Submitted:
15 October 2025
Posted:
16 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
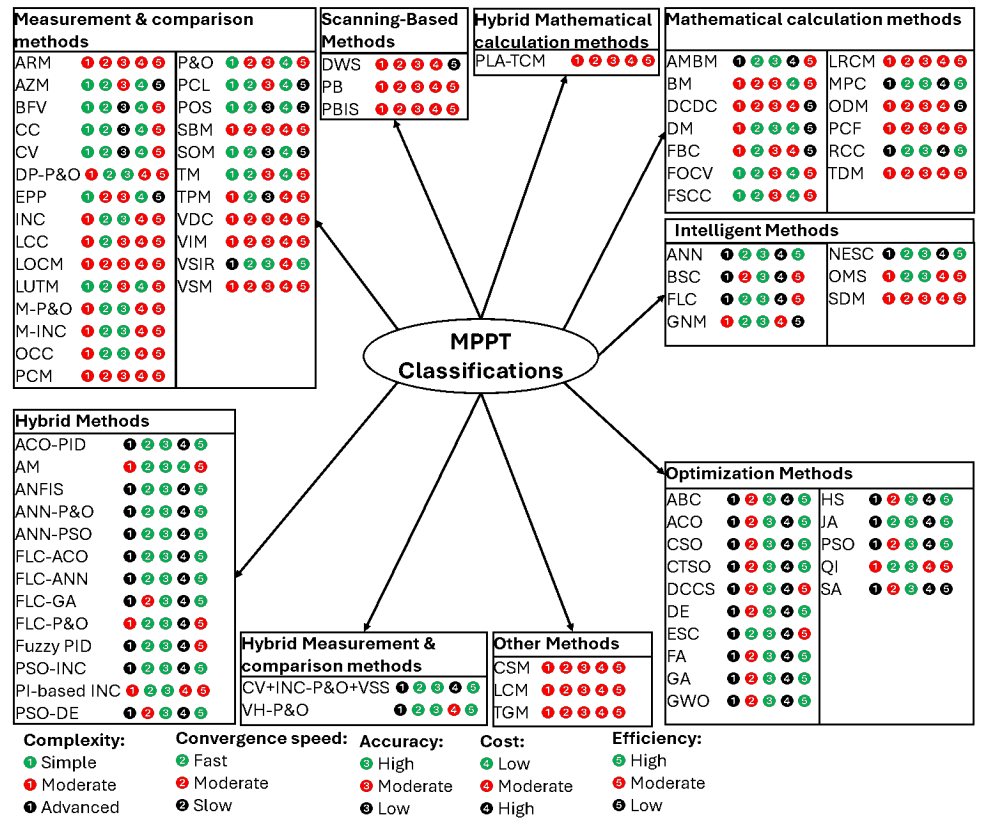
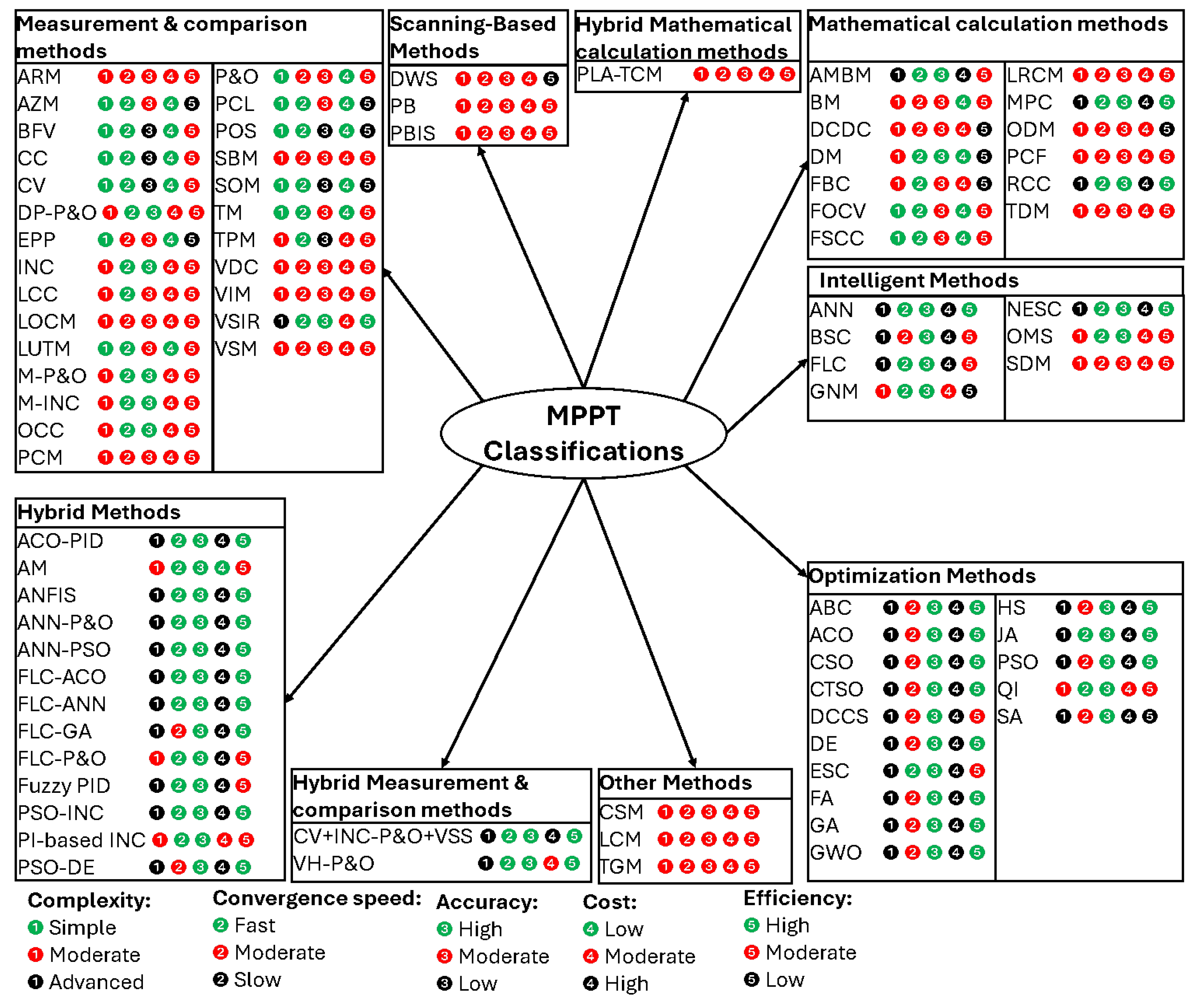
- Classification of MPPT algorithms based on their efficiency, accuracy, cost, convergence speed, and complexity using multi-criteria decision-making algorithm.
- Evaluate the efficiency performance of each MPPT technique.
- Compare PV applications’ dependency on the MPPT technique.
- Distinguish MPPT accuracy based on their precision to reach the peak point.
- Illustrate the parameters influencing the MPPT algorithms.
2. Novel Classification of MPPT Methods
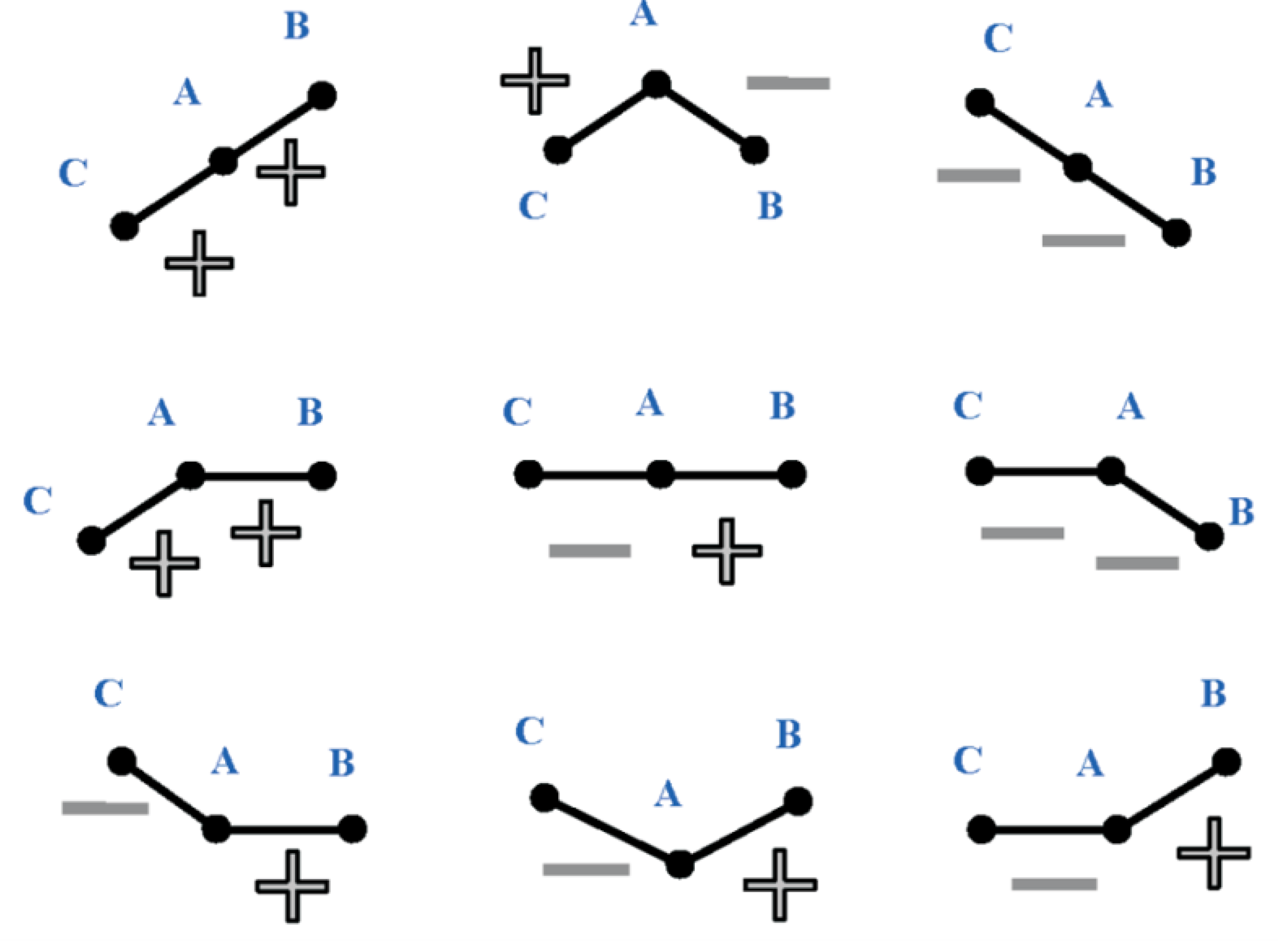
 represents an advantage, such as low cost, high efficiency, etc. The number in red color
represents an advantage, such as low cost, high efficiency, etc. The number in red color  represents a moderate value, such as medium cost, moderate efficiency. While the number in black circle
represents a moderate value, such as medium cost, moderate efficiency. While the number in black circle  represents a disadvantage, such as high cost, and low efficiency. By arranging and comparing the five above mentioned criteria of the MPPT algorithms into a single figure, it becomes much easier to select the method that meets specific requirements. As an example, if we want to select an algorithm that has a low cost, high accuracy, and medium efficiency, we look for the numbers that have the following sequence color:
represents a disadvantage, such as high cost, and low efficiency. By arranging and comparing the five above mentioned criteria of the MPPT algorithms into a single figure, it becomes much easier to select the method that meets specific requirements. As an example, if we want to select an algorithm that has a low cost, high accuracy, and medium efficiency, we look for the numbers that have the following sequence color: 
 . Then, from the figure, we try to find the algorithms that have the closest performance. In this case, it is the AM (Analytic method) algorithm.
