Submitted:
06 October 2025
Posted:
07 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
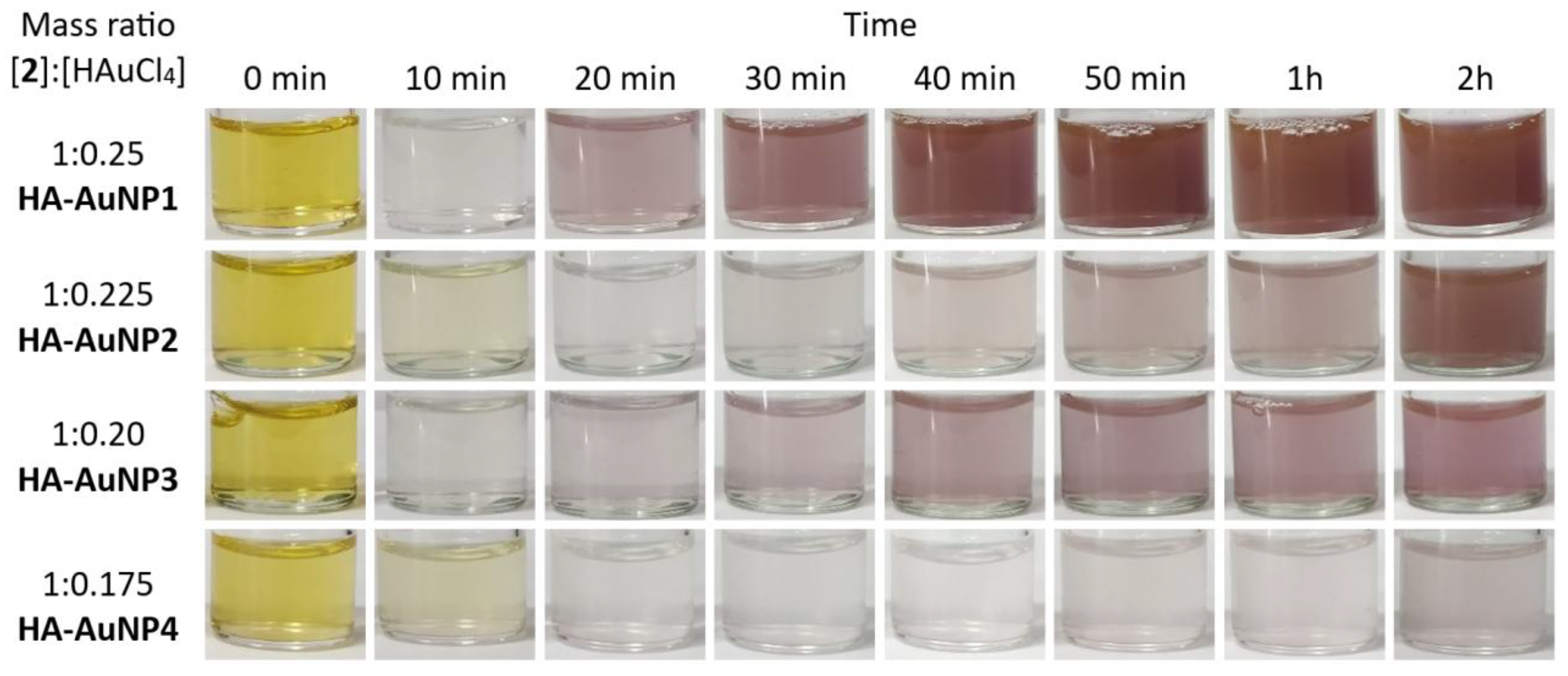
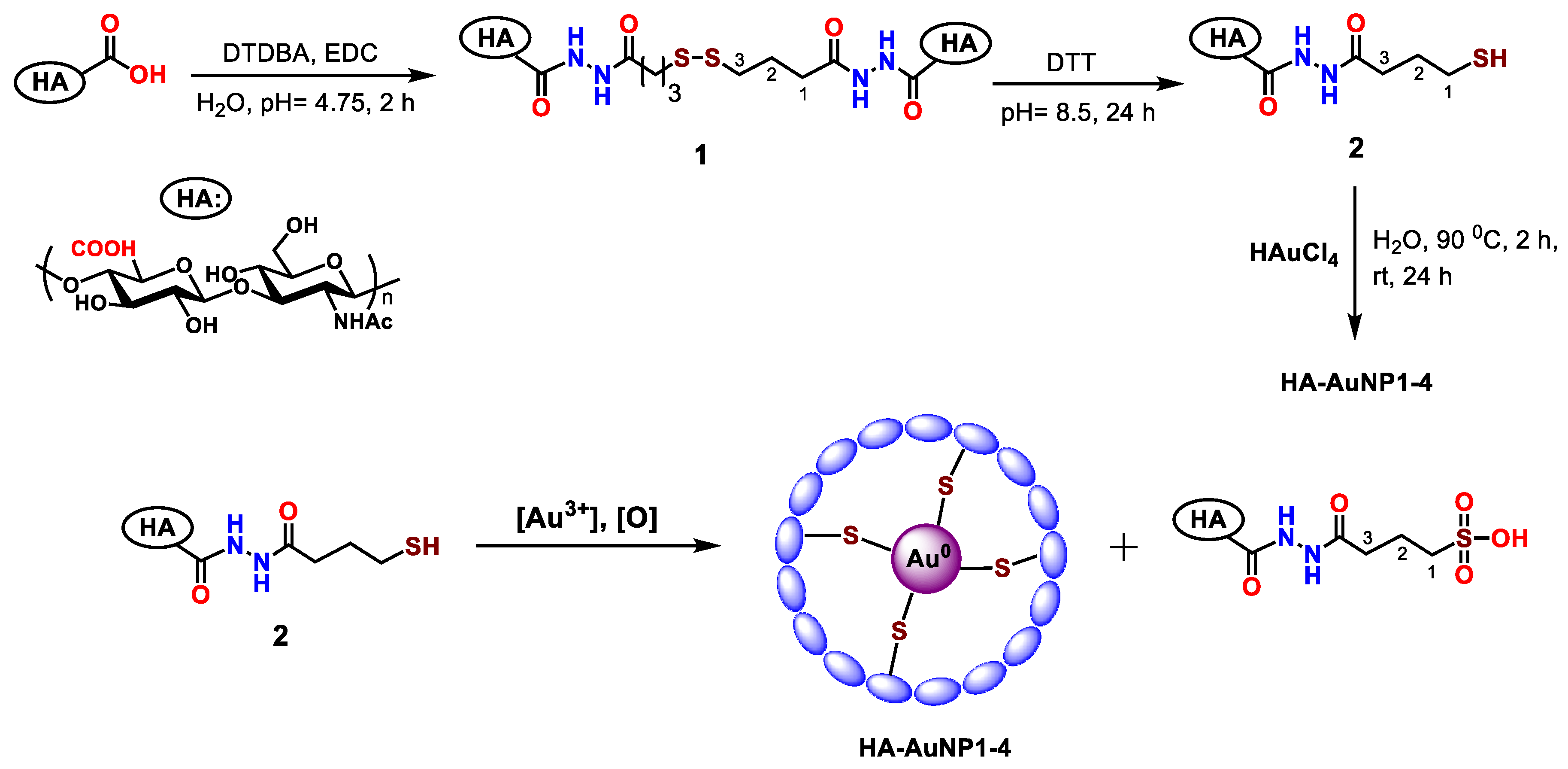
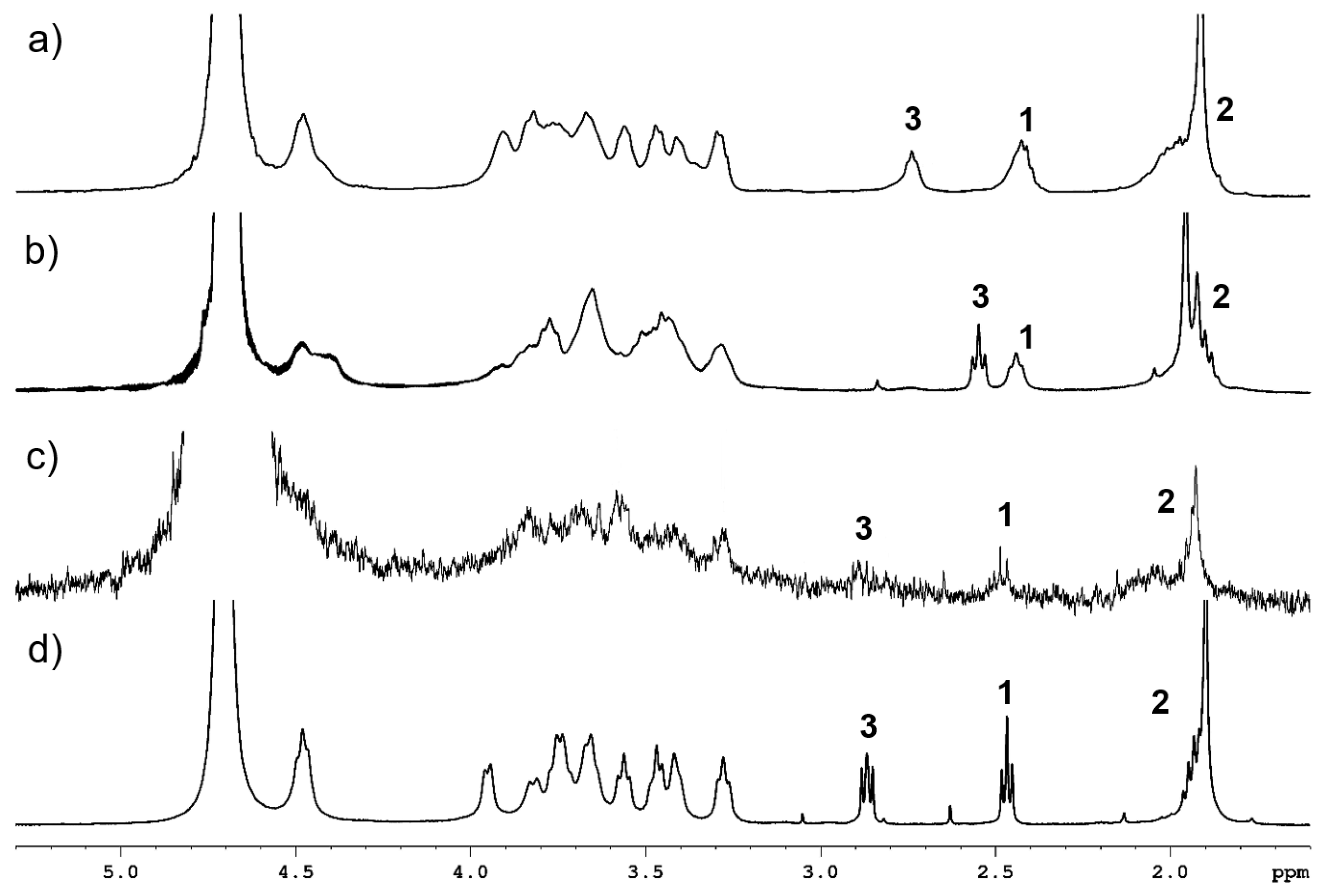
2.1. HA-AuNP Synthesis
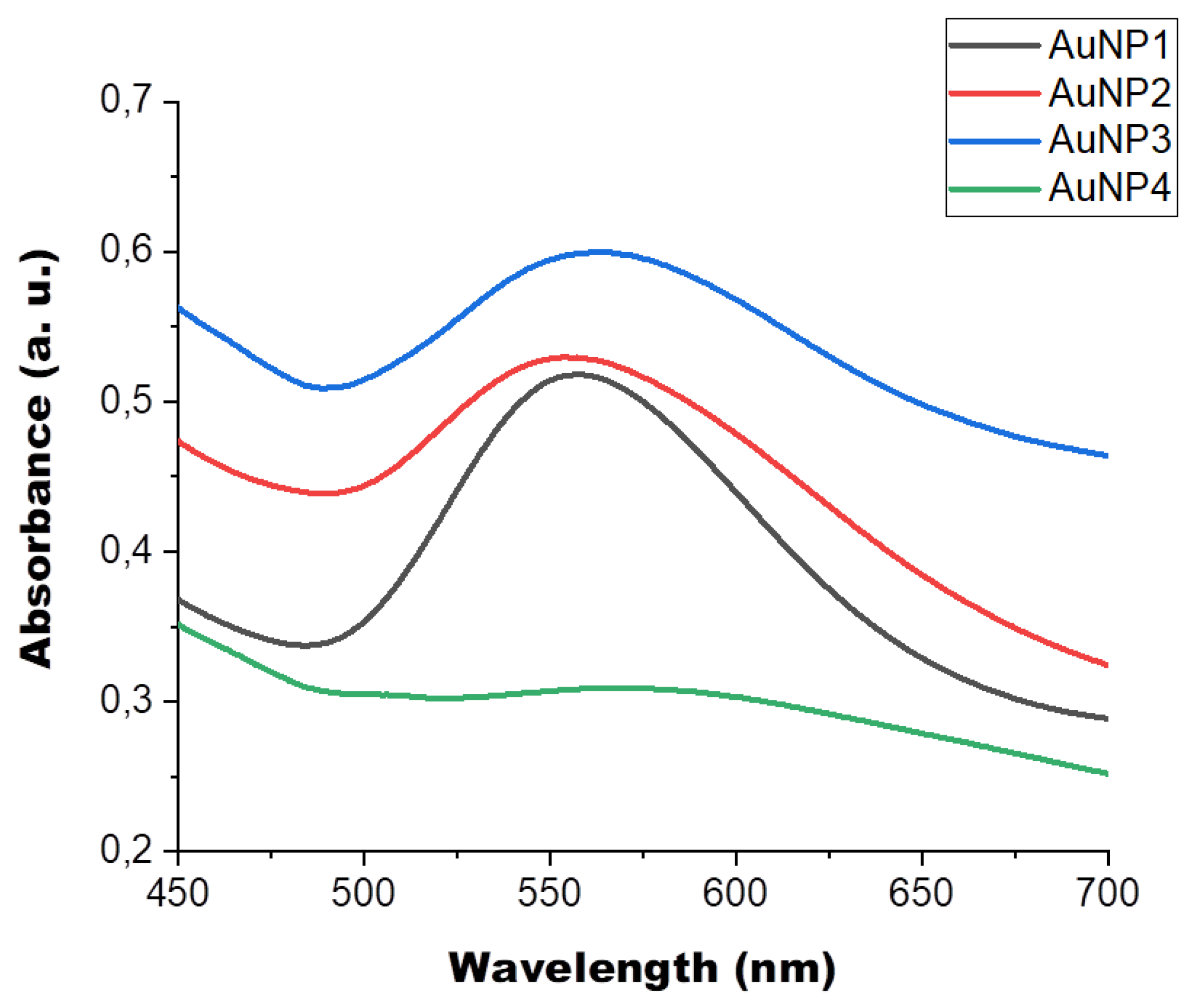
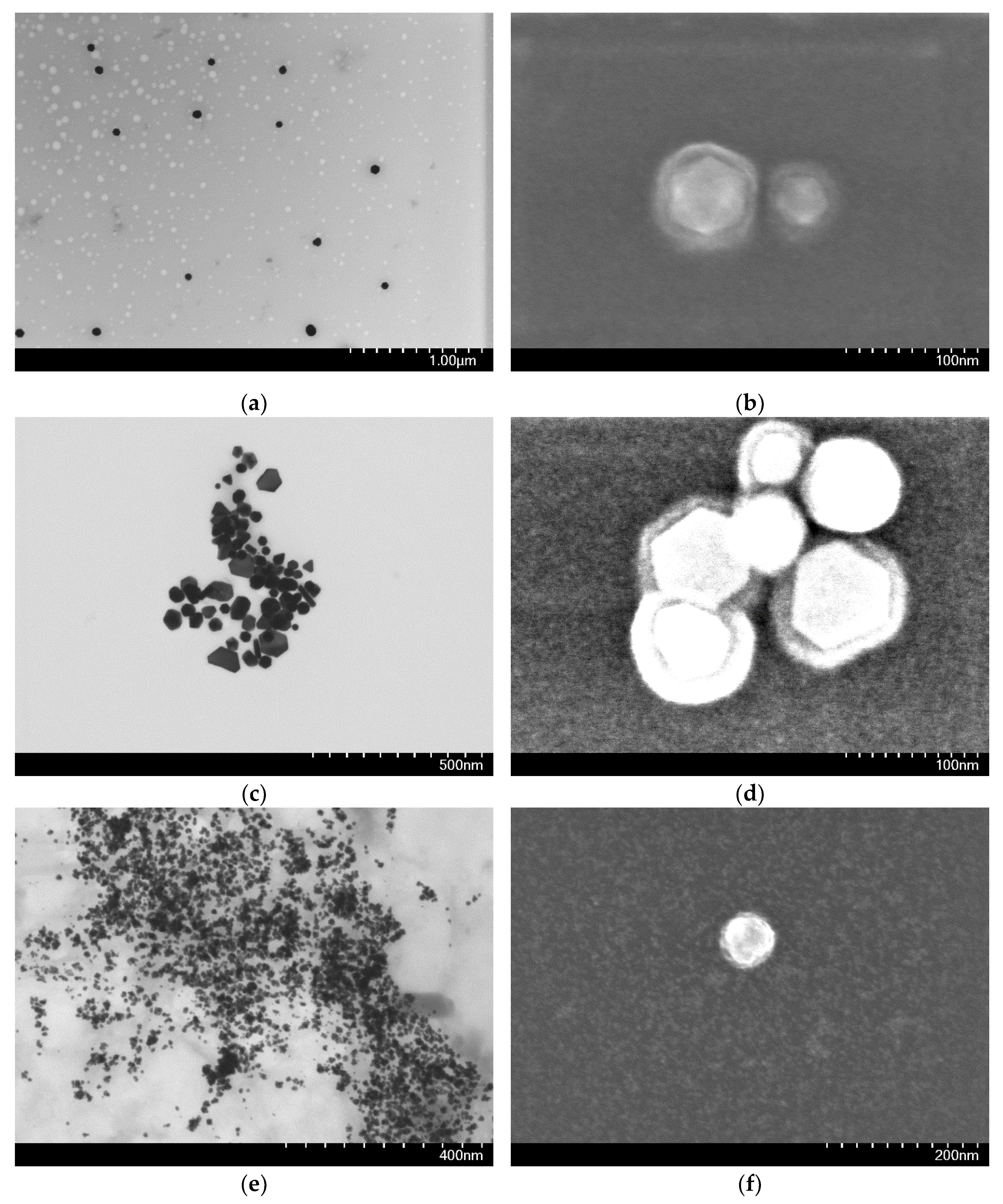
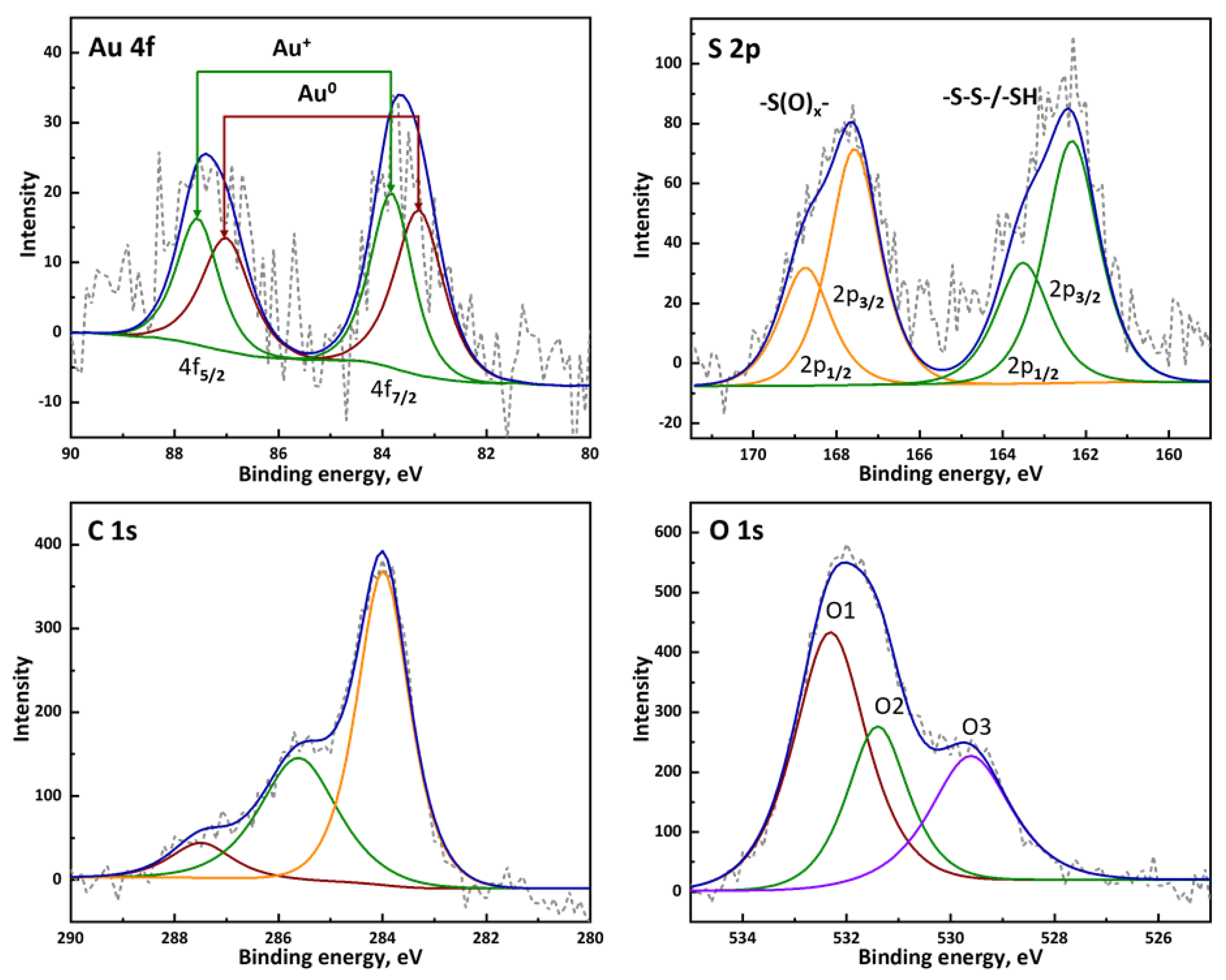
2.2. HA-AuNP Characterization
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, A.; Rayhan, M.T.; Mobarak, M.H.; Rimon, M.I.H.; Hossain, N.; Islam, S.; Kafi, S.M.A.A. Advances and significances of gold nanoparticles in cancer treatment: A comprehensive review. Results in Chemistry 2024, 8, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov, M.; Zhou, Y.; Khachatryan, W.; Multhoff, G.; Gao, H. Recent Advances in Gold Nanoformulations for Cancer Therapy. Curr Drug Metab 2018, 19, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.; Salaheldeen, M.; El-Dabea, T. Recent Advances in Development of Gold Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Systems. Journal of Modern Nanotechnology 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.C.; Estroff, L.A.; Kriebel, J.K.