Submitted:
13 October 2025
Posted:
17 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study Design and Data Sources
Classification of Syphilis Burden
Outcome Measures
Statistical Analyses
Data Availability and Code
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Bivariate Comparisons
3.2. Adjusted Models and Temporal Interactions
3.3. Correlations and Economic Impact
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| DATASUS | Sistema de Informações Hospitalares do Sistema Único de Saúde (Hospital Information System of the Unified Health System) |
| IBGE | Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics) |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| R$ | Brazilian Real (currency) |
| SINAN | Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação (Notifiable Diseases Information System) |
| STI | Sexually Transmitted Infection |
| SUS | Sistema Único de Saúde (Unified Health System) |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Hook EW 3rd, Peeling RW. Syphilis control—a continuing challenge. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(2):122-124. [CrossRef]
- Holmes KK, Sparling PF, Stamm WE, et al. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 4th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2008.
- Domingues RMSM, Saraceni V, Hartz ZMA, Leal MC. Syphilis in pregnancy and congenital syphilis: reality in a Brazilian metropolis. Rev Saude Publica. 2017;51:109. [CrossRef]
- Santos MM, Rosendo TMS, Lopes AKB, Roncalli AG, Lima KC. Congenital syphilis in Brazil: analysis of national surveillance data from 2008 to 2017. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2020;44:e45. [CrossRef]
- Brazil Ministry of Health. Epidemiological Bulletin: Syphilis 2019. Brasília, DF: Ministry of Health. 2019. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/pub/2019/boletim-epidemiologico-sifilis-2019 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Heggtveit HA. Syphilitic aortitis: a clinicopathologic autopsy study of 100 cases, 1950 to 1960. Circulation. 1964;29:346-355. [CrossRef]
- Drago F, Merlo G, Rebora A, Parodi A. Syphilitic aortitis: a modern reappraisal. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(8):e310-e311. [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Edusei K Jr, Chesson HW, Gift TL, et al. The estimated direct medical cost of selected sexually transmitted infections in the United States, 2008. Sex Transm Dis. 2013;40(3):197-201. [CrossRef]
- Chesson HW, Peterman TA, Gift TL. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydia and gonorrhea and implications for syphilis. Sex Transm Dis. 2019;46(2):e12-e14. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global health sector strategy on sexually transmitted infections 2016–2021. Geneva: WHO. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-RHR-16.09 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Ghanem KG, Moore RD, Rompalo AM, Erbelding EJ, Zenilman JM, Gebo KA. Antiretroviral therapy is associated with reduced serologic failure rates for syphilis among HIV-infected patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(2):258-265. [CrossRef]