. Then, from the figure, we try to find the algorithms that have the closest performance. In this case, it is the AM (Analytic method) algorithm.3. Scanning-Based MPPT Algorithms
3.1. Decremented Window Scanning (DWS)
3.2. Peak Bracketing (PB)
3.3. Peak Bracketing with Initial Scanning (PBIS)
4. MPPT Intelligent Control Techniques
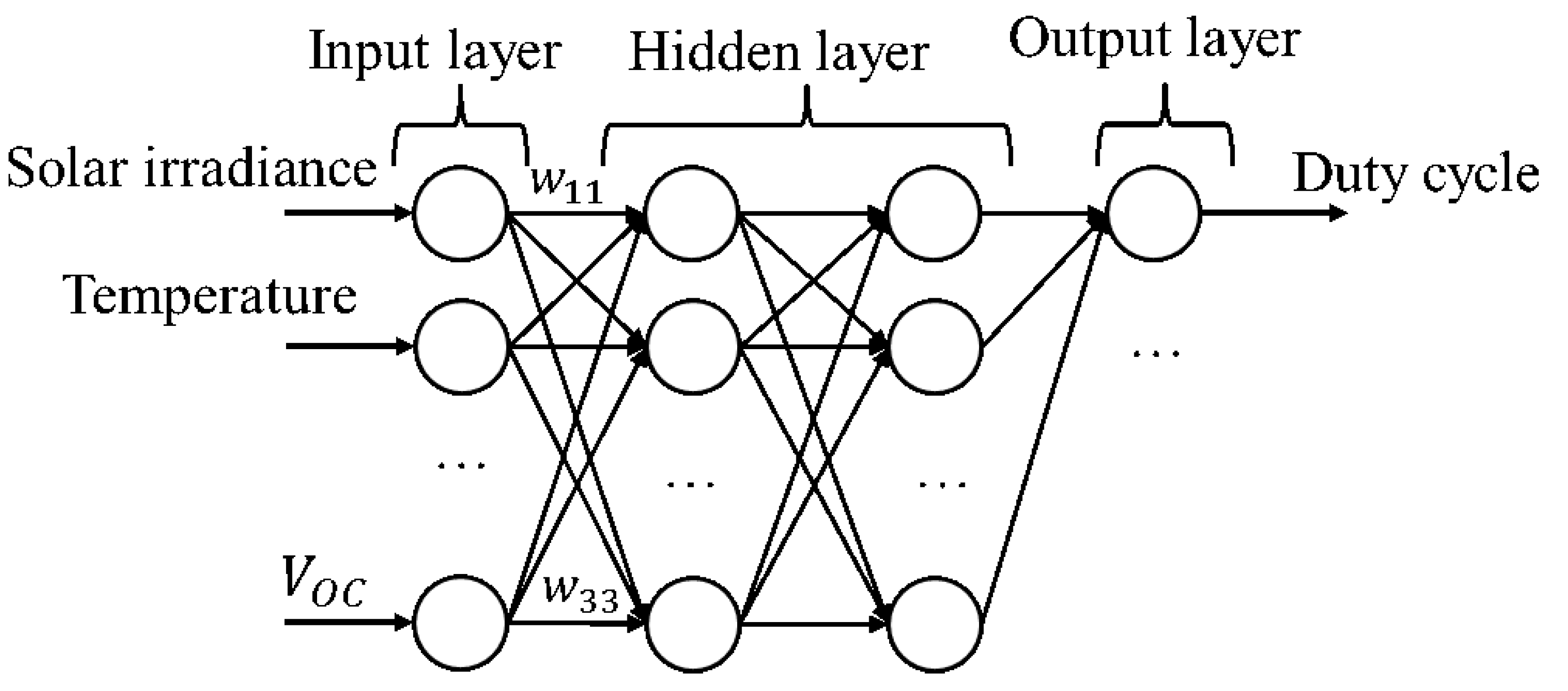
4.1. Neural Network
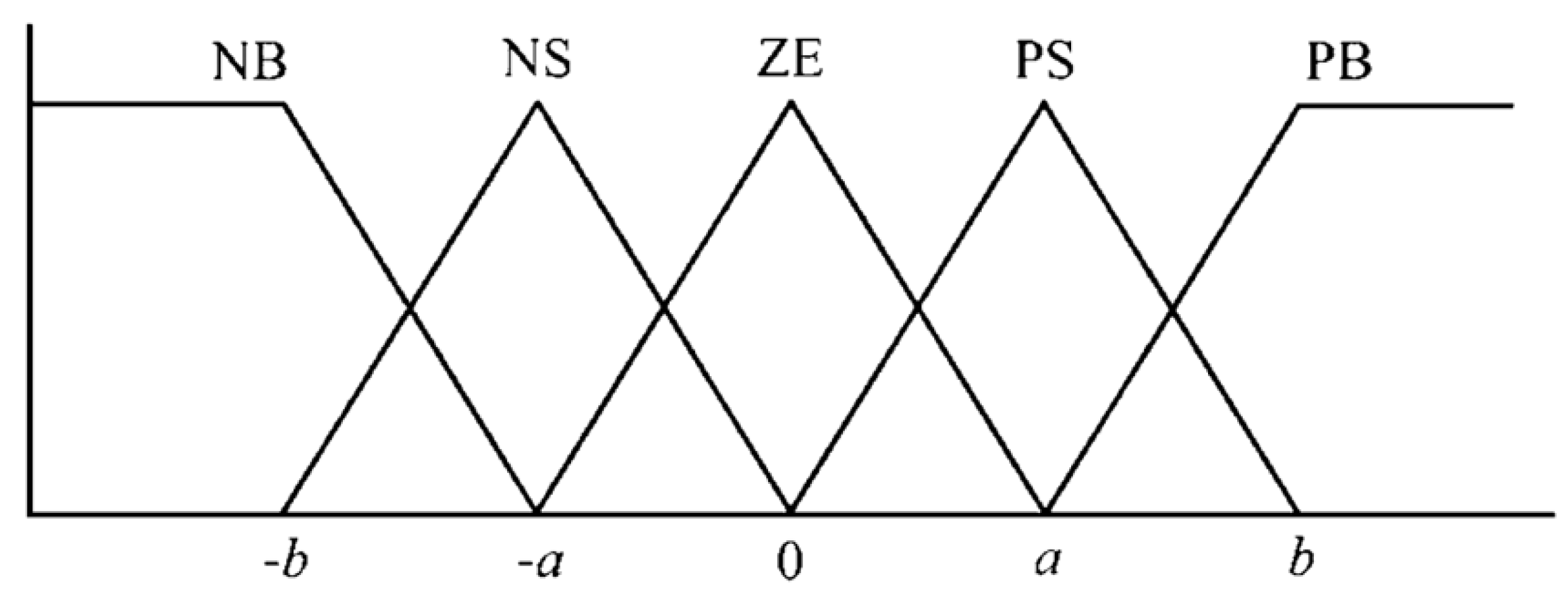
4.2. Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC)
4.3. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Based on the Technique of Perturb & observe (P&O)-MPPT
4.4. Gauss-Newton Method
4.5. Steepest-Descent Method
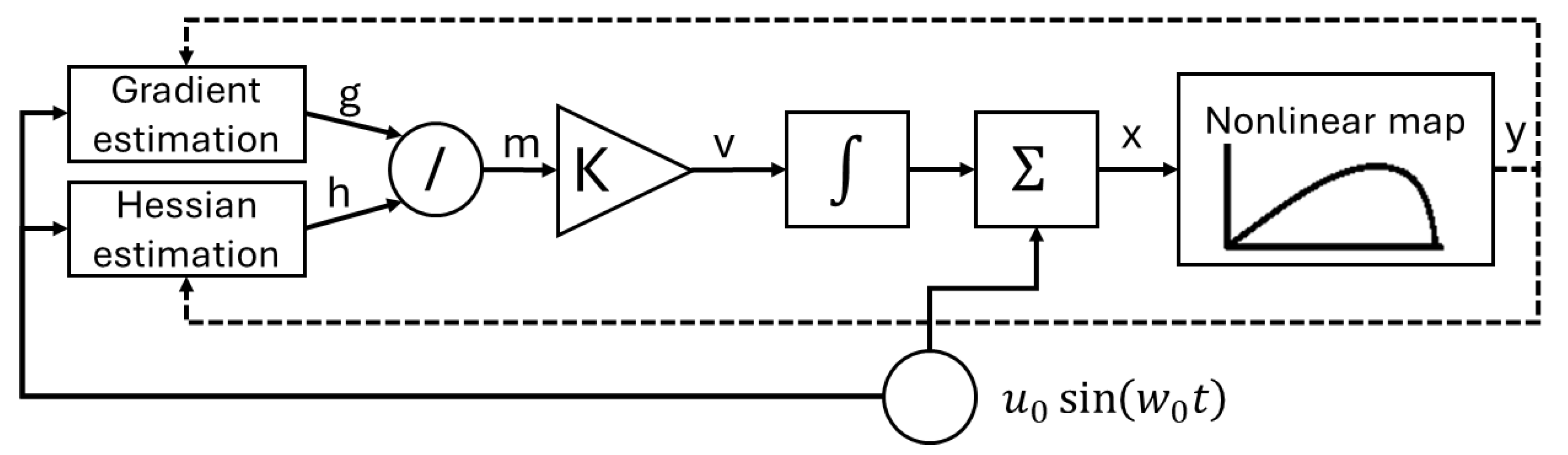
4.6. Newton-Like Extremum Seeking Control Method
4.7. On-Line MPP Search Algorithm
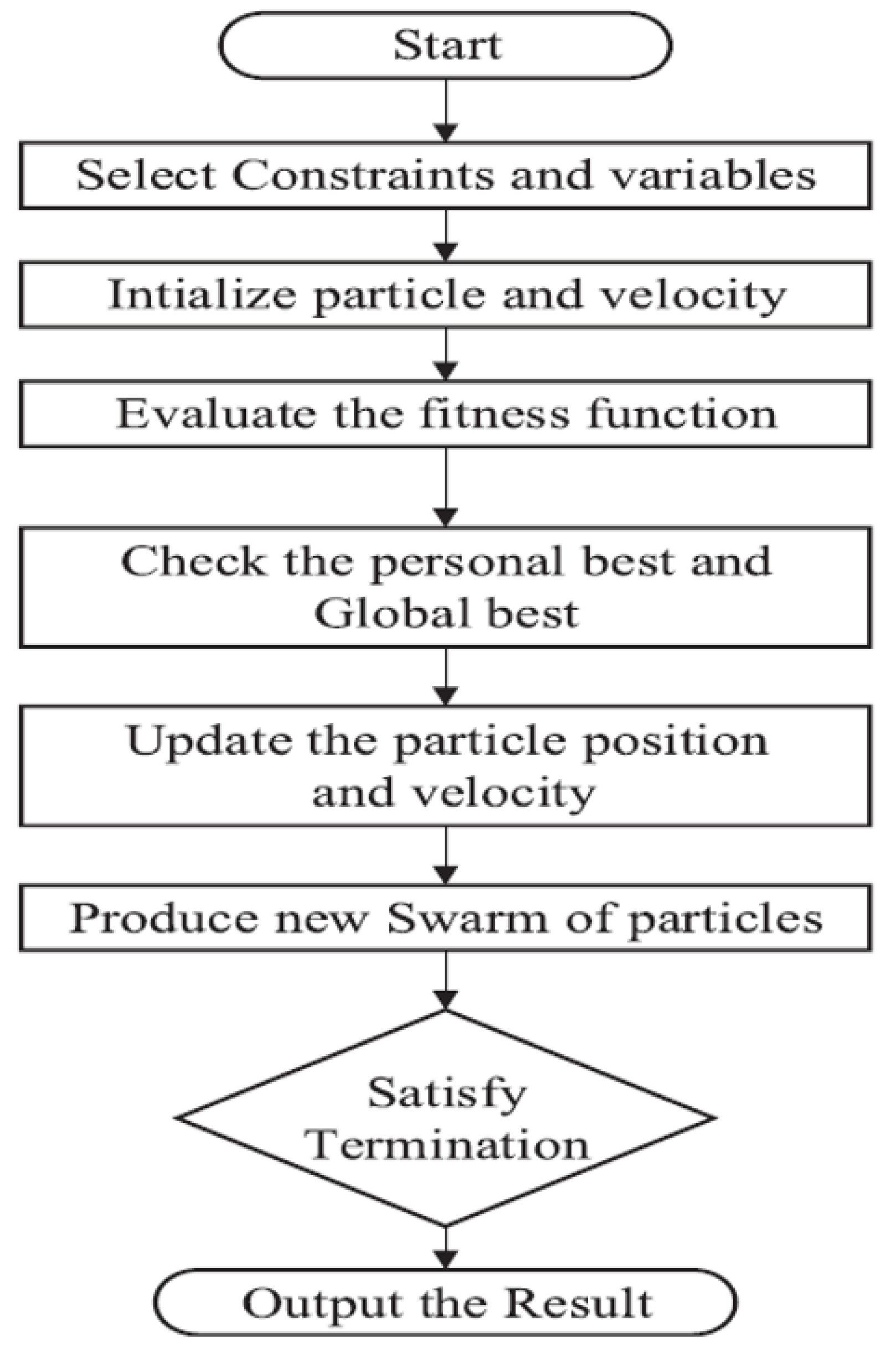
4.8. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Algorithm
5. Hybrid Intelligent Control Algorithms
5.1. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
5.2. Hybrid Genetic Algorithmic
5.3. Fuzzy-PID
5.4. Ant Colony Optimization
5.5. Fuzzy-Neural Network
5.6. Analytic Method
5.7. PI Based Incremental Conductance (INC)
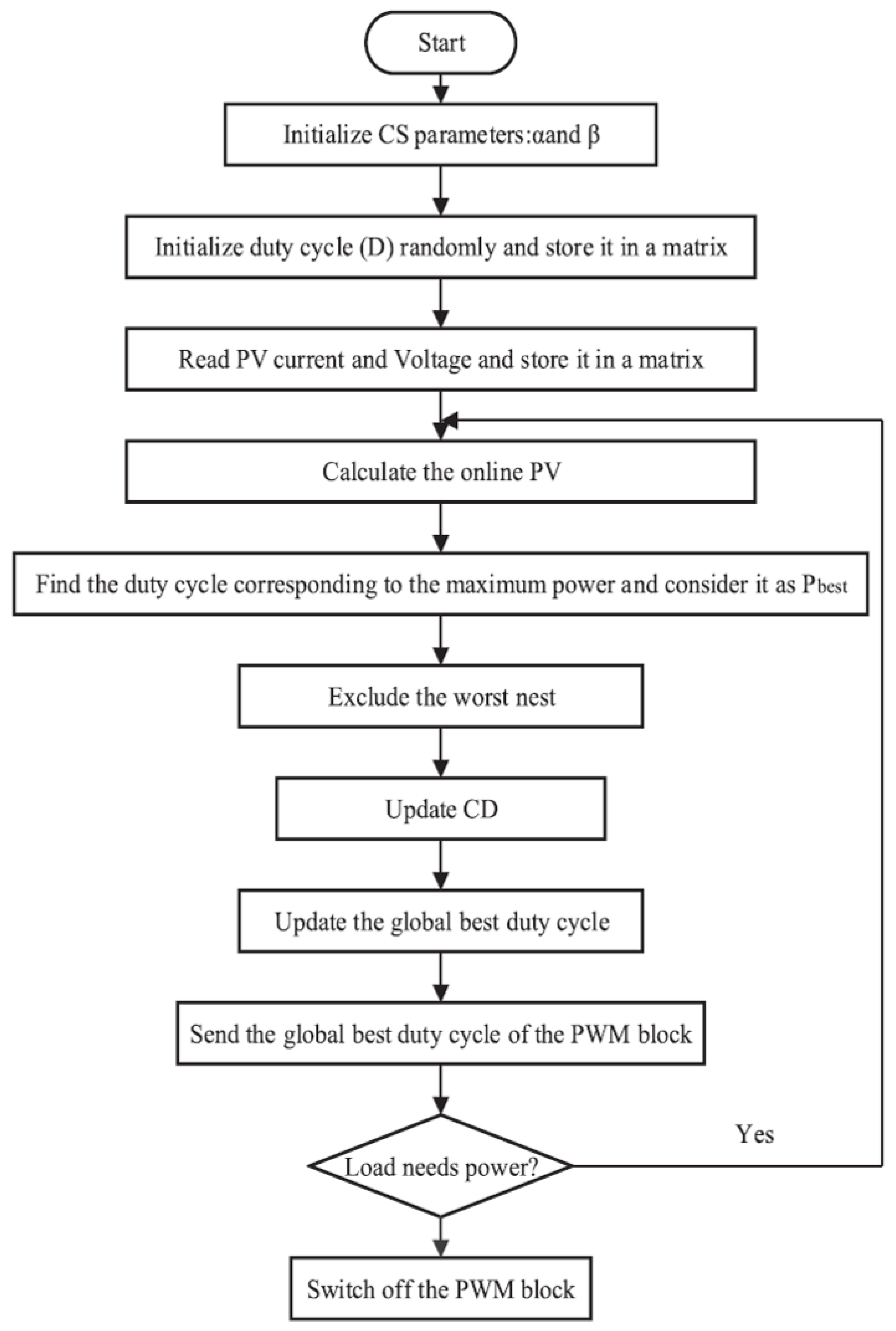
5.8. PSO-INC Structure
6. Measurement MPPT Methods and Comparison
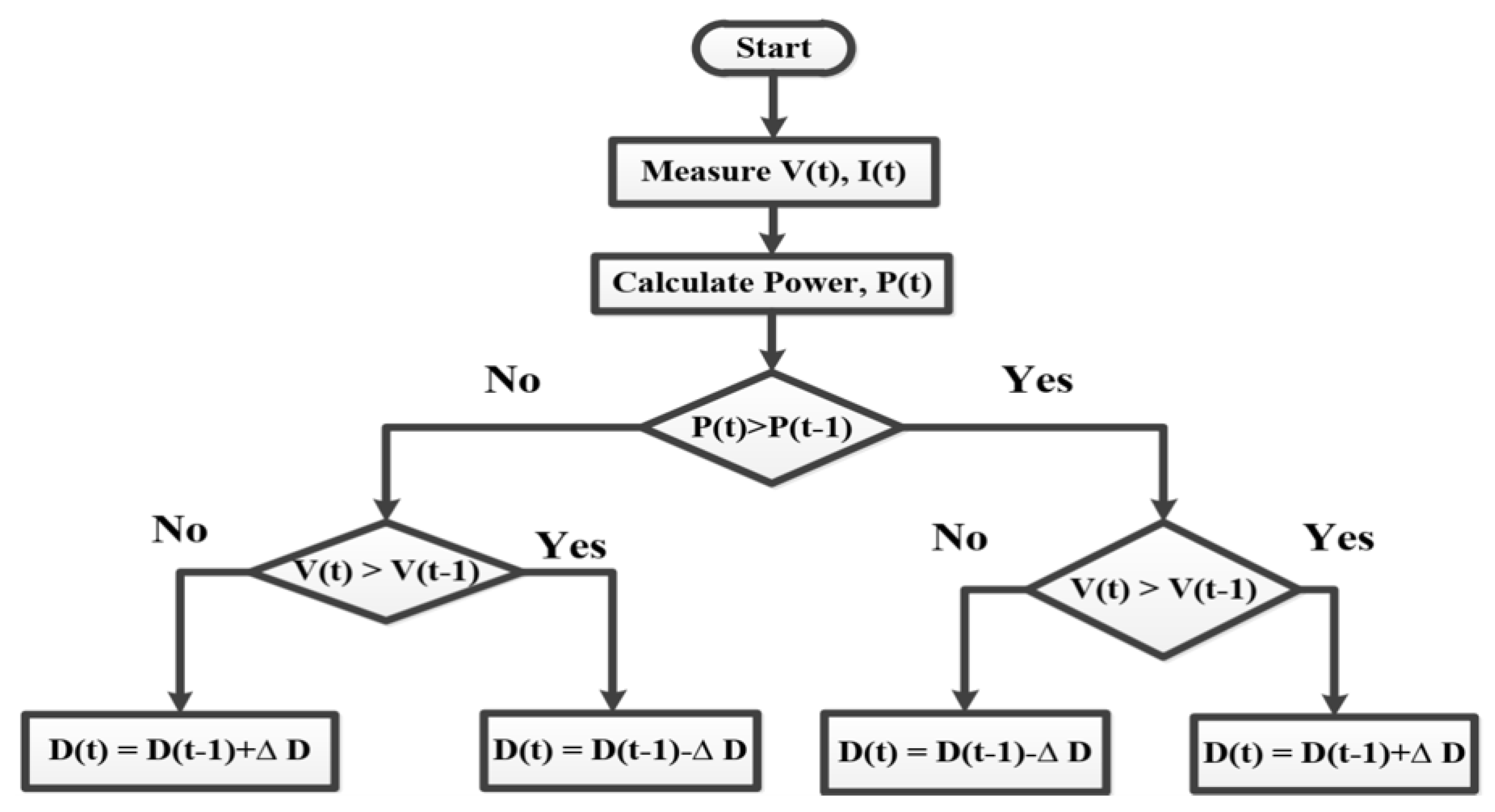
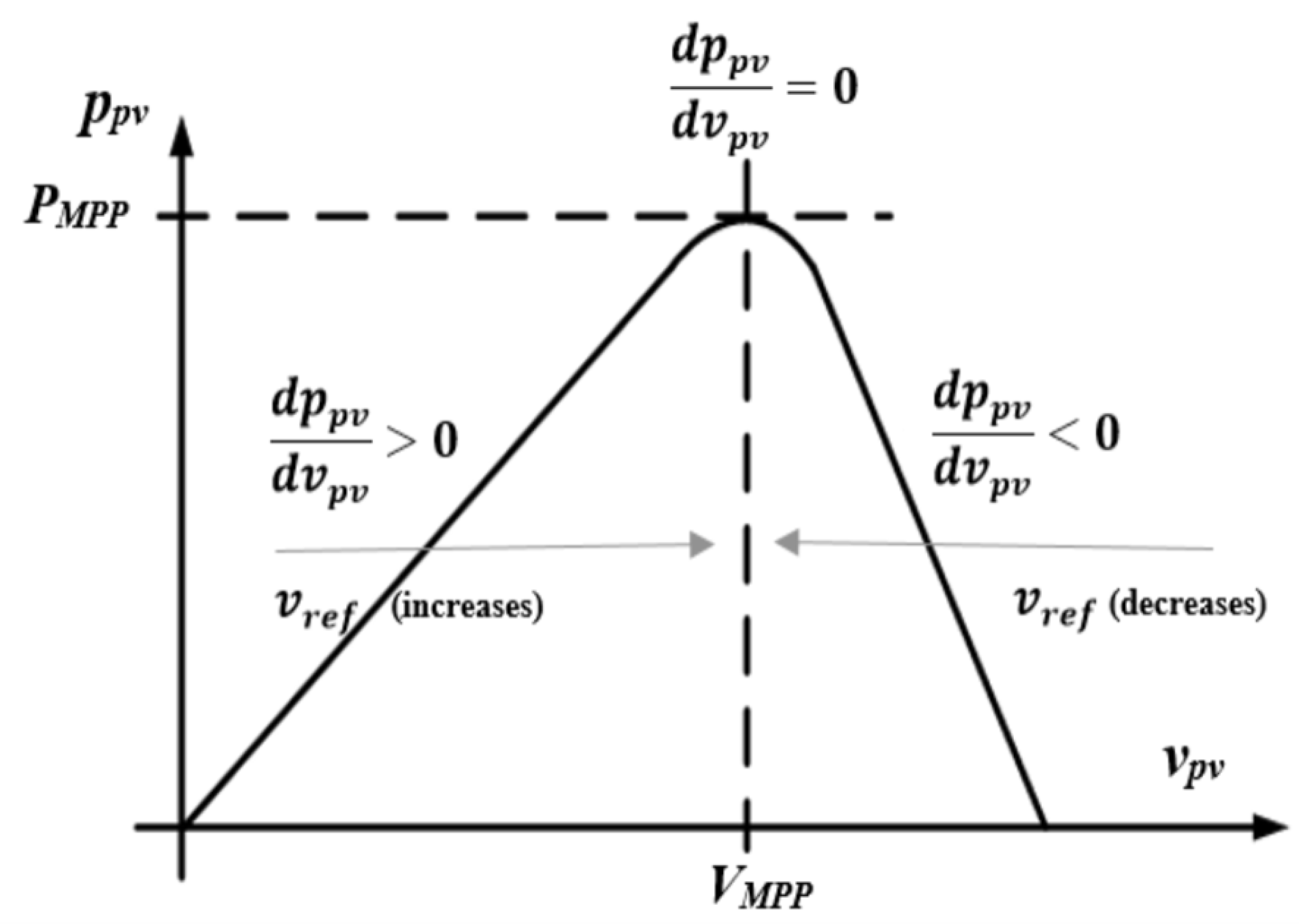
6.1. Perturb & Observe (P&O)
6.2. Incremental Conductance Algorithm
6.3. Short Circuit Current Method
6.4. Open Circuit Voltage Method
6.5. Parasitic Capacitances ()
6.6. Temperature Method
6.7. System Oscillation Method
6.8. Constant Voltage Method
6.9. Method of Look-Up Table
6.10. Array Reconfiguration Method
6.11. State-Based MPPT Method
6.12. One-Cycle Control (OCC) Method
6.13. Best Fixed Voltage (BFV) Algorithm
6.14. Three-Point Method
6.15. The Method of PV Output Senseless (POS)
6.16. Variable Inductor MPPT Method
6.17. Variable Step-Size Incremental Resistance (INR) Method
6.18. DP-P&O MPPT
6.19. Pilot Cell
6.20. Modified Perturb and Observe
6.21. Estimate Perturb and Perturb (EPP)
6.22. CVT + INC-CON (P&O) + VSS Method
6.23. VH-P&O MPPT Algorithm
6.24. Variable DC-Link Voltage
6.25. Modified INC Algorithm
6.26. Azab Method
6.27. Voltage Scanning-Based MPPT Method
7. Mathematical Calculation MPPT Methods
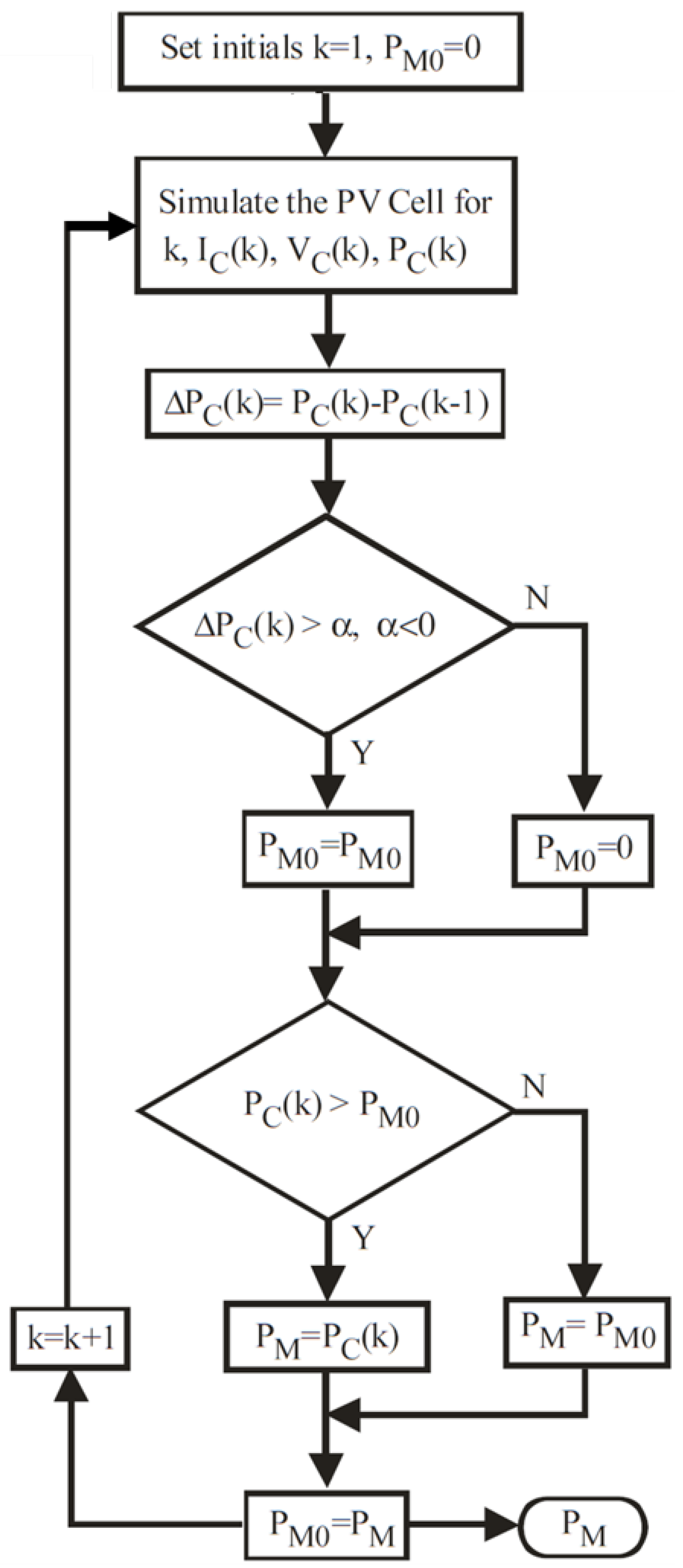
7.1. Model-Based MPPT
7.2. Piecewise Linear Approximation with Temperature Compensated Method
7.3. A What’s Termed Fit Line
7.4. Beta Method
7.5. Ripple Correlation Control (RCC)
7.6. Current Sweep
7.7. DC-Link Capacitor Droop Control
7.8. Feedback Control
7.9. The Method of Linear Current Control
7.10. Linear Reoriented Coordinates Method (LRCM)
7.11. Polynomial Curve Fitting (PCF)
7.12. Differentiation Method (DM)
7.13. MPP Locus Characterization
8. MPPT Optimization Methods
8.1. IMPP and VMPP Computation Method
8.2. Numerical Method - Quadratic Interpolation (QI)
8.3. Extremum Seeking Control Method (ESC)
8.4. Dual Carrier Chaos Search Algorithm
8.5. Algorithm for Stimulated Annealing (SA)
9. Comparison of MPPT Techniques
| Algorithm | PV Array Dependency | MPPT Accuracy | Type (D/A) | Periodic Tuning | Convergence Speed | Complexity | Parameters |
| Algorithm | PV Array Dependency | MPPT Accuracy | Type (D/A) | Periodic Tuning | Convergence Speed | Complexity | Parameters |
| Continued on next page | |||||||
| P&O/ HCS [288-291] | No | Yes | D and A | No | Different | Simple | V, I |
| INC Algorithm [157, 266, 290-293] | No | Yes | D | No | Different | Simple | V, I |
| Fractional Isc [290, 291, 294, 295] | Yes | No | D and A | Yes | Moderate | Moderate | I |
| Fractional Voc [290, 291, 294, 295] | Yes | No | D and A | Yes | Moderate | Simple | V |
| Parasitic Capacitances (Cp) [14, 157, 296] | No | Yes | A | No | Fast | Simple | V, I |
| FLC [183, 290, 291, 297] | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | Fast | High | Diverse |
| Temperature Methods [163, 183] | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | Moderate | Simple | V, T |
| Beta Method [183] | Yes | Yes | D | No | Fast | High | V, I |
| Neural Network [183, 291] | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | Fast | High | Diverse |
| RCC [183, 290, 298] | No | Yes | A | No | Fast | Simple | V, I |
| Current Sweep [183] | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | Low | High | V, I |
| DC Link Capacitor Droop Control [183] | No | No | D and A | No | Medium | Simple | V |
| dP/dV or dP/dI Feedback Control [183] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| System Oscillation Method [183] | Yes | No | A | No | N/A | Simple | V |
| Constant Voltage Tracker [161, 183] | Yes | No | D | Yes | Moderate | Simple | V |