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-Assembled Monolayers of Thiolates on Metals as a Form of Nanotechnology. Chemical Reviews 2005, 105, 1103–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Supported gold nanoparticles as catalysts for organic reactions. Chemical Society Reviews 2008, 37, 2096–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Maragò, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: a review. J Phys Condens Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergievskaya, A.; Chauvin, A.; Konstantinidis, S. Sputtering onto liquids: a critical review. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2022, 13, 10–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shi, X.; D’Arcy, R.; Tirelli, N.; Zhai, G. Amphiphilic polysaccharides as building blocks for self-assembled nanosystems: molecular design and application in cancer and inflammatory diseases. Journal of Controlled Release 2018, 272, 114–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchi, D.P.; da Cruz, J.A.; Bonafé, E.G.; Pereira, A.G.B.; Fajardo, A.R.; Venter, S.A.S.; Monteiro, J.P.; Muniz, E.C.; Martins, A.F. Polysaccharide-Based Materials Associated with or Coordinated to Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Medical Application. Curr Med Chem 2017, 24, 2701–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thodikayil, A.T.; Sharma, S.; Saha, S. Engineering Carbohydrate-Based Particles for Biomedical Applications: Strategies to Construct and Modify. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2021, 4, 2907–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Meng, F.; Su, C.; Li, J. Polysaccharide-based gold nanomaterials: Synthesis mechanism, polysaccharide structure-effect, and anticancer activity. Carbohydrate Polymers 2023, 321, 121284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Cong, F. Hyaluronan-Inorganic Nanohybrid Materials for Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1677–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Yan, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, G. Photothermally Controlled MHC Class I Restricted CD8+ T-Cell Responses Elicited by Hyaluronic Acid Decorated Gold Nanoparticles as a Vaccine for Cancer Immunotherapy. