Submitted:
13 October 2025
Posted:
14 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Discovery of Biocatalysis and Chirality
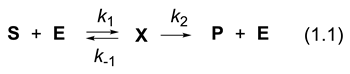
1.2. Kinetic Enantioselectivity
1.3. Chiral Catalysts Are Temporary Chiral Auxiliaries
2. Biocatalysis
2.1. Hydroxynitrile Lyases
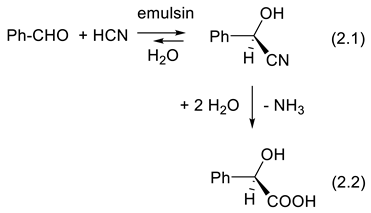
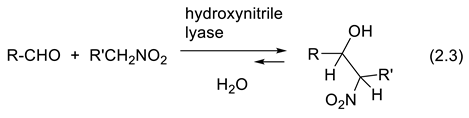
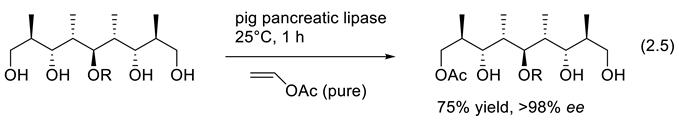
2.2. Esterases
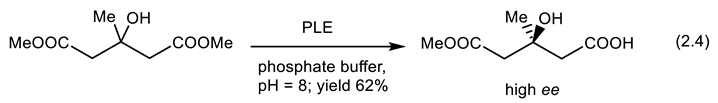
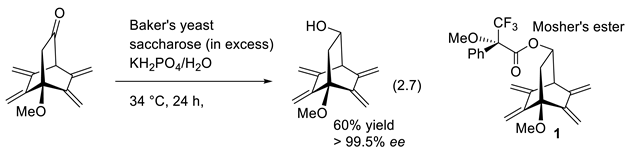
2.3. Baker’s Yeast
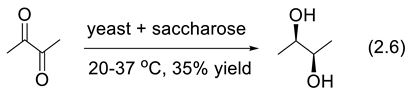
2.4. Fermentative Oxidation
2.5. Aldolases
2.6. Other Asymmetric Biocatalyzed C-C Bond-Forming Reactions.
3. Asymmetric Amino-Catalysis: The Queen of Organocatalysis
3.1. Cinchona Alkaloids and Derivatives as Catalysts
3.1.1. Cinchona Alkaloids as Chiral Brønsted Bases
3.1.2. Cinchona Alkaloids and Derivatives Are Capable of Providing Hydrogen Bonding
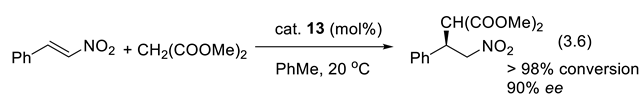
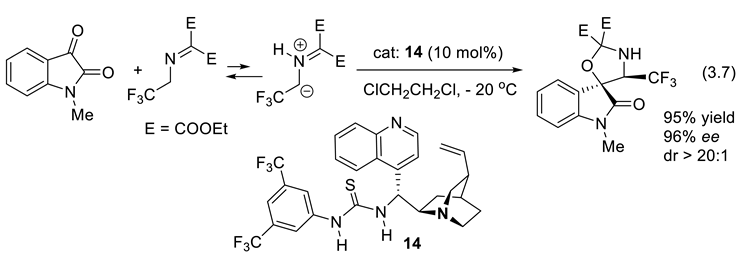
3.1.3. Conjugate Acids of Cinchona Alkaloids and Simpler Chiral Amines as Enantioselective Protonation Catalysts
3.1.4. Cinchona Alkaloid Derivatives as Nucleophilic Activators
3.1.5. Iminium Ion Mode of Activation by Cinchona Alkaloids
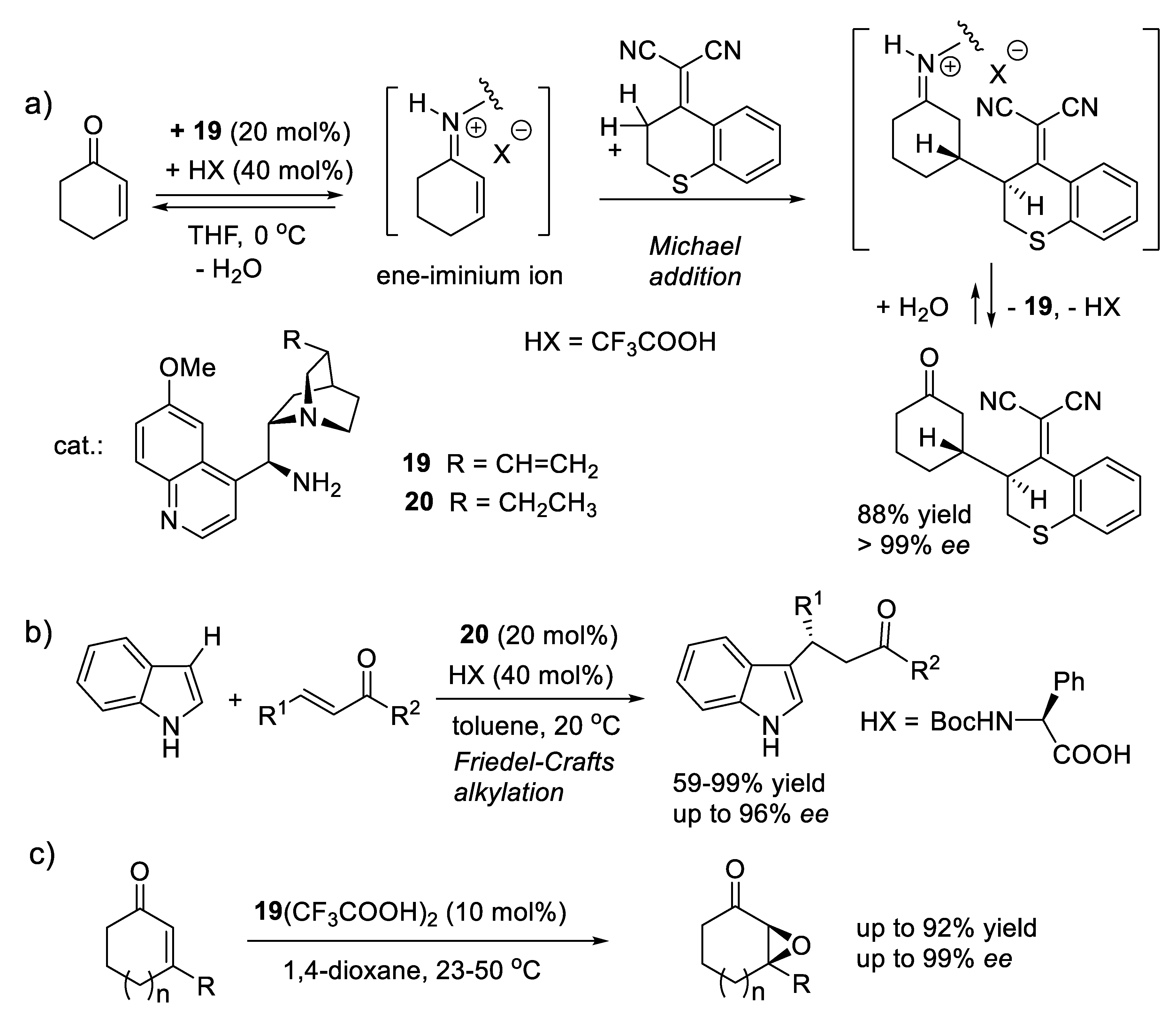
3.1.6. Enamine Mode of Activation by Cinchona Alkaloids
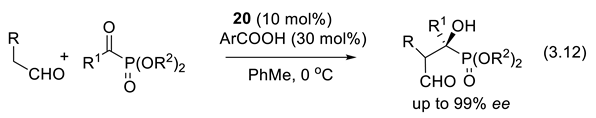
3.1.7. Cinchona Alkaloid Derivatives with Halogen Bond (XB) Donors
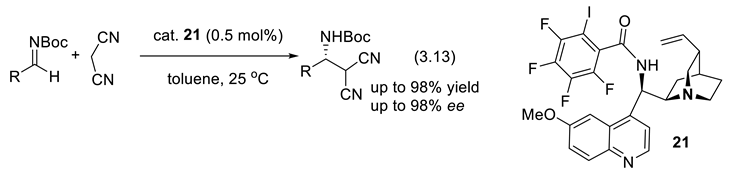
3.2. Cinchona Alkaloid-Derived Ammonium Salts: Enantioselective Phase Transfer Catalysts (PTCs)
3.2.1. Early Enantioselective Phase Transfer Catalyzed Applications
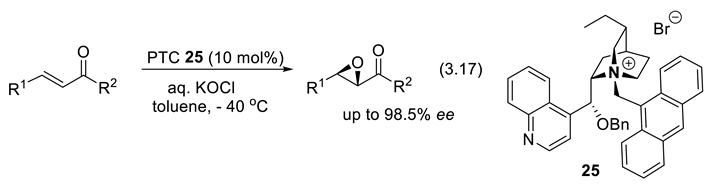
3.2.2. Industrial Applications of Chiral PTCs
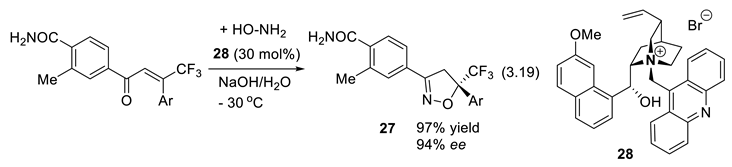
3.2.3. Polyfunctional Cinchona-Derived Polyfunctional PTCs
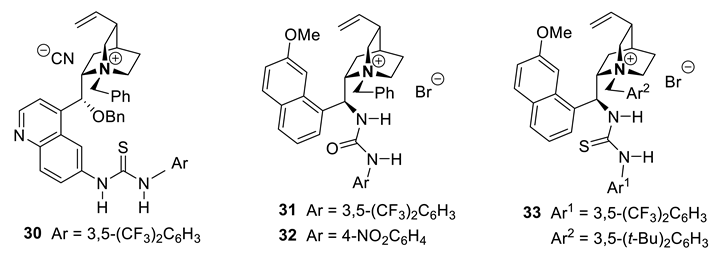
3.2.4. Non-Cinchona-Derived Chiral Ammonium Phase Transfer Catalysts
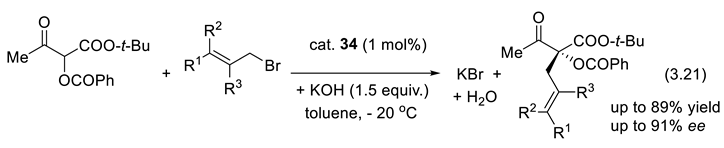
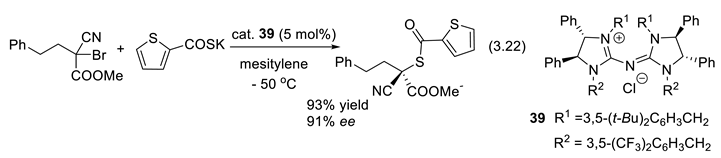
3.3. Asymmetric Hydrogen Atom Abstraction with Cinchona Alkaloid Derivatives
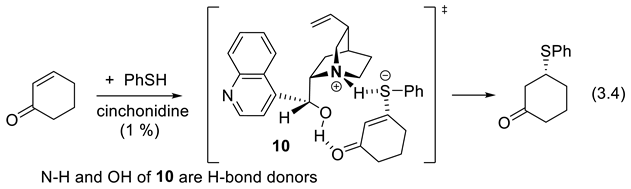
3.4. Iminium Ion Mode of Activation by Simple Chiral Amines
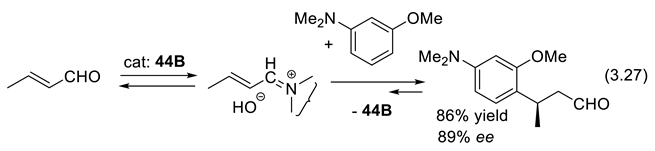
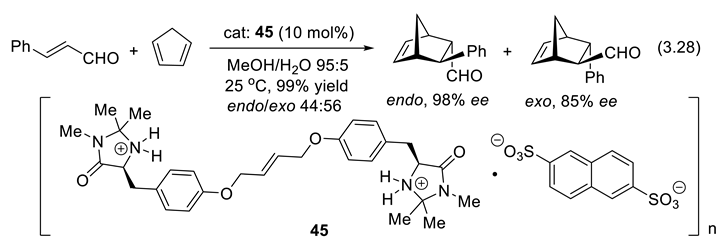
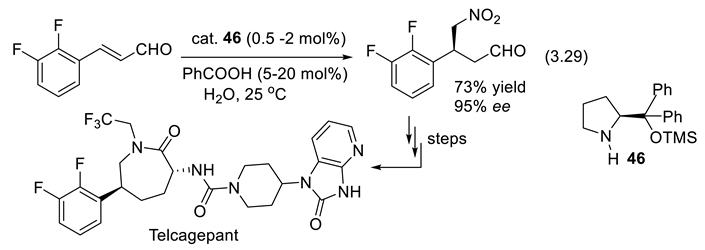
3.5. Enamine Mode of Activation by Simple Chiral Amines
3.5.1. Asymmetric Michael Additions
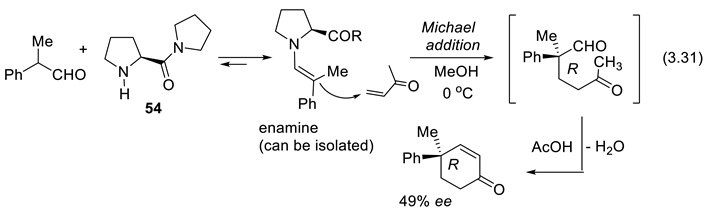
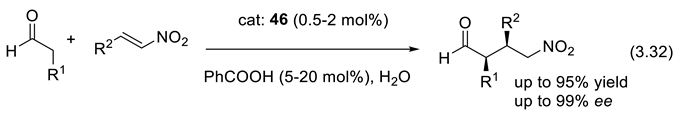
3.5.2. Asymmetric Aldol Reactions
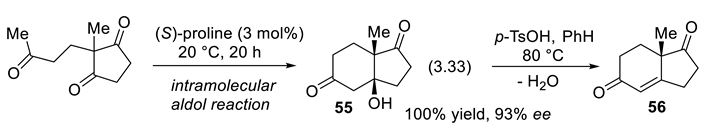
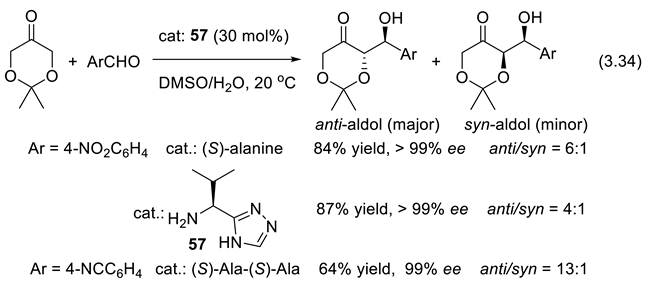
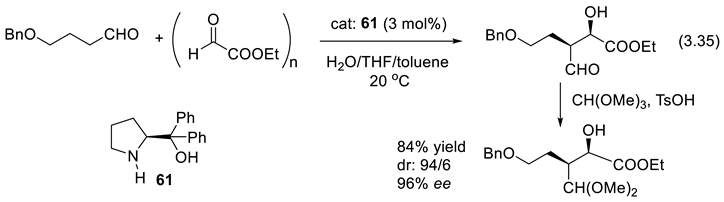
3.5.3. Asymmetric Mannich Condensations
3.5.4. Asymmetric Diels-Alder Reactions with Inverse-Electron-Demand
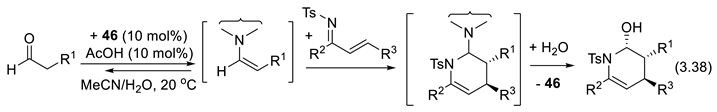
3.5.5. Asymmetric α Halogenations
3.5.6. Asymmetric α-Benzylation of Aldehydes with Alcohols
3.6. Dienamine and Trienamine Mode of Activation
3.7. Asymmetric Amine-Catalyzed Domino Reactions
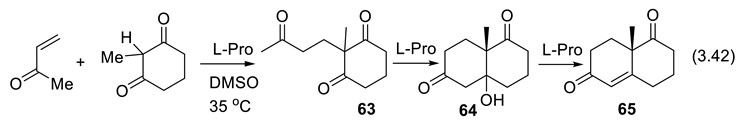
3.8. Asymmetric Amine Catalyzed Multicomponent Synthesis
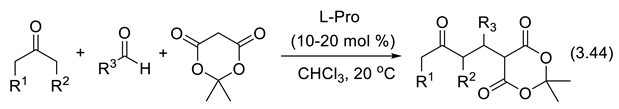
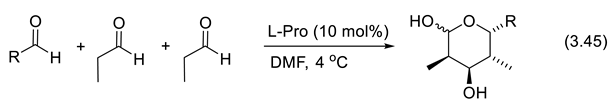
3.9. Ene-Aminium Radical-Cation Mode of Activation
3.10. Asymmetric Morita-Baylis-Hillman Reactions Catalyzed by Amines
3.11. Chiral Lewis Bases That Are Not Amines as Organo-Catalysts
3.11.1. Chiral Guadinines
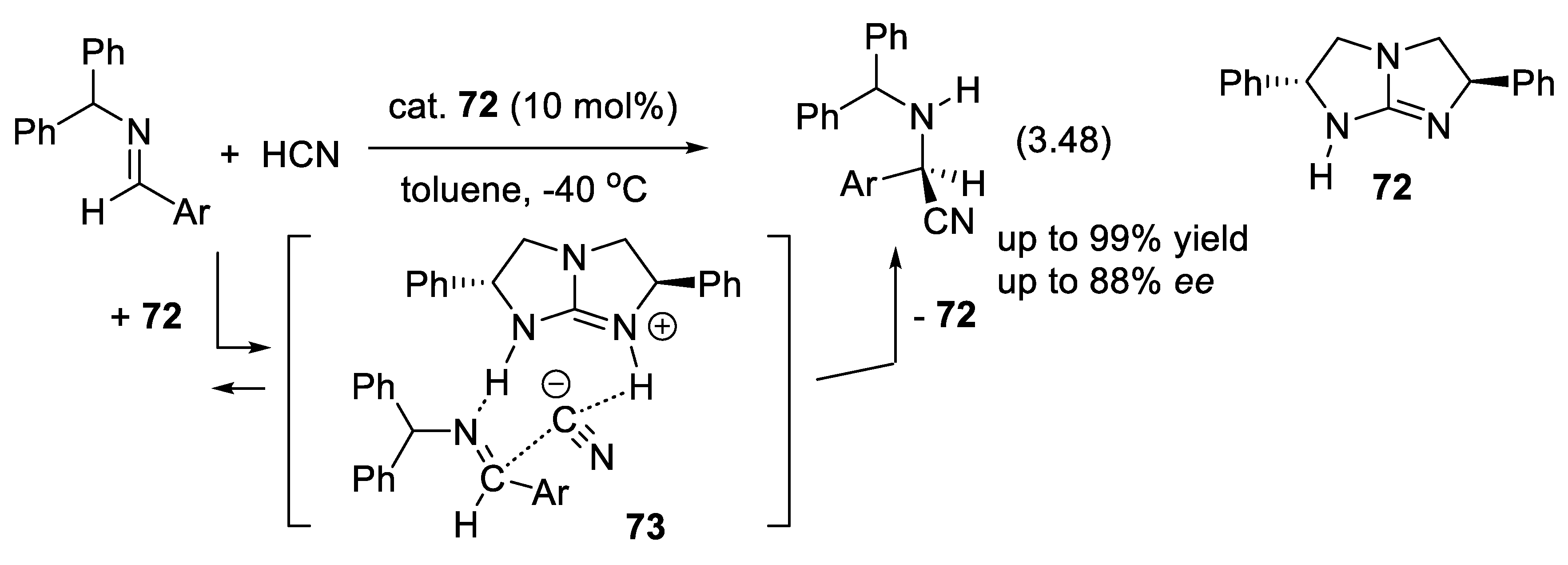
3.11.2. Benzotetramisoles
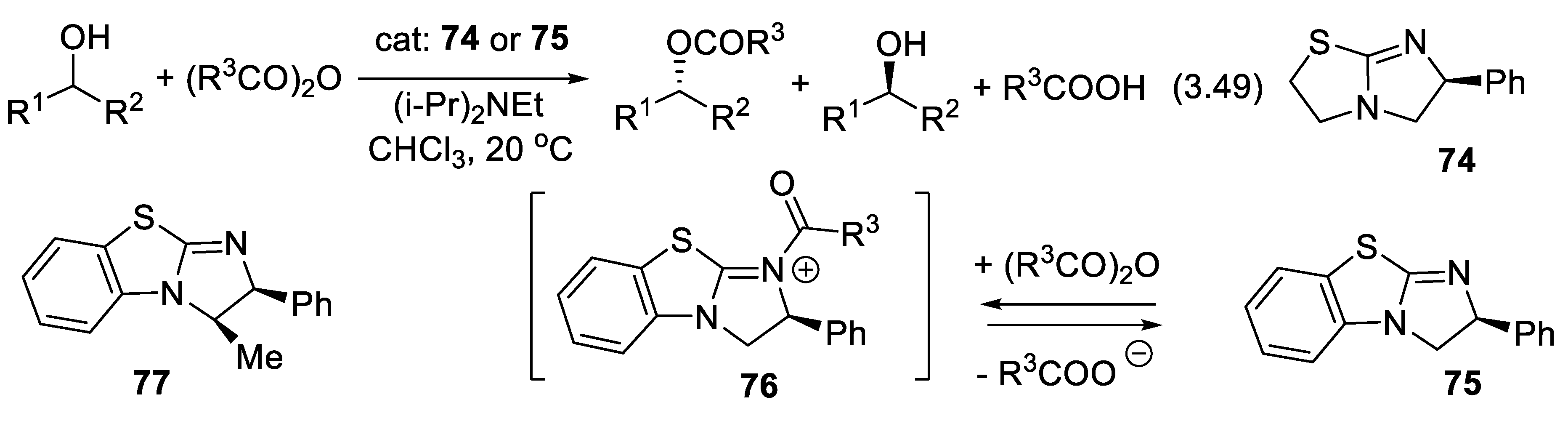
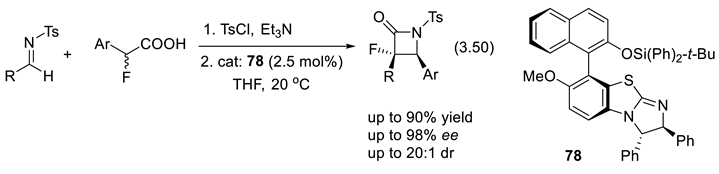
3.11.3. Acylammonium Mode of Activation
3.11.4. Carbamates
4. Asymmetric Organo-Catalysis with Peptides
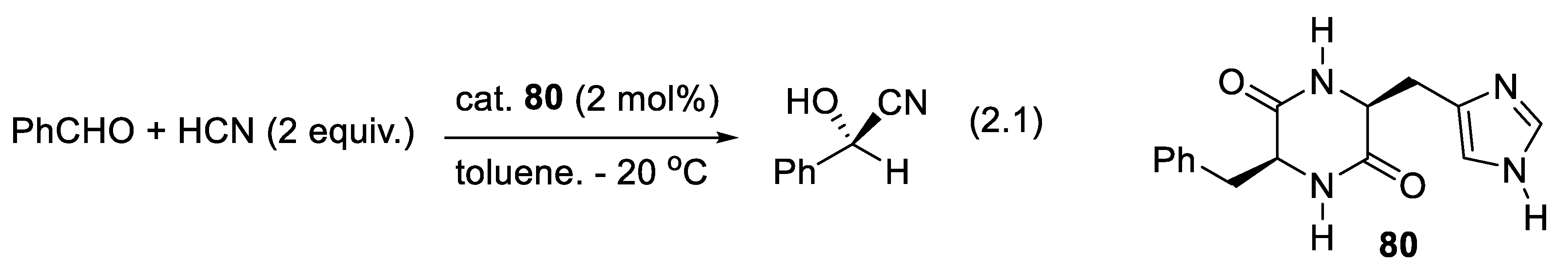
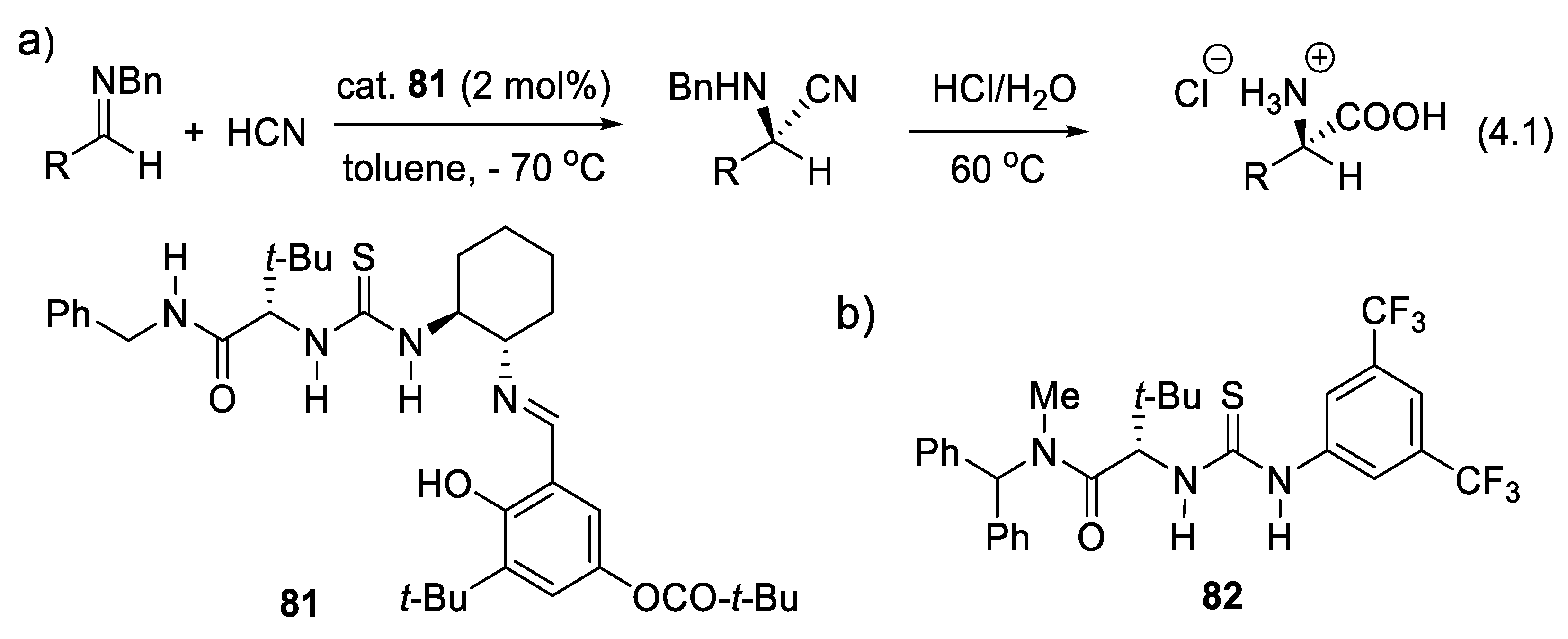
4.1. Asymmetric Hydrocyanations
4.2. Asymmetric Oxidations
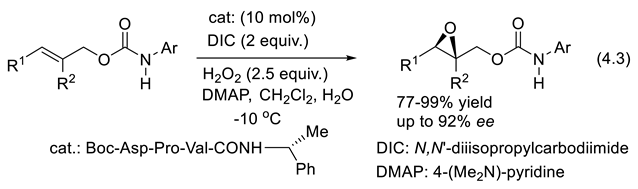
4.3. Asymmetric Intermolecular Aldol Reactions
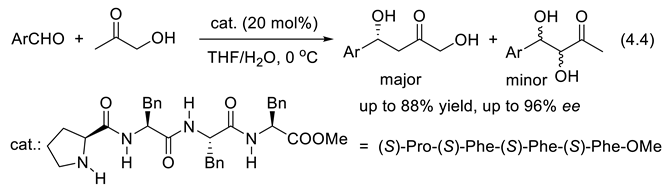
4.4. Peptide-Catalyzed Conjugate Additions
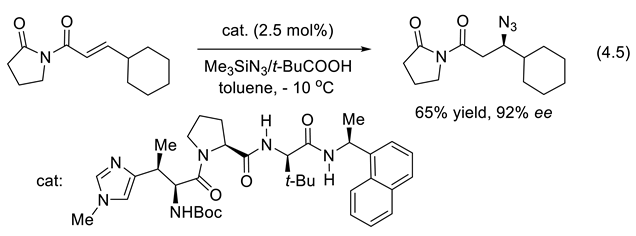
4.5. Peptide-Catalyzed Morita-Baylis-Hillman Reaction
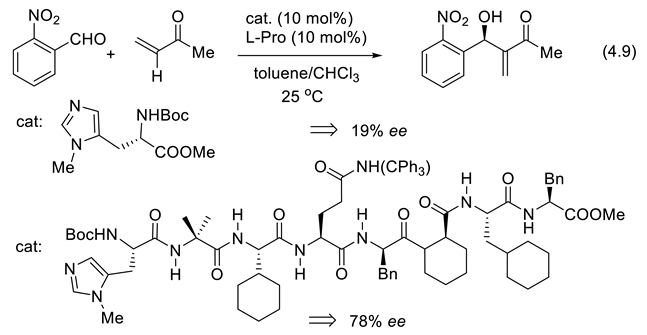
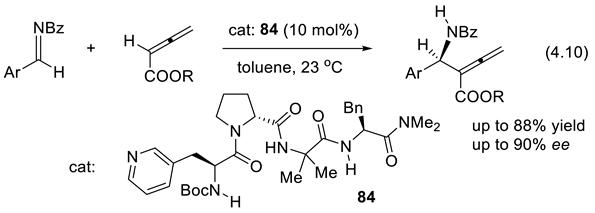
4.6. Catalytic Enantioselective Enolate Protonation by Peptides
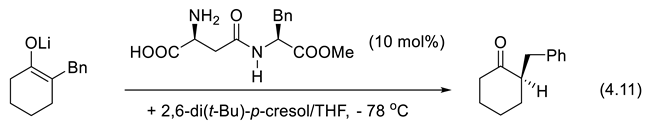
5. Phosphorous-Based Catalysis
5.1. Nucleophilic Activation by Chiral Phosphines
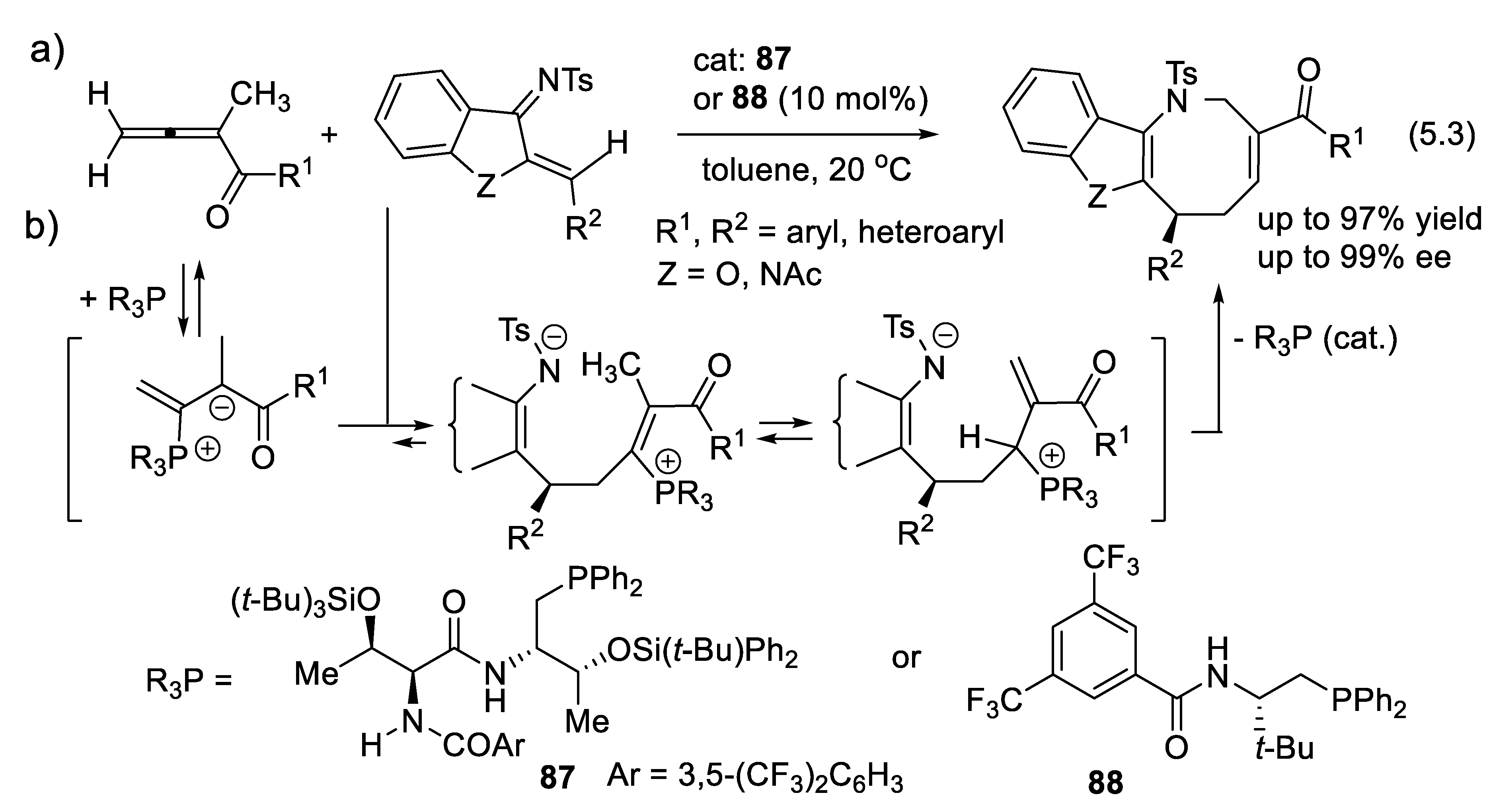
5.2. Enantioselective Wittig and Staudinger-Aza-Wittig Reactions
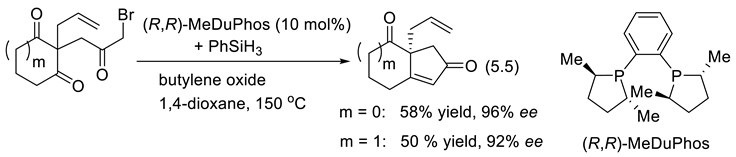
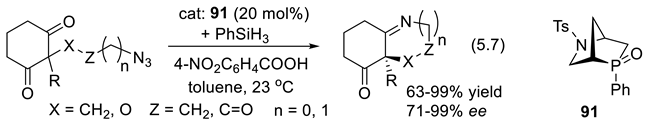
5.3. Chiral Phosphonium Salts as Phase Transfer Catalysts
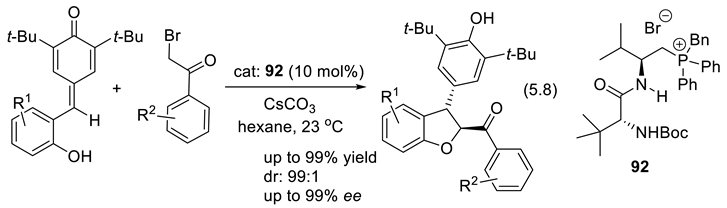
5.4. Chiral Phosphoramides as Lewis Base Catalysts
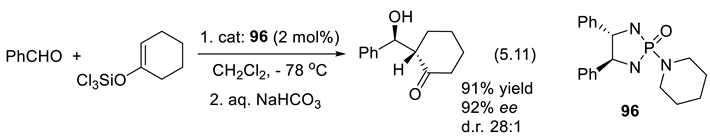
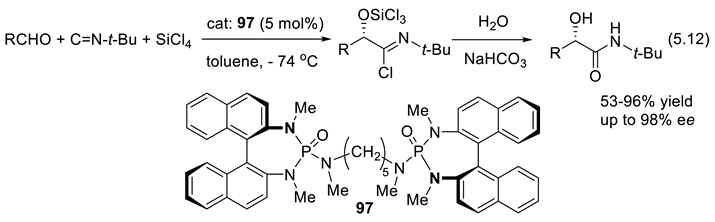
5.5. Chiral Phosphine Oxides as Organocatalysts
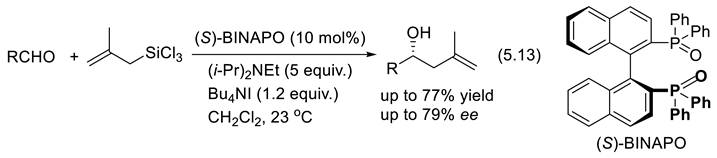
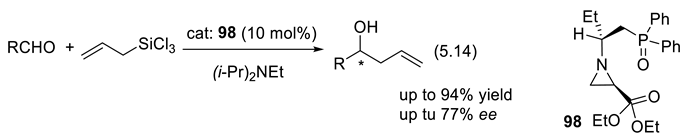
6. Asymmetric Organocatalysis by Sulfur Compounds
6.1. Asymmetric Aldehyde Epoxidations Catalyzed by Chiral Dialkylsulfides
6.2. Asymmetric Halo- and Chalcolactonization Catalyzed by Sulfides
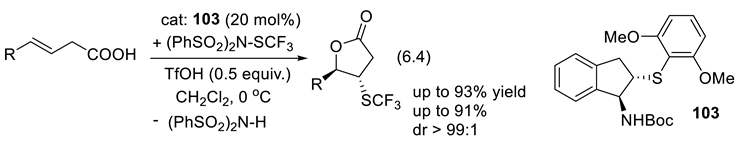
6.3. Enantioselective Hydrogen-Atom Transfer Catalyzed by Chiral Thiols
6.4. Asymmetric Rauhut-Currier Reaction Catalyzed by a Chiral Thiols
6.5. Sulfonium Salts as Chiral PTCs
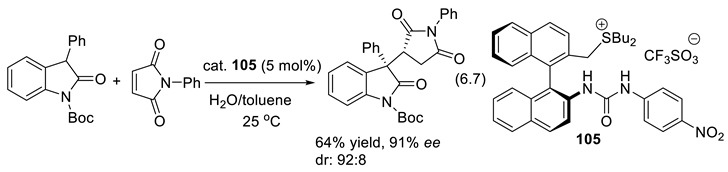
6.6. Chiral Sulfoxides
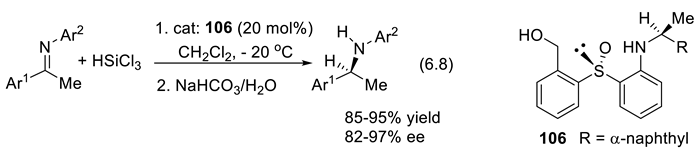
6.7. Chiral Amino-Thiocarbamates
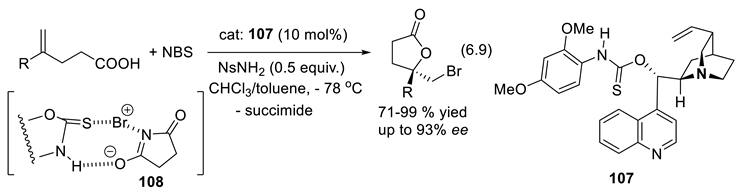
6.8. Chiral Sulfinamides
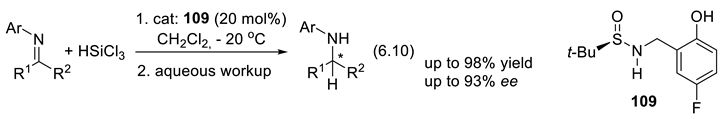
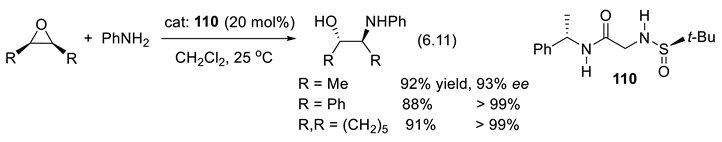
6.9. Chiral Thiophosphoramides
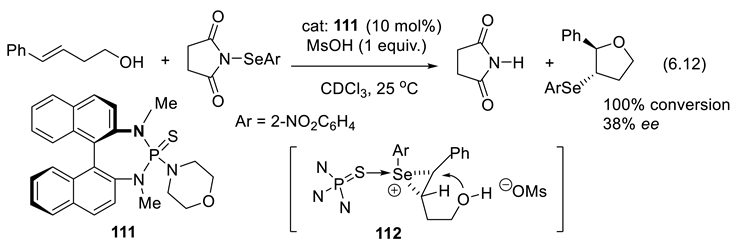
7. Asymmetric Catalysis with Organo-Selenium Compounds
7.1. Aminodiselenides as Chiral Pre-Catalysts
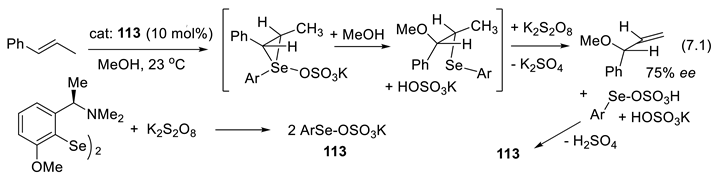
7.2. Selenophosphoramides as Chiral Catalyts
7.3. Selenides as Chiral Catalysts
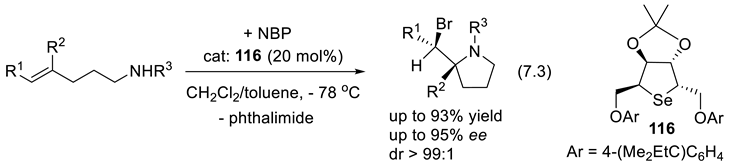
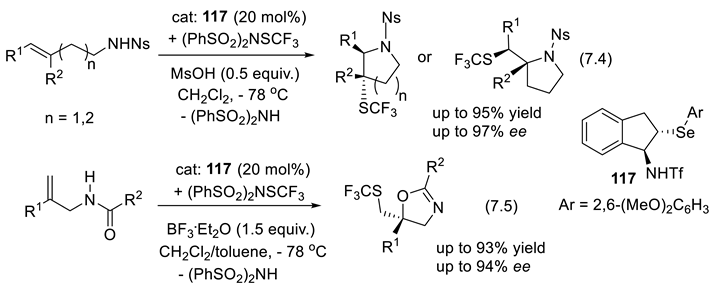
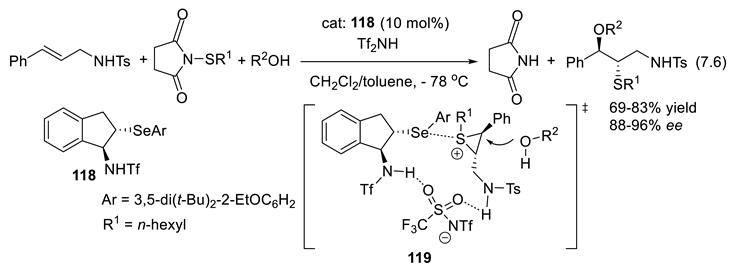
7.4. Chiral Trivalent Selenonium Salts as PTCs
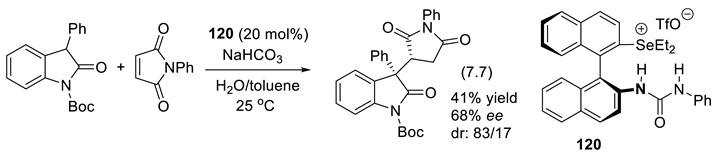
8. Asymmetric Organocatalysis with Electron-Rich Carbene Intermediates
8.1. NHC-Catalyzed Asymmetric Benzoin Condensations
8.2. NHC-Catalyzed Asymmetric Aza-Benzoin Condensations
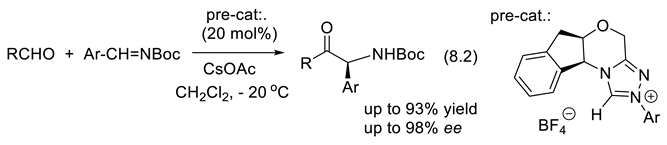
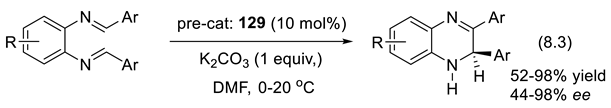
8.3. NHC-Catalyzed Asymmetric Stetter Reactions
8.4. NHC-Catalyzed Asymmetric Aza-Stetter Reactions
8.5. NHC-Catalyzed Asymmetric Cycloadditions
8.6. NHC Catalyzed Asymmetric (3,3)-Sigmatropic Rearrangements
8.7. Umpolung of Michael Acceptors by NHCs: Conversion of Enones into Homoenolates
8.8. Radical Reactions Promoted by NHC Catalysts
8.9. NHC-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of Atropisomers
9. Enantioselective Organocatalysis by Hydrogen Bonding
9.1. Applications of Chiral Diols as Organocatalysts
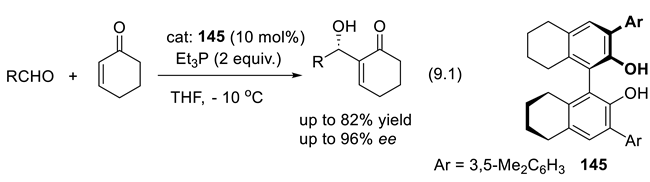
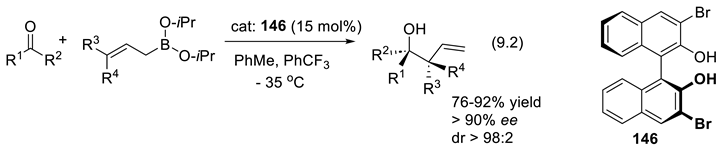
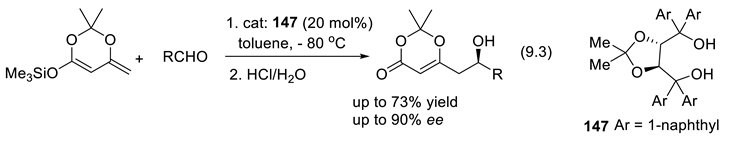
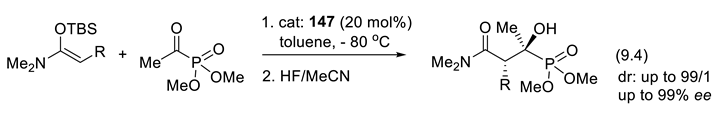
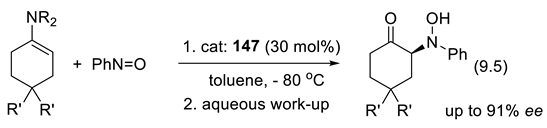
9.2. Silane-1,1-Diols as Chiral Catalysts
9.3. Applications of Chiral Urea and Thiourea Catalysts
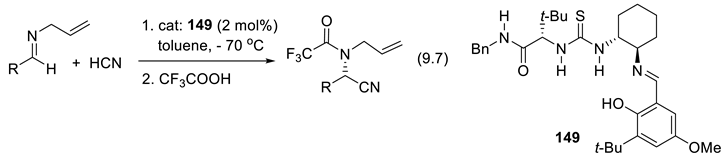
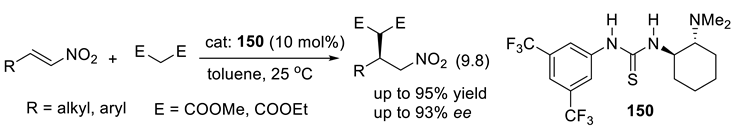
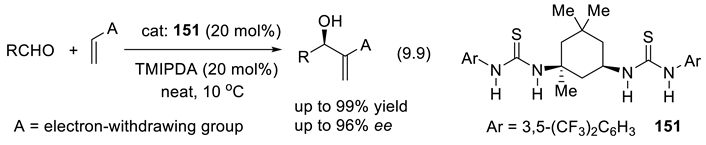
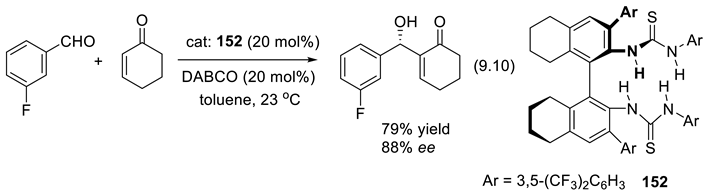
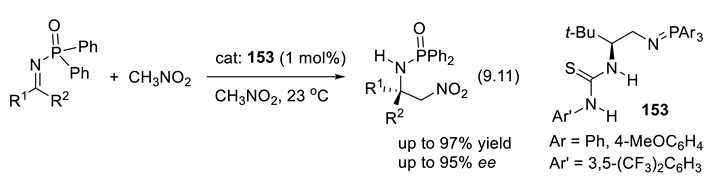
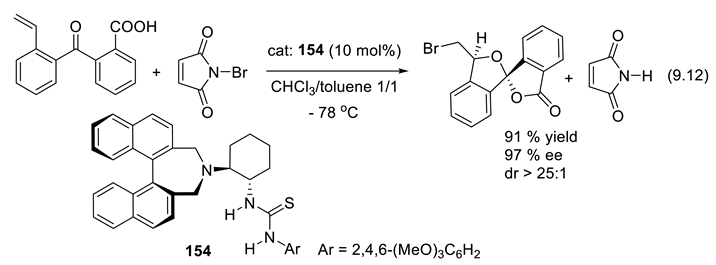
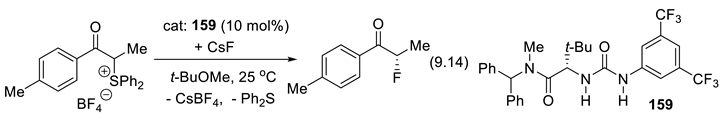
9.4. Applications of Chiral Squaramide-Containing Catalysts
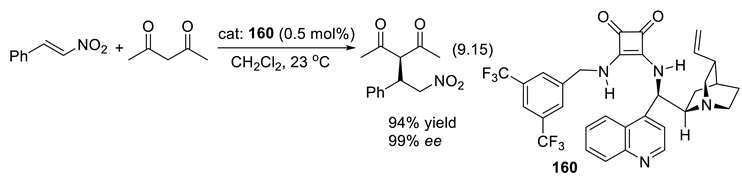
9.5. Amidinium Ions as Chiral Organo-Catalysts
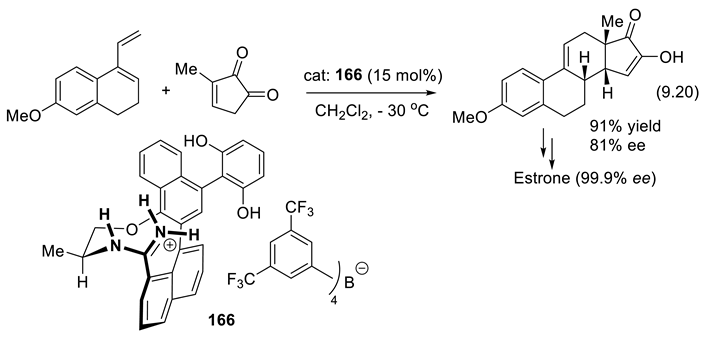
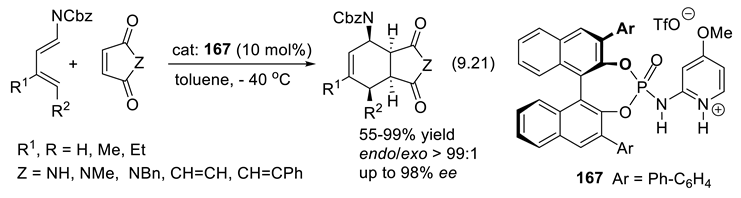
9.6. Other H-Bond Donor Chiral Catalysts
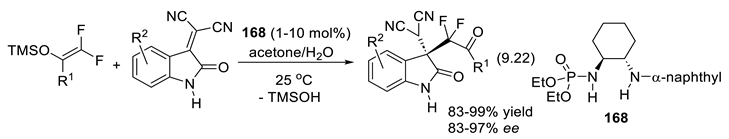
10. Acid Catalysis by Chiral Brønsted Acids
10.1. Chiral Diol Phosphate Catalysts
10.1.1. BINOL Phosphates
10.1.2. Other Diol Phosphates
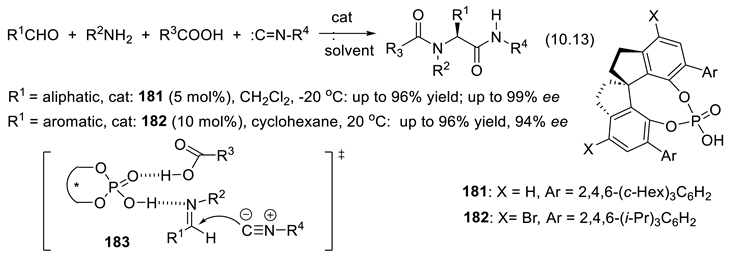
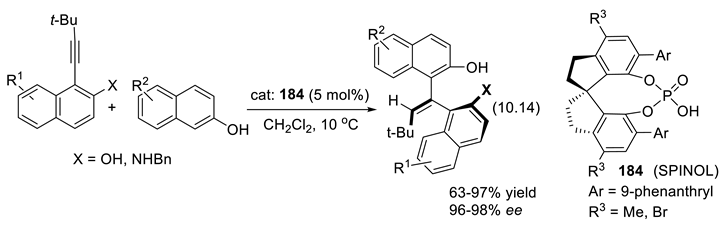
10.2. Stronger Acids Than Diolphosphates
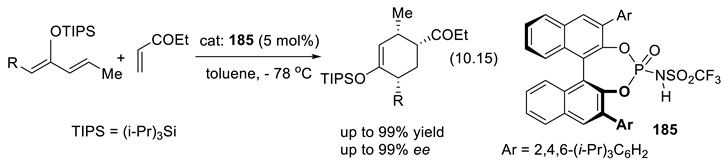
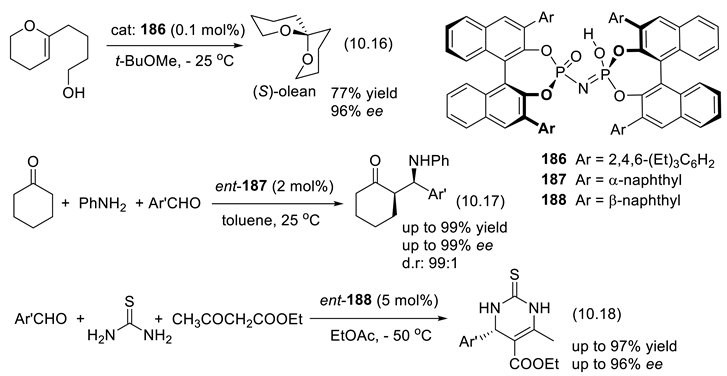
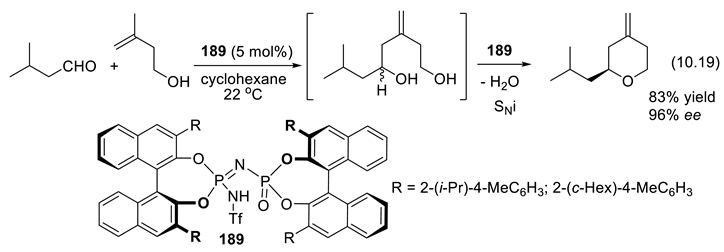
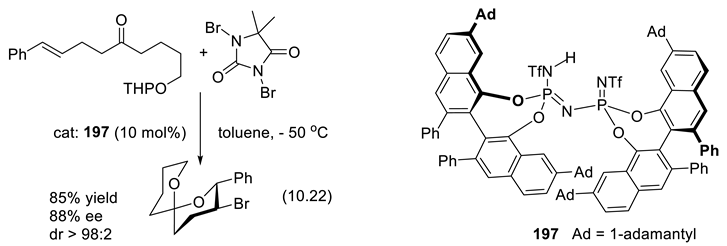
10.3. Diolphosphates as Chiral Anionic Phase Transfer Catalysts for Electrophilic Fluorination
10.4. Chiral Borate and Boroxinate Brønsted Acids
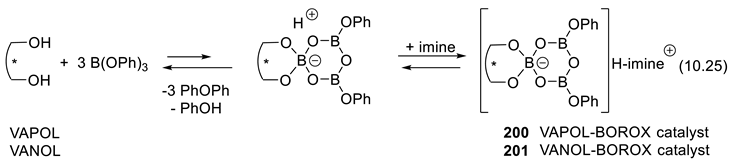
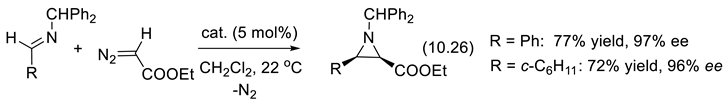
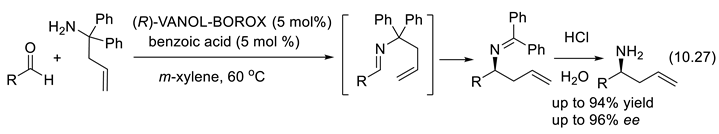
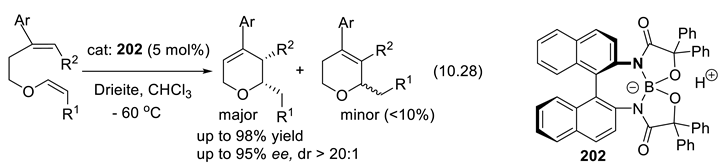
10.5. Chiral Disulfonic Acids and Their Ammonium Salts
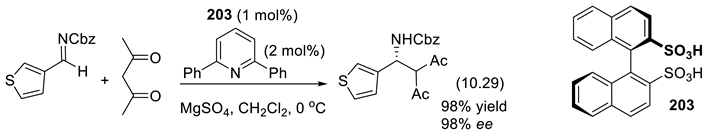
10.6. Chiral Disulfonimides
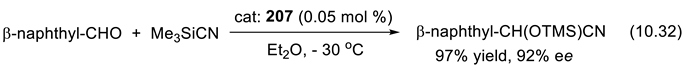
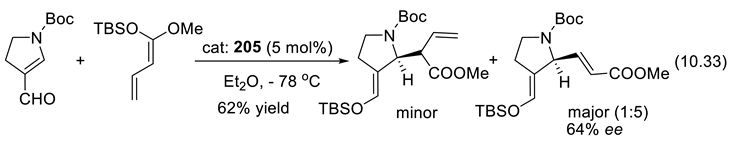
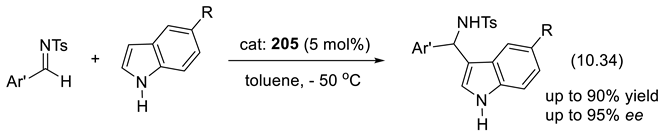
11. Other Asymmetric Organo-Catalysts
11.1. Asymmetric Alkene Epoxidation Catalyzed by Chiral Ketones
11.2. Asymmetric Alkene Epoxidation Catalyzed by Chiral Iminium Salts
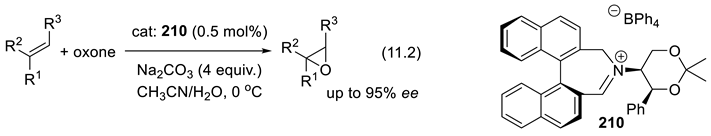
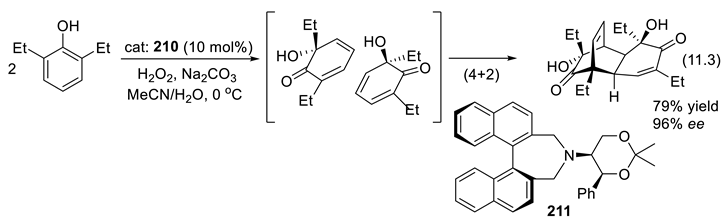
11.3. Crown Ethers
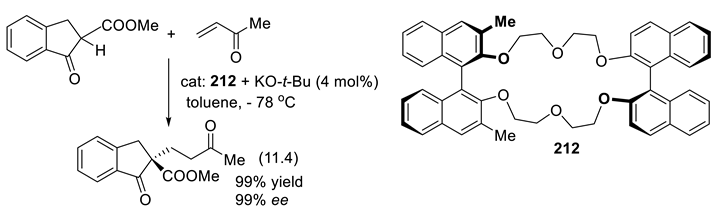
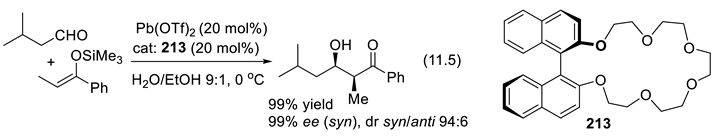
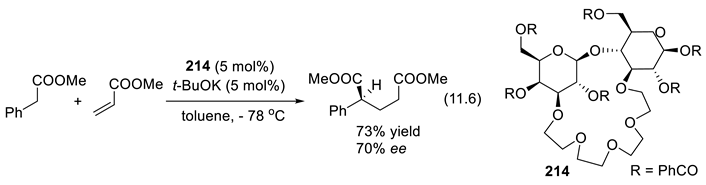
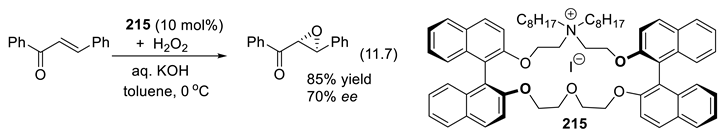
11.4. Chiral N-Amine Oxides
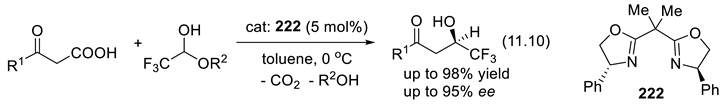
11.5. Chiral Oxazolines and Bisoxazolines
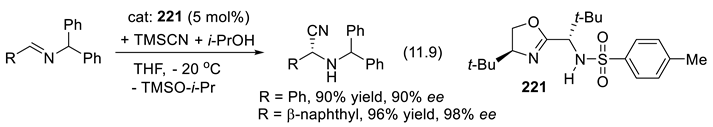
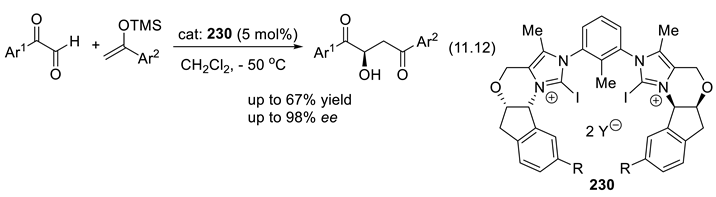
11.6. Chiral Iodine(I) Lewis Acids (XB Donor, σ-Hole Catalysts)
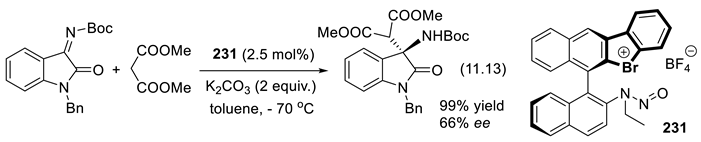
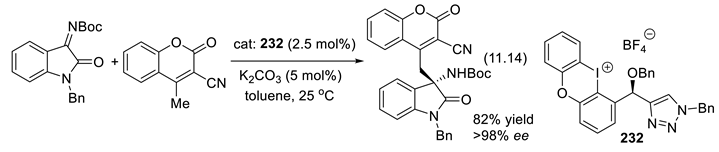
11.7. Chiral Halonium Salts as σ-Hole Catalysts
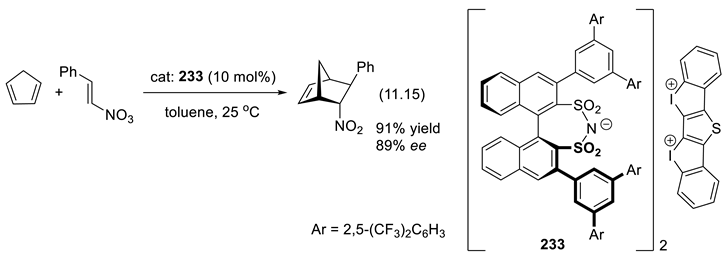
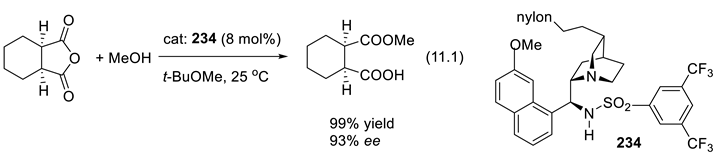
12. Epilogue
References
- Mila, A.; Ooi, T.; Bach, T. Modern enantioselective catalysis in organic chemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 7615–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, J, Cabrera, S. Applications of asymmetric organocatalysis in medicinal chemistry. Chem Soc Rev. 2013, 42, 774–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, S.; Mondal, D. Asymmetric Synthesis in Medicinal Chemistry, Encyclopedia Phys. Org. Chem. First edition; Wang, Z. Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2017, pp. 1-150; ISBN 978—1-118-46858-6.