| Lookup Table Method [161, 183, 289] | Yes | No | D | Yes | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| On-line MPP Search Algorithm [183] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | High | V, I |
| Array Reconfiguration [183] | Yes | No | D | Yes | Low | High | V, I |
| Linear Current Control [183] | Yes | No | D | Yes | Fast | Moderate | Ir |
| IMPP and VMPP Computation | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | N/A | Moderate | Ir, T |
| State Based MPPT [183] | Yes | Yes | D and A | Yes | Fast | High | V, I |
| OCC MPPT [183] | Yes | No | D and A | Yes | Fast | Moderate | I |
| BFV [183] | Yes | No | D and A | Yes | N/A | Low | None |
| LRCM | Yes | No | D | No | N/A | High | V, I |
| Slide Control [161, 183, 289, 295, 297, 299] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Three Point Weight Comparison [183] | No | Yes | D | No | Low | Simple | V, I |
| POS Control [183] | No | Yes | D | No | N/A | Simple | Current |
| Biological Swarm Chasing MPPT [183] | No | Yes | D | No | Varies | High | V, I, Ir, T |
| Variable Inductor MPPT [183] | No | Yes | D | No | Different | Moderate | V, I |
| INR method [183] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| dP-P&O MPPT [191] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Pilot Cell [300] | Yes | No | D and A | Yes | Moderate | Simple | V, I |
| Modified Perturb and Observe [208] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Estimate, Perturb and Perturb EPP [208] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Numerical Method - Quadratic Interpolation (QI) [268] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| MPP Locus Characterization [262, 299] | N/A | Yes | N/A | N/A | Fast | Simple | V, I |
| CVT + INC-CON (P&O) + VSS Method [209] | Yes | Yes | D and A | No | Fast | Moderate | V |
| Piecewise Linear Approximation with Temp Compensation [301] | Yes | Yes | D and A | Yes | Fast | Simple | V, I, Ir, T |
| PSO Algorithm [136, 298] | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| PSO-INC Structure [136] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Simple | V, I |
| Dual carrier chaos search algorithm [275, 298] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Algorithm for Stimulated Annealing (SA)[298, 302] | Yes | Yes | D | No | Fast | High | V, I |
| Artificil neural network (ANN) based P&O MPPT [57, 291] | No | Yes | D and A | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| VH-P&O MPTT Algorithm [211] | No | Yes | D | No | Moderate | Moderate | V |
| Ant Colony Algorithm [303] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Variable DC-Link Voltage Algorithm [216] | No | Yes | D | No | Moderate | Moderate | V |
| ESC Method [304] | No | Yes | D and A | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Gauss-Newton Method [69] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Simple | V, I |
| Steepest-Descent Method [69, 305] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Analytic Method [305] | Yes | No | D and A | Yes | Moderate | High | V, I |
| PCF [257] | Yes | No | D | Yes | Low | Simple | V |
| DM [306] | No | Yes | D | Yes | Fast | High | V, I |
| IC Based on PI [163, 298] | No | Yes | D | No | Fast | Moderate | V, I |
| Azab Method [224] | Yes | Yes | D | Yes | Moderate | Simple | N/A |
| Modified INC Algorithm [191] | No | Yes | D | No | Moderate | High | V, I |
| Newton-Like Extremum Seeking Control Method [74] | No | Yes | D and A | No | Fast | Hogh | V, I |
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony |
| ACO | Ant colony optimization |
| ACO-PID | Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) + Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
| (PID) controller | |
| AM | Analytic method |
| AMBM | Adaptive Model-Based Methods |
| ANFIS | Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| ANN-P&O | Artificial Neural Network + Perturb and Observe |
| ANN-PSO | Artificial Neural Network + Particle Swarm Optimization |
| ARM | Array Reconfiguration Method |
| AZM | Azab method |
| BFV | Best fixed voltage method |
| BM | Beta Method |
| BSC | Biological Swarm Chasing method |
| CC | Constant Current (also known as Short Circuit Current Method) |
| Cp | Parasitic capacitances |
| CSM | Current Sweep Method |
| CSO | Cuckoo Search Optimization |
| CTSO | Cat Swarm Optimization |
| CV | Constant Voltage (also known as Open Circuit Voltage method) |
| CV+INC-P&O+VSS | Constant Voltage Tracking + Incremental Conductance with Perturb and |
| Observe + Variable Step Size | |
| D | Duty cycle point |
| DCDC | DC-link capacitor droop control |
| DCCS | Dual carrier chaos search |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
