout, J.A.; Laubscher, G.J.; Steenkamp, J.; Kell, D.B. Persistent clotting protein pathology in Long COVID/ Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) is accompanied by increased levels of antiplasmin. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021, 20, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Venter, C.; Laubscher, G.J.; Kotze, M.J.; Oladejo, S.; Watson, L.R.; Rajaratnam, K.; Watson, B.W.; Kell, D.B. (2022) Prevalence of symptoms, comorbidities, fibrin amyloid microclots and platelet pathology in individuals with Long COVID/ Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) Cardiovasc Diabetol. 21, 148. [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Khan, M.A.; Putrino, D.; Woodcock, A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Long COVID: pathophysiological factors and abnormal coagulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2023, 34, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Laubscher, G.J.; Khan, M.A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. (2023) Accelerating discovery: A novel flow cytometric method for detecting fibrin(ogen) amyloid microclots using long COVID as a model Heliyon. 9, e19605. [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Nunes, M.; Pretorius, J.; Kell, D.B. (2024) Flow clotometry: measuring amyloid microclots in ME/CFS, long COVID, and healthy samples with imaging flow cytometry. Research Square. [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Thierry, A.; Sanchez, C.; Ha, T.; Pastor, B.; Mirandola, A.; Pisareva, E.; Prevostel, C.; Laubscher, G.; Usher, T.; Venter, C.; Turner, S.; Waters, M.; Kell, D.B. (2024) Circulating microclots are structurally associated with Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and their amounts are strongly elevated in long COVID patients. Res Square https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-4666650/v4666651. [CrossRef]
- McDougall, A.C.; Salter, D.C. Thermography of the nose and ear in relation to the skin lesions of lepromatous leprosy, tuberculosis, leishmaniasis, and lupus pernio. J Invest Dermatol 1977, 68, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzola, G.P.; Dalla Volta, G.; Balestrieri, G. Headache in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical and telethermographic findings. Arch Neurol 1988, 45, 1061–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębiec-Bąk, A.; Skrzek, A.; Woźniewski, M.; Malicka, I. Using Thermography in the Diagnostics of Lymphedema: Pilot Study. Lymphat Res Biol 2020, 18, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra Estupiñán, A.; Pons Playa, G.; Ferández Garrido, M.; Zamora Alarcon, P.; Olivares Dominguez, L.; Vega García, C.; Masia Ayala, J. Correlation between Indocyanine green lymphography and thermography to evaluate areas of dermal backflow in lymphedema. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2020, 73, 1897–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatley, J.A.; Kay, S. Using thermal imaging to measure changes in breast cancer-related lymphoedema during reflexology. Br J Community Nurs 2020, 25, S6–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanumakka, C.R.; Maroju, N.K.; Chandrashekar, L. Utility of infrared thermography in differentiating cellulitis from pseudocellulitis of the lower limbs-A diagnostic accuracy study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2021, 84, 1705–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Karim, M.J.; Sultan Mahmood, A.S.M.; Al Kawsar, A.; Khair, A.; Betts, H.; Douglass, J.; Forrer, A.; Taylor, M.J. Infrared Thermal Imaging as a Novel Non-Invasive Point-of-Care Tool to Assess Filarial Lymphoedema. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Siva Alves Gomes, V.M.; Brioschi, M.L.; Cardozo da Silva, A.R.; Tenório, N.; Oliveira, L.R.P.; Souza da Silva, A.C.; Maia, J.N.; Dantas, D. Accuracy of Infrared Thermography in Diagnosing Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. J Clin Med 2024, 13, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, S.J.; Grau, G.E.; Hunt, N.H. The microcirculation in severe malaria. Microcirculation 2004, 11, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.; Lee, S.J.; Hossain, M.A.; Anstey, N.M.; Charunwatthana, P.; Maude, R.J.; Kingston, H.W.; Mishra, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Plewes, K.; Piera, K.; Hassan, M.U.; Ghose, A.; Faiz, M.A.; White, N.J.; Day, N.P.; Dondorp, A.M. Microvascular obstruction and endothelial activation are independently associated with the clinical manifestations of severe falciparum malaria in adults: an observational study. BMC Med 2015, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, R.Y.; Levin-Kotler, L.; Rabin, N.; Ovadia-Blechman, Z.; Zimmer, Y.; Sternfeld, A.; Finchelman, J.M.; Unis, R.; Lewis, N.; Tepper-Shaihov, O.; Naftali-Shani, N.; Balint-Lahat, N.; Safran, M.; Ben-Ari, Z.; Grossman, E.; Leor, J.; Hoffer, O. Automated thermal imaging for the detection of fatty liver disease. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidov, Y.; Brzezinski, R.Y.; Kaufmann, M.I.; Likhter, M.; Hod, T.; Pappo, O.; Zimmer, Y.; Ovadia-Blechman, Z.; Rabin, N.; Barlev, A.; Berman, O.; Ben Ari, Z.; Hoffer, O. (2024) Incorporating artificial intelligence in portable infrared thermal imaging for the diagnosis and staging of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Biophotonics, e202400189. [CrossRef]