- Yang, H.; Yu, H-x; Stolarzewicz, I. A.; Tang, W-j. Enantioselective transformations in the synthesis of therapeutic agents. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 9397–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A. M.; Zanotti-Gerosa, A. Homogenous asymmetric hydrogenation: Recent trends and industrial applications. Curr. Opin. Drug. Discov. Develop. 2010, 13, 698–716. [Google Scholar]
- Bulger, P. G. Industrial applications of organocatalysis. 9, 2012; 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröger, H. Shibasaki catalysts and their use for asymmetric synthetic applications by the chemical industry. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 24, 4116–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dylong, D.; Hansoul, P. J. C.; Palkovits, R.; Eisenacker, M. Synthesis of (-)-menthol: industrial synthesis routes and recent development. Flavour Fragrance J. 2022, 37, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Snajdrova, R.; Moore, J. C.; Baldenius, K.; Bornscheuer, U. T. Biocatalysis: Enzymatic synthesis for industrial applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 88–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukland, Miles, H. ; List, B. Organocatalysis emerging as a technology. Pure Appl. Chem. 2021, 93, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D. L. Highlights of the recent patent literature: Focus on asymmetric organocatalysis. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2022, 26, 2224–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. K. The importance of organocatalysis (asymmetric and non-asymmetric) in agrochemicals. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202300204, pp. 1-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmchen, G. Definition of the term asymmetric synthesis—History and revision. Chirality 2024, 35, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talapatra, S. K. , Talapatra, B. Asymmetric Synthesis. In Basic Concepts in Organic Stereochemistry. Springer Nature, Cham, CH, 2022, pp. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.; Slimmer, M. Versuche über asymmetrische Synthese. Ber. dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1903, 36, 2575–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwald, W. Ueber asymmetrische Synthese. Ber. dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1904, 37, 1368–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A. Studies in asymmetric synthesis. I/II J Chem Soc. 1904, 85, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bada, J. L. Origins of homochirality. Nature 1995, 374, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, C.; Filippi, J-J. ; Nahon, L.; Hoffmann, S. V.; d’Hendecourt, L.; de Marcellus, P.; Bredehöft, J. H.; Thiemann, W. H-P.; Meierhenrich, U. J. Photochirogenesis: photochemical models on the origin of biomolecular homochirality. Symmetry 2010, 2, 1055–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmond, D. G. The origin of biological homochirality. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, article nb. 032540, pp. 1-12; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnick, J.; Gao, M. On the emergence of homochirality and life itself. Biochem. 2021, 43, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, J. The discovery of stereoselectivity at biological receptors: Arnaldo Piutti and the taste of the asparagine enantiomers-History and analysis on the 125th anniversary. Chirality 2012, 24, 959–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandula, J. S.; Rayala, V. V. S. P. K.; Pullapanthula, R. Chirality: An inescapable concept for the pharmaceutical, bio-pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. Sep. Sci. plus 2023, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W. H.; Guida, W. C.; Daniel, K. G. The significance of chirality in drug design and development. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkadi, H.; Jbeily, R. Role of chirality in drugs: An overview. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Franchini, A.; De Luca, M.; Saturnino, C.; Andreu, I.; Sinicropi, M. S.; Catalano, A. A look at the importance of chirality in drug activity: Some significative examples. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, article–nb.10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S-j. ; Zhu, Y-y.; Luo, C-y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F-y.; Li, R-x.; Lin, G-q.; Zhang, J-g. Chiral drugs: Sources, absolute configuration identification, pharmacological applications, and future research trends. LabMed Discovery 2024, 1, article nb. 100008, pp. 1-9; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicker, R. U.; O’Boyle, N. M. Chirality of new drug approvals (2013–2022): Trends and perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67(4), 2305–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S. K.; Colburn, W. A.; Tracewell, W. G.; Kook, K. A.; Stirling, D. I.; Jaworsky, M. S.; Scheffler, M. A.; Thomas, S. D.; Laskin, O. L. Clinical pharmacokinetics of thalidomide. Clin. Pharmacokinetics 2004, 43, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitchagno, G. T. M.; Nchiozem-Ngnitedem, V. A.; Melchert, D; Fobotou, S. A. Demystifying racemic natural products in the homochiral world. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 806–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasteur, L. Mémoire sur la fermentation de l'acide tartrique. Compt. rend. hebd. séa. Acad. Sci. 1858, 46(13), 615-618; see also: Gal, J. The discovery of biological enantioselectivity: Louis Pasteur and the fermentation of tartaric acid, 1857--A review and analysis 150 yr later. Chirality 2008, 20(1), 5-19; [CrossRef]
- Contesini, F. J.; Lopes, D. B.; Macedo, G. A.; Nascimento, M. d. G.; Carvalho, P. d. O. Aspergillus sp lipase: Potential biocatalyst for industrial use. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzymatic. [CrossRef]
- Patel, R. N. Biocatalysis: Synthesis of key intermediates for development of pharmaceuticals. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1056–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Adamusiak, R.; Strub, D.; Lochynski, S. Application of microorganisms towards synthesis of chiral terpenoid derivatives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechn. 2012, 95, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislieri, D.; Green, A. P.; Pontini, M.; Willies, S. C.; Rowles, I.; Frank, A.; Grogan, G.; Turner, N. J. Engineering an enantioselective amine oxidase for the synthesis of pharmaceutical building blocks and alkaloid natural products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10863–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reetz, M. T. Biocatalysis in organic chemistry and biotechnology: past, present, and future. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12480–12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, M.; Farnberger, J. E.; Kroutil, W. The industrial age of biocatalytic transamination. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 32, 6965–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, R.; Hayashi, T.; Buller, R. M. Directed evolution of carbon-hydrogen bond activating enzymes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 60, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E. Einfluss der Configuration auf die Wirkung der Enzyme. Ber. dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1894, 27, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Chapman, J.; Ismail, A. E.; Zoica Dinu, C. Industrial applications of enzymes: Recent advances, techniques, and outlooks. Catalysts 2018, 8(6), article nb. 238, pp. 1-26; https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8060238; b) Wu, S.; Snajdrova, R.; Moore, J. C.; Baldenius, K.; Bornscheuer, U. T. Biocatalysis: enzymatic synthesis for industrial applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 60(1), 88-119. [CrossRef]
- IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 3rd ed. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry; 2006. Online version 3.0.1, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Micha, D. A. Molecular interactions: concepts and methods. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York, USA, 2020, pp. 9: 1-385; Print ISBN: 9780470290743; Online ISBN, 9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, V. Théorie générale de l'action de quelques diastases, Compt. rend. hebd. séa. Acad. Sci. 1902, 135, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, L.; Menten, M. L. Die Kinetik der Invertinwirkung, Biochemische Zeitschrift 1913, 49, 333-369. 49.
- Michaelis, L.; Menten, M. L.; Johnson, K. A.; Goody, R. S. The original Michaelis constant: translation of the 1913 Michaelis-Menten paper. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8264–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchot, C.; Samuel, O.; Dunach, E.; Zhao, S.; Agami, C.; Kagan, H. B. Nonlinear effects in asymmetric synthesis. Examples in asymmetric oxidations and aldolization reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaneux, D. , Zhao, S.-H., Samuel, O., Rainford, D.; Kagan, H. B. Nonlinear effects in asymmetric catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 9430–9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soai, K. , Shibata, T., Morioka, H.; Choji, K. Asymmetric autocatalysis and amplification of enantiomeric excess of a chiral molecule. Nature 1995, 378, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmond, D. G. ; Kinetic aspects of nonlinear effects in asymmetric catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athavale, S.; Simon, A.; Houk, K. N.; Denmark, S. E. Demystifying the asymmetry-amplifying, autocatalytic behaviour of the Soai reaction through structural, mechanistic and computational studies. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, T.; Geiger, Y.; Bellemin-Laponnaz, S. Observation of hyperpositive non-linear effect in asymmetric organozinc alkylation in presence of N-pyrrolidinyl norephedrine. Molecules 2022, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Suh, S-E. ; Kang, H. Advances in exploring mechanisms of oxidative phenolic coupling reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, 366, 4347–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, A. Homogeneous catalysis of diene syntheses. A new type of third-order reaction. J. Chem. Soc, 1942; 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, P.; Houk, K. N. Organic Chemistry, Theory, Reactivity and Mechanisms in Modern Synthesis, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2019, Chap. 5.3.9-11, pp. 387-396, Chap. 7.6.6-7, pp. 849-853; ISBN 978-3-527-34532-8.
- Gröger, H.; Asano, Y. Introduction – Principles and historical landmarks of enzyme catalysis in organic synthesis. In “Enzyme Catalysis in Organic Synthesis”. Drauz K.; Gröger, H.; May, O. Eds., Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, Print: ISBN: 9783527325474; Online ISBN: 978352763 9861, 2012, Chap. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeller, K. , Wong, C-H. Enzymes for chemical synthesis. Nature 2001, 409, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Hanfeld, H. Enzyme catalysis in organic synthesis. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugai, T.; Higashibayashi, S.; Hanaya, K. Recent examples of the use of biocatalysts with high accessibility and availability in natural product synthesis. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 3469–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanfeld, U.; Hollmann, F.; Paul, C. E. Biocatalysis making waves in organic chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 594–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Recent advances in enzymatic carbon-carbon bond formation. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 25932–25974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- a) O’Connell, A.; Barry, A.; Burke, A. J.; Hutton, A: E.; Bell, E. L.; Green, A: P.; O’Reilly, E. Biocatalysis: landmark discoveries and applications in chemical synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 53(6), 2828-2850; https://doi.org/10.1039/d3cs00689a; b)Wu, S-k.; Snajdrova, R.; Moore, J. C.; Baldenius, K.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Biocatalysis: Enzymatic synthesis for industrial applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60(1),88-119; [CrossRef]
- Gilio, A. K.; Thorpe, T. W.; Turner, N.; Grogan, G. Reductive aminations by imine reductases: from milligrams to tons. Chem. Science 2022, 13, 4697–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Mateos, A. I.; Roura, P. D.; Francesca, P. Multistep enzyme cascades as a route towards green and sustainable pharmaceutical syntheses. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G. F. S.; Seong-Heun Kim, S.-H.; Castagnolo, D. Harnessing biocatalysis as a green tool in antibiotic synthesis and discovery. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 30396–30410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D. R.; Lohman, D. C.; Wolfenden, R. Catalytic proficiency: The extreme case of S–O cleaving sulfatases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J. John Cornforth (1917–2013). Nature 2014, 506, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunitz, J. Vladimir Prelog (1906-98). Nature 1998, 391, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, R.; Mallojjala, S: C. ; Wheeler, S: E. Electrostatic interactions in asymmetric organocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. Asymmetric catalysis by chiral hydrogen-bond donors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1520–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal P., K. A biophysical perspective on enzyme catalysis. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R. A. Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data Analysis. 3rd. Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New Jersey, USA, 2023; ISBN: 9781119793250.
- Goodman, C. Jean-Marie Lehn. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. The shape of things. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, G. Chemistry beyond the molecule. Nature 2001, 412, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, M. Donald J. Cram (1919–2001). Nature 2001, 412, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Helgeson, R. C.; Houk, K. N. Building on Cram’s legacy: stimulated gating in hemicarcerand. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifazi, D. A universal receptor. Nature Nanotech. 2013, 8, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C. R.; Ling, S.; Jacobsen, E. N. The cation-pi interaction in small-molecule catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12596–12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornscheuer, U. T.; Huisman, G-W. ; Kazlauskas, R.; Lutz, S.; Moore, J. C.; Robins, K. Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis. Nature 2012, 485(7397), 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M. S.; Liu, D. R. Methods for the directed evolution of proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, B. A.; Hyster, T. K. Emerging strategies for expanding the toolbox of enzymes in biocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 55, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M. P.; Peñafel, I.; Cosgrove, S. C.; Turner, N. J. Biocatalysis using immobilized enzymes in continuous flow for the synthesis of fine chemicals. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsalami, S. M.; Mirsalami, M.; Ghodousian, A. Techniques for immobilizing enzymes to create durable and effective biocatalysts. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Hodgson, D. R. W.; O'Donoghue, A. C. Going full circle with organocatalysis and biocatalysis: The latent potential of cofactor mimics in asymmetric synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 7619–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Gocke, D.; Pohl, M. Exploitation of ThDPdependent enzymes for asymmetric chemoenzymatic synthesis. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2894–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasparyan, E.; Richter, M.; Dresen, C.; Walter, L. S.; Fuchs, G.; Leeper, F. J.; Wacker, T.; Andrade, S. L.; Kolter, G.; Pohl, M.; Müller, M. Asymmetric Stetter reactions catalyzed by thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9681–9690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouali, N.; Gana, I.; Dorra, A.; Khelifi, F.; Nouioui, A.; Masri, W.; Belwaer, I.; Hayet Ghorbel, H.; Hedhili, A. Potential toxic levels of cyanide in almonds (Prunus amygdalus), apricot kernels (Prunus armeniaca), and almond syrup. Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Toxicology (Hindawi Publ. Corp.) 2013, article nb. 610648, pp. [CrossRef]
- Wöhler, F.; Liebig, J. Ueber die Bildung des Bittermandelöls. Ann. Pharm. 1837, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthaler, L. Durch Enzyme bewirkte asymmetrische Synthesen. Biochem. Z., 1908, 14, 238–253. [Google Scholar]
- Effenberger, F. Synthesis and reactions of optically active cyanohydrins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1994, 33, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, F.; Förster, S.; Wajant, H. Hydroxynitrile lyases in stereoselective synthesis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkarthofer, T.; Skranc, W. , Schuster, C.; Griengl, H. Potential and capabilities of hydroxynitrile lyases as biocatalysts in the chemical industry. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashipour, M.; Asano, Y. Hydroxynitrile lyases insights into biochemistry, discovery, and engineering. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1121–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prixa, B. V.; Padhi, S K. Hydroxynitrile lyase discovery, engineering, and promiscuity towards asymmetric synthesis: Recent progress. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M. Directed evolution of enantioselective enzymes: An unconventional approach to asymmetric catalysis in organic chemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5767–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 96. Arnold, F. H. Innovation by evolution: Bringing new chemistry to life (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14420–14426. [CrossRef]
- Bornscheuer, U. T.; Hauer, B.; Jaeger, K. E.; Schwaneberg, U. Directed evolution empowered redesign of natural proteins for the sustainable production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J. K.; Li, F-L. ; Lin, Z.; Lin, G-Q.; Hong, R.; Yu, H-L.; Xu, J-H. Structure-guided tuning of a hydroxynitrile lyase to accept rigid pharmaco aldehydes. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5757–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M. T. ; García-Borràs. The unexplored importance of fleeting chiral intermediates in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14939–14950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkarthofer, T.; Gruber, K.; Gruber-Khadjawi, M.; Waich, K.; Skranc, W.; Mink, D.; Griengl, H. A biocatalytic Henry reaction--the hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis also catalyzes nitroaldol reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3454–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhshuku, K.; Asano, Y. Synthesis of (R)-β-nitro alcohols catalyzed by R-selective hydroxynitrile lyase from Arabidopsis thaliana in the aqueous-organic biphasic system. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 153(3-4),153-159. [CrossRef]
- von Langermann, J.; Nedrud, D. M.; Kazlauskas, R. J. Increasing the reaction rate of hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis toward mandelonitrile by copying active site residues from an esterase that accepts aromatic esters. Chembiochem. 2014, 15, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekerle-Bogner,M. ; Gruber-Khadjawi, M.; Wiltsche, H.; Wiedner, R.; H. Schwab, H.; Steiner, K. (R)-Selective nitroaldol reaction catalyzed by metal-dependent bacterial hydroxynitrile lyases ChemCatChem, 2016, 8, 2214–2216. [CrossRef]
- Priya, B. V.; Rao, D. H. S.; Chatterjee, A.; Padhi, S. K. Hydroxynitrile lyase engineering for promiscuous asymmetric Henry reaction with enhanced conversion, enantioselectivity and catalytic efficiency. Chem. Commun. 2023, 12274–12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busto, E.; Gotor-Fernández, V.; Gotor, V. Hydrolases: catalytically promiscuous enzymes for non-conventional reactions in organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, (11), 4504–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Iglesias, M,.; Gotor-Fernández, V. Recent advances in biocatalytic promiscuity: hydrolase-catalyzed reactions for nonconventional transformations. Chem. Rec, 2015; 743–759. [CrossRef]
- Poddar, H.; Rahimi, M.; Geertsema, E. M.; Thunnissen, A. M.; Poelarends, G. J. Evidence for the formation of an enamine species during aldol and Michael-type addition reactions promiscuously catalyzed by 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase. Chembiochem. 2015, 16, 738–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, S.D. Shining light on enzyme promiscuity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 47, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-C.; Lee, L. F. H.; Mittal, R. S. D.; Ravikumar, P. R.; Chan, J. A.; Sih, C. J.; Capsi, E.; Eck, C. R. Preparation of (R)- and (S)-mevalonic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 4144–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.; Waespe-Sarevi, N.; Tamm, C.; Gawronska, K.; Gawronski, J. A study of stereoselective hydrolysis of symmetrical diesters with pig liver esterase. Helv. Chim. Acta 1983, 66, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Urdiales, E.; Alfonso, I.; Gotor, V. Enantioselective enzymatic desymmetrization in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105(1), 313–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutter, U.; Iding, H.; Spurr, P.; Wirz, B. New, efficient synthesis of Oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu) via enzymatic desymmetrization of a meso-1,3-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid diester. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedee, B. R.; Soni, S.; Sharma, M.; Bhaumik, J.; Laha, J. K.; Banerjee, U. C Promiscuity of lipase-catalyzed reactions for organic synthesis: A recent update. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 2441–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W. Natural polypropionates in 1999–2020: An overview of chemical and biological diversity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, P.; Sordo Gonzalo, J. A. Expeditious asymmetric synthesis of polypropionates relying on sulfur dioxide-induced C–C bond forming reactions. Catalysts 2021, 11, article nb.1267, pp. 1-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chênevert, R.; Rose, Y. S. Enzymatic desymmetrization of a meso polyol corresponding to the C(19)-C(27) segment of Rifamycin S. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 1707–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ihori, T.; Ohta, H. Enzyme-mediated enantioface-differentiating hydrolysis of alpha-substituted cycloalkanone enol esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 9614–9619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, J. T.; Hong, A. Y.; Stoltz, B. M. Enantioselective protonation. Nat. Chem, 2009; 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg, C. Biochemical reductions at the expense of sugars. Adv. Carbohyd. Chem. 1949, 4, 75–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, C. J.; Chen, C-S. Microbial asymmetric catalysis—Enantioselective reduction of ketones [New Synthetic Methods]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1984, 23, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebach, D.; Roggo, S.; Maetzke, T.; Braunschweiger, H.; Cercus, C.; Krieger, M. Diasterio- und enantioselektive Reduktion von β-Ketoestern mit Cyclopentanon-, Cyclohexanon-, Piperidon- und Tetralon-Struktur durch nicht fermentierende Bäcker-Hefe. Helv. Chim. Acta 1987, 70, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Hosomi, K.; Araki, M.; Nishida, K.; Node, M. Enantioselective reduction of σ-symmetric bicyclo[3.3.0]octane-2,8-diones with baker's yeast. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1995, 6, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R. de S. The use of Baker’s yeast in the generation of asymmetric centers to produce chiral drugs and other compounds. Crit. Rev. Biotechn. [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, A.; Dlugy, C.; Tavor, D.; Blumefeld, J. Baker’s yeast catalyzed asymmetric reduction in glycerol. Tetrahedon Asymmetry 2006, 17, 2043–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J. C.; Pollard, D. J.; Kosjek, B.; Devine, P. N. Advances in the enzymatic reduction of ketones. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberg, C.; Nord, F. F. Die phytochemische Reduktion der Ketone. Biochemische Darstellung optisch-aktiver sekundärer Alkohole. Ber. deutch. chem. Ges. 1919, 52, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, R.; Prosser, H.; Fickentscher, L.; Lanyi, J.; Mosher, H. S. Asymmetric Reductions. XII. Stereoselective Ketone Reductions by Fermenting Yeast. Biochemistry 1964, 3, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prelog, V. Specification of the stereospecificity of some oxido-reductases by diamond lattice sections. Pure Appl. Chem. 1964, 9, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "prochirality". [CrossRef]
- Burnier, G. , Vogel, P. Synthesis and circular dichroism of optically pure (-)-( 1S,2S,5S)-5-methoxy-3,4,6,7-tetramethylidenebicyclo[3.2.l]oct-2-yl derivatives. Baker's yeast reduction of 4-methoxy-5,6,7,8-tetramethylidenebicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-one. Helv. Chim. Acta 1990, 73, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J. A.; Dull, D. L.; Mosher, H. S. J. Org. Chem. 1969, 34(9), 2543-2549. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, H. Recent advances in chiral liquid chromatography stationary phases for pharmaceutical analysis. J. Chromat. A. 2023, 1708, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaka, M.; Konishi, S.; Mizuoka, A.; Ohkubo, T.; Sakai, T.; Tauboi, S. ; Takeda, A: Asymmetric reduction of the prochiral carbon-carbon double bond of methyl 2-chloro-2-alkenoates by use of fermenting bakers' yeast J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 4989–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D. T.; Koch, J. R.; Schuld, C. L.; Kallio, R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. II. Metabolism of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochemistry 1968(11), 3795–3802. [CrossRef]
- Zylstra, G. J.; Gibson, D. T. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1. Nucleotide sequence of the todC1C2BADE genes and their expression in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 14940–14946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoma, M. A.; Bui, V. P.; Hansen, J.; Hudlicky, T. Medium-scale preparation of useful metabolites of aromatic compounds via whole-cell fermentation with recombinant organisms. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2002, 6, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J. A. Microbial arene oxidations. Org. React, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carless, H. A. J. The use of cyclohexa-3,5-diene-1,2-diols in enantiospecific synthesis. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1992, 31, 795–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudlicky, T.; Gonzalez, D.; Gibson, D. T. Enzymatic dihydroxylation of aromatics in enantioselective synthesis: expanding asymmetric methodology. Aldrichim. Acta 1999, 32, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, M. G.; Edwards, A: J. ; Harfoot, G. J.; Jolliffe, K. A.; McLeod, M. D.; McRae, K. J.; Stewart, S. G.; Vögtle, M. Chemoenzymatic methods for the enantioselective preparation of sesquiterpenoid natural products from aromatic precursors. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003, 75, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudlicky, T.; Reed, J. W. Applications of biotransformations and biocatalysis to complexity generation in organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 8, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, E. S.; Banwell, M. G.; Buckler, J. N.; Yan, Q.; Lan, P. The exploitation of enzymatically-derived cis-1,2-dihydrocatechols and related compounds in the synthesis of biologically active natural products. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudlicky, T. Benefits of unconventional methods in the total synthesis of natural products. ACS Omega, 2018, 3, 17326–17340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart Stollmaier, J.; Hudlicky, T. Sequential enzymatic and electrochemical functionalization of bromocyclohexadienediols: Application to the synthesis of (−)-conduritol C. Tetrahedron 2020, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhof, O. , Lohmann, K. Über den Nachweis von Triosephosphorsäure als Zwischenprodukt bei der enzymatischen Kohlehydratspaltung. Naturwissenschaften 1934, 22, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, N.; Simoni, R. D.; Hill, R. L. Otto Fritz Meyerhof and the elucidation of the glycolytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. , Christian, W. Isolierung und Kristallisation des Gärungsferments Enolase. Naturwissenschaften 1941, 29, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Christian, W. Isolierung und Kristallisation des Gärungsferments Zymohexase. Naturwissenschaften 1942, 30, 731–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Christian, W. Isolierung und Kristallisation des Gärungsferments Zymohexase Biochem. Z. 1943, 314, 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, O. C.; Rutter, W. J. Preparation and properties of yeast aldolase, J. Biol. Chem. 1961, 236, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Gawehn, K. Z.; Lange, G. Ueber das Verhalten von Ascites-Kbresbzellen zu Zymhexase. Naturforsch. 1954, 9b, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J. K.; Sephton, H. H. Synthesis of D-glycero-D-altro-, L-glycero-L-galacto-, D-glycero-L-gluco-, and D-glycero-L-galato-octulose. Can J. Chem. 1960, 38, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, M. D.; Simon, E. S.; Bischofberger, N.; Fessner, W.-D.; Kim, M.-J.; Lees, W.; Saito, T.; Waldmann, H.; Whitesides, G. M. J. Am. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 627–635. [CrossRef]
- Toone, E. J.; Simon, E. S.; Bednarski, M. D.; Whitesides, G. M. Enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of carbohydrates. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 5365–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-H.; Halcomb, R. L.; Ichikawa, Y.; Kajimoto, T. Enzymes in organic synthesis: Application to the problems of carbohydrate recognition (Part 2). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C-H. ; Halcomb, R. L.; Ochikawa, Y.; Kajimoto. Enzymes in organic synthesis: Application to the problems of carbohydrate recognition (Part 1). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machajewski, T. D.; Wong, C.-H. The catalytic asymmetric aldol reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1352–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S. M.; Greenberg, W. A.; Wong, C-H. Recent advances in aldolase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapés, P.; Garrabou, X. Current trends in asymmetric synthesis with aldolases. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2263–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hélaine, V; Gastaldi, C; Lemaire, M.; Clapès, P.; Guérard-Hélaine, C Recent advances in the substrate selectivity of aldolases. ACS Catal 2022, 12, 733–761.
- Lee, S-H. ; Yeom, S-J.; Kim. S-E.; Oh, D-K. Development of aldolase-based catalysts for the synthesis of organic chemicals. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, W.; Whitesides, G. M. A New approach to cyclitols based on rabbit muscle aldolase (RAMA). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 9670–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugai, T., Kajimoto, T. Synthesis of biologically relevant monosaccharides. In: Fraser-Reid, B. O.; Tatsuta, K.; Thiem, J. (eds). Glycoscience: Chemistry and Chemical Biology I–III. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2001, Chapt. 4.3, 907-1021. [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, M. G. , Camici, M., Mascia, L., Sgarrella, F., Ipata, P. L. Pentose phosphates in nucleoside interconversion and catabolism. FASEB J. 2006, 273, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, H. J. M. , Wong, C.-H., Sequential one-pot aldol reactions catalyzed by 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, H. J. M. , Wong, C.-H., Sequential three- and four-substrate aldol reactions catalyzed by aldolases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7585–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, W. A.; Varvak, A.; Hanson, S. R.; Wong, K.; Huang, H.; Chen, P.; Burk, M. J. , Development of an efficient, scalable, aldolase-catalyzed process for enantioselective synthesis of statin intermediates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5788–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of building blocks for statin side chains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wong, C. H. Aldolase-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of novel pyranose synthons as a new entry to heterocycles and epothilones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ošlaj, M.; Cluzeau, J.; Orkić, D.; Kopitar, G.; Mrak, P.; Časar,Z. A highly productive, whole-cell DERA chemoenzymatic process for the production of key lactonized side-chain intermediates in statin synthesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z. Some recent examples in developing biocatalytic pharmaceutical processes, in Asymmetric Catalysis, Eds.: Blaser, H-U.; Federsel, H-J. Wiley Online Books, 2010. Chap. 1. pp. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Dückers, N.; Baer, K.; Simon, S.; Gröger, H.; Hummel, W. Threonine aldolases-screening, properties and applications in the synthesis of non-proteinogenic beta-hydroxy-alpha-amino acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 409−424; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, S. E.; Stewart, J. D. Threonine aldolases. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 88, 57–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligibel, M.; Moore, C.; Bruccoleri, R.; Snajdrova, R. Identification and application of threonine aldolase for synthesis of valuable α-amino, β-hydroxy-building blocks. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom, 2020; 1868, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesko, K.; Reisinger, C.; Steinreiber, J.; Weber, H.; Schürmann,M. ; Griengl, H. Four types of threonine aldolases: Similarities and differences in kinetics/thermodynamics. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2008, 52, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T. A.; Heine, D.; Qin, Z.; Wilkinson, B. An l-threoninetransaldolase is required for l-threo-β-hydroxy-α-amino acid assembly during Obafluorin biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, S. E.; Stewart, J. D. Threonine aldolases. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 88, 57–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fansher, D. J.; Palmer, D. R. J. A. Type 1 aldolase, NahE, catalyzes a stereoselective nitro-Michael reaction: Synthesis of β-aryl-γ-nitrobutyric acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e292214539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G. J.; Domann, S.; Nelson, A.; Berry, A. Modifying the stereochemistry of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by directed evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3143–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, S.; Kullartz, I.; Pietruszka, J. Cloning and characterisation of a new 2-deoxy-D-ribose-5-phosphate aldolase from Rhodococcus erythropolis. J. Biotechn. 2012, 161, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, S.; Roldan, R.; Joosten, H. J.; Clapés, P.; Fessner, W. D. Complete switch of reaction specificity of an aldolase by directed evolution in vitro: Synthesis of generic aliphatic aldol products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 57(32),10153–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, D.; Ma, Y. Improving and inverting cβ-stereoselectivity of threonine aldolase via substrate-binding-guided mutagenesis and a stepwise visual screening. ACS Catal, 2019; 9, 4462–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widersten, M. Engineering aldolases for asymmetric synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 2020, 644, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Yu, H.; Fang, S.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Yang, L.; Wu, J. Directed evolution of L-threonine aldolase for the diastereoselective synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 3198–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W. Comprehensive screening strategy coupled with structure-guided engineering of l-threonine aldolase from Pseudomonas putida for enhanced catalytic efficiency towards l-threo-4-methylsulfonylphenylserine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.; Lerner, R. A.; Barbas, C. F. III. Efficient aldolase catalytic antibodies that use the enamine mechanism of natural enzymes. Science 1995, 270, 1797–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B.; Shabat, D.; Barbas, C. F. III.; Lerner, R. A. Enantioselective total synthesis of some Brevicomins using aldolase antibody 38C2. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B.; Shabat, D.; Zhong, G.; Turner, J. M.; Li, T.; Bui, T.; Anderson, J.; Lerner, R. A.; Barbas, C. F. III. A catalytic enantioselective route to hydroxy-substituted quaternary carbon centers: resolution of tertiary aldols with a catalytic antibody. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 7283–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hu, Q.; Fu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, Z. Design and evolution of an enzyme for the asymmetric Michael addition of cyclic ketones to nitroolefins by enamine catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönherr, H.; Cernak, T. Profound methyl effects in drug discovery and a call for new C-H methylation reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12256–12267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetzsche, L. E.; Narayan A. R., H. Broadening the scope of biocatalytic C-C bond formation. Nat. Rev. Chem, h: 334-346, 1038. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, S. , Kuzelka, K. P., Guo, R.; Krohn-Hansen, B.; Wi, J.; Nair, S. K.; Yang, Y. A biocatalytic platform for asymmetric alkylation of α-keto acids by mining and engineering of methyltransferases. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B. Introduction: organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5413–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, D. W. C. The advent and development of organocatalysis. Nature 2008, 455, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, C.; Guidotti, M. Organocatalysts for enantioselective synthesis of fine chemicals: definitions, trends and developments. ScienceOpen Res. 2015, 0, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S. H.; Tan, B. Advances in asymmetric organocatalysis over the last 10 years. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, J. M. Spotting trends in organocatalysis for the next decade. Nat. Commun, 3787; 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; He, X-H. ; Liu, Y-Q.; He, G.; Peng, C.; Li, J-L. Asymmetric organocatalysis: an enabling technology for medicinal chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 122–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Mancheño, O.; Waser, M. Recent developments and trends in asymmetric organocatalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, E.; Prieto, L.; Milelli, A. Asymmetric organocatalysis: A survival guide to medicinal chemists. Molecules 2023, 28, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P. T.; Warner, J. C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice, Oxford, 2000; online edn, Oxford Academic, 31 Oct. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B. M. The atom economy-a search for synthetic efficiency. Science 1991, 254, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B.; Lerner, R. A.; Barbas, C. F. III. Proline-catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendt, K. A.; Borths, C. J.; MacMillan, D. W.C. New strategies for organic catalysis: The first highly enantioselective organocatalytic Diels−Alder reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122(17), 4243–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B. Asymmetric aminocatalysis, Synlett 2001(11), 1675-1686; https//doi.org/ 10.1055/s-2001-18074.
- Melchiorre, P.; Marigo, M.; Carlone, A.; Bartoli, G. Asymmetric aminocatalysis - Gold rush in organic chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6138–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.; Worgull, D.; Zweifel, T.; Gschwend, B.; Bertelsen, S.; Jorgensen, K. A. Mechanisms in aminocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 632–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, F. Amines as catalysts: Dynamic features and kinetic control of catalytic asymmetric chemical transformations to form C−C bonds and complex molecules. Chem. Rec. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retamosa, M. de G.; Blanco-López, E.; Poyraz, S.; Döndas, H. A.; Sansano, J. M.; Cossio. F. R. Chap.3: Enantioselective C–C, C–halogen and C–H bond forming reactions promoted by organocatalysts based on non-proteinogenic α-amino acid derivatives. Adv. Catal. 2023, 73, 143–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoevenagel, E. Ber .dtsch. chem. Ges. 1896, 29, 172–174. [CrossRef]
- List, B. Emil Knoevenhagel and the roots of aminocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1730–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A. G.; Jacobsen, E. N. Small-molecule H-bond donors in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5713–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Deiana, L.; Zhao, G. L.; Sun, J.; Córdova, A. Dynamic one-pot three-component catalytic asymmetric transformation by combination of hydrogen-bond-donating and amine catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7624–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, R. R.; Jacobsen, E. N. Attractive noncovalent interactions in asymmetric catalysis: links between enzymes and small molecule catalysts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010, 107, 20678–20685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Sinibaldi, A.; Nori, V.; Giorgianni, G.; Di Carmine, G.; Pesciaioli, F. Synergistic strategies in aminocatalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Q-Q. ; Du, W.; Chen, Y-C. Asymmetric organocatalysis involving double activation. Tetrahedron Chem. 2022, 2, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Q.; Luo, S. Enantioselective transformations by “1 + x” synergistic catalysis with chiral primary amines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson Afewerki, S.; Córdova. A. Combinations of aminocatalysts and metal catalysts: A powerful cooperative approach in selective organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 13512–13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicewicz, D. A.; MacMillan, D. W. Merging photoredox catalysis with organocatalysis: the direct asymmetric alkylation of aldehydes. Science 2008, 322, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welin, E. R.; Warkentin, A. A; Conrad, J. C.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective α-alkylation of aldehydes by photoredox organocatalysis: Rapid access to pharmacophore fragments from β-cyanoaldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 968–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvi, M.; Melchiorre, P. Enhancing the potential of enantioselective organocatalysis with light. Nature 2018, 554, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredig, G.; Fiske, P. S. Biochem. Z. 1912, 46, 7–23; Fiske, P. S. Durch katalysatoren bewirkte asymmetrische synthese (Doctoral dissertation, ETH Zurich) 1911; https://www.researchcollection. ethz.ch/handle/20.500.11850/136453.
- Pracejus, H. Organische Katalysatoren. LXI. Asymmetrische Synthesen mit Ketenen. I. Alkaloid-katalysierte asymmetrische Synthesen von α phenyl-proponsaüreestern. Liebigs Ann. Chem, 1960; 634, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G. S. , Yeboah, E. M. Recent applications of Cinchona alkaloid-based catalysts in asymmetric addition reactions. Rep. Org.Chem. 2016, 6, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeboah, E. M.O.; Yeboah, S. O.; Singh, G. S. Recent applications of Cinchona alkaloids and their derivatives as catalysts in metal-free asymmetric synthesis. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 1725–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Miyairi, S. Recent advances in cinchona alkaloid catalysis for enantioselective carbon-nitrogen bond formation reactions. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolani, C.; Centonze, G.; Righi, P.; Bencivenni, G. Role of cinchona alkaloids in the enantio- and diastereoselective synthesis of axially chiral compounds. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3551–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreiro, E. P.; Burke, A: J. ; Hermann, G. J.; Federsel, H-J. Continuous flow enantioselective processes catalyzed by cinchona alkaloid derivatives. Tetrahedron Green Chem. 2023, 1, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdenpera, A. S. K.; Dhankhar, J.; Davies, D. J.; Lam, N. Y. S.; Bucos, P. D.; De la Vega-Hernández, K.; Philipps, R. J. Chiral hydrogen atom abstraction catalyst for the enantioselective epimerization of meso-diols. Science 2024, 386, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesell, J. K.; Felman, S. W. Asymmetric induction. 3. Enantioselective deprotonation by chiral lithium amide bases. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornblum, N.; DeLaMare, H. E. The base-catalyzed decomposition of dialkyl peroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 880–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuch, J.-P.; Vogel, P. Asymmetric induction in the rearrangement of monocyclic endoperoxides into γ-hydroxy-α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. Chem. Commun. 1980, (22), 1062–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staben, S. T.; Linghu. ; Toste, F. D. Enantioselective synthesis of gamma-hydroxyenones by chiral base-catalyzed Kornblum DeLaMare rearrangement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12658–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.; Candeias, N. R.; Barbas III, C. F. Dimeric quinidine-catalyzed enantioselective aminooxygenation of oxindoles: An organocatalytic approach to 3-hydroxyoxindole derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5574–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lian, Z.; Xu, Q, Shi, M. Asymmetric [4+2] annulations of isatins with but-3-yn-2-one. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2013, 355, 3344–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H. C.; Van Nieuwenhze, M. S.; Sharpless, K. B. Catalytic asymmetric dihydroxylation. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 2483–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelMonte, A. J.; Haller, J.; Houk, K. N.; Sharpless, K. B.; Singleton, D. A.; Strassner, T.; Thomas, A. A. Experimental and theoretical kinetic isotope effects for asymmetric dihydroxylation. Evidence supporting a rate-limiting "(3 + 2)" cycloaddition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 9907–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentges, S. G.; Sharpless, K. B. Asymmetric induction in the reaction of osmium tetroxide with olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4263–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E. N.; Markó, I.; Mungall, W. S.; Schröder, G.; Sharpless, K. B. Asymmetric dihydroxylation via ligand-accelerated catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 116, 1968–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, B.; Ali, A. A.; Boruah, P. R.; Sarma, D.; Barua, N. C. Pd(OAc)2 and (DHQD)2PHAL as a simple, efficient and recyclable/reusable catalyst system for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions in H2O at room temperature. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 2440–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. A.; Chetia, M.; Saikia, P. J.; Sarma, D. (DHQD)2PHAL ligand-accelerated Cu-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition reactions in water at room temperature. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 64388–64392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, L. X.; Mai, W. P.; Xia, A. X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S. B. Enantioselective iodolactonization catalyzed by chiral quaternary ammonium salts derived from cinchonidine, J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 2874–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, D. C.; Yousefi, R.; Jaganathan, A.; Borhan, B. An organocatalytic asymmetric chlorolactonization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Braddock, D. C.; Jones, A. X.; Clark, S. Catalytic asymmetric bromolactonization reactions using (DHQD)2PHAL-benzoic acid combinations. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 7004–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braddock, D. C.; Lancaster, B. M. J.; Tighe, C. J.; White, A. J. P. Surmounting byproduct inhibition in an intermolecular catalytic asymmetric alkene bromoesterification reaction as revealed by kinetic profiling. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 8904–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, H.; Wynberg, H. Addition of aromatic thiols to conjugated cycloalkenones, catalyzed by chiral beta-hydroxy amines. A mechanistic study of homogeneous catalytic asymmetric synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, T.; van der Haas, R. N. S.; van Maarseveen, J. H.; Hiemstra, H. Asymmetric organocatalytic Henry reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, L. Organocatalytic applications of cinchona alkaloids as a potent hydrogen-bond donor and/or acceptor to asymmetric transformations: A review. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2016, 13, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, H.; Singh, V. K. Cinchona derivatives as bifunctional H-bonding organocatalysts in asymmetric ninylogous conjugate addition reactions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2022, 11, e202100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCooey, S. H.; Connon, S. J. Urea- and thiourea-substituted cinchona alkaloid derivatives as highly efficient bifunctional organocatalysts for the asymmetric addition of malonate to nitroalkenes: inversion of configuration at C9 dramatically improves catalyst performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6367–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W-R. ; Su, Q.; Lin, N.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z-W.; Weng, J.; Lu, G. Organocatalytic synthesis of chiral CF3-containing oxazolidines and 1,2-amino alcohols: asymmetric oxa-1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of trifluoroethylamine-derived azomethine ylides: Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3452–3458. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y-R. ; Xu, J.; Jiang, H-F., Fang, R-J., Zhang, Y-J., Chen, L., Sun, C., Eds.; Xiong, F. Bifunctional sulfonamide as hydrogen bonding catalyst in catalytic asymmetric reactions: Concept and application in the past decade. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, article nb. e202201081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Bhowmick, S.; Ghosh, A.; Chanda, T.; Bhowmick, K. C. Advances on asymmetric organocatalytic 1,4-conjugate addition reactions in aqueous and semi-aqueous media. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2017, 28, 849–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Duhamel, L. C. R. C. R. Acad. Sci. 1976, 282C, 125-127 ; b) Duhamel, L.; Plaquevent, J.-C. Déracemisation par protonation enantioselective. Tetrahedron Lett. [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, L.; Duhamel, P.; Plaquevent, J.-C. Enantioselective protonations: fundamental insights and new concepts. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2004, 15, 3653–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, C.; Galindo, J. Catalytic enantioselective protonation of enolates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1994, 33, 1888–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, C. Enantioselective protonation of enolates and enols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1996, 35, 2566–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, C. Catalytic enantioselective tauromerization of isolated enols. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2007, 46, 7119–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. S.; Salunkhe, R. V.; Rane, R. A.; Dike, S. Y. Novel catalytic enantioselective protonation (proton transfer) in Michael addition of benzenethiol to α-acrylacrylates: synthesis of (S)-naproxen and α-arylpropionic acids or esters. Chem. Commun. 1991, (7), 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Ono, M.; Nagaoka, Y.; Tomioka, K. Catalytic enantioselective protonation of lithium ester enolates generated by conjugate addition of arylthiolate to enoates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J. P.; Ellman, J. A. Conjugate addition-enantioselective protonation reactions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 1203–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, P.; Houk, K. N. Organic Chemistry: Theory, Reactivity, and Mechanisms in Modern Synthesis. Wiley VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2019, Chap. 1.6.1, pp. 10-11; ISBN: 978-3-527-34532-8.
- Hintermann, L.; Ackerstaff, J.; Boeck, F. Inner workings of a cinchona alkaloid catalyzed oxa-Michael cyclization: Evidence for a concerted hydrogen-bond-network mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.; Zhuang, W.; Jørgensen, K. A. Asymmetric conjugate addition of azide to α,β-unsaturated compounds catalyzed by cinchona alkaloids. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 5849–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukata, T.; Koga, K. Enantioselective protonation of achiral lithium enolates using a chiral amine in the presence of lithium bromide. Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 1993, 4, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, P.; Koga, K. An approach to catalytic enantioselective protonation of prochiral lithium enolates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 7589–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łowicki, D.; Watral, J.; Jelecki, M.; Bohusz, W.; Kwit, M. Stereoselective protonation of 2-methyl-1-tetralone lithium enolate catalyzed by salan-type diamines. Tetrahedron 2021, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, K.; Ito, R.; Arai, T.; Yanagisawa, A. Catalytic asymmetric protonation of lithium enolates using amino acid derivatives as chiral proton sources. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, T.; Dalla, V.; Marsais, F.; Dupas, G.; Oudeyer, S.; Levacher, V. Organocatalytic enantioselective protonation of silyl enolates mediated by cinchona alkaloids and a latent source of HF. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7090–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claraz, A.; Landelle, G.; Oudeyer, S.; Levacher, V. Asymmetric organocatalytic protonation of silyl enolates catalyzed by simple and original betaines derived from cinchona alkaloids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 7693–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, H,; Baur, M. A. α-Amino acid derivatives by enantioselective decarboxylation. Eur. J. Org. Chem, 2854. [CrossRef]
- George, K. M.; Frantz, M.; Bravo-Altamirano, K.; LaValle, C. R.; Tandon, M.; Leimgruber, S.; Sharlow, E.R.; Lazo, J. S.; Wang, Q. J.; Wipf, P. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3(2), 186-22. [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Yamagami, M.; Vellalath, S.; Romo, D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6527–6531. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y-L. ; Rodriguez, J.; Coquerel, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wei Du, W. ; Chen, Y-C. Modified cinchona alkaloid-catalysed enantioselective [4+4] annulations of cyclobutenones and 1-azadienes. Chem. Commun, 7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J. W.; Chen, W.; Li, R.; Zeng, M.; Du, W.; Yue, L.; Chen, Y. C.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Deng, J. G. Highly asymmetric Michael addition to alpha,beta-unsaturated ketones catalyzed by 9-amino-9-deoxyepiquinine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, G.; Bosco, M.; Carlone, A.; Pesciaioli, F.; Sambri, L.; Melchiorre, P. Organocatalytic asymmetric Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indoles with simple alpha,beta-unsaturated ketones. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, J. L.; Badia, D.; Carrillo, L. Organocatalytic enantioselective Michael and hetero-Michael reactions. Synthesis 2007, (14), 2065–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Reisinger, C. M.; List, B. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of cyclic enones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6070–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooey, S. H.; Connon, S. J. Readily accessible 9-epi-amino cinchona alkaloid derivatives promote efficient, highly enantioselective additions of aldehydes and ketones to nitroolefins. Org Lett. 2007, 9, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.; Naganaboina, V. K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Q.; Rout, L.; Zhao, C-G. Organocatalytic highly enantioselective synthesis of β-formyl-α-hydroxyphosphonates. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, P.; Beeson, T. D.; Conrad, J. C.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective organocatalytic α-fluorination of cyclic ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1738–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Milani, R.; Pilati, T.; Priimagi, A.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601. [CrossRef]
- Beer, P. D.; Brown, A. Halogen bonding anion recognition. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8645–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutar, R. L.; Huber, S. M. Catalysis of organic reactions through halogen bonding. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9622–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckmann, A.; Pena, M. A.; Bolm, C. Organocatalysis through halogen-bond activation. Synlett 2008, (6), 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, S.; Suzuki, T.; Hosaka, Y.; Arai, T. A chiral organic base catalyst with halogen-bonding-donor functionality: asymmetric Mannich reactions of malononitrile with N-Boc aldimines and ketimines. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3847–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, S.; Nishida, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Arai, T. Catalytic asymmetric Mannich-type reaction of malononitrile with N-Boc α-ketiminoesters using chiral organic base catalyst with halogen bond donor functionality. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarrigle, E.; Myers, E. L.; Illa, O.; Shaw, M. A, Riches S. L, Aggarwal, V. K. Chalcogenides as organocatalysts. Chem Rev. 2007, 107, 5841–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breugst, M.; Koenig, J. J. σ-Hole interactions in catalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 34, 5473–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Zheng, M.; Xu, C.; Chen. F.-E. Harnessing noncovalent interaction of chalcogen bond in organocatalysis: From the catalyst point of view. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makosza, M. Reactions of organic anions II. Catalytic alkylation of indene. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966, 38, 4621–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, C. M. Phase-transfer catalysis. I. Heterogeneous reactions involving anion transfer by quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder, R.; Hummelen, J. C.; Laane, R. W. P. M.; Wiering, J. S.; Wynberg, H. Catalytic asymmetric induction in oxidation reactions. The synthesis of optically active epoxides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976, 17, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluim, H.; Wynberg, H. Catalytic asymmetric induction in oxidation reactions. Synthesis of optically active epoxynaphthoquinones. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 2498–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cornwall, R. G.; Shi, Y. Organocatalytic asymmetric epoxidation and aziridination of olefins and their synthetic applications. Chem Rev. 2014, 114, 8199–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschona, F.; Savvopoulou, I.; Tsitopoulou, M.; Tataraki, D.; Rassias, G. Epoxide syntheses and ring-opening reactions in drug development. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolling, U. H.; Davis, P.; Grabowski, E. J. Efficient catalytic asymmetric alkylations. 1. Enantioselective synthesis of (+)-indacrinone via chiral phase-transfer catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M. J.; Bennett, W. D.; Wu, S. The stereoselective synthesis of α-amino acids by phase-transfer catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 2353–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, E.; Siva, A. Synthesis of asymmetric N-arylaziridine derivatives using a new chiral phase-transfer catalyst. Synthesis, 2005; 2022–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Lygo, B.; Wainwright, P. G. A new class of asymmetric phase-transfer catalysts derived from Cinchona alkaloids–application in the enantioselective synthesis of α-amino acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 8595–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E. J.; Xu, F.; Noe, M. C. A rational approach to catalytic enantioselective enolate alkylation using a structurally rigidified and defined chiral quaternary ammonium salt under phase transfer conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 12414–12415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E. J.; Zhang, F.-Y. Mechanism and conditions for highly enantioselective epoxidation of alpha,beta-enones using charge-accelerated catalysis by a rigid quaternary ammonium salt. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Nagai, A.; Hamasaki, A.; Tokunaga, M. Catalytic asymmetric hydrolysis: Asymmetric hydrolytic protonation of enol esters catalyzed by phase-transfer catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7178–7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, S.; Maruoka, K. Recent developments in asymmetric phase-transfer reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4312–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yasuda, N. Transfer catalysts: Large-scale industrial applications. Org. Proc. Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, D. C. M.; Penso, M. New trends in asymmetric phase transfer catalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Maruoka, K. Recent development and application of chiral phase-transfer catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5656–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Yasuda, N. Contemporary asymmetric phase transfer catalysis: Large-scale industrial applications. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. J.; Maruoka, K. Asymmetric phase-transfer catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haripriya, P. , Rai, R. Vijayakrishna, K. Polymer anchored cinchona alkaloids: Synthesis and their applications in organo-catalysis. Top. Curr. Chem. (Z) 2025, 383, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
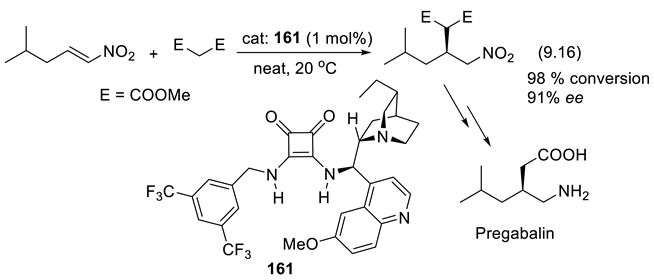
- Moccia, M.; Cortigiani, M.; Monasterolo, C.; Torri, F.; del Fiandra, C.; Fuller, G.; Kelly, B.; Adamo, M. F. A. Development and scale-up of an organocatalytic enantioselective process to manufacture (S)-Pregabalin. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgianni, G.; Bernardi, L.; Fini, F.; Pesciaioli, F.; Secci, F.; Carlone, A. Asymmetric organocatalysis—A powerful technology platform for academia and industry: Pregabalin as a case study. Catalysts 2022, 12, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Han, X-L. ; Yu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wu, K.; Li. Z.; Luo, J.; Deng, L. Organocatalytic asymmetric α-C–H functionalization of alkyl amines. Nat. Catal. 2024, 7, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Y. Chiral phase-transfer catalysts with hydrogen bond: A powerful tool in the asymmetric synthesis. Catalysts 2019, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, P.; Fernández, R.; Lassaletta, J. M. Organocatalytic asymmetric cyanosilylation of nitroalkenes. Chemistry 2010, 16, 7714–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K. M.; Rattley, M. S.; Sladojevich, F.; Barber, D. M.; Nuñez, M. G.; Goldys, A. M.; Dixon, D. J. A new family of cinchona-derived bifunctional asymmetric phase-transfer catalysts: application to the enantio- and diastereoselective nitro-Mannich reaction of amidosulfones. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2492–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Woods, P. A.; Smith, M. D. Cation-directed enantioselective synthesis of quaternary-substituted indolenines. Chem. Science 2013, 4, 2907–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Fang, Y.; Gao. ; Wei, Z.; Cao, J.; Liang, D.; Lin, Y.; Duan, H. Bifunctional thiourea-ammonium salt catalysts derived from cinchona alkaloids: Cooperative phase-transfer catalysts in the enantioselective aza-Henry reaction of ketimines. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Q.; Deng, Y. L.; Ling, D.; Li, T. T.; Chen, L. Z.; Jin, Z. C. ; Recent progress in chiral quaternary ammonium salt-promoted asymmetric nucleophilic additions. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 1973–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, T.; Shibuguchi, T.; Fukuta, Y.; Shibasaki, M. Catalytic asymmetric phase-transfer reactions using tartrate-derived asymmetric two-center organocatalysts. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 7743–7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, M.; Gratzer, K.; Herchl, R.; Müller, N. Design, synthesis, and application of tartaric acid derived N-spiro quaternary ammonium salts as chiral phase-transfer catalysts. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10(2), 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Tan, C.-H. Phase-transfer and ion-pairing catalysis of pentanidiums and bisguanidiniums. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Feng, X.; Liu, X. Chiral guanidines and their derivatives in asymmetric synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8525–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, Z, Ye, X. ; Tan, C.-H, Ion-pair catalysts-pentanidinium. Chem. Record 2023, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. S.; Lu, K.; Li, C. X.; Zhao, Z, H. ; Zhang, X. M.; Zhang, F. M.; Tu, Y. Q. Chiral 1,2,3-triazolium salt catalyzed asymmetric mono- and dialkylation of 2,5-diketopiperazines with the construction of tetrasubstituted carbon centers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, T.; Kameda, M.; Maruoka, K. ; Design of N-spiro C2-symmetric chiral quaternary ammonium bromides as novel chiral phase-transfer catalysts: synthesis and application to practical asymmetric synthesis of alpha-amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5139–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Sasaki, K.; Fukumoto, K.; Murase, Y.; Abe, N.; Ooi, T.; Maruoka, K. Phase-transfer-catalyzed asymmetric alkylation of α-benzoyloxy-β-keto esters: Stereoselective construction of congested 2,3-dihydroxycarboxylic acid esters. Chem. Asian. J. 2010, 5, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H. W.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Y.; Lee, J. K.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Park, H.-g. Phase-transfer catalyzed enantioselective α-alkylation of α-acyloxymalonates: construction of chiral α-hydroxy quaternary stereogenic centers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 77427–77430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C. M.; Franckevicius, V. The catalytic asymmetric allylic alkylation of acyclic enolates for the construction of quaternary and tetrasubstituted stereogenic centres. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 20, e202304289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, J.; Tan, S. M.; Tan, D.; Lee, R.; Tan, C. H. An enantioconvergent halogenophilic nucleophilic substitution (SN2X) reaction. Science 2019, 363, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novacek, J.; Waser, M. Syntheses and applications of (thio)urea-containing chiral quaternary ammonium salt catalysts. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014(4), 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciber, L.; Požgan, F.; Brodnik, H.; Štefane, B.; Svete, J.; Waser, M.; Grošelj, U. Synthesis and catalytic activity of bifunctional phase-transfer organocatalysts based on camphor. Molecules 2023, 28, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, R. L.; Engelage, E.; Stoll, R.; Huber, S. M. Bidentate chiral bis(imidazolium)-based halogen-bond donors: Synthesis and applications in enantioselective recognition and catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6806–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, J- L. ; Terrett, J. A.; MacMillan, D. W. C. O-H hydrogen bonding promotes H-atom transfer from α-C-H bonds for C-alkylation of alcohols. Science 2015, 349, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J. A.; Adrianov, T.; Taylor, M. S. Understanding the origins of site selectivity in hydrogen atom transfer reactions from carbohydrates to the quinuclidinium radical cation: A computational study. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 5713–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Huang, T.; Lin, Y-M. ; Gong, L. Advancements in organocatalysis for radical-mediated asymmetric synthesis: A recent perspective. Chem Catal. 2024, 4, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagib, D. A. Asymmetric catalysis in radical chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15989–15992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrup, A. B.; MacMillan, D. W. C. The first general enantioselective catalytic Diels-Alder reaction with simple α,β-unsaturated ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 2458–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelais, G.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Modern strategies in organic catalysis: The advent and development of iminium activation. Aldriquimica Acta 2006, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Erkkilä, A.; Majander, I.; Pihko, P. M. Iminium catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5416–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, G.; Melchiorre, P. A novel organocatalytic tool for the iminium activation of α,β-unsaturated ketones. Synlett 2008, 2008(12), 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paras, N. A.; MacMillan, D. W. C. The enantioselective organocatalytic 1,4-Addition of electron-rich benzenes to α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 7894–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronina, Y.A.; Teglyai, L. A.; Ponyaev, A. I.; Petrov, M. L.; Boitsov, V. M.; Stepakow, A. V. Organocatalysis in 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions (A review). Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2024, 94, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, N.; Takenaka, N.; Najwa, A.; Takahara, Y.; Mun, M. K.; Itsuno, S. Synthesis of main-chain ionic polymers of chiral imidazolidinone organocatalysts and their application to asymmetric Diels–Alder reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 2018(1), 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zacuto, M.; Yoshikawa, N.; Desmond, R.; Hoerrner, S.; Itoh, T.; Journet, M.; Humphrey, G. R.; Cowden, C.; Strotman, N.; Devine, P. Asymmetric synthesis of telcagepant, a CGRP receptor antagonist for the treatment of migraine. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75(22), 7829–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z. Y.; Ghosh, T.; Melchiorre, P. Enantioselective radical conjugate additions driven by a photoactive intramolecular iminium-ion-based EDA complex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Yang, J. W.; Hoffmann, S.; List, B. Asymmetric enamine catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5471–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burés, J.; Armstrong, A.; Blackmond, D. G. Explaining anomalies in enamine catalysis: “downstream species” as a new paradigm for stereocontrol. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, K.; Notz, W.; Bui, T.; Barbas, C. F. III. Amino acid catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reactions: a bioorganic approach to catalytic asymmetric carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5260–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. K. Efficient catalytic methods for asymmetric cross-aldol reaction of aldehydes. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Gotoh, H.; Hayashi, T.; Shoji, M. Diphenylprolinolsilyl ethers as efficient organocatalysts for the asymmetric Michael reaction of aldehydes and nitroalkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4212–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Zahoor, A. F.; Ahmad, S.; Akhtar, R.; Qurban, W.; Mehreen, A. Recent trends in the development of novel catalysts for asymmetric Michael reaction. Curr. Org. Chem. 2020, 24, 1397–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasuparthy, S. D.; Maiti, B. Enantioselective organocatalytic Michael addition reactions catalyzed by proline/prolinol/supported proline based organocatalysts: An overview. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, A. The direct catalytic asymmetric Mannich reaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, A.; Schaus, S. E. Organocatalytic asymmetric Mannich reactions: New methodology, catalyst design, and synthetic applications. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, (35), 5797–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, W.; Tanaka, F.; Barbas, C. F. Enamine-based organocatalysis with proline and diamines: The development of direct catalytic asymmetric aldol, Mannich, Michael, and Diels-Alder reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J-L. ; Liu, T-Y.; Chen, Y-C. Aminocatalytic asymmetric Diels–Alder reactions via HOMO activation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, R. Recent developments in catalytic asymmetric inverse-electron-demand Diels-Alder reaction. Chem Rev. 2013, 113, 5515–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Kano, T.; Maruoka, K. Organocatalyzed direct asymmetric α-halogenation of carbonyl compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, T.; Phipps, R. J.; Toste, F. D. Advances in catalytic enantioselective fluorination, mono-, di-, and trifluoromethylation, and trifluoromethylthiolation reactions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 826–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigo, M.; Wabnitz, T. C.; Fielenbach, D.; Jørgensen, K. A. Enantioselective organocatalyzed α-sulfenylation of aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthaler, R. O. Proline-catalyzed asymmetric α-amination of aldehydes and ketones-An astonishing simple access to optically active α-hydrazino carbonyl compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 41, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, S.; Landa, A.; Mielgo, A.; Ganboa, I.; Oiarbide, M.; Soloshonok, V. Catalytic asymmetric α-functionalization of α-branched aldehydes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Otani, G. Asymmetric synthesis with amino acid. 2. Asymmetric synthesis of optically active 4,4-disubstituted -2-cyclohexenone. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969, 10, 4237–42401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, N.; Peng, Y. Prolinol tert-butyldiphenylsilyl ether as an organocatalyst for the asymmetric Michael addition of cyclohexanone to nitroolefins. Synlett 2007, (15), 2415–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Gotoh, H.; Hayashi, T.; Shoji, M. Diphenylprolinol silyl ethers as efficient organocatalysts for the asymmetric Michael reaction of aldehydes and nitroalkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4212–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, J.; Marigo, M.; Fielenbach, D.; Wabnitz, T. C.; Kjærsgaard, A.; Jørgensen, K. A. A general organocatalyst for direct α-functionalization of aldehydes: Stereoselective C−C, C−N, C−F, C−Br, and C−S bond-forming reactions. Scope and mechanistic insights. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 18296–18304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajos, Z. G.; Parrish, D. R. Asymmetric synthesis of polycyclic organic compounds. German Patent DE 2102623 ( 1971.