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2018, 7, 1701439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skardal, A.; Zhang, J.; McCoard, L.; Oottamasathien, S.; Prestwich, G.D. Dynamically Crosslinked Gold Nanoparticle—Hyaluronan Hydrogels. Advanced Materials 2010, 22, 4736–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Kao, W.-C.; Yeh, C.-A.; Chen, H.-J.; Lin, S.-Z.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Sun, W.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Hung, H.-S. Hyaluronic acid-fabricated nanogold delivery of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein-2 siRNAs inhibits benzo[a]pyrene-induced oncogenic properties of lung cancer A549 cells. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, V.; Caruso, V.C.; Cucci, L.M.; Inturri, R.; Vaccaro, S.; Satriano, C. Hyaluronan-Metal Gold Nanoparticle Hybrids for Targeted Tumor Cell Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Raja, M.D.; Sundar, D.S.; Gover Antoniraj, M.; Ruckmani, K. Hyaluronic acid co-functionalized gold nanoparticle complex for the targeted delivery of metformin in the treatment of liver cancer (HepG2 cells). Carbohydrate Polymers 2015, 128, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, N.; Su, Q.; Lv, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhan, H. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and Study of Their Inhibitory Effect on Bulk Cancer Cells and Cancer Stem Cells in Breast Carcinoma. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, P.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Sun, Y. One-pot synthesis of hyaluronic acid–coated gold nanoparticles as SERS substrate for the determination of hyaluronidase activity. Microchimica Acta 2020, 187, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vávrová, A.; Čapková, T.; Kuřitka, I.; Vícha, J.; Münster, L. One-step synthesis of gold nanoparticles for catalysis and SERS applications using selectively dicarboxylated cellulose and hyaluronate. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 206, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Yang, J.A.; Jung, H.S.; Beack, S.; Choi, J.E.; Hur, W.; Koo, H.; Kim, K.; Yoon, S.K.; Hahn, S.K. Hyaluronic acid-gold nanoparticle/interferon α complex for