- Farrell, G.C.; Teoh, N.C.; McCuskey, R.S. Hepatic microcirculation in fatty liver disease. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2008, 291, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.J.; Xue, H.Z.; Cai, R.; Jiang, B.Y.; Mi, B.H.; Chen, Z.J.; Shi, Y.C.; Xiao, Y.H.; Zhang, W.Z. A Preliminary Study on Infrared Thermograph of Metabolic Syndrome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 851369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.H.; Zhang, W.Z.; Xiao, Y.H.; Hong, W.X.; Song, J.L.; Tu, J.F.; Jiang, B.Y.; Ye, C.; Shi, G.X. An exploration of new methods for metabolic syndrome examination by infrared thermography and knowledge mining. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xue, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; An, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Y. Infrared thermography-based radiomics for early detection of metabolic syndrome. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; An, Y.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Niu, J.M.; Li, X.R.; Xue, H.Z.; Yang, Y.M.; Cai, L.Q.; Xia, Y.C.; Chen, Q.Y.; Cai, B.Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Xiao, Y.H. Preliminary study on objective evaluation algorithm of human infrared thermogram seriality and its clinical application in population with metabolic syndrome. BMJ Health Care Inform 2025, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, J.W.; Anthony, M. Thermographic studies in vascular headache. Med J Aust 1971, 1, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Lance, J.W. Extracranial vascular changes and the source of pain in migraine headache. Ann Neurol 1983, 13, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Lance, J.W. Facial temperature in migraine, tension-vascular and tension headache. Cephalalgia 1984, 4, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, B.; Dieter, J.N. The validity of the vascular “cold patch” in the diagnosis of chronic headache. Headache 1986, 26, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Volta, G.; Anzola, G.P. Are there objective criteria to follow up migrainous patients? A prospective study with thermography and evoked potentials. Headache 1988, 28, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D. Disturbances in ocular sympathetic function and facial blood flow in unilateral migraine headache. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1990, 53, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Volta, G.; Anzola, G.P.; DiMonda, V. The disappearance of the “cold patch” in recovered migraine patients: thermographic findings. Headache 1991, 31, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonaci, F.; Rossi, E.; Voiticovschi-Iosob, C.; Dalla Volta, G.; Marceglia, S. Frontal infrared thermography in healthy individuals and chronic migraine patients: Reliability of the method. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracasso, B.V.; Castro, R.B.; Brioschi, M.L.; Malysz, T. Exploring Facial Thermography Patterns in Women with Chronic Migraine. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, S.; Bester, J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Erythrocyte health and the possible role of amyloidogenic blood clotting in the evolving haemodynamics of female migraine-with-aura pathophysiology: Results from a pilot study. Frontiers Neurol 2019, 10, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaléo, R.M.; Teixeira, M.J.; Brioschi, M.L. (2016) Infrared thermography to evaluate pain in a multiple sclerosis patient. Case report. Rev Dor. São Paulo. 17, 232-235. [CrossRef]
- Faraji, J.; Bettenson, D.; Babatunde, S.; Gangur-Powell, T.; Yong, V.W.; Metz, G.A.S. Thermoregulatory dynamics reveal sex-specific inflammatory responses to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice: Implications for multiple sclerosis-induced fatigue in females. Brain Behav Immun Health 2022, 23, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.L.; Wilson, T.E.; White, A.T.; Frohman, E.M. Thermoregulation in multiple sclerosis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2010, 109, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumowski, J.F.; Leavitt, V.M. Body temperature is elevated and linked to fatigue in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, even without heat exposure. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2014, 95, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.L.; Jay, O.; Wilson, T.E. Thermoregulatory dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Handb Clin Neurol 2018, 157, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sériès, F.; Marc, I. Upper airway mucosa temperature in obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome, nonapnoeic snorers and nonsnorers. Eur Respir J 1998, 12, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnalo, M.; Vardasca, R.; Mendes, J.G.; Drummond, M. Antero-cervical thermophysiological characterization of obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Breath 2018, 22, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.L.P.; Castelo, P.M.; Zanato, L.E.; Poyares, D.; Tufik, S.; Bommarito, S. Relation between oro-facial thermographic findings and myofunctional characteristics in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. J Oral Rehabil 2021, 48, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokam, D.; Lehmann, C. Clinical assessment of arthritic knee pain by infrared thermography. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, J.H.L.; Branco, R.L.L.; Siqueira, T.C.; de Souza, L.C.; Dalago, K.M.S.; Andrade, A. Clinical applicability of infrared thermography in rheumatic diseases: A systematic review. J Therm Biol 2022, 104, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marziani, L.; Boffa, A.; Angelelli, L.; Andriolo, L.; Di Martino, A.; Zaffagnini, S.; Filardo, G. Infrared Thermography in Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis: Joint Temperature Differs Based on Patient and Pain Characteristics. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrigna, L.; Amato, A.; Roggio, F.; Trovato, B.; Musumeci, G. Thermal threshold for knee osteoarthritis people evaluated with infrared thermography: A scoping review. J Therm Biol 2024, 123, 103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, F.S. Infrared thermography in pain medicine. Korean J Pain 2013, 26, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, E.B.; Vilaça-Alves, J.; Rosa, C.; Reis, V.M. Thermography in Neurologic Practice. Open Neurol J 2015, 9, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, N.F.; Lopes, B.S. Musculoskeletal applications of infrared thermography on back and neck syndromes: a systematic review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 2021, 57, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhatt, S.; Krauss, E.M.; Winston, P. The Role of FLIR ONE Thermography in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Case Series. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2021, 100, e48–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.N.S.; de Souza Ferreira, S.L.; Balata, P.M.M.; da Cunha, D.A.; Pernambuco, L.; da Silva, H.J. Thermography in complementary assessments of head and neck muscles: A scoping review. J Oral Rehabil 2022, 49, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Rubio, I.; Madrid-Navarro, C.J.; Salazar-López, E.; Pérez-Navarro, M.J.; Sáez-Zea, C.; Gómez-Milán, E.; Mínguez-Castellanos, A.; Escamilla-Sevilla, F. Abnormal thermography in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2015, 21, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purup, M.M.; Knudsen, K.; Karlsson, P.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Borghammer, P. Skin Temperature in Parkinson’s Disease Measured by Infrared Thermography. Parkinsons Dis 2020, 2020, 2349469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, B.; Karnam Anantha, S.; Arjunan, S.P.; Balasubramanian, V.; Murugesan, M.; R, K. A Non-Invasive IR Sensor Technique to Differentiate Parkinson’s Disease from Other Neurological Disorders Using Autonomic Dysfunction as Diagnostic Criterion. Sensors (Basel) 2021, 22, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Hagiwara, W.; Itaya, S.; Abe, K.; Maeda, T.; Inaba, A.; Orimo, S. Ten-Second Cold Water Stress Test Differentiates Parkinson’s Disease from Multiple System Atrophy: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.; Nunes, J.M.; Page, M.J.; Roberts, T.; Carr, J.; Nell, T.A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Parkinson’s disease: a systemic inflammatory disease accompanied by bacterial inflammagens. Front Ag Neurosci 2019, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Page, M.J.; Mbotwe, S.; Kell, D.B. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) can reverse the amyloid state of fibrin seen or induced in Parkinson’s disease. PlosOne 2018, 13, e0192121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, M.J.; Nell, T.A.; Carr, J.A.; KellD.B.; Pretorius, E. Iron dysregulation and inflammagens related to oral and gut health are central to the development of Parkinson’s disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 30. [CrossRef]
