Submitted:
11 October 2025
Posted:
14 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. 5q Deletion in MDS
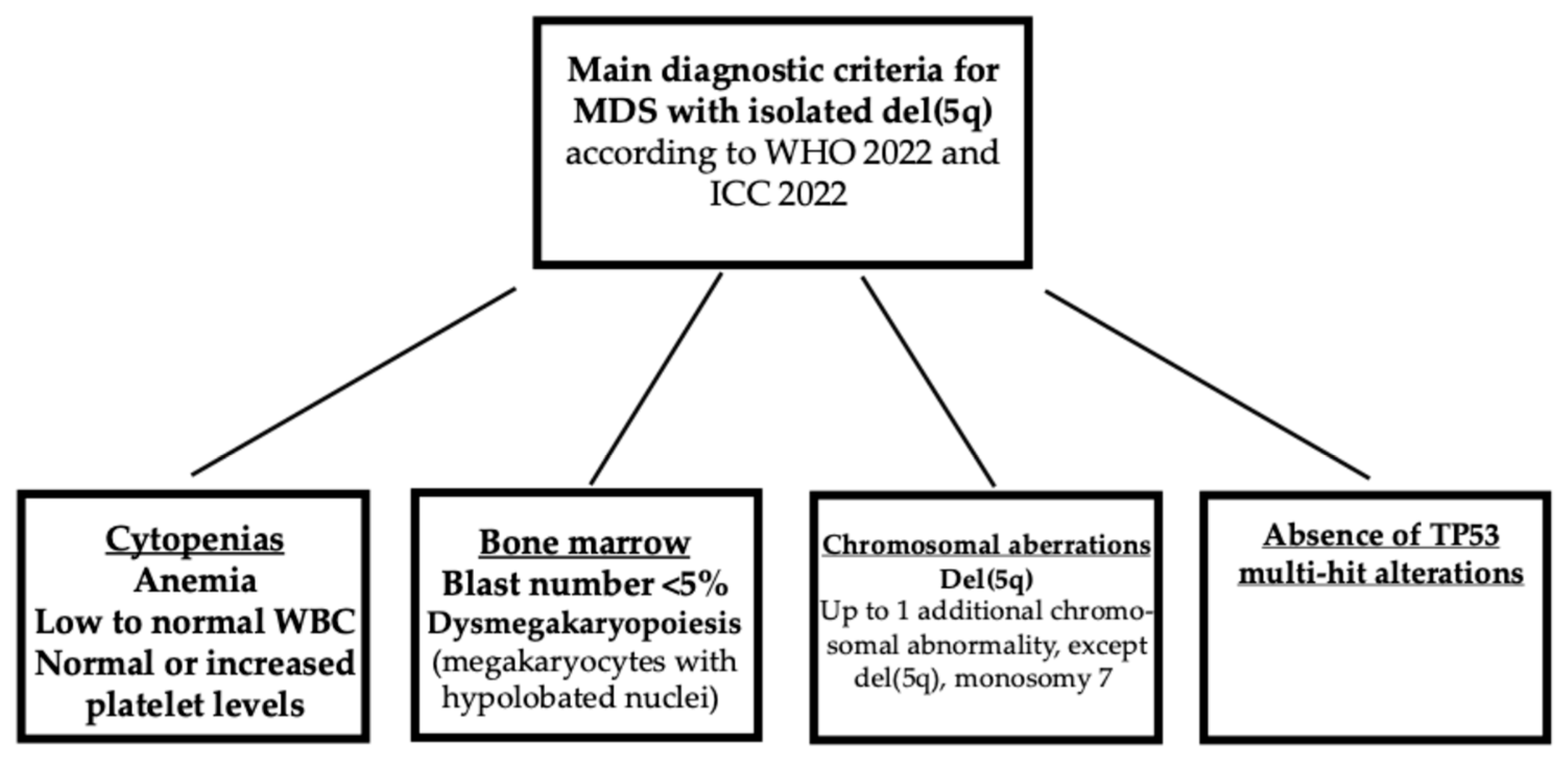
3. Classification of MDS Associated with del(5q)
4. Molecular Pathogenesis of MDS-del(5q)
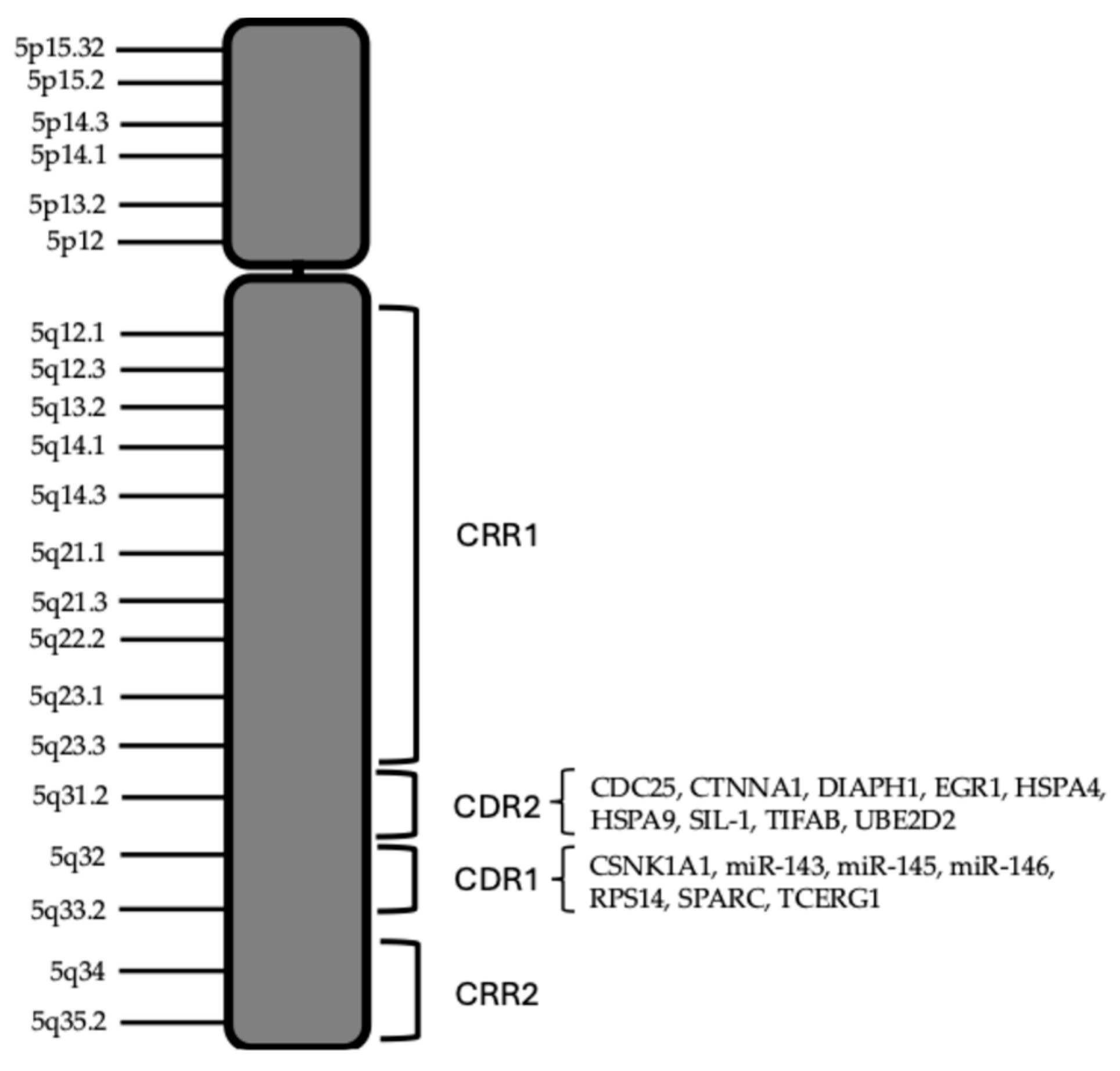
| Gene | Location | Biological Activity |
Gene Knockout Hematologic Phenotype |
| CDC25C | Proximal CDR (5q31.2) | It regulates the transition from G2 to the M phase of the cell cycle | CDC25 knockout mice are viable and display co alterations of cell cycle. CDC25 haploinsufficiency confers sensitivity to lenalidomide |
| CTNNA1 | Proximal CDR (5q31.2) | Catenin 1 alpha mediates the anchorage of actin filaments, signal transduction | Growth advantage to HSCs |
| DIAPH1 | Proximal CDR (5q31.3) | Cytoskeleton formation Tumor suppressor |
Development of age-dependent myelo- Proliferation or MDS. |
| EGR1 | Proximal CDR (5q31.2) | Transcription factor | Fitness advantage to HSCs |
| HSPA9 | Proximal CDR (5q31.2) | Control of cell proliferation and response to stress, inhibition of apoptosis | Apoptosis of hematopoietic progenitors. Block of erythroid maturation |
| TIFAB | Proximal CDR (5q31.1) | Inhibition of NF-kB signaling | Deregulation of TRAF6, NF-kB activation in HSCs, induction of ineffective hematopoiesis |
| CSNK1A1 | Distal CDR (5q32) | Serine/threonine kinase involved in multiple cellular processes and pathways | CSNK1A1 haploinsufficiency confers growth advantage to HSCs/HPCs |
| miR-145 | Distal CDR (5q33.1) | It targets various tumor-specific genes | miR-145 and miR-146a loss induces dysmegakaryopoiesis, thrombocytosis and innate immune signaling |
| miR-146a | Distal CDR (5q33.3) | It targets genes involved in the regulation of inflammation and innate immune system | miR-145 and miR-146a loss induces dysmegakaryopoiesis, thrombocytosis and innate immune signaling |
| RPS14 | Distal CDR (5q33) | 40S ribosomal protein | Macrocytic anemia |
| SPARC (Osteonectin) |