- Hajos, Z. G.; Parrish, D. R. Asymmetric synthesis of bicyclic intermediates of natural product chemistry. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajos, Z. G.; Parrish, D. R. Synthesis and conversion of 2-methyl-2-(3-oxobutyl)-1,3-cyclopentanedione to isomeric racemic ketols of [3.2.1]bicyclooctane of perhydroindan series. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, U.; Sauer, G.; Weichert, R. Total synthesis of optically active steroids. 6. New type of asymmetric cyclization to optically active steroid CD partial structures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1971, 10, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, W.; List, B. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of anti-1,2-diols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7386–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K. L.; Dickmeiss, G.; Jiang, H.; Albrecht, L.; Jørgensen, K. L. The diarylprolinol silyl ether system: A general organocatalyst. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meninno, S.; Lattanzi, A. Asymmetric organocatalysis mediated by α,α-L-diaryl prolinols: Recent advances. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donslund, B. S.; Johansen, T. K.; Poulsen, P. H.; Halskov, K. S.; Jørgensen, K, A. The diarylprolinol silyl ethers: Ten years after. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13860–13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valapil, G. G.; Kadagathur, M.; Shankaraiah, N. Stereoselective aldol and conjugate addition reactions mediated by proline-based catalysts and its analogues: A concise review. Eur. Org. Chem. 2021, (37), 5288–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Aguilar, M.; Ramos-Martín, M.; Ríos-Lombardía, N.; Cicco, L.; García-Álvarez, J.; Concellón, C.; del Amo, V. Synergistic one-pot tandem combination of Cu and proline catalysis: Stereodivergent synthesis of chiral aldols from primary alcohols. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanna, K. Amino acids and peptides organocatalysts: A brief overview on its evolution and applications in organic asymmetric synthesis. Curr. Organocatal. 2021, 8, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanna, K. Organocatalysts based on natural and modified amino acids for asymmetric reactions. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2022, 7, 429–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, A.; Zou, W.; Dziedzic, P.; Ibrahem, I.; Reyes, E.; Xu, Y. Direct asymmetric intermolecular aldol reactions catalyzed by amino acids and small peptides. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 5383–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartók, M. Advances in immobilized organocatalysts for the heterogenous asymmetric direct aldol reactions. Catal. Rev. 2015, 57, 192–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajahan, R.; Sarang, R.; Saithalavi, A. Polymer supported proline-based organocatalyts in asymmetric aldol reactions. A review. Curr. Organocatal. 2022, 9, 124–146. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Landfester, K.; Zhang, K. A. I.; Muñoz-Espi, R. Proline-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as highly performing asymmetric catalysts. Macromol. Rap. Commun. 2024, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmanyar, S.; Houk, K. N.; Martin, H. J.; List, B. Quantum mechanical predictions of the stereoselectivities of proline-catalyzed asymmetric intermolecular aldol reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F. R.; Houk, K. N. Computational evidence for the enamine mechanism of intramolecular aldol reactions catalyzed by proline. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 116, 5890–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Clemente, F. R.; Houk, K. N.; Meyer, M. P. Rate limiting step precedes C–C bond formation in the archetypical proline-catalyzed intramolecular aldol reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1632–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M. B.; Zeitler, K.; Gschwind, R. M. The elusive enamine intermediate in proline-catalyzed aldol reactions: NMR detection, formation pathway, and stabilization trends. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4997–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L-J, Coote, M. L. Electrostatic switching of stereoselectivity in aldol reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 9076–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L-J. ; Blyth, M. T.; Coote, M. L. Re examination of proline catalyzed intermolecular aldol reactions: An ab Initio kinetic modelling study. Top. Catal. 2022, 65, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agami, C.; Meynier, F.; Richot, C. New insights into the mechanism of the proline-catalyzed asymmetric Robinson cyclization; structure of two intermedaites. Asymmetric dehydration. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebach, D.; Beck, A. K.; Badine, D. M.; Limbach, M.; Eschenmoser, A.; Treasurywala, A. M.; Hobi, R.; Prikosvovich, W.; Linder, B. Are oxazolidinones really unproductive, parasitic species in proline catalysis? Thoughs and experiments pointing to an alternative view. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 425–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. K,.; Sunoj, R. B. Enamine versus oxazolidinone: what controls stereoselectivity in proline-catalyzed asymmetric aldol reactions? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6373–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzer, T.; Wennemers, H. Deactivation of secondary amine catalysts via aldol reaction-amine catalysis under solvent-free conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 7633–7640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Aikawa, T.; Shimasaki, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Tomioka, Y.; Miki, T.; Takeda, M.; Ikemoto, T. Research and development of an efficient synthesis of a key building block for anti-AIDS drugs by diphenylprolinol-catalyzed enantio- and diastereoselective direct cross aldol reaction. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2016, 20, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushima, T.; Yasui, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Hayashi, Y. Polymeric ethyl glyoxylate in an asymmetric aldol reaction catalyzed by diarylprolinol. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2966–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdova, A. The direct catalytic asymmetric Mannich reaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkade, J.; van Hemert, L. J.; Quaedflieg, P, J. ; Rutjes, F. P. Organocatalysed asymmetric Mannich reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B. The direct catalytic asymmetric three-component Mannich reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9336–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B.; Porjalev, P.; Biller, W. T.; Martin, H. J. The proline-catalyzed direct asymmetric three-component Mannich reaction: Scope, optimization, and application to the highly enantioselective synthesis of 1,2-amino alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Hüttl, M. R. H. Direct organocatalytic α-fluorination of aldehydes and ketones. Synlett 2005, 2005(6), 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigo, M.; Fielenbach, D.; Braunton, A.; Kjaersgaard, A.; Jørgensen, K. A. Enantioselective formation of stereogenic carbon-fluorine centers by a simple catalytic method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3703–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D. D.; Mase, N.; Barbas, C. F. III. Direct asymmetric alpha-fluorination of aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int.Ed. 2005, 44, 3706–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, T. D.; Macmillan, D. W. Enantioselective organocatalytic alpha-fluorination of aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8826–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelsen, S.; Halland, N.; Bachmann, S.; Marigo, M.; Braunton, A.; Jørgensen, K. A. Organocatalytic asymmetric α-bromination of aldehydes and ketones. Chem. Commun, 4821. [Google Scholar]
- Nacsa, E. D.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Spin-center shift-enabled direct enantioselective α-benzylation of aldehydes with alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H. W.; Van der Wal, M. N.; Grange, R. L.; MacMillan, D. W. Enantioselective α-benzylation of aldehydes via photoredox organocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13600–13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertelsen, S.; Marigo, M.; Brandes, S.; Dinér, P.; Jørgensen, K. A. Dienamine catalysis: organocatalytic asymmetric gamma-amination of alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12973–12980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z-J. ; Jiang, H.; Li, J-L.; Gschwend, B.; Li, Q-Z.; Yin, X.; Grouleff, J.; Chen, Y-C.; Jørgensen, K. A. Trienamines in asymmetric organocatalysis: Diels Alder and tandem reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5053–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arceo, E.; Melchiorre, P. Extending the aminocatalytic HOMO-raising activation strategy: where is the limit? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5290–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Melchiorre, P. Aminocatalytic enantioselective 1,6-additions of alkyl thiols to cyclic dienones: vinylogous iminium ion activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6439–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, L. F. Domino reactions in organic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C. J.; Frost, C. G. Tandem and domino catalytic strategies for enantioselective synthesis. Synthesis, 2007; 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G-L. ; Ibrahem, I.; Dziedzic, P.; Sun, J.; Bonneau, C.; Córdova, A. One-pot catalytic enantioselective domino nitro-Michael/Michael Synthesis of cyclopentanes with four stereocenters. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 10007–10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Mahajan, S.; Enders, D. Achieving molecular complexity via stereoselective multiple domino reactions promoted by a secondary amine organocatalyst. Acc Chem Res. 2017, 50, 2809–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chando, T.; Gui Zhao, J. C. Recent progress in organocatalytic asymmetric domino transformations. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 360, 2–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Grondal, C.; Hüttl, M. R. Asymmetric organocatalytic domino reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, H. Recent developments in asymmetric organocatalytic domino reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 237–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volla, C. M.; Atodiresei, I.; Rueping, M. Catalytic C-C bond-forming multi-component cascade or domino reactions: pushing the boundaries of complexity in asymmetric organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2390–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghtmann, J.; Andresen, P. S. S.; Østergaard, R. A, Jørgensen, A. K. Enantioselective cascade reactions of aminocatalytic dienamines and trienamines initiated by a cycloaddition reaction. Chem. Eur.J. 2024; e202403656,. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.; Barbas, C. F. III. A proline-catalyzed asymmetric Robinson annulation reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41(36), 6951–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halland, N.; Aburel, P. S.; Jørgensen, K. A. Highly Enantio- and diastereoselective organocatalytic asymmetric domino Michael–aldol reaction of β-ketoesters and α,β-unsaturated ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Okano, T.; Aratake, S.; Hazelard, D. Diphenylprolinol silyl ether as a catalyst in an enantioselective, catalytic, tandem Michael/Henry reaction for the control of four stereocenters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4922–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas, W.; Notz, K.; Sakthivel, T.; Bui, G.; Zhong, G.; Barbas, C. F. III Amine-catalyzed direct asymmetric Mannich-type reactions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, A. The direct catalytic asymmetric cross-Mannich reaction: A highly enantioselective route to 3-amino alcohols and α-amino acid derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Urushima, T.; Shoji, M.; Uchimaru, T.; Shiina, I. The direct, enantioselective, one-pot, three-component, cross-Mannich reaction of aldehydes: The reason for the higher reactivity of aldimine versus aldehyde in proline-mediated Mannich and aldol reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, P.; Ibrahem, I.; Córdova, A. Direct catalytic asymmetric three-component Mannich reactions with dihydroxyacetone: enantioselective synthesis of amino sugar derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chandler, C.; Stadler, M.; Kampen, D.; List, B. Proline-catalysed Mannich reactions of acetaldehyde. Nature 2008, 452, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, Y-C. ; Lau, J-J.; Wu, M-C. Direct asymmetric three-component Mannich reactions catalyzed by a siloxy serine organocatalyst in water. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2008, 19, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, B.; Castello, C. A novel proline-catalyzed three-component reaction of ketones, aldehydes, and Meldrum’s acid. Synlett 2001, 11, 1687–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, A.; Notz, W.; Barbas, C. F. III. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdari, N. S.; Ramachary, D. B.; Córdova, A.; Barbas, C. F. III. Proline-catalyzed asymmetric assembly reactions: enzyme-like assembly of carbohydrates and polyketides from three aldehyde substrates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 9591–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Hüttl, M. R.; Runsink, J.; Raabe, G.; Wendt, B. Organocatalytic one-pot asymmetric synthesis of functionalized tricyclic carbon frameworks from a triple-cascade/Diels-Alder sequence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H-Y. ; Hong, J-B.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective organocatalytic singly occupied molecular orbital activation: The enantioselective α-enolation of aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7004–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, T. D.; Mastracchio, A.; Hong, J-B. ; Ashton, K.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective organocatalysis using SOMO activation. Science 2007, 316, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mečiarová, M.; Pavol Tisovský, P.; Sebesta, R. Enantioselective organocatalysis using SOMO activation. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4855–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Suzuki, Z.; Hirose, H. A tertiary phosphine-catalyzed reaction of acrylic compounds with aldehydes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1968, 41, 2815–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4Baylis, A. B.; Hillman, M. E. D. Acrylic compounds. Chem. Abstr. 1972, 77, 34174q. [Google Scholar]
- Maneesha, M.; Haritha, S. H.; Aneeja, T.; Anilkumar, G. Recent progress and prospects in the organocatalytic Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 14949–14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shi, M. Recent advances in organocatalytic asymmetric Morita–Baylis–Hillman/aza-Morita–Baylis–Hillman reactions. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6659–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, P.; Houk, K. N. Organic Chemistry: Theory, Reactivity and Mechanisms in Modern Synthesis. Wiley VCH GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2019, Chap. 7.5.56,pp. 9: 826-828; ISBN, 3453. [Google Scholar]
- Pélissier, H. Asymmetric organocatalytic Morita−Baylis−Hillman reaction and asymmetric organocatalytic transformations of Morita−Baylis−Hillman adducts. An update. Tetrahedron 2025, 172, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, P. R.; Kannan, V.; Reddy, P. V. N. N-methylprolinol catalysed asymmetric Baylis-Hillman reaction. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menkudle, M. S.; Pendalwar, S. S.; Goswami, S. V.; Jadhav, W. N.; Bhusare, S. R. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 672–677. [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, R.; Nájera, C.; Sánchez-Agulló, P. Enantiomerically pure guanidine-catalysed asymmetric nitroaldol reaction. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1994, 5, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, P. Guanidine organocatalysis. Synthesis 2013, 45, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H. C.; Leow, D.; Tan, C. H. Recent advances in chiral guanidine-catalyzed enantioselective reactions. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 3803–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S. Q.; Bao, X. Z.; Nawaz, S.; Qu, J. ; Wang, B, Identification of a tartrate-based modular guanidine towards highly asymmetric Michael addition of 3-aminooxindoles to nitroolefins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 64, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E. J.; Grogan, M. J. Enantioselective synthesis of alpha-amino nitriles from N-benzhydryl imines and HCN with a chiral bicyclic guanidine as catalyst. Org Lett. 1999, 1, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leow, D.; Tan, C. H. Chiral guanidine catalyzed enantioselective reactions. Chem Asian J. 2009, 4, 488–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birman, V. B.; Li, X. Benzotetramisole: a remarkably enantioselective acyl transfer catalyst. Org Lett. 2006, 8, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, M. R.; Birman, V. B. Organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of α-fluoro-β-amino acid derivatives. Org Lett. 2018, 20, 7550–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zi, W. Design, preparation, and implementation of axially chiral benzotetramisoles as Lewis base catalysts for asymmetric cycloadditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasov, M. E.; Hudson, B. M.; Tantillo, D. J.; Romo, D. Acylammonium salts as dienophiles in Diels−Alder/lactonization organocascades. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4492–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. A.; Yu, W. Z.; Yeung, Y. Y. Carbamate-catalyzed enantioselective bromolactamization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12102–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira Ribeiro, F. W.; Matsushima, J. E.; Obeid, G.; Vinhato, E.; Rodrigues, A.; Correra, T. C. Mechanistic Investigation of an organocatalytic bromocyclization of O-allyl carbamates. ChemCatChem 2025, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkessel, A. The discovery of catalytically active peptides through combinatorial chemistry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol, 1016. [Google Scholar]
- Revell, J. D.; Wennemers, H. Peptidic catalyst developed by combinatorial screening methods. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 11, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Kodadek, T. Solid-phase synthesis of β-hydroxy ketones via DNA-compatible organocatalytic aldol reactions. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S. J. In search of peptide-based catalysts for asymmetric organic synthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davie, E. A.; Mennen, S. M.; Xu, Y.; Miller, S. J. Asymmetric catalysis mediated by synthetic peptides. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5759–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennemers, H. Asymmetric catalysis with peptides. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12036–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metrano, A. J.; Chinn, A. J.; Shugrue, C. R.; Stone, E. A.; Kim, B.; Miller, S. J. Asymmetric catalysis mediated by synthetic peptides, version 2.0: Expansion of scope and mechanisms. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11479–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, K. ; Asymmetric peptide catalysis. In Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis, 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons., Inc. 2022, Chap. 5, pp. [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Valagussa, B.; Boanoni, E.; Gentilucci, L. Expedient recycling of peptide organocatalysts using nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite catching systems. Sust. Chem. Pharm. 2024, 37, 157–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, M.; Chawla, V.; Singh, Y. Ceria nanoparticles immobilized with self-assembling peptide for biocatalytic applications. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 16887–16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, H.; Ohashi, S.; Inoue, S. Asymmetric synthesis catalyzed by poly(5-benzyl L-glutamate). Makromol. Chem. 1975, 176, 2751–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Inoue, S. Asymmetric synthesis catalyzed by poly(4-benzyl L-aspartate). Makromol. Chem. 1975, 176, 3609–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyanagi, K.; Inoue, S. Asymmetric synthesis catalyzed by poly-L-alanine. Makromol. Chem. 1976, 177, 2807–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrea, G.; Colonna, S.; Kelly, D. R.; Lazcano, A:, Ottolina, G-; Roberts, S. M. Polyamino acids as synthetic enzymes: mechanism, applications and relevance to prebiotic catalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel-Pinter, M.; Samanta, M.; Ashkenasy, C.; Leman, L. J. Prebiotic peptides: Molecular hubs in the origin of life. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 4707–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chu, F.; Chen, G.; Zhou, S.; Sun, C.; Feng, H.; Pan, Y. Prebiotic formation of peptides through bubbling and arc plasma. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ying, J. Amino acid analogues provide multiple plausible pathways to prebiotic peptides. J. R. Soc. Interface, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlouchová, K. Peptides en route from prebiotic to biotic catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zozulia, O.; Dolan, M. A.; Korendovych, I. V. Catalytic peptide assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3621–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girvin, Z. C.; Gellman, S. H. Foldamer catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17211–17223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R. O.; Demapan, D.; Cui, Q. Complete computational reaction mechanism for foldamer-catalyzed aldol condensation. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 7624–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khettar, I.; Araszczuk, A.M.; Schettini, R. Peptidomimetic-based asymmetric catalysts. Catalysts 2023, 13, article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oku, J.-i.; Ito, N.; Inoue, S. Asymmetic cyanohydrin synthesis catalyzed by synthetic dipeptides, 1. Makromol. Chem. 1979, 180, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, W.; Oku, J.-i. Asymmetric cyanohydrin synthesis catalysed by a synthetic cyclic dipeptide. Chem. Commun. 1981, 1981(5), 229–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaky, K.; Mori, A.; Inoue, S. The cyclic dipeptide cyclo[(S)-phenylalanyl-(S)-histidyl] as a catalyst for asymmetric addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvo, Y.; Gal, M.; Becker, Y.; Elgavi, A. Asymmetric hydrocyanation of aldehydes with cyclo-dipeptides: A new mechanistic approach. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1996, 7, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.; Gigstad, K. M.; Namdev, N. D.; Lipton, M. Asymmetric catalysis of the Strecker amino acid synthesis by a cyclic dipeptide. Amino Acids, 1996; 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, M. S.; Jacobsen, E. N. Schiff base catalysts for the asymmetric Strecker reaction identified and optimized from parallel synthetic libraries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4901–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, M. S.; Vachal, P.; Jacobsen, E. N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1279–1281. [CrossRef]
- Vachal, P.; Jacobsen, E. N. Structure-based analysis and optimization of a highly enantioselective catalyst for the Strecker reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10012–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuend, S. J.; Coughlin, M. P.; Lalonde, M. P.; Jacobsen, E. N. Nature, 2009; 461, 968–971. [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, A.; Sahu, D.; Ganguly, B.; Khan, N. U.; Kureshy, R. I.; Abdi, S. H.; Suresh, E.; Bajaj, H. C. Oxazoline-based organocatalyst for enantioselective Strecker reactions: a protocol for the synthesis of levamisole. Chemi. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 14224–14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliá, S.; Masana, J.; Vega, J. "Synthetic Enzymes". Highly stereoselective epoxidation of chalcone in a triphasic toluene/water-poly[(S)-alanine system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1980, 19, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, S.; Molinari, H.; Banfi, S.; Juliá, S.; Masana, J.; Alvarez, A. Synthetic enzymes—4: Highly enantioselective epoxidation by means of polyaminoacids in a triphase system: Influence of structural variations within the catalysts. Tetrahedron 1983, 39, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. V.; Bergeron, S.; Griffiths, M. J.; Mukherjee, S.; Roberts, S. M.; Williamson, N. M.; Wu, L. E. Juliá–Colonna asymmetric epoxidation reactions under non-aqueous conditions: rapid, highly regio- and stereo-selective transformations using a cheap, recyclable catalyst. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1998; 3173–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, R. W.; Geller, T. P.; Petty, S. A.; Roberts, S. M.; Skidmore, J.; Volk, M. Efficient asymmetric epoxidation of α,β-unsaturated ketones using a soluble triblock polyethylene glycol−polyamino acid catalyst. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, T.; Gerlach, A.; Krüger, C. M.; Militzer, H.-C. The Juia-Colonna epoxidation: Access to chiral, non-racemic epoxides. J. Mol. Catal. A; Chem. 2006, 252, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, T.; Sharpless, K. B. The first practical method for asymmetric epoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 5974–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-C.; Shi, X.-Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.-Z.; Wang, M. Liquid-phase synthesis of chiral tartrate ligand library for enantioselective Sharpless epoxidation of allylic alcohols. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, R. D.; Schlegel, H. B. Mechanism of the Sharpless epoxidation reaction: A DFT study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2024, 128, 2072–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Loebach, J. L.; Wilson, S. R.; Jacobsen, E. N. Enantioselective epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins catalyzed by salen manganese complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 2801–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E. N.; Zhang, W.; Muci, A. R.; Ecker, J. R.; Deng, L. Highly enantioselective epoxidation catalysts derived from 1,2-diaminocyclohexane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, R.; Noda, K.; Ito, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Katsuki, T. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins using chiral (salen)manganese(III) complexes. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1991, 2, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkessel, A.; Gasch, N.; Glaubitz, K.; Koch, C. Highly enantioselective enone epoxidation catalyzed by short solid phase-bound peptides: Dominant role of peptide helicity. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3839–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, P. A.; Cappi, M. W.; Flood, R. W.; Roberts, S. M.; Smith, J. A. Towards a mechanistic insight into the Julia-Colonna asymmetric epoxidation of α,β-unsaturated ketones using discrete lengths of poly-leucine. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 9297–9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsuno, S.; Sakakura, M.; Ito, K. Polymer-supported poly(amino acids) as new asymmetric epoxidation catalyst of alpha,beta.-unsaturated ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 6047–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, G.; Jakobsche, C. E.; Miller, S. J. Aspartate-catalyzed asymmetric epoxidation reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8710–8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, G.; Miller, S. J. A nonenzymatic acid/peracid catalytic cycle for the Baeyer−Villiger oxidation. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3049–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, S. E.; Stone, E.; Miller, S. J. Selective oxidation of disparate functional groups mediated by a common aspartic acid-based peptide catalyst platform. Acc. Chem. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofoed, J.; Nielsen, J.; Reymond, J.-L. Discovery of new peptide-based catalysts for the direct asymmetric aldol reaction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 12, 2445–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Jiang, F.; Yu, L.-T; Cui, X.; Gong, L.-Z.; Mi, A.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Wu, Y.-D. Novel small organic molecules for a highly enantioselective direct aldol reaction. J. Am. Chem.Soc. 2003, 125, 5262–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, H. J.; List, B. Mining sequence space for asymmetric aminocatalysis: N-Terminal prolyl-peptides efficiently catalyze enantioselective aldol and Michael reactions. Synlett 2003, 1901–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, Z.-H.; Cui, L.-F.; Gong, L.-Z.; Mi, A.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-Z. Small peptides catalyze highly enantioselective direct aldol reactions of aldehydes with hydroxyacetone: Unprecedented regiocontrol in aqueous media. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 2285–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofoed, J.; Darbre, T.; Reymond, J.-L. Artificial aldolases from peptide dendrimer combinatorial libraries. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3268–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, T. E.; Guerin, D. J.; Miller, S. J. Asymmetric conjugate addition of azide to alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyl compounds catalyzed by simple peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3635–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zou, W.; Sundén, H.; Ibrahem, I.; Córdova, A. Small peptide-catalyzed enantioselective addition of ketones to nitroolefins. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsogoeva, S. B.; Jagtap, S. B.; Ardemasova, Z. A. 4-trans-Amino-proline based di- and tetrapeptides as organic catalysts for asymmetric C–C bond formation reactions. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2006, 17, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, M.; Revell, J. D.; Wennemers, H. Tripeptides as efficient asymmetric catalysts for 1,4-addition. Reactions of aldehydes to nitroolefins–A rational approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbriglio, J. E.; Vasbinder, M. M.; Miller, S. J. Dual catalyst control in the amino acid-peptide-catalyzed enantioselective Baylis-Hillman reaction. Org Lett. 2003, 5, 3741–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowen, B. J.; Saunders, L. B.; Miller, S. J. Pyridylalanine (pal)-peptide catalyzed enantioselective allenoate additions to N-acyl imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6105–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, L. B.; Cowen, B. J.; Miller, S. J. Pyridylalanine (Pal)-peptide catalyzed enantioselective allenoate additions to N-acyl imines proceed via an atypical “aza-Morita-Baylis-Hillman” mechanism. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4800–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, K.; Ito, R.; Arai, T.; Yanagisawa, A. Catalytic asymmetric protonation of enolates using amino acid derivatives as chiral proton sources. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fan, Y. C.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Y.; Kwon, O. Phosphine organocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10049–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Smaligo, A. J.; Song, X. R.; Kwon, O. Phosphorus-based catalysis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7(4), 536–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methot, J. L.; Roush, W. R. Nucleophilic phosphine organocatalysis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherton, M. R.; Fu, G. C. Air-stable trialkylphosphonium salts: Simple, practical, and versatile replacements for air-sensitive trialkylphosphines. Applications in stoichiometric and catalytic processes. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 4295–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashina, N.; Price, C. C. A Crystalline hexamer from acrylonitrile. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhut, M. M.; Currier, H. Dialkyl 2-methyleneglutarates. US. Patent 3 074 999, 1958. Chem. Abstr. 1963, 58, 66109. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, X. New chiral phosphorus ligands for enantioselective hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3029–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M. M.; Calvete, M. J. F.; Carrilho, R. M. B.; Abreu, A. R. Synthesis of binaphthyl based phosphine and phosphite ligands. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6990–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Chen, W-L. ; Lu, Y. Phosphine-catalyzed asymmetric organic reactions. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9344–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, X. Phosphine-catalyzed cycloaddition of 2,3-butadienoates or 2-butynoates with electron-deficient olefins. A novel [3 + 2] annulation approach to cyclopentenes. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 2906–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Xiao, D.; Cao, P.; Zhang, X. Asymmetric [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 2,3-butadienoates with electron-deficient olefins catalyzed by novel chiral 2,5-dialkyl-7-phenyl-7-phosphabicyclo[2.2.1]heptanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3836–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, Q.; Xiao, D.; Cao, P.; Zhang, X. Asymmetric formation of quaternary carbon centers catalyzed novel chiral 2,5-dialkyl-7-phenyl-7-phosphabicyclo[2.2.1]heptanes. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shi, M. Applications of chiral phosphine-based catalysts in catalytic asymmetric synthesis. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 2720–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Tang, X.; Zheng, W.; Yao, W.; Ullah, N.; Lu, Y. Enantioselective phosphine-catalyzed formal [4 + 4] annulation of α,β-unsaturated imines and allene ketones: Construction of eight-membered rings. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14222–14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lv, X. Recent advances in [4 + 4] annulation of conjugated heterodienes with 1,4-dipolar species for the synthesis of eight-membered heterocycles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, C.; Atodiresei, I. L.; Patureau, F. W. Phosphine-catalyzed dearomative [3 + 2] cycloaddition of benzoxazoles with a cyclopropenone. Org Lett. 2022, 24, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S-S. ; Wang, R-X.; Gu, Q.; You, S-L. Phosphine-catalyzed asymmetric dearomative [3+2] annulation reaction of benzimidazoles with cyclopropenones CCS Chem. 2025, 7, 194–204. [CrossRef]
- Jana, K.; Sparr, C. Enantioselective Wittig reactions controlled by PIII/PV=O redox catalysis. Synlett 2025, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Hoffmann, M.; Deshmukh, S. First enantioselective catalytic Wittig reaction. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 6630–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L. M.; Schmiedel, V. M.; Pecchioli, T.; Lentz, D.; Merten, C.; Christmann, M. Asymmetric synthesis of carbocyclic propellanes. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2310–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiedel, V. M.; Hong, Y. J.; Lentz, D.; Tantillo, D. J.; Christmann, M. Synthesis and structure revision of dichrocephones A and B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2419–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorton C; Castanheiro T; Voituriez A Catalytic and asymmetric process via PIII/PV=O redox cycling: Access to (trifluoromethyl)cyclobutenes via a Michael addition/Wittig olefination reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10142–10147. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S. R.; Pasternak, A. Preparation of a new class of C2-symmetric chiral phosphines: The first asymmetric Staudinger reaction. Synlett 1990, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertpibulpanya, D.; Marsden, S. P.; Rodriguez-García, I.; Kilner, C. A. Asymmetric aza-Wittig reaction: Enantioselective synthesis of β-quaternary azacycles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5000–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S.; Lepage, R. J.; Houk, K. N.; Krenske, E.; Kwon, O. Catalytic asymmetric Staudinger-aza-Wittig reaction for the synthesis of heterocyclic amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9537–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Kim, J.; Mai, B, K. ; Cao, S.; Ye, R.; Wang, X. Y.; Liu, P.; Kwon, O. Enantioselective synthesis of quaternary oxindoles: Desymmetrizing Staudinger-aza-Wittig reaction enabled by a bespoke HypPhos oxide catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21318–21327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Z.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y. Chiral bisphosphine-catalyzed asymmetric Staudinger/aza-Wittig reaction: An enantioselective desymmetrizing approach to Crinine-type Amaryllidaceae alkaloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 14136–14148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, K. Synthesis of novel chiral quaternary phosphonium salts with a multiple hydrogen-bonding site, and their application to asymmetric phase-transfer alkylation. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 14465–14476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, Y.; Li. T.; Hu, D.; Ren, X.; Wang, T. Asymmetric nucleophilic additions promoted by quaternary phosphonium ion-pair catalysts. CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 2110–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, D.; Sakaki, S.; Ooi, T. Chiral tetraaminophosphonium salt-mediated asymmetric direct Henry reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12392–12393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R. J.; Ding, C. H.; Maruoka, K. Phosphonium salts as chiral phase-transfer catalysts: Asymmetric Michael and Mannich reactions of 3-aryloxindoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4559–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D. D.; Chai, Z.; Zhang, J. X.; Ye, Z. Q.; Xiao, H.; Wang, H. Y.; Chen, J. H.; Wu, X. Y.; Zhao, G. Thiourea-phosphonium salts from amino acids: Cooperative phase-transfer catalysts in the enantioselective aza-Henry reaction. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5972–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kumatabara, Y.; Shirakawa, S. Chiral quaternary phosphonium salts as phase-transfer catalysts for environmentally benign asymmetric transformations. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, Z. Chiral quaternary phosphonium salt phase transfer catalyst, preparation method and application thereof. CN109718851A, May 7, 2019.
- Denmark, S. E.; Fu, J. Catalytic enantioselective addition of allylic organometallic reagents to aldehydes and ketones. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2763–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Coe, D. M.; Pratt, N. E.; Griedel, B. D. Asymmetric allylation of aldehydes with chiral Lewis bases. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 6161–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S, E. ; Fu, J. Catalytic, enantioselective addition of substituted allylic trichlorosilanes using a rationally-designed 2,2'-bispyrrolidine-based bisphosphoramide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9488–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denmark, S. E.; Fu, J.; Lawler, M. J. Chiral phosphoramide-catalyzed enantioselective addition of allylic trichlorosilanes to aldehydes. Preparative studies with bidentate phosphorus-based amides. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denmark, S. E.; Beutner, G. L. Lewis base catalysis in organic chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1560–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Stavenger, R. A.; Wong, K-T. ; Su, X. Chiral phosphoramide-catalyzed aldol additions of ketone enolates. Preparative aspects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 4982–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Beutner, G. L.; Wynn, T.; Eastgate, M. D. Lewis base activation of Lewis acids: catalytic, enantioselective addition of silyl ketene acetals to aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3774–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Heemstra, J. R. Jr.; Beutner, G. L. Catalytic, enantioselective, vinylogous aldol reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4682–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Barsanti, P. A.; Beutner, G. L.; Wilson, T. W. Enantioselective ring opening of epoxides with silicon tetrachloride in the presence of a chiral Lewis base: Mechanism studies. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Fan, Y. The first catalytic, asymmetric alpha-additions of isocyanides. Lewis-base-catalyzed, enantioselective Passerini-type reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7825–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, C.; Sugiura, M.; Kobayashi, S. Stereospecific, enantioselective allylation of alpha-hydrazono esters by using allyltrichlorosilanes with BINAP dioxides as neutral-coordinate organocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6491–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Kotani, S.; Ishizuka, T.; Hashimoto, S. Chiral phosphine oxide BINAPO as a catalyst for enantioselective allylation of aldehydes with allyltrichlorosilanes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, S.; Shimoda, Y.; Sugiura, M. ; Novel enantioselective direct aldol-type reaction promoted by a chiral phosphine oxide as an organocatalyst. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4602–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaglia, M.; Rossi, S. Chiral phosphine oxides in present-day organocatalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3824–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M. Recent advances in asymmetric phosphine oxide catalysis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Benincori, T.; Raimondi, L.; Benaglia, M. 3,3′-Bithiophene-based chiral bisphosphine oxides as organocatalysts in silicon-derived Lewis acid mediated reactions. Synlett 2020, 31, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X. Direct covalent immobilizaion of chiral phosphine oxide: Hollow mesoporous polystyrene nanospheres as a platform for efficient heterogeneous enantioselective reductive aldol reaction. Mol. Catal. 2023, 547, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.; Bulut, A.; Recimer, M. Chiral phosphine oxide aziridinyl phosphonate as a Lewis base catalyst for enantioselective allylsilane addition to aldehydes. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2015, 26, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- a) Johnson, A. W.; LaCount, R. B. 9-Dimethylsulfonium fluorenylide. Chem. Ind. (London) 1958, 1440−1441; b) Johnson, A. W.; LaCount, R. B. The chemistry of ylids. VI. Dimethylsulfonium fliorenylide-A synthesis of epoxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1961; 83, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E. J.; Chaykovsky, M. J. Dimethyloxosulfonium methylide ((CH3)2SOCH2) and dimethylsulfonium methylide ((CH3)2SCH2). Formation and application to organic synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, N.; Sugihara, Y.; Fujihara, H. Camphoryl sulfide as a chiral auxiliary and a mediator for one-step synthesis of optically active 1,2-diaryloxiranes. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 4222–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julienne, K.; Metzner, P.; Henyron, V. Asymmetric synthesis of epoxides from aldehydes mediated by (+)-(2R,5R)-2,5-dimethylthiolane. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1999; 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, C. L.; Bellanie, B.; Goodman, J. M. A highly enantioselective one-pot sulfur ylide epoxidation reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 5427–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V. K.; Winn, C. L. Catalytic, asymmetric sulfur ylide-mediated epoxidation of carbonyl compounds: Scope, selectivity, and applications in synthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denmark, S. E.; Kuester, W. E.; Burk, M. T. Catalytic, asymmetric halofunctionalization of alkenes: A critical perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10938–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S. ; Zhang, B-Q.; Xiao, W-Y.; Li, Y-L.; Deng, J. Recent advances in catalytic asymmetric syntheses of functionalized heterocycles via halogenation/chalcogenation of carbon-carbon unsaturated bonds. Adv. Synth. Catal, 2022; 364, 3974–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, Y.; Nishiyori, R.; Shirakawa, S. Synthesis of a BINOL-derived sulfide catalyst bearing a diphenylmethanol unit and its application in asymmetric bromolactonizations. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2025, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; An, R.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X. Enantioselective trifluoromethylthiolating lactonization catalyzed by an indane-based chiral sulfide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5846–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, S.; López-Andarias. J.; Mareda, J.; Sakai, N.; Matile, S. Catalysis with chalcogen bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, G.; Nair, V. V.; Zhu, J. Chalcogen bonding catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Xie, D.; Zhou, P-P. Chalcogen bonding catalysis in irganic synthesis. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2025, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, B.; Roberts, B. P.; Tocher, D. A. Enantioselective radical-chain hydrosilylation of alkenes using homochiral thiols as polarity-reversal catalysts. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1998; 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Roberts, B. P.; Tocher, D. A. Carbohydrate-derived thiols as protic polarity-reversal catalysts for enantioselective radical-chain reactions. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 2002; 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroyan, C. E.; Miller, S. J. Enantioselective Rauhut-Currier reactions promoted by protected cysteine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Maruoka, K.; Shirakawa, S. Chiral tertiary sulfonium salts as effective catalysts for asymmetric base-free neutral phase-transfer reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4819–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B. M.; Rao, M. Development of chiral sulfoxide ligands for asymmetric catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5026–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otocka, S.; Kwiatkowska, M.; Madalińska, L.; Kiełbasiński, P. Chiral organosulfur ligands/catalysts with a stereogenic sulfur atom: Applications in asymmetric synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4147–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C-R. ; Sun, J-N.; Li. Y.; Li, J-H. Recent advances in catalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral sulfinyl compounds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2025, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wujkowska, Z. , Leśniak, S., Kiełbasiński, P., Rachwalski, M. Highly enantioselective asymmetric reduction of aromatic ketimines promoted by chiral enantiomerically pure sulfoxides as organocatalysts. J. Sulfur Chem. 2018, 39, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tan, C, K. ; Jiang, X.; Chen, F.; Yeung, Y. Y. Asymmetric bromolactonization using amino-thiocarbamate catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15474–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tay, D. W.; Chen, J.; Leung, G. Y. C.; Yeung, Y.-Y. Enantioselective synthesis of 2-substituted and 3-substituted piperidines through a bromoaminocyclization process. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4412–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinér, P.; Sadhukhan, A.; Blomkvist, B. Chiral sulfinamides as highly enantioselective organocatalysts. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 3063–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, J. A.; Owens, T. D.; Tang, T. P. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 984–995. [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. S-chiral sulfinamides as highly enantioselective organocatalysts. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5913–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, M.; Sun, J. Rationally-designed S-chiral bissulfinamides as highly enantioselective organocatalysts for reduction of ketimines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kureshy, R. I.; Saravanan, S.; Verma, S.; Jakhar, A.; Khan, N. H.; Abdi, S. H. R.; Bajaj, H. C. Org. Lett. 2014, 16. [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Kalyani, D.; Collins, W. R. Preparative and mechanistic studies toward the rational development of catalytic, enantioselective selenoetherification reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15752–15765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyori, R.; Maynard, J. R. J.; Shirakawa, S. ; Chiral bifunctional selenide catalysts for asymmetric bromolactonization. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020, 9, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadel, J. T.; Back, T. G. Asymmetric synthesis with organoselenium compounds – The past twelve years. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, 2202304074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Singh, T.; Andersson, P. G.; Zhou, T. Asymmetric synthesis and applications of chiral organoselenium compounds: A review. Molecules 2024, 29, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Häupli, S.; Leuenberger, M. Catalytic asymmetric oxyselenenylation–elimination reactions using chiral selenium compounds. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1998, 9, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, C.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Tidei, C.; Bagnoli, L.; Wirth, T. Stereoselective selenium catalyzed dihydroxylation and hydroxymethoxylation of alkenes. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 10530–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A. L.; Paixão, M. W.; Lüdtke, D. S.; Silveira, C. C.; Rodrigues, O. E. D. Synthesis of new chiral aliphatic amino diselenides and their application as catalysts for the enantioselective addition of diethylzinc to aldehydes. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2635–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A. L.; Lüdtkr, D. S.; Vargas, F.; Braga, R. C. Catalytic applications of chiral organoselenium compounds in asymmetric synthesis. Synlett, 1453. [Google Scholar]
- Okuno, K.; Nakamura, T.; Shirakawa, S. ; Asymmetric catalysis of chiral bifunctional selenides and selenonium salts bearing a urea group. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2021, 10, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B. B.; Eey, S. T.-C.; Ryabchuk, P.; Garry, O.; Denmark, S. E. catalyzed enantioselective syn-dichlorination of unbiased alkenes. Tetrahedron, 2019; 75, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 609. Denmark, S. E.; Kornfilt, D. J. P.; Vogler, T. Catalytic asymmetric thiofunctionalization of unactivated alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 135, 15308–15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matviitsuk, A.; Panger, J. L.; Denmark, S. E. Catalytic, enantioselective sulfenofunctionalization of alkenes: Development and recent advances. Angew. Chem. Int.. Ed. 2020, 59, 19796–19819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matviitsuk, A.; Lee Panger, J.; Denmark, S. E. Enantioselective inter- and intramolecular sulfenofunctionalization of unactivated cyclic and (Z)-alkenes. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 7377–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tan, C. K.; Yeung, Y. Y. C2-symmetric cyclic selenium-catalyzed enantioselective bromoaminocyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X. Chiral selenide-catalyzed enantioselective construction of saturated trifluoromethylthiolated azaheterocycles. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 3434–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Jiang, Q.; Ji, J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X. Chiral selenide-catalyzed enantioselective construction of saturated trifluoromethylthiolated azaheterocycles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X. Enantioselective construction of chiral sulfides via catalytic electrophilic azidothiolation and oxythiolation of N-allyl sulfonamides. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6896–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, X.; Tse, Y. S.; Ke, Z.; Yeung, Y. Y. Applications of selenonium cations as Lewis acids in organocatalytic reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12869–12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukai, T.; Tanaka, R.; Dokawa, T. A. A new catalyst for acyloin condensation. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1943, 63, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Breslow, R. On the mechanism of thiamine action. IV.1 Evidence from studies on model systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 3719–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, H. ; Rämsch, R, Y.; Kuhlmann, H. Über die präparative Nutzung der Thiazoliumsalz-katalysierten Acyloin- und Benzoin-Bildung, I. Herstellung von einfachen Acyloinen und Benzoinen. Synthesis, 1976; 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, H.; Dämbkes, G. Über die präparative Nutzung der Thiazoliumsalz-katalysierten Acyloin- und Benzoin-Bildung; II 1. Herstellung unsymmetrischer Acyloine und α-Diketone. Synthesis, 1977; 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, H.; Dämbkes, G. Über die präparative Nutzung der 1,3-Thiazoliumsalz-katalysierten Acyloin- und Benzoin-Bildung; III 1. Eine neue Methode zur Herstellung von substituierten Enol-trimethylsilyl-ethern des 1,2-Cyclopentandions. Synthesis, 1980; 309–310. [Google Scholar]
- Flanigan, D. M.; Romanov-Michailidis, F.; White, N. A.; Rovis, T. Organocatalytic reactions enabled by N-heterocyclic carbenes. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9307–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieszkowski, K.; Barańska, I.; Mroczyńska, K.; Słotwiński, M.; Rafiński, Z. Organocatalytic name reactions enabled by NHCs. Materials (Basel) 2020, 13, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.; Biju, A. T. N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) organocatalysis using aliphatic aldehydes. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 15484–15495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, P.; Koy, M.; Hopkinson, M.; Glorius, F. Recent advances in the chemistry and applications of N-heterocyclic carbenes. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 771–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Barik, S.; Biju, A. T. N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) organocatalysis: from fundamentals to frontiers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 1102–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X-Y. ; Cao, Z-H.; Ye, S. Bifunctional N-heterocyclic carbenes derived from L-pyroglutamic acid and their applications in enantioselective organocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, J. C.; Hunneman, D. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 3666–3667. [CrossRef]
- Breslow, R. The mechanism of thiamine action: predictions from model experiments. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 98, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, J. C.; Hara, T. Asymmetric thiazolium salt catalysis of the benzoin condensation. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkessel, A.; Yatham, V. R.; Elfert, S.; Neudörfl, J. M. Characterization of the key intermediates of carbene-catalyzed umpolung by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction: breslow intermediates, homoenolates, and azolium enolates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11158–11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Breuer, K.; Teles, J.H. A novel asymmetric benzoin reaction catalyzed by a chiral triazolium salt: Preliminary communication. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Kallfass, U. An efficient nucleophilic carbene catalyst for the asymmetric benzoin condensation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1743–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Niemeier, O.; Balensiefer, T. Asymmetric intramolecular crossed-benzoin reactions by N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, H.; Hachisu, Y.; Bode, J. W.; Suzuki, K. Catalytic enantioselective crossed aldehyde-ketone benzoin cyclization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 3492–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M. S.; Rovis, T. Enantioselective synthesis of quaternary stereocenters via a catalytic asymmetric Stetter reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126(29), 8876–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, J.; López-Calahorra, F.; Bassedas, M.; Urrios, P. A new thiazolium salt-catalyzed synthesis of α-aminoketones from aldehydes and iminium salts. Synthesis. [CrossRef]
- Murry, J. A.; Frantz, D. E.; Soheili, A.; Tillyer, R.; Grabowski, E. J.; Reider P., J. Synthesis of alpha-amido ketones via organic catalysis: thiazolium-catalyzed cross-coupling of aldehydes with acylimines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9696–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennen, S. M.; Gipson, J. D.; Kim, Y. R.; Miller, S. J. Thiazolylalanine-derived catalysts for enantioselective intermolecular aldehyde-imine cross-couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1654–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiRocco, D. A.; Rovis, T. Catalytic asymmetric cross-aza-benzoin reactions of aliphatic aldehydes with N-Boc-protected imines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5904–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Mou, C.; Zhu, T.; Song, B. A.; Chi, Y. R. N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed chemoselective cross-aza-benzoin reaction of enals with isatin-derived ketimines: Access to chiral quaternary aminooxindoles. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3272–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Das, T. K.; Jain, S.; Gonnade, R. G.; Biju, A. T. N-Heterocyclic-carbene-catalyzed Umpolung of imines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2730–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T. K.; Ghosh, A.; Balanna, K.; Behera, P.; Gonnade, R. G.; Marelli, U. K.; Das, A. K.; Biju, A. T. ACS Catal. 9, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovic, S.; Frison, J-C. ; Koyuncu, H.; Whitwood, A. C.; Douthwaite, R. E. Addition of N-heterocyclic carbenes to imines: phenoxide assisted deprotonation of an imidazolium moiety and generation of breslow intermediates derived from imines. Org Lett. 2009, 11, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRocco, D. A.; Oberg, K. M.; Rovis, T. Isolable analogues of the Breslow intermediate derived from chiral triazolylidene carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6143–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R. C.; Barik, S.; Kunhiraman, A. A.; Goswani, A.; Mondal, A.; De, M.; Biju, A: T. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed imine Umpolung/semipinacol rearrangement cascade for the synthesis of indoxyls. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 4202–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, H.; Kuhlmann, H. Addition of aliphatic aldehydes to activated double bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1974, 13, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Breuer, K.; Runsink, J,; Teles, J. H. The first asymmetric intramolecular Stetter reaction. Preliminary communication. Helv. Chim. Acta 1996, 79, 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Han, J.; Henseler, A. Asymmetric intermolecular Stetter reactions catalyzed by a novel triazolium derived N-heterocyclic carbene. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3989–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M. S.; Read de Alaniz, J.; Rovis, T. A highly enantioselective catalytic intramolecular Stetter reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10298–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Alaniz, J. R.; Rovis, T. The catalytic asymmetric intramolecular Stetter reaction. Synlett 2009, 1189–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D, Breuer, K. Addition of acyl carbanion equivalents to carbonyl groups and enones. In: Jacobsen, E. N.; Pfaltz, A.; Yamamoto, H, editors. Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis I–III. Vol. 3. Springer-Verlag; Berlin, Germany: 1999, p. 1093. [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Balensiefer, T. Nucleophilic carbenes in asymmetric organocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennen, S. M.; Blank, J. T.; Tran-Dube, M. B.; Imbriglio, J. E.; Miller, S. J. A Peptide-catalyzed asymmetric Stetter reaction. Chem. Commun. 2005, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, D.; Han, J. Asymmetric intermolecular Stetter reactions of aromatic heterocyclic aldehydes with arylidenemalonates. Synthesis 2008, (23), 3864–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Perreault, S.; Rovis, T. Catalytic asymmetric intermolecular Stetter reaction of glyoxamides with alkylidenemalonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14066–14067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRocco, D. A.; Oberg. K. M.; Dalton, D. M.; Rovis, T. Catalytic asymmetric intermolecular Stetter reaction of heterocyclic aldehydes with nitroalkenes: Backbone fluorination improves selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131(31), 10872–10874; [CrossRef]
- DiRocco, D. A.; Rovis, T. Catalytic asymmetric intermolecular Stetter reaction of enals with nitroalkenes: Enhancement of catalytic efficiency through bifunctional additives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10402–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRocco, D: A. ; Noey, E. L.; Houk, K. N.; Rovis, T. Catalytic Asymmetric intermolecular Stetter reactions of enolizable aldehydes with nitrostyrenes: Computational study provides insight into the success of the catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, J. E. M.; Nakano, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lupton, D. W. Enantioselective N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis that exploits imine Umpolung. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4007–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T. K.; Biju, A. T. Imines as acceptors and donors in N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) organocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8537–8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Struble, J. R.; Bode, J. W. Highly enantioselective azadiene Diels-Alder reactions catalyzed by chiral N-heterocyclic carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8418–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Uc, G. J.; Bode, J. W. Chiral N-heterocyclic carbene catalyzed, enantioselective oxodiene Diels-Alder reactions with low catalyst loadings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15088–15089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Chen, X.; Chi, Y. R. Enantioselective Diels-Alder reactions of enals and alkylidene diketones catalyzed by N-heterocyclic carbenes. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4708–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Mo, J.; Fang, X.; Chi, Y. R. Formal Diels-Alder reactions of chalcones and formylcyclopropanes catalyzed by chiral N-heterocyclic carbenes. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5366–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. R.; He, L.; Wu, X.; Shao, P. L.; Ye, S. Chiral N-heterocyclic carbene catalyzed Staudinger reaction of ketenes with imines: Highly enantioselective synthesis of N-boc β-lactams. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, M.; Wouters, J.; Demonceau, A.; Delaude, L. Mechanistic insight into the Staudinger reaction catalyzed by N-heterocyclic carbenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9668–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lv, H.; Zhang, Y. R.; Ye, S. Formal cycloaddition of disubstituted ketenes with 2-oxoaldehydes catalyzed by chiral N-heterocyclic carbenes. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 8101–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shao, P.; Lv, H.; Ye, S. Enantioselective synthesis of β-trifluoromethyl-β-lactones via NHC-catalyzed ketene−ketone cycloaddition reactions. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4029–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravina, A. G.; Mahatthananchai, J.; Bode, J. W. Enantioselective, NHC-catalyzed annulations of trisubstituted enals and cyclic N-sulfonylimines via α,β-unsaturated acyl azoliums. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9433–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, P.; Houk, N. Organic Chemistry. Theory, Reactivity an Mechanisms in Modern Synthesis. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co., KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2019, Chap. 5.5.9, pp. 476-495; ISBN 978-3-527-34532-8. [CrossRef]
- Maruoka, K.; Banno, H.; Yamamoto, H. Asymmetric Claisen rearrangement catalyzed by chiral organoaluminum reagent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 7791–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T. P.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective Claisen rearrangements: Development of a first generation asymmetric acyl-Claisen reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2911–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, L.; Czerwonka, R.; Hiersemann, M. The Catalytic enantioselective Claisen rearrangement of an allyl vinyl ether. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 4700–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeda, C.; Jacobsen, E. N. Enantioselective Claisen rearrangements with a hydrogen-bond donor catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9228–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, R. M.; Shah, S. K.; Mason, R. W. Stereoselective total synthesis of (±)-Gymnomitrol via reduction-alkylation of a-cyano ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeobamrung, J.; Mahatthananchai, J.; Zheng, P.; Bode, J. W. An enantioselective Claisen rearrangement catalyzed by N-heterocyclic carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8810–8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, B.; Mahatthananchai, J.; Bode, J. W. Enantioselective synthesis of dihydropyridinones via NHC-catalyzed aza-Claisen reaction. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5378–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahatthananchai, J.; Kaeobamrung, J.; Bode, J. W. Chiral N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed annulations of enals and ynals with stable enols: A highly enantioselective Coates-Claisen rearrangement. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G. T.; Gu, Q.; You, S. L. Enantioselective annulation of enals with 2-naphthols by triazolium salts derived from L-phenylalanine. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4273–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadamoto, M.; Phillips, E. M.; Reynolds, T. E.; Scheidt, K. A. Enantioselective synthesis of α,α-disubstituted cyclopentenes by an N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed desymmetrization of 1,3-diketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10098–10099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X. B.; Nakano, Y.; Lupton, D. W. Polarity inversion catalysis by the 1,4-addition of N-heterocyclic carbenes. Aust. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, A. T.; Padmanaban, M.; Wurz, N. E.; Glorius, F. N-Heterocyclic carbene catalyzed umpolung of Michael acceptors for intermolecular reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8412–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Smith, S. W.; Powell, D. A.; Fu, G. C. Umpolung of Michael acceptors catalyzed by N-heterocyclic carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1472–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Lupton, D. W. Enantioselective N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis by the Umpolung of α,β-unsaturated ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3135–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.; Nakano, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lupton, D. W. Enantioselective N-heterocyclic carbene catalyzed cyclopentene synthesis via the β-azolium ylide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10299–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breugst, M.; Lupton, D. W. N-Heterocyclic carbene catalyzed (5+1) annulations exploiting a vinyl dianion synthon strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11483–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Kamitani, M.; Tobisu, M. N-Heterocyclic carbene catalyzed concerted nucleophilic aromatic substitution of aryl fluorides bearing α,β-unsaturated amides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14157–14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Kamitani, M.; Fujimoto, H.; Tobisu, M. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed Truce–Smiles rearrangement of N-arylacrylamides via the cleavage of unactivated C(aryl)–N bonds. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.; Shee, S.; Biju, A. T. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed Umpolung of cyclopent-4-ene-1, 3-diones for activated olefin–isatin cross-coupling. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6066–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, B. E.; Scheidt, K. A. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed oxidation of unactivated aldehydes into esters. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4331–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, R. C.; Maji, B.; De Sarkar, S.; Bergander, K.; Fröhlich, R.; Mück-Lichtenfeld, C.; Mayr, H.; Studer, A. Nucleophilic addition of enols and enamines to α,β-unsaturated acyl azoliums: mechanistic studies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5234–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetra, S. R.; Kaicharla, T.; Kunte, S. S.; Gonnade, R.; Biju, A. T. Asymmetric N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-catalyzed annulation of modified enals with enolizable aldehydes. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5202–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzieszkowski, K.; Rafiński, Z. N-Heterocyclic carbene catalysis under oxidizing conditions. Catalysts 2018, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, J.; Yan, J-L. N-Heterocyclic carbene catalyzed reactions involving acetylenic Breslow and/or acylazolium as key intermediates. Chem. Rec. 2024, 24, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Shee, S.; Poisson, T.; Besset, T.; Biju, A.T. Enantioselective N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed cascade reaction for the synthesis of pyrroloquinolines via N–H functionalization of indoles. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 6998–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Yetra, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Biju, A. T. NHC-Catalyzed generation of α,β-unsaturated acylazoliums for the enantioselective synthesis of heterocycles and carbocycles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarkas, S.; Studer, A. Oxidative amidation and azidation of aldehydes by NHC catalysis. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, B. E.; Scheidt, K. A. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed oxidation of unactivated aldehydes to esters. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4331–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N. A.; Rovis, T. Enantioselective N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed β-hydroxylation of enals using nitroarenes: an atom transfer reaction that proceeds via single electron transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14674–14677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Mathi, G. R.; Hong, S.; Hong, S. Enantioselective functionalization at the C4 position of pyridinium salts through NHC catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. B.; Li, X. N.; Li, Z. C.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. X.; Gao, Z. H.; Ye, S. Enantioselective acylation of benzylic C(sp3)-H bond enabled by a cooperative photoredox and N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202421151. [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa, S. ; Salem, M, Editors; Atropisomerism in Asymmetric Organic Synthesis: Challenges and Applications, Wiley-VCH GmbH, Weinheim, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–336. ISBN 9783527352838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T. A.; Hutskalova, V.; Sparr, C. Atroposelective catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, J. E.; Butler, N. M.; Keller, P. A. A twist of nature--the significance of atropisomers in biological systems. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1562–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S-J. ; Zhao, Q.; Liu, X-C.; Gamble, A. B.; Huang, W.; Yang, Q-Q.; Han, B. Bioactive atropisomers: Unraveling design strategies and synthetic routes for drug discovery. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 1971–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Guo, D.; Munkerup, K.; Huang, K-W. ; Li, F.; Wang, J. Enantioselective [3+3] atroposelective annulation catalyzed by N-heterocyclic carbenes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, T. Atroposelective arene formation by carbene-catalyzed formal [4+2] cycloaddition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17625–17630. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J. L.; Maiti, R.; Ren, S. C.; Tian, W.; Li, T.; Xu, J.; Mondal, B.; Jin, Z.; Chi, Y. R. Carbene-catalyzed atroposelective synthesis of axially chiral styrenes. Nat Commun. 2022, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanna, K.; Barik, S.; Barik, S.; Shee, S.; Manoj, N.; Gonnade, R. G.; Biju, A. T. N-Heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed atroposelective synthesis of N–N axially chiral 3-amino quinazolinones. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 8752–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hine, J.; Linden, S. M.; Kanagasabapathy, V. M. Double-hydrogen-bonding catalysis of the reaction of phenyl glycidyl ether with diethylamine by 1,8-biphenylenediol. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 5096–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohma, H.; Takizawa, S.; Watanabe, H.; Fukuoka, Y.; Maegawa, T.; Kita, K. Hypervalent iodine(V)-induced asymmetric oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides mediated by reversed micelles: Novel nonmetallic catalytic system. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 3519–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ube, H.; Fukuchi, S.; Terada, M. Enantioselective aza-Friedel–Crafts reaction catalyzed by a water inclusion complex of O,O’-diacyl tartaric acid. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Barbato, K. S.; Moquist, P. N.; Kodama, T.; Schaus, S. E. Enantioselective synthesis of 1,2-dihydronaphthalene-1-carbaldehydes by addition of boronates to isochromene acetals catalyzed by tartaric acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3233–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunel, J.-M. BINOL: A versatile chiral reagent. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 857–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L. Regioselective substitution of BINOL. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 6643–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, A.; Yasuda, A.; Takaya, H.; Toriumi, K.; Ito, T.; Souchi, T.; Noyori, R. Synthesis of 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl (BINAP), an atropisomeric chiral bis(triaryl)phosphine, and its use in the rhodium(I)-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of α-acylamino)acrylic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7932–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L. 1,1‘-Binaphthyl dimers, oligomers, and polymers: Molecular recognition, asymmetric catalysis, and new materials. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2405–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. N.; Chen, P.-A.; Setthakarn, K.; May, J. A. Chiral diol-based organocatalysts in enantioselective reactions. Molecules 2018, 23, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, D. P.; Kuo, L. H. Acceleration of a dipolar Claisen rearrangement by hydrogen bonding to a soluble diaryl urea. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 6647–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, S.; García-Urricelqui, A.; Mielgo, A.; Oiarbide, M. Progress in (thio)urea and squaramide-based Brønsted base catalysts with multiple H-bond donors. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 26, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotke, M.; Schreiner, P. R. Acid-free, organocatalytic acetalization. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brak, K.; Jacobsen, E. N. Asymmetric ion-pairing catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 534–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereka, B.; Yu, Q.; Lewis, N. H.; Carpenter, W. B.; Bowman, J. M.; Tokmakoff, A. Crossover from hydrogen to chemical bonding. Science 2021, 371, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schreiner, P. R. (Thio)urea organocatalysis – What can be learnt from anion recognition? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N. H.; Beer, P. D. Advances in anion supramolecular chemistry: From recognition to chemical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11716–11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busschaert, N.; Caltagirone, C.; Van Rossom, W.; Gale, P. A. Applications of supramolecular anion recognition. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8038–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, G.; Tancon, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lippert, K. M.; Schreiner, P. R. (Thio)urea organocatalyst equilibrium acidities in DMSO. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 1724–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwland, C.; Fonseca Guerra, C. How the chalcogen atom size dictates the hydrogen-bond donor capability of carboxamides, thioamides, and selenoamides. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussee, J.; Jansen, A. C. A. A highly stereoselective synthesis of S-(−)-[1,1′-binaphthalene]-2,2′-diol. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 3261–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Hu, J.; Shen, X.; Ji, B.; Ding, K. Discovery of exceptionally efficient catalysts for solvent-free enantioselective hetero-Diels-Alder reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124(1), 10-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougal, N. T.; Schaus, S. E. Asymmetric Morita-Baylis-Hillman reactions catalyzed by chiral Brønsted acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 12094–12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, S.; Moquist, P. N.; Schaus, S. E. Asymmetric allylboration of ketones catalyzed by chiral diols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12660–12661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J. A.; Lou, S.; Schaus, S. E. Enantioselective addition of boronates to acyl imines catalyzed by chiral biphenols. Angew. Chem. Int.. Ed. 2009, 48, 4337–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, K. S.; Luan, Y.; Ramella, D.; Panek, J. S.; Schaus, S. E. Enantioselective multicomponent condensation reactions of phenols, aldehydes, and boronates catalyzed by chiral biphenols. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5812–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Schaus, S. E. Asymmetric Petasis borono-Mannich allylation reactions catalyzed by chiral biphenols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wulff, W. D. Vaulted biaryls as chiral ligands for asymmetric catalytic Diels-Alder reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 3814–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Osminski, W. E. G.; Ren, H.; Wullf, W. D. Scalable syntheses of the vaulted biaryl ligands VAPOL and VANOL via the cycloaddition/electrocyclization cascade. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2011, 15, 1089–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wulff, W. D. Vaulted biaryls in catalysis: A structure-activity relationship guided tour of the immanent domain of the VANOL ligand. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15565–15571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, C.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Guiry, P. J. A family of chiral ferrocenyl diols: Modular synthesis, solid-state characterization, and application in asymmetric organocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11115–11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L.; Guiry, P. J. Design and synthesis of a ferrocene-based diol library and application in the hetero-Diels-Alder reaction. Chem. Eur. J, 2022; 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhao, D.; Ding, K. Enantioselective catalysis of the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction between Brassard's diene and aldehydes by hydrogen-bonding activation: A one-step synthesis of (S)-(+)-Dihydrokawain. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 5964–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasker Gondi, V.; Gravel, M.; Rawal, V. H. Hydrogen bond catalyzed enantioselective vinylogous Mukaiyama aldol reaction. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 5657–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGilvra, J. D.; Unni, A. K.; Modi, K.; Rawal, V. H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 6130–6133. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momiyama, N.; Yamamoto, H. Brønsted acid catalysis of achiral enamine for regio- and enantioselective nitroso aldol synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1080–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.-i.; Harada, T.; Tanaka, R.; Unno, M. Anion recognition by a silanediol-based receptor. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4621–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, A. G.; Wieting, J. M.; Mattson, A. E. Silanediols: a new class of hydrogen bond donor catalysts. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5228–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N. T.; Min, T.; Franz, A. K. Silanediol hydrogen bonding activation of carbonyl compounds. Chem. Eur.J. 2011, 17, 9897–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, A. E.; Andrew, A. G.; Wieting, J. M.; Fisher, T. J. Chiral silanediols in anion-binding catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11321–11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman-Baldwin, A. M.; Visco, M. D.; Wieting, J. M.; Stern, C.; Kondo, S.; Mattson, A. E. Silanediol-catalyzed chromenone functionalization. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3766–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, M. D.; Attard, J.; Guan, Y.; Mattson, A. E. Anion-binding catalyst designs for enantioselective synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 2623–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okino, T.; Hoashi, Y.; Takemoto, Y. Enantioselective Michael reaction of malonates to nitroolefins catalyzed by bifunctional organocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 12672–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S-f. ; Yan, M.; Shi, J-y.; Li, G-x.; Zhao, J-z. Enantioselective sulfonation of enones with sulfinates by thiourea/tertiary-amine catalysis. Synlett 2024, 35, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zu, L.; Jiang, W.; Xie, H.; Duan, W.; Wang, W. Organocatalytic enantioselective conjugate additions to enones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12652–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guong, J.; Zhao, C.-G. Organocatalytic enantioselective tandem aldol-cyclization reaction of α-isothiocyanato imides and activated carbonyl compounds. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkessel, A.; Roland, K.; Neudörfl, J. M. Asymmetric Morita-Baylis-Hillman reaction catalyzed by isophoronediamine-derived bis(thio)urea organocatalysts. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4195–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Liu, X-G. Asymmetric Morita-Baylis-Hillman reaction of arylaldehydes with 2-cyclohexen-1-one catalyzed by chiral bis(thio)urea and DABCO. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. J.; Dong, X. Q.; Zhang, Z. H.; Xue, Z. Y.; Teng, H. L. Highly anti-selective asymmetric nitro-Mannich reactions catalyzed by bifunctional amine-thiourea-bearing multiple hydrogen-bonding donors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8606–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grošelj, U.; Golobič, A.; Stare, K.; Svete, J.; Stanovnik, B. Synthesis and structural elucidation of novel camphor-derived thioureas. Chirality 2012, 24, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricko, S.; Golobič, A.; Svete, J.; Stanovnik, K. B.; Grošelj, U. Synthesis of novel camphor-derived bifunctional thiourea organocatalysts. Chirality 2015, 27, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, M. G.; Farley, A. J.; Dixon, D. J. Bifunctional iminophosphorane organocatalysts for enantioselective synthesis: application to the ketimine nitro-Mannich reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16348–16351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, X.; Ng, W-H. ; Tse, Y-L. S.; Yeung, Y-Y. Catalytic enantio- and diastereoselective domino halocyclization and spiroketalization. Nature Catal. 2020, 3, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 763. Manabe, K. 763. Manabe, K. Asymmetric phase-transfer alkylation catalyzed by a chiral quaternary phosphonium salt with a multiple hydrogen-bonding site.Tetrahedron Lett. 1998; 135, 5807–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohtome, Y.; Hashimoto, Y. ; Nagasawa, K Guanidine-thiourea bifunctional organocatalyst for the asymmetric Henry (nitroaldol) reaction. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wei, Z.; Cao, J.; Liang, D.; Lin, Y.; Duan, H. Asymmetric phase-transfer catalysts bearing multiple hydrogen-bonding donors: highly efficient catalysts for enantio- and diastereoselective nitro-Mannich reaction of amidosulfones. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6432–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meanwell, N. A. Fluorine and fluorinated motifs in the design and application of bioisosteres for drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5822–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Sumii, Y.; Shibata, N. Contributions of organofluorine compounds to pharmaceuticals. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10633–10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Tokunaga, E.; Kobayashi, O.; Hirai, K.; Shibata, N. Current contributions of organofluorine compounds to the agrochemical industry. Science 2020, 23, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, J.; Shibata, N.; Sodeoka, M.; Soloshonok, V. A.; Coelho, J. A. S.; Toste, F. D. Modern approaches for asymmetric construction of carbon–fluorine quaternary stereogenic centers: Synthetic challenges and pharmaceutical needs. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3887–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozatian, N.; Hodgson, D. R. W. Reactivities of electrophilic N–F fluorinating reagents. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 683–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, R.; Gouverneur, V.; Lin, J.-H.; Meanwell, M.; Ni, C.; Pupo, G.; Xiao, J.-C.; Hu, J. Contemporary synthetic strategies in organofluorine chemistry. Nat. Rev. Meth. Primers 2021, 1, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupo, G.; Ibba, F.; Ascough, D. M. H.; Vicini, A. C.; Ricci, P.; Christensen, K. E.; Pfeifer, L.; Morphy, J. R.; Brown, J. M.; Paton, R. S.; Gouverneur, V. Asymmetric nucleophilic fluorination under hydrogen bonding phase-transfer catalysis. Science 2018, 360, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicini, A. C.; Alozie, D. M.; Courtes, P.; Roagna, G.; Aubert, C.; Certal, V.; El-Ahmad, Y.; Roy, S.; Gouveneur, V. Scalable synthesis of (R,R)-N,N-dibenzyl-2-fluorocyclohexan-1-amine with CsF under hydrogen bonding phase-transfer catalysis. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2021, 25, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupo, G.; Gouverneur, V. Hydrogen bonding phase-transfer catalysis with alkali metal fluorides and beyond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5200–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Fan, S.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Catalytic enantioselective α-fluorination of ketones with CsF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 10059–10065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Kamo, T.; Fukushi, K.; Hiramatsu, T.; Tokunaga, E.; Dohi, T.; Kita, Y.; Shibata, N. Iodoarene-catalyzed fluorination and aminofluorination by an Ar-I/HF·pyridine/mCPBA system. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, L. Catalytic fluorination of α-branched ketones with nucleophilic fluorine. Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 3452–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, T.; Yadav, R.; Choudhury, L. H. Recent applications of thiourea-based organocatalysts in asymmetric multicomponent reactions (AMCRs). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 5513–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerich, J. P.; Hagihara, K.; Rawal, V. H. Chiral squaramide derivatives are excellent hydrogen bond donor catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14416–14417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán, J.; Parra, A.; Jiang, H.; Jørgensen, K. A. Squaramides: bridging from molecular recognition to bifunctional organocatalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6890–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 781. Carlone, A.; Bernardi, L.; McCormack, P.; Warr, T.; Oruganti, S.; Cobley, C. J. Asymmetric organocatalysis and continuous chemistry for an efficient and cost-competitive process to Pregabalin. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2021, 25, 2795–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Malerich, J. P.; Rawal, V. H. Squaramide-catalyzed enantioselective Michael addition of diphenyl phosphite to nitroalkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ma, G.; Lv, A.; Zhu, H. L.; Zhao, J.; Rawal, V. H. Squaramide-catalyzed enantioselective Friedel-Crafts reaction of indoles with imines. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3004–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Requena, J. V.; Marqués-López, E.; Herrera, R. P. Trifunctional squaramide catalyst for efficient enantioselective Henry reaction activation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendlandt, A.; Vangal, P.; Jacobsen, E.N. Quaternary stereocentres via an enantioconvergent catalytic SN1 reaction. Nature 2018, 556, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, T.; Bauch, M.; Durner, G.; Göbel, M, W. Axially chiral amidinium ions as inducers of enantioselectivity in Diels-Alder reactions. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimar, M.; Dürner, G.; Bats, J. W.; Göbel, M. M. Enantioselective synthesis of (+)-estrone exploiting a hydrogen bond-promoted Diels−Alder reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 2718–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Nakano, S.; Tahira, Y.; Terazawa, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Kitamura, C.; Hara, O. Chiral pyridinium phosphoramide as a dual Brønsted acid catalyst for enantioselective Diels-Alder reaction. Org Lett. 2016, 18, 2004–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J-S. ; Liao, F-M.; Gao, W-M.; Liao, K.; Zuo, R-L.; Zhou, J. Michael addition catalyzed by chiral secondary amine phosphoramide using fluorinated silyl enol ethers: Formation of quaternary carbon stereocenters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7381–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Itoh, J.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Enantioselective Mannich-type reaction catalyzed by a chiral Brønsted acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. Chiral Brønsted acid-catalyzed direct Mannich reactions via electrophilic activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, R.; Mallojjala, S. C.; Wheeler, S. E. Chiral phosphoric acid catalysis: from numbers to insights. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Gupta, A. K.; Huang, L.; Zhao, W.; Yin, X.; Osminski, W. E. G.; Huang, R. H.; Wulff, W. D.; Izzo, J. A.; Vetticatt, M. J. Pyro-borates, spiro-borates, and boroxinates of BINOL-assembly, structures, and reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10267–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, D.; Sugiono, E.; Raja, S.; Rueping, M. Complete field guide to asymmetric BINOL-phosphate derived Brønsted acid and metal catalysis: history and classification by mode of activation; Brønsted acidity, hydrogen bonding, ion pairing, and metal phosphates. Chem Rev. 2014, 114, 9047–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- a) Zhu, C.; Saito, K.; Yamanaka, M.; Akiyama, T. Benzothiazoline: Versatile hydrogen donor for organocatalytic transfer hydrogenation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 388–398; https://doi.org/10.1021/ar500414x; b) Jiménez, E. I. An update on chiral phosphoric acid organocatalyzed stereoselective reactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 3477-3502; https://doi.org/10.1039/D3OB00212H.