- Ilo, A.; Romsi, P.; Mäkelä, J. Infrared Thermography as a Diagnostic Tool for Peripheral Artery Disease. Adv Skin Wound Care 2020, 33, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Deus, P.a.s.s.o.s. M.; Ferreira da Rocha, A. Evaluation of infrared thermography with a portable camera as a diagnostic tool for peripheral arterial disease of the lower limbs compared with color Doppler ultrasonography. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis 2022, 7, e66–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, G.; Crepaldi, A.; Zenunaj, G.; Caruso, L.; Rinaldo, N.; Gasbarro, V.; Lamberti, N.; Lopez-Soto, P.J.; Manfredini, F. The Value of Infrared Thermography to Assess Foot and Limb Perfusion in Relation to Medical, Surgical, Exercise or Pharmacological Interventions in Peripheral Artery Disease: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crepaldi, A.; Caruso, L.; Piva, G.; Traina, L.; Gasbarro, V.; Manfredini, R.; Lamberti, N.; Rinaldo, N.; Manfredini, F.; Lopez-Soto, P.J. Foot Temperature by Infrared Thermography in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease before and after Structured Home-Based Exercise: A Gender-Based Observational Study. J Pers Med 2023, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Kenny, L.C. A dormant microbial component in the development of pre-eclampsia. Front Med Obs Gynecol 2016, 3, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, A.C. The two-stage placental model of preeclampsia: An update. J Reprod Immunol 2019, 134-135, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Sugulle, M.; Fiskå, B.S.; Jacobsen, D.P.; Fjeldstad, H.E.; Staff, A.C. Placental Senescence and the Two-Stage Model of Preeclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol 2024, 92, e13904. [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Kell, L.; Kenny, L.C.; Merriel, A.; Moore, J.B.; Pretorius, E. The roles of placental senescence, autophagy and senotherapeutics in the development and prevention of pre-eclampsia: a focus on ergothioneine. J Reprod Immunol 2025, 171, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warshaw, T.G. Thermal studies in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 1973, 60, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, F.; Di Carlo, A.; Carducci, M.; Leone, G.; Frascione, P. Cyclosporin A and psoriasis: a thermographic study. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1989, 146, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Martínez, C.; Valdes-Rodríguez, R.; Kolosovas-Machuca, E.S.; Moncada, B.; González, F.J. Use of digital infrared imaging in the assessment of childhood psoriasis. Skin Res Technol 2013, 19, e549–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.K.; Moore, T.L.; Manning, J.B.; Taylor, C.; Griffiths, C.E.; Herrick, A.L. Noninvasive imaging techniques in the assessment of scleroderma spectrum disorders. Arthritis Rheum 2009, 61, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, J.D.; Shipley, J.A.; Harris, N.D.; McHugh, N.J. Use of infrared thermography as an endpoint in therapeutic trials of Raynaud’s phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2012, 30, S103–S115. [Google Scholar]
- Herrick, A.L.; Murray, A. The role of capillaroscopy and thermography in the assessment and management of Raynaud’s phenomenon. Autoimmun Rev 2018, 17, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, G.; Cappella, M.; Culpo, R.; Vittadello, F.; Sprocati, M.; Zulian, F. (2019) Infrared thermography in children: a reliable tool for differential diagnosis of peripheral microvascular dysfunction and Raynaud’s phenomenon? Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 17, 68. [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L.; Heal, C.; Wilkinson, J.; Dinsdale, G.; Manning, J.; Gunnarsson, K.; Jakobsson, P.J.; Murray, A. Temperature response to cold challenge and mobile phone thermography as outcome measures for systemic sclerosis-related Raynaud’s phenomenon. Scand J Rheumatol 2021, 50, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, L.; Kristensen, B.; Thomsen, J.F.; Eldrup, E.; Jensen, L.T. Characteristic Features of Infrared Thermographic Imaging in Primary Raynaud’s Phenomenon. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, L.; Kristensen, B.; Eldrup, E.; Thomsen, J.F.; Jensen, L.T. Infrared Thermography as a Method of Verification in Raynaud’s Phenomenon. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021, 11, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kow, J.; Tan, Y.K. An update on thermal imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 2023, 90, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuidenhout, J.; Venter, C.; Roberts, T.; Tarr, G.; Kell, D.; Pretorius, E. (2020) The Atypical Fibrin Fibre Network in Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Relation to Autoimmunity, Inflammation and Thrombosis. bioRxiv, 2020.2005.2028.121301v121301. [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Oberholzer, H.M.; van der Spuy, W.J.; Swanepoel, A.C.; Soma, P. Scanning electron microscopy of fibrin networks in rheumatoid arthritis: a qualitative analysis. Rheumatol Int 2012, 32, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Akeredolu, O.