| DM | Differentiation method |
| DP-P&O | Dual Perturb and Observe MPPT method |
| DWS | Decremented window scanning |
| EPP | Estimate perturb and perturb |
| ESC | Extremum seeking control |
| FA | Firefly Algorithm |
| FBC | Feedback control |
| FLC | Fuzzy logic controller |
| FLC-ACO | Fuzzy Logic Controller + Ant Colony Optimization |
| FLC-ANN | Fuzzy Logic Controller + Artificial Neural Network |
| FLC-GA | Fuzzy Logic Controller + Genetic Algorithm |
| FLC-P&O | Fuzzy Logic Controller + Perturb and Observe |
| FOCV | Fractional Open Circuit Voltage |
| FSCC | Fractional Short Circuit Current Fuzzy PID (Fuzzy Logic + Proportional- |
| Integral-Derivative) | |
| HS | Harmony Search |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GMPP | Global maximum power point |
| GNM | Gauss-Newton method |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimization |
| INC | Incremental conductance |
| Isc | Short circuit current |
| IMPP | Maximum power point current |
| JA | Jaya Algorithm |
| LCM | Load Current Maximization |
| LCC | Linear Current Control method |
| LMPP | Local maximum power point |
| LOCM | Locus Characterization MPP Method |
| LRCM | Linear reoriented coordinates method |
| LUTM | Look-up Table Method |
| MF | Membership Functions |
| M-INC | Modified INC method |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| M-P&O | Modified Perturb and Observe |
| MPP | Maximum power point |
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking |
| NESC | Newton-based Extremum Seeking Control Method |
| OCC | One-cycle Control Method |
| ODM | One-diode model |
| OMS | Online MPP Search |
| P | Power |
| PB | Peak bracketing method |
| PBIS | Peak bracketing with initial scanning method |
| PCL | Pilot Cell method |
| PCF | Polynomial curve fitting method |
| PCM | Parasitic Capacitance Method |
| PI | Proportional Integral |
| PID | Proportional Integral Differential |
| PI-based INC | (Proportional-Integral + Incremental Conductance) |
| PLA-TCM | Piecewise linear approximation with temperature compensated method |
| P&O | Perturb and Observe |
| POS | PV Output Senseless Method |
| PPV | PV power |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization |
| PSO-INC | (Particle Swarm Optimization + Incremental Conductance) |
| PSO-DE | (Particle Swarm Optimization + Differential Evolution) |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| QI | Quadratic interpolation |
| RCC | Ripple correlation control |
| SA | Stimulated annealing |
| SBM | State-Based MPPT method |
| SDN | Steepest-descent method |
| SI | System Identification |
| SNNs | Simulated neural networks |
| SOM | System Oscillation Method |
| TDM | Two-diode model |
| TGM | Temperature Gradient Method |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion |
| TM | Temperature Method |
| TPM | Three-Point Method |
| V | Voltage |
| VDC | Variable DC-link voltage |
| VSM | Voltage Scanning-Based MPPT method |
| VH-P&O | Variable Hill-Climbing Perturb and Observe Maximum Power Point |
| Tracking | |
| VIM | Variable Inductor MPPT Method |
| VSIR | Variable Step-Size Incremental Resistance Method |
References
- Katche, M.L.; et al. A comprehensive review of maximum power point tracking (mppt) techniques used in solar pv systems. Energies 2023, 16, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; et al. Simple modeling and simulation of photovoltaic panels using Matlab/Simulink. Adv. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 73, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, A.; Saini, R. A review on Integrated Renewable Energy System based power generation for stand-alone applications: Configurations, storage options, sizing methodologies and control. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.-Y.; Wang, H.-Y. A photovoltaic power system using a high step-up converter for DC load applications. Energies 2013, 6, 1068–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.S.; et al. Practical electrical energy production to solve the shortage in electricity in palestine and pay back period. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, L.E.; Benalcazar, P. Hybrid renewable energy systems for sustainable rural development: Perspectives and challenges in energy systems modeling. Energies 2023, 16, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubalo, M.; et al. Hybrid wind-solar power system with a battery-assisted quasi-Z-source inverter: Optimal power generation by deploying minimum sensors. Energies 2023, 16, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.S.A. Maximum power point tracking control scheme for small scale wind turbine. PhD Thesis, 2019.
