Submitted:
02 October 2025
Posted:
03 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Neuroplasticity Dysregulation in Depression
3. Adiponectin: From Peripheral Hormone to Brain Modulator
4. Linking Exercise, Adiponectin, and Neuroplasticity
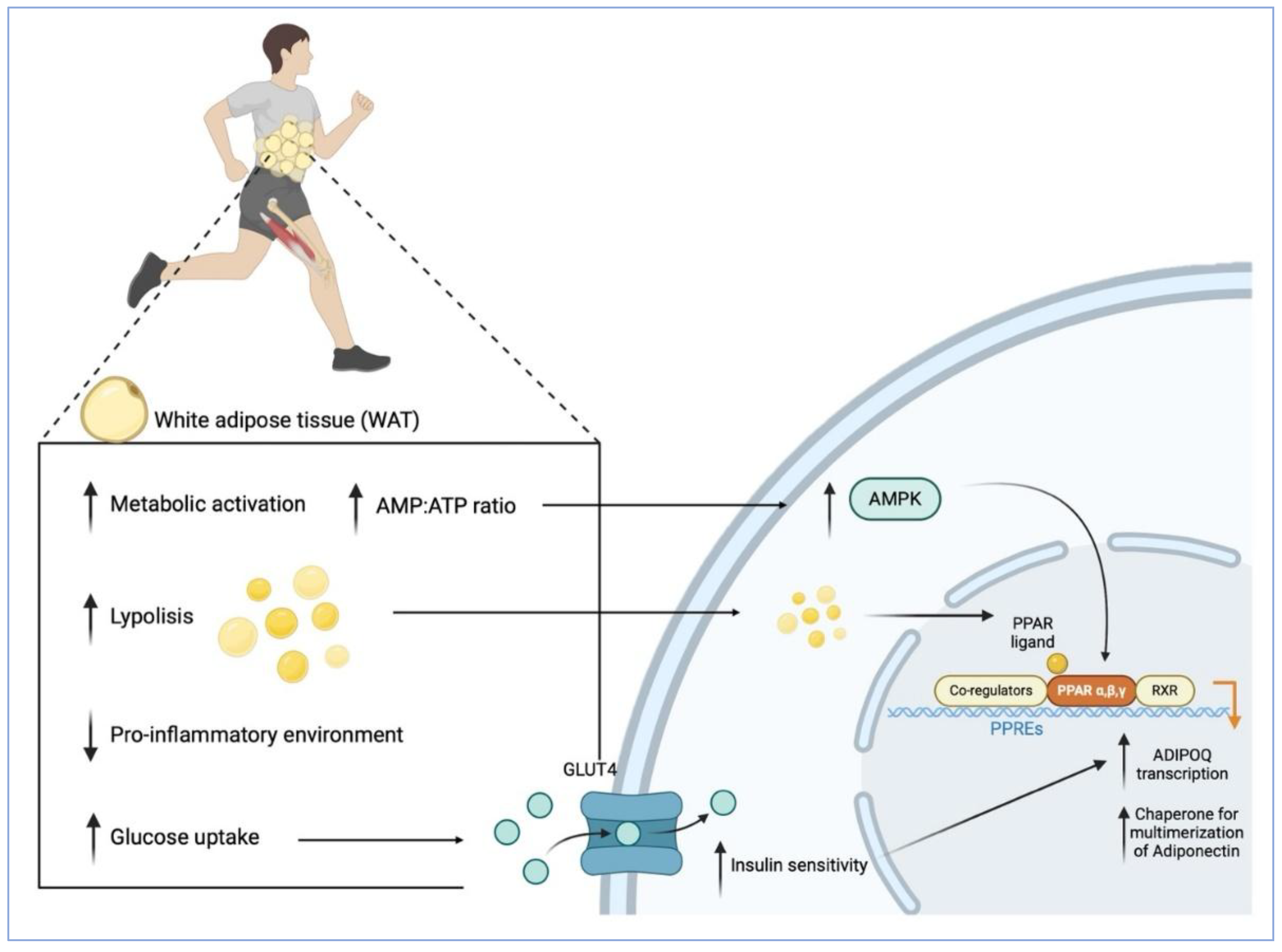
4.1. How Exercise Enhances Adiponectin Levels: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms
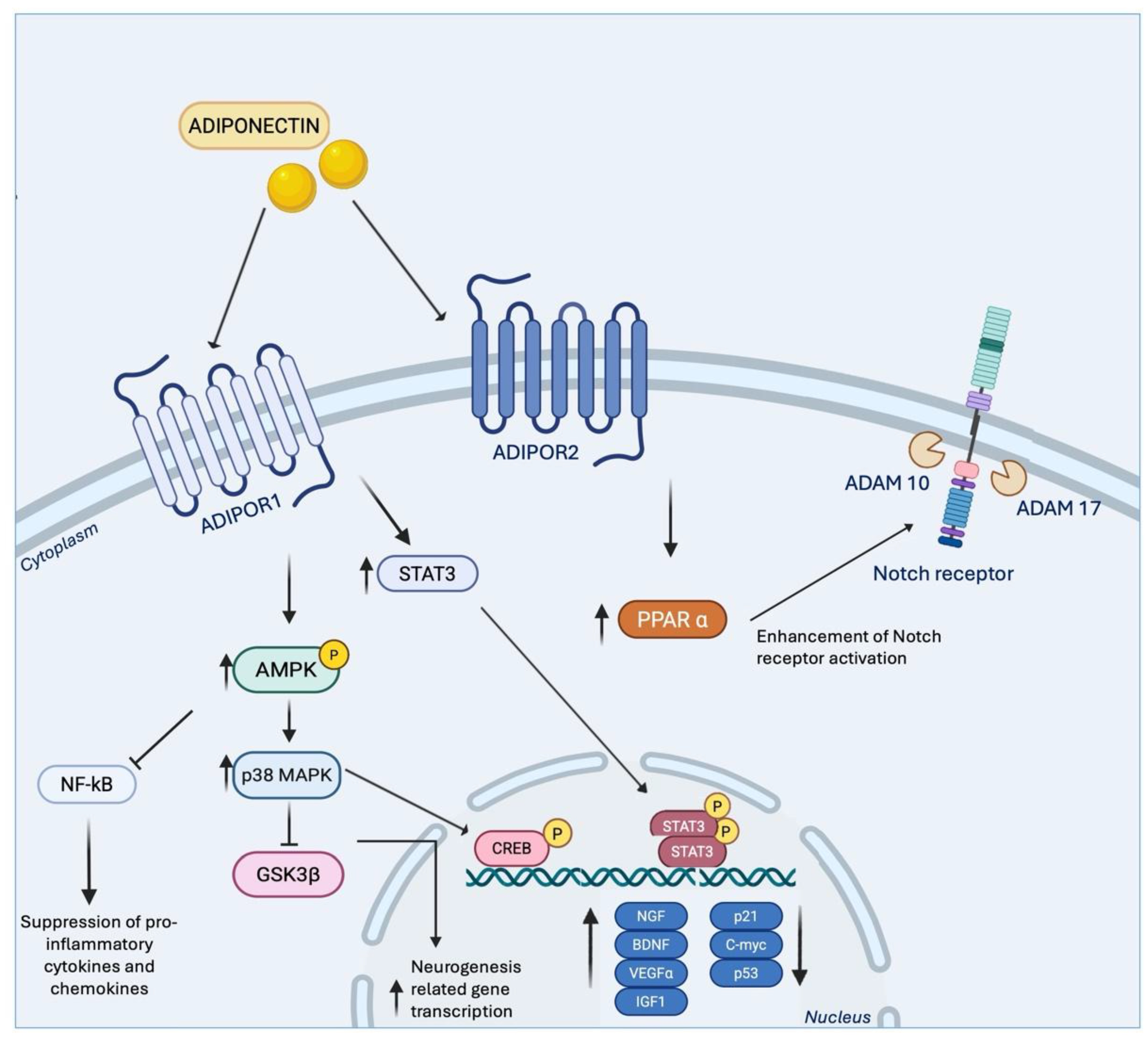
4.2. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Adiponectin’s Effects on Neurogenesis and Neuroplasticity
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| LTP | Long-Term Potentiation |
| AHN | Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis |
| NSC | Neural Stem Cells |
| SGZ | Subgranular Zone |
| DG | Dentate Gyrus |
| LTD | Long-Term Depression |
| L-LTP | Late Phase Long-Term Potentiation |
| TRKB | Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-3 Kinase |
| mTOR | Mammalian Target Of Rapamycin |
| AMPK | AMP-Activated Protein Kinase |
| SSRI