-O.; Soma, P.; Kell, D.B. Major involvement of bacterial components in rheumatoid arthritis and its accompanying oxidative stress, systemic inflammation and hypercoagulability. Exp Biol Med 2017, 242, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, R.; Sekiguchi, M.; Ryuzin, Y.; Kobayashi, F.; Hiraga, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Mochizuki, I.; Kobayashi, T.; Tamura, S.; Hosoda, Y. Changes in the peripheral vasculature of various organs in patients with sarcoidosis--possible role of microangiopathy. Heart Vessels 1986, 2, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, T.J.; Morsy, M.; Naseer, S.; Keresztes, K.; Hussain, S.; Dexter, K.; Sims, M.R. A pilot study of the Leicester ED medical infrared imaging protocol in fever and sepsis. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0201562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, A.; Bouisse, C.; Mottard, N.; Thiollière, F.; Anselin, S.; Piriou, V.; Allaouchiche, B. Mottling score and skin temperature in septic shock: Relation and impact on prognosis in ICU. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0202329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amson, H.; Vacheron, C.H.; Thiolliere, F.; Piriou, V.; Magnin, M.; Allaouchiche, B. Core-to-skin temperature gradient measured by thermography predicts day-8 mortality in septic shock: A prospective observational study. J Crit Care 2020, 60, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazune, S.; Vasiljevs, E.; Caica-Rinca, A.; Marcinkevics, Z.; Grabovskis, A. Infrared Thermography Imaging for Assessment of Peripheral Perfusion in Patients with Septic Shock. Bioengineering (Basel) 2023, 10, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Goutam, A.; Tripathi, M.; Kumar, V.; Malviya, D.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, R.R.S. Utility of core to skin temperature gradient and capillary refill time in determining prognosis for patients with septic shock: A prospective observational study. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci 2025, 15, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, G.; Bruhn, A.; Ince, C. Microcirculation in sepsis: new perspectives. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2013, 11, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ince, C. The microcirculation is the motor of sepsis. Crit Care 2005, 9 Suppl 4, S13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajnik, V.; Maarouf, R. Sepsis and the microcirculation: the impact on outcomes. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2022, 35, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, C.P.; Delaney, K.M.; Gorbach, A.M.; Xu, D.; Lee, C.C.; Malik, N.; Koroulakis, A.; Antalek, M.; Maivelett, J.; Peters-Lawrence, M.; Novelli, E.M.; Lanzkron, S.M.; Axelrod, K.C.; Kato, G.J. Vasculopathy, inflammation, and blood flow in leg ulcers of patients with sickle cell anemia. Am J Hematol 2014, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, C.P.; Gorbach, A.M.; Xu, D.; Hon, Y.Y.; Delaney, K.M.; Seidel, M.; Malik, N.; Peters-Lawrence, M.; Cantilena, C.; Nichols, J.S.; Mendelsohn, L.; Conrey, A.; Grimes, G.; Kato, G.J. Topical sodium nitrite for chronic leg ulcers in patients with sickle cell anaemia: a phase 1 dose-finding safety and tolerability trial. Lancet Haematol 2014, 1, e95–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreau, K.; Callan, C.; Kottaiyan, R.; Zhang, A.; Yoon, G.; Aquavella, J.V.; Zavislan, J.; Hindman, H.B. Temperatures of the Ocular Surface, Lid, and Periorbital Regions of Sjögren’s, Evaporative, and Aqueous-Deficient Dry Eyes Relative to Normals. Ocul Surf 2016, 14, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanklyn, P.; Ilsley, D.W.; Greenstein, D.; Hampton, I.F.; Roper, T.A.; Kester, R.C.; Mulley, G.P. The cold hemiplegic arm. Stroke 1994, 25, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, F.M.; Massaro, A.R.; Filippo, T.R.; Portes, L.A.; Battistella, L.R. Evaluation of body temperature in individuals with stroke. NeuroRehabilitation 2017, 40, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Dias, C.; Alfieri, F.M.; Dos Santos, A.C.A.; Battistella, L.R. Body temperature and esthesia in individuals with stroke. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 10106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedüs, B. The Potential Role of Thermography in Determining the Efficacy of Stroke Rehabilitation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2018, 27, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaszewski, B.; Carpenter, T.K.; Thomas, R.G.; Armitage, P.A.; Lymer, G.K.; Marshall, I.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Relationships between brain and body temperature, clinical and imaging outcomes after ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2013, 33, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlasek, A.; Petrov, I.; Stankov, Z.; Snyder, K.; Alvarez, C.A.; Musialek, P.; Grunwald, I.Q. Thermography in Stroke-A Systematic Review. Medicina (Kaunas) 2025, 61, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Zendron, L.A.; Gomez Mateos, M.; Bermejo Gil, B.M.; Calleja Caballero, A.; Santos Rodriguez, V.; Perez-Robledo, F.; Martin Nogueras, A.M. Thermography analysis as a tool for assessing thermal asymmetries and temperature changes after therapy in patients with stroke: a pilot study. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. (2017) Proteins behaving badly. Substoichiometric molecular control and amplification of the initiation and nature of amyloid fibril formation: lessons from and for blood clotting. Progr Biophys Mol Biol. 123, 16-41. [CrossRef]