- Terada, M. Binaphthol-derived phosphoric acid as a versatile catalyst for enantioselective carbon–carbon bond forming reactions. Chem. Commun. 2008, 4097–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z. Y.; Gong, L. Z. Chiral bisphosphoric acids and their applications in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Rec, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Lin, X. Development and application of chiral spirocyclic phosphoric acids in asymmetric catalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 4753–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, J.; Lin, X. Atroposelective phosphoric acid catalyzed three-component cascade reaction: Enantioselective synthesis of axially chiral N-arylindoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15824–15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, D.; Reisinger, C. M.; List, B. Chiral Brønsted acids for asymmetric organocatalysis. Top. Curr. Chem. 2010, (291), 395–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldegiorgis, A. G.; Han, Z.; Lin, X. Recent advances in chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed asymmetric organic reactions: An overview. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1297, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Han, Z.; Huang, H.; Hong, B.; Sun, J. Organocatalytic enantioselective nucleophilic addition of indole imine 5-methides. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, G. B.; Zhang, H.; Rowland, E. B.; Chennamadhavuni, S.; Wang, Y.; Antilla, J. C. Brønsted acid-catalyzed imine amidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15696–15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueping, M.; Sugiono, E.; Azap, C. A highly enantioselective Brønsted acid catalyst for the Strecker reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2617–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueping, M.; Sugiono, E.; Moreth, S. A. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 759–764. [CrossRef]
- Terada, M.; Machioka, K.; Sorimachi, K. High substrate/catalyst organocatalysis by a chiral Brønsted acid for an enantioselective aza-ene-type reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2254–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomutnyk, Y, Y. ; Argüelles, A. J.; Winschel, G. A.; Sun, Z.; Zimmerman, P. M.; Nagorny, P. Studies of the mechanism and origins of enantioselectivity for the chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed stereoselective spiroketalization reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Xue, F.; Guan, H.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Shi, Y. Enantioselective bromocyclization of olefins catalyzed by chiral phosphoric acid. Org Lett. 2011, 13, 6350–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S.; Burk, M. T. Enantioselective bromocycloetherification by Lewis base/chiral Brønsted acid cooperative catalysis. Org Lett. 2012, 14, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Burk, M. T. Development and mechanism of an enantioselective bromocycloetherification reaction via Lewis base/chiral Brønsted acid cooperative catalysis. Chirality 2013, 26, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Wang, M-X.; Wang, D-X.; Masson, G.; Zhu, J. Brønsted acid catalyzed enantioselective three-component reaction involving the alpha addition of isocyanides to imines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009; 48, 6717–6721. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S-X. ; Cheng, D-J.; Liu, X-Y.; Tan, B. Phosphoric acid-catalyzed asymmetric classic Passerini reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14039–14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, H. G. O.; Pinheiro, D. L. J.; Carvalho-Silva, V. H.; Fioramonte, M.; Gozzo, F. C.; da Silva, W. A.; Amarante, G. W.; Neto, B. A. D. Combined role of the asymmetric counteranion-directed catalysis (ACDC) and ionic liquid effect for the enantioselective Biginelli multicomponent reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83(19), 12143–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C. O. A reexamination of the mechanism of the Biginelli dihydropyrimidine synthesis. Support for an N-acyliminium ion intermediate (1). J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7201–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, G. A.; Oppelaar, B.; List, B. An unexpected α-oxidation of cyclic ketones with 1,4-benzoquinone by enol catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10756–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Y.; Gao, C. H.; Ma, C.; Wu, X. Y.; Ni, S. F.; Tan, W.; Shi, F. Design and catalytic asymmetric synthesis of furan-indole compounds bearing both axial and central chirality. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, S.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F. Catalytic asymmetric (3+3) cycloaddition between different 2-indolylmethanols. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Li, S-Y. ; Sun, H.; Xiang, S-H.; Wang, J.; Houk, K. N.; Tan, B. Asymmetric phosphoric acid–catalyzed four-component Ugi reaction. Science 2018, 361, pp. 1-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-B.; Yu, P.; Zhou, Z.-P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, S.-H.; Q. -S. Gu, Q.-S.; Houk, K. N.; Tan, B. Rational design, enantioselective synthesis and catalytic applications of axially chiral EBINOLs. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelet, B.; Martin-Mingot, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Thibaudeau, S.; Bonne, D. Enantioselective organocatalysis and superacid activation: Challenges and opportunities. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlingham, B. T.; Widlanski, T. S. Synthesis and biological activity of N-sulfonylphosphoramidates: probing the electrostatic preferences of alkaline phosphatase. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7561–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, D.; Yamamoto, H. Design of chiral N-triflyl phosphoramide as a strong chiral Brønsted acid and its application to asymmetric Diels-Alder reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9626–9627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čorić, I.; List, B. Asymmetric spiroacetalization catalysed by confined Brønsted acids. Nature 2012, 483, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Čorić, I.; Wang, Q.; List, B. Activation of H2O2 by chiral confined Brønsted acids: a highly enantioselective catalytic sulfoxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10765–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H.; Čorić, I.; Vellalath, S.; List, B. The catalytic asymmetric acetalization. Angew. Chem. Int Ed. 2013, 52, 4474–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y-Y. ; Jiang, Y-J.; Fan, Y-S.; Sha, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, S-Q. Double axially chiral bisphosphorylimides as novel Brønsted acids in asymmetric three-component Mannich reaction. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2012, 23, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K. ; Jiang, Y-J.; Fan, Y-S.; Sha, D.; Zhang, S-Q. Double axially chiral bisphosphorylimides catalyzed highly enantioselective and efficient Friedel–Crafts reaction of indoles with imines. Chem. Eur. J, 2013; 19, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Fan, Y-S. ; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Z-Q.; Zheng, L-Y.; Zhang, S-Q. Highly enantioselective Biginelli reaction catalyzed by double axially chiral bisphosphorylimides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kaib, P. S.; Tap, A.; List, B. A general catalytic asymmetric Prins cyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10822–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Kennemur, J. L.; Buyck, T.; Lee, S.; Prévost, S.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Bykov, D.; Farès, C.; List, B. Activation of olefins via asymmetric Brønsted acid catalysis. Science 2018, 359, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Das, S.; Guin, A.; De, C. K.; List, B. Organocatalytic regio- and stereoselective cyclopropanation of olefins. Nat. Catal. 2025, 8, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadlou, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Maday, M.; Yin, X.; Zheng, L.; Gholami, H.; Ashtekar, K.; Staples, R.; Wulff, W. D.; Borhan, B. Structure guided design of VANOL-imidodiphosphorimidate catalysts for the catalytic enantioselective bromospiroketalization reaction. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-H.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Gong, L.-Z. Asymmetric organocatalytic three-component 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition: control of stereochemistry via a chiral Brønsted acid activated dipole. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5652–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yamamoto, H. A powerful chiral phosphoric acid catalyst for enantioselective Mukaiyama-Mannich reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8970–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, V.; Lackner, A. D.; Hamilton, G. L.; Toste, F. D. Asymmetric electrophilic fluorination using an anionic chiral phase-transfer catalyst. Science 2011, 334, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, R. J.; Toste, F. D. Chiral anion phase-transfer catalysis applied to the direct enantioselective fluorinative dearomatization of phenols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1268–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L. W.; Wang, X. D.; Ao, Y. F.; Wang, D. X.; Wang, Q. Q. Chiral bis-phosphate macrocycles for catalytic, efficient, and enantioselective electrophilic fluorination. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Huang, L.; Huang, R. H.; Wulff, W. D. Evidence for a boroxinate based Brønsted acid derivative of VAPOL as the active catalyst in the catalytic asymmetric aziridination reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15615–15617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A. A.; Wulff, W. D. Controlled diastereo- and enantioselection in a catalytic asymmetric aziridination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13100–13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osminski, W. E. G.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Mohammadlou, A.; Yin, X.; Matthews, E. C.; Canestraight, V. M.; Staples, R. J.; Allen, C. J.; Hirschi, J, S. ; Wulff, W. D. Probing catalyst function - Electronic modulation of chiral polyborate anionic catalysts. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 17762–17773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antilla, J. C.; Wulff, W. D. Catalytic asymmetric aziridination with a chiral VAPOL-boron Lewis acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5099–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antilla, J. C.; Wulff, W. D. Catalytic asymmetric aziridination with arylborate catalysts derived from VAPOL and VANOL ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wulff, W. D. Direct access to N-H-aziridines from asymmetric catalytic aziridination with borate catalysts derived from vaulted binaphthol and vaulted biphenanthrol ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7185–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Desai, A.; Lu, Z.; Hu, G.; Ding, Z.; Wulff, W.D. Catalytic asymmetric aziridination with borate catalysts derived from VANOL and VAPOL ligands: Scope and mechanistic studies. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3785–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wulff, W. D. Direct catalytic asymmetric aminoallylation of aldehydes: synergism of chiral and nonchiral Brønsted acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5656–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, D.; Ueoka, F.; Tanaka, N.; Kizu, T.; Takahashi, W.; Ooi, T. A structurally robust chiral borate ion: Molecular design, synthesis, and asymmetric catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11456–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, M.; Maki, T.; Moriyama, K.; Arinobe, M.; Ishihara, K. Pyridinium 1,1'-binaphthyl-2,2'-disulfonates as highly effective chiral Brønsted acid-base combined salt catalysts for enantioselective Mannich-type reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16858–16860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, M.; Ishihara, K. Chiral 1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-disulfonic acid (BINSA) and its derivatives for asymmetric catalysis. Asian. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 3, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, M.; Sugiura, Y.; Akakura, M.; Ishihara, K. Enantioselective Friedel-Crafts aminoalkylation catalyzed by chiral ammonium 1,1′-binaphthyl-2,2′-disulfonates. Synlett 2011, (9), 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, T.; Satake, S.; Hatano, M.; Ishihara, K.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, S. Synthesis of 1,1'-spirobiindane-7,7'-disulfonic acid and disulfonimide: Application for catalytic asymmetric aminalization. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 2378–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothermel, K.; Zabka, M.; Hioe, J.; Gschwind, R. M. Disulfonimides versus phosphoric acids in Brønsted acid catalysis: The effect of weak hydrogen bonds and multiple acceptors on complex structures and reactivity. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 13221–13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treskow, M.; Neudörfl, J.; Giernoth, R. BINBAM – A new motif for strong and chiral Brønsted acids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, (22), 3693–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcίa-Garcίa, P.; Lay, F.; Rabalakos, C.; List, B. A powerful chiral counteranion motif for asymmetric catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4363–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, B.; Ghosez, L. N-Trimethylsilyl-bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide: A better carbonyl activator than trimethylsilyl triflate. Tetrahedon Lett. 1997, 38, 5407–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, L.; García-García, P.; Lay, F.; Beck, M. E.; List, B. Disulfonimide-catalyzed asymmetric vinylogous and bisvinylogous Mukaiyama aldol reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlau, M.; List, B. Asymmetric counteranion-directed catalysis: concept, definition, and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, T.; van Gemmeren, M.; List, B. Development and applications of disulfonimides in enantioselective organocatalysis Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9388–9409. [Google Scholar]
- Guin, J.; Rabalakos, C.; List, B. Highly enantioselective hetero-Diels-Alder reaction of 1,3-bis(silyloxy)-1,3-dienes with aldehydes catalyzed by chiral disulfonimide. Angew. Chem.. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8859–8863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bae, H. Y.; Guin, J.; Rabalakos, C.; van Gemmeren, M.; Leutzsch, M.; Klussmann, M.; List, B. Asymmetric counteranion-directed Lewis acid organocatalysis for the scalable cyanosilylation of aldehydes. Nat. Commun, 1247; 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, M. C.; France, S. Chiral disulfonimides: a versatile template for asymmetric catalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 7485–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G, S. ; Namkoong, G.; Park, J.; Chen, D. Y. Total synthesis of strychnine. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 16189–16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatzenmeier, T.; Kaib, P. S. J.; Lingnau, J. B.; Goddard, R.; List, B. The catalytic asymmetric Mukaiyama-Michael reaction of silyl ketene acetals with α,β-unsaturated methyl esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Y.; He, H.; Chan, W. H.; Lee, A. W. Chiral sulfonimide as a Brønsted acid organocatalyst for asymmetric Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indoles with imines. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 7141–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triandafillidi, I.; Tzaras, D. I.; Kokotos, C. G. Green organocatalytic oxidative methods using activated ketones. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2521–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Du, H. Shi epoxidation: A great shortcut to complex compounds. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, R.; Fiorentino, M.; Serio, M. R. Asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized alkenes by dioxirane intermediates generated from potassium peroxomonosulfate and chiral ketones. Chem. Commun. 1984, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E; Wu, Z. Dioxiranes are the active agents in ketone-catalyzed epoxidations with oxone. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 8964–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yip, Y-C. ; Tang, M-W.; Wong, M-K.; Zheng, J-H.; Cheung, K-K. A C2 Symmetric chiral ketone for catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. ; Wong, M-K. ; Yip, Y-C.; Wang, X-C.; Tang, M-W.; J.-H. Zheng, J-H.; Cheung, K-K. Design and synthesis of chiral ketones for catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5943–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S. E.; Wu, Z. 6-Oxo-1,1,4,4-tetramethyl-1,4-diazepinium salts. A new class of catalysts for efficient epoxidation of olefins with oxone. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2810–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A. Catalytic enantioselective epoxidation of alkenes with a tropinone-derived chiral ketone. Chem. Commun. 1998, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Ahmed, G.; Dominguez-Fernandez, B.; Hayter, B. R.; Wailes, J. S. Enantioselective epoxidation of alkenes catalyzed by 2-fluoro-N-carbethoxytropinone and related tropinone derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 8610–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Shi, Y. An efficient asymmetric epoxidation method for trans-olefins mediated by a fructose-derived ketone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 9806–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-X.; Shi, Y. Practical synthesis of an L-fructose-derived ketone catalyst for asymmetric epoxidation of olefins. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5377–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, X.; Wu, T.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Q.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D. Scalable, efficient and rapid chemical synthesis of L-fructose with high purity. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 480, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Shi, Y. Asymmetric epoxidation using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as primary oxidant. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 8721–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ager, D. J.; Anderson, K.; Oblinger, E.; Shi, Y.; VanderRoest, J. An epoxidation approach to a chiral lactone: Application of the Shi epoxidation. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2007, 11, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, A.; Milliet, P.; Lusinchi, X. Action de l'acide p-nitroperbenzoïque et de l'eau oxygénée sur un sel d'immonium hétérocyclique stéroïdique et sur l'énamine correspondante. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976, 17, 1577–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohé, L.; Lusinchi, M.; Lusinchi, X. Oxygen atom transfer from a chiral oxaziridinium salt. Asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 880. del Río, R. E.; Wang, B.; Achab, S.; Bohé, L. Highly enantioselective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides by a new oxaziridinium salt. Highly enantioselective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides by a new oxaziridinium salt. Org Lett. 2007, 9(12), 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F. A.; Harakal, M. E.; Awad, S. B. Chemistry of oxaziridines. 4. Asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized alkenes using chiral 2-sulfonyloxaziridines: evidence for a planar transition state geometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 3123–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman Page, P. C.; Buckley, B. R.; Blacker, A. J. Iminium salt catalysts for asymmetric epoxidation: the first high enantioselectivities. Org. Lett, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman Page, P. C.; Buckley, B. R.; Heaney, H.; Blacker, A. J. Asymmetric epoxidation of cis-alkenes mediated by iminium salts: highly enantioselective synthesis of levcromakalim. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 375–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulman Page, P. C.; Parker, P.; Rassias, G. A.; Buckley, B. R.; Bethell, D. Iminium salt-catalysed asymmetric epoxidation using hydrogen peroxide as stoichiometric oxidant. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman Page, P. C.; Parker, P.; Buckley, B.; Rassias, G. A.; Bethell, D. Organocatalysis of asymmetric epoxidation by iminium salts using sodium hypochlorite as the stoichiometric oxidant. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 15–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman Page, P. C.; Bartlett, C. J.; Chan, Y.; Allin, S. M.; McKenzie, M. J.; Lacour, J.; Jone, G. A. New biphenyl iminium salt catalysts for highly enantioselective asymmetric epoxidation: role of additional substitution and dihedral angle. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 4220–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Arcy, T. D.; Elsegood, M. R. J.; Buckley, B. R. Organocatalytic enantioselective synthesis of bicyclo[2.2.2]octenones via oxaziridinium catalysed ortho-hydroxylative phenol dearomatization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61(30), article nb. e202205278, pp. 1-6; [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, C. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967; 89(26), 7017-7036. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, L. Supramolecular chemistry: An enabling tool for asymmetric catalysis. Synlett 2025, 36, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Supramolecular asymmetric catalysis mediated by crown ethers and related recognition systems. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, D. G.; Sogah, G. D. Y. Chiral crown complexes catalyse Michael addition reactions to give adducts in high optical yields. Chem. Commun. 1981, (13), 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, S.; Kobayashi, S. A novel chiral lead(II) catalyst for enantioselective aldol reactions in aqueous media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11531–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-López, M.; Martín-Lomas, M.; Penadés, S. Asymmetric Michael reaction using macrocyclic lactose-derivatives as chiral catalysts. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, (27), 3551–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Sato, I.; Yamashita, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Catalytic asymmetric direct-type 1,4-addition reactions of simple amides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4336–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Tamura, M.; Tani, K.; Nishiwaki, N.; Ariga, M.; Tohda, Y. Asymmetric epoxidation catalyzed by novel azacrown ether-type chiral quaternary ammonium salts under phase-transfer catalytic conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, (47), 3115–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Saito, M.; Motoo, S.; Hashimoto, S-i. (S)-3,3‘-Dimethyl-2,2‘-biquinoline N,N‘-dioxide as an efficient catalyst for enantioselective addition of allyltrichlorosilanes to aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6419–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Kina, A.; Ikeda, S.; Hayashi, T. A novel axially chiral 2,2'-bipyridine N,N'-dioxide. Its preparation and use for asymmetric allylation of aldehydes with allyl(trichloro)silane as a highly efficient catalyst. Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 2799–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkov, A. V.; Orsini, M.; Pernazza, D.; Muir, K. W.; Langer, V.; Meghani, P.; Kocovský, P. Chiral 2,2'-bipyridine-type N-monoxides as organocatalysts in the enantioselective allylation of aldehydes with allyltrichlorosilane. Org Lett. 2002, 4, 1047–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkov, A. V.; Dufková, L.; Farrugia, L.; Kocovský, P. ; Quinox, a quinoline-type N-oxide, as organocatalyst in the asymmetric allylation of aromatic aldehydes with allyltrichlorosilanes: the role of arene-arene interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3674–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Arenas, A.; Ramírez-López, P.; Iglesias-Sigüenza, J.; Fernández, R.; Ros, A.; Lassaletta, J. M. Axially chiral N-oxide catalysts for the allylation and crotylation of aromatic aldehydes: Exploiting nonlinear effects. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, K.; Mizuno, S.; Kuroki, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Asymmetric allylation with chiral formamide catalysts. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, A. I. Chiral oxazolines and their legacy in asymmetric carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 6137–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connon, R.; Roche, B.; Rokade, B. V.; Guiry, P. J. Further developments and applications of oxazoline-containing ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 6373–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Y.; Zeng, J. L.; Ren, N.; Meng, W.; Nie, J.; Ma, J. A. C2-Symmetric chiral bisoxazolines as hydrogen-bond-acceptor catalysts in enantioselective aldol reaction of β-carbonyl acids with trifluoroacetaldehyde hemiacetals. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6364–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, M. E. Cyclization of N-halogenated amines (the Hofmann–Löffler reaction). Chem. Rev. 1963, 63, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Mao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Hong, X.; Lu, Z. Asymmetric Hofmann–Löffler–Freytag-type reaction via a transient carbenium ion complex merging organocatalysis and photocatalysis. Nat. Catal. 2025, 8, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostler, F.; Piekarski, D. G.; Danelzik, T.; Taylor, M. S.; García Mancheño, O. Neutral chiral tetrakis-iodo-triazole halogen-bond donor for chiral recognition and enantioselective catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuper, A. C.; Fengler, K.; Ostler, F.; Danelzik, T.; Piekarski, D. G.; García Mancheño, O. Fine-tuning substrate-catalyst halogen-halogen interactions for boosting enantioselectivity in halogen-bonding catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed, 2023; 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Mohanan, M. P.; Robidas, R.; Sutar, R.; Engelage, E.; Legault, C. Y.; Huber, S. M. Highly enantioselective organocatalysis with bidentate halogen bond donors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreger, A.; Wonner, P.; Engelage, E.; Walter, S. M.; Stoll, R.; Huber, S. M. A halogen-bonding-catalysed Nazarov cyclisation reaction: Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8262–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Ao, T.; Mino, T.; Sakamoto, M. Chiral bromonium salt (hypervalent bromine(III)) with N-nitrosamine as a halogen-bonding bifunctional catalyst. Molecules 2023, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Fujimura, T.; Mino, T.; Sakamoto, M. Chiral binaphthyl-based iodonium salt (hypervalent iodine(III)) as hydrogen- and halogen-bonding bifunctional catalyst: Insight into abnormal counteranion effect and asymmetric synthesis of N,S-acetals. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damrath, M.; Scheele, T.; Duvinage, D.; Neudecker, T.; Nachtsheim, B. J. Chiral triazole-substituted iodonium salts in enantioselective halogen bond catalysis. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, D. L.; Iniutina, A.; Reese, S.; Shaw, T.; Merten, C.; List, B.; Huber, S. M. Asymmetric counteranion-directed halogen bonding catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147(10), 8107–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, J. L. The chemical space project. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, Z.; Richter, D.; Dargó, G.; Kupai, J. Factors influencing the performance of organocatalysts immobilized on solid supports: A review. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2129–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Mayer-Gall, T.; Opwis, K.; Song, C. E.; Gutmann, J. S.; List, B. Science, 2013; 341, 1225–1229. [CrossRef]
- Putman, J. I.; Armstrong, D. W. Recent advances in the field of chiral crystallisation. Chirality 2022, 34, 1338–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
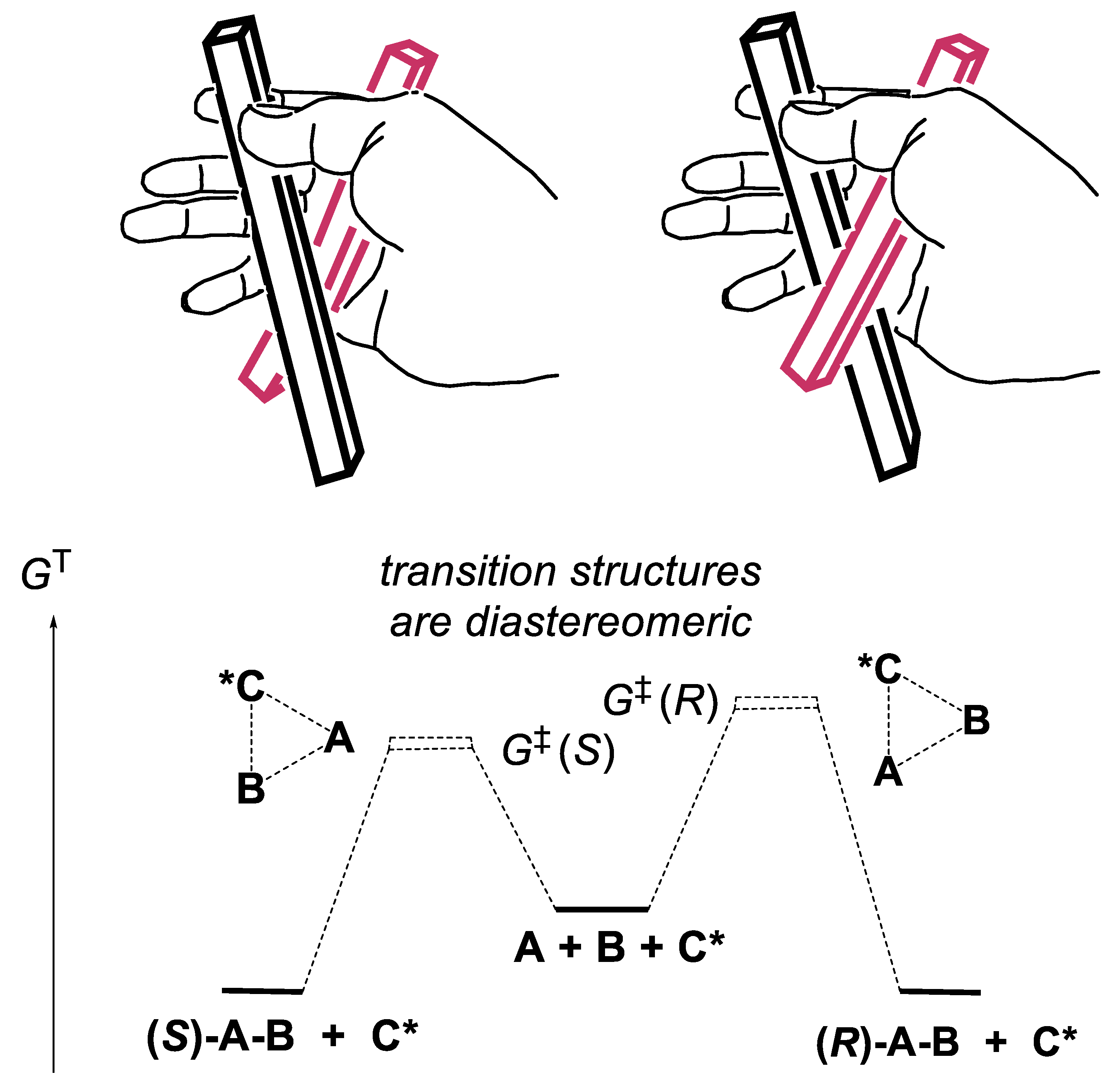
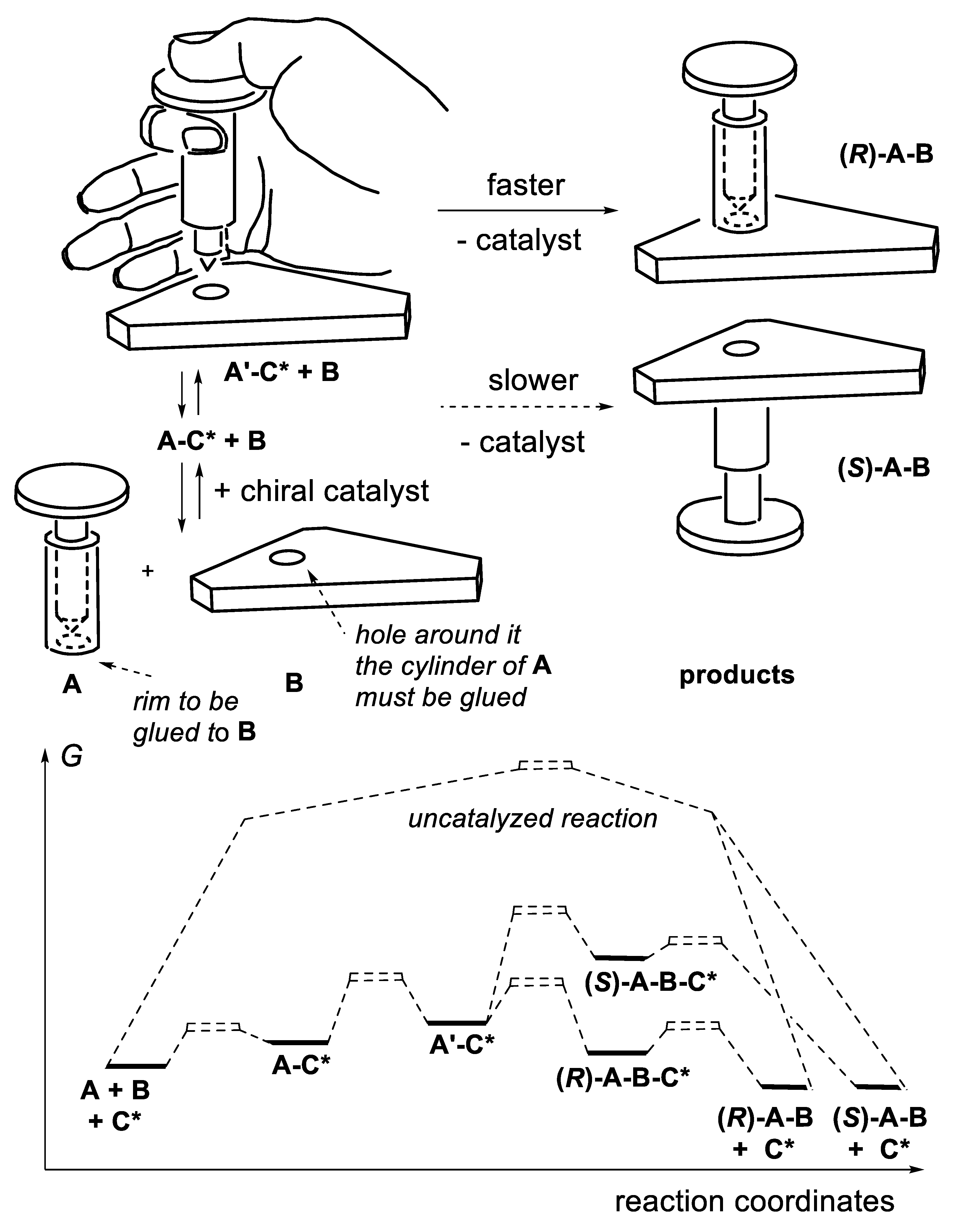
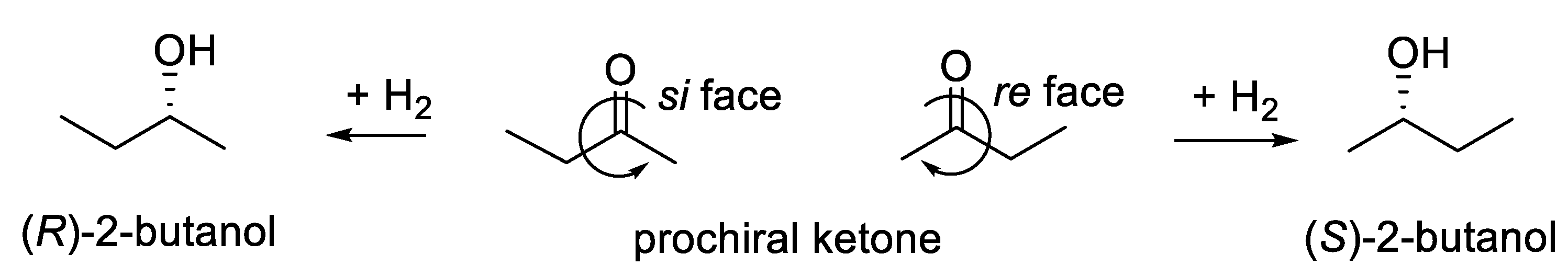
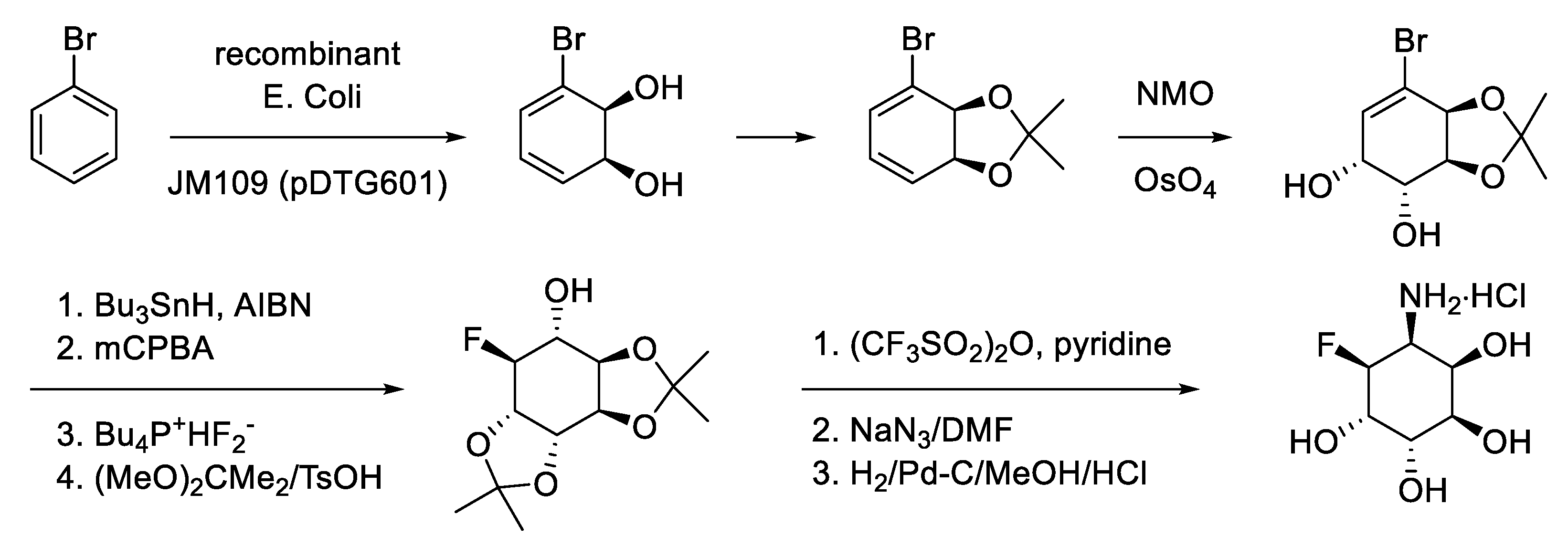
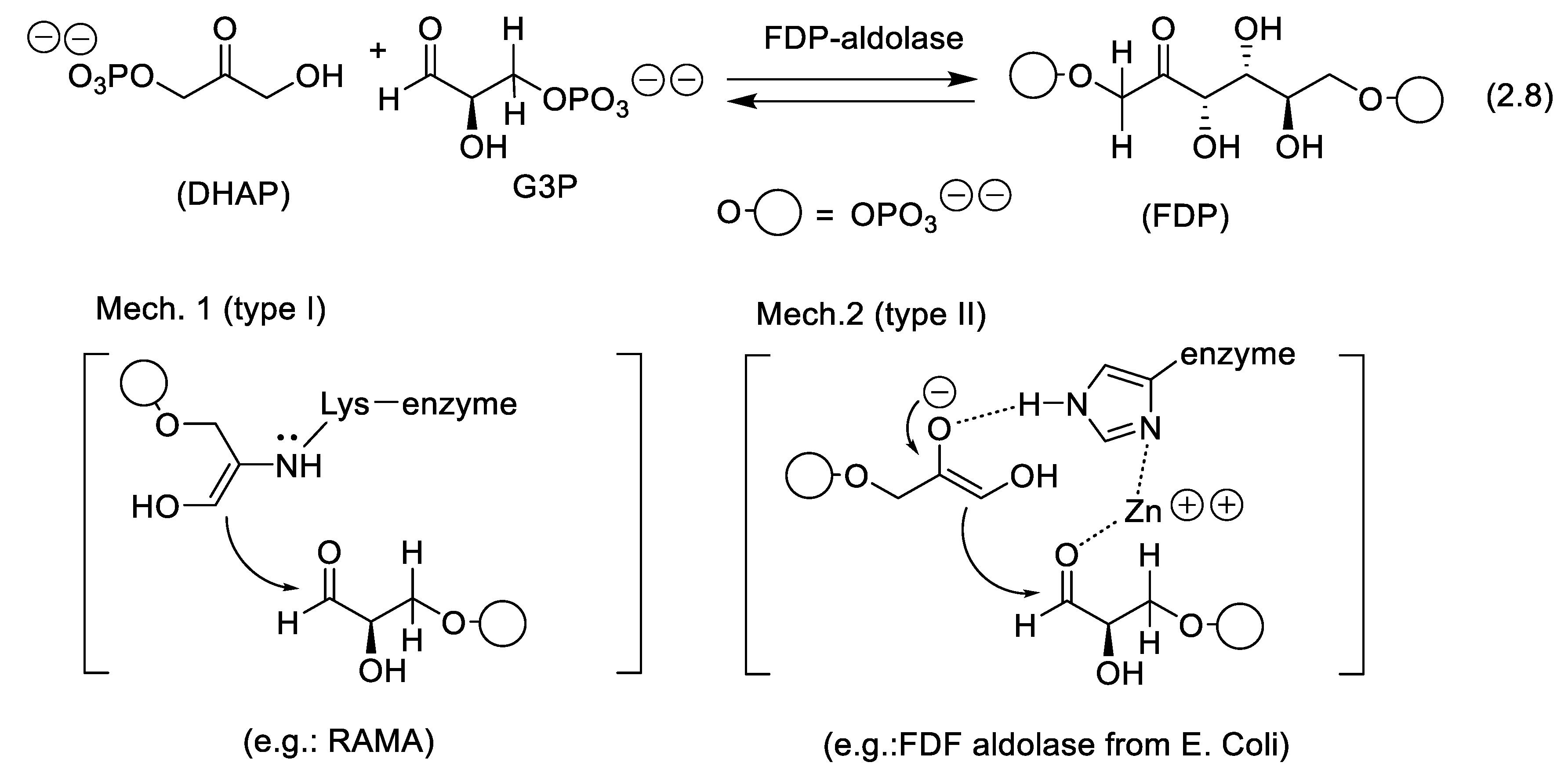
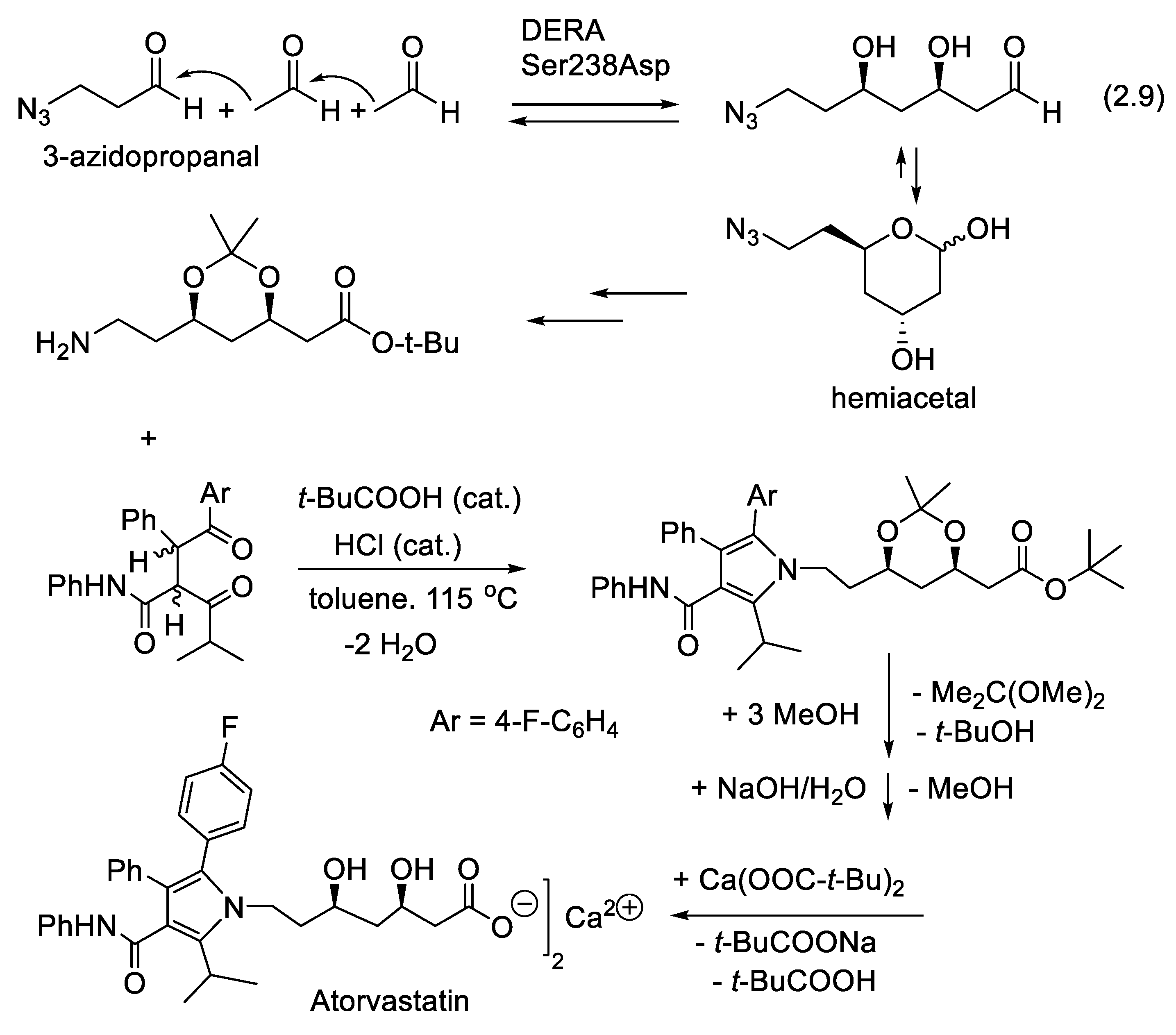
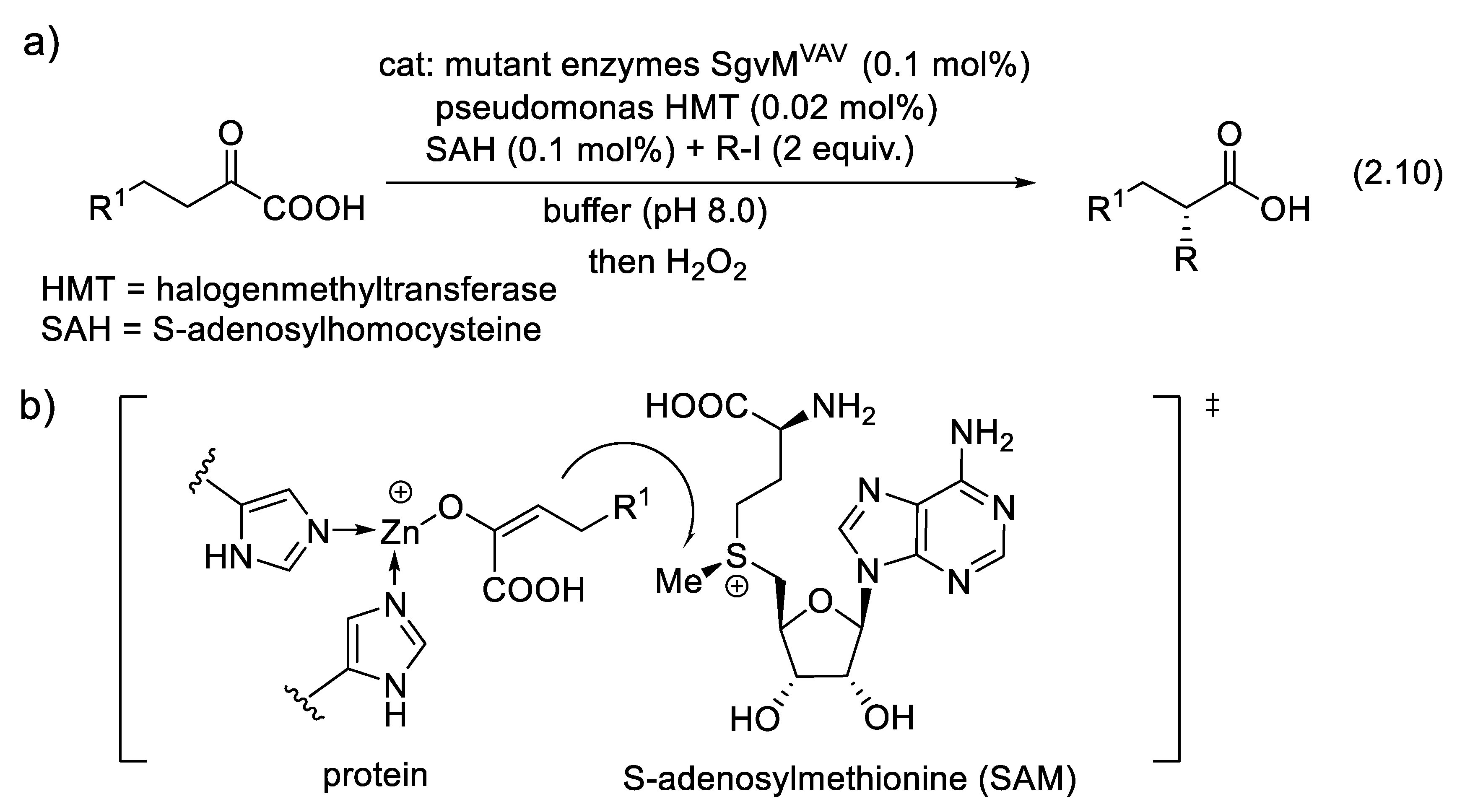
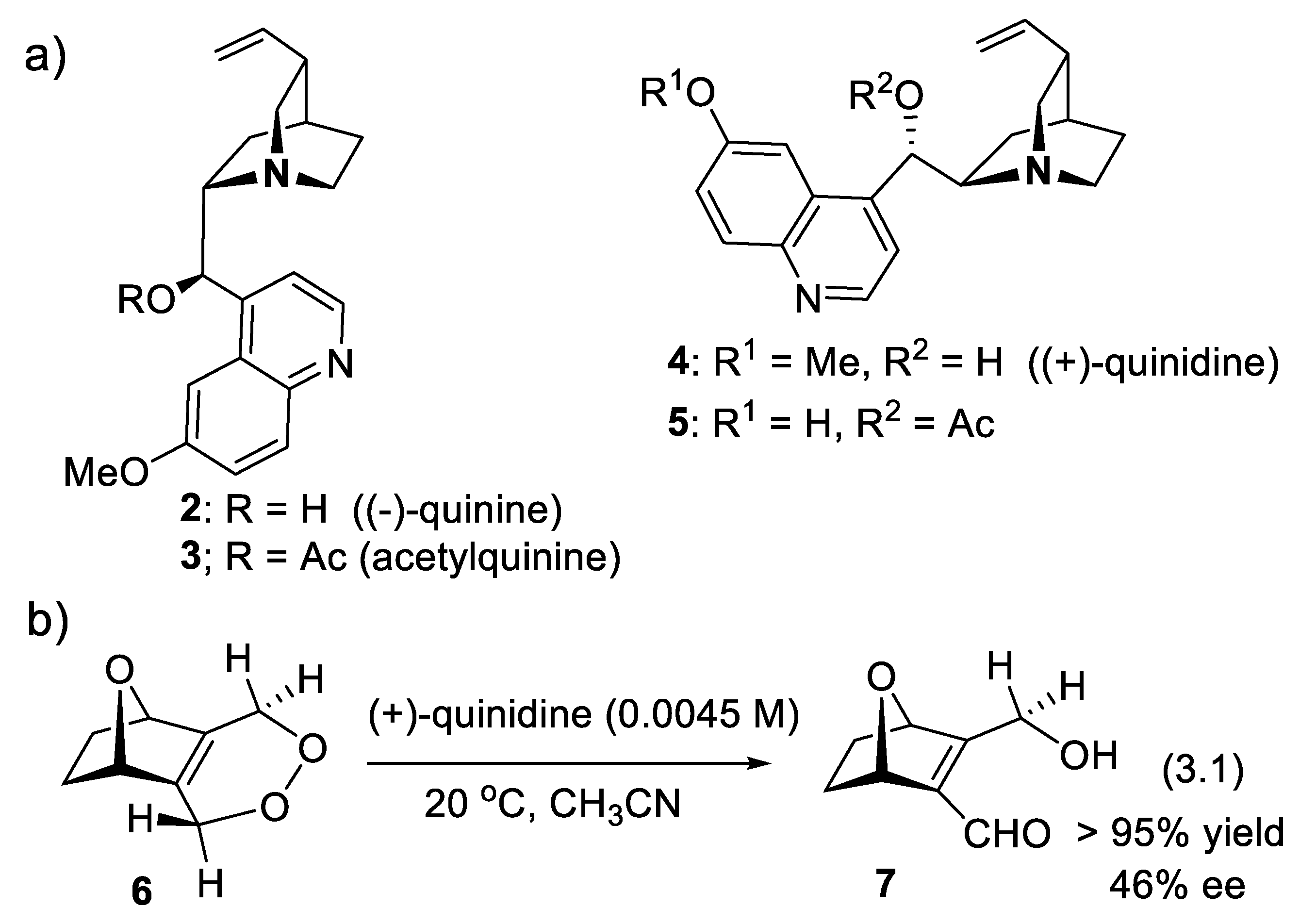
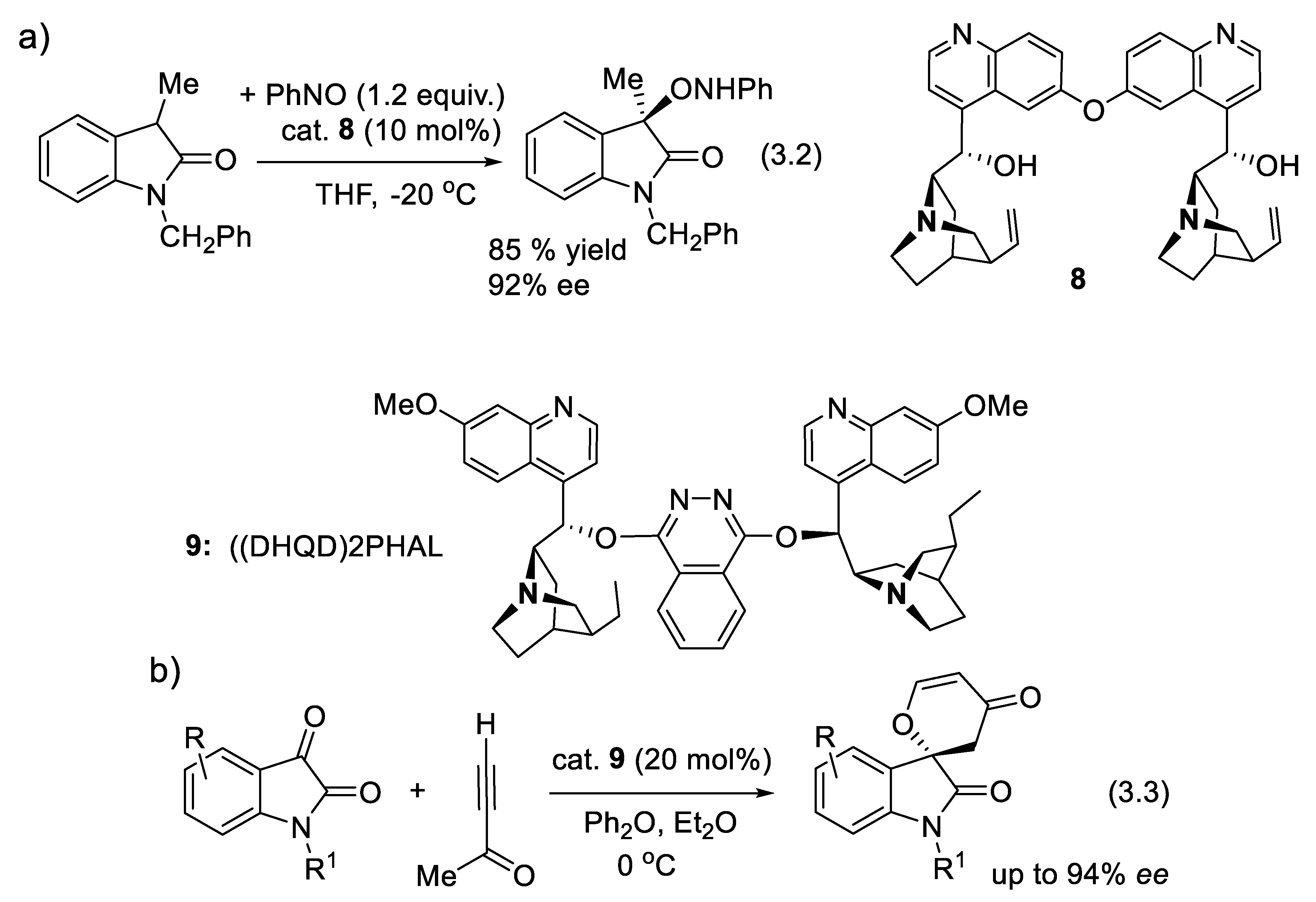
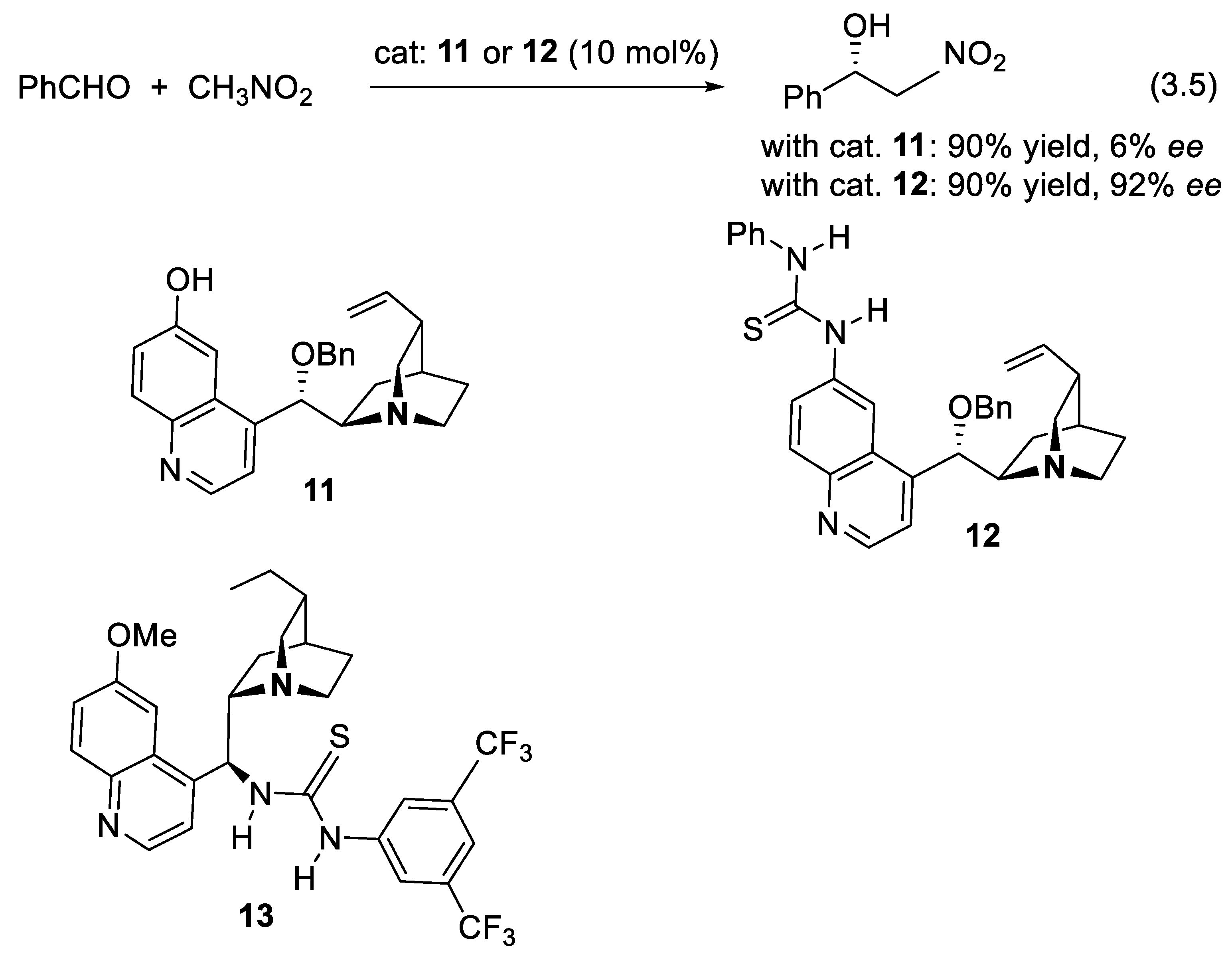
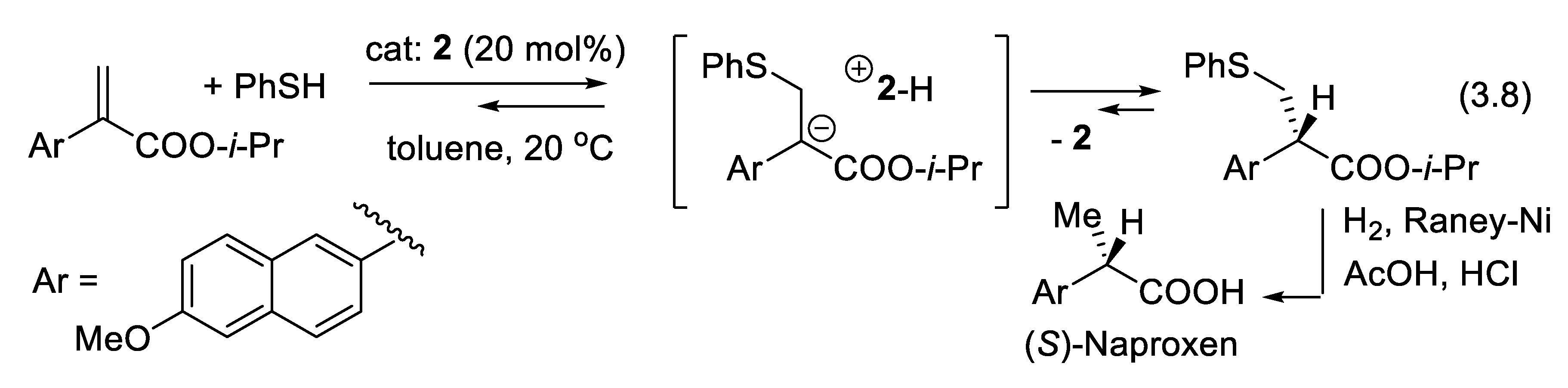
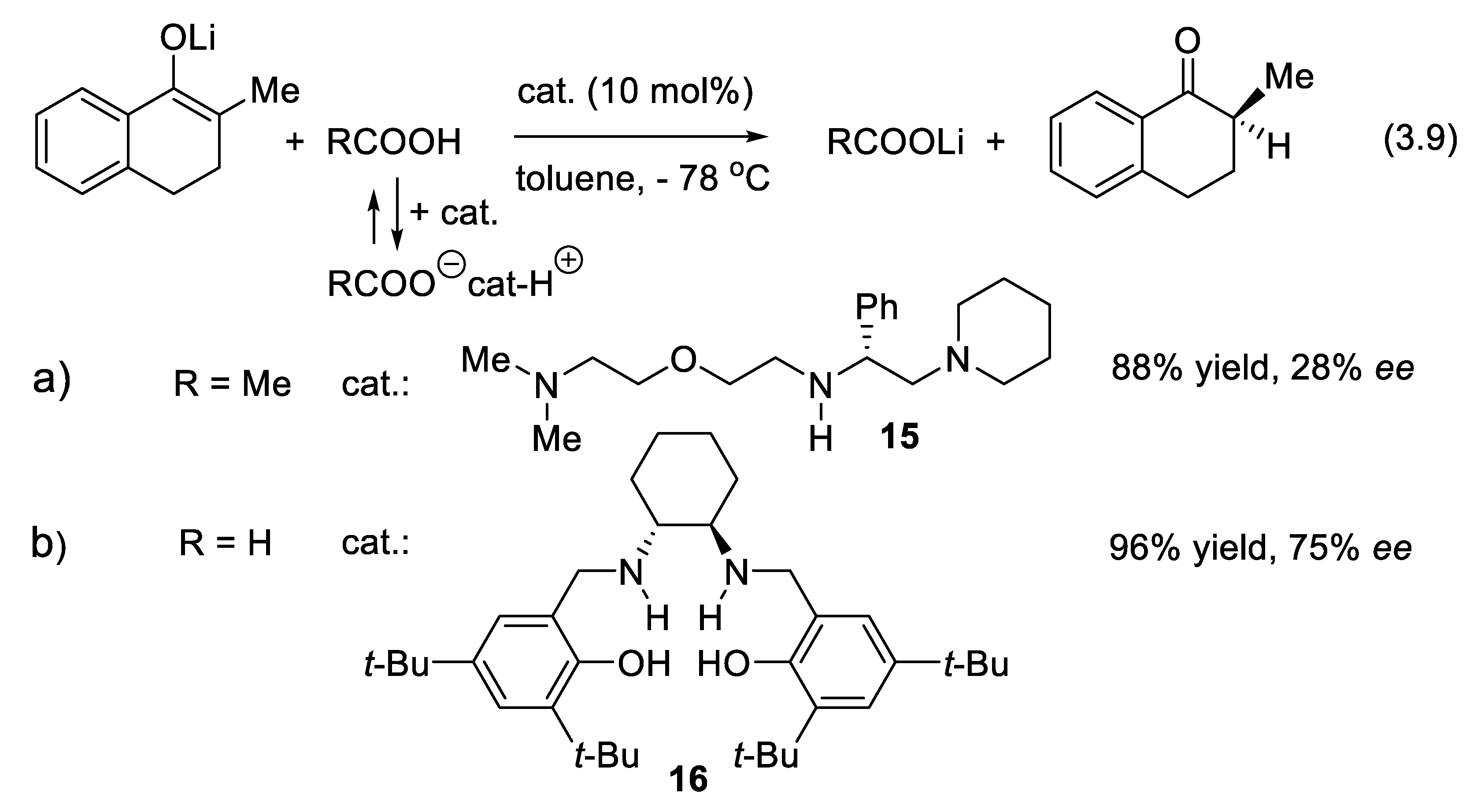
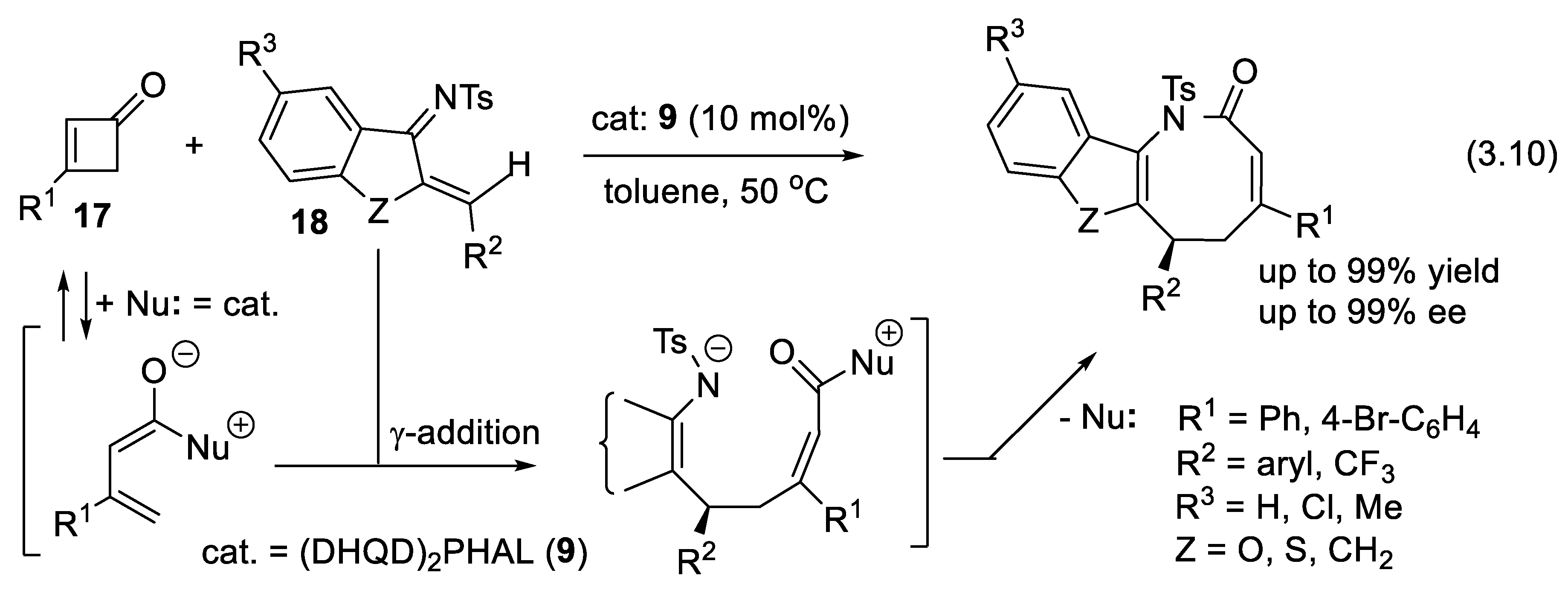
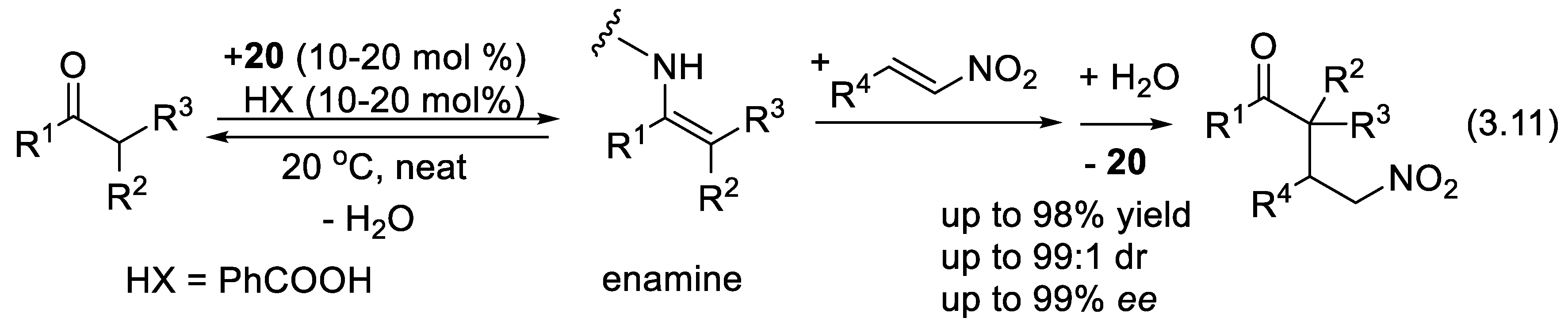
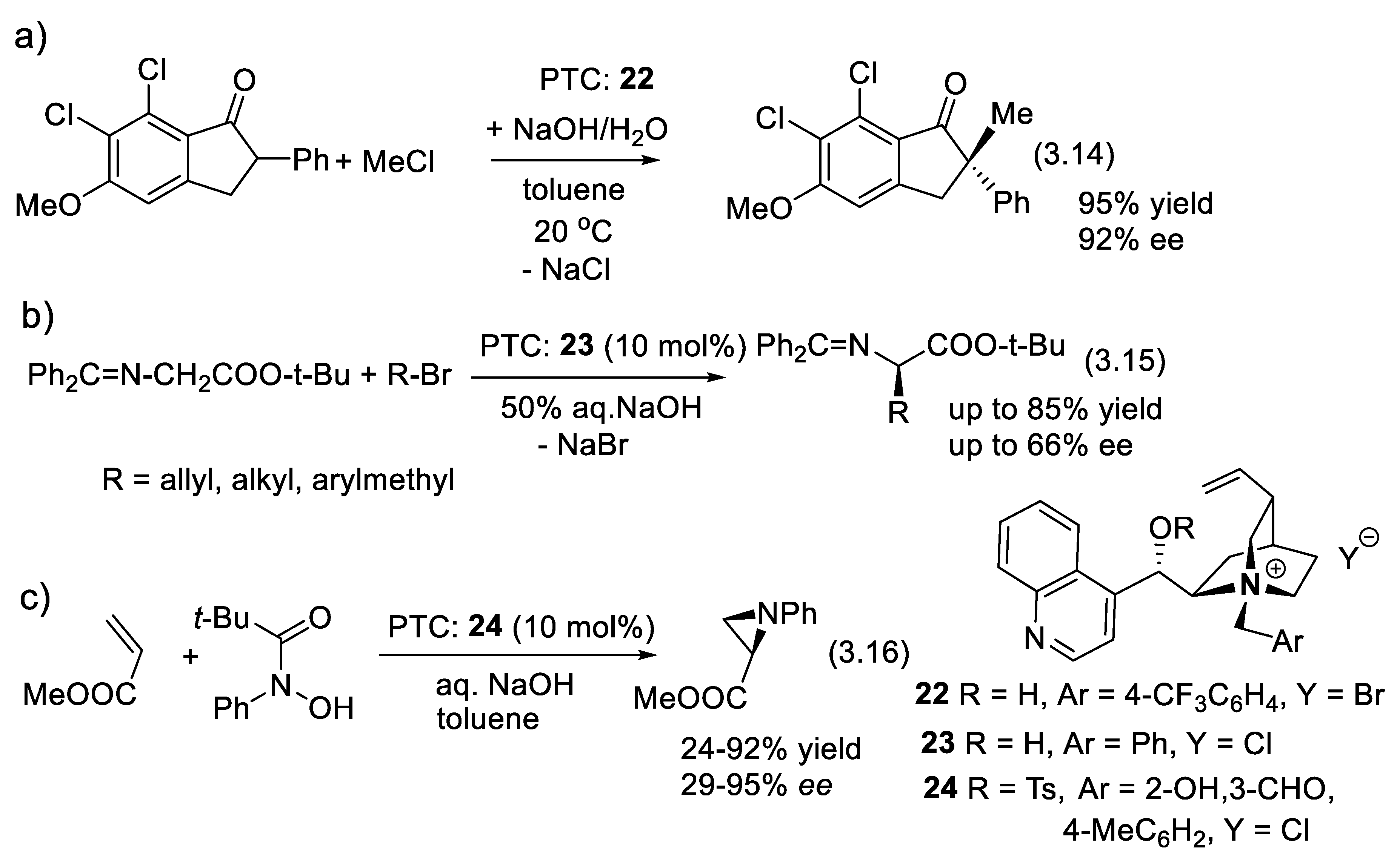
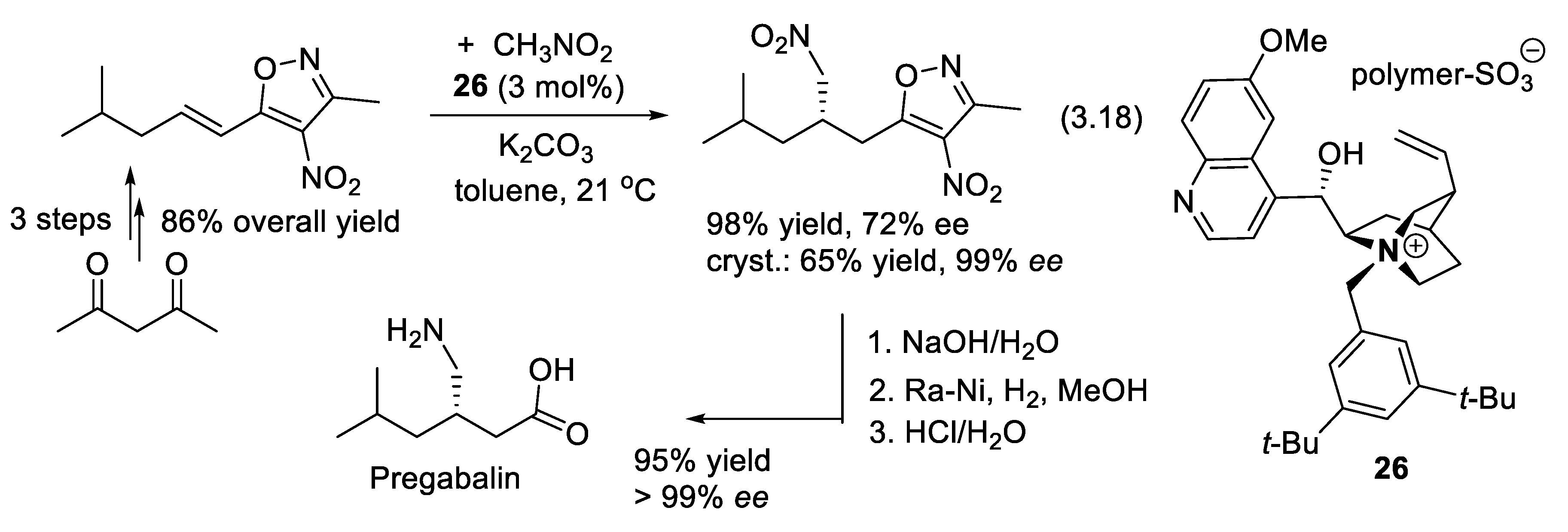
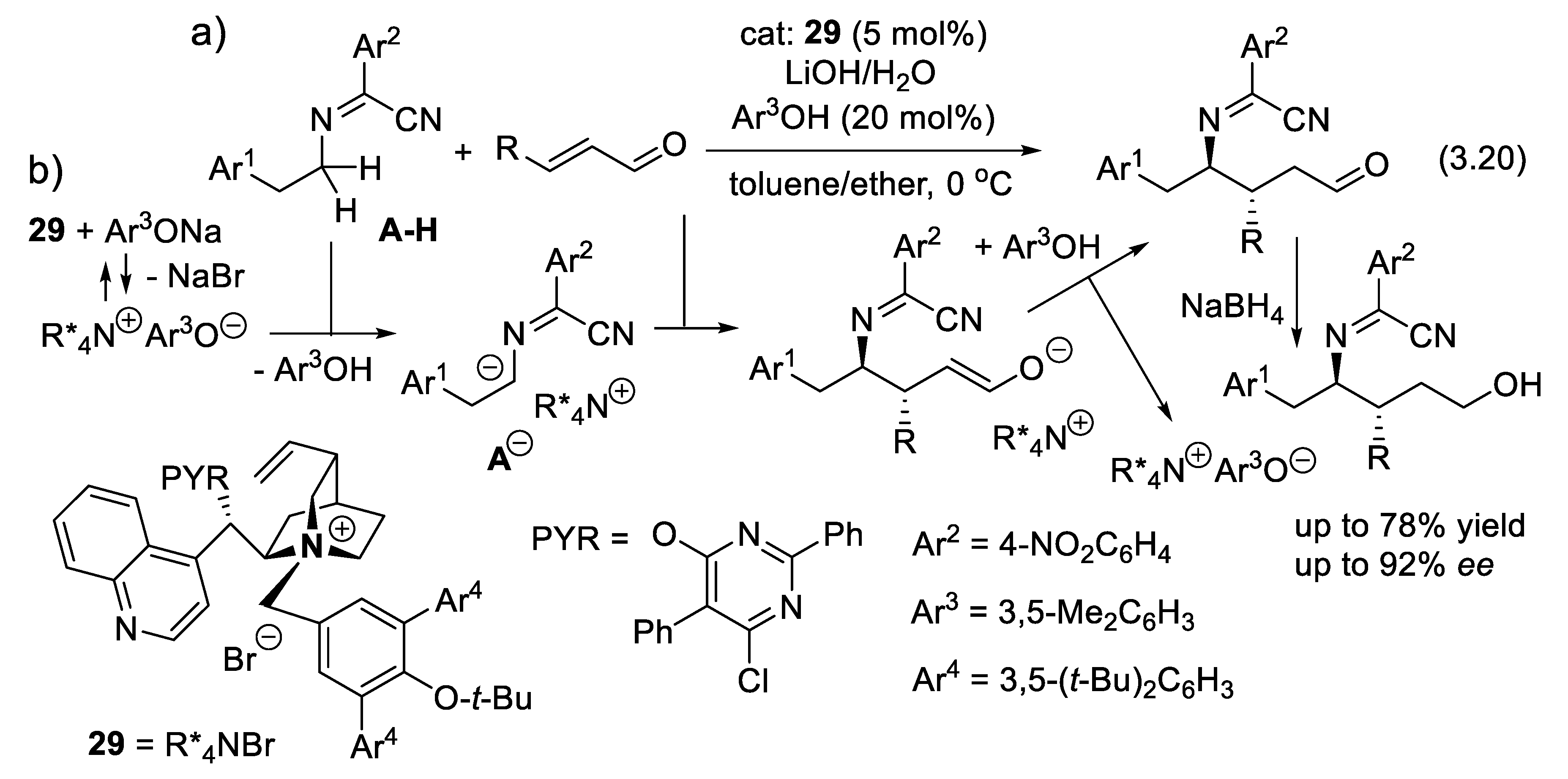
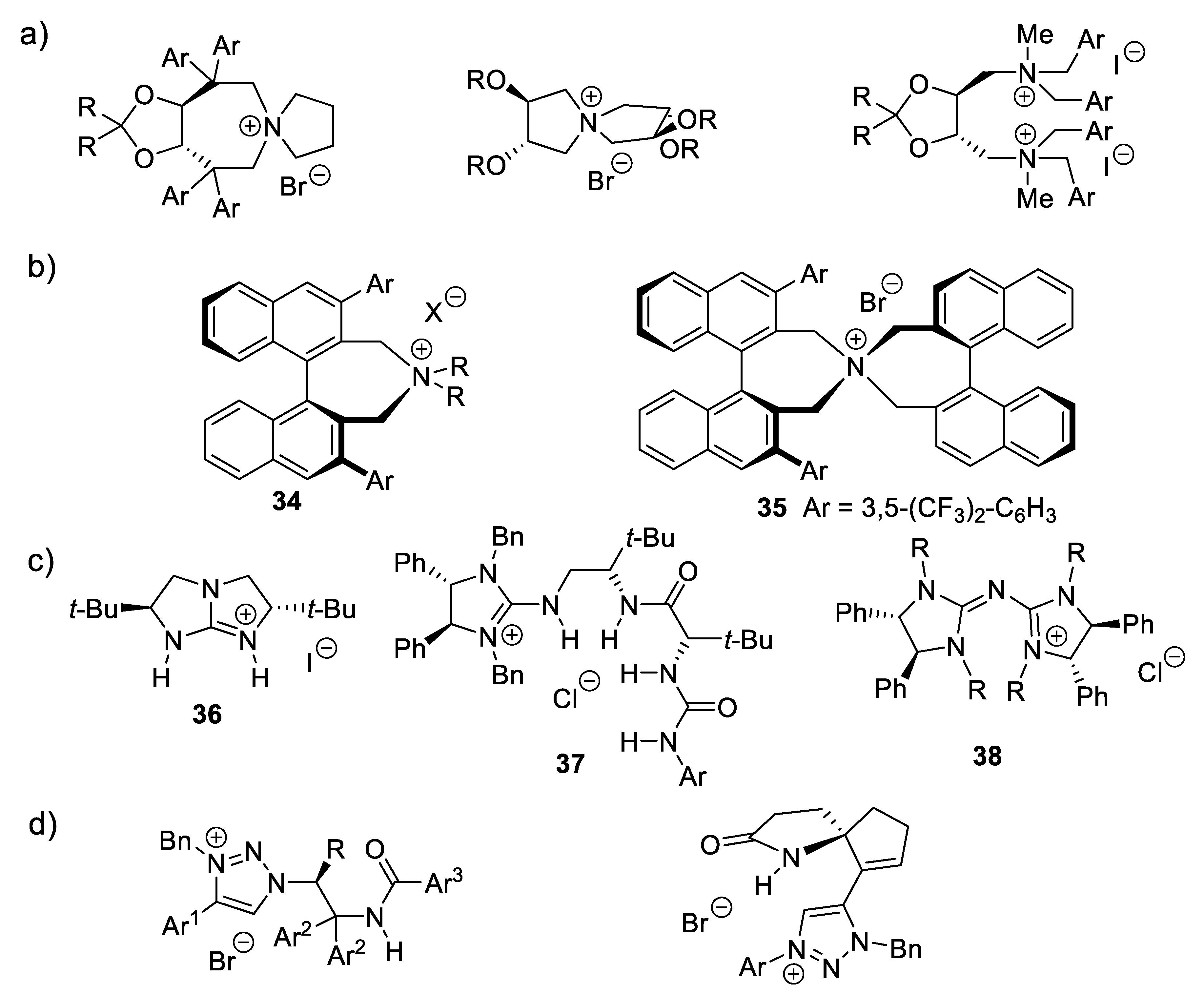
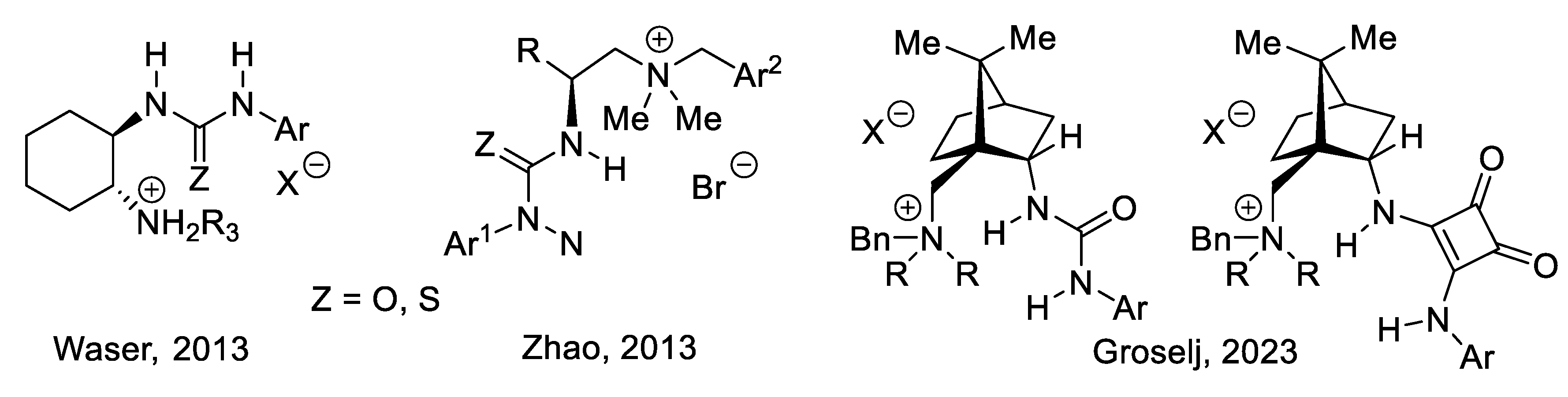
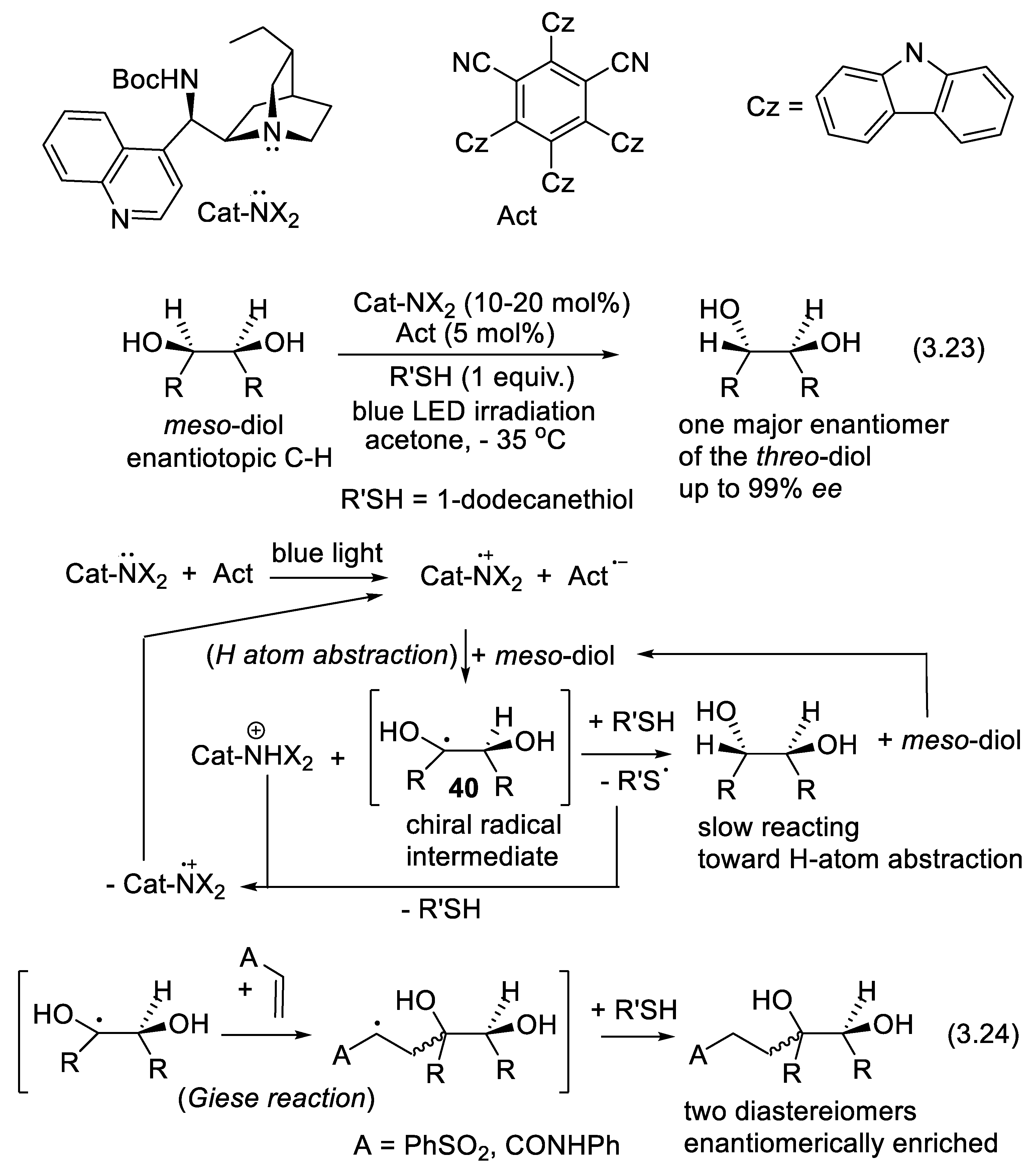
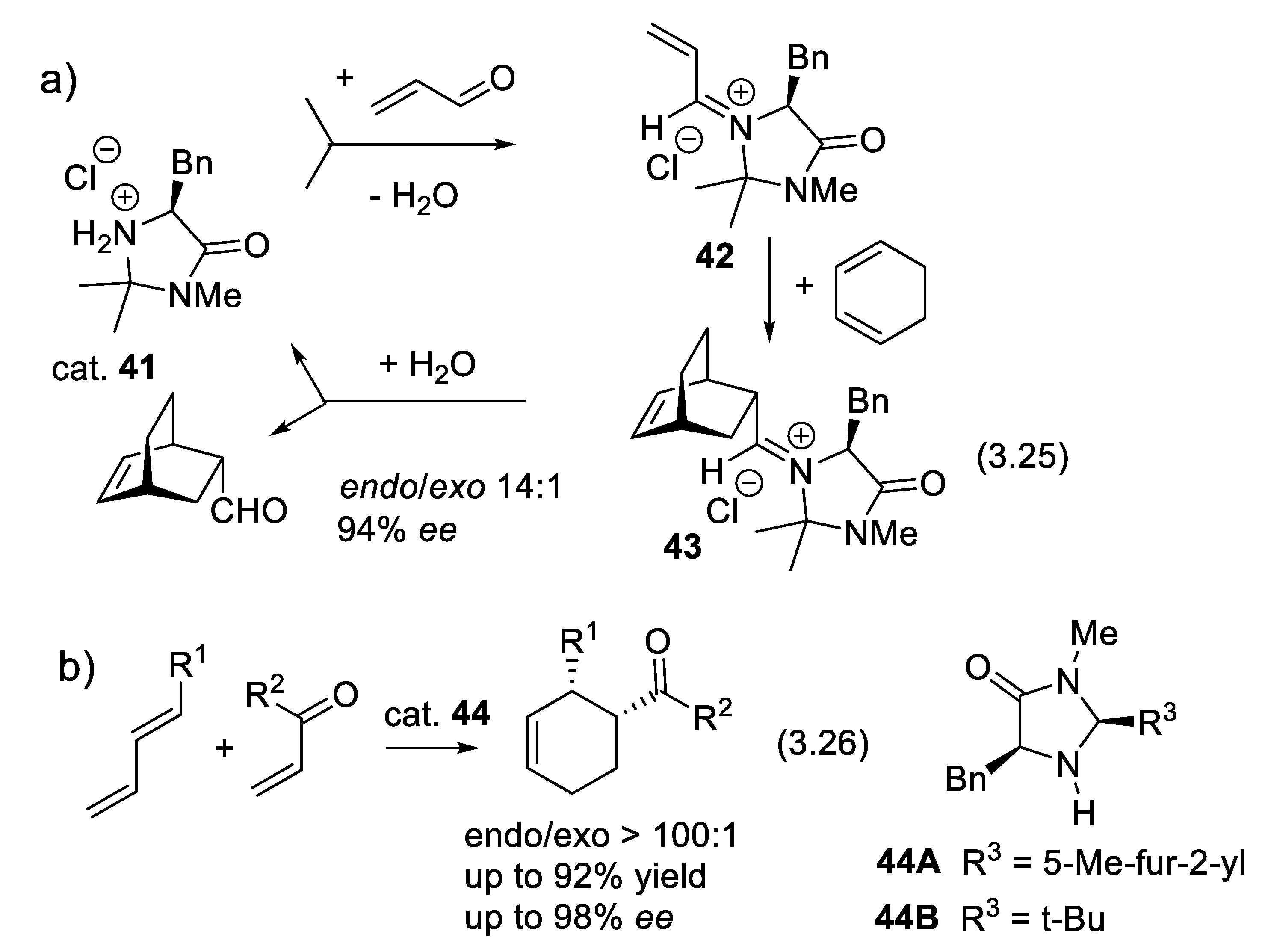
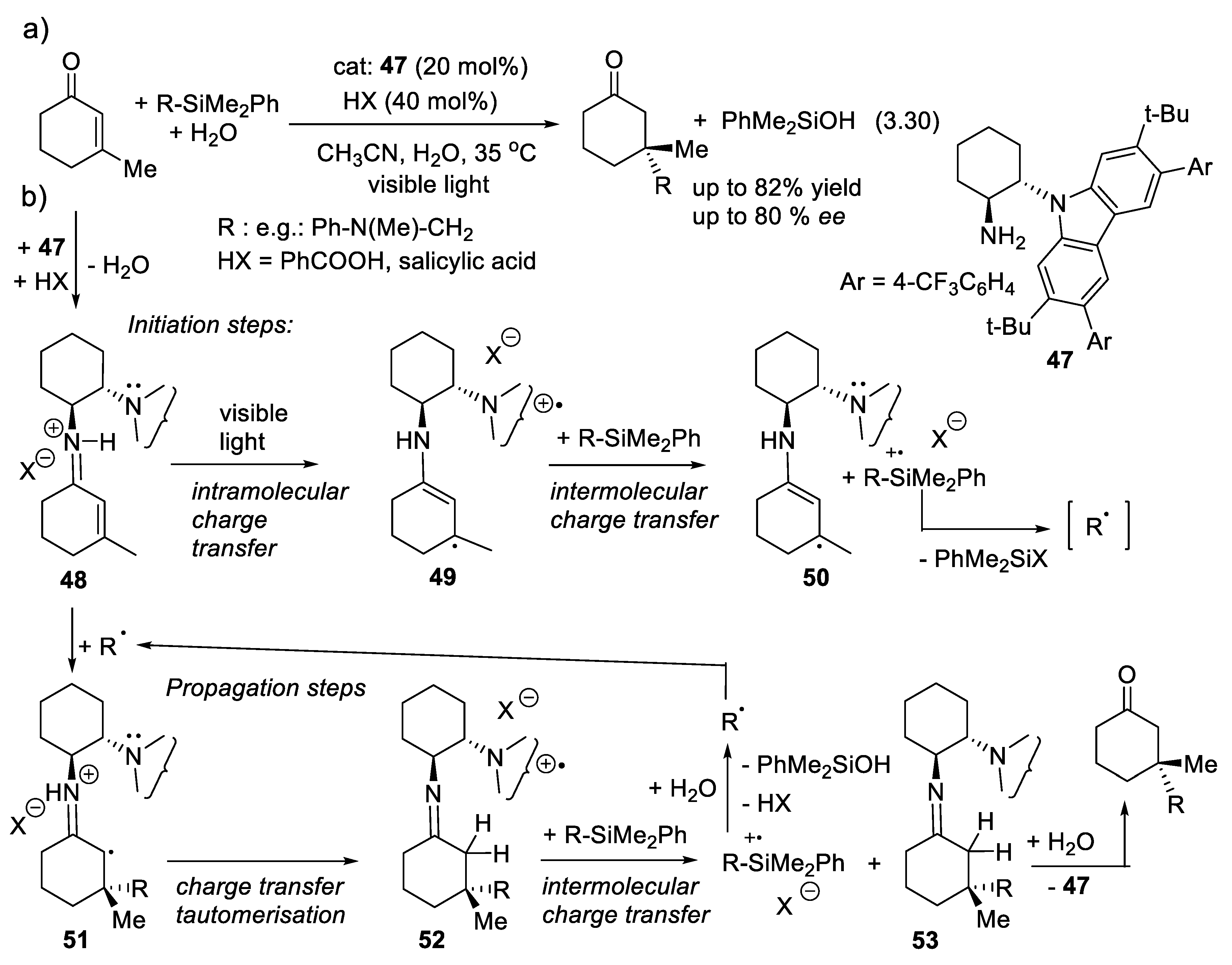
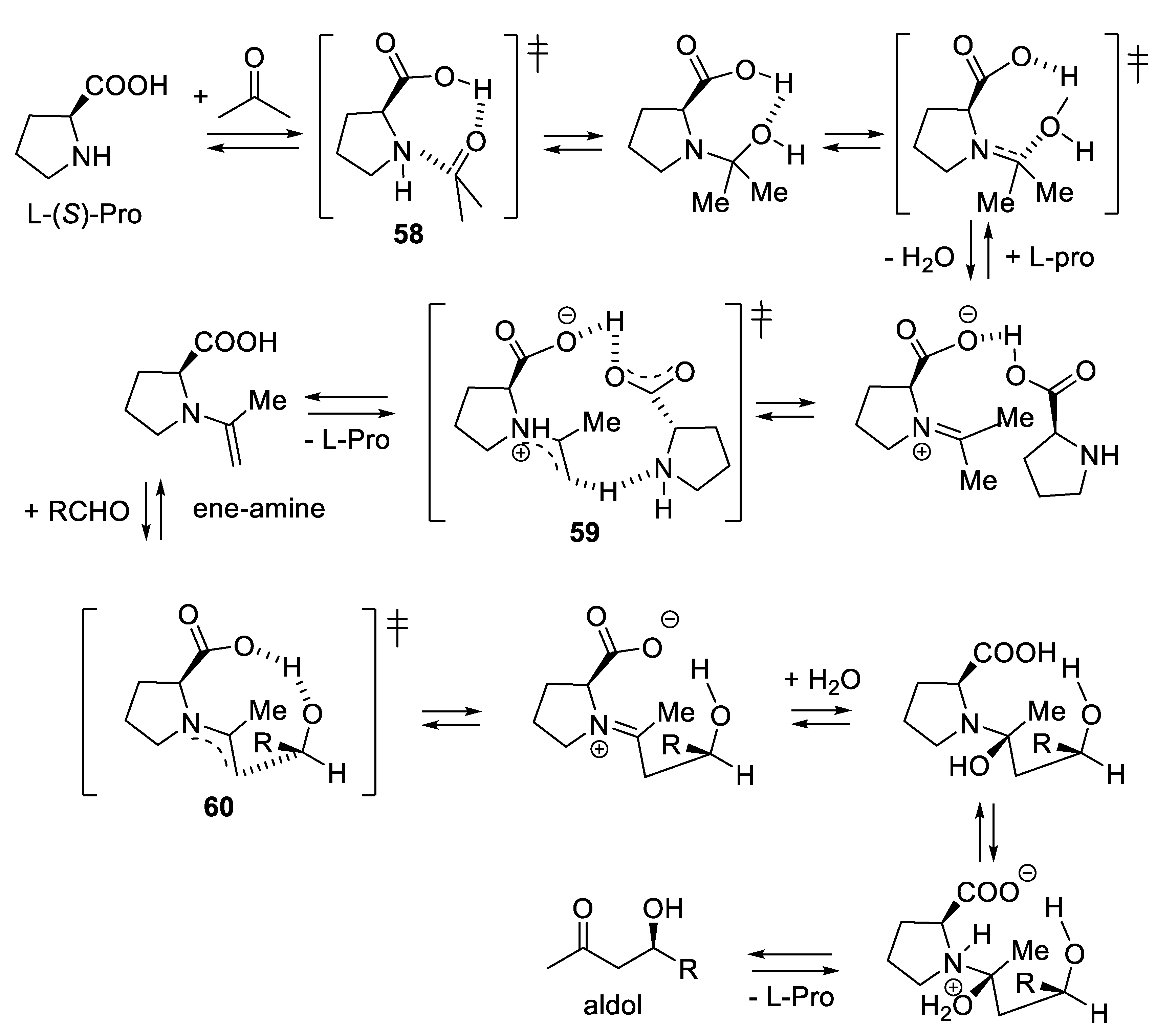
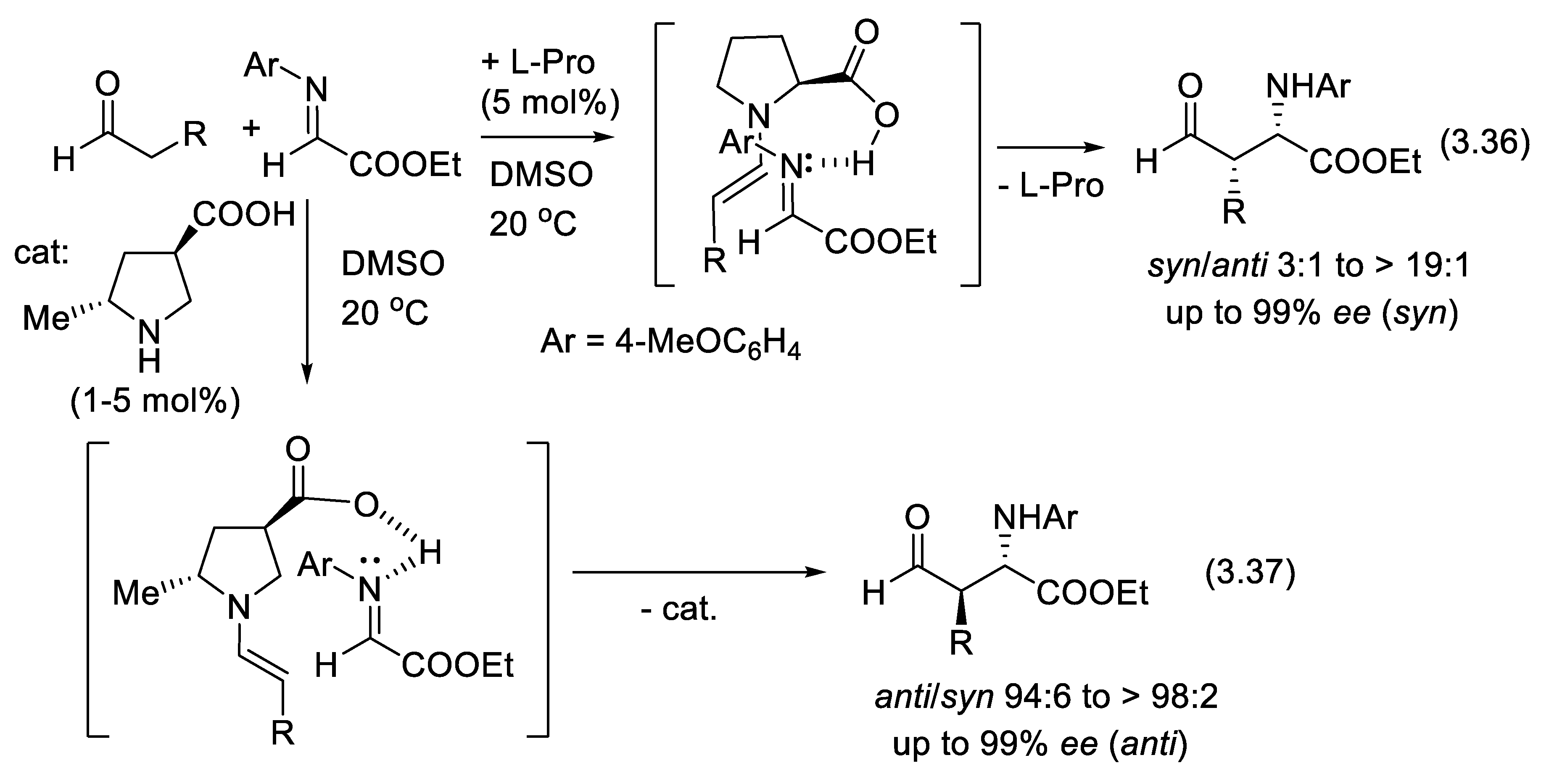
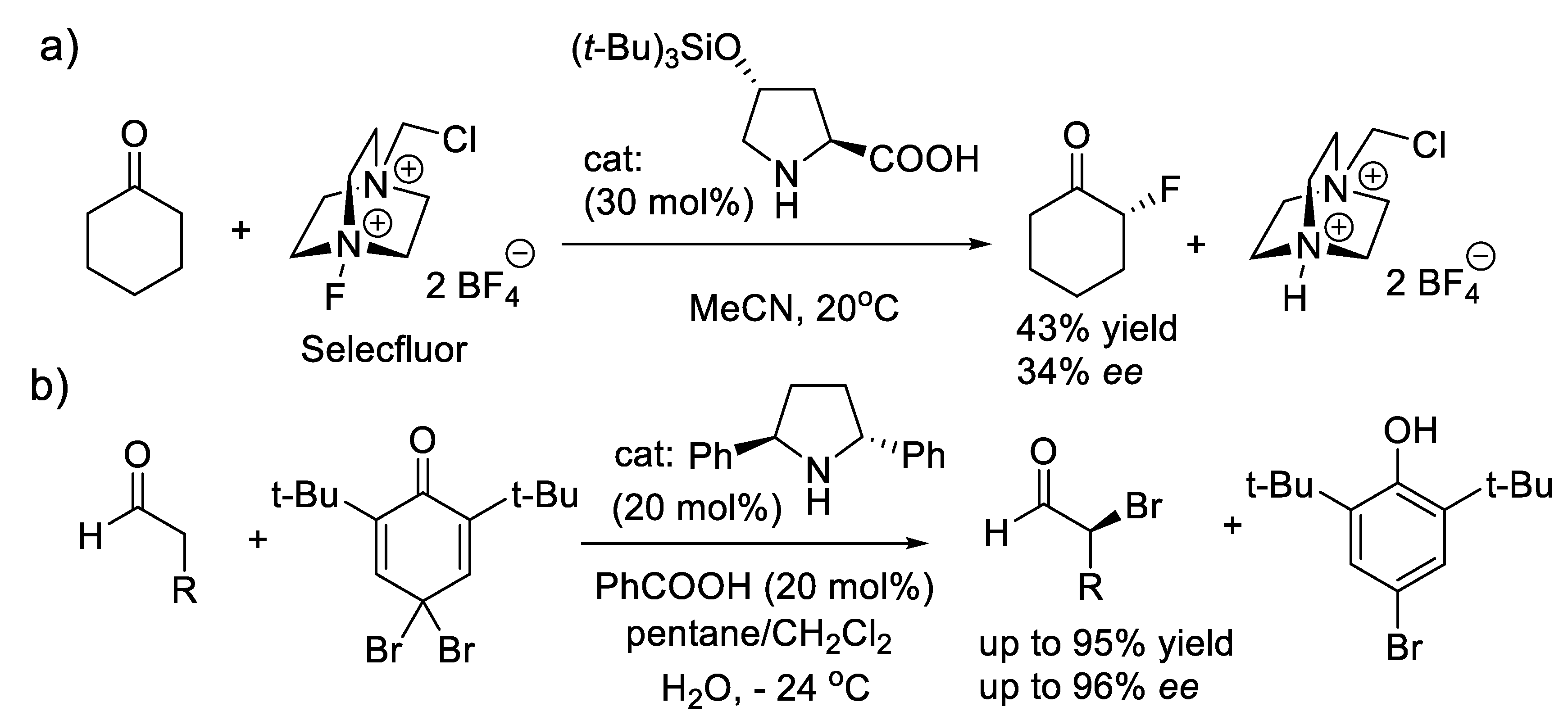
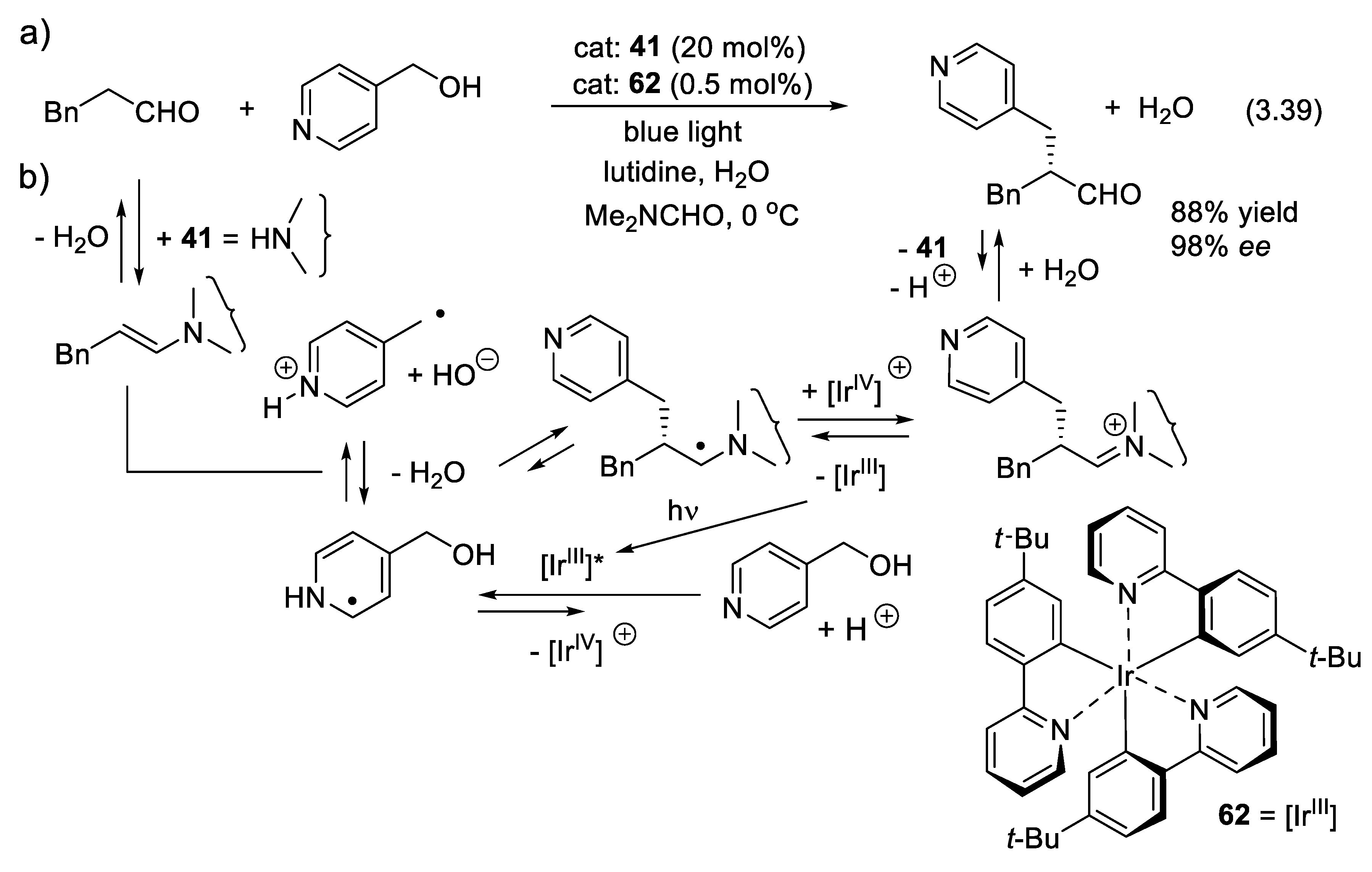
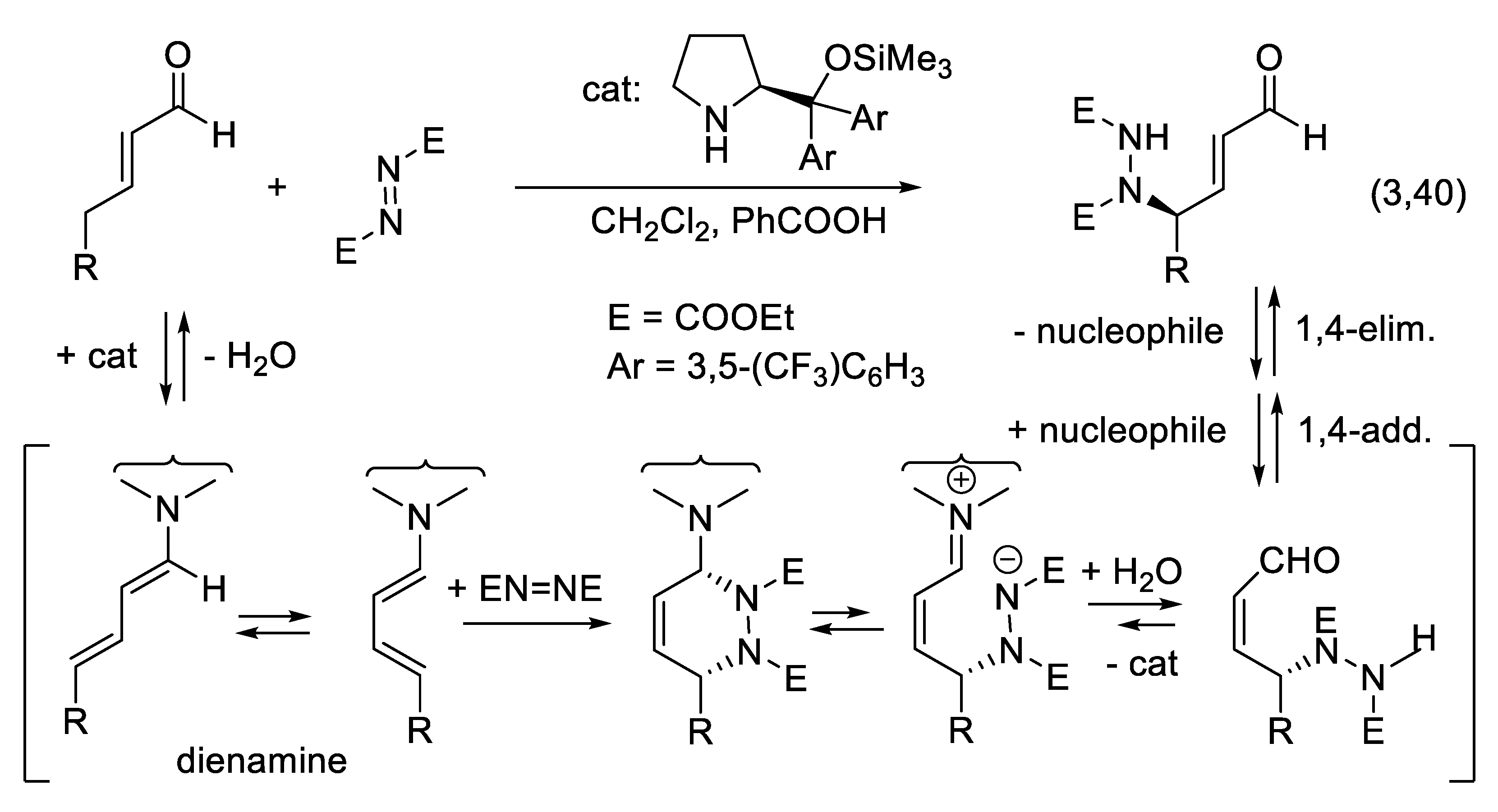
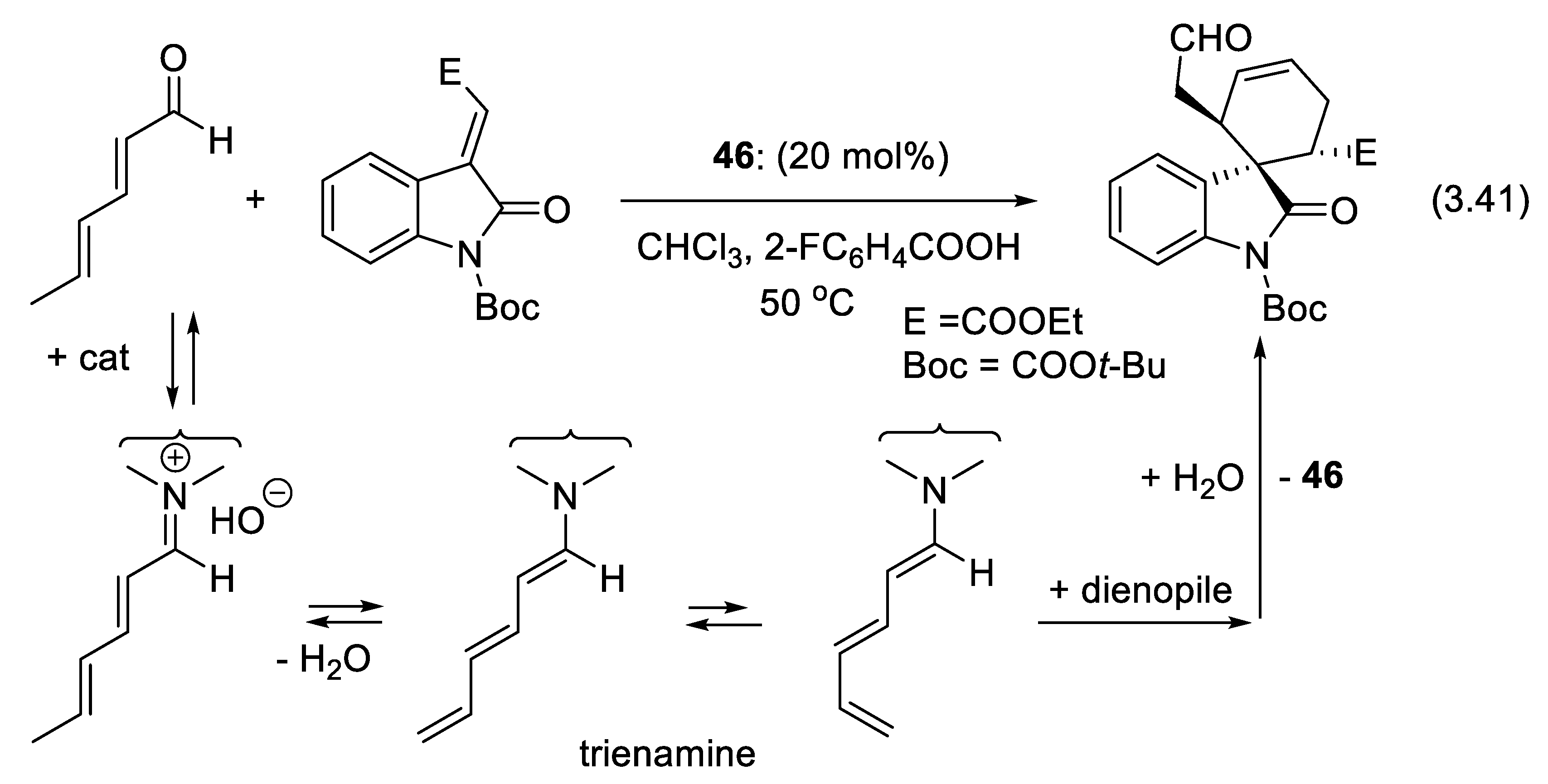
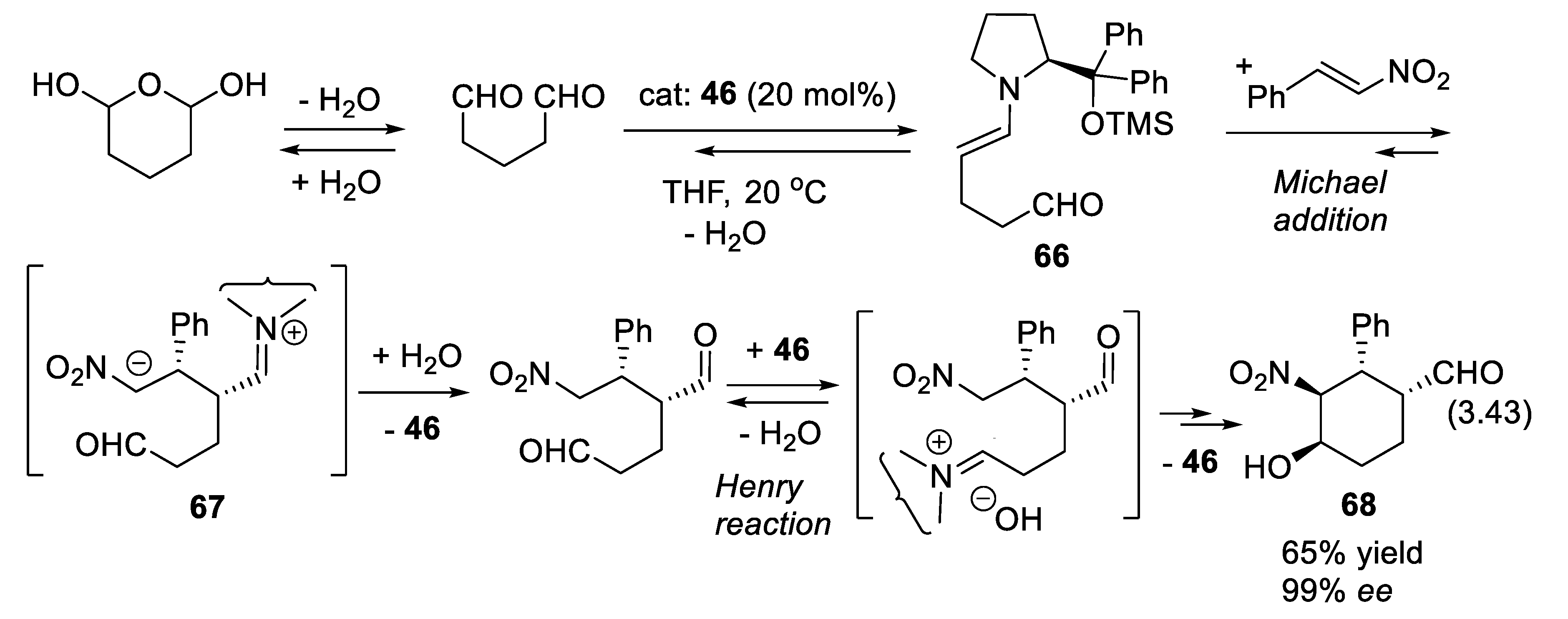
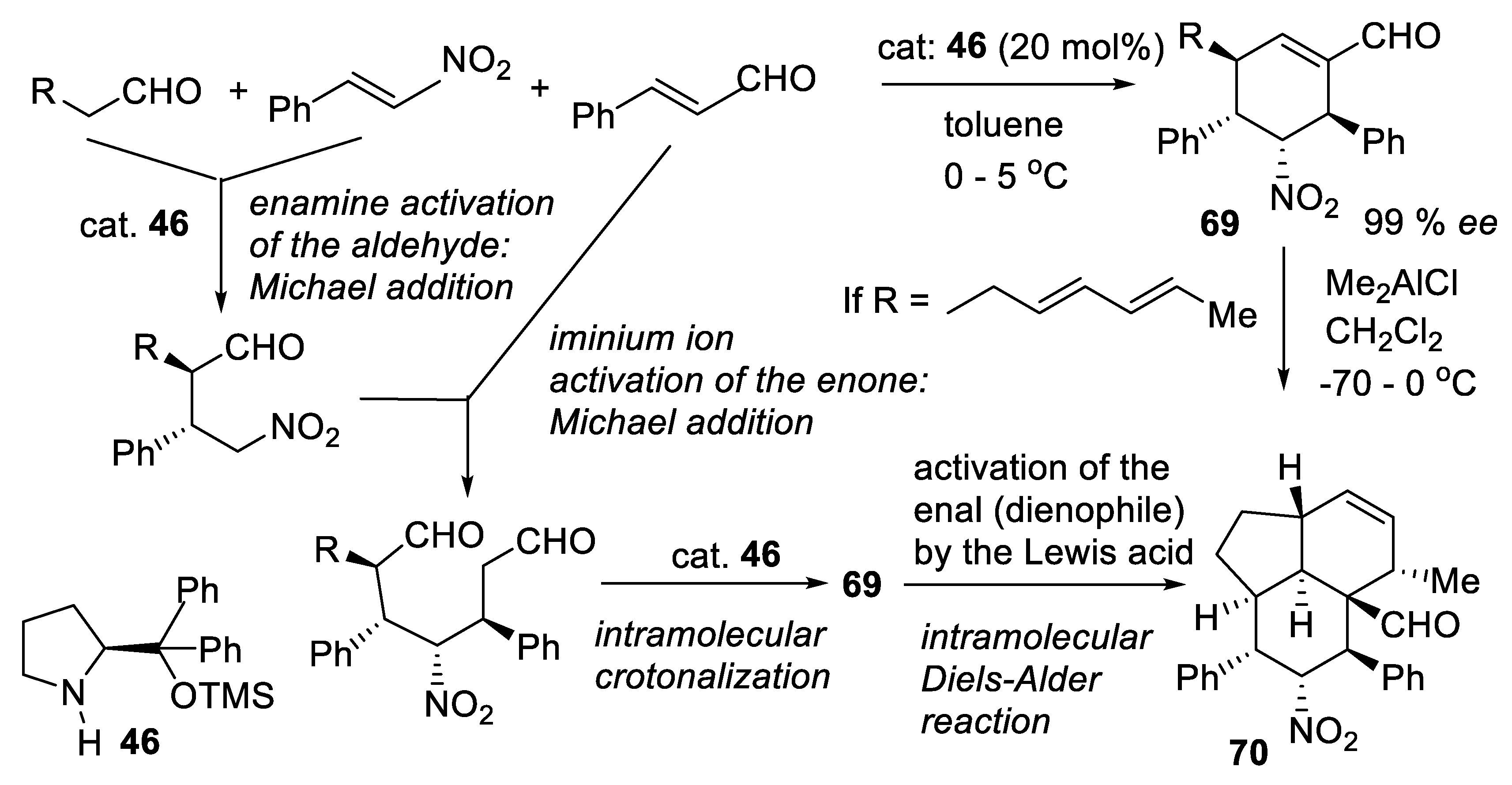
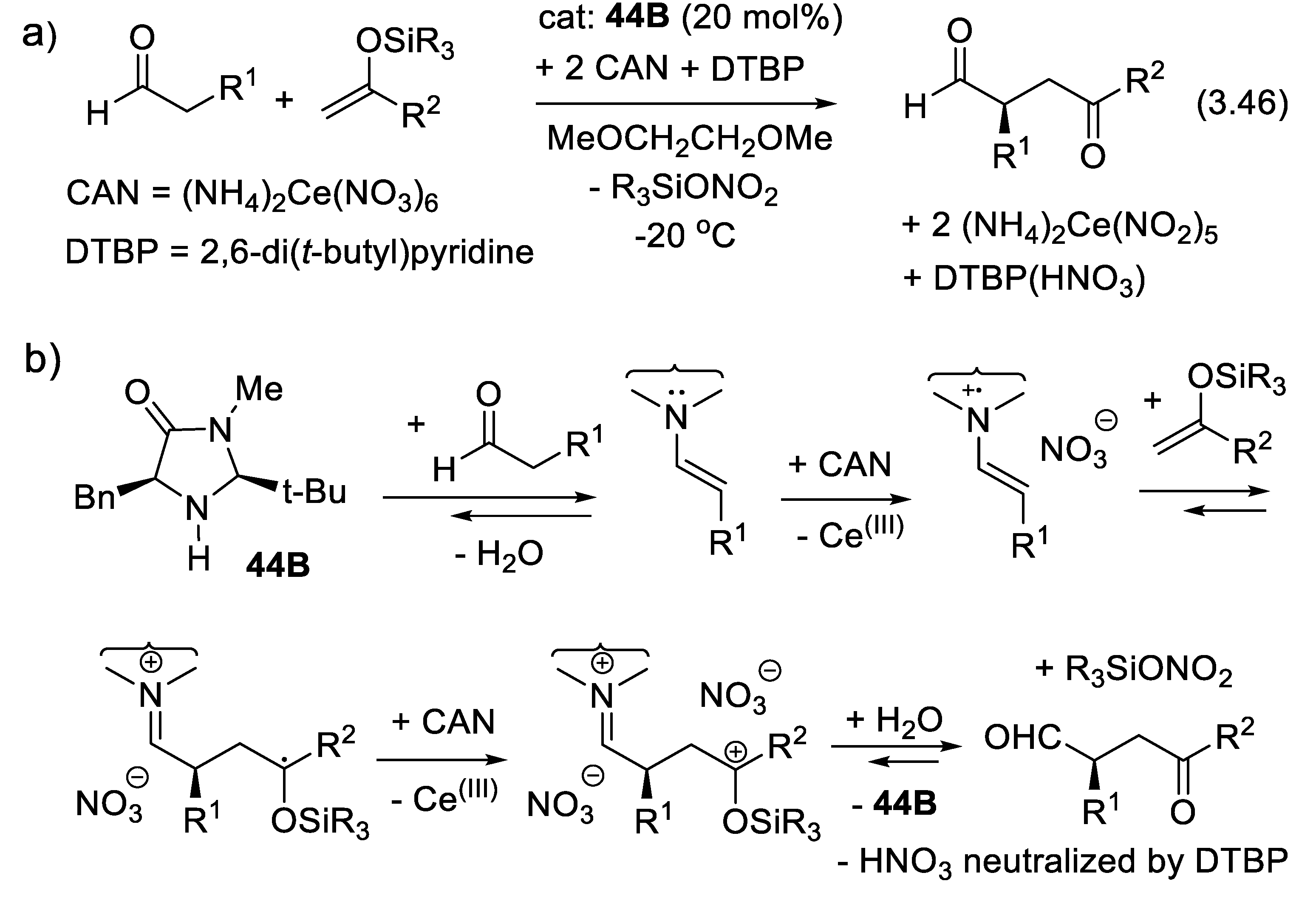
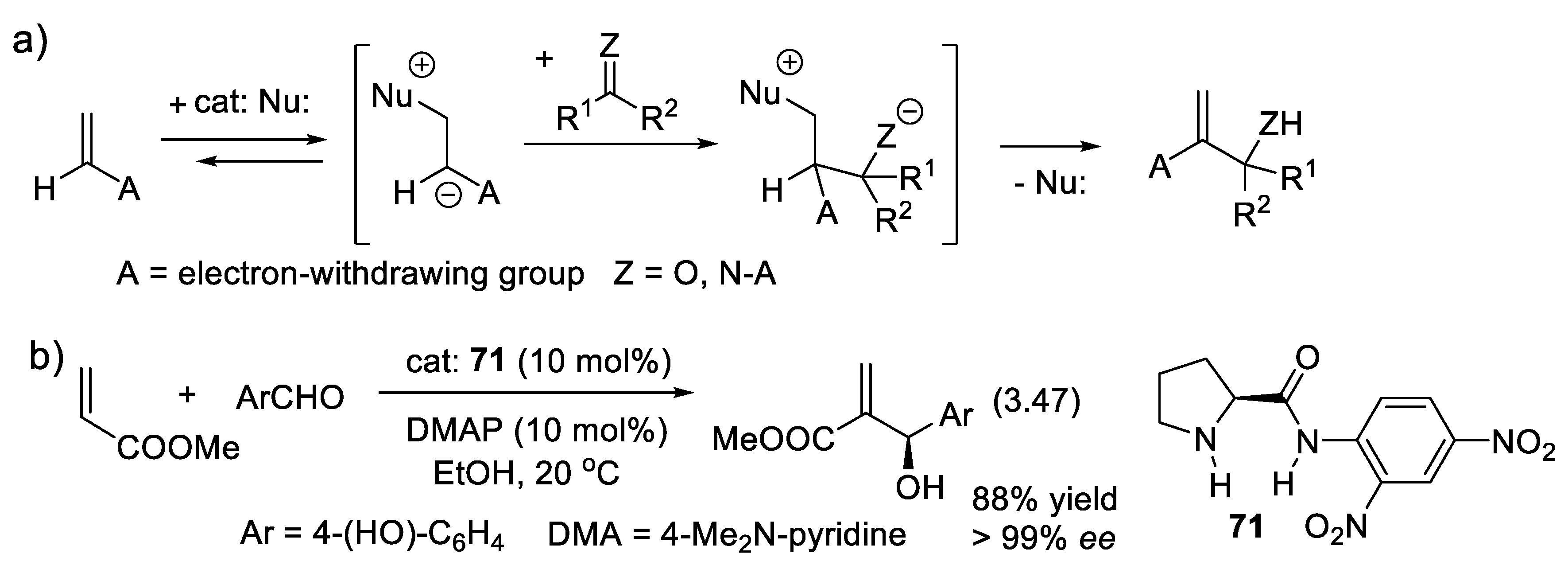
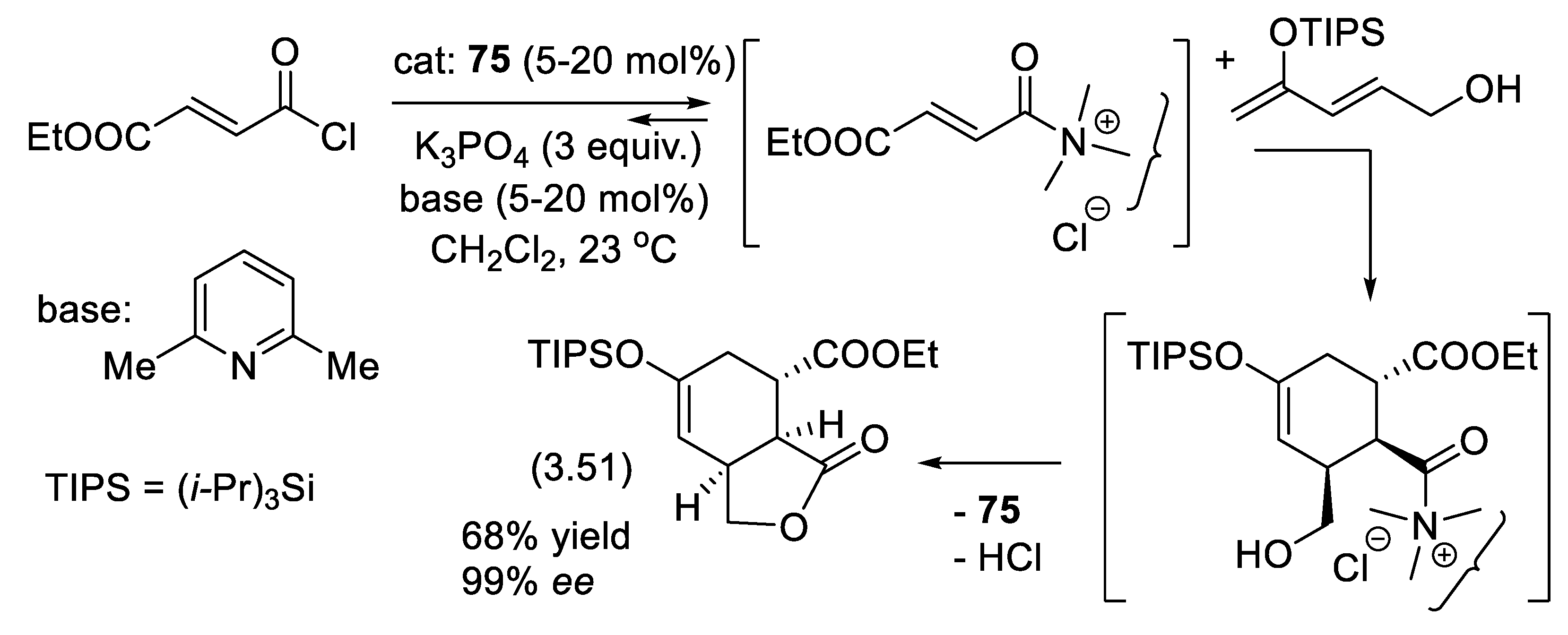
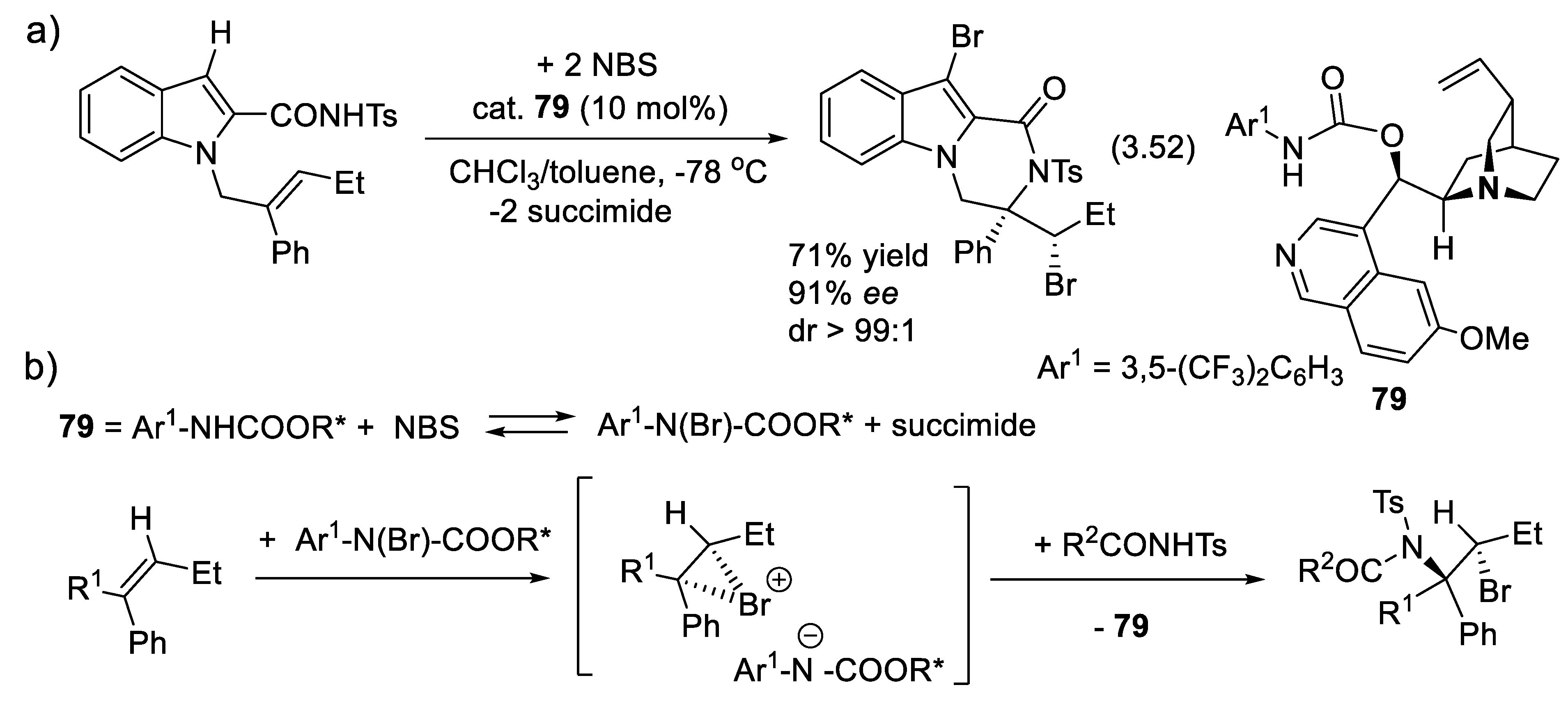
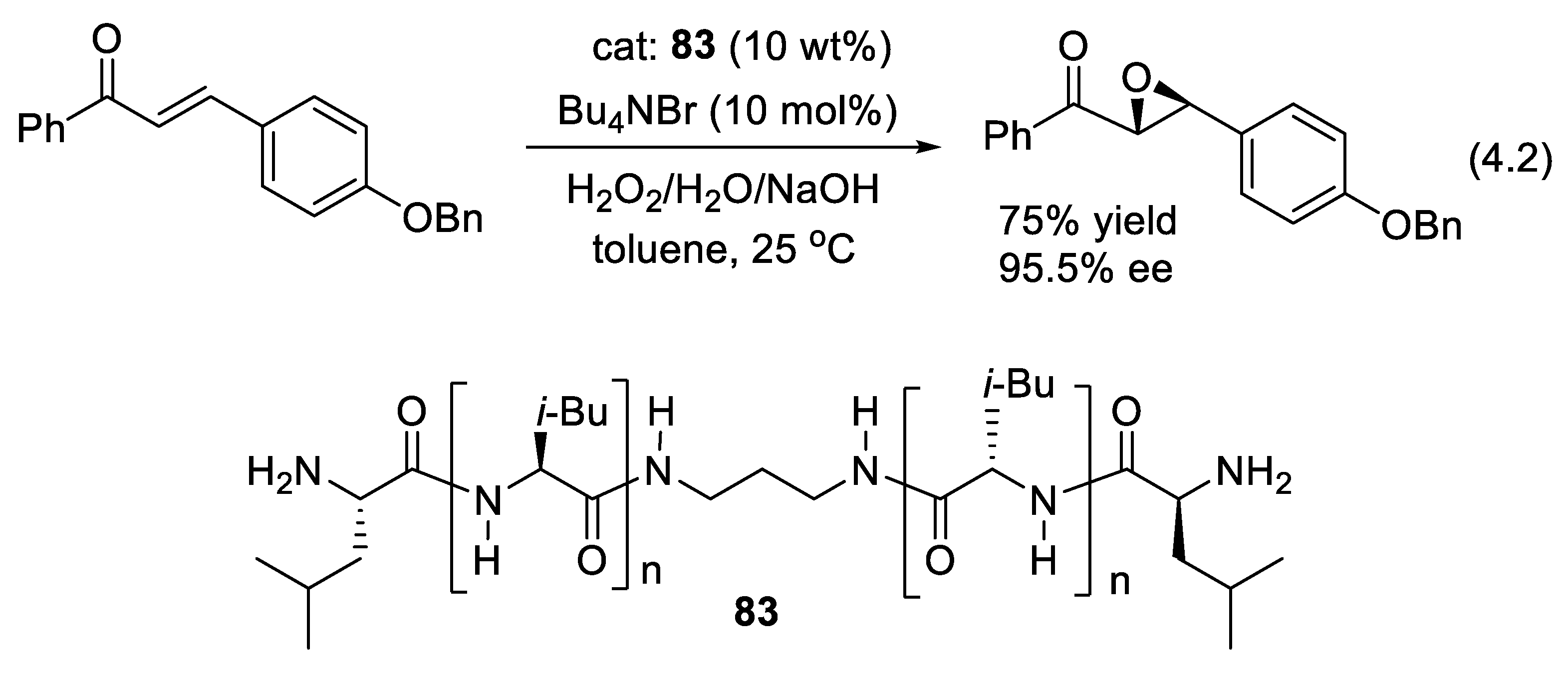
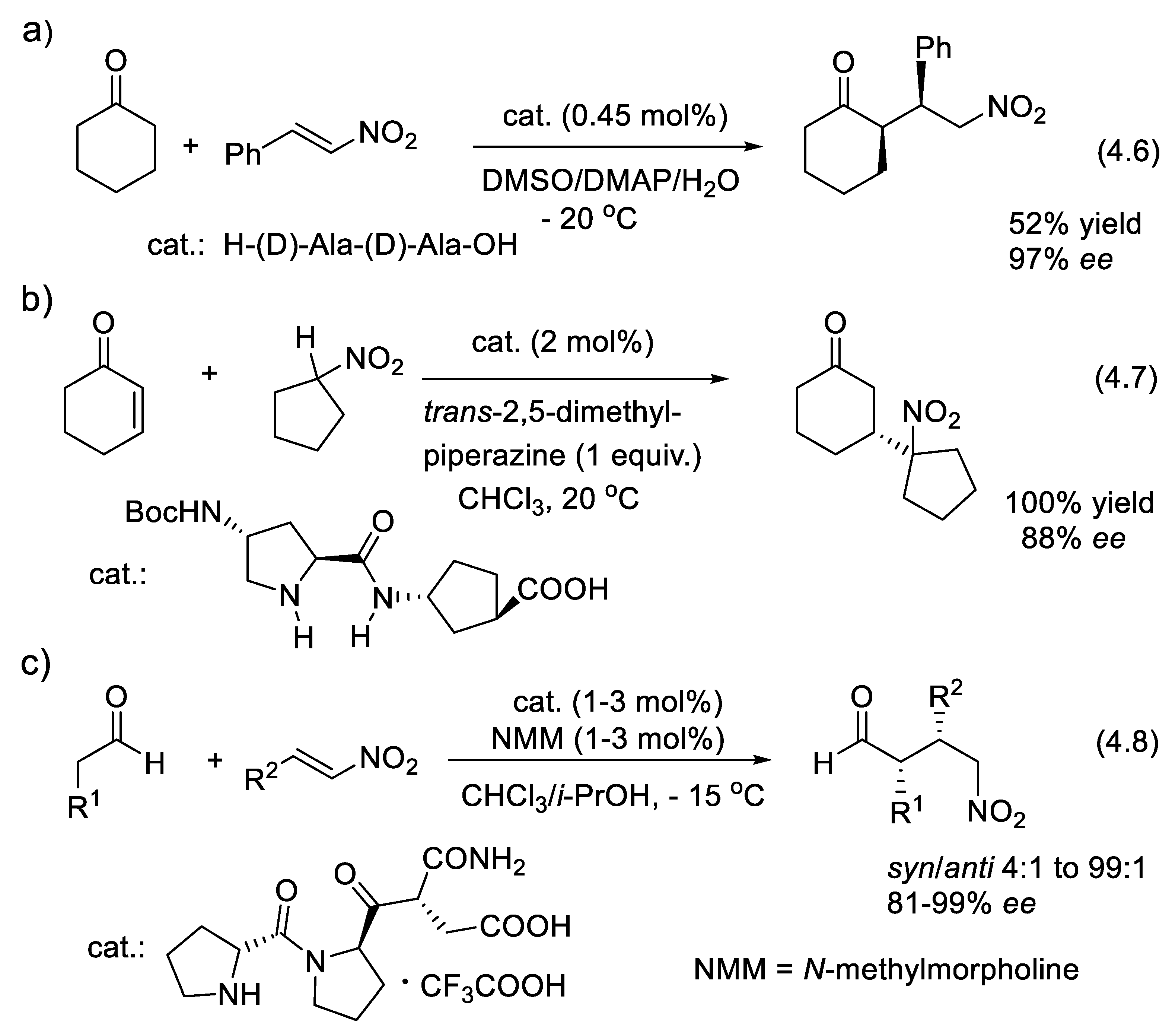
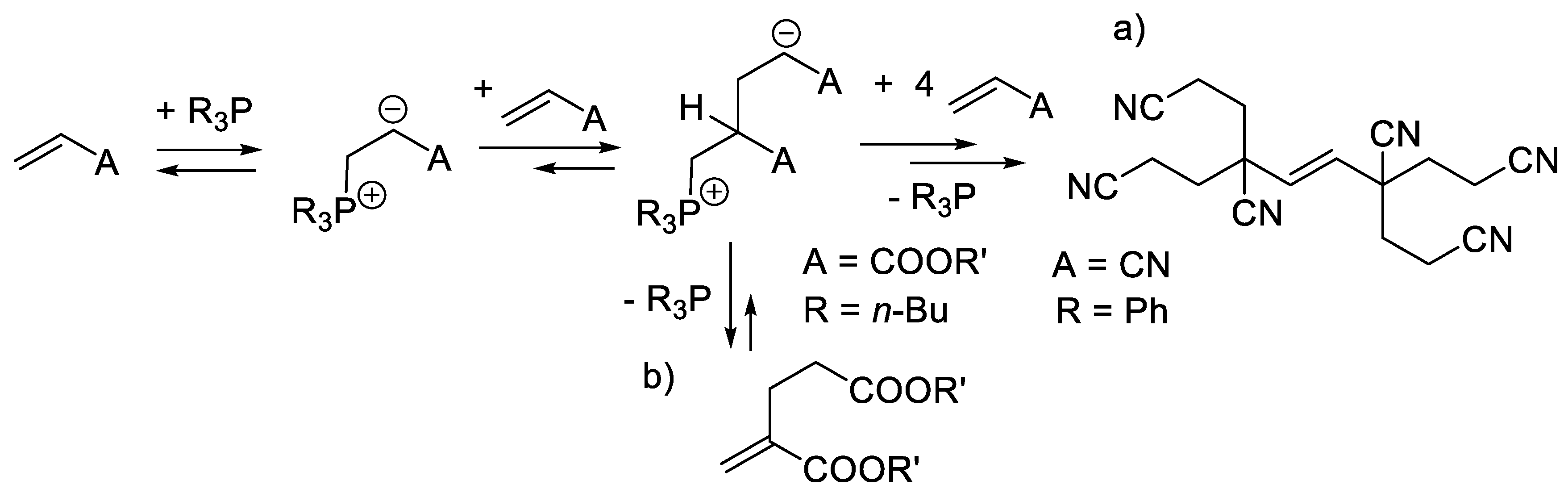
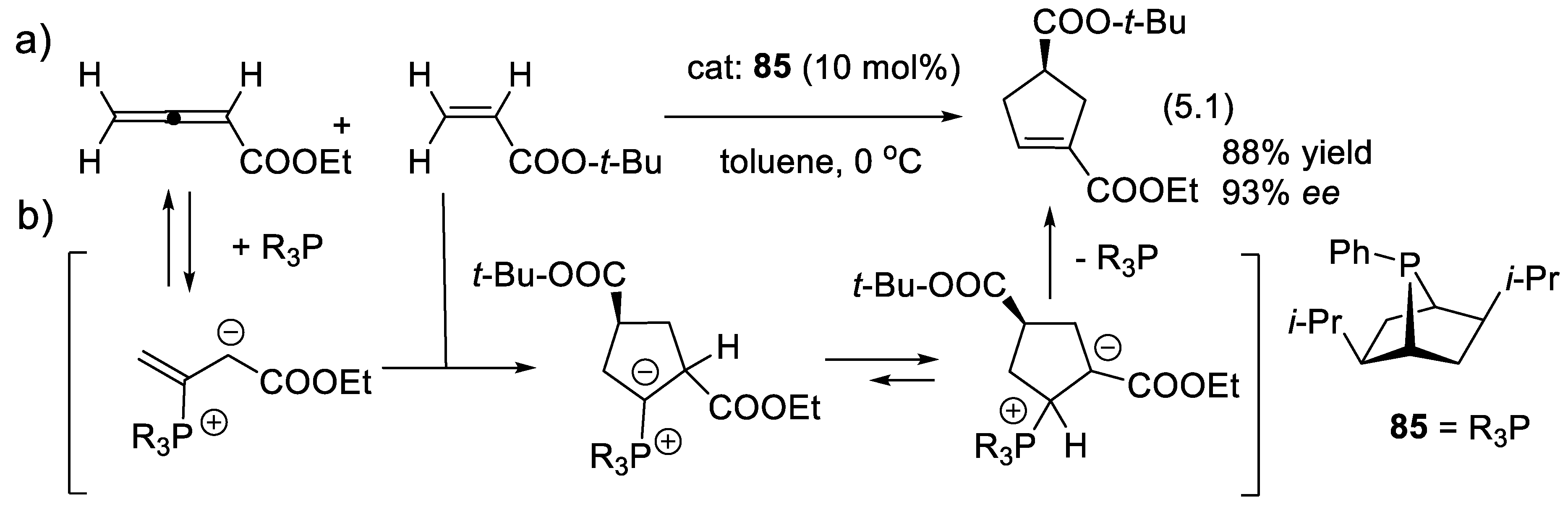
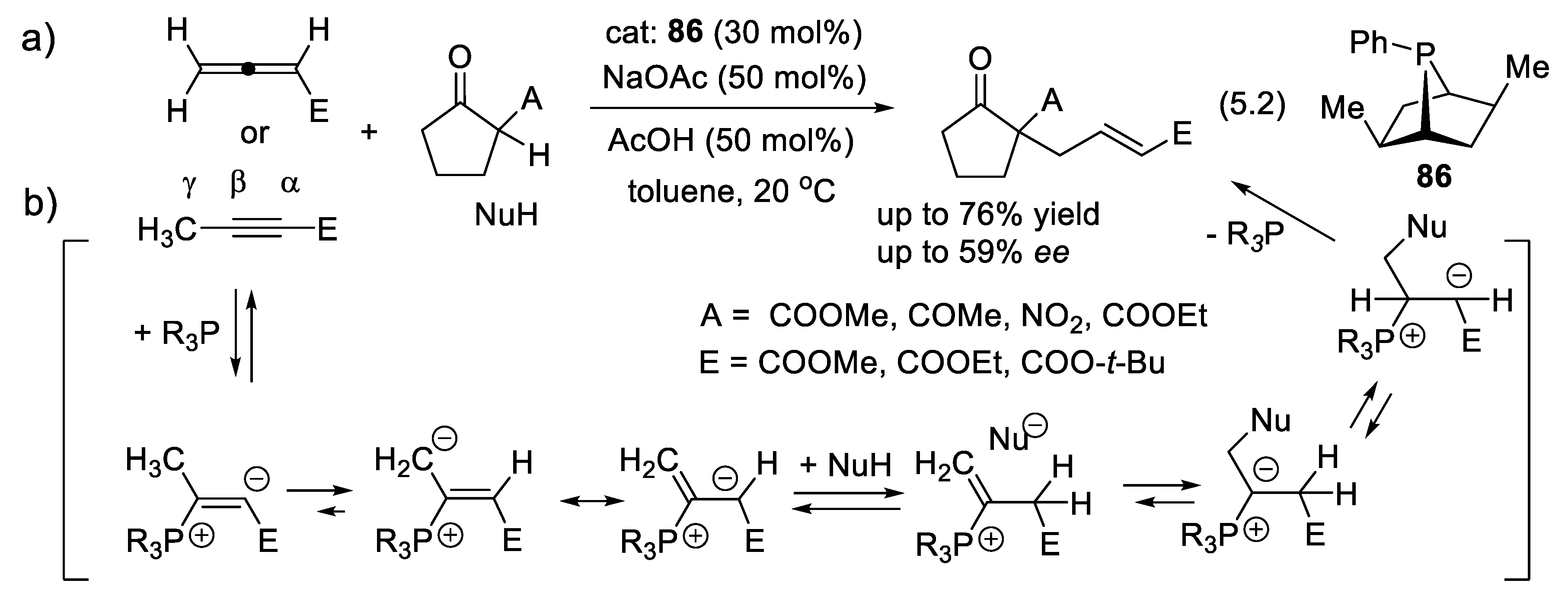
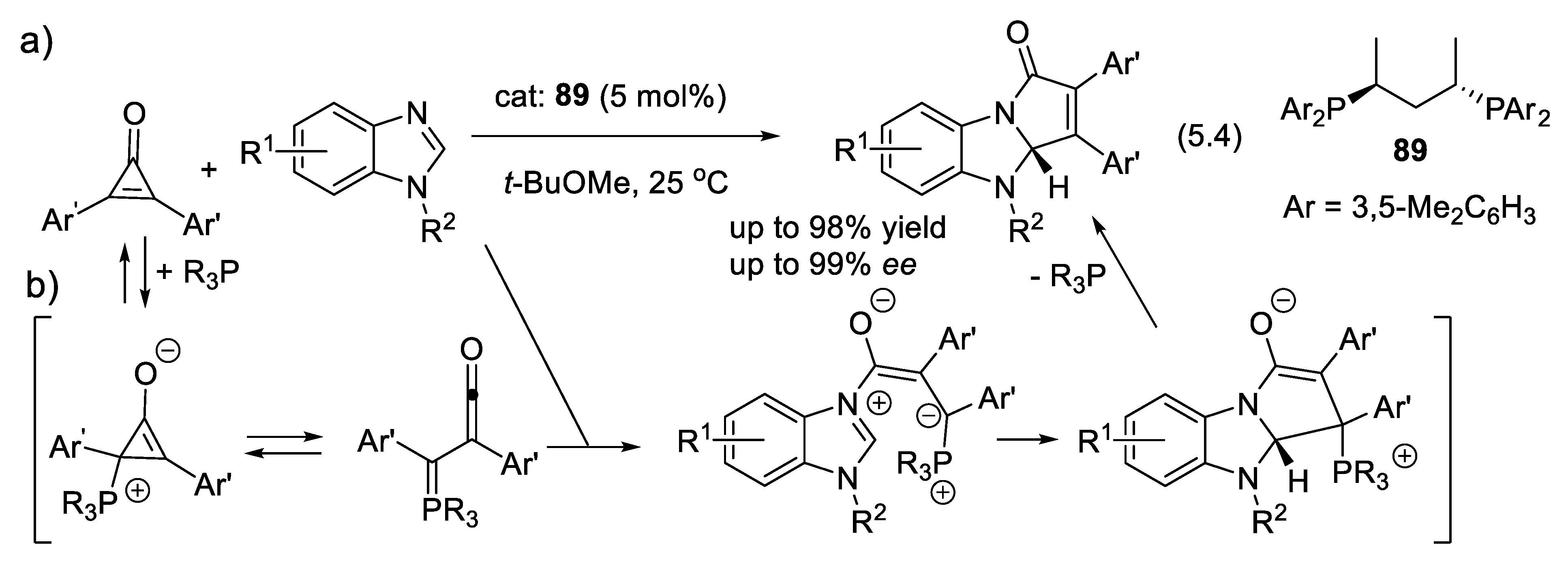
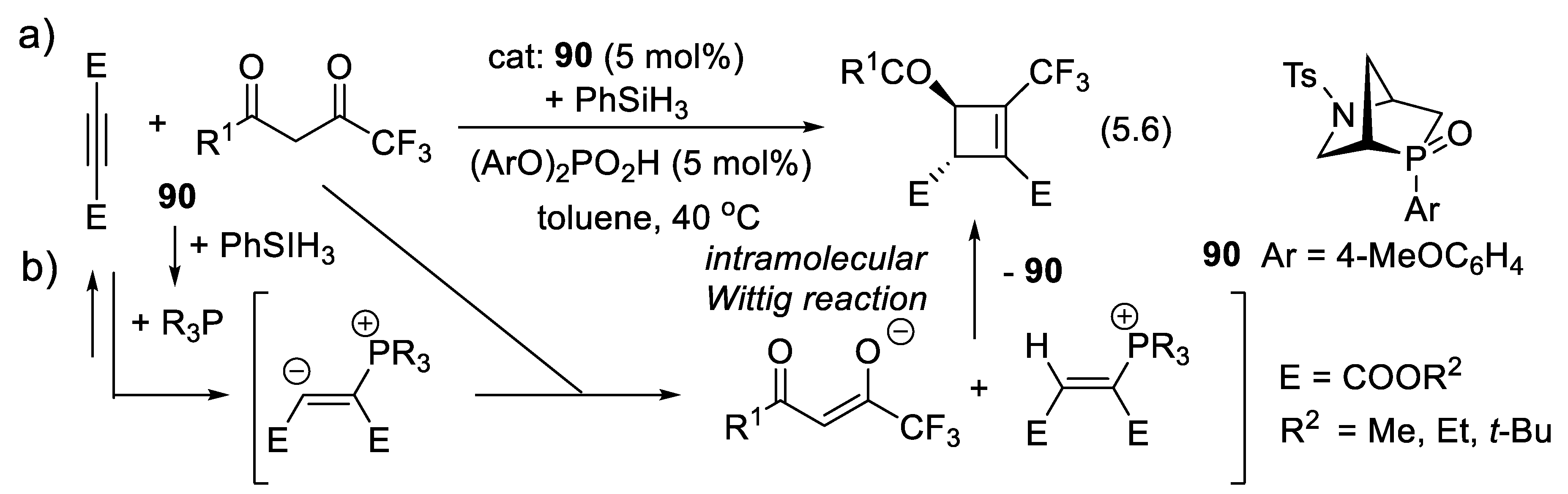
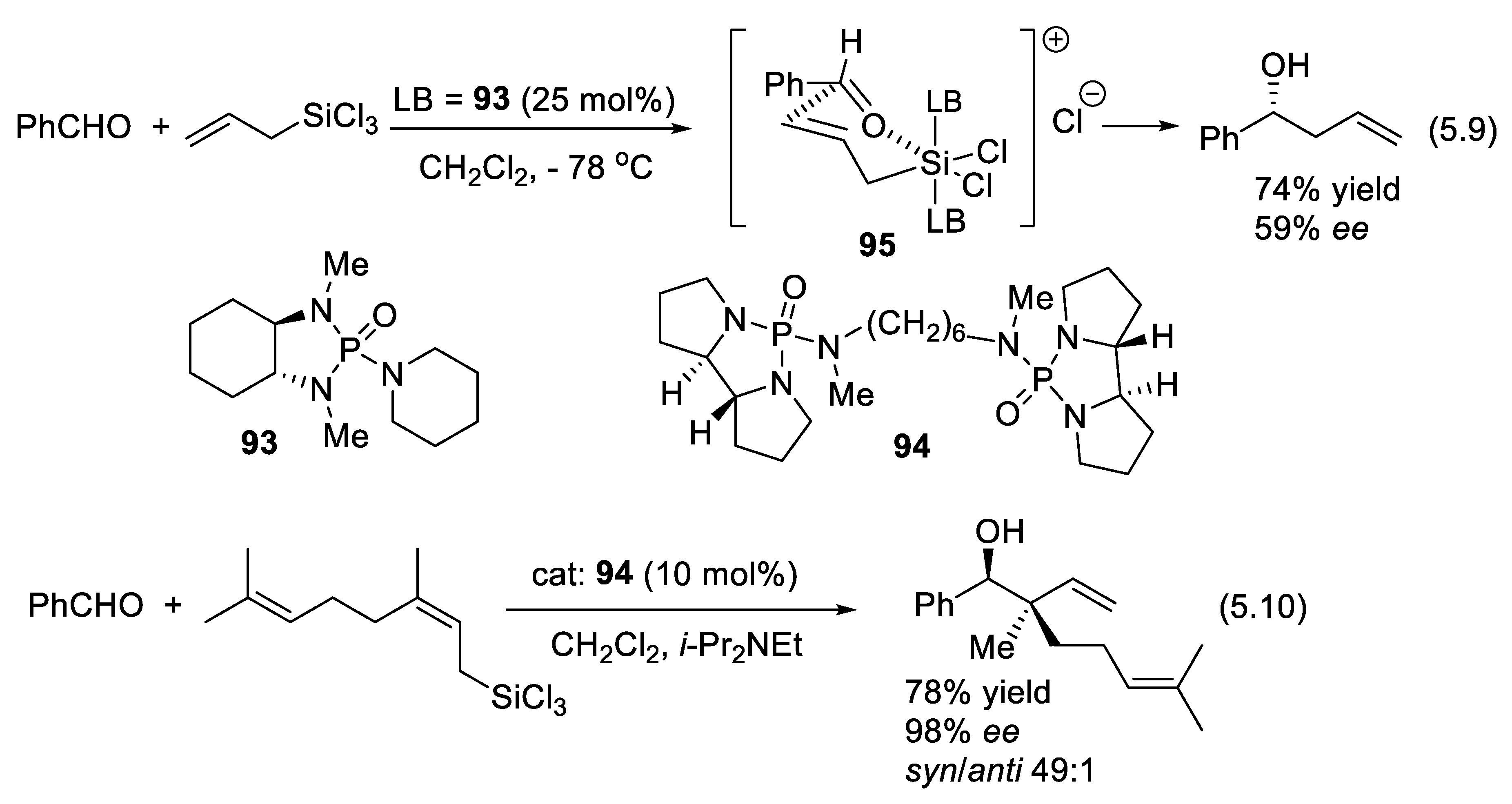
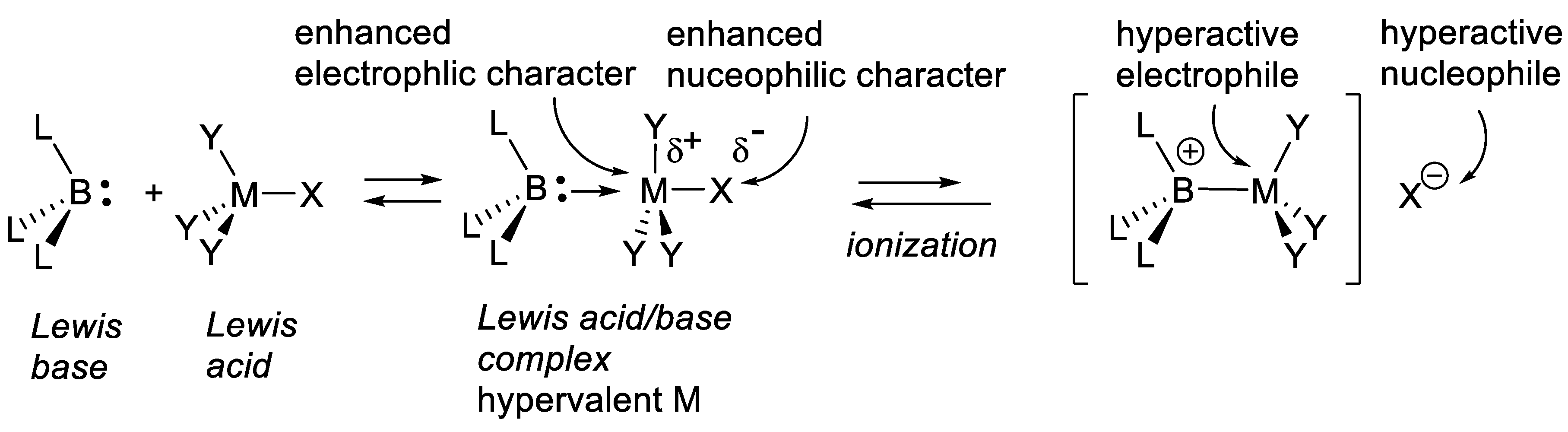
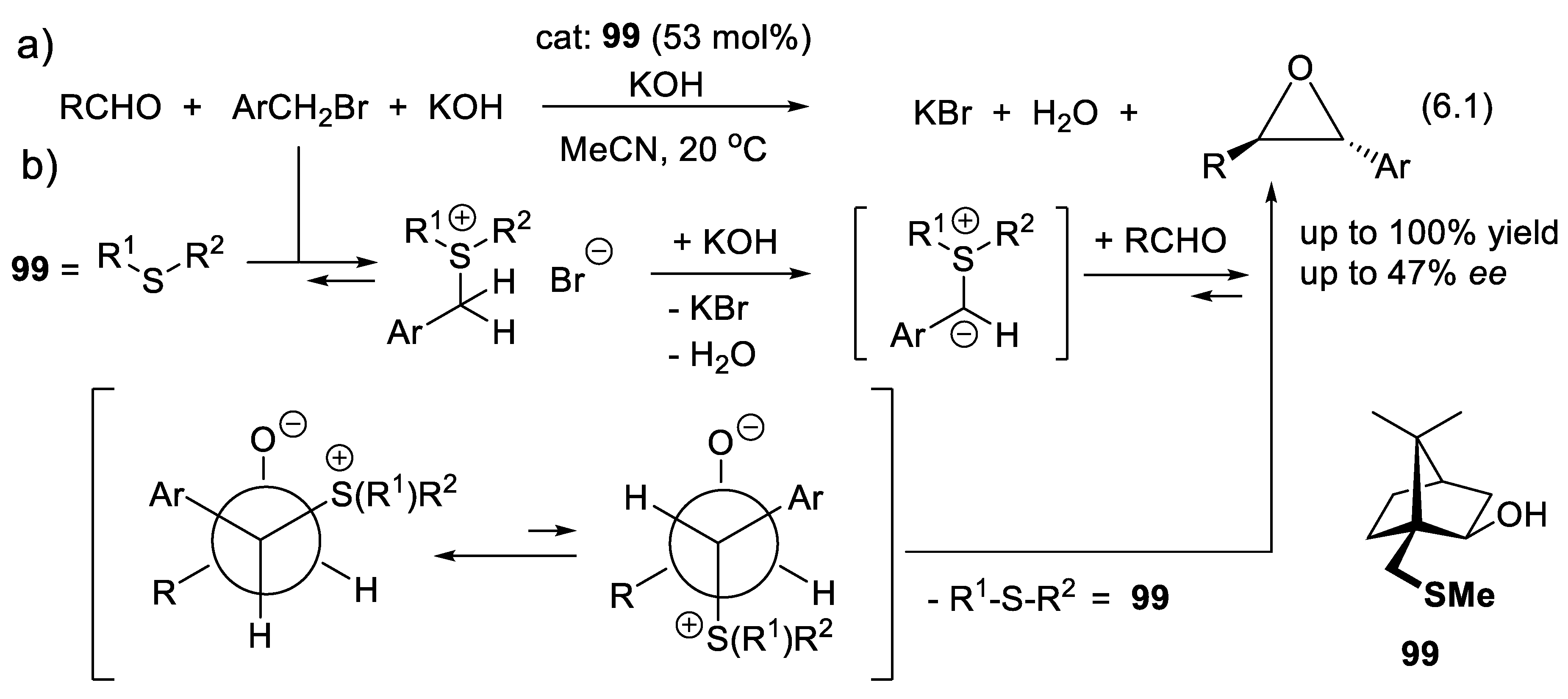
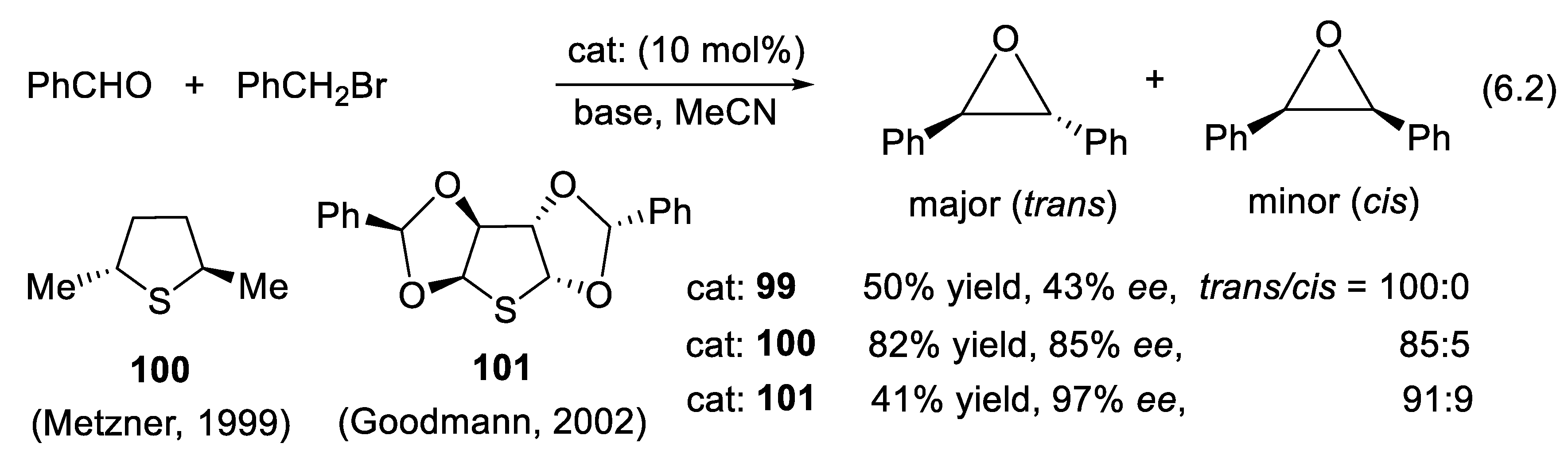
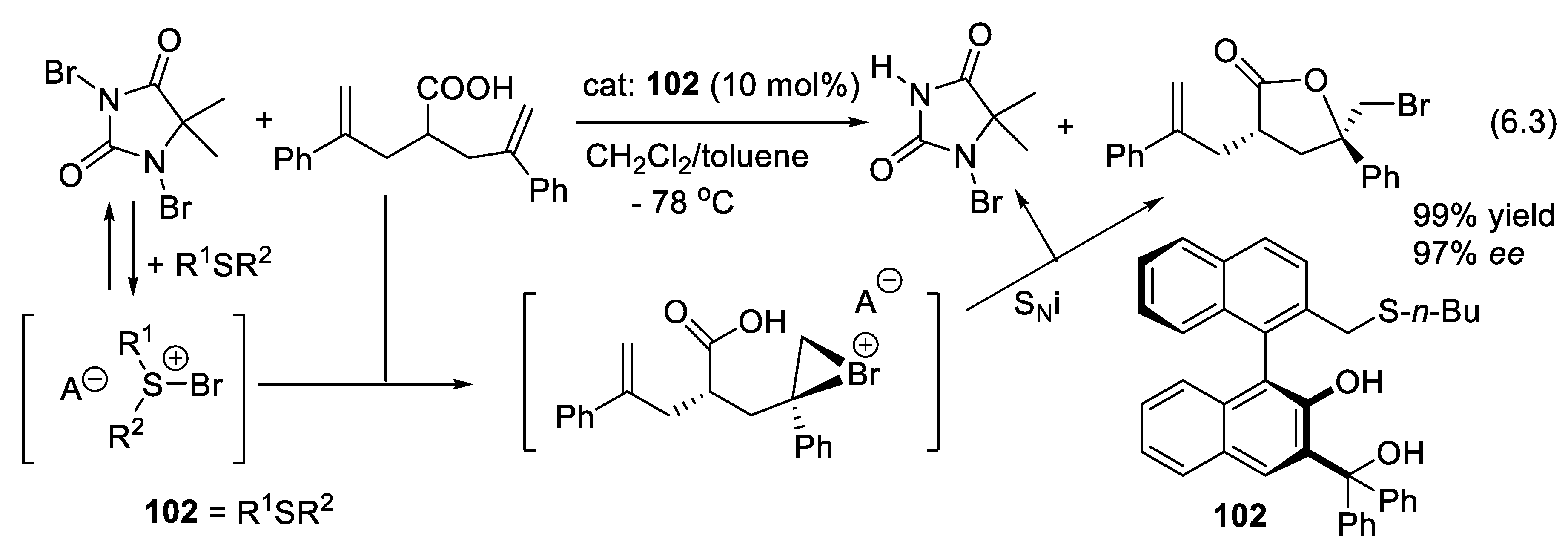
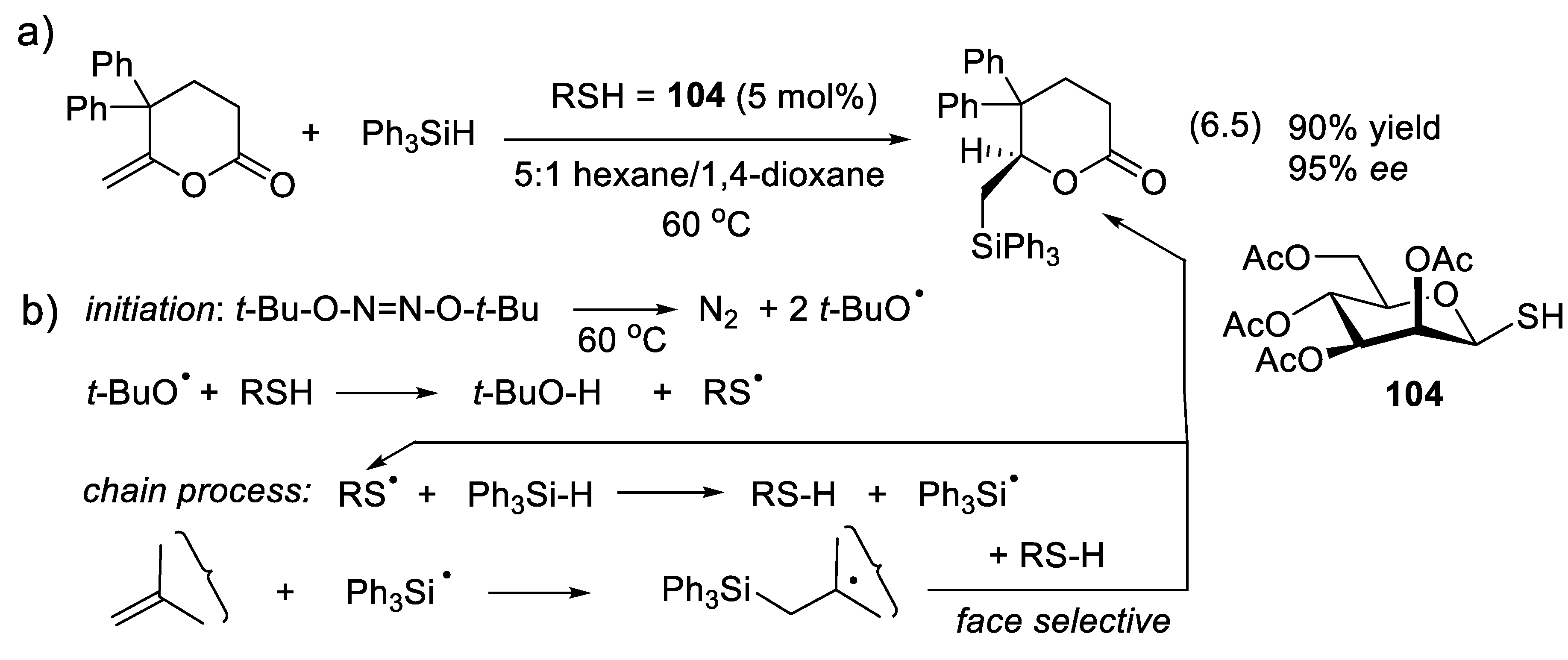
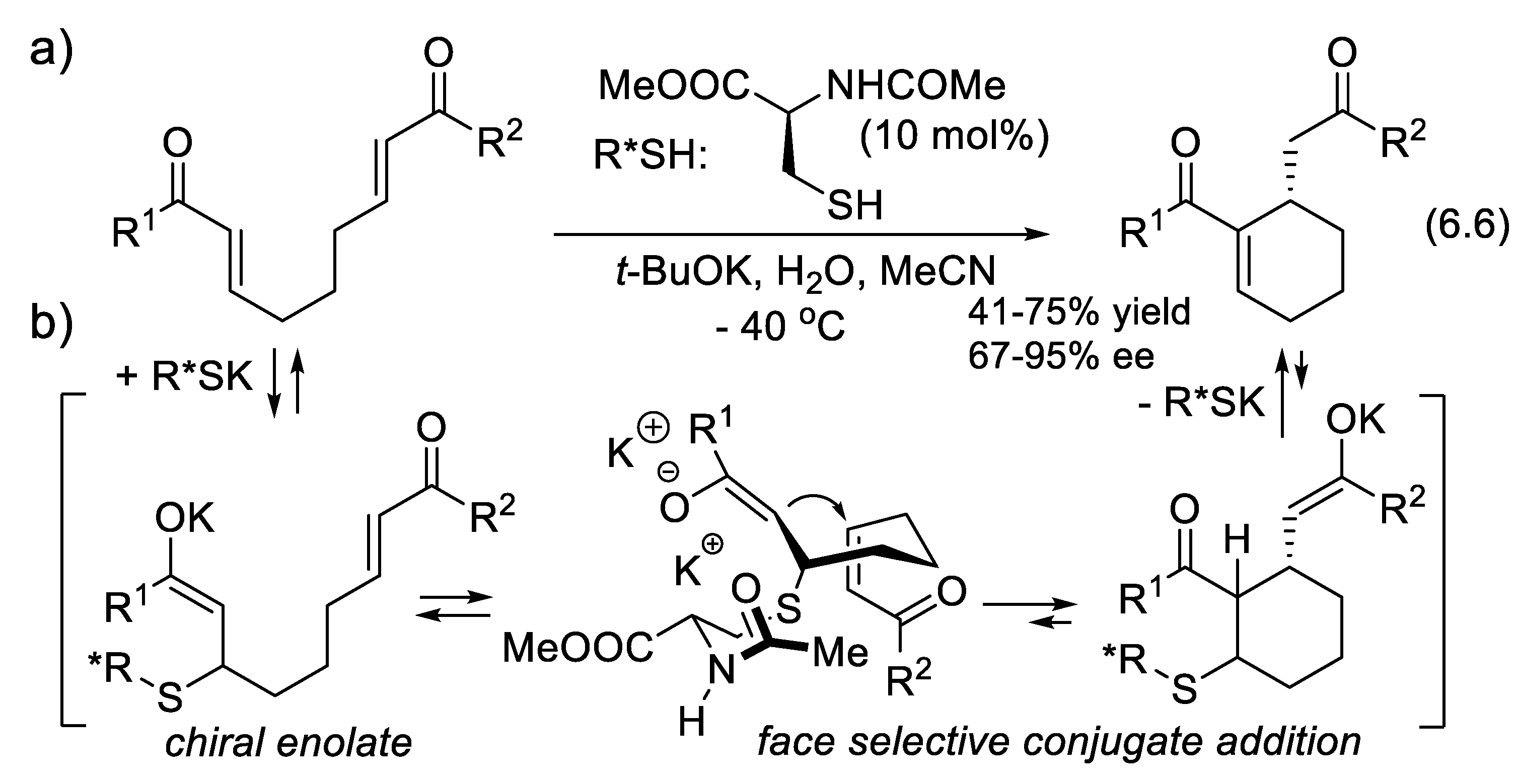
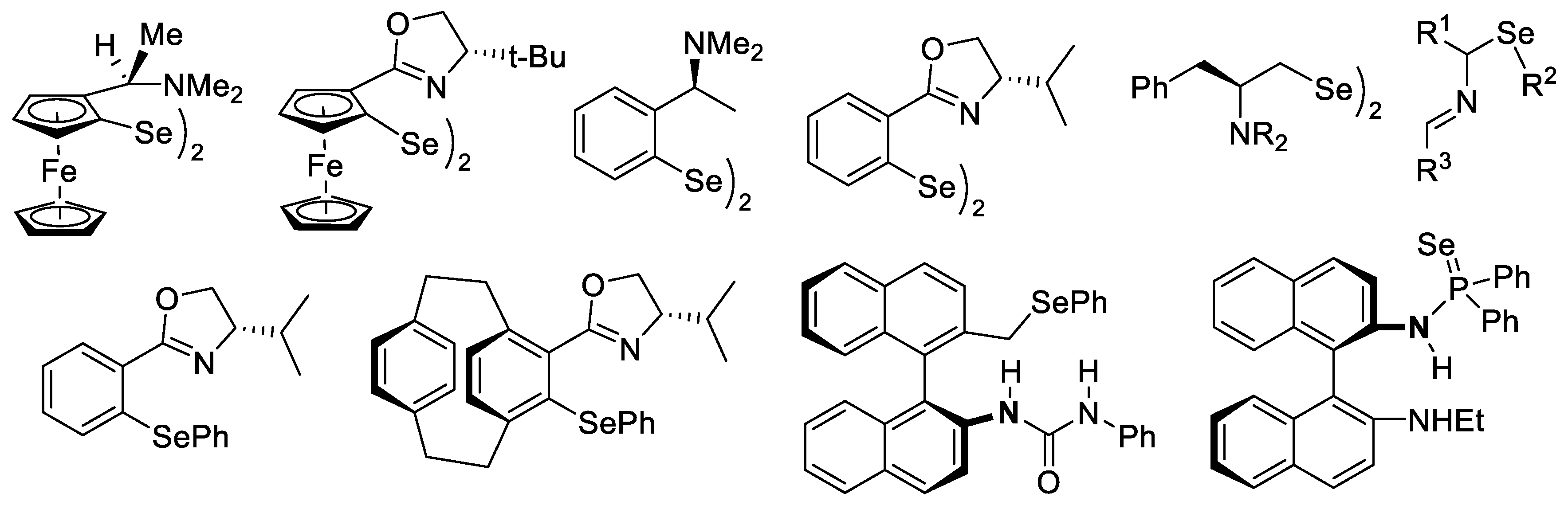
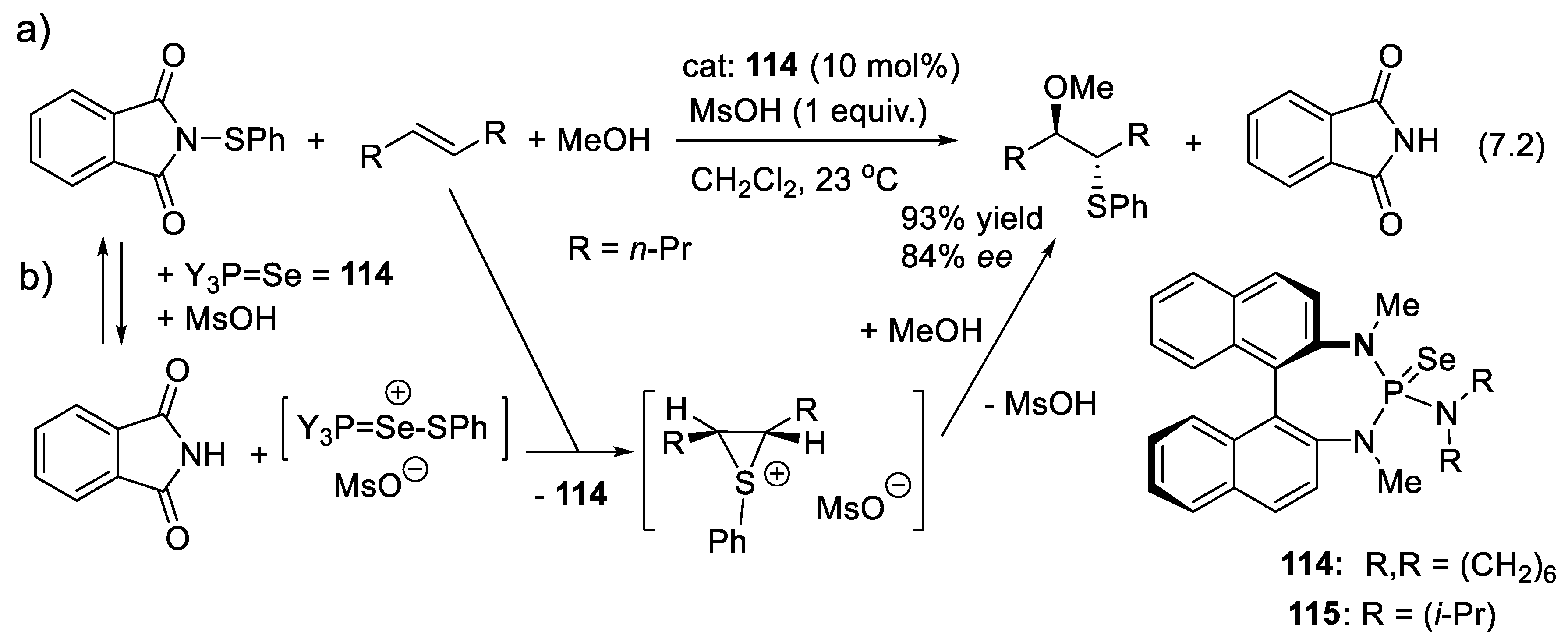
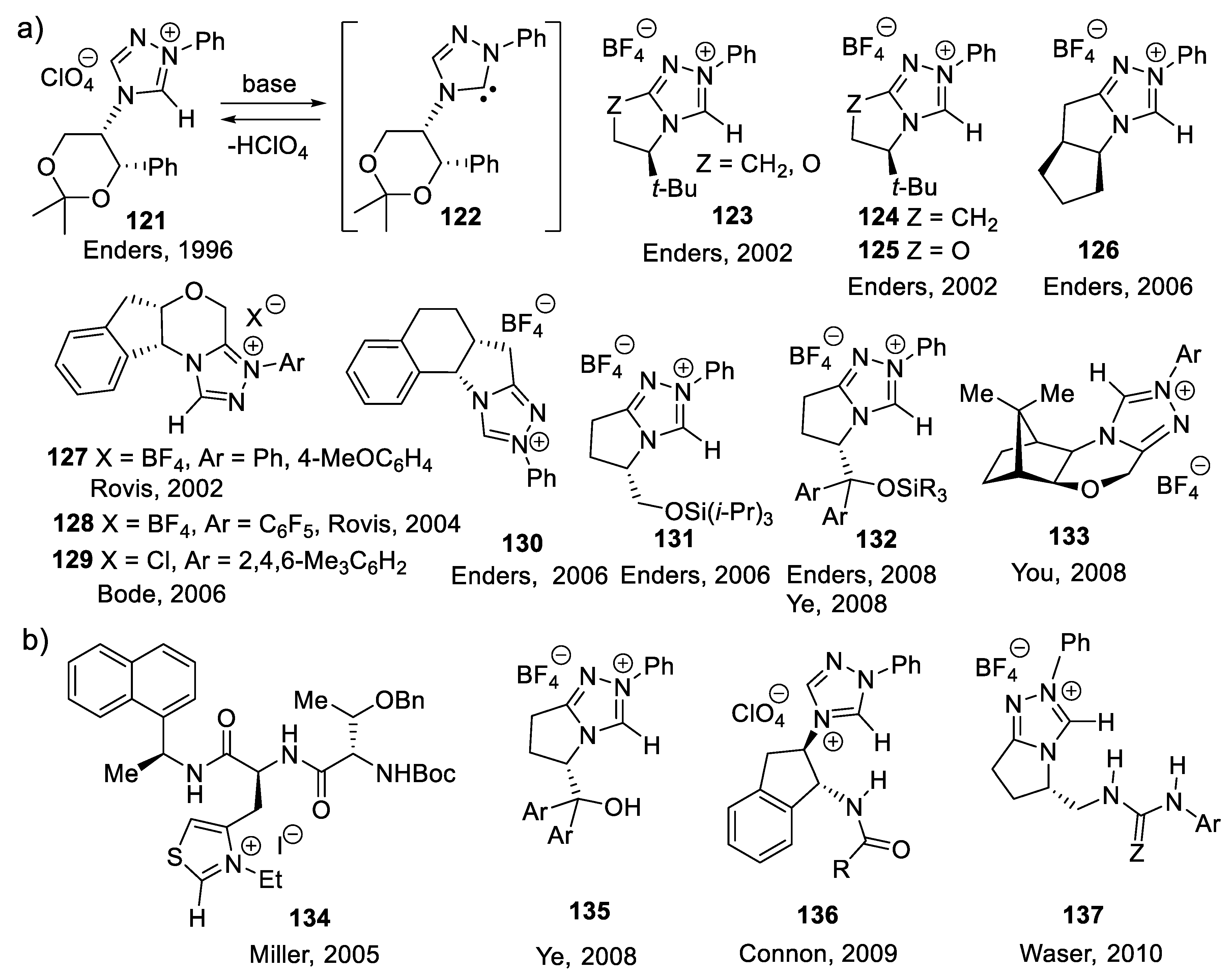
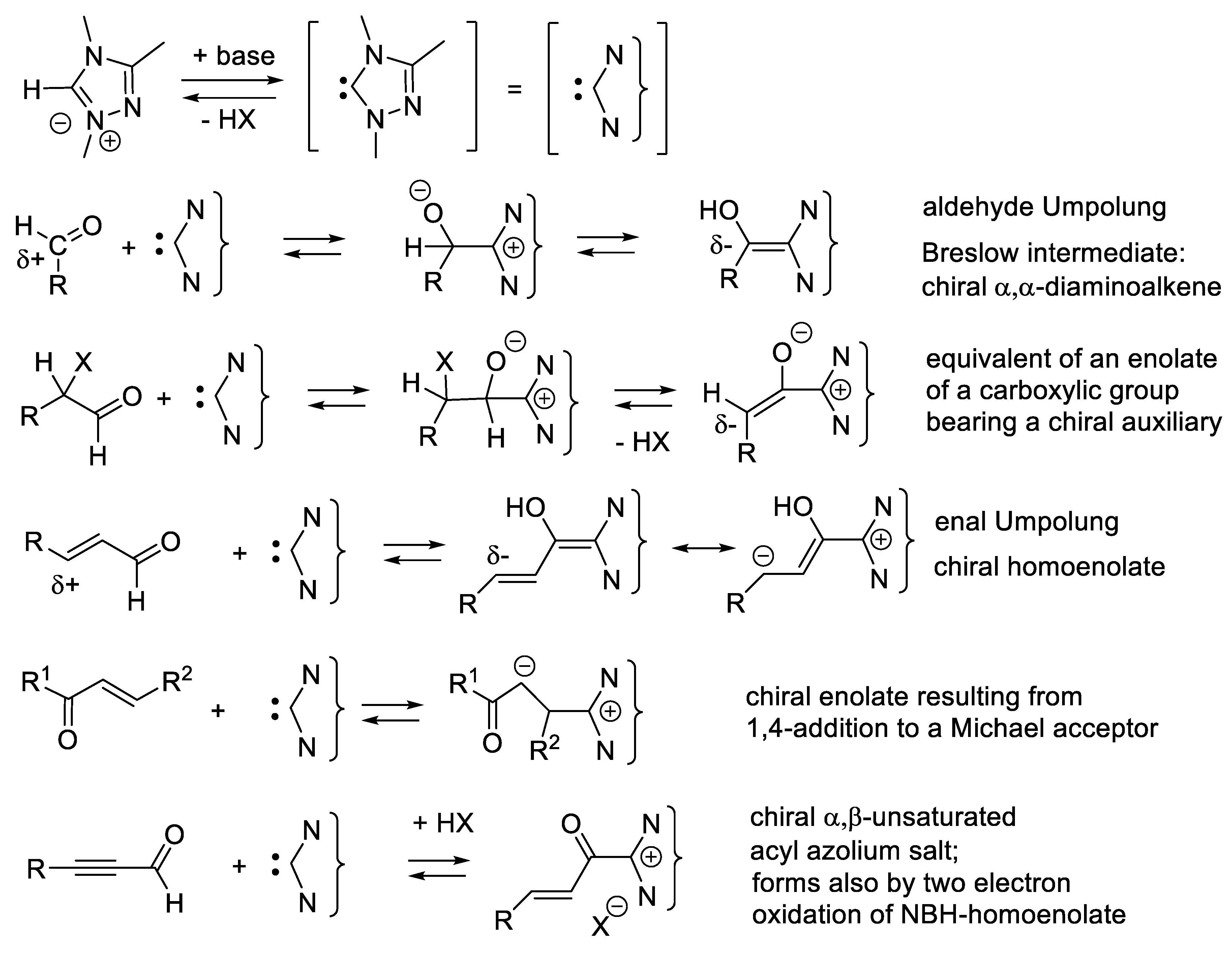
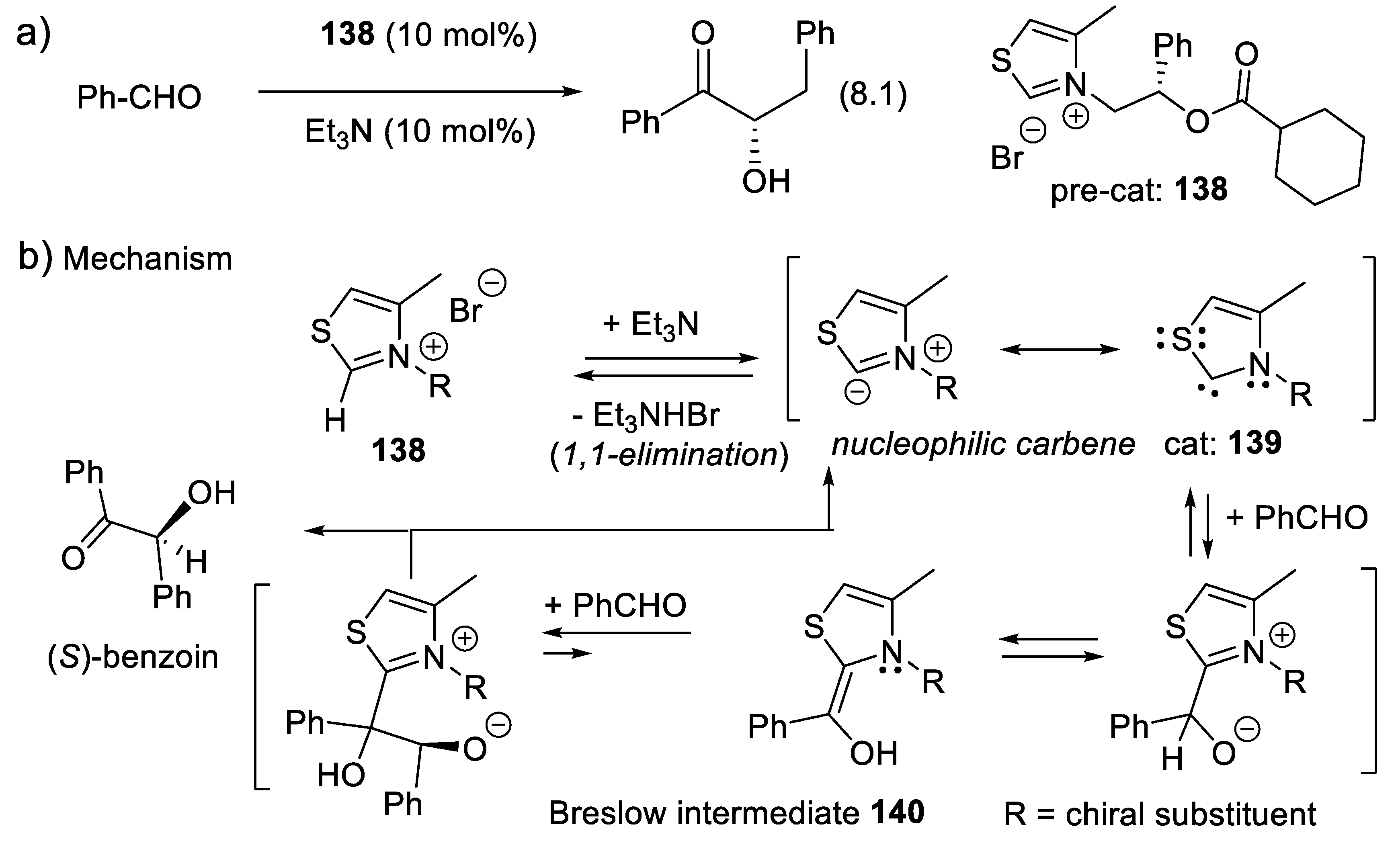
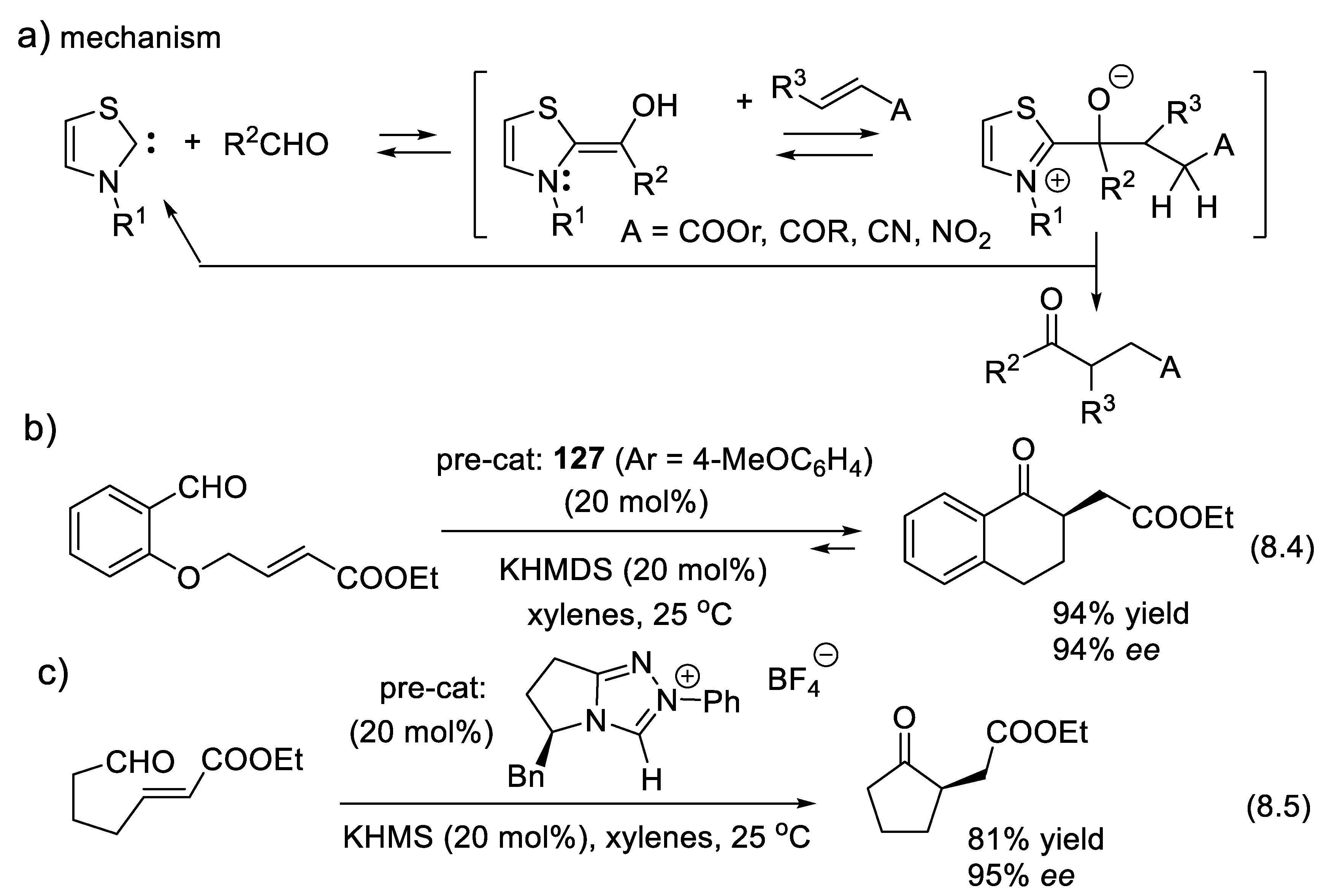
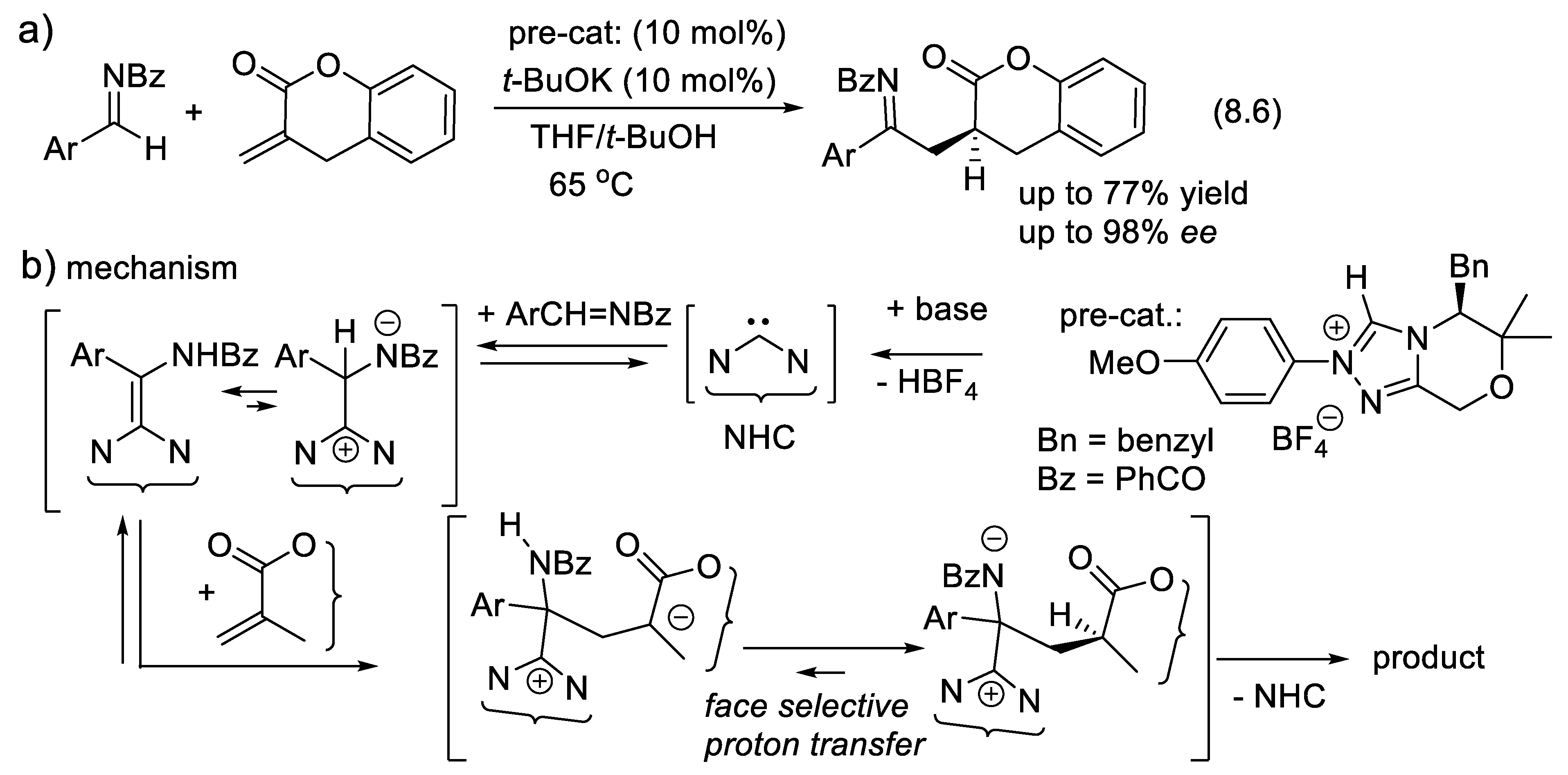
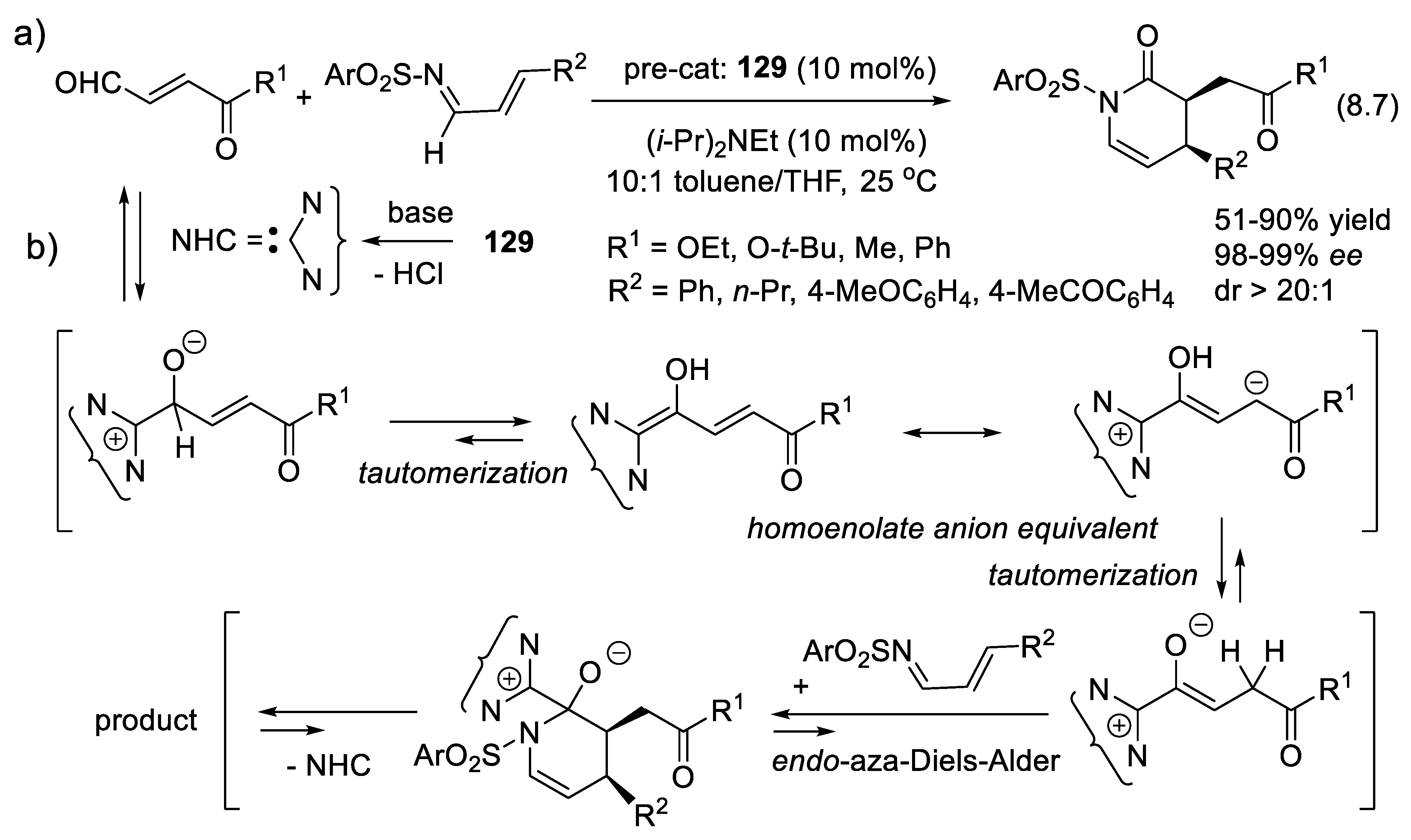
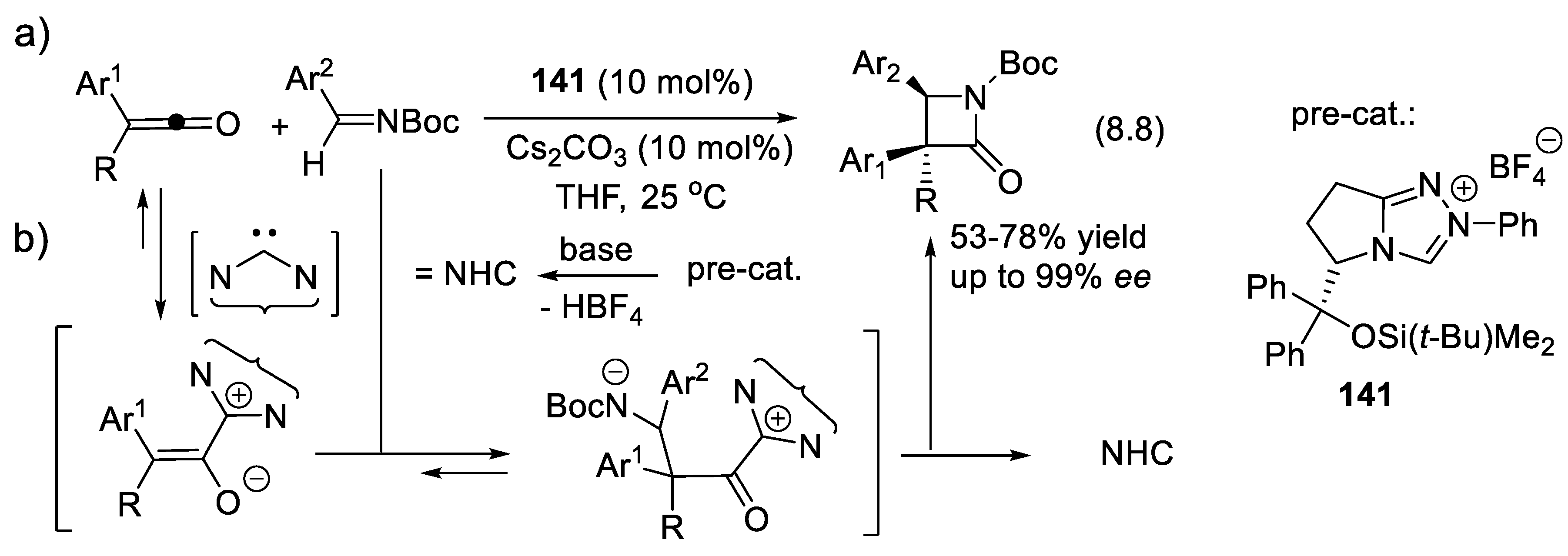
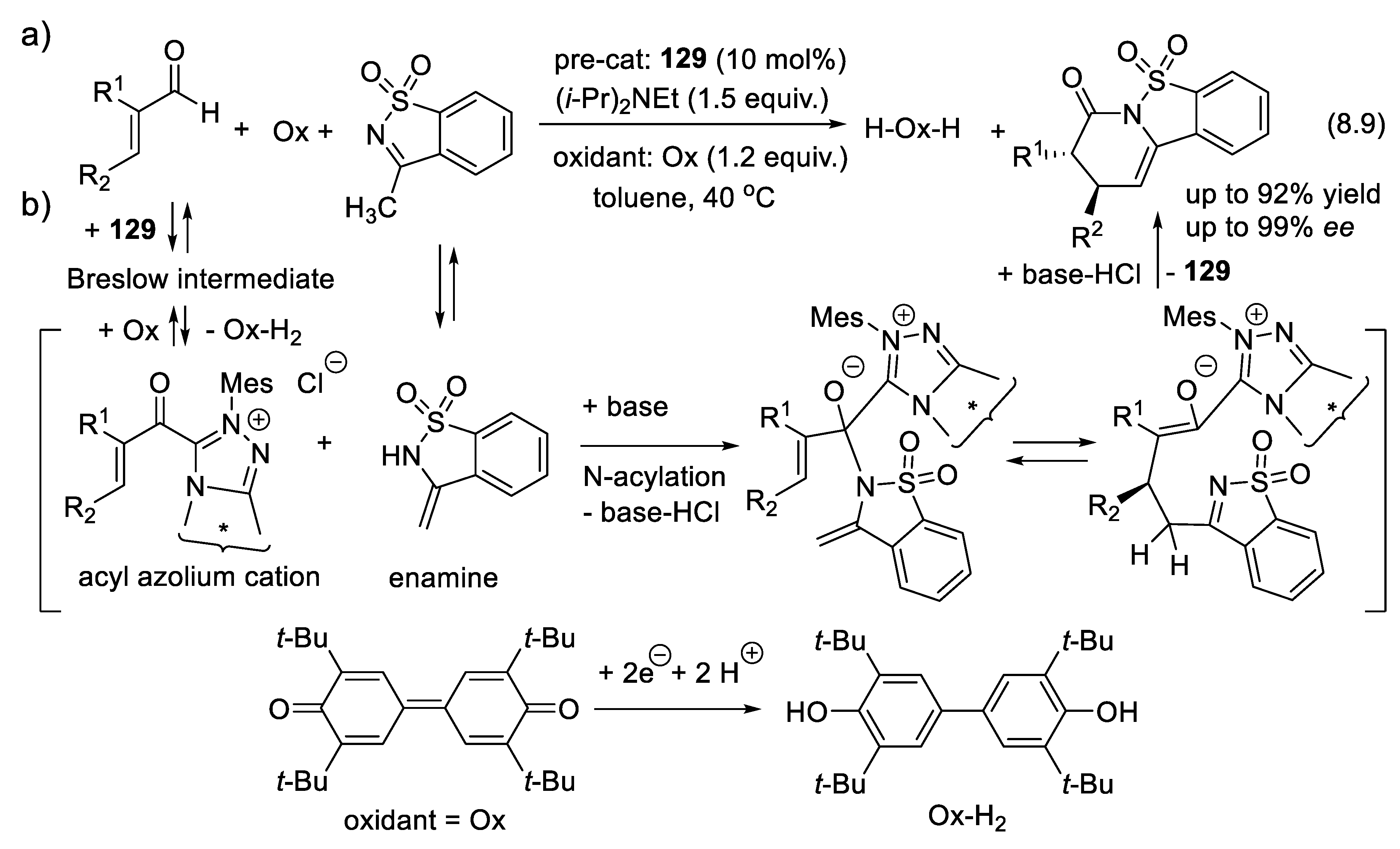
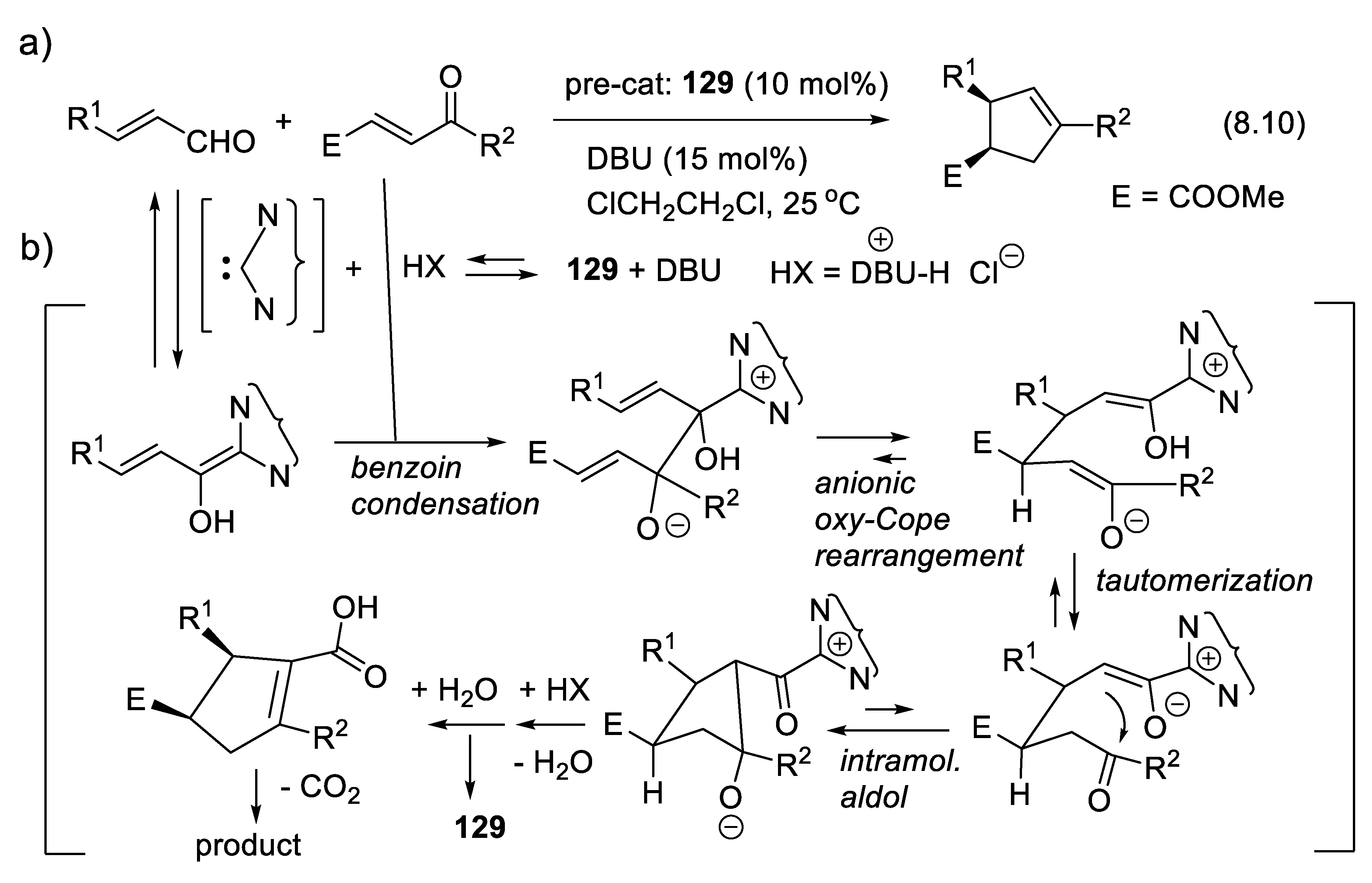
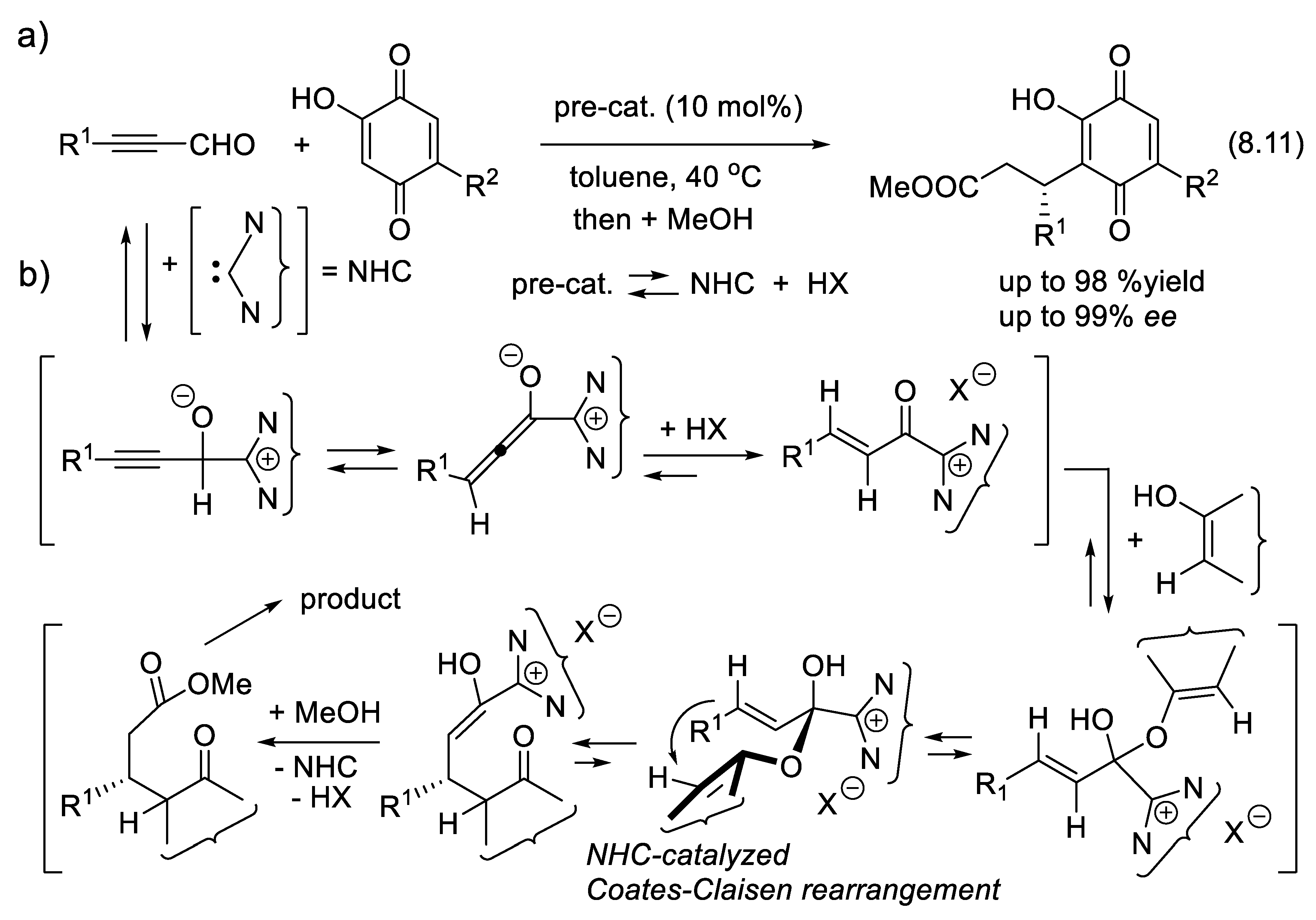
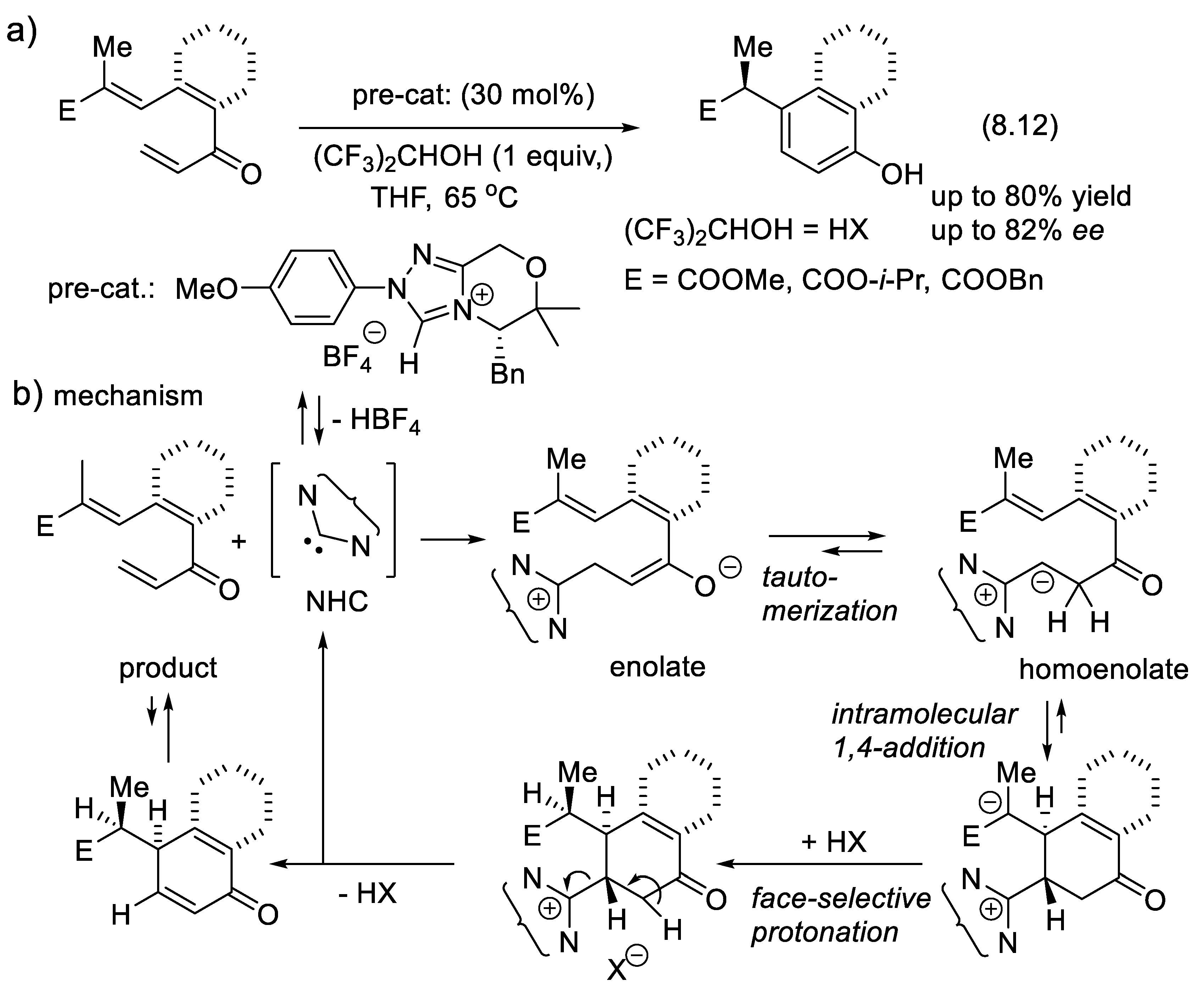
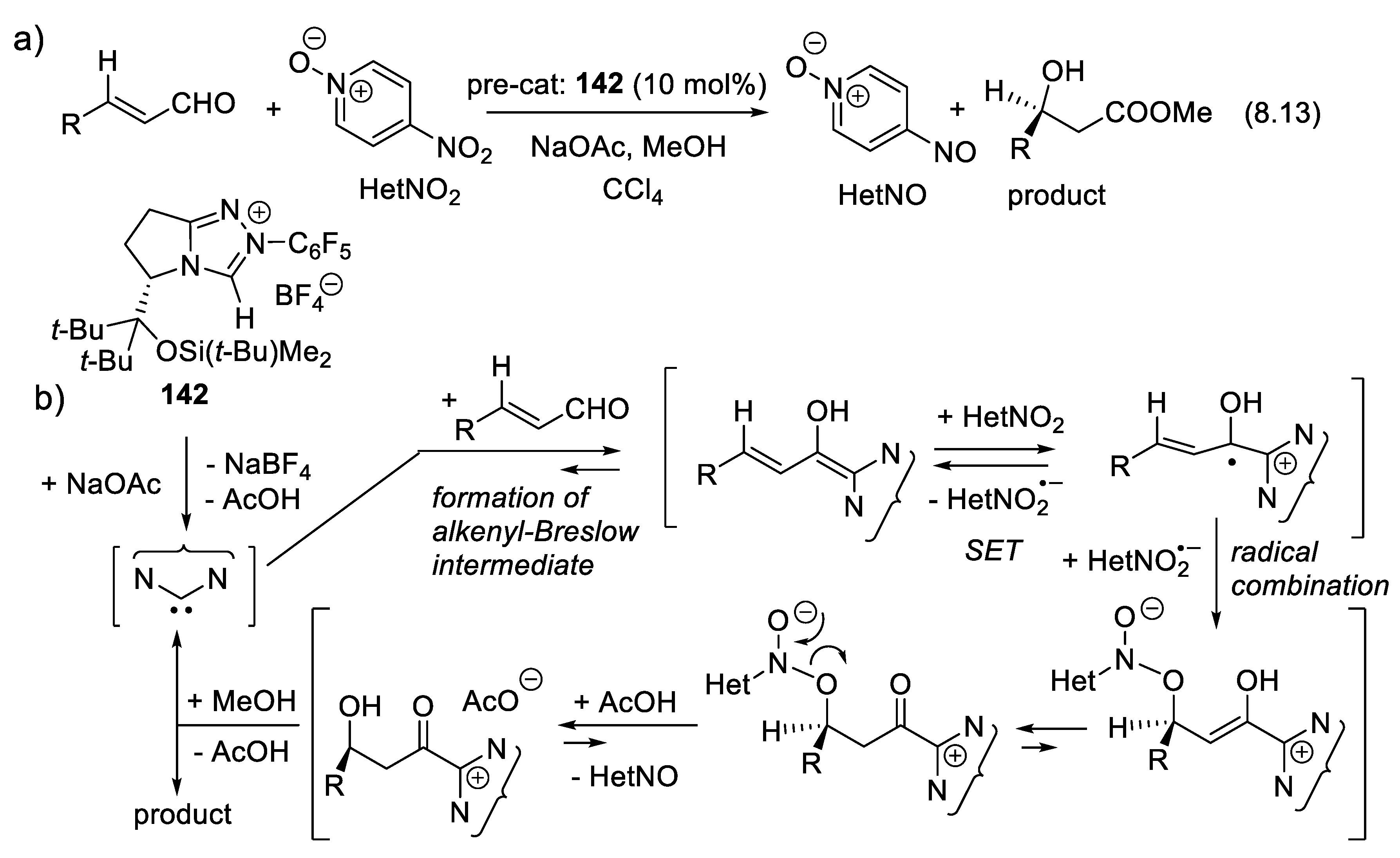
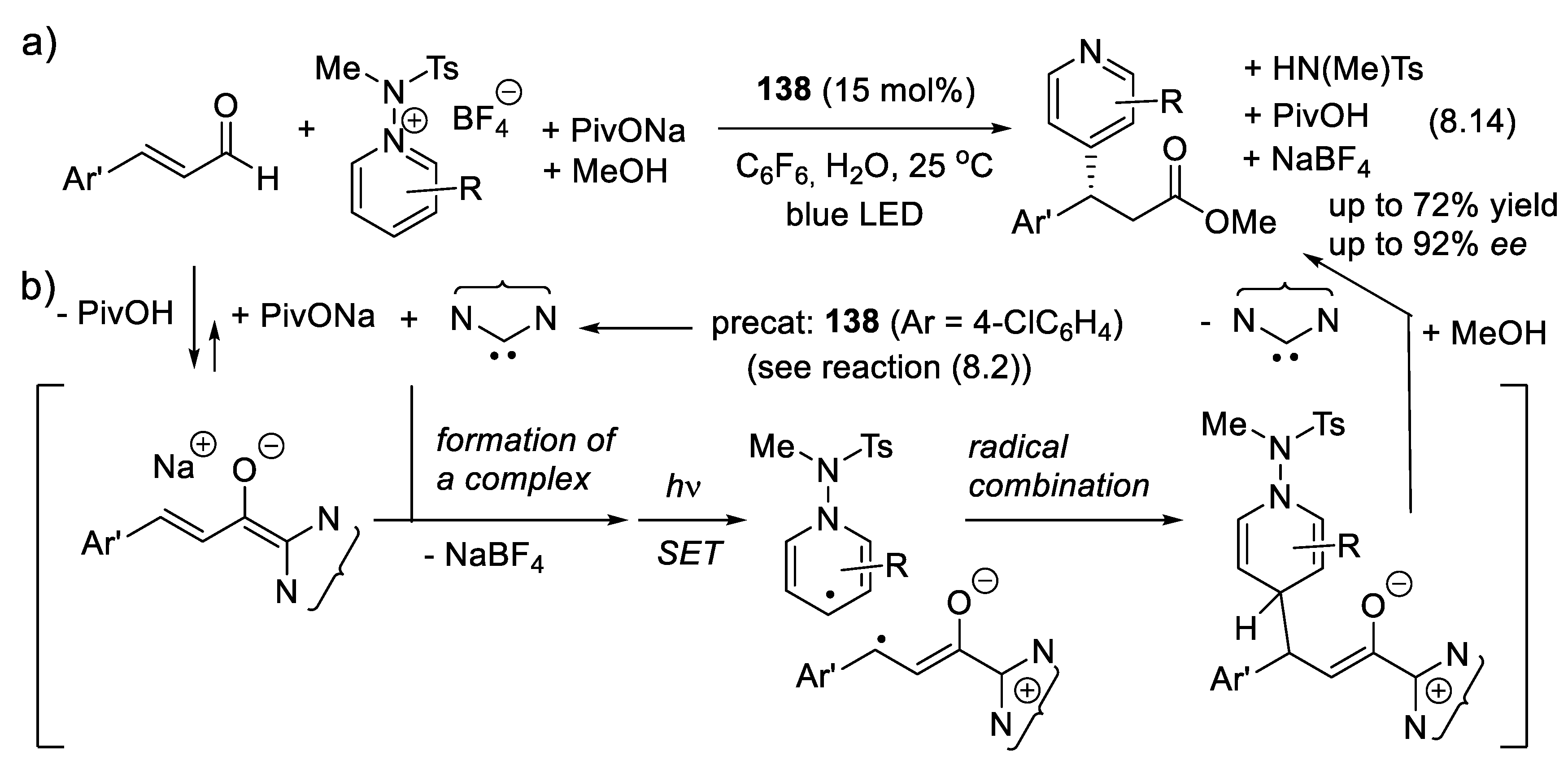
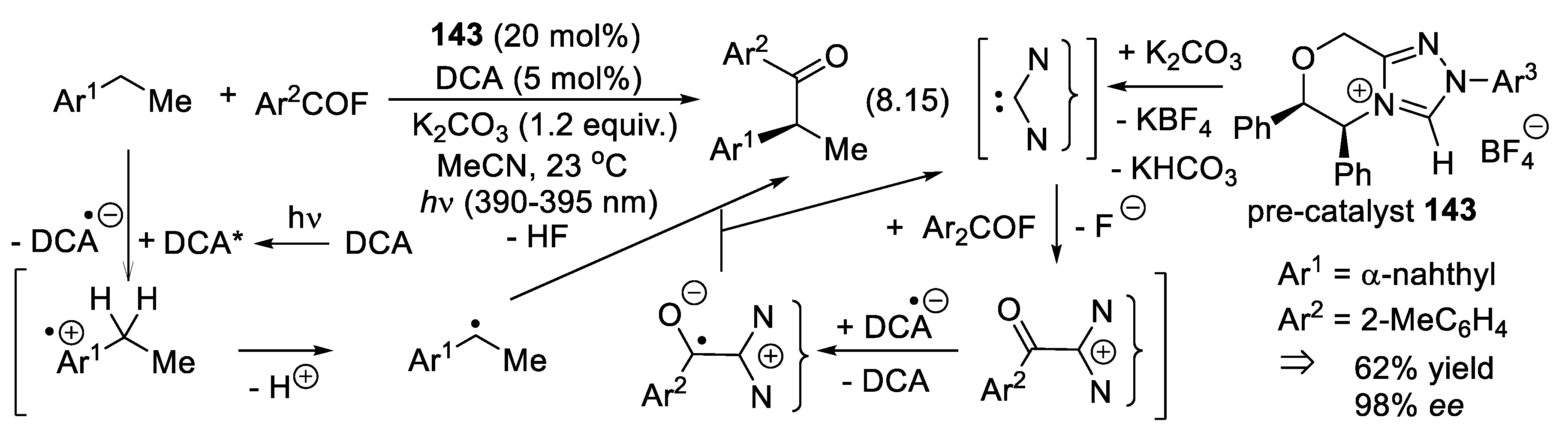
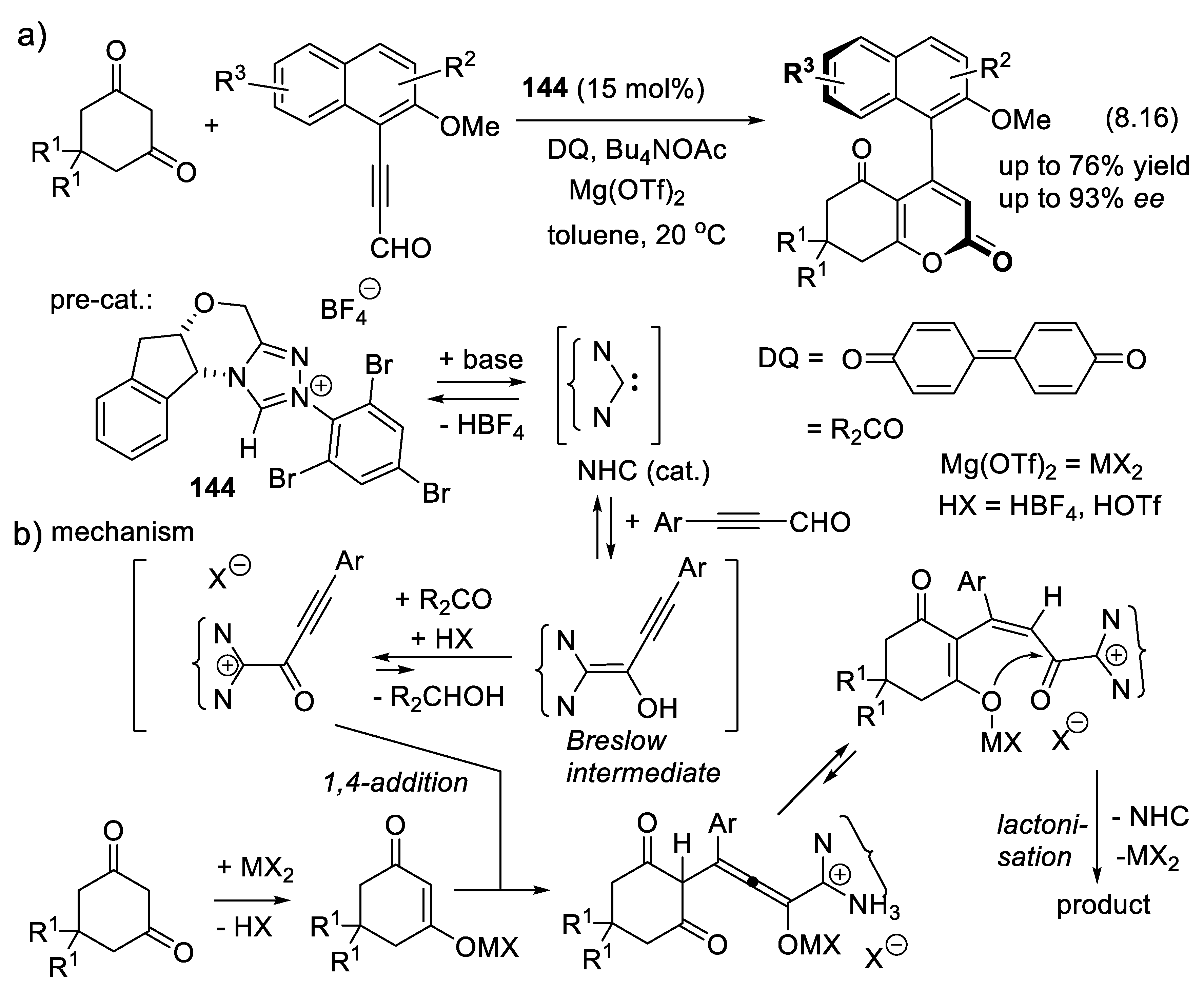
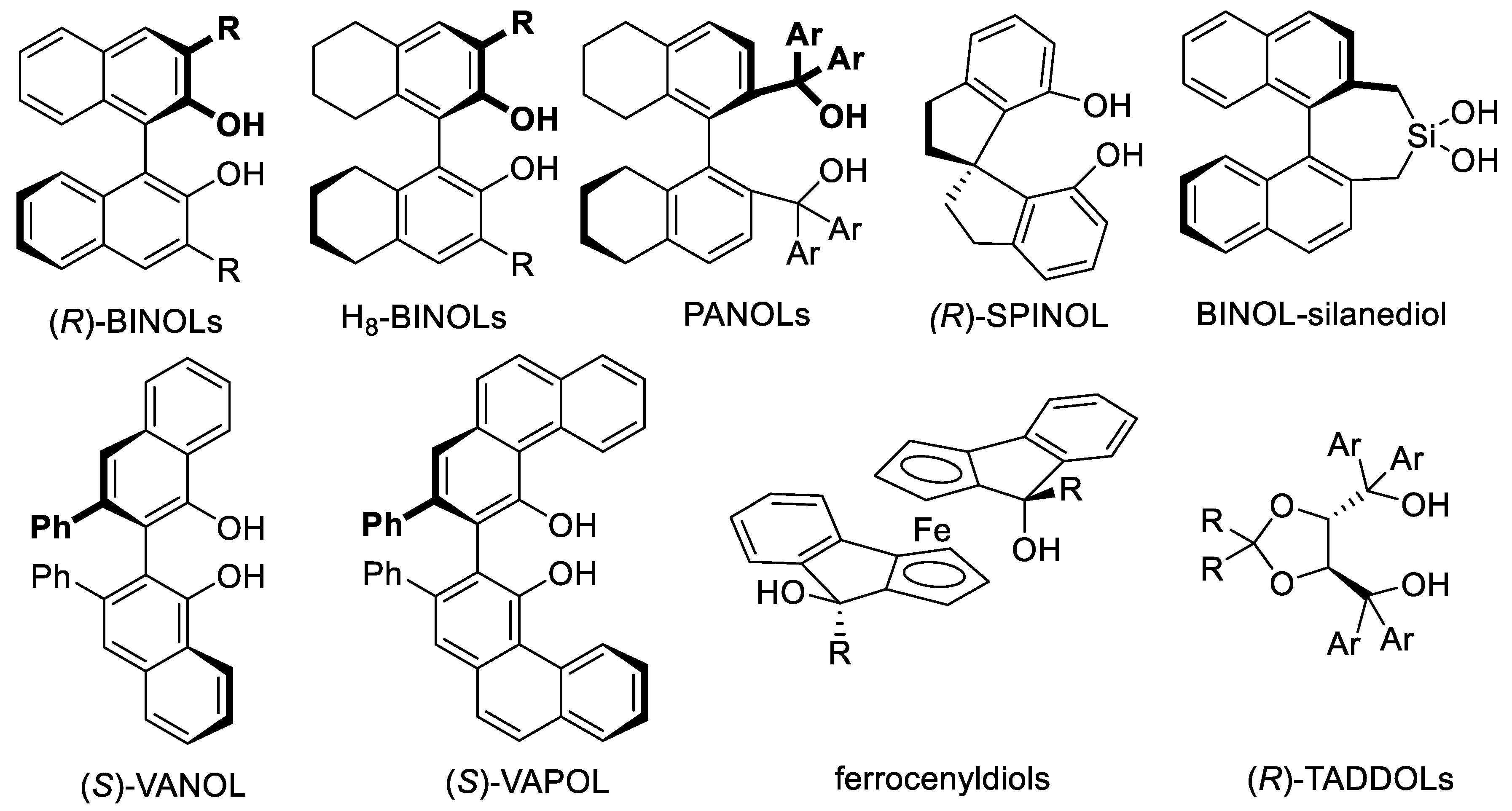
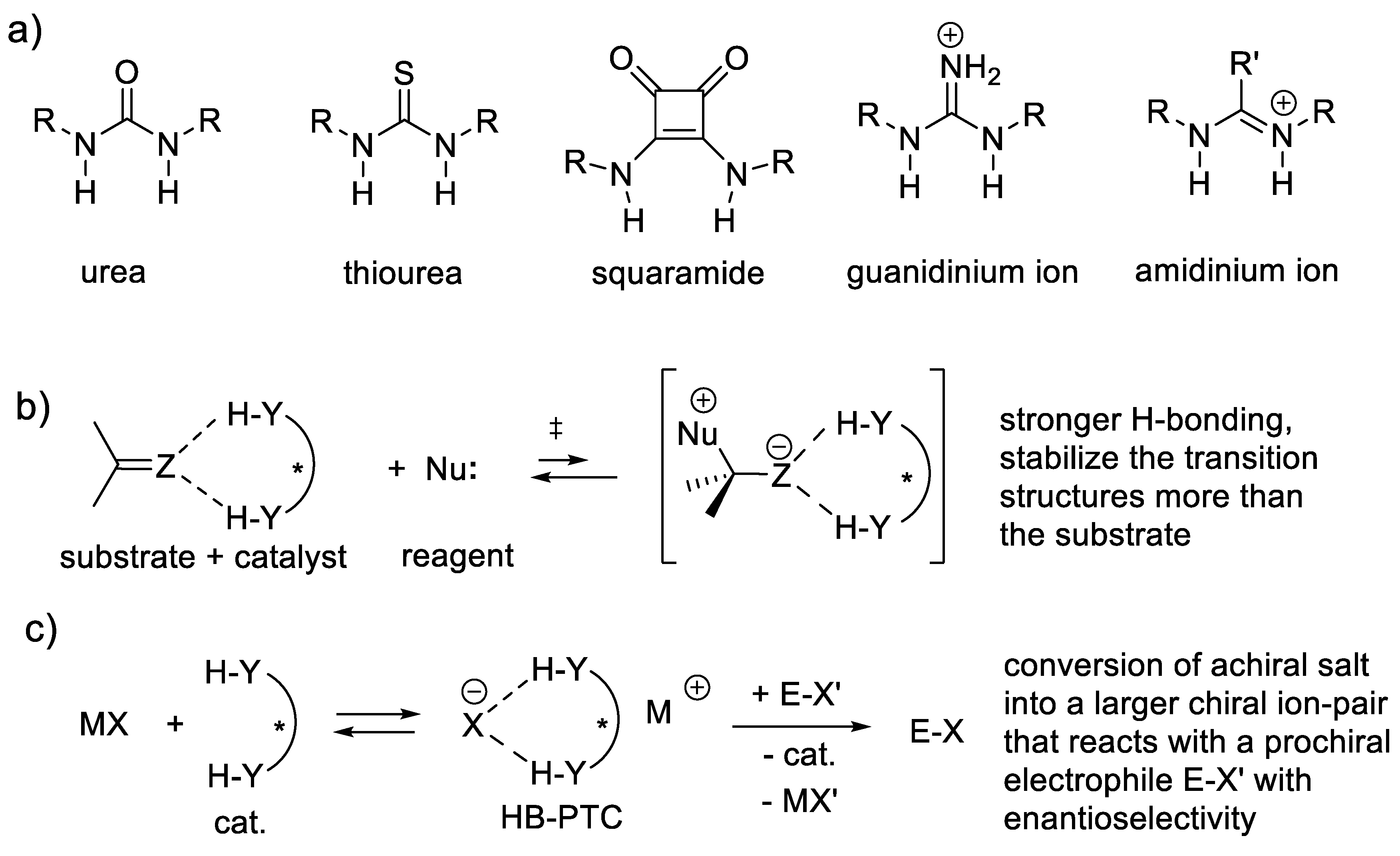
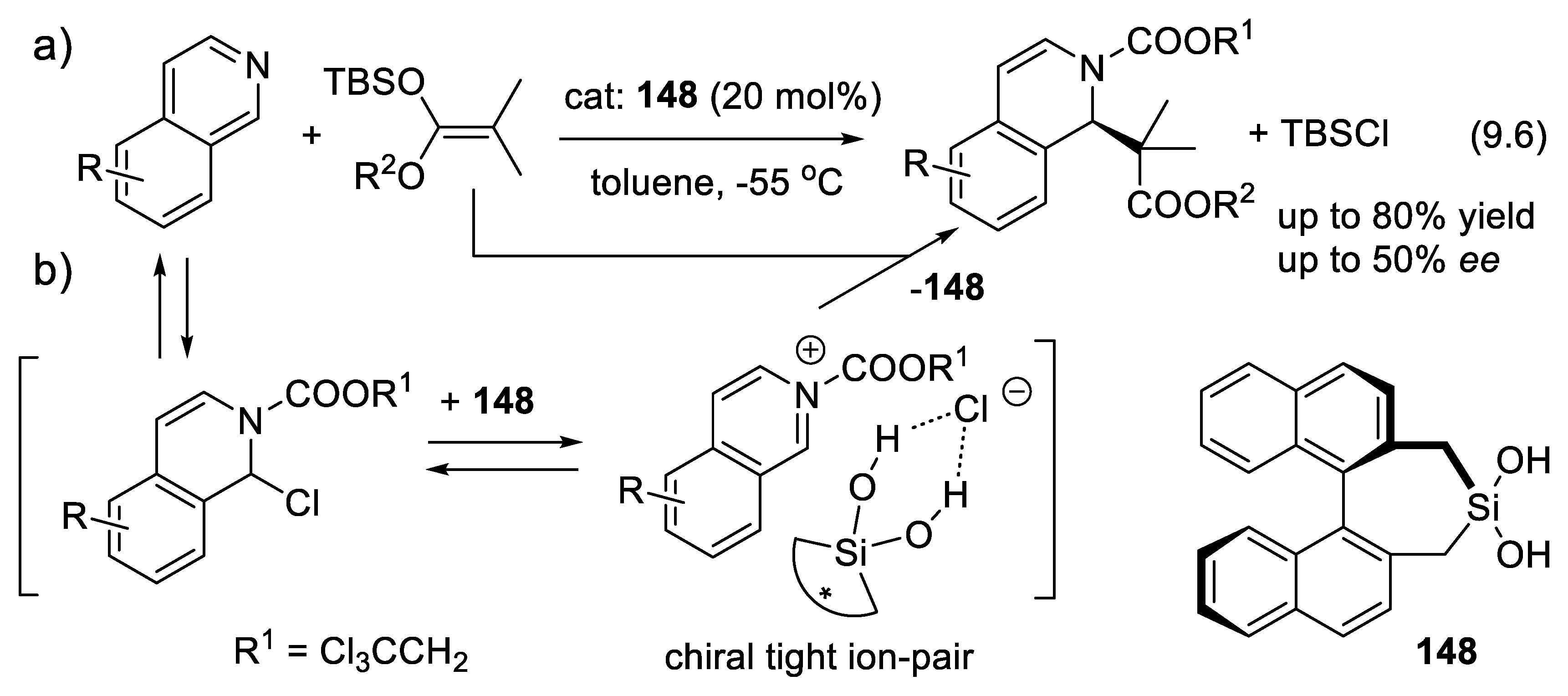
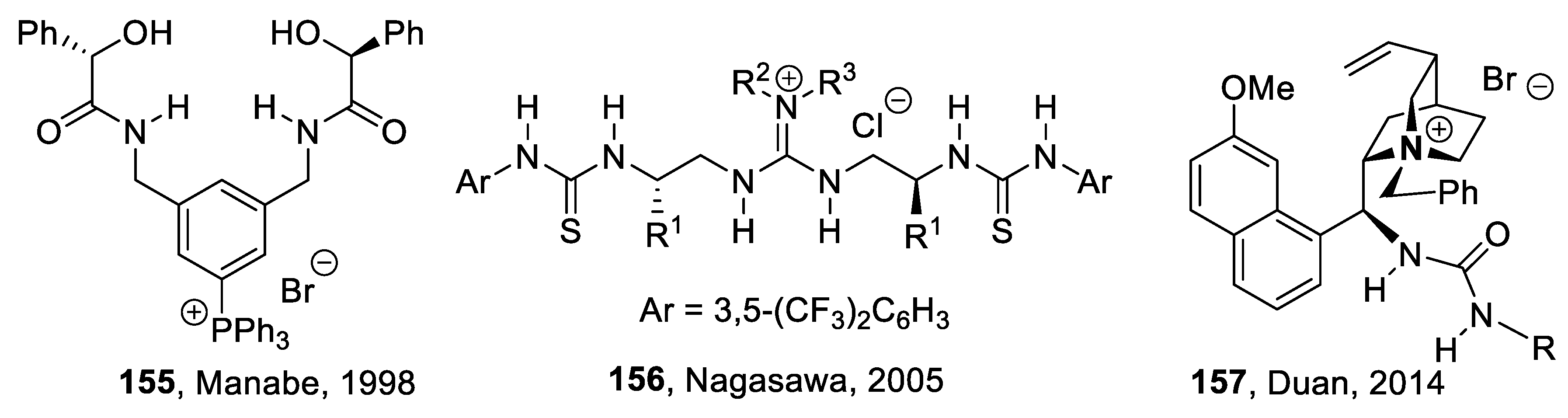
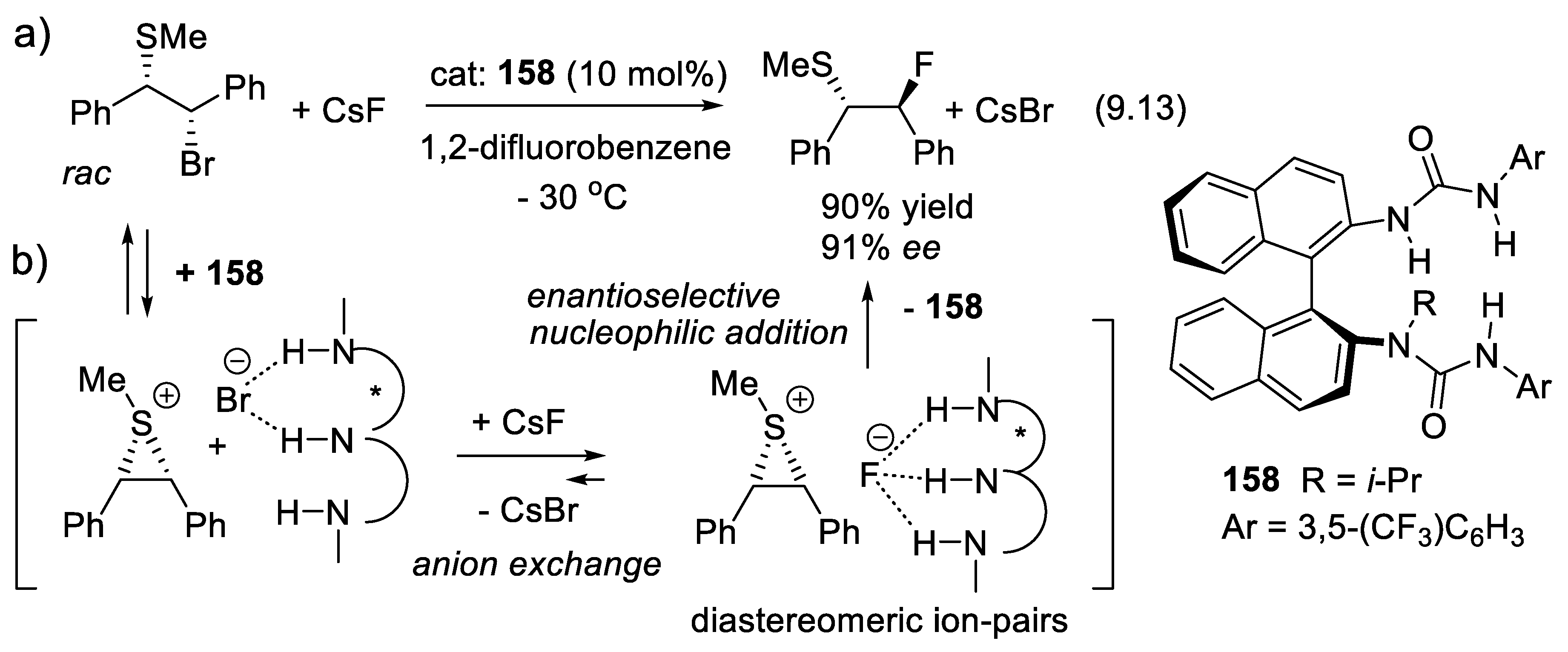
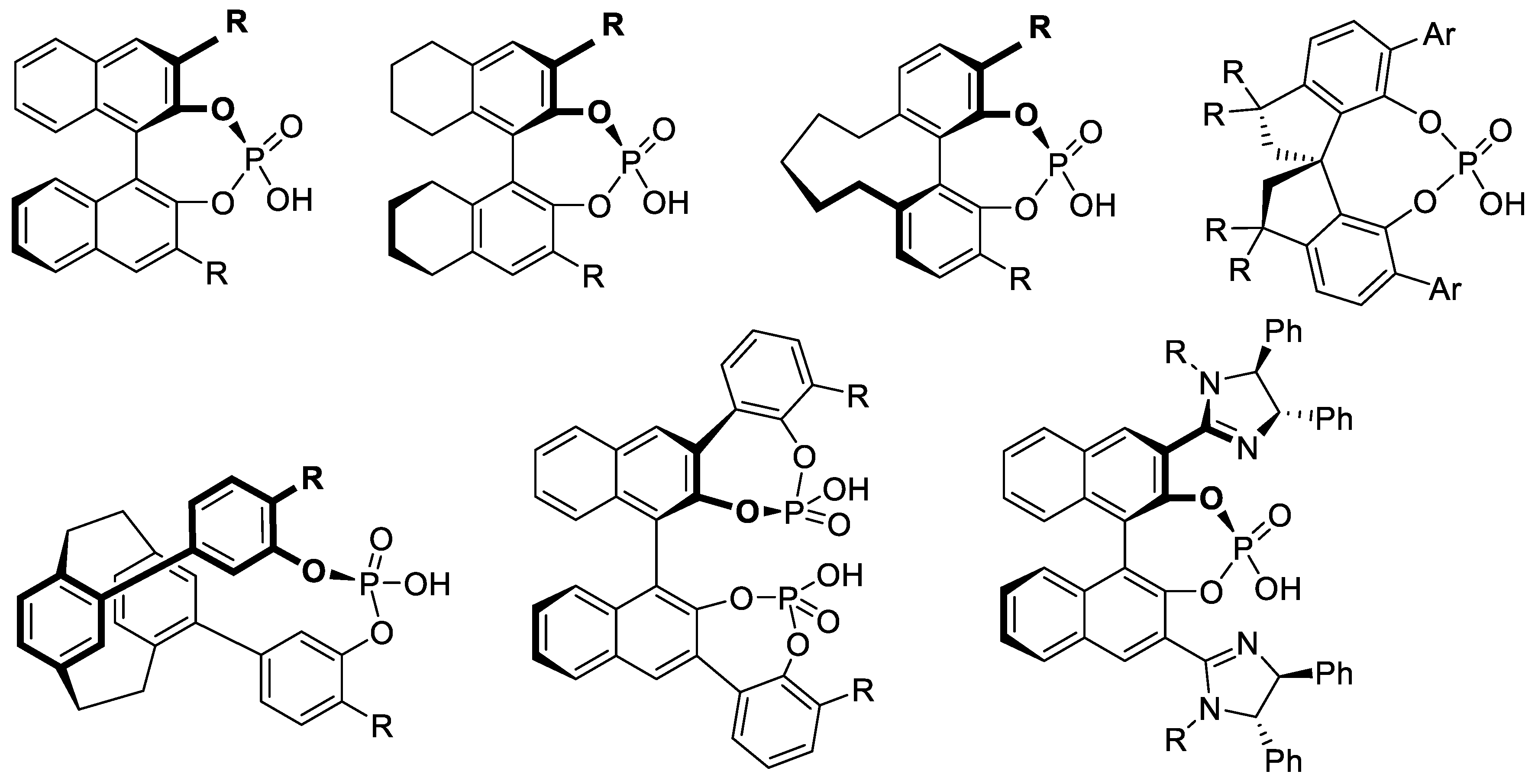
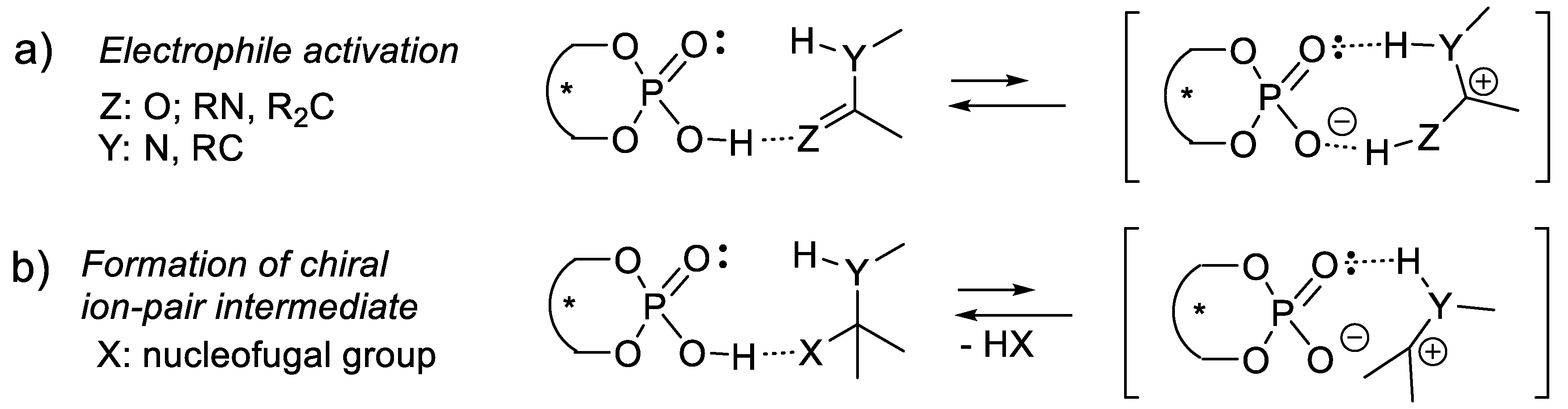
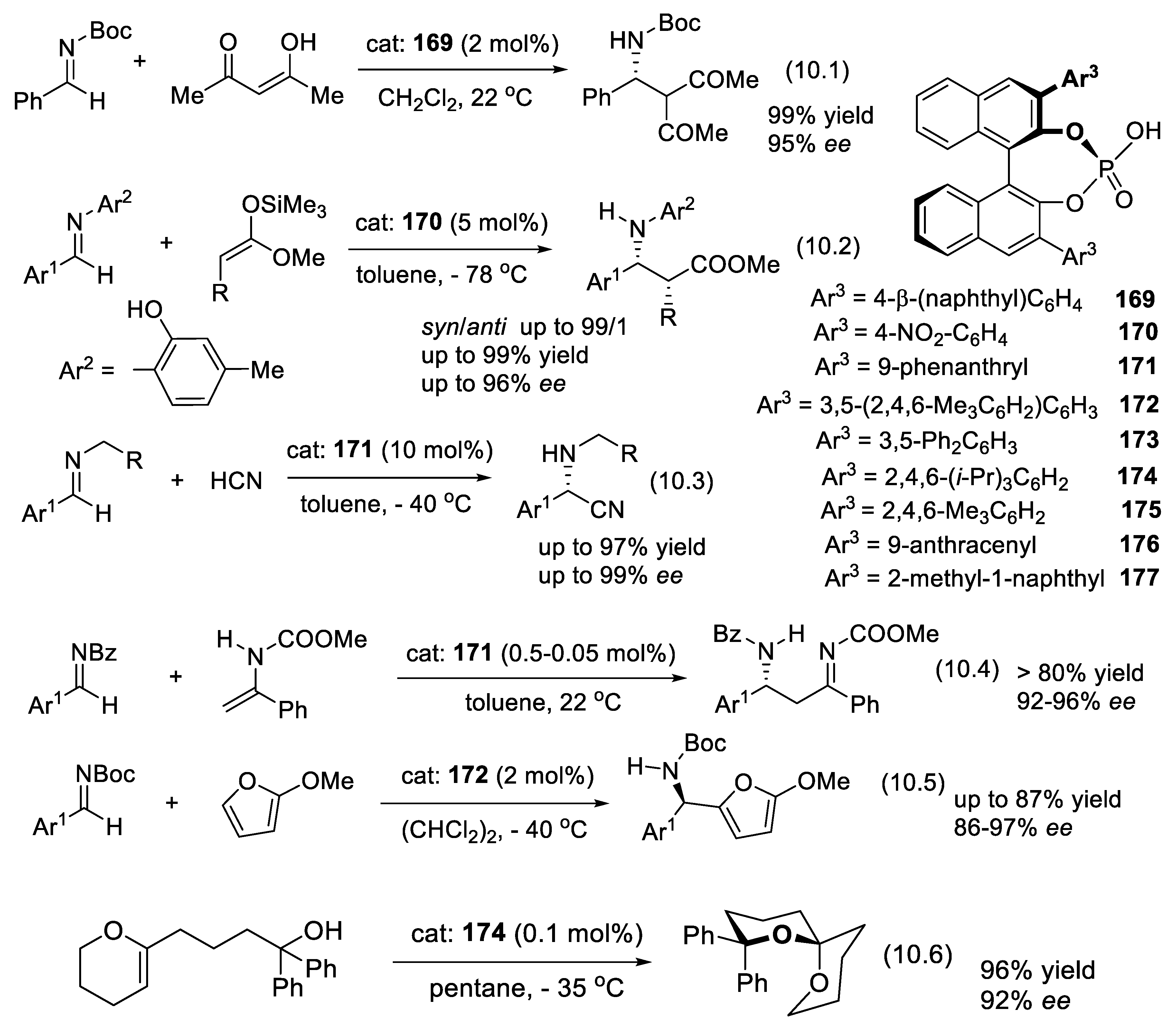
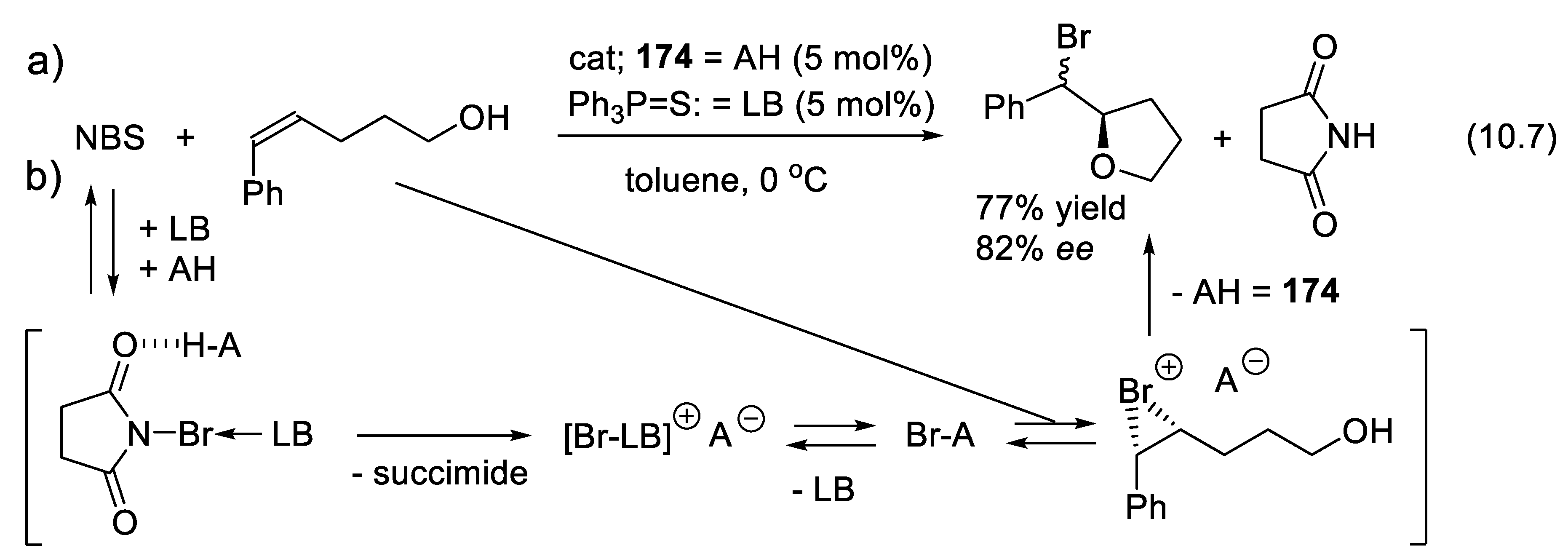
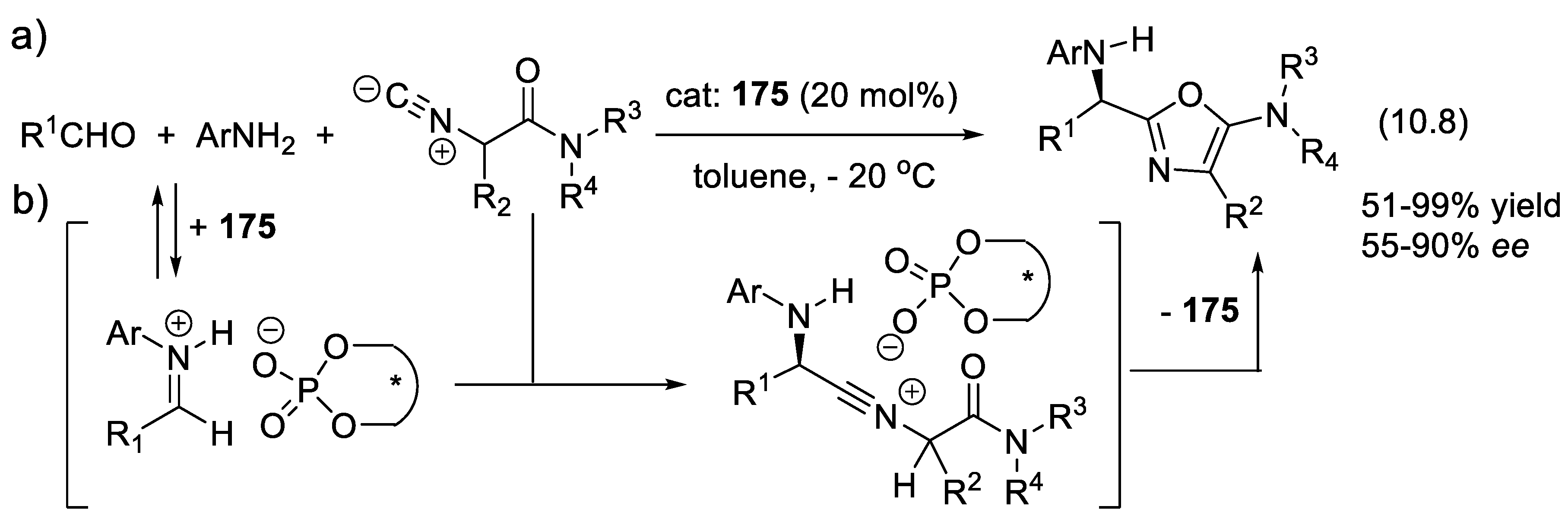
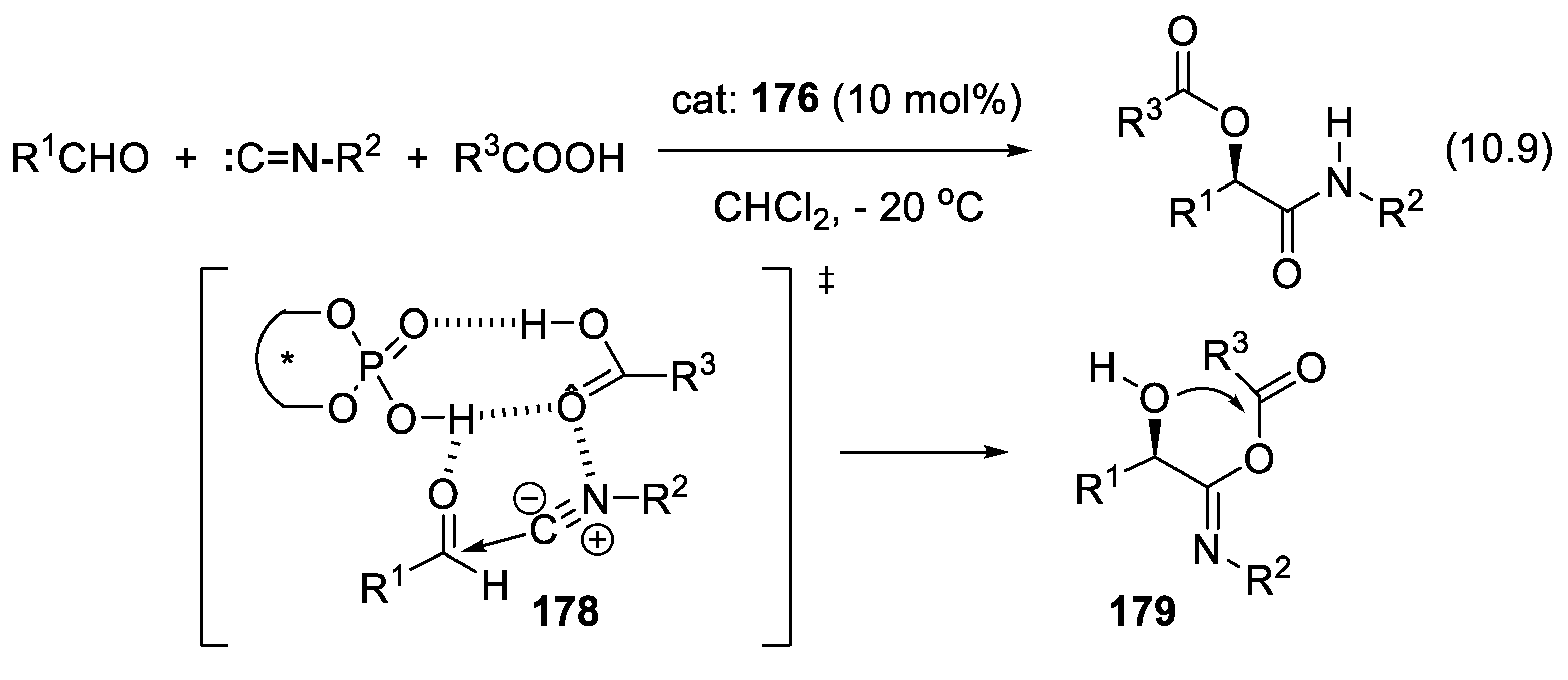
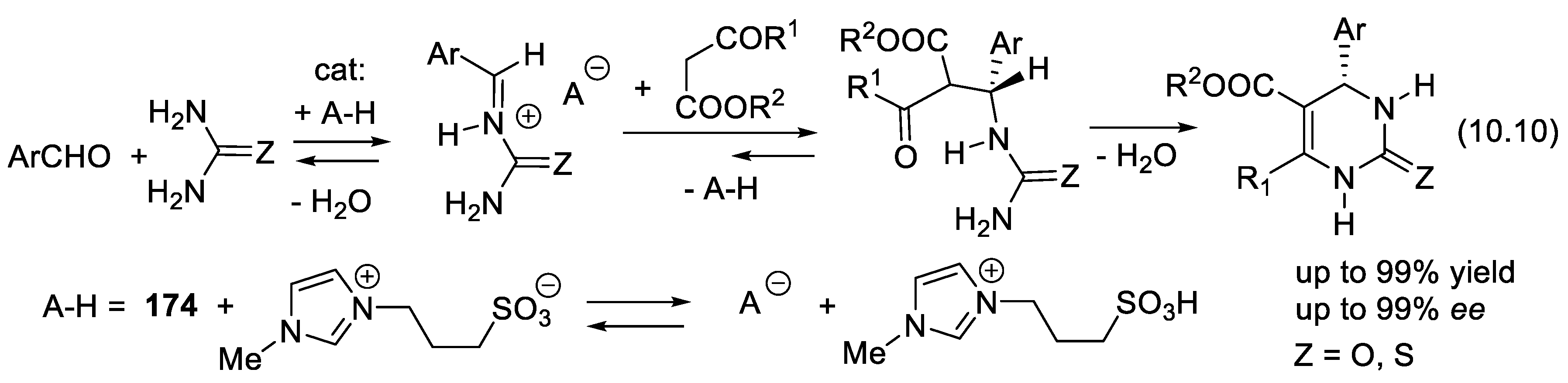
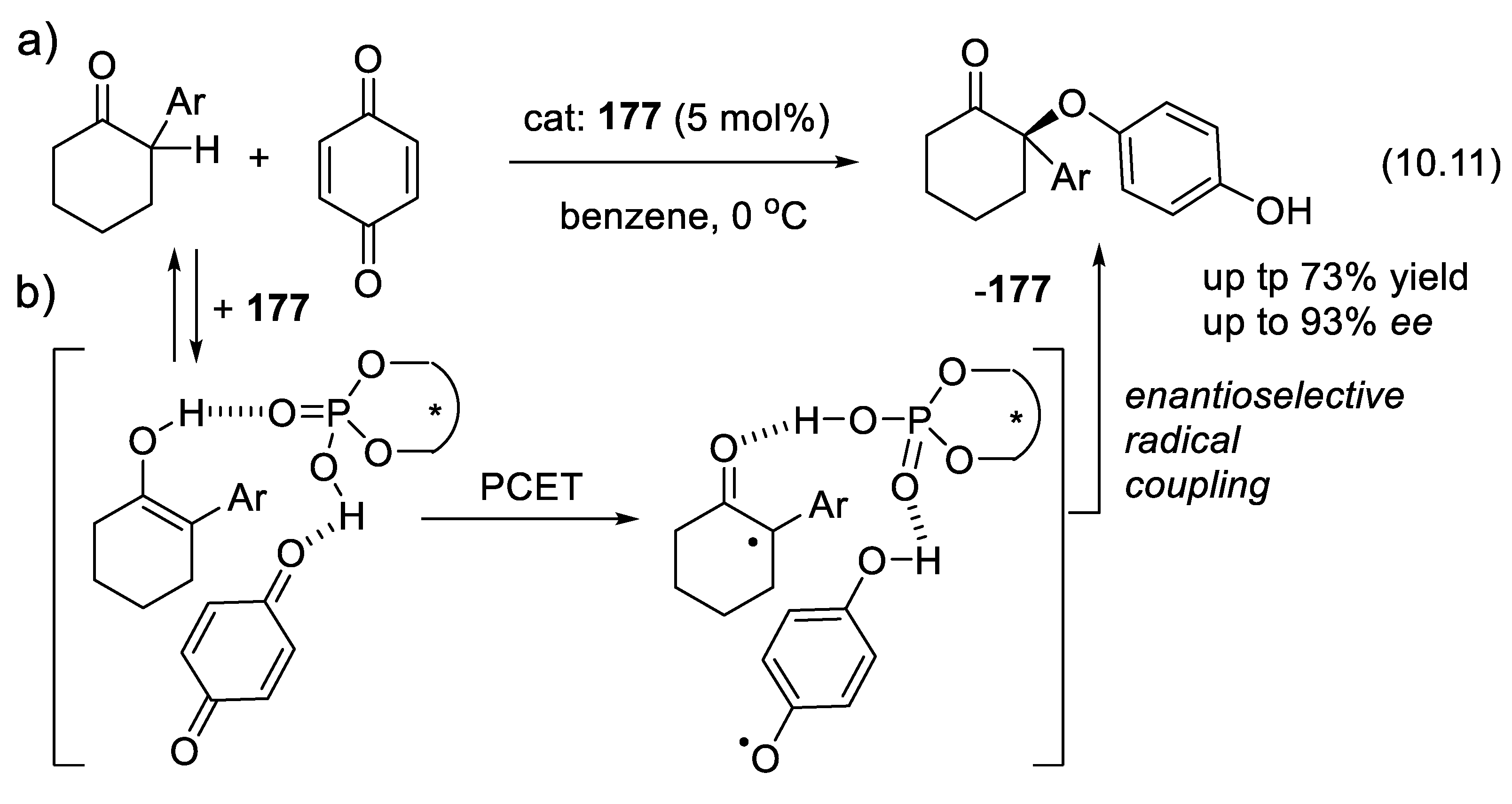
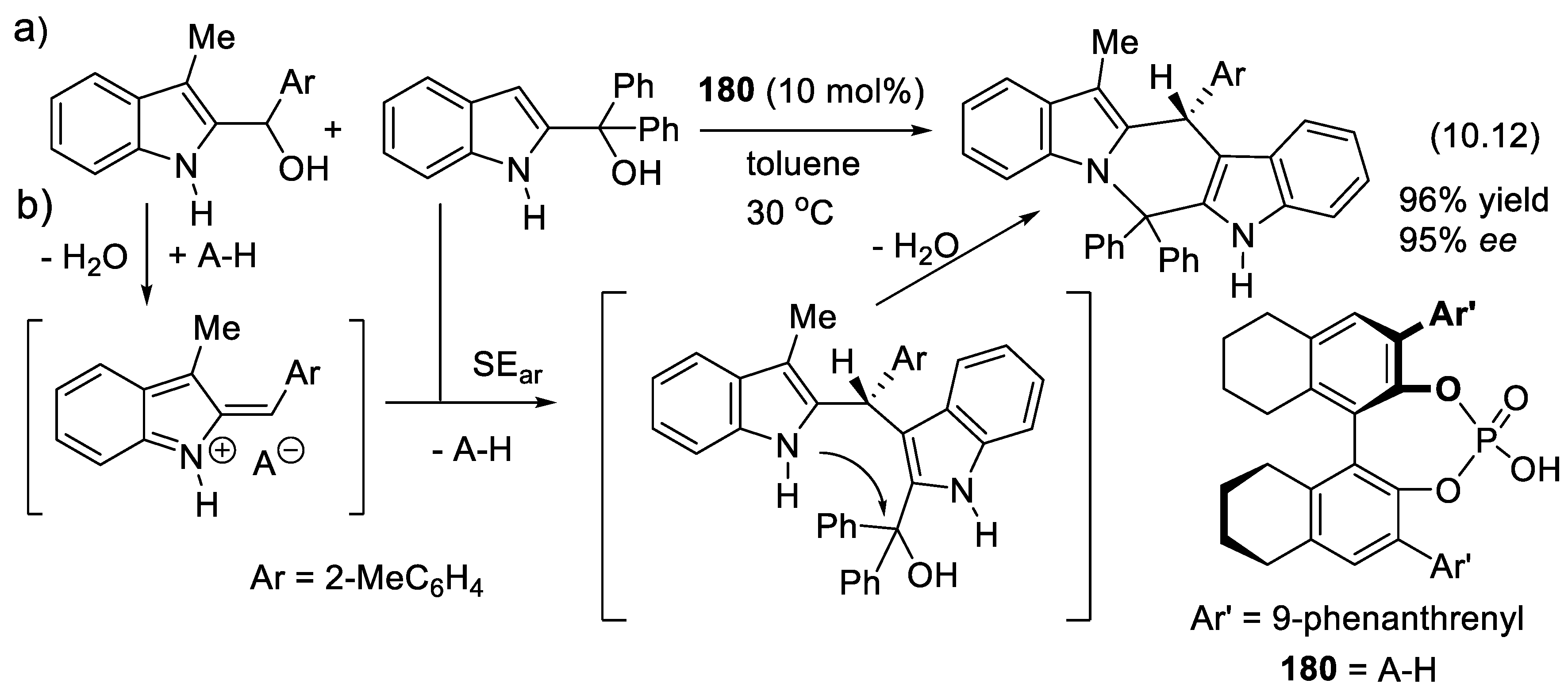
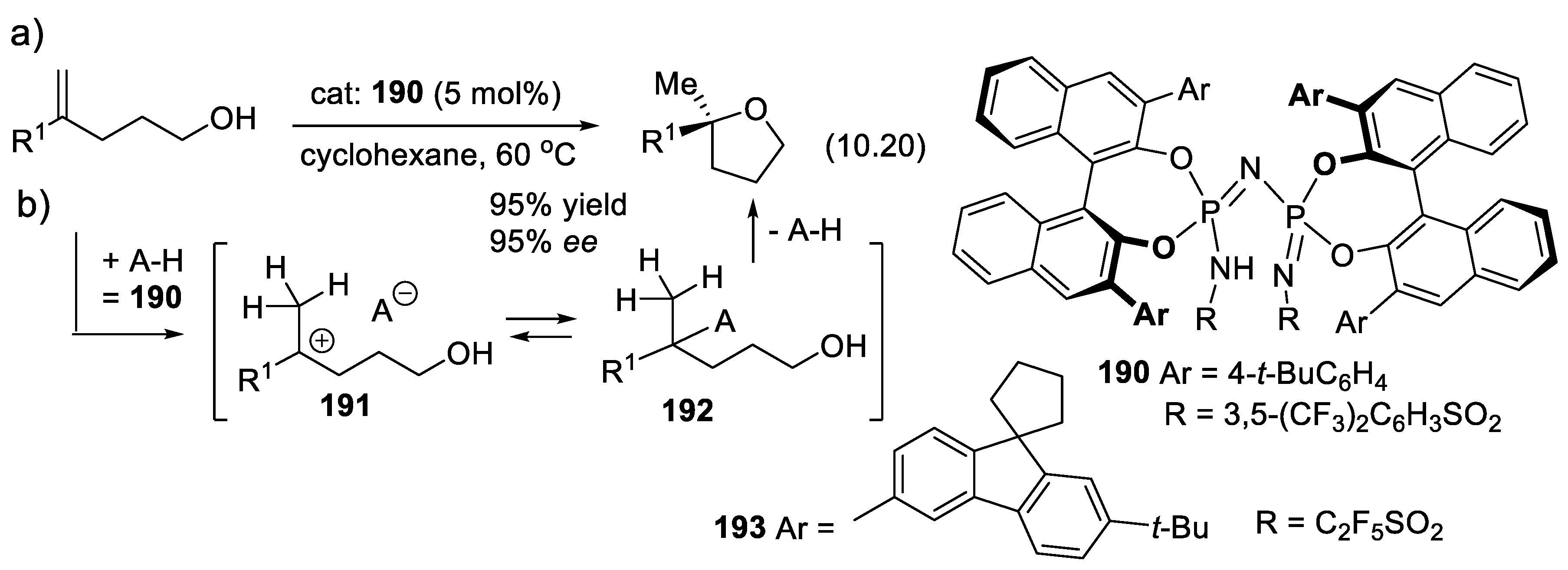
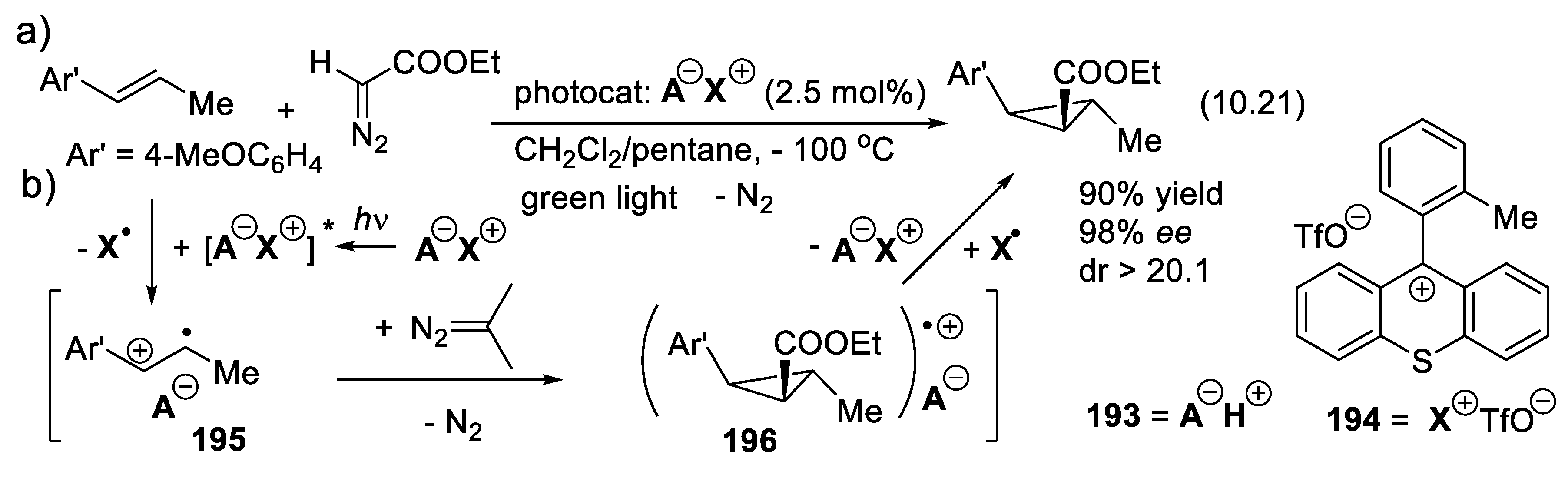
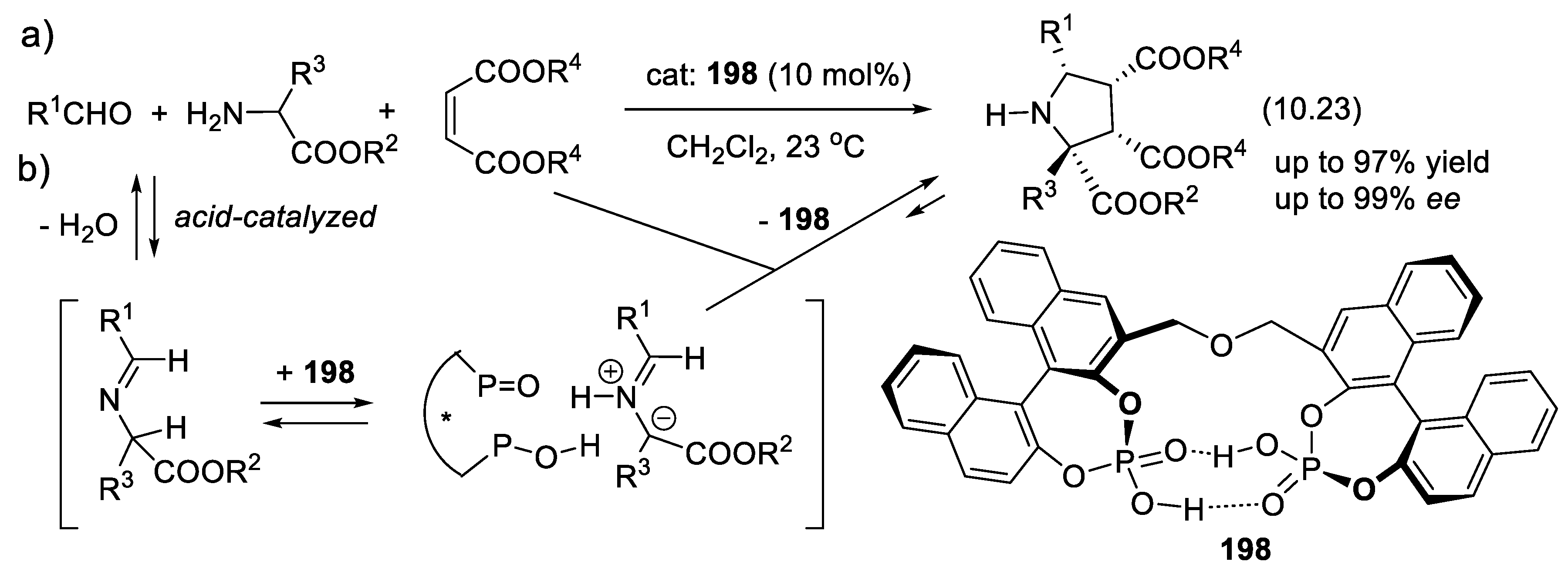
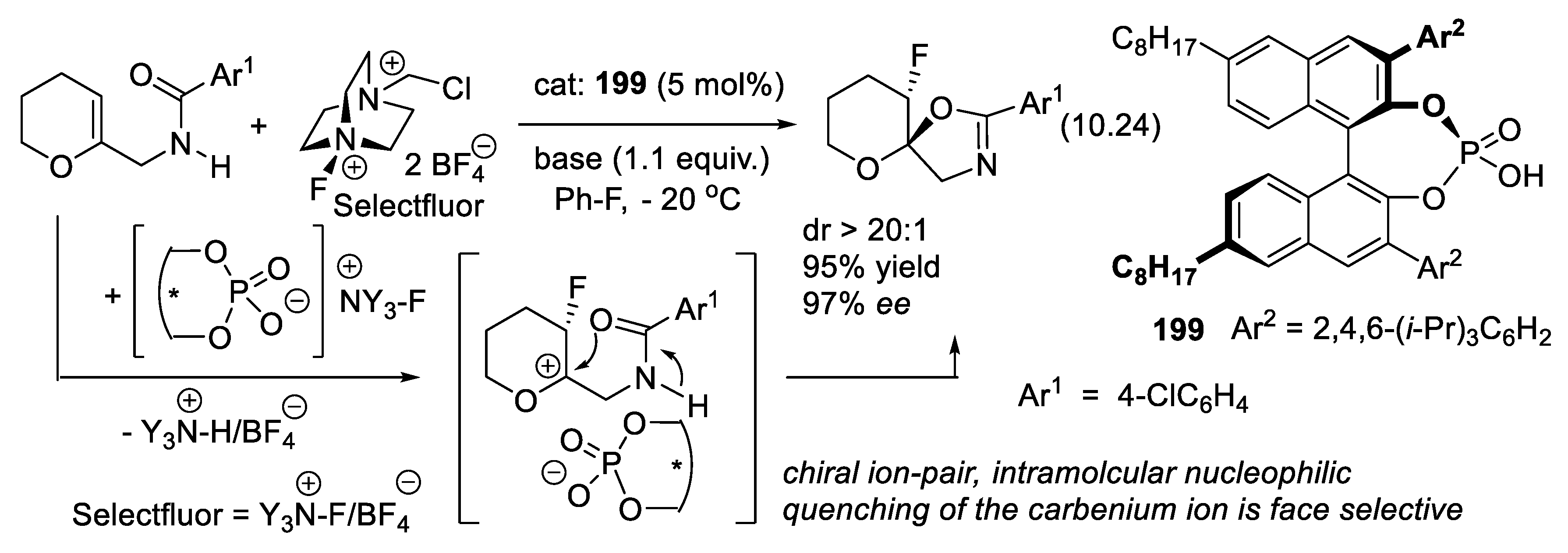
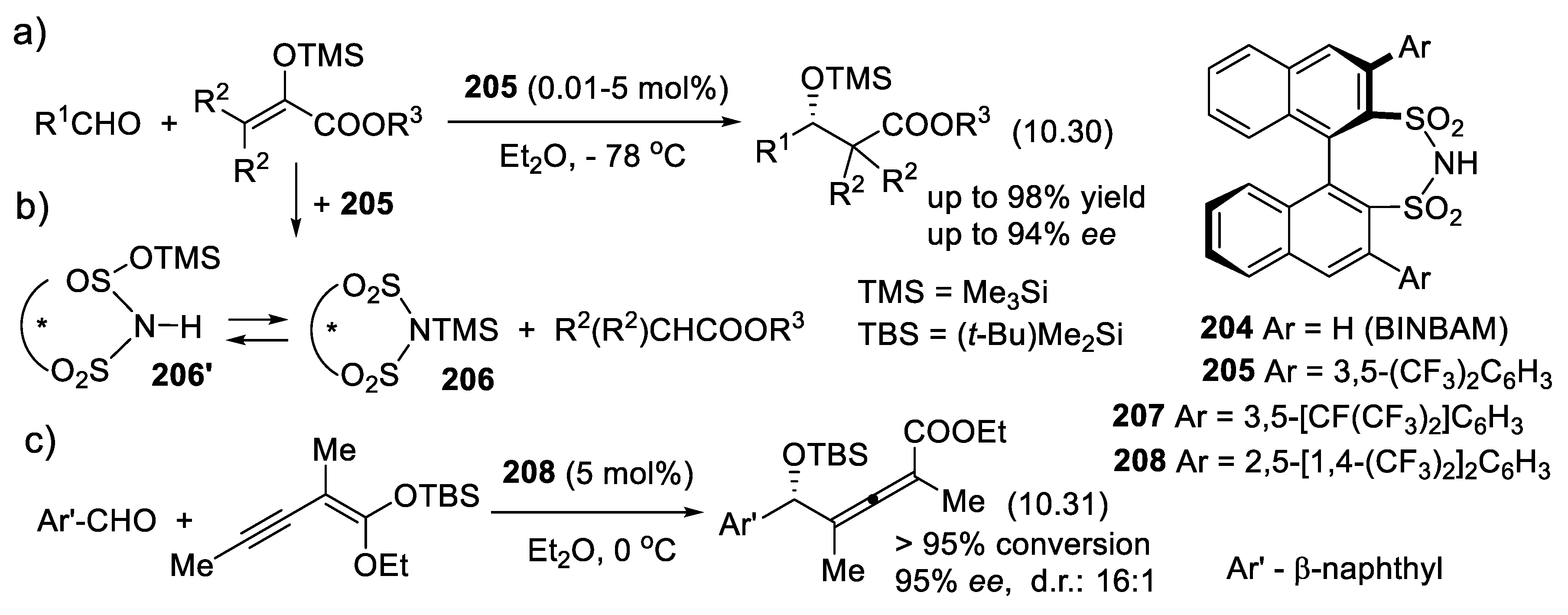
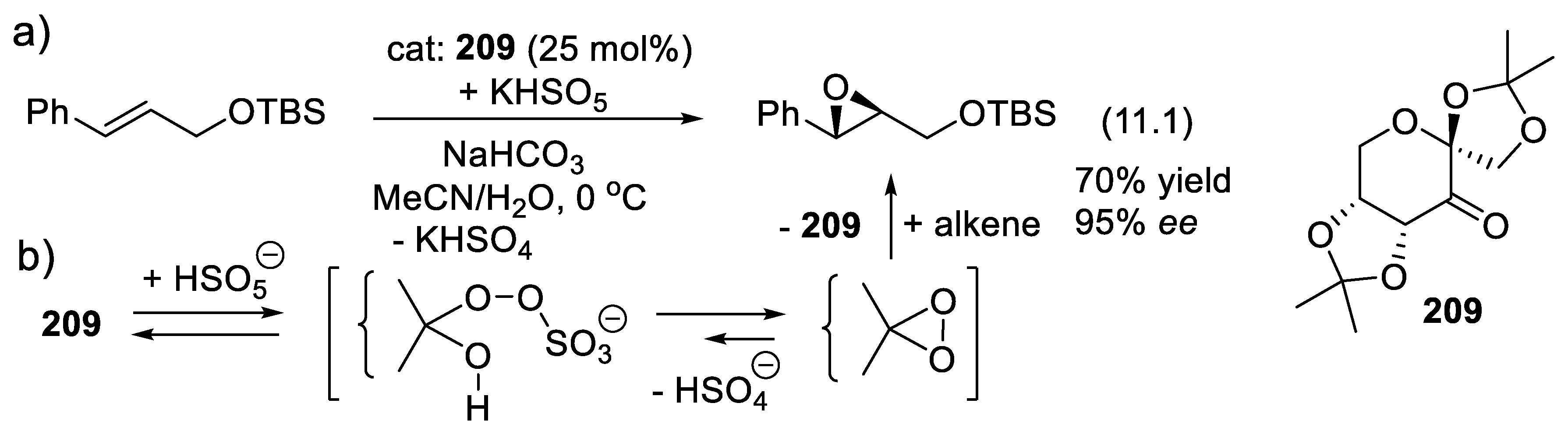
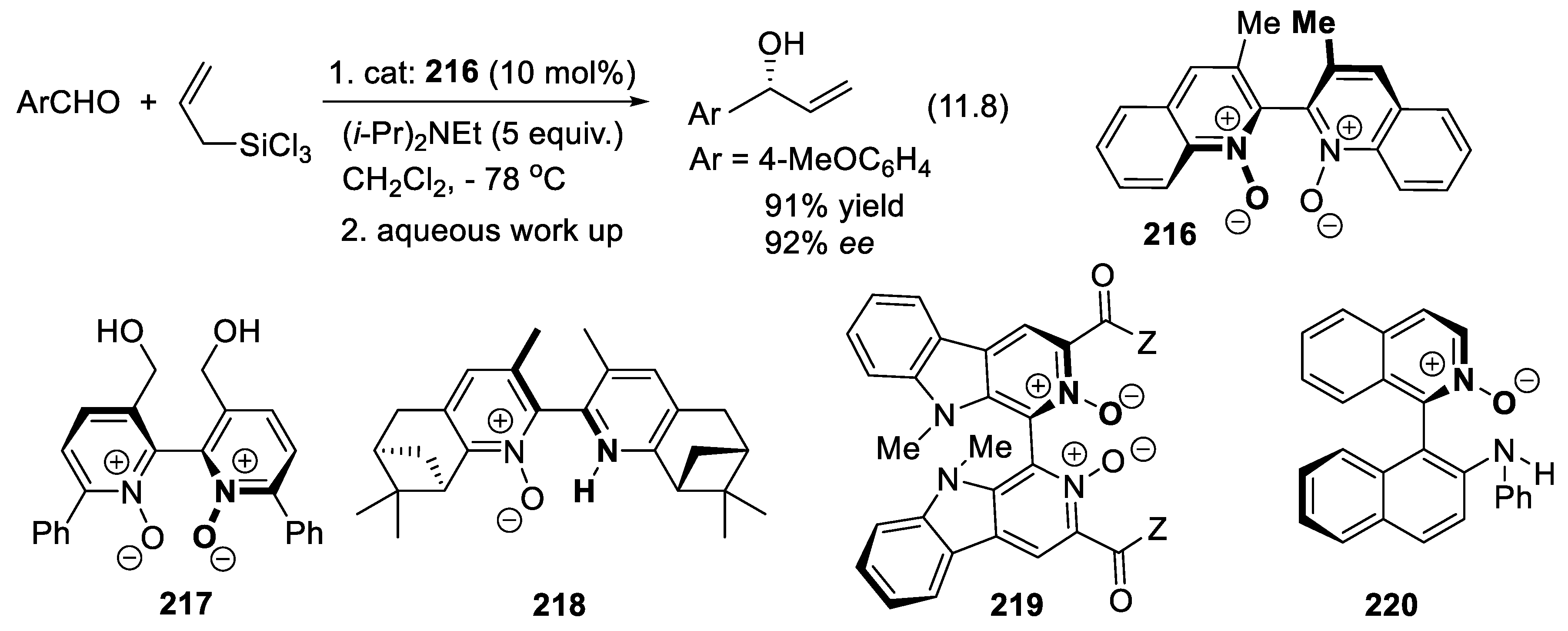
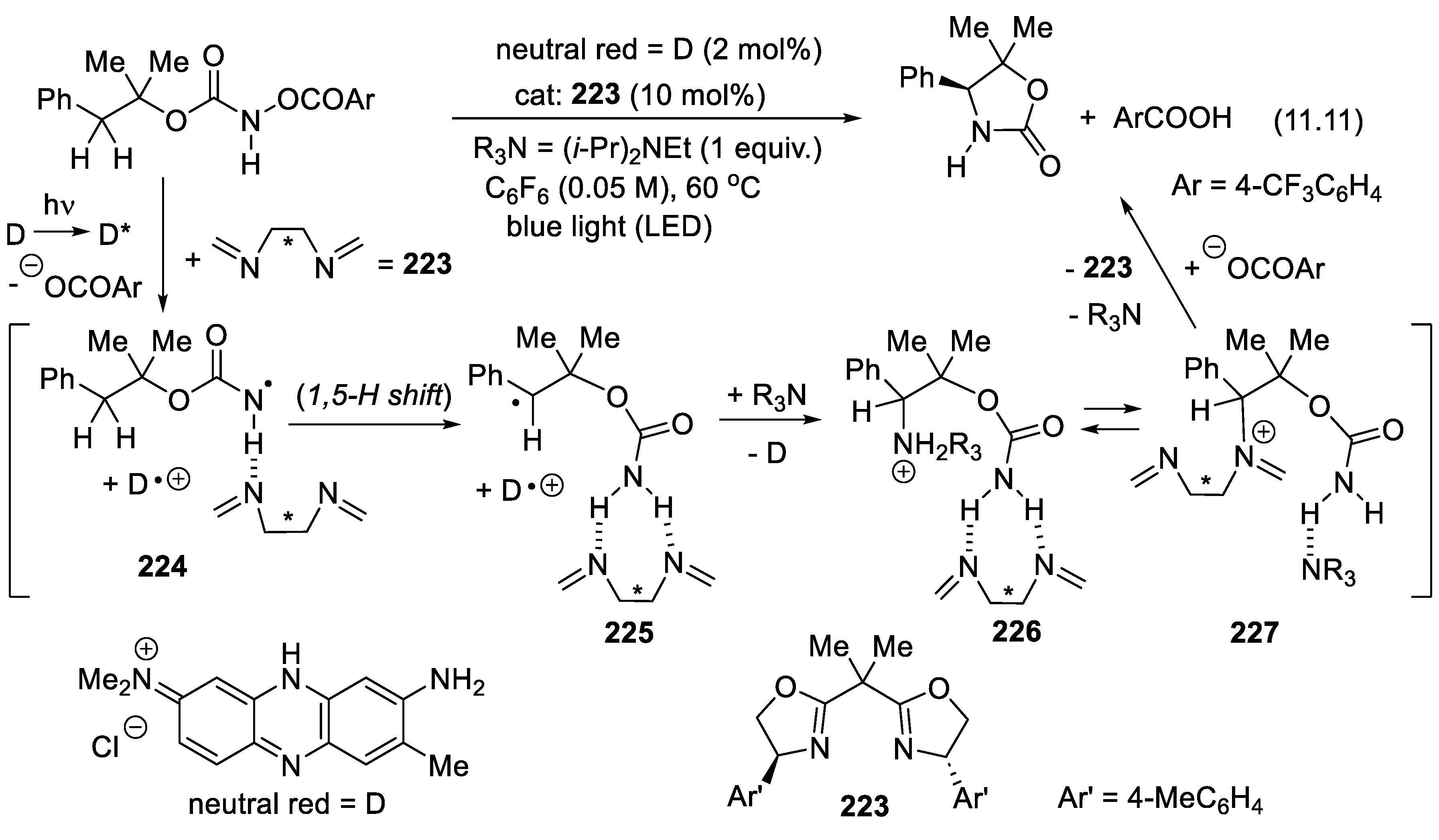
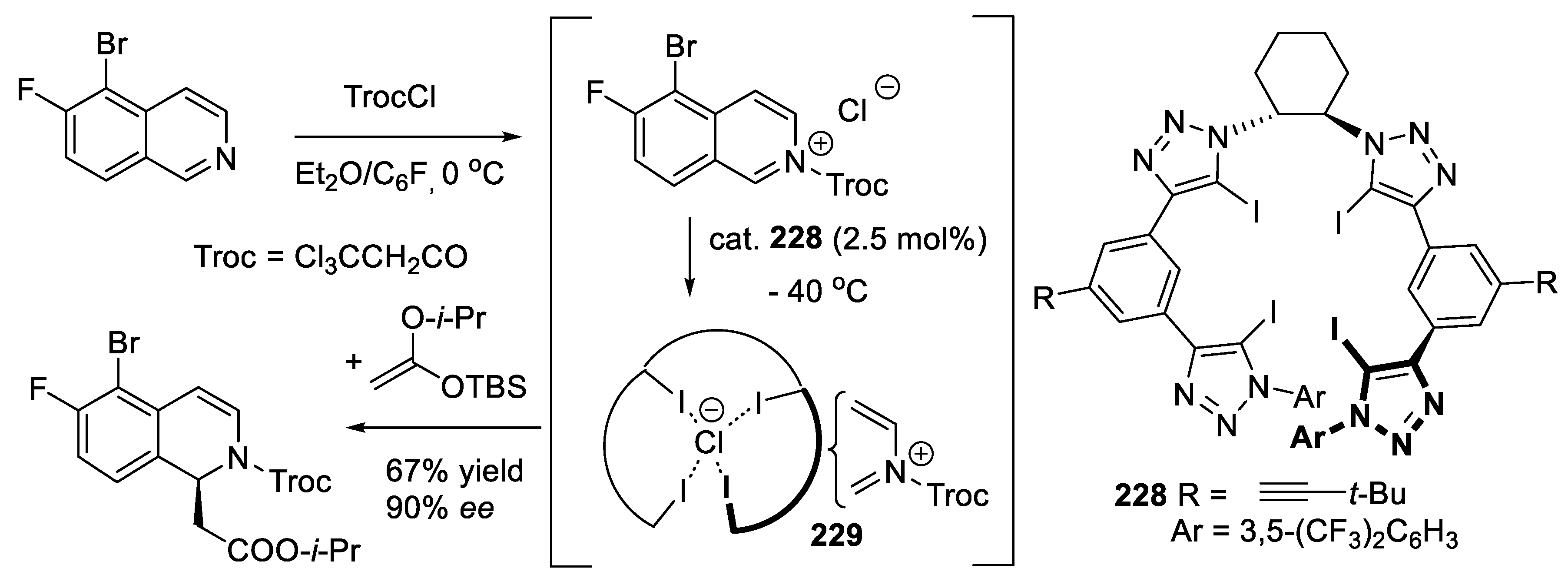
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