targeted treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9522–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Nurunnabi, M.; Li, L.; Khan, H.A.; Cho, K.J.; Huh, K.M.; Lee, Y.-k. Hybrid photoactive nanomaterial composed of gold nanoparticles, pheophorbide-A and hyaluronic acid as a targeted bimodal phototherapy. Macromolecular Research 2015, 23, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyani, T.; Prestwich, G.D. Functionalized Derivatives of Hyaluronic Acid Oligosaccharides: Drug Carriers and Novel Biomaterials. Bioconjugate Chemistry 1994, 5, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, O.P.; Sun, W.; Hilborn, J.; Ossipov, D.A. In Situ Cross-Linkable High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan−Bisphosphonate Conjugate for Localized Delivery and Cell-Specific Targeting: A Hydrogel Linked Prodrug Approach. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2009, 131, 8781–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglein, A. Radiolytic Preparation of Ultrafine Colloidal Gold Particles in Aqueous Solution: Optical Spectrum, Controlled Growth, and Some Chemical Reactions. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6738–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chemical Society Reviews 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, N.Q.; Van Phu, D.; Duy, N.N.; Quoc, L.A. Radiation synthesis and characterization of hyaluronan capped gold nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polymers 2012, 89, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meen, T.-H.; Tsai, J.-K.; Chao, S.-M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wu, T.-C.; Chang, T.-Y.; Ji, L.-W.; Water, W.; Chen, W.-R.; Tang, I.T.; et al. Surface plasma resonant effect of gold nanoparticles on the photoelectrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale Research Letters 2013, 8, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyholm, R.; Berndtsson, A.; Martensson, N. Core level binding energies for the elements Hf to Bi (Z=72-83). Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics 1980, 13, L1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Chastain, J.; King, R.C. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data; Physical Electronics: 1995.