Distal CDR (5q32) | Glycoprotein that binds calcium | Thrombocytopenia Anemia (reduced erythroid progenitors) |
4.1. RPS14
4.2. miR-145 and miR-146a
4.3. CSNK1A1
4.4. HSPAP9 and SPARC
4.5. CTNNA1
4.6. EGR1
4.7. CDC25 and PP2A
4.8. DELE1
4.9. DIAPH1
4.10. TIFAB
4.11. NPM1
5. MDS-del(5q) as a Contiguous Gene Syndrome
6. Therapy-Related MDS-del(5q)
7. Progression and Disease Evolution in MDSA-del(5q)
8. Treatment of MDS-del(5q)
| Comutation |
Frequency in MDS-del(5q) |
Biologic and Clinical Implications |
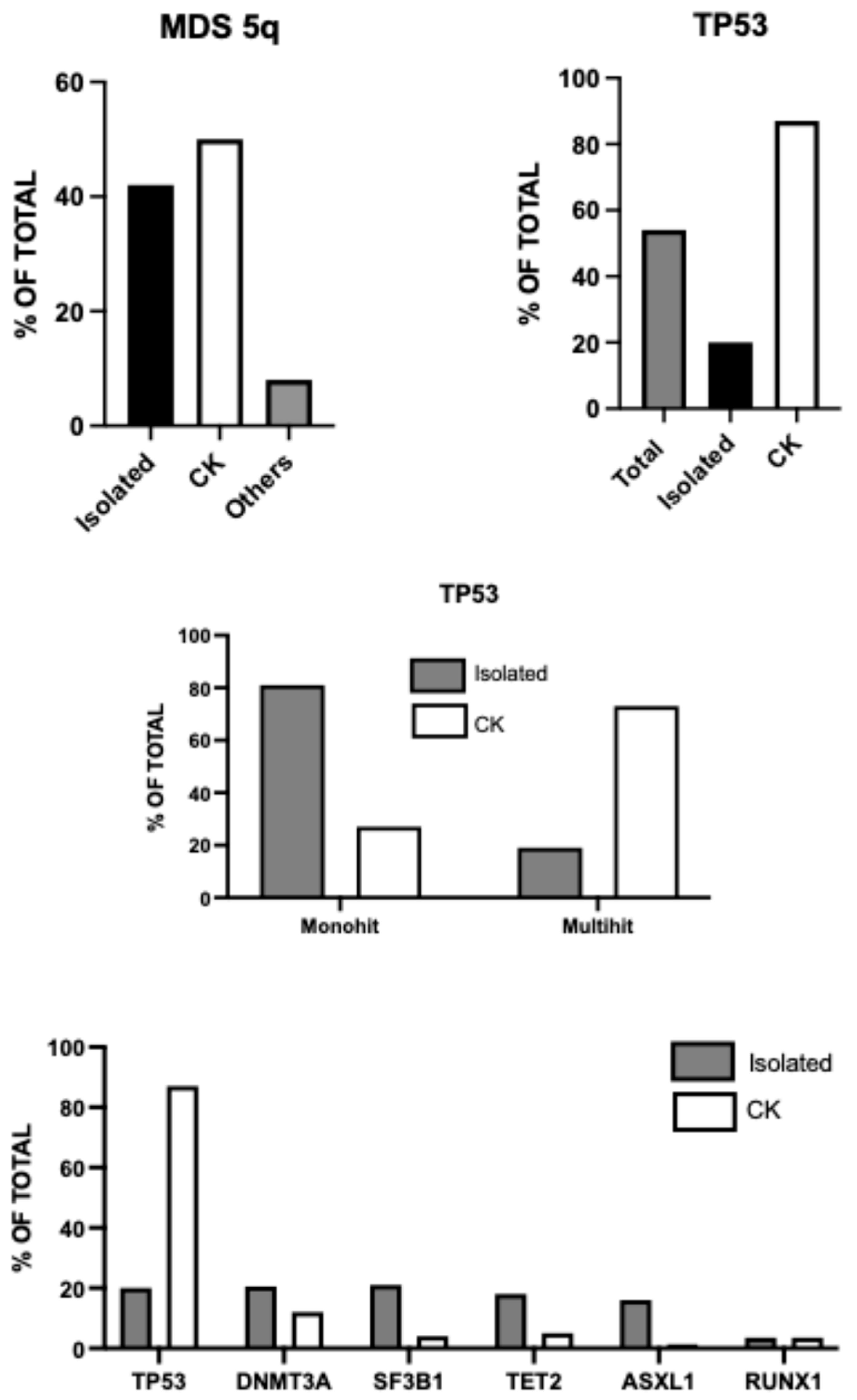
| SF3B1 | 15-20% | Concomitant SF3B1 mutations are associated with lower response rate to lenalidomide, lower OS and increased arte of leukemic transformation. MDS-del(5q)/SF3B1-mutant are frequently associated with TP53 and RUNX1 mutations and display phenotypic properties of both SF3B1-mutant and MDS-del(5q) |
|
TP53 (monoallelic mutation) |
15-20% | Clinical impact of concomitant TP53 mutations depending on VAF frequency of mutant allele: <20% no effect on AML transformation rate and OS; >20% increased AML transformation rate and shorter OS. MDS-del(5q) with concomitant TP53 mutations have a trend to a reduced rate of response to lenalidomide. |
| RUNX1 | 1-3% | RUNX1 mutations are associated with reduced response to lenalidomide, reduced overall survival and a high risk of AML progression and the generation of t-MNs. |
| CSNK1A1 | 8-10% | CSNK1A1 mutation occurring at the level of the non-deleted CSNK1A1 allele is associated with reduced response to lenalidomide and increased risk of progression to a t-MN. |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van den Berghe, H.; Cassiman, J.J.; Frins, J.P.; Michaux, J.L.; Sokal, G. Distinct hematological disorder with deletion of long arm of no. 5 chromosome. Nature 1974, 251, 437-438. [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Vardiman, J. World Health Organization classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (ed 3rd) 2001 Lyon; IARC.