- Pinto VM, Tancredi MV, Tancredi Neto A, Buchalla CM. Sexually transmitted disease/HIV and heterosexual risk among miners in a Brazilian Amazon city. Rev Saude Publica. 2012;46(6):938-945. [CrossRef]
- Silva RJ, Santos NJ, Beck M, et al. Early diagnosis of syphilis in primary health care: a systematic review. Cad Saude Publica. 2018;34(4):e00058917. [CrossRef]
- Kiarie J, Mishra CK, Temmerman M, Newman L. Accelerating the dual elimination of mother-to-child transmission of syphilis and HIV: why now? Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2015;130 Suppl 1:S1-S3. [CrossRef]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). National Health Survey 2019: primary health care and anthropometric information. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE. 2020. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/en/statistics/social/health/16840-national-survey-of-health.html (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Szwarcwald CL, Souza Júnior PRB, Marques AP, Almeida WDS, Montilla DER. Inequalities in healthy life expectancy by Brazilian geographic regions: findings from the National Health Survey, 2013. Int J Equity Health. 2016;15:141. [CrossRef]
- Barreto ML, Teixeira MG, Bastos FI, Ximenes RA, Barata RB, Rodrigues LC. Successes and failures in the control of infectious diseases in Brazil: social and environmental context, policies, interventions, and research needs. Lancet. 2011;377(9780):1877-1889. [CrossRef]
- Travassos C, Martins M. A review of concepts in health services access and utilization. Cad Saude Publica. 2004;20 Suppl 2:S190-S198. [CrossRef]
- Dantas E, Costa J, Carvalho S, et al. Syphilis Exposure During Pregnancy and Childhood Hospitalization. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(4):e246025. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira TR, Gracie R, Malta MS, et al. Burden of syphilis in Brazil and federated units, 1990-2016: an analysis of attributable fractions by the GBD 2019 study. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2022;55:e0243. [CrossRef]
- Sousa SV, Carvalho MS, Santos MM. Hospitalization costs for congenital syphilis in the state of Ceará, 2010-2018. Cogitare Enferm. 2023;28:e81168. [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Sander N, Soni S. Aneurysm and dissection in a patient with syphilitic aortitis. Braz J Infect Dis. 2017;21(4):471-472. [CrossRef]
- Passos MJ, Santos RS. Syphilis as a marker of ethnoracial inequalities in Brazil. Lancet Glob Health. 2023;11(12):e1834-e1835. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira LGD, Santos AKN, Santos MJ, et al. Spatial Distribution of Gestational Syphilis in Brazil: Socioeconomic and Health Care Factors Associated from 2008 to 2018. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023;109(1):42-50. [CrossRef]