- Badawi, A.; et al. Novel technique for hill climbing search to reach maximum power point tracking. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; et al. Performance evaluation of concentrator photovoltaic systems integrated with a new jet impingement-microchannel heat sink and heat spreader. Sol. Energy 2020, 199, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallanza, A.; et al. A sizing approach for stand-alone hybrid photovoltaic-wind-battery systems: A Sicilian case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, J.; Niroomand, M. Optimization methods of MPPT parameters for PV systems: review, classification, and comparison. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkambule, M.S.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of machine learning MPPT algorithms for a PV system under different weather conditions. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohm, D.; Ropp, M.E. Comparative study of maximum power point tracking algorithms. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2003, 11, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.S.; et al. Paper review: maximum power point tracking for wind energy conversion system. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Control and Instrumentation Engineering (ICECIE), IEEE; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, V.; et al. Review of the maximum power point tracking algorithms for stand-alone photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 1555–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmroukh, A.N. Thermal regulation of photovoltaic panel installed in Upper Egyptian conditions in Qena. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 14, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce de León Puig, N.I.; Acho, L.; Rodellar, J. Design and experimental implementation of a hysteresis algorithm to optimize the maximum power point extracted from a photovoltaic system. Energies 2018, 11, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.S.; et al. Power prediction mode technique for Hill Climbing Search algorithm to reach the maximum power point tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Control and Instrumentation Engineering (ICECIE), IEEE; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, S.; Barik, M.; Subudhi, B. A Zero Steady-State Oscillation MPPT Algorithm Using Voltage Sensor.
- Aygül, K.; et al. Butterfly optimization algorithm based maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic systems under partial shading condition. Energy Sources Part A 2023, 45, 8337–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.; Hussain, A. A comprehensive review of global maximum power point tracking algorithms for photovoltaic systems. Energy Syst. 2023, 14, 293–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.; Zain, J.M.; Muranaka, K. A novel global MPPT technique to enhance maximum power from PV systems under variable atmospheric conditions. Soft Comput. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, H.; et al. A novel improved grey wolf algorithm based global maximum power point tracker method considering partial shading. IEEE Access 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagadurga, T.; Devarapalli, R.; Knypiński, Ł. Comparison of Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithms for Global Maximum Power Point Tracking of Partially Shaded Solar Photovoltaic Systems. Algorithms 2023, 16, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.-R.; Hefny, M.M.; Ali, A.I.M. Investigation of single and multiple MPPT structures of solar PV-system under partial shading conditions considering direct duty-cycle controller. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussaian Basha, C.; et al. A novel on design and implementation of hybrid MPPT controllers for solar PV systems under various partial shading conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.; et al. Hybrid global search with enhanced INC MPPT under partial shading condition. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaouas, N.; et al. A new approach of PV system structure to enhance performance of PV generator under partial shading effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samman, F.A.; Rahmansyah, A.A. Iterative decremented step-size scanning-based MPPT algorithms for photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Information Technology and Electrical Engineering (ICITEE), IEEE; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, S.F.; Abdul Azis, S.R. Peak Bracketing and Decremented Window-Size Scanning-Based MPPT Algorithms for Photovoltaic Systems. 2018, 14, 1015.
- Mamur, H.; Üstüner, M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.R.A. Future perspective and current situation of maximum power point tracking methods in thermoelectric generators. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 50, 101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samman, F.A.; Piarah, W.H.; Djafar, Z. Power transfer maximization of thermoelectric generator system using peak trapping and scanning-based MPPT algorithms. ICIC Express Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.K.; et al. Shading mitigation techniques: State-of-the-art in photovoltaic applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samman, F.A.; et al. MPPT algorithm using decremented window-scanning method for home scale photovoltaic-based power supply systems. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2021, 17, 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Samman, F.A.; Piarah, W.H.; Djafar, Z. Variable Step-Size Decremented Window-Size Scanning-based MPPT Algorithms for Thermoelectric Generator Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Applied Electromagnetic Technology (AEMT), IEEE; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Suhaebri, T.; Samman, F.A.; Achmad, A. Microcontroller Implementation of an MPPT Algorithm using Decremented Windows Size Scanning Method for Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th Southern Power Electronics Conference (SPEC), IEEE; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yaragatti, U.R.; Rajkiran, A.N.; Shreesha, B.C. A novel method of fuzzy controlled maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, IEEE; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nugraha, D.A.; Lian, K.-L. A novel MPPT method based on cuckoo search algorithm and golden section search algorithm for partially shaded PV system. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 42, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroni, M.J.; Wirateruna, E.S. 4 Section method for MPPT optimization in Solar Panel Experiments under PSC v221023. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart-Green Technology in Electrical and Information Systems (ICSGTEIS), IEEE; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kota, V.R.; Bhukya, M.N. A novel global MPP tracking scheme based on shading pattern identification using artificial neural networks for photovoltaic power generation during partial shaded condition. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Mier, C.G.; et al. Artificial neural networks in MPPT algorithms for optimization of photovoltaic power systems: A review. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messalti, S.; Harrag, A.; Loukriz, A. A new variable step size neural networks MPPT controller: Review, simulation and hardware implementation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, N.; et al. The MPPT control of PV system by using neural networks based on Newton Raphson method. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC), IEEE; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rezk, H.; Hasaneen, E.-S. A new MATLAB/Simulink model of triple-junction solar cell and MPPT based on artificial neural networks for photovoltaic energy systems. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2015, 6, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elobaid, L.M.; Abdelsalam, A.K.; Zakzouk, E.E. Artificial neural network-based photovoltaic maximum power point tracking techniques: A survey. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2015, 9, 1043–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; et al. A novel beta parameter based fuzzy-logic controller for photovoltaic MPPT application. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.M.; Addoweesh, K.E.; Mashaly, H.M. A fuzzy logic control method for MPPT of PV systems. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012–38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.-C.; et al. Optimization of a fuzzy-logic-control-based MPPT algorithm using the particle swarm optimization technique. Energies 2015, 8, 5338–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L.; et al. An asymmetrical fuzzy-logic-control-based MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems. Energies 2014, 7, 2177–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khozondar, H.J.; et al. A review study of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking algorithms. Renewables Wind. Water Sol. 2016, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.N.; et al. Promising MPPT methods combining metaheuristic, fuzzy-logic and ANN techniques for grid-connected photovoltaic. Sensors 2021, 21, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.-u.; et al. A novel algorithm for MPPT of an isolated PV system using push pull converter with fuzzy logic controller. Energies 2020, 13, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchafaa, F.; Beriber, D.; Boucherit, M. Modeling and simulation of a grid-connected PV generation system with MPPT fuzzy logic control. In Proceedings of the 2010 7th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices, IEEE; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Robles Algarín, C.; Taborda Giraldo, J.; Rodriguez Alvarez, O. Fuzzy logic-based MPPT controller for a PV system. Energies 2017, 10, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.R.; et al. Reduced simulative performance analysis of variable step size ANN-based MPPT techniques for partially shaded solar PV systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 48875–48889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrouche, B.; Belhamel, M.; Guessoum, A. Artificial intelligence based P&O MPPT method for photovoltaic systems. Rev. Energies Renouvelables ICRESD-07 Tlemcen.
- Al-Majidi, S.D.; Abbod, M.F.; Al-Raweshidy, H.S. Design of an intelligent MPPT based on ANN using a real photovoltaic system data. In Proceedings of the 2019 54th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), IEEE; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, A.; Gaur, P. Comparison of ANN and ANFIS based MPPT Controller for grid connected PV systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), IEEE; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wedderburn, R.W. Quasi-likelihood functions, generalized linear models, and the Gauss—Newton method. Biometrika 1974, 61, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.H.; Dahlin, T. A comparison of the Gauss–Newton and quasi-Newton methods in resistivity imaging inversion. J. Appl. Geophys. 2002, 49, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.V.; Ferris, M.C. A Gauss—Newton method for convex composite optimization. Math. Program. 1995, 71, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, H.O. The modified Gauss-Newton method for the fitting of non-linear regression functions by least squares. Technometrics 1961, 3, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, M.; Arridge, S.R.; Nissilä, I. Gauss–Newton method for image reconstruction in diffuse optical tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.; Lawless, A.S.; Nichols, N.K. Approximate Gauss–Newton methods for nonlinear least squares problems. SIAM J. Optim. 2007, 18, 106–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.M. The iterated Kalman smoother as a Gauss–Newton method. SIAM J. Optim. 1994, 4, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanidis, P.K.; Lane, R.W. Maximum likelihood parameter estimation of hydrologic spatial processes by the Gauss-Newton method. J. Hydrol. 1985, 79, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartis, C.; Roberts, L. A derivative-free Gauss–Newton method. Math. Program. Comput. 2019, 11, 631–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; et al. Application of centered differentiation and steepest descent to maximum power point tracking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.; Subudhi, B. A steepest-descent based maximum power point tracking technique for a photovoltaic power system. In Proceedings of the 2012 2nd International Conference on Power, Control and Embedded Systems; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Kumar, N.; Panigrahi, B.K. Steepest descent Laplacian regression based neural network approach for optimal operation of grid supportive solar PV generation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 68, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; et al. Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) techniques: Recapitulation in solar photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, H.; et al. MPPT for photovoltaic modules via newton-like extremum seeking control. Energies 2012, 5, 2652–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, H.; Leyva, R.; Castillo, E. Analysis of newton-like extremum seeking control in photovoltaic panels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ ‘12), Santiago de Compostela, Spain; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Malek, H.; Dadras, S.; Chen, Y. An improved maximum power point tracking based on fractional order extremum seeking control in grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-H.; Yau, H.-T.; Hung, W. Design and study on sliding mode extremum seeking control of the chaos embedded particle swarm optimization for maximum power point tracking in wind power systems. Energies 2014, 7, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, I.H.; Sharaf, A.M. A novel photovoltaic on-line search algorithm for maximum energy utilization. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. on Communication, 2007., Computer and Power (ICCCP).
- Ma, J.; et al. A hybrid MPPT method for photovoltaic systems via estimation and revision method. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), IEEE; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; et al. Improving power-conversion efficiency via a hybrid MPPT approach for photovoltaic systems. Elektron. Ir Elektrotechnika 2013, 19, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.O.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Classification and evaluation review of maximum power point tracking methods. Sustain. Futures 2020, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-R.; et al. A biological swarm chasing algorithm for tracking the PV maximum power point. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouilouta, A.; Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. New MPPT method for stand-alone photovoltaic systems operating under partially shaded conditions. Energy 2013, 55, 1172–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Fathy, A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. A comparison of different global MPPT techniques based on meta-heuristic algorithms for photovoltaic system subjected to partial shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; et al. A two-stage particle swarm optimization algorithm for MPPT of partially shaded PV arrays. Int. J. Green Energy 2017, 14, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, D.; He, Z. MPPT of a PV system based on the particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT), IEEE; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque, K.; et al. An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO)–based MPPT for PV with reduced steady-state oscillation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3627–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farayola, A.M. Comparative study of different photovoltaic MPPT techniques under various weather conditions. PhD Thesis, University of Johannesburg, 2017.
- Mlakić, D.; Majdandžić, L.; Nikolovski, S. ANFIS used as a maximum power point tracking algorithm for a photovoltaic system. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 2018, 8, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.A.; et al. ANFIS control for photovoltaic systems with DC-DC converters. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Automation, Control and Robots; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Blaabjerg, F.; Wang, H. An overview of artificial intelligence applications for power electronics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 4633–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; et al. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy.
- Amara, K.; et al. Improved performance of a PV solar panel with adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system ANFIS based MPPT. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), IEEE; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moyo, R.T.; Tabakov, P.Y.; Moyo, S. Design and modeling of the ANFIS-based MPPT controller for a solar photovoltaic system. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2021, 143, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfy, O.F.; Noor, S.B.M.; Marhaban, M.H. A simplified adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) controller trained by genetic algorithm to control nonlinear multi-input multi-output systems. Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 6475–6486. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; et al. A comparative study of artificial neural network, adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and support vector machine for forecasting river flow in the semiarid mountain region. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokun, O.M.; Onyesolu, M.O. Developing and evaluating a neuro-fuzzy expert system for improved food and nutrition in Nigeria. Open Access Libr. J. 2021, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yerokun, O.; Onyesolu, M. On the Development of Neuro-Fuzzy Expert System for Detection of Leghemoglobin (NFESDL) in Legumes. J. Digit. Innov. Contemp. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garud, K.S.; Jayaraj, S.; Lee, M.Y. A review on modeling of solar photovoltaic systems using artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, genetic algorithm and hybrid models. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Parian, J.A. Intelligent MPPT for photovoltaic panels using a novel fuzzy logic and artificial neural networks based on evolutionary algorithms. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mihoub, T.A.; et al. Hybrid Genetic Algorithms: A Review. Eng. Lett. 2006, 13, 124–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, Y.-T.; Zahara, E. A hybrid genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for multimodal functions. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, C.-F. A hybrid genetic algorithm for the open shop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 124, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cai, Y.; Xu, X. A hybrid genetic algorithm for feature selection wrapper based on mutual information. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2007, 28, 1825–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xiao, L. An improved adaptive genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the SHS Web of Conferences, EDP Sciences; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; et al. A Hybrid Computational Intelligence Method of Newton’s Method and Genetic Algorithm for Solving Compatible Nonlinear Equations. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci.