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvanicka, H.M.; Bagg, W.A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; Beso-Ramos, C.E.; et al. International Consensus Classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemias: integrating morphologic, clinical and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200-1228. [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O; Akkori, Y.; Aleggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.; et al. The 5th edition of the world Health Organization Classification of hematolymphoid tumors: myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703-1719.
- Bernard, E.; Hasserjian, R.; Greenberg, P.L.; Ossa, J.E.; Creignou, M.; Tuechler, H.; Gutierrez-Abril, J.; Domenico, D.; Medina-Martinez, J.S.; Farmoud, N.; et al. Molecular taxonomy of myelodysplastic syndromes and its clinical implications. Blood 2024, 144, 1617-1632. [CrossRef]
- Meggendorfer, M.; Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T. Molecular analysis of myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated deletion of the long arm of chromosome 5 reveals a specific spectrum of molecular mutations with prognostic impact: a study on 123 patients and 27 genes. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1502-1510. [CrossRef]
- Montoro, M.J.; Palomo, L.; Haferlach, C.; Acha, P.; Chan, O.; Navarro, V.; Kubota, Y.; Schultz, F.I.; Meggendorfer, M.; Briski, R.; et al. Influence of TP53 gene mutations and their alleliuc status in myelodysplastic syndromes with isolated 5q deletion. Blood 2024, 144, 1722-1732. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Al Ali, N.; Zhang, L.; Papenhausen, P.; Volpe, V.O.; Chan, O.; Kuykendall, A.; Yun, S.; Walker, A.; Sweet, K.; et al. Clinical correlation and prognostic impact of cytogenetic clone size for myelodysplastic syndromes/neoplasm. Blood Neoplasia 2025, 2, 100062. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, D.; Stevenson, K.E.; Neuberg, D.; Macjeweski, J.P.; Nazha, A.; Sekeres, M.A.; Ebert, B.L.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Haferlach, C.; Haferlach, T.; et al. TP53 mutation status divides myelodysplastic syndromes with complex karyotypes into distinct prognostic subgroups. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1747-1758. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.; Hutter, S.; Baer, C.; Meggendorfer, M.; Hoermann, G.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. Two ways to complex karyotype in MDS-the role of del(5q) and TP53. Blood Cancer J 2025, 15, 96. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kewan, T.; Durmaz, A.; Bahaj, W.; Gurnari, C.; Terkawi, L.; Awada, H.; Ogbue, O.; Ahmed, R.; Pagliuca, S.; Awada, H.; et al. Molecular patterns identify distinct subclasses of myeloid neoplasia. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3136. [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.L.; Tuechler, H.; Schanz, J.; Sanz, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Solé, F.; Bennett, J.M.; Bowen, D.; Fenaux, P.; Dreyfus, F.; et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012, 120, 24534-2465. [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Tuechler, H.; Greenberg, P.L.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Arongo Ossa, J.E.; Nannya, Y.; Devlin, S.M.; Creignou, M.; Pinel, P.; Monnier, L.; et al. Molecular international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. NEJM Evid 2022, 1, EVIDoa22000008.
- Montero, M.J.; Palomo, L.; Haferlach, C.; Acha, P.; Chan, O.; Navarro, V.; Kubota, Y.; Schulz, F.; Briski, R.; Al Ali, N.; et al. Newly developed prognostic score for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with isolated 5q deletion (IPSS-del(5q)). Blood 2024, 144 (suppl.1), 666-668. [CrossRef]
- Komrokji, R.S.; Lanino, L.; Ball, S.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Marchetti, M.; Maggioni, G.; Travaglino, E.; Al Ali, N.; Fenaux, P.; Platzbecker, U.; et al. Data-driven, harmonized classification system for myelodysplastic syndromes: a consensus paper from the International Consortium for Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Lancer Hematol 2024, 11, e862-e872. [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Nannya, Y.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Devlin, S.M.; Tuechler, H.; Medina-Martinez, J.S.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiozawa, Y.; Suki, R.; Malcovati, L.; et al. Implications of TP53 allelic state for genome stability, clinical presentation and outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1549-1556. [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Meggendorfer, M.; Walter, V.; Baer, C.; Nadarajah, N.; Hutetr, S.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. Interplay of TP53 allelic state, blast count, and complex karyotype on survival of patients with AML and MDS. Blood Adv 2023, 7, 5540-5548. [CrossRef]
- Pandiri, M.; Stengel, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Shao, H.; Velmurugan, S.; Jacob, A.; Symes, E.; Kaur, A.; Rojek, A.; et al. Karyotypic clonal fraction predicts adverse outcome in TP53-mutated myeloid neoplasms: an international TP53 investigators network (iTiN) study. J Clin Pathol 2025, 78, 629-635. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.V.; Hung, K.; Baranwal, A.; Kutyna, M.; Al-Kali, A.; Toop, C.; Greipp, P.; Brown, A.; Shah, S.; Khanna, S.; et al. Evidence-based risk stratification of myeloid neoplasms harboring TP53 mutations. Blood Adv 2025, 9, 3370-3380. [PubMed]
- Boultwood J., Fidler C., Lewis S., Kelly S., Sheridan H., Littlewood T., Buckle V., Wainscoat J. Molecular Mapping of Uncharacteristically Small 5q Deletions in Two Patients with the 5q- Syndrome: Delineation of the Critical Region on 5q and Identification of a 5q- Breakpoint. Genomics. 1994; 19:425–432.