- Casaletto, M.P.; Longo, A.; Martorana, A.; Prestianni, A.; Venezia, A.M. XPS study of supported gold catalysts: the role of Au0 and Au+δ species as active sites. Surface and Interface Analysis 2006, 38, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.R.; Ke, S.-C. Spin-Orbit Coupling Effects in Au 4f Core-Level Electronic Structures in Supported Low-Dimensional Gold Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatoo, M.A.; Wehbe, N.; Kharbatia, N.; Guo, X.; Mishra, H. Why do some metal ions spontaneously form nanoparticles in water microdroplets? Disentangling the contributions of the air–water interface and bulk redox chemistry. Chemical Science 2025, 16, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, Q. Adsorption of phosphorylated chitosan on mineral surfaces. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2013, 436, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxhet, P.G.; Genet, M.J. XPS analysis of bio-organic systems. Surface and Interface Analysis 2011, 43, 1453–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Ren, Z.; Qian, G.; Wang, Z. Black Hydroxylated Titanium Dioxide Prepared via Ultrasonication with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. Scientific Reports 2015, 5, 11712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castner, D.G.; Hinds, K.; Grainger, D.W. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Sulfur 2p Study of Organic Thiol and Disulfide Binding Interactions with Gold Surfaces. Langmuir 1996, 12, 5083–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, B.J.; Hamrin, K.; Johansson, G.; Gelius, U.; Fahlman, A.; Nordling, C.; Siegbahn, K. Molecular Spectroscopy by Means of ESCA II. Sulfur compounds. Correlation of electron binding energy with structure. Physica Scripta 1970, 1, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, P.M.; Hanumantha, P.J.; Ramalinga, K.; Gattu, B.; Datta, M.K.; Kumta, P.N. Sulfonic Acid Based Complex Framework Materials (CFM): Nanostructured Polysulfide Immobilization Systems for Rechargeable Lithium–Sulfur Battery. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2019, 166, A1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tao, Q.; He, H.; Liu, H.; Komarneni, S. An efficient SO2-adsorbent from calcination of natural magnesite. Ceramics International 2017, 43, 12557–12562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudino, T.C.; Nunes, R.S.; Mandelli, D.; Carvalho, W.A. Influence of Dimethylsulfoxide and Dioxygen in the Fructose Conversion to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Mediated by Glycerol’s Acidic Carbon. Frontiers in Chemistry 2020, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Roberts, M.C.; Prestwich, G.D. Disulfide Cross-Linked Hyaluronan Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, H.J. Organic Chemistry Data Collection. Available online: https://organicchemistrydata.org/hansreich/resources/nmr/?page=05-hmr-15-aabb%2F (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Herke, R.; Rasheed, K. Addition of bisulfite to α-olefins: Synthesis of n-alkane sulfonates and characterization of intermediates. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society 1992, 69, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.-H.; Moyers, J.S.; Michael, M.D.; Durham, T.B.; Cramer, J.W.; Qian, Y.; Lin, A.; Wu, L.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Active-Site-Directed, Highly Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Low-Molecular-Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 65, 13892–13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, D. Recent Developments in Disulfide Bond Formation. Synthesis 2008, 2008, 2491–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, N.M.R.; McDonnell, C.; Hambrook, M.; Back, T.G. Oxidation of Disulfides to Thiolsulfinates with Hydrogen Peroxide and a Cyclic Seleninate Ester Catalyst. Molecules 2015, 20, 10748–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliopoulou, N.; Kokotos, C.G. Photochemical metal-free aerobic oxidation of thiols to disulfides. Green Chemistry 2021, 23, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, I.V. The chemistry of disulfides. Russian Chemical Reviews 1994, 63, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagiyan, G.A.; Koroleva, I.K.; Soroka, N.V.; Ufimtsev, A.V. Oxidation of thiol compounds by molecular oxygen in aqueous solutions. Russian Chemical Bulletin 2003, 52, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bergen, L.A.H.; Roos, G.; De Proft, F. From Thiol to Sulfonic Acid: Modeling the Oxidation Pathway of Protein Thiols by Hydrogen Peroxide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2014, 118, 6078–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, C.N.; Gomes, A.J.; Rocha, F.S.; De Tommaso, J.; Patience, G.S. Experimental methods in chemical engineering: Zeta potential. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering 2021, 99, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, J.-P.R.; Pratt, D.A. On the Reactions of Thiols, Sulfenic Acids, and Sulfinic Acids with Hydrogen Peroxide. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2017, 56, 6255–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercruysse, K.P.; Marecak, D.M.; Marecek, J.F.; Prestwich, G.D. Synthesis and in Vitro Degradation of New Polyvalent Hydrazide Cross-Linked Hydrogels of Hyaluronic Acid. Bioconjugate Chemistry 1997, 8, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| HA-AuNP1 | HA-AuNP2 | HA-AuNP3 | HA-AuNP4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta-potential (mV) | -27.6±3.4 | -28.6±1.7 | -41.0±4.0 | -41.5±1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