- Anwaar, A.; et al. Genetic Algorithms: Brief review on Genetic Algorithms for Global Optimization Problems. In Proceedings of the 2022 Human-Centered Cognitive Systems (HCCS), 1-6. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Du, Z. Genetic algorithm with simulated annealing for resolving job shop scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology (ICCSNT), IEEE; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maroufi, O.; Choucha, A.; Chaib, L. Hybrid fractional fuzzy PID design for MPPT-pitch control of wind turbine-based bat algorithm. Electr. Eng. 2020, 102, 2149–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Gizi, A. MPPT Of Solar Energy Converter With High-Sensitive Fuzzy PID Controller. WSEAS Trans. Comput. 2021, 20, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamanpira, M.; et al. A novel MPPT technique to increase accuracy in photovoltaic systems under variable atmospheric conditions using Fuzzy Gain scheduling. Energy Sources Part A 2021, 43, 2960–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghdisi, M.; Balochian, S. Maximum power point tracking of variable-speed wind turbines using self-tuning fuzzy PID. Technol. Econ. Smart Grids Sustain. Energy 2020, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; et al. Industrial heating furnace temperature control system design through fuzzy-PID controller. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International IoT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference (IEMTRONICS), IEEE; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ardhenta, L.; et al. Improvement of PID parameters for Ćuk converter using fuzzy logic in PV system. Int. J. Smart Grid Clean Energy 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Gizi, A.J.; Atillia, C.D.; Thajeel, S.M. PLC Fuzzy PID Controller of MPPT of Solar Energy Converter. WSEAS Trans. Syst. Control 2021, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaas, Z.; et al. Analysis and enhancement of MPPT technique to increase accuracy and speed in photovoltaic systems under different conditions. Optik 2023, 289, 171208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussama, M.; Abdelghani, C.; Lakhdar, C. Efficiency and robustness of type-2 fractional fuzzy PID design using salps swarm algorithm for a wind turbine control under uncertainty. ISA Trans. 2022, 125, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; et al. Non-singleton interval type-2 fuzzy PID control for high precision electro-optical tracking system. ISA Trans. 2022, 120, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; et al. A new optimal control methodology for improving MPPT based on FOINC integrated with FPI controller using AHA. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 224, 109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan G, S.; et al. MPPT in PV systems using ant colony optimisation with dwindling population. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, K.-H.; Rizal, M.N. A hybrid MPPT controller based on the genetic algorithm and ant colony optimization for photovoltaic systems under partially shaded conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhieb, Y.; et al. MPPT Optimization Using Ant Colony Algorithm: Solar PV Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 21st International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA), IEEE; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.-H.; Chao, K.-H.; Lee, T.-W. An Improved Photovoltaic Module Array Global Maximum Power Tracker Combining a Genetic Algorithm and Ant Colony Optimization. Technologies 2023, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.H.; et al. A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm based MPPT control technique for PV systems under complex partial shading condition. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101367. [Google Scholar]
- Sundareswaran, K.; et al. Development of an improved P&O algorithm assisted through a colony of foraging ants for MPPT in PV system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 12, 187–200. [Google Scholar]
- Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. MPPT-based artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic systems and its implementation into field programmable gate array chips: Review of current status and future perspectives. Energy 2014, 70, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.A. A review of fuzzy logic and artificial neural network technologies used for MPPT. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12, 2912–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, L.; Haddouche, A.; Haddouche, A. Comparison between proposed fuzzy logic and ANFIS for MPPT control for photovoltaic system. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.; Rezk, H. An improved fuzzy logic control-based MPPT method to enhance the performance of PEM fuel cell system. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; et al. Neural Network and Fuzzy Control Based 11-Level Cascaded Inverter Operation. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; et al. An adaptive robust fuzzy PI controller for maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic system. Optik 2022, 259, 168942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, R.; et al. A systematic review of gait analysis methods based on inertial sensors and adaptive algorithms. Gait Posture 2017, 57, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkholy, A.; Abou El-Ela, A. Optimal parameters estimation and modelling of photovoltaic modules using analytical method. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feroz Mirza, A.; et al. Advanced variable step size incremental conductance MPPT for a standalone PV system utilizing a GA-tuned PID controller. Energies 2020, 13, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, T.P.; Dixit, T. Modelling and analysis of Perturb & Observe and Incremental Conductance MPPT algorithm for PV array using Ċuk converter. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science, IEEE; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, A.F.; et al. Advanced variable step size incremental conductance MPPT for a standalone PV system utilizing a GA-tuned PID controller. Energies 2020, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal Mandour, R. Optimization of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of photovoltaic system using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. 2013.
- Dangi, P.; et al. A Comprehensive Study on Adaptive MPPT Control Techniques for Efficient Power Generation. In Proceedings of the Advancement in Materials, Manufacturing and Energy Engineering, Vol. I: Select Proceedings of ICAMME 2021, Springer; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayvargiya, S.P.; Sharma, V.K.; Nema, P. A novel topology for power quality improvement using EPO incremental conductance MPPT controller for SPV system with 51-level inverter. Electr. Eng. 2023, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femia, N.; et al. Predictive & adaptive MPPT perturb and observe method. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmelegi, A.; Ahmed, E.M. Study of Different PV Systems Configurations Case Study: Aswan Utility Company. In Proceedings of the 17th International Middle East Power Systems Conference, Mansoura University, Egypt; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bollipo, R.B.; Mikkili, S.; Bonthagorla, P.K. Critical review on PV MPPT techniques: classical, intelligent and optimisation. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 1433–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, D.C.; Dunnigan, M.W. Development and comparison of an improved incremental conductance algorithm for tracking the MPP of a solar PV panel. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tey, K.S.; Mekhilef, S. Modified incremental conductance algorithm for photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions and load variation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5384–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahhir, S.; et al. Modeling of photovoltaic system with modified incremental conductance algorithm for fast changes of irradiance. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuesong, Z.; et al. The simulation and design for MPPT of PV system based on incremental conductance method. In Proceedings of the 2010 WASE International Conference on Information Engineering, IEEE; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chafle, S.R.; Vaidya, U.B. Incremental conductance MPPT technique for PV system. Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Eng. 2013, 2, 2720–2726. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh Ahmadi, S.; et al. Improving MPPT performance in PV systems based on integrating the incremental conductance and particle swarm optimization methods. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A. Performance Analysis of Incremental Conductance INC and Adaptive Hill Climbing Search HCS MPPT Algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, N.; Luna, A.; Duarte, O. Improved MPPT short-circuit current method by a fuzzy short-circuit current estimator. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, IEEE; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sher, H.A.; et al. A new sensorless hybrid MPPT algorithm based on fractional short-circuit current measurement and P&O MPPT. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 6, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Ankaiah, B.; Nageswararao, J. Enhancement of solar photovoltaic cell by using short-circuit current MPPT method. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2013, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Baimel, D.; et al. Improved fractional open circuit voltage MPPT methods for PV systems. Electronics 2019, 8, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebani, M.M.; Iqbal, T.; Quaicoe, J.E. Comparing bisection numerical algorithm with fractional short circuit current and open circuit voltage methods for MPPT photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), IEEE; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, A.F.; et al. A novel hybrid MPPT technique for solar PV applications using perturb & observe and fractional open circuit voltage techniques. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference MECHATRONIKA, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P. Maximum power tracking based open circuit voltage method for PV system. Energy Procedia 2016, 90, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiazzi, G.; Buso, S.; Mattavelli, P. Analysis of MPPT algorithms for photovoltaic panels based on ripple correlation techniques in presence of parasitic components. In Proceedings of the 2009 Brazilian Power Electronics Conference; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zainudin, H.N.; Mekhilef, S. Comparison study of maximum power point tracker techniques for PV systems. 2010.
- TOZLU, Ö.F.; ÇALIK, H. A review and classification of most used MPPT algorithms for photovoltaic systems. Hittite J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faranda, R.; Leva, S. Energy comparison of MPPT techniques for PV Systems. WSEAS Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 3, 446–455. [Google Scholar]
- Faranda, R.; Leva, S.; Maugeri, V. MPPT techniques for PV systems: Energetic and cost comparison. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting-Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, IEEE; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, R.F.; Concer, F.M.; Martins, D.C. A MPPT approach based on temperature measurements applied in PV systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies (ICSET), IEEE; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Brito, M.A.; et al. Comparative analysis of MPPT techniques for PV applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), IEEE; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Brito, M.A.G.; et al. Evaluation of the main MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, M.; et al. Performance enhancement of constant voltage based MPPT for photovoltaic applications using genetic algorithm. Energy Procedia 2016, 100, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wu, X. Compensation loop design of a photovoltaic system based on constant voltage MPPT. In Proceedings of the 2009 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, IEEE; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aldair, A.A.; Obed, A.A.; Halihal, A.F. Design and implementation of ANFIS-reference model controller based MPPT using FPGA for photovoltaic system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2202–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; et al. Performance characteristics of photovoltaic cold storage under composite control of maximum power tracking and constant voltage per frequency. Appl. Energy 2022, 305, 117840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapkitticharoenchai, Y.; Jangwanitlert, A. Lookup Table Technique by using Irradiation Intensity and Duty Cycle for Faster MPPT Application. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Business and Industrial Research (ICBIR), IEEE; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sulthan, S.M.; Devaraj, D.; Raj, V. Development and analysis of a Two-stage Hybrid MPPT algorithm for solar PV systems. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; et al. PV arrays reconfiguration for partial shading mitigation: Recent advances, challenges and perspectives. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 247, 114738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, B.K.; Karmakar, G. A current supported PV array reconfiguration technique to mitigate partial shading. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, B.; Rajasekar, N. A novel competence square based PV array reconfiguration technique for solar PV maximum power extraction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 174, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, S.; et al. Photovoltaic array reconfiguration under partial shading conditions for maximum power extraction: A state-of-the-art review and new solution method. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 258, 115468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmahmoudian, M.; et al. State-of-the-art artificial intelligence-based MPPT techniques for mitigating partial shading effects on PV systems–A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, H.H.; Youssef, A.-R.; Mohamed, E.E. State-of-the-art perturb and observe MPPT algorithms based wind energy conversion systems: A technology review. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 126, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamarelis, E.; Petrone, G.; Spagnuolo, G. A two-steps algorithm improving the P&O steady-state MPPT efficiency. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 414–421. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, A. Amplitude limiting for the photovoltaic (PV) grid-connected inverter with the function of active power filter. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems, IEEE; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dhande, M.D.P.; Chaudhari, A.; Mahajan, G. A Review of Various MPPT Techniques for Photovoltaic System. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Smedley, K.M. A cost-effective single-stage inverter with maximum power point tracking. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femia, N.; et al. Optimized one-cycle control in photovoltaic grid-connected applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2006, 42, 954–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltawil, M.A.; Zhao, Z. MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, A.K.; Roy, N.K.; Pota, H.R. MPPT methods for solar PV systems: a critical review based on tracking nature. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.N.A.; et al. A survey of maximum PPT techniques of PV systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Energytech, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fatemi, S.M.; Shadlu, M.S.; Talebkhah, A. Comparison of three-point P&O and hill climbing methods for maximum power point tracking in PV systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Power Electronics, Drive Systems and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), IEEE; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dolara, A.; Faranda, R.; Leva, S. Energy comparison of seven MPPT techniques for PV systems. J. Electromagn. Anal. Appl. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-A.; et al. Maximum power tracking for photovoltaic power systems. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2005, 8, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-J.; et al. The experimental analysis of the grid-connected PV system applied by POS MPPT. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), IEEE; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, N.; Moubayed, N.; Outbib, R. General review and classification of different MPPT Techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.; Kanchan, D.S. Analysis of photovoltaic systems to achieve maximum power point tracking with variable inductor. Int. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. Telecommun. 2015, 1, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; et al. Optimization of self-adaptive INR-MPPT for R-Mode RED stacks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), IEEE; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mastromauro, R.A.; Liserre, M.; Dell’Aquila, A. Control issues in single-stage photovoltaic systems: MPPT, current and voltage control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 8, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sera, D.; et al. Improved MPPT method for rapidly changing environmental conditions. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, IEEE; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpetta, F.; Liserre, M.; Mastromauro, R.A. Adaptive distributed MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012-38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abouadane, H.; et al. Multiple-power-sample based P&O MPPT for fast-changing irradiance conditions for a simple implementation. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2020, 10, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Salameh, Z.M.; Dagher, F.; Lynch, W.A. Step-down maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy 1991, 46, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayod-Rújula, Á.-A.; Cebollero-Abián, J.-A. A novel MPPT method for PV systems with irradiance measurement. Sol. Energy 2014, 109, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femia, N.; et al. Optimizing sampling rate of P&O MPPT technique. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE 35th Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37551), IEEE; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Killi, M.; Samanta, S. Modified perturb and observe MPPT algorithm for drift avoidance in photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, V.K.; et al. A modified Perturb & Observe MPPT technique to tackle steady state and rapidly varying atmospheric conditions. Sol. Energy 2017, 157, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, S.A.M.; Hamada, A.M.; Abdellatif, W.S. Comparative analysis of the modified perturb & observe with different MPPT techniques for PV grid-connected systems. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2020, 10, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, M. Derated mode of power generation in PV system using modified perturb and observe MPPT algorithm. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 9, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileep, G.; Singh, S. Maximum power point tracking of solar photovoltaic system using modified perturbation and observation method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Duque, J.E.; Ortiz-Rivera, E.I.; González-Llorente, J. Modified perturb and observe MPPT algorithm based on a narrow set of initial conditions. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE ANDESCON, IEEE; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Raiker, G.A.; Loganathan, U. Current control of boost converter for PV interface with momentum-based perturb and observe MPPT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 4071–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; et al. Control of MPPT for photovoltaic systems using advanced algorithm EPP. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Power Systems; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Samantara, S.; et al. Modeling and simulation of integrated CUK converter for grid-connected PV system with EPP MPPT hybridization. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 2015.