- Boultwood J., Fidler C., Strickson A.J., Watkins F., Gama S., Kearney L., Tosi S., Kasprzyk A., Cheng J.-F., Jaju R.J., et al. Narrowing and Genomic Annotation of the Commonly Deleted Region of the 5q- Syndrome. Blood. 2002; 99:4638–4641.
- Jaju R., Boultwood J., Oliver F., Kostrzewa M., Fidler C., Parker N., McPherson J., Morris S., Müller U., Wainscoat J., et al. Molecular Cytogenetic Delineation of the Critical Deleted Region in the 5q- Syndrome. Genes Chromosom. Cancer. 1998; 22:251–256.
- Jerez A., Gondek L.P., Jankowska A.M., Makishima H., Przychodzen B., Tiu R.V., O’Keefe C.L., Mohamedali A.M., Batista D., Sekeres M.A., et al. Topography, Clinical, and Genomic Correlates of 5q Myeloid Malignancies Revisited. JCO. 2012; 30:1343–1349.
- La Starza, R.; Matteucci, C.; Gorello, P.; Brandimarte, L.; Pierini, V.; Crescenzi, B.; Nofrini, V.; Rosati, R.; Gottardi, E.; Saglio, G.; et al. NPM1 deletion is associated with groos chromosomal rearrangements in leukemia. PLos One 2010, 5, e12855. [CrossRef]
- Nofrini, V.; La Starza, R.; Crescenzi, B.; Pierini, V.; Barba, G.; Mecucci, C. Different boundaries characterize isolated and non-isolated 5q deletions in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. Haematologica 2012, 97, 792-794. [CrossRef]
- Rea, B.; Aggarwal, N.; Yetsenko, S.A.; Bailey, N.; Liu, Y.C. Acute myeloid leukemia with isolated del(5q) is associated with IDH1/IDH2 mutations and better prognosis when compared to acute myeloid leukemia with complex karyotype including del(5q). Modern Patology 2020, 33, 566-575.
- Stengel, A.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Meggendorfer, M.; Haferlach, C. The 5q deletion size in myeloid malignancies is correlated with additional chromosomal aberrations and to TP53 mutations. Genes Chrom Cancer 2016, 55, 777-785. [CrossRef]
- Zemanova, Z.; Michalova, K.; Buryova, H.; Brezinova, J.; Lizcova, L.; Kostykova, K.; Sarova, I.; Izakova, S.; Rnasdorfova, S.; Krejcik, Z.; et al.
- Warnstorf, D.; Bawadi, R.; Schienke, A.; Starsser, R.; Schmidt, G.; Illig, T.; Tauscher, M.; Thol, F.; Heuser, M.; Steinemann, D.; et al. Unbalanced translocation del(5;17) resulting in TP53 loss as recurrent aberration in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia with complex karyotype. Genes Chrom Cancer 2021, 60, 452-457. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, S.; Kohlmann, A.; Schnittger, S.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. Association of the type of 5q loss with complex karyotype, clonal evolution, TP53 mutation status, and prognosis in acute myeloid leiukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Genes Chrom Cancer 2014, 53, 402-410. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boultwood,J.; Pellagatti, A.; Cattan, H. Gene expression profiling of CD34+ cells in patients with 5q- syndrome. Br J Haematol 2007, 139, 578-589.
- Adema, V.; Paloma, L.; Walter, W.; Mallo, M, Hutter, S.; La Franboise, T.; Arenillas, L.; Meggendorfer, M.; Radivoyevitch, T.; Xicoy, B.; et al. Pathophysiologic and clinical implications of molecular profiles resultant from deletion 5q. eBiomedicine 2022, 80, 104059. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaju, R.J.; Boutlwood, J.; Oliver, F.J.; Kostrezva, M.; Fidler, C.; Parker, N.; McPherson, J.D.; Morris, S.W.; Muller, U.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Molecular cytogenetic delineation of the critical deleted region in the 5q- syndrome. Genes Chrom Cancer 1998, 22, 251-256. [CrossRef]
- Ebert, B.L.; Pretz, J.; Bosco, J.; Chang, C.Y.; Tamayo, P.; Galili, N.; Raza, A.; Root, D.E.; Attar, E.; Dellis, S.R.; et al. Identification of RPS14 as a 5q- syndrome gene by RNA interference screen. Nature 2008, 451, 335-339. [CrossRef]
- Dutt, S.; Narla, A.; Lin, K.; Mullally, A.; Abayasekara, N.; Megerdichian, C.; Wilson, F.H.; Currie, T.; Khanna-Gupta, A.; Berliner, N.; et al. Haploinsufficiency for ribosomal protein genes causes selective activation of p53 in huma erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 2011, 117, 2567-2576. [CrossRef]
- Pellagatti, A.; Marafioti, T. Paterson, J.C.;; Barlow, J.L.; Drynan, L.F.; Giagounidis, A.; Pileri, S.A.; Cazzola, M.; McKenzie, A.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Induction of p53 and up-regulation of the p53 pathway in the human 5q- syndrome. Blood 2010, 115, 2721-2723.
- Barlow, J.L.; Drynan, L.F.; Hewett, D.R.; Holmes, L.R.; Lorenzo-Abalkde, S.; Lane, A.L.; Jolin, H.E.; Pannell, R.; Middleton, A.; Wong, S.H.; et al. A p53-dependent mechanism underlies macrocytic anemia in a mouse model of human 5q- syndrome. Nat Med 2010, 16, 59-66. [CrossRef]
- Pellagatti, A.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E.; Giagounidis, A.; Perry, J.; Malcovati, L.; Della Porta, M.; Jadersten, M.; Killick, S.; Fidler, C.; Cazzola, M.; et al. Haloinsufficiency of RPS14 in 5q- syndrome is associated with deregulation of ribosomal- and translation-related genes. Brit J Haematol 2008, 142, 57-64. [CrossRef]
- Pellagatti, A.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E.; Giagounidis, A.; Perry, J.; Malcovati, L.; Della Porta, M.; Jadersten, M.; Killick, S.; Sohal, D.; Verma, A.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of RPS14 and deregulation of ribosomal- and translation-related genes in MDS patients with del(5q). Blood 2008, 112 (suppl.1), 3641. [CrossRef]
- Cziberre, A.; Bruns, I.; Junge, B.; Kobbe, G.; Haas, R.; Germing, U. Low RPS14 expression is common in myelodysplastic syndromes without 5q- aberration and defines a subgroup of patients with prolonged survival. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1453-1455. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, C. Low Rps14 expression in MDS without 5q- aberration confers higher apoptosis rate of nucleated erythrocytes and predict prolonged survival and possible response to lenalidomide in lower risk non-5q- patients. Eur J Haematol 2013, 90, 486-493. [CrossRef]
- Linares, M.; Rapado, I.; Ruiz-Heredia, Y.; Cedena, M.T.; Quiroz, K.; Barrio, S.; Ayala, R.; Martinez, J. 5q+ MDS patients with low RPS14 expression are candidates to immune-modulating drugs. Blood 2017, 130, 5303.