- Grixti, J.M.; Chandran, A.; Pretorius, J.H.; Walker, M.; Sekhar, A.; Pretorius, E.; Kell, D.B. (2024) The clots removed from ischaemic stroke patients by mechanical thrombectomy are amyloid in nature. medRxiv, 10.1101/2024.1111.1101.24316555v24316551. [CrossRef]
- Grixti, J.M.; Chandran, A.; Pretorius, J.H.; Walker, M.; Sekhar, A.; Pretorius, E.; Kell, D.B. Amyloid presence in acute ischemic stroke thrombi: observational evidence for fibrinolytic resistance. Stroke 2025, 56, e165–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frech, T.M. Imaging techniques for assessment of vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2022, 34, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.M.; Valenzuela, A. Vascular, Soft Tissue, and Musculoskeletal Imaging in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2024, 50, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Wilkinson, J.; Moore, T.; Manning, J.; New, P.; Dinsdale, G.; Murray, A.; Herrick, A.L. Thermographic Abnormalities are Associated with Future Digital Ulcers and Death in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J Rheumatol 2016, 43, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.; Dinsdale, G.; Manning, J.; Heal, C.; Murray, A.; Herrick, A.L. Mobile phone thermography of the toes in patients with systemic sclerosis-a pilot study. Rheumatol Adv Pract 2024, 8, rkae068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, E.; Moore, T.L.; Manning, J.B.; Dinsdale, G.; Wilkinson, S.; Dickinson, M.R.; Herrick, A.L.; Murray, A.K. Systemic sclerosis-related digital calcinosis; a pilot study of cutaneous oxygenation and perfusion. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2020, 59, 3573–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Bournia, V.K.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Mavrogeni, S.I. Raynaud phenomenon and microvasculopathy in systemic sclerosis: multi-modality imaging for diagnosis and evaluation. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2023, 35, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, D. [Diagnostic value of thermography in Raynaud’s phenomenon associated with systemic lupus erythematosus]. Ann Acad Med Stetin 2009, 55, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.K.; Moore, T.L.; Wragg, E.; Ennis, H.; Vail, A.; Dinsdale, G.; Muir, L.; Griffiths, C.E.; Herrick, A.L. Pilot study assessing pathophysiology and healing of digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis using laser Doppler imaging and thermography. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2016, 34 Suppl 100, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, J.D.; Leggett, S.A.; Marjanovic, E.J.; Moore, T.L.; Allen, J.; Anderson, M.E.; Britton, J.; Buch, M.H.; Del Galdo, F.; Denton, C.P.; Dinsdale, G.; Griffiths, B.; Hall, F.; Howell, K.; MacDonald, A.; McHugh, N.J.; Manning, J.B.; Pauling, J.D.; Roberts, C.; Shipley, J.A.; Herrick, A.L.; Murray, A.K. A Multicenter Study of the Validity and Reliability of Responses to Hand Cold Challenge as Measured by Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging and Thermography: Outcome Measures for Systemic Sclerosis-Related Raynaud’s Phenomenon. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018, 70, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capistrant, T.D.; Gumnit, R.J. Thermography following a carotid transient ischemic episode. JAMA 1970, 211, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L.M.; Nauriyal, V.; Nagaraj, S.; Finch, A.; Pearlstein, K.; Szymanowski, A.; Sproule, C.; Rich, P.B.; Guenther, B.D.; Pearlstein, R.D. Infrared imaging of trauma patients for detection of acute compartment syndrome of the leg. Crit Care Med 2008, 36, 1756–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspers, M.E.H.; Carrière, M.E.; Meij-de Vries, A.; Klaessens, J.H.G.M.; van Zuijlen, P.P.M. The FLIR ONE thermal imager for the assessment of burn wounds: Reliability and validity study. Burns 2017, 43, 1516–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, E. d. F.