- Alkhawaldeh, L.; et al. An enhanced EPP-MPPT algorithm with modified control technique in solar-based inverter applications: Analysis and experimentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 8158–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, B.; Cheung, R. Advanced algorithm for MPPT control of photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the Canadian Solar Buildings Conference, Montreal; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Go, S.-I.; et al. Simulation and analysis of existing MPPT control methods in a PV generation system. J. Int. Counc. Electr. Eng. 2011, 1, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, A.; et al. A comprehensive review of PV-driven electrical motors. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 278–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, I.; Zhang, L.; Corda, J. Voltage-hold perturbation & observation maximum power point tracking algorithm (VH-P&O MPPT) for improved tracking over transient atmospheric changes. In Proceedings of the 2011 14th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, IEEE; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Salam, M.; EL-Mohandes, M.-T.; Goda, M. On the improvements of perturb-and-observe-based MPPT in PV systems. Mod. Maximum Power Point Track. Tech. Photovolt. Energy Syst. 2020, 165–198. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Salam, M.; El-Mohandes, M.-T.; Goda, M. An improved perturb-and-observe based MPPT method for PV systems under varying irradiation levels. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, I.; Corda, J.; Zhang, L. Optimal control of a multilevel DC-link converter photovoltaic system for maximum power generation. Renew. Energy 2016, 92, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, M.; EL-Mohandes, M.-T.; Goda, M. History of Maximum Power Point Tracking. Mod. Maximum Power Point Track. Tech. Photovolt. Energy Syst. 2020, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-S.; Lee, K.B. Variable DC-link voltage algorithm with a wide range of maximum power point tracking for a two-string PV system. Energies 2013, 6, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, M.; et al. A neural networks-based maximum power point tracker with improved dynamics for variable dc-link grid-connected photovoltaic power plants. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2013, 43, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.K.; Myneni, H.; Kumar, G.S. Power quality improvement and PV power injection by DSTATCOM with variable DC link voltage control from RSC-MLC. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Singh, B. A three-phase grid tied SPV system with adaptive DC link voltage for CPI voltage variations. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjai, T.; et al. Implementation of a modified incremental conductance MPPT algorithm with direct control based on a fuzzy duty cycle change estimator using dSPACE. Sol. Energy 2014, 110, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punitha, K.; Devaraj, D.; Sakthivel, S. Artificial neural network-based modified incremental conductance algorithm for maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions. Energy 2013, 62, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farayola, A.M.; Hasan, A.N.; Ali, A. Comparison of modified incremental conductance and fuzzy logic MPPT algorithm using modified CUK converter. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), IEEE; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, P.K.; et al. Modified incremental conductance MPPT algorithm for SPV-based grid-tied and stand-alone systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2022, 16, 776–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, M. A new maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic systems. Waset. Org 2008, 34, 571–574. [Google Scholar]
- Azab, M. Global maximum power point tracking for partially shaded PV arrays using particle swarm optimisation. Int. J. Renew. Energy Technol. 2009, 1, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, M. Flexible PQ control for single-phase grid-tied photovoltaic inverter. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2017 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), IEEE; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Celikel, R.; Yilmaz, M.; Gundogdu, A. A voltage scanning-based MPPT method for PV power systems under complex partial shading conditions. Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalh, A.; et al. Global MPPT of photovoltaic system based on scanning method under partial shading condition. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başoğlu, M.E. An enhanced scanning-based MPPT approach for DMPPT systems. Int. J. Electron. 2018, 105, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, L.; et al. MPPT definition and validation: A new model-based approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, Y.; Abdelwahed, M.; El-Saadany, E.F. An enhanced MPPT method combining model-based and heuristic techniques. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2015, 7, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y. A model-based MPPT with improved tracking accuracy. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018-44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, IEEE; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cristaldi, L.; et al. An improved model-based maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic panels. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 63, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshksar, E.; Ghanbari, T. A model-based algorithm for maximum power point tracking of PV systems using exact analytical solution of single-diode equivalent model. Sol. Energy 2018, 162, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; et al. Performance Evaluation of PV Model-Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques. Electronics 2022, 11, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.-K.; Wei, Y.-C.; Lee, M.-Y. Fuzzy controller for a voltage-regulated solar-powered MPPT system for hybrid power system applications. Energies 2015, 8, 3292–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Yi, W.D.; Jwo, K.W. High efficiency MPPT using piecewise linear approximation and temperature compensation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 772, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; et al. An improved MPPT method for PV system with fast-converging speed and zero oscillation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 5051–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Grandi, G. A single-phase multilevel PV generation system with an improved ripple correlation control MPPT algorithm. Energies 2017, 10, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, J.W.; Krein, P.T. Digital ripple correlation control for photovoltaic applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, IEEE; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei, M.; Abdolmaleki, M.; Mehrabi, A.H. A new method of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of photovoltaic (PV) cells using impedance adaption by ripple correlation control (RCC). In Proceedings of the 2012 Proceedings of 17th Conference on Electrical Power Distribution; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, S.; et al. A two-level MPPT algorithm in dynamic partial shading condition using ripple correlation control. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), IEEE; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, P.; Dey, R. Maximum Power Point Tracking for Photovoltaic Systems Using Ripple Correlation Control. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation, 2021., Power and Signal Processing (CAPS).
- Tsang, K.; Chan, W.L. Maximum power point tracking for PV systems under partial shading conditions using current sweeping. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 93, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; et al. Notice of Retraction: Research of PV Model and MPPT Methods in Matlab. In Proceedings of the 2010 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, IEEE; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; et al. Analysis and comparison of PV array MPPT techniques to increase output power. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE); 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, J.G.; Araújo, R.E. Virtual inertia and droop control using DC-link in a two-stage PV inverter. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 14th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG), IEEE; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; et al. Droop control with improved disturbance adaption for a PV system with two power conversion stages. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6073–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wesabi, I.; et al. Direct sliding mode control for dynamic instabilities in DC-link voltage of standalone photovoltaic systems with a small capacitor. Electronics 2022, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalili, D.; et al. State feedback control and variable step size MPPT algorithm of three-level grid-connected photovoltaic inverter. Sol. Energy 2013, 98, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-E.; Song, J.-H. A dP/dV feedback-controlled MPPT method for photovoltaic power system using II-SEPIC. J. Power Electron. 2009, 9, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-S.; et al. Tracking system and MPPT control for efficiency improvement of photovoltaic. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F. A novel method to estimate the maximum power for a photovoltaic inverter system. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE 35th Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37551), IEEE; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bianconi, E.; et al. A fast current-based MPPT technique employing sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamarelis, E.; Petrone, G.; Spagnuolo, G. Design of a sliding-mode-controlled SEPIC for PV MPPT applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 3387–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihal, A.; et al. An improved MPPT scheme employing adaptive integral derivative sliding mode control for photovoltaic systems under fast irradiation changes. ISA Trans. 2019, 87, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farayola, A.M.; Hasan, A.N.; Ali, A. Curve fitting polynomial technique compared to ANFIS technique for maximum power point tracking. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), IEEE; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- González-Castaño, C.; et al. A fast-tracking hybrid MPPT based on surface-based polynomial fitting and P&O methods for solar PV under partial shaded conditions. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2732. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, P.; Kumar, N.; Panigrahi, B.K. A framework of reduced sensor rooftop SPV system using parabolic curve fitting MPPT technology for household consumers. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2022, 69, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; et al. Maximum photovoltaic power tracking for the PV array using the fractional-order incremental conductance method. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 4840–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Camacho, R.I.; et al. Transient differentiation maximum power point tracker (TD-MPPT) for optimized tracking under very fast-changing irradiance: a theoretical approach for mobile PV applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, V.V.; Buso, S.; Spiazzi, G. Low-complexity MPPT technique exploiting the PV module MPP locus characterization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 56, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Bansal, M. MPPT Techniques—A Review. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1055, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; et al. A comparative study on photovoltaic MPPT algorithms under EN50530 dynamic test procedure. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 4153–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, C.F.; et al. Computing solar irradiance and average temperature of photovoltaic modules from the maximum power point coordinates. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2020, 10, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esram, T.; Chapman, P.L. Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besheer, A.; Adly, M. Ant colony system based PI maximum power point tracking for stand-alone photovoltaic system. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H. A novel MPPT control algorithm based on numerical calculation for PV generation systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 6th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, IEEE; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qaraad, M.; et al. An innovative quadratic interpolation salp swarm-based local escape operator for large-scale global optimization problems and feature selection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 17663–17721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; et al. A multi-strategy enhanced salp swarm algorithm for global optimization. Eng. Comput. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemofouet, S.; Rufer, A. Hybrid energy storage system based on compressed air and super-capacitors with maximum efficiency point tracking (MEPT). IEEJ Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 126, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; et al. Extremum seeking control-based integration of MPPT and degradation detection for photovoltaic arrays. In Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference, IEEE; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zazo, H.; Leyva, R.; del Castillo, E. MPPT based on newton-like extremum seeking control. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, IEEE; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffari, A.; Krstić, M.; Seshagiri, S. Power optimization for photovoltaic microconverters using multivariable newton-based extremum seeking. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; et al. Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) control of a photovoltaic system based on dual carrier chaotic search. J. Control Theory Appl. 2012, 10, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, Z.; Ahmed, J.; Merugu, B.S. The application of soft computing methods for MPPT of PV system: A technological and status review. Appl. Energy 2013, 107, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, E.N.; et al. Simulated Annealing-MPPT in Partially Shaded PV Systems. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2016, 14, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; et al. Enhanced simulated annealing-based global MPPT for different PV systems in mismatched conditions. J. Power Electron. 2017, 17, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, K.; Andrean, V. A new MPPT method for partially shaded PV system by combining modified INC and simulated annealing algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Power Systems (ICHVEPS); 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, A.A.Z. MPPT of PV system under partial shading conditions based on hybrid whale optimization-simulated annealing algorithm (WOSA). Mod. Maximum Power Point Track. Tech. Photovolt. Energy Syst. 2020, 355–378. [Google Scholar]
- Lyden, S.; Haque, M. A comprehensive study of the key parameters of the Simulated Annealing method for maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), IEEE; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carannante, G.; et al. Experimental performance of MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic sources subject to inhomogeneous insolation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4374–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, A.F.; et al. Rapid active power control of photovoltaic systems for grid frequency support. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.; et al. Comparative analysis of speed of convergence of MPPT techniques. In Proceedings of the 2011 6th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems, IEEE; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.-H.; et al. A real maximum power point tracking method for mismatching compensation in PV array under partially shaded conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 26, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; et al. Application of bio-inspired algorithms in maximum power point tracking for PV systems under partial shading conditions–A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 840–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, T.T.; et al. An improved indirect maximum power point tracking method for standalone photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the 9th WSEAS international conference on applications of electrical engineering, Selangor, Malaysia; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sera, D.; et al. Improved MPPT algorithms for rapidly changing environmental conditions. In Proceedings of the 2006 12th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, IEEE; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulmajeed, Q.M.; et al. Photovoltaic maximum tracking power point system: review and research challenges. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. (IJATCSE) 2013, 2, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jusoh, A.; et al. A Review on favourable maximum power point tracking systems in solar energy application. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control) 2014, 12, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarzaman, N.A.; Tan, C.W. A comprehensive review of maximum power point tracking algorithms for photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.P.K.; et al. Comparison of mppt algorithms for dc-dc converters based pv systems. Int. J. Adv. Res. Electr. Electron. Instrum. Eng. 2012, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M. Power Electronics Handbook [Electronic Resource]: Devices, Circuits, and Applications. Elsevier/BH: Amsterdam, 2011.
- Kumari, J.S.; Babu, C.S. Comparison of maximum power point tracking algorithms for photovoltaic system. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2011, 1, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. Advanced electrical and electronics engineering. Springer, 2011.
- Rekioua, D.; Matagne, E. Optimization of photovoltaic power systems: modelization,simulation and control. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
- Rahmani, R.; et al. Implementation of fuzzy logic maximum power point tracking controller for photovoltaic system. 2013.