- Adema, V.; Kongkiatkamon, S.; Palomo, L.; Walter, W.; Hutter, S.; LaFrambiose, T.; Diez-Campelo, M.; Mallo, M.; Xicoy, B.; Meggendorfer, M.; et al. Deficiency of RPs14 beyond the haploinsufficient loss in del(5q). Blood 2021, 138 Suppl.1), 2591. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.K.; Schenone, M.; Ventura Ferreira, M.; Kramann, R.; Joyce, C.E.; Hartigan, C.; Beier, F.; Brummendorf, T.H.; Germin, L.; Pletzbecker, U.; et al. Rps14 haploinsufficiency causes a block in erythroid differentiation mediated by S100A8 and S100A9. Nat Med 2016, 22, 288-297. [CrossRef]
- Starczynowski, D.T.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Argiropoulos, B.; Sung, S.; Morin, R.; Muranyi, A.; Hirst, M.; Hogge, D.; Marra, M.; Wells, R.A.; et al. Identification of MiR-145 and MiR-146a as Mediators of the 5q– Syndrome Phenotype. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 49–58. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Narla, A.; Nonami, A.; Mullally, A.; Dimitrova, N.; Ball, B.; McAuley, J.R.; Poveromo, L.; Kutok, J.L.; Galili, N.; et al. Coordinate Loss of a MicroRNA and Protein-Coding Gene Cooperate in the Pathogenesis of 5q- Syndrome. Blood 2011, 118, 8. [CrossRef]
- Schneider R.K.; Adema, V.; Heckl, D.; Jaras, M.; Mallo, M.; Lord, A.; Chu, L.; McConkey, M.; Kramann, R.; Mullally, A.; et al. Role of casein kinase 1A1 in the biology and targeted therapy of del(5q) MDS. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 509-520. [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.E.; Kulakaseraj, A.; Jiang, J.; Mian, S.; Mohamedali, A.; Gaken, J.; Ireland, R.; Czepulkowski, B.; Best, S.; Mufti, G.J.; et al. CSNK1A1 mutations and isolated del(5q) abnormality in myelodysplastic syndrome: a retrospective mutational analysis. Lancet Hematol 2015, 2, e212-e221. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuser, M.; Meggendorfer, M.; Cruz, M.M.; Fabisch, J.; Klesse, S.; Kohler, L.; Gohring, G.; Ganster, C.; Shirneshan, K.; Gutermuth, A.; et al. Frequency and prognostic impact of casein kinase 1A1 mutations in MDS patients with deletion of chromosome 5q. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1942-1945. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalmann, U.; Ticconi, F.; Snoeren, I.; Li, R.; Gleitz, H.; Coeley, G.; McConkey, M.; Wong, A.; Smitz, S.; Fuchs, S.; et al. Genetic barcoding systematically compares genes in del(5q) MDS and reveals a central role for CSNK1A1 in clonal expansion. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 1780-1786. [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.; Stalmann, U.; Snoeren, I.; Bindels, E.; Schmitz, S.; Banjamin, B.; Hoogenboezem, R.; van Herk, S.; Saad, M.; Walter, W.; et al. Collaborative effect of CSNK1A1 haploinsufficiency and mutant p53 in Myc induction can promote leukemic transformation. Blood Adv 2024, 8, 766-774. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollotzek, F.; Mott, K.; Fischer, M.; Findik, B.; Gob, V.; Manke, M.C.; Borst, C.E.; Polzin, A.; Burkhalter, M.D.; Eckly, A.E.; et al. Casein kinase 1α essentially regulates thrombopoiesis by driving megakaryocyte maturation and cytoskeleton organization. Blood 2025, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Schobrunn, E.; Chen, J. Tumor-derived CK1α mutations enhance MDMX inhibition of p53. Oncogene 2020, 39, 176-186. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahanian, N.; Knoblsch, C.D.; Bowman, C.A.; Rezvani, K. Mortalin: protein partners, biological impacts, pathological role, and therapeutic opportunities. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 10228519. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Kambai, A.; Krysiak, K.; Walhauser, M.A.; Raju, G.; Tibbitts, J.F.; Walter, M.J. Kockdown of Hspa9, a del(5q31.2), results in a decrease in hematopoietic progenitors in mice. Blood 2010, 117, 1530-1539.