- Silva PS, Macêdo VC, Miranda AE, et al. Temporal trend and factors associated with spatial distribution of congenital syphilis in Brazil: an ecological study. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1109271. [CrossRef]
- Santos MM, Santos AC, Santos MJ, et al. Analyses and impacts on the syphilis epidemic in Brazil: the experience of the learning pathway “Syphilis and other STIs”. Front Public Health. 2022;10:952022. [CrossRef]
- Bezerra ML, Fernandes FEC, Nunes JPO, et al. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Point-of-Care Rapid Testing Versus Laboratory-Based Testing for Antenatal Screening of Syphilis in Brazil. Value Health Reg Issues. 2020;23:66-73. [CrossRef]
| Burden Categories | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Overall (n=405) | High (n=105) | Low (n=105) | Intermediate (n=195) | p-value | ||
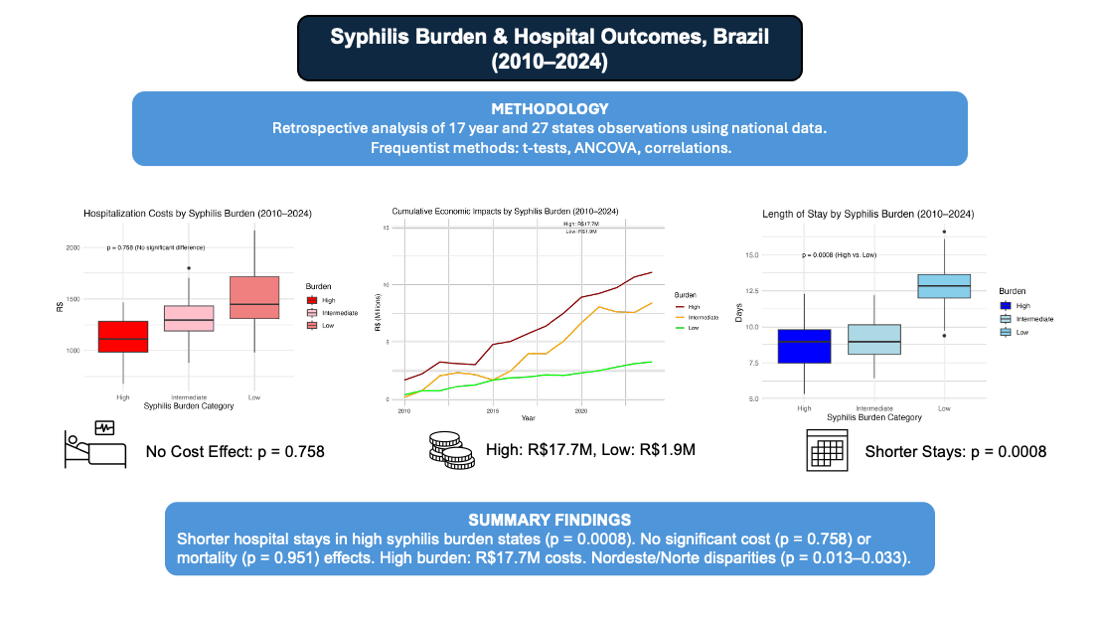
| Syphilis Rate (median [IQR]) | 0.49 [0.25, 0.83] | 0.88 [0.54, 1.58] | 0.29 [0.13, 0.56] | 0.46 [0.26, 0.70] | <0.001* | ||
| Syphilis Incidence (median [IQR]) | 28.88 [7.51, 72.50] | 51.22 [10.23, 86.34] | 25.41 [7.01, 52.38] | 27.12 [6.06, 63.16] | 0.014* | ||
| Aneurysm Correction Mortality (median [IQR]) | 13.72 [10.45, 17.78] | 13.72 [11.21, 16.67] | 13.43 [8.33, 20.83] | 13.75 [10.53, 17.70] | 0.7316* | ||
| Length of Stay (median [IQR]) | 10.10 [7.50, 13.40] | 9.10 [6.60, 13.60] | 12.50 [9.80, 14.40] | 9.20 [7.20, 12.15] | 0.0001* | ||
| Aneurysm Correction Cost (median [IQR]) | 1285.81 [1030.54, 1686.56] | 1212.71 [1091.22, 1616.06] | 1449.05 [842.76, 1998.19] | 1314.41 [1032.54, 1622.28] | 0.6141* | ||
| Hospital Complexity (median [IQR]) | 1.73 [0.92, 2.33] | 1.95 [1.37, 2.90] | 1.24 [0.74, 2.23] | 1.72 [0.98, 2.17] | 0.002* | ||
| Regional Breakdown | |||||||
| Region | Centro-Oeste | Nordeste | Norte | Sudeste | Sul | p-value | |
| Syphilis Rate (median [IQR]) | 0.55 [0.32, 1.08] | 0.43 [0.23, 0.67] | 0.34 [0.18, 0.58] | 0.83 [0.57, 1.21] | 0.73 [0.43, 1.15] | <0.001 | |
| Syphilis Incidence (median [IQR]) | 40.22 [8.62, 77.94] | 16.62 [4.85, 37.97] | 25.49 [4.82, 69.51] | 63.56 [22.53, 92.67] | 68.99 [20.28, 124.21] | <0.001 | |
| Aneurysm Correction Mortality (median [IQR]) | 13.64 [9.96, 18.89] | 14.29 [10.49, 18.64] | 13.58 [7.69, 21.43] | 13.05 [11.13, 14.97] | 13.79 [11.40, 17.13] | 0.486 | |
| Length of Stay (median [IQR]) | 9.60 [7.50, 14.45] | 11.50 [9.15, 13.65] | 11.90 [9.70, 15.00] | 8.10 [6.60, 9.30] | 6.30 [4.90, 7.60] | <0.001 | |
| Aneurysm Correction Cost (median [IQR]) | 1427.24 [1183.46, 1789.91] | 1345.68 [975.69, 1895.36] | 1260.14 [799.13, 1997.38] | 1223.99 [1129.31, 1504.58] | 1205.24 [1134.26, 1450.64] | 0.135 | |