- Lyden, S.; Haque, M.E. Maximum Power Point Tracking techniques for photovoltaic systems: A comprehensive review and comparative analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1504–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, J. Summary of maximum power point tracking methods for photovoltaic cells. electronic matter, retrieved on May, 2015.
- Kumar, C.K.; Dinesh, T.; Babu, S.G. Design and Modelling of PV system and Different MPPT algorithms. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. (IJETT) 2013, 4, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, Z. A MPPT method using piecewise linear approximation and temperature compensation. 2013.
- Rahman, M.H.; Poddar, S. Efficiency comparison between different algorithms for maximum power point tracker of a solar system. Int. J. Sci. Res. Manag. (IJSRM) 2013, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, F.; Nan, T. A Strategy research on MPPT technique in photovoltaic power generation system. TELKOMNIKA Indones. J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 11, 7627–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisi, A.R.; Moradi, M.H.; Jamasb, S. Classification and comparison of maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic system: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Amaratunga, G.A. Analytic solution to the photovoltaic maximum power point problem. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2007, 54, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, R. A review of the numerical methods for recognising and analysing racial differentiation. Numer. Taxon. 1983, 404–423. [Google Scholar]
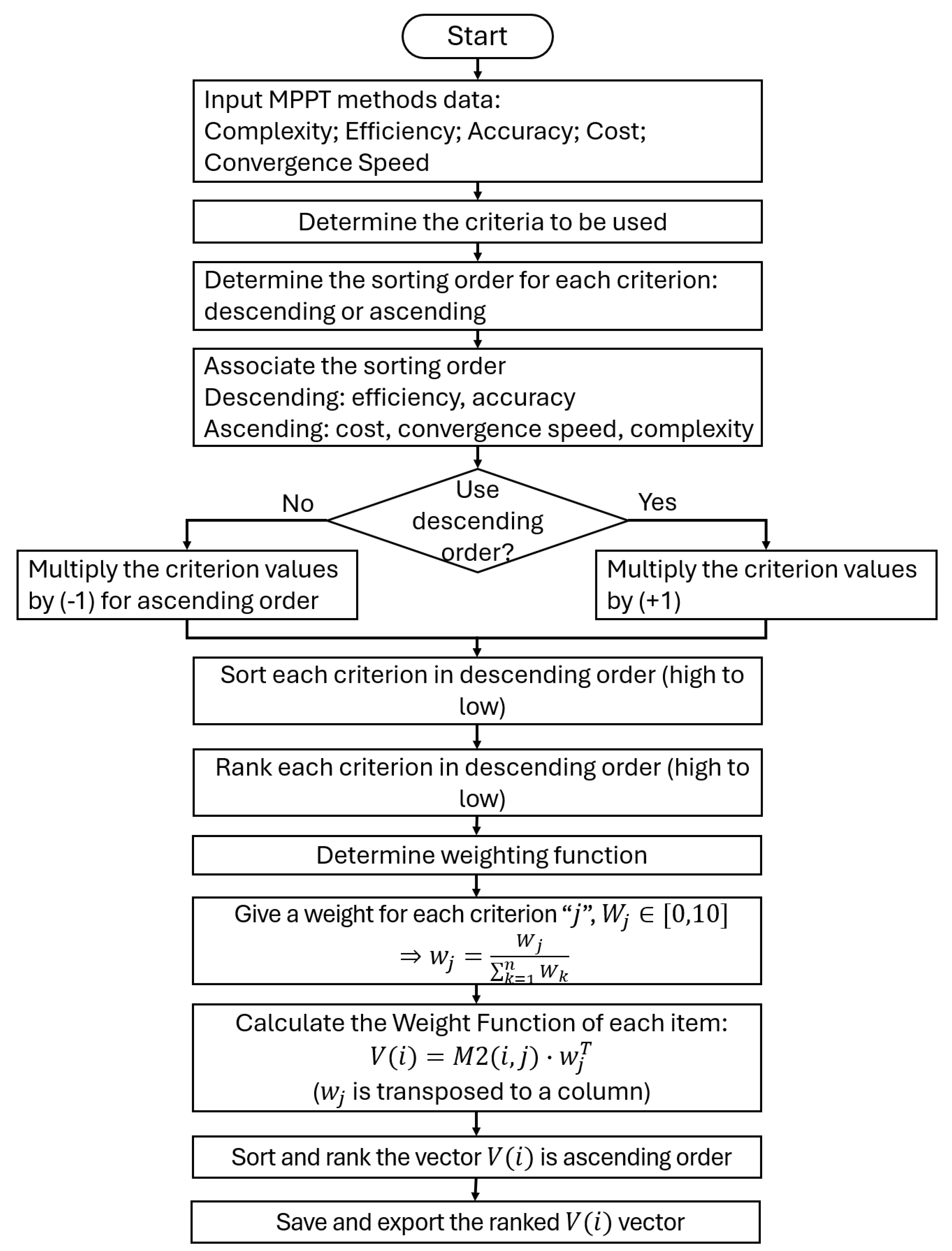
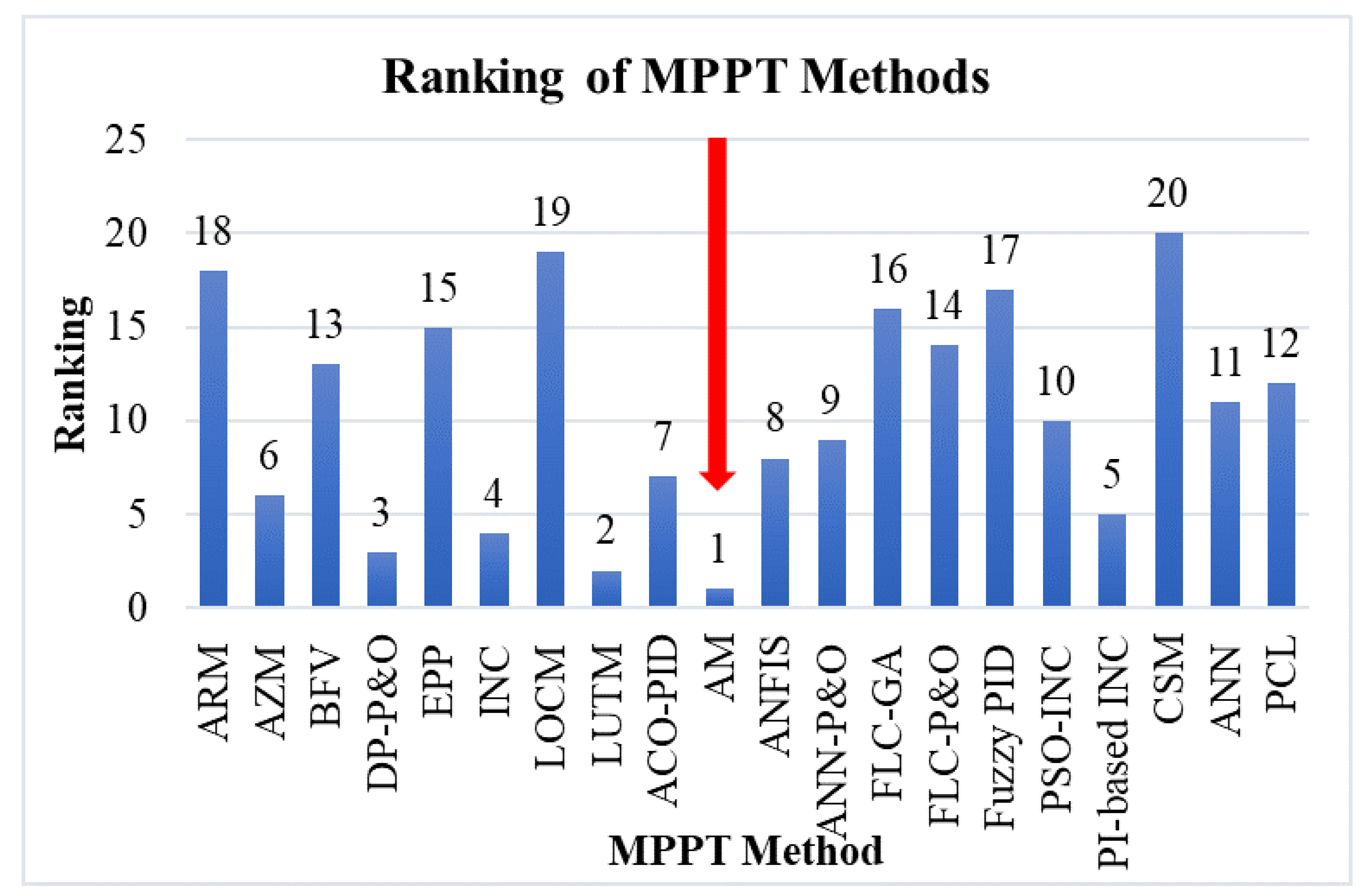
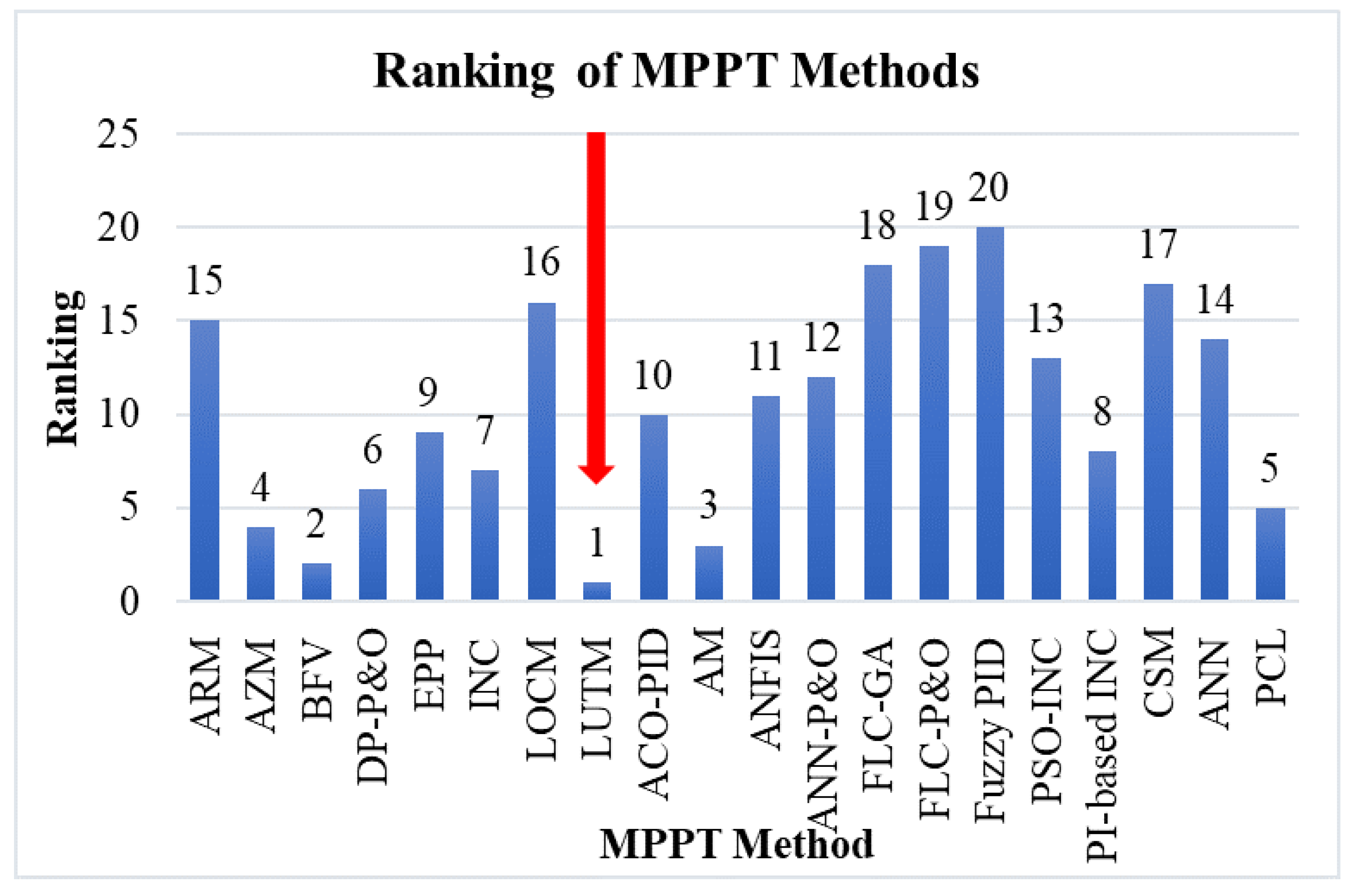

| Weighting Factor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Convergence Speed | Accuracy | Cost | Efficiency | |
| Example 1 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Example 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 10 | 10 |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| PV array dependencies | No specific configurations required or a predefined parameters value |
| MPPT accuracy | When the actual MPPT is compared to an inaccurate one, Pout will decrease with respect to the actual value. |
| Type of operation | Relies on the circuit category. |
| Tuning over periodic sets of time | Any oscillation involved in this scenario. |
| Convergence speed | How fast to converge and reach MPP. |
| Complexity | Describes the complexity of the module. |
| Parameters | Relies on variables’ factors. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