-R., Ochoa, E.E.M., López, R.L.; Díaz, L.G.L. (2018) Infrared thermography brain mapping surveillance in vascular neurosurgery for anterior communicating artery aneurysm clipping. . Surg Neurol Int 9, 188. [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.D.; Kahn, S.A.; Vickers, A.L.; Crockett, E.S.; Whitehead, J.D.; Krecker, A.K.; Lee, Y.L.; Miller, A.N.; Patterson, S.B.; Richards, W.O.; Wagner, W.W., Jr. Early Assessment of Burn Depth with Far Infrared Time-Lapse Thermography. J Am Coll Surg 2018, 226, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, M.E.; de Haas, L.E.M.; Pijpe, A.; Meij-de Vries, A.; Gardien, K.L.M.; van Zuijlen, P.P.M.; Jaspers, M.E.H. Validity of thermography for measuring burn wound healing potential. Wound Repair Regen 2020, 28, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, J.; Nizamoglu, M.; Tan, A.; Gerrish, H.; Cranmer, K.; El-Muttardi, N.; Barnes, D.; Dziewulski, P. A prospective study comparing the FLIR ONE with laser Doppler imaging in the assessment of burn depth by a tertiary burns unit in the United Kingdom. Scars Burn Heal 2020, 6, 2059513120974261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.; Lin, M.; Tan, C.; Pham, C.H.; Huang, S.; Hulsebos, I.F.; Yenikomshian, H.; Gillenwater, J. Use of Infrared Thermography for Assessment of Burn Depth and Healing Potential: A Systematic Review. J Burn Care Res 2021, 42, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castonguay, T.; Dover, G. Infrared Thermography-A Novel Tool for Monitoring Fracture Healing: A Critically Appraised Topic With Evidence-Based Recommendations for Clinical Practice. J Sport Rehabil 2023, 32, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorga, M.; Schneider, N.; Cho, J.; Tate, M.C.; Parrish, T.B. A Novel Intraoperative Mapping Device Detects the Thermodynamic Response Function. Brain Sci 2023, 13, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, M. Infrared thermography for detection of blunt-force trauma injuries during animal abuse investigations. Can Vet J 2024, 65, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, R.; Souza Martins, L.; Freire, R.M.; do Nascimento Silva, R.K.; de Almeida Ferreira, J.J.; do Nascimento, J.A.; Rodrigues de Andrade, P. Accuracy of infrared thermography evaluation in burn wound healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Wound Care 2024, 33, cxviii–cxxix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.T.; Boyle, A.M.; Kutuzov, V.; Warner, C.; Staniland, T.; Barlow, G.; Sharma, H. Current Use of Infrared Thermography in Orthopaedic and Bone or Joint Trauma Patients-Can We Identify Postoperative Infection? A Narrative Systematic Review. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2024, 19, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimoto, S.; Harada, Y.; Shimizu, T. A thermal imaging camera at the work office trigged the diagnosis of Takayasu arteritis. QJM 2023, 116, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Echeverria, A.; Poi, M.J. Infrared thermography in the diagnosis and management of vasculitis. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech 2017, 3, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oura, K.; Yamaguchi Oura, M.; Itabashi, R.; Maeda, T. Vascular Imaging Techniques to Diagnose and Monitor Patients with Takayasu Arteritis: A Review of the Literature. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021, 11, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
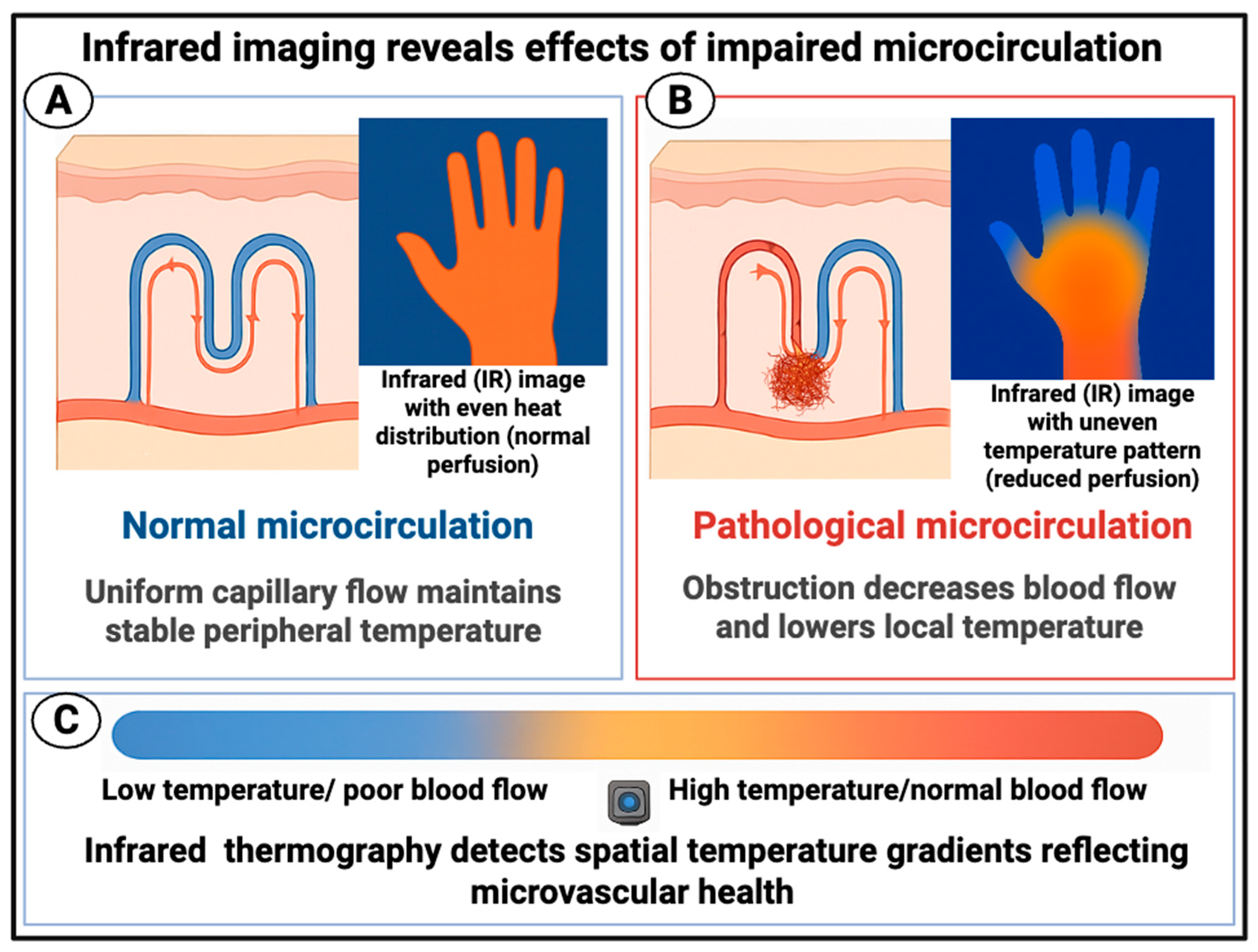
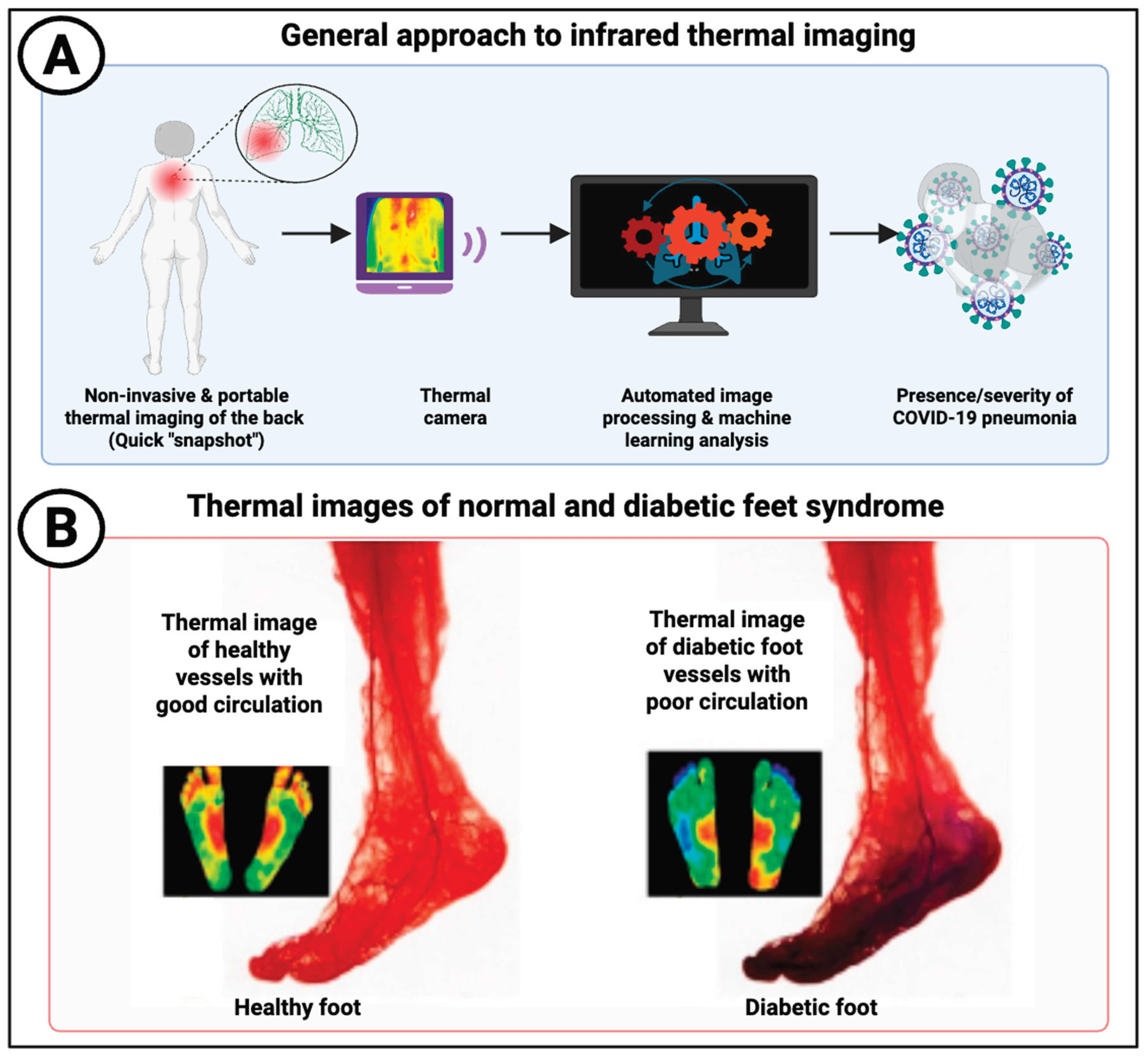
| Disease or syndrome | Selected references using thermal imaging to assess the disease | Comments | References showing fibrinaloid microclot complexes (where tested) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute COVID-19 | [26,30,31,87,88,89,90,91] | Thermal imaging was widely used in airports to detect fever rather than microcirculation issues [92,93]. However, spatial imaging to detect deranged microcirculation was also used [26,88,89,94] | [95,96,97,98,99,100] |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome | [101,102] | Mostly thermodilution assays | |
| Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) | [103,104,105] | Result can be a balance between inflammatory Temp increase and microcirculation-based decrease | |
|
Alzheimer’s dementia (including mild cognitive impairment) |
[68,72,106] | Also relates to functional capacity | [107,108,109,110,111] |
| Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) | [112] | Large effect in the one example studied | |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome | [113] | Surprising lack of studies given its clear relation to microcirculation dysfunction | |
| Asthma | [114] | ||
| Atopic dermatitis | [115,116] | Surprisingly little recent literature | |
| Behçet’s disease | [117] | A thermographic technique involving placing feet in a water bath at 42ºC | |
| Cancers | [36,118,119,120,121,122] | Due to the significance of vascularisation to tumour growth there is a massive literature. The list at left is purposely highly selective. However, there is necessarily a tendency for assessments to be localised | |
| Chronic fatigue syndrome | Nothing as yet; huge opportunity! | [9,123] | |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | [124,125,126] | Relatively little literature, but impaired microcirculation evident | |
| Chronic venous insufficiency | [60,127,128] | Can manifest e.g. as leg ulcers | |
| Connective tissue disorders | [49,65,129,130,131] | ||