| Hospital Complexity (median [IQR]) | 1.87 [1.60, 2.40] | 1.03 [0.57, 1.74] | 1.10 [0.65, 2.18] | 2.20 [1.84, 2.87] | 2.48 [2.13, 2.99] | <0.001 | |
| Adjusted Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Term | Estimate | Std. Error | p-value | Adjusted RR2 |
| Procedure Cost | Low Burden | 37.6 | 122 | 0.758 | 0.068 |
| Intermediate Burden | -152 | 107 | 0.156 | ||
| Hospital Complexity | -73.8 | 45.1 | 0.102 | ||
| Year | 58.5 | 10.7 | <0.001 | ||
| Procedure Mortality | Low Burden | -0.077 | 1.26 | 0.951 | 0.073 |
| Intermediate Burden | 0.194 | 1.10 | 0.861 | ||
| Hospital Complexity | -2.46 | 0.466 | <0.001 | ||
| Year | -0.0609 | 0.111 | 0.583 | ||
| Length of Stay | Low Burden | 2.11 | 0.626 | 0.0008 | 0.103 |
| Intermediate Burden | -0.948 | 0.549 | 0.0849 | ||
| Hospital Complexity | -0.941 | 0.232 | <0.001 | ||
| Year | 0.112 | 0.0552 | 0.0425 | ||
| Temporal Interactions | |||||
| Outcome | Term | Estimate | Std. Error | p-value | Adjusted RR2 |
| Procedure Mortality | Intermediate Burden | 0.170 | 0.665 | 0.798 | 0.0556 |
| Procedure Cost | Intermediate Burden | -50.39 | 62.42 | 0.420 | 0.107 |
| Length of Stay | Intermediate Burden | 0.5139 | 0.2953 | 0.0826 | 0.2729 |
| Sensitivity (Alternative Thresholds) | |||||
| Outcome | Term | Estimate | Std. Error | p-value | Adjusted RR2 |
| Cost | Low Burden | 256 | 144 | 0.0764 | 0.0703 |
| Mortality | Intermediate Burden | -2.92 | 0.952 | 0.0023 | 0.0939 |
| Length of Stay | Low Burden | 2.59 | 0.757 | 0.0007 | 0.0643 |
| Sensitivity (No Outliers) | |||||
| Outcome | Term | Estimate | Std. Error | p-value | Adjusted RR2 |
| Cost | Low Burden | 43.4 | 84.2 | 0.607 | 0.1040 |
| Mortality | Low Burden | 0.485 | 1.09 | 0.657 | 0.0494 |
| Length of Stay | Low Burden | 1.64 | 0.535 | 0.0024 | 0.0997 |
| Correlations (Pearson) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Metric | Value [95% CI] | p-value |
| Incidence vs. Syphilis Hospitalizations | 0.422 [0.338, 0.499] | <0.0001 |
| Syphilis Burden vs. Mortality | -0.051 [-0.147, 0.0469] | 0.308 |
| Correlations (Spearman) | ||
| Syphilis Burden vs. Mortality | -0.065 [-0.161, 0.033] | 0.192 |
| Syphilis Rate vs. Incidence | 0.542 [0.462, 0.614] | <0.0001 |
| Syphilis Rate vs. Mortality | -0.065 [-0.161, 0.033] | 0.192 |
| Length of Stay vs. Cost | 0.297 [0.204, 0.385] | <0.0001 |
| Economic Impact | ||
| Metric | Value [95% CI] | p-value |
| Total Cost (High) | R$17,706,806 | -- |
| Total Cost (Low) | R$1,853,377 | -- |
| Total Cost (Intermediate) | R$11,960,451 | -- |
| Cost Difference (High vs. Low) | -236.34 R$ [- 529.48, 56.80] | 0.6141 |
| Cost Difference (High vs. Intermediate) | -101.70 R$ [-398.54, 195.14] | 0.682 |
| Power Analysis | ||
| Metric | Value | p-value |
| Aneurysm Mortality Rate (d=-0.1) | 0.111 | -- |
| Length of Stay (d=-0.484) | 0.937 | -- |
| Average Hospitalization Cost (d=-0.064) | 0.075 | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