- Liu, T.; Krysiak, K.; Shirai, C.L.; Kim, S.; Shao, J.; Ndonwi, M.; Walter, M.J. Knockdown of HSPA9 induces TP53-dependent apoptosis in human hematopoietic progenitor cells. PlOS ONE 2017, 12, e0170470. [CrossRef]
- Butler, C.; Dunmire, M.; Choi, J.; Szalai, G.; Johnson, A.; Lei, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Walter, M.J.; Liu, T. SSPA9/mortalin inhibition disrupts erythroid maturation through a TP53-dependent mechanism in human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 2024, 29, 300-311. [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; O’Kelly, J.; Raynaud, S.; Funk, S.E.; Sage, E.H.; Koeffler, H.P. Common deleted genes in the 5q- syndrome: thrombocytopenia and reduced erythroid colony formation in SPARC null mice. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1931-1936. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Luo, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, L. SPARC promotes the development of erythroid progenitors. Exp Hematol 2012, 40, 828-836. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.X.; Becker, M.W.; Jelinck, J.; Wu, W.S.; Deng, M.; Mikhalkevich, N.; Hsu, K.; Blomfield, C.; Stone, R.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; et al. Chromosome 5 deletion and epigenetic suppression of the gene encoding α-catenin (CTNNA1) in myeloid cell transformation. Nat Med 2007, 13, 78-83. [CrossRef]
- Joslin, J.M.; Fernald, A.A.; Qian, Z.; Crispino, J.D.; LeBeau, M. Egr1, a candidate gene within the commonly deleted segment of chromosome 5, plays a role in murine erythropoiesis and leukemogenesis. Blood 2005, 106 (suppl.1), 663. [CrossRef]
- Joslin, J.M.; Fernald, A.A.; Tennant, T.R.; Davis, E.M.; Kogan, S.C.; Anastasi, J.; Crispino, J.D.; LeBeau, M. Haploinsufficiency of EGR1, a candidate gene in the del(5q), leads to the development of myeloid disorders. Blood 2007, 110, 719-726. [CrossRef]
- Stoddart, A.; Fernald, A.A.; Davis, E.M.; McNerney, M.E.; LeBeau, M. EGR1 haploinsufficiency confers a fitness advantage to hematopoietic stem cells following chemotherapy. Exp Hematol 2022, 115, 54-67. [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Rocha, K.; Williams, A.; Chen, X.; Burnette, P.K.; Djeu, J.Y.; Liu, Q.; Byrd, J.; Sokol, L.; Lawrence, N.; et al. Gene dosage of the cell cycle regulatory phosphatases Cdsc25C and PP2A determines sensitivity to lenalidomide in del(5q) MDS. Blood 2007, 110 (suppl.1), 118. [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Chen, X.; Rocha, K.; Epling-Burnette, P.K.; Dieu, J.Y.; Liu, Q.; Byrd, J.; Sokol, L.; Lawrence, N.; Pireddu, R.; et al. A critical role for phosphatase haploinsufficiency in the selective suppression of deletion 5q MDS by leniladomide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009, 106, 12974-12979. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinell, J.F.; Chanbgroul, J.; Moison, C.; Lavallée, V.P.; Bolin, I.; Gracias, D.; Lavallée, S.; Richard Carpentier, G.; Beliveau, F.; Hébert, J.; et al. DELE1 haploinsufficiency causes resistance to mitochondrial stress-induced apoptosis in monosomy 5/del(5q) AML. Leukemia 2024, 38, 530-537. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Kitchen, S.M.; West, R.A.; Sigler, R.; Eisenmann, K.M.; Alberts, A.S. Myeloproliferative defects following targeting of the Drfg1 gene encoding the mammalian diaphanous-related formin mDia1. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 7675-7671. [CrossRef]
- Keerthivasan, G.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L.; Harris, C.E.; Gao, J.; Basiorka, A.A.; Schipma, M.J.; McElherme, J.; Verma, A.K.; et al. Aberrant overexpression of CD14 on granulocytes sensitizes the innate immune response in mDia1 heterozygous del(5q) MDS. Blood 2014, 124, 780-790. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Lodier, L.; Meyran, D.; Rameau, P.; Lecluse, Y.; Kitchen-Goosen, S.; Badirou, I.; Mokrani, H.; Narumya, S.; Alberts, A.S.; Vainchenker, W.; et al. The forming DIAPH1 (mDia1) regulates megakaryocyte proplatelet formation by remodeling the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons. Blood 2014, 124, 3967-3977. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, D. DIAPH1 mutations predict favorable outcome for de novo MDS. Cancer Letters 2024, 598, 217125. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ohyama, C.; Sakamoto, M.; Toma, T.; Tateishi, H.; Matsuo, M.; Chirifu, M.; Ikemizu, S.; Morioka, H.; Fujita, M.; et al. TIFAB regulates the TIFA-TRAF6 signaling pathway involved in innate immunity by forming a heterodimer complex with TIFA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2024, 121, e2318794121. [PubMed]
- Varney, M.; Christie, S.; Niederkom, M.; Fang, J.; Jerez, A.; Maciejewski, D.T.; Inoue, J.; Starczynowski, D.T. Deletion of TIFAB, a novel candidate gene on chromosome 5q, results in hematopoietic defects by changing the dynamic range of innate immune pathway activation. Blood 2013, 122 (suppl.1), 102. [CrossRef]
- Varney, M.E.; Niederkon, M.; Konno, H.; Matsumara, T.; Gohdfa, J.; Yoshida, N.; Akiyama, T.; Christie, S.; Fang, J.; Miller, D.; et al. Loss of Tifab, a del(5q) MDS gene, alters hematopoiesis through derepression of Toll-like receptor-TRAF6 signaling. J Exp Med 2015, 212, 1967-1985. [CrossRef]
- Niederkon, M.; Hueneman, K.; Choi, K.; Varney, M.E.; Romano, L.; Pujato, M.A.; Greis, K.D.; Inoue, J.; Meetei, R.; Starczynowski, D.T. TIFAB regulates USP15-mediated p53 signaling during stressed and malignant hematopoiesis. Cell Rep 2020, 30, 2776-2790. [CrossRef]
- Raval, A., Kusler, B.; Weissman, I.L.; Mitchell, B.S.; Park, C.Y. Effect of nucleophosmin 1 haploinsufficiency on hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 2012, 26, 853-855. [PubMed]
- Morganti, C.; Ito, K.; Yanase, C.; Verma, A.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Ito, K. NPM1 ablation induces HSC aging and inflammation to develop myelodysplastic syndrome exacerbated by p53 loss. EMBO Rep 2022, 23, e54262.
- Ribezzo, F.; Snoeren, I.; Ziegler, S.; Stoelben, J.; Olofsen, P.A.; Henic, A.; Ventura Ferreira, M.; Chen, S.; Stalmann, U,; et al. Rps14, Csnk1A1 and miR145/miR146a deficiency cooperate in the clinical phenotype and activation of the innate immune system in the 5q- syndrome. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1759-1772.
- Varney, M.E.; Choi, K.; Bolanos, L.; Epistasis between TIFAB and miRT-146a: neighboring genes in del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2017, 31, 491-495.
- Muto, T.; Walker, C.S.; Agarwal, P.; Vick, E.; Sampson, A.; Choi, K.; Niederkon, M.; Ishikawa, C.; Hueneman, K.; Varney, M.; et al. Inactivation of p53 provides a competitive advantage to del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome hematopoietic stem cells. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2715-2729. [CrossRef]
- Berggren, D.M.; Garelius, H.; Hjielm, P.W.; Nilsson, L.; Ramussen, B.; Elbult, C.E.; Lambe, M.; Lehmann, S.; Heelstrom-Lindberg, E.; Jadersten, M.; et al. Therapy-related MDAS dissected based in primary disease and treatment-a nation-wide perspective. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1103-1112.
- Wong, T.N.; Ramsingh, G.; Young, A.L.; Miller, C.A.; Touma, W.; Welch, J.S.; Lamprecht, T.L.; Shen, D.; Hundal, J.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Nature 2015, 518, 552-555.
- Lindsley, R.C.; Saber, W.; Nar, B.G.; Wang, T.; Haagenson, M.D.; Grauman, P.V.; Hu, Z.H.; Spellman, R.R.; Lee, S.J.; Verneris, M.R.; et al. Prognostic mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome after stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 2017, 376, 536-547. [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Le Beau, M.; Huo, D.; Karrison, T.; Sobecks, R.M.; Anastasi, J.; Varrdiman, J.W.; Rowley, J.D.; Lrason, R.A. Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: the University of Chicago series. Blood 2003, 102, 43-52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidan, A.M.; Al Ali, N.; Barnard, J.; Padron, E.; Lancet, J.E.; Sekeres, M.A.; Steensma, D.P.; DeZern, A.; Roboz, G.; Jabbour, E.; et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and prognostic utility of risk stratification tools in patients with therapy-related vs de novo myelodysplastic syndromes: a report on behalf of the MDS clinical research consortium. Leukemia, 31, 1391-1397.