| Deep vein thrombosis | [132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139] | Very strong signals of thermal horspots | |
| Dengue fever | [92] | ||
| Dermatology | [140] | ||
| Diabetes mellitus, type 1 | [141,142,143,144] | ||
| Diabetes mellitus, type 2 | [105,145,146,147,148] | [100,107,149,150,151] | |
| Diabetic foot and foot ulcers | [29,35,152,153,154,155,156,157,158] | Caused by derangment of the microcirculation; thermography is frequently used in diagnosis and prognosis | |
| Diabetic retinopathy | [105,159,160] | Measurement of ocular surface temperature | |
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation | Astonishingly, given the links at right, seemingly nothing using thermal imaging—another massive opportunity in the ICU | [161] and see [162]; microparticles predicted DIC with an odds ratio exceeding 50 [161]. | |
| Endothelial (dys)function generally | [163,164,165,166,167,168,169,170,171,172,173] | Commonly done (as ‘vascular reactivity’) by studying thermal flow after a change in temperature or occlusion with a cuff | [174] |
| Erectile dysfunction | [62,175,176,177] | Inadequate blood flow clearly closely involved | |
| Fibromyalgia | [131,178,179,180,181] | Quite variable results, and not yet seen as reliable | |
| Hypertension | [173,182,183] | Most easily explained by increased resistance of microcirculation building up blood pressure [184] | |
| Influenza | No thermal imaging papers, though microcirculation clearly affected [185] | ||
| Leg ulcers | [186,187,188] | Related to chronic venous insufficiency. Textural analysis of images also useful. | |
| Long COVID | [189,190] | Surprisingly few given the ease of measurement and the well-established derangement of the microcirculation | [10,12,14,174,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198] |
| Lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE) | [49,65,113,199,200] | ||
| Lymphoedema | [201,202,203,204,205,206] | ||
| Malaria | While the microcirculation is strongly affected [207,208] no thermal imaging papers seem to have been published | ||
| Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) | [209,210] | More based on surface temperature measurements than the established microcirculation [211] effects | |
| Metabolic syndrome | [212,213,214,215] | Based of temperature differences between separate locations | |
| Migraine | [216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224] | Clear evidence of impaired perfusion in migraineurs, consistent with the microclot complexes observed | [225] |
| Multiple sclerosis | [226,227] | Mostly studied in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Note that thermoregulation is dysfunctional in MS [228,229,230] | |
| Obstructive sleep apnoea | [231,232,233] | Observable signals but literature sparse | |
| Osteoarthritis | [49,131,234,235,236,237] | Mostly detects inflammation. Standardisation especially important incl equilibration to ambient temperature. | |
| Pain in general | [238,239,240,241,242] | ||
| Parkinson’s disease | [243,244,245,246] | Clear evidence for impaired micrcirculation, consistent with fibrinaloid microclot complexes | [107,247,248,249] |
| Peripheral artery disease | [250,251,252,253] | Best assessed spatially | |
| Pre-eclampsia | Surprisingly, given its aetiology (e.g. [254,255,256,257]), there seem to be no measurements using thermal imaging | ||
| Psoriasis | [258,259,260] | Clear effects of inadequate perfusion | |
| Raynaud’s phenomenon | [235,261,262,263,264,265,266,267] | Thermography is seen as an effective method of assessment | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | [49,131,235,268] | Focus tends to be more on inflammation | [269,270,271] |
| Sarcoidosis | [199,272] | Clear relation with poor perfusion but negligible recent literature | |
| Sepsis and septic shock | [84,273,274,275,276,277] | Classic disease of the microcirculation [3,278,279,280], Thermography can be useful, but not always predictive of mortality. Also related to skin mottling. Capillary fill time and core-to-skin temperature gradient most predictive | [161] and see [162] (high predictive power for mortality) |
| Sickle cell disease | [166,281,282] | Includes leg ulcers as caused by hypoperfusion that Is a consequence of sickling | |
| Sjögren’s syndrome | [131,283] | ||
| Stroke (ischaemic) | [284,285,286,287,288,289,290] | Reasonably widely applied; stroke causes desymmetrisation of temperaturehomogeneity seen in healthy controls | Amyloid observed in both microclot complexes [291] and macroclots [292,293] |
| Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) | [129,261,262,265,294,295,296,297,298,299,300,301,302] | Widely and effectively used here | |
| Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) | [289,303] | Usefully predictive | |
| Traumatic brain injury and other traumas | [34,304,305,306,307,308,309,310,311,312,313,314,315] | Very clear signals, including in assessment of burns | |
| Vasculitis | [316,317,318] | Includes arteritis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