- Hiwase, D.; Hahn, C.; Tran, E.N.H.; Chhetri, R.; Baronwal, A.; Al-kali, A.; Sharplin, K.; Hillins, R.; Greipp, P.; et al. TP53 mutation in therapy-related myeloid neoplasms defines a distinct molecular subtype. Blood 2023, 141, 1087-1091. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.V.; Tran, E.H.N.; Shah, S.; Chhetri, R.; Baranawl, A.; Ladon, D.; Shultz, C.; Al-kali, A.; Brown, A.L.; Chen, D.; et al. TP 53 mutation variant allele frequency of ≥10% is associated with poor prognosis in therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. Blood Cancer J 2023, 13, 51. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Li, B.; Qin, T.; Xu, Z.; Qu, S.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Pan, L.; Gao, Q.; Jiao, M.; et al. Molecular characteristics and clinical implications of TP53 mutations in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Cancer J 2025, 15, 58. [CrossRef]
- Lessard, M.; Hélias, C.; Struski, S.; Perrusson, N.; Uetwiller, F.; Mozziconacci, M.J.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M.; Dastugue, N.; Terré, C.; Brizard, F.; et al. Groupe francophone de cytogénétique hématologique. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of 110 hematopoietic disorders with chromosome 5 abnormalities: do de novo and therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome-acute myeloid leukemia actually differ? Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2007, 176, 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Fleti, F.; Singh, A.; Al-Kali, A.; Foran, J.M.; Elliott, M.A.; Begna, K.; Badar, T.; Khera, N.; Shah, M.V.; Alkhateeb, H.B.; et al. Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes with isolated del(5q): a comparative analysis of phenotype and long-term survival. Blood 2022, 140, 6940-6941. [CrossRef]
- Jadersten, M.; Saft, L.; Pellegatti, A.; Gohring, G.; Wainscopat, J.S.; Boutwood, J.; Porwit, A.; Schagelberger, B.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E. Clonal heterogeneity in the 5q- syndrome: p53 expressing progenitors prevail during lenalidomide treatment and expand at disease progression. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1762-1766. [CrossRef]
- Schagelberger, B.; Giai, V.; Pellagatti, A.; Saft, L.; Dimitriou, M.; Jansson, M.; Jadersten, M.; Grandien, A.; Davagi, I.; Neuberg, D.S.; et al. Progression in patients with low- and intermediate-risk del(5q) myelodysplastic syndromes is predicted by a limited subset of mutations. Haematologica 2017, 102, 498-508.
- Mossner, M.; Jann, J.C.; Witting, J.; Nolte, F.; Fey, S.; Nowak, V.; Oblander, J.; Pressler, J.; Palme, I.; Xanthopoulos, C.; et al. Mutational hierarchies in myelodysplastic syndromes dynamically adapt and evolve upon therapy response and failure. Blood 2016, 128, 1246-1259. [CrossRef]
- Mossner, M.; Jann, J.C.; Nowak, D.; Platzbecker, U.; Giagounidis, A.; Gotze, K.; Prevalence, clonal dynamics and clinical impact of TP53 mutations in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated deletion (5q) treated with lenalidomide: results from a prospective multicenter study of the German MDS study group (GMDS). Leukemia 2016, 30, 1956-1959. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lode, L.; Menard, A.; Flet, L.; Richebourg, S.; Loirat, M.; Eveillard, M.; et al. Emergence and evolution of TP53 mutations are key features of disease progression in myelodysplastic patients with lower-risk del(5q) treated with lenalidomide. Haematologica 2018, 103, e143-e146. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, A.S.; Guerra, V.; Kennedy, J.A.; Yan, Y.; Hsu, J, Wang, F.; Nguyen, A.T.; Miller, P.G.; McConkey, M.; Quevedo Barrios, V.; et al. Lenalidomide promotes the development of TP53-mutated therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. Blood 2022, 140, 1753-1763.
- Abdallah, M.; Reichard, K.; Gnagat, N.; Tefferi, A. Treatment-emergent mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome with del (5q)-lenalidomide related or disease-intrinsic clonal evolution. Blood Cancer J 2024, 14, 49. [CrossRef]
- Feurstein, S.; Thomay, K.; Hofmann, W.; Buesche, G.; Kreipe, H.; Thol, F.; Heuser, M.; Ganser, A.; Schlegelberger, B.; Gihring, G. Routes of clonal evolution into complex karyotypes in myelodysplastic syndrome patients with 5q deletion. Int Mol Sci 2018, 19, 3269. [CrossRef]
- Merz, A.M.A.; Platzbecker, U. Treatment of lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Hamatologica 2025, 110, 330-338. [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.; Raddi, M.G.; Mohan, S.; Santini, V. New approvals in low- and intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2025, 45, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Roncador, M.; Bernard, E.; Hasserjian, R.; Boulwood, J.; Elena, C.; Galli, A.; Gurnari, C.; Mecacci, C.; Michaux, L.; Mittelman, M.; et al. A precision medicine approach to the myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated deletion 5q, fifty years after its discovery. Blood 2025, in press.
- Huber, S.; Haferlach, T.; Meggendorfer, M.; Hutter, S.; Hoermann, G.; Baer, C.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C. SF3B1 mutated MDS: blast count, genetic co-abnormalities and their impact on classification and prognosis. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2894-2902. [CrossRef]
- Chan, O.; Al Ali, N.; Sallman, D.A.; Padron, E.; Lancet, J.E.; Komrokji, R. SF3B1 mutations and not TP53 are associated with outcomes in patients with del(5q) myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Blood 2020, 136 (suppl.1), 25-26. [CrossRef]
- Duetz, C.; Westers, T.; Hout, F.; Cremers, E.; Alhan, C.; Venniker-Punt, B.; Visser-Wisselaar, B.; Chitu, D.; de Graaf, A.; Smit, L.; et al. DFistinct bone marrow immunophenotypic features define the splicing factor 3B subunit 1 (SF3B1)-mutant myelodysplastic syndromes subtype. Brit J Haematol 2021, 193, 798-803. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Gao, Q.; Arcila, M.; Roshal, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Chan, A. Diagnostic challenges and proposed classification of myeloid neoplasms with overlapping features of thrombocytosis, ring sideroblasts and concurrent del(5q) and SF3B1 mutations. Haematologica 2024, 109, 2676-2681.
- Komrokji, R.S.; Schwabkey, Z.I.; Al Ali, N.K.; Aguirre, L.E.; Stahl, M.; Ball, S.; Mason, E.F.; Savona, M.R.; Santini, V.; Consagra, A.; et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes with concomitant SF3B1 mutation and deletion of the long arm of chromosome 5 (SF3B1del5q): outcomes and response to treatment. Blood 2024, 144 (suppl.1), 1845-1847. [CrossRef]
- Marinez-Heter, S.; Deng, Y.; Parker, J.; Jiang, J.; Mo, A.; Decking, T.R.; Gharaee, N.; Li, J.; Umlandt, P.; Fuller, M.; et al. Loss of lenalidomide-induced megakaryocytic differentiation leads to therapy resistance in del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome. Nat Cell Biol 2020, 22, 526-533.
- Barreyro, L.; Sampson, A.M.; Hueneman, K.; Choi, K.; Christie, S.; Ramesh, V.; Wyder, M.; Wang, D.; Pujato, M., Greis, K.D.; et al. Dysregulated innate immune signaling cooperates with RUNX1 mutations to transform an MDS-like disease to AML. I Science 2024, 27, 109809.
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Santini, V.; Zeidan, A.M.; Komrokoji, R.S.; Pozharskaya, V.; Rose, S.; Keeperman, K.; Lai, Y.; Karsekar, S.; Aggarwal, B.; et al. Long-term transfusion independence with Luspatercept versus epoietin alfa in erythropoiesis-stimulating agent-naïve, lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes in the COMMANDS trial. Adv Ther 2025, 42, 3676-3689. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Porta, M.G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Santini, V.; Zeidan, A.M.; Komrokji, R.S.; Shortt, J.; Valcarcel, D.; Jonasova, A.; Dimicoli-Salazar, S.; Tiong, I.S.; et al. Luspatercept versus epoietin alfa in erythropoiesis-stimulating agent-naïve, transfusion-dependent, lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (COMMANDS): primary analysis of a phase 3, open-label, randomized, controlled trial. Lancet Hematol 2024, 11, e646-e659. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platzbacker, U.; Della Porta, M.G.; Santini, V.; Zeidan, A.M.; Komrokji, R.S.; Shott, J.; Valcarcel, D.; Jonasova, A.; Dimicoli-Salazar, S.; Tiong, I.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of luspatercept versus epoietin alfa in erythropoiesis-stimulating agent-naïve, transfusion-dependent, lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (COMMANDS): interim analysis of a phase 3, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 373-385. [CrossRef]
- Fenaux, P.; Platzbecker, U.; Mufti, G.J.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Buckskin, R.; Santini, V.; Dier-Compelo, M.; Finelli, C.; Cazzola, M.; Ilhan, D.; et al. Luspatercept in patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 140-151. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, E.N.; Poloni, A.; Frairia, C.; Riva, M.; Capodanno, I.; Delfino, I.M.; D’Errigo, M.G.; Mammì, C.; Ianni, G.; Zini, G.; et al. Luspatercept for the treatment of transfusion-dependent anemia in patients with myelodysplastic neoplasms with del5q, refractory/resistant/intolerant to prior treatments (QOL_ONE Phoenix). Blood 2024, 144 (suppl.1), 6741-6742. [CrossRef]
- Patsialos, I.; Kontandreopoulou, C.N.; Vlachopoulou, D.; Safylidis, C.; Syriopoulou, S.; Kalala, F.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Mantzrourani, M; et al. A myelodysplastic neoplasm with del(5q) treated with luspatercept uncovers unexplored mechanisms of action for the drug. Brit J Haematol 2024, 205, 1641-1644.
- Fenaux, P.; Mufti, G.J.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E.; et al. Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of conventional care regimens in the treatments of myelodysplastic syndromes: a randomized, open-label, phase III study. Lancet Oncol 2009, 10: 223-232.
- Sekeres, M.A.; Othus, M.; List, A.F.; et al. Randomized phase II study of azacitidine alone or in combination with lenalidomide or verinostat in higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: North American Intergroup Study sWOG S1117. J Cin Oncol 2017, 35, 2745-2753. [CrossRef]
- Bernal, T.; Martinez-Camblor, P.; Sanchez-Garcia, J.; et al. Effectiveness of azacitidine in unselected high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes: results from the Spanish registry. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1875-1881. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.S.; Platbecker, U.; Odenike, O.; Fleming, S.; Fong, C.Y.; Borate, U.; Jacoby, M.A.; Nowak, D.; Baer, M.R.; Petrlin, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of venetoclax plus azacitidine for patients with treatment-naïve high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2025, 145, 1126-1135. [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, A.; Loghavi, S.; Wei, Y.; Bataller, A.; Sasaki, K.; Arani, N.; Darbaniyan, F.; Chien, K.; Hammond, D.; Bouligny, I.; et al. Leukemia 2025, 39, 2256-2265.
- Huber, S.; Haferlach, T.; Muller, H.; Meggendorfer, M.; Hutter, S.; Hoerman, G.; Haferlach, C. MDS subclassification-do we still have to count blasts? Leukemia 2023, 37, 942-945. [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Khanna, V.; Jensen, A.; Stehr, H.; Tan, B.; Yatsenko, S.; Greenberg, P.L. Molecular taxonomy of MDS/CMML patients influences responses to hypomethylating agents and clinical outcomes. Leuk Res 2025, 156, 107736. [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, P.P.; Al Amri, R.; Baloda, V.; Aarabi, M.; Aggarwal, N.; Djokic, M.; Monaghan, S.A.; Moore, E.M.; Rea, B.; Bailey, N.G. Validation of clinicopathologic features of a genetic myelodysplastic syndrome classification in an independent cohort. J Hematopathol 2025, 18, 42. [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.; Haferlach, T.; Hutter, S.; Hoermann, G.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C. Relevance of blast counts for genetic subclassification in MDS. Leukemia 2025, 39, 271-273. [CrossRef]
- Al Amri, R.; Baloda, V.; Monaghan, S.A.; Rosado, F.G.; Moore, E.M.; Rea, B.; Diokic, M.; Aggarwal, N.; Yatsenko, S.A.; Bailey, N.G. Validation of independent prognostic significance of blast count in a large cohort of MDS patients. Leukemia 2024, 38, 2064-2067. [CrossRef]
- Zampini, M.; Riva, E.; Lanino, L.; Sauta, E.; Dos Reis, R.A.; Ejarque, R.M.A.; Maggioni, G.; Termanini, A.; Merlotti, A.; Campagna, A.; et al. Characterization and clinical implications of p53 dysfunction in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol 2025, 43, 2069-2083.
- Rasmussen, B.; Gohring, G.; Bernard, E.; Nilsson, L.; Tobiasson, M.; Jadersten, M.; Garelius, H.; Dybedal, I.; Gronbaeck, K.; Ejerblad, E.; et al. Randomized phase II study of azacitidine ± lenalidomide in higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia with a karyotype including Del(5q). Leukemia 2022, 36, 1436-1439. [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, B.; Nilsson, L.; Tobiasson, M.; Jadersten, M.; Garelius, H.; Dybedal, I.; Gronbaek, K.; Ejerblad, E.; Lorenz, F.; Flogegard, M.; et al. Influence of cytogenetics on the outcome of patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome including deletion 5q treated with azacitidine with or without lenalidomide. Genes Chrom Cancer 2025, 64, e70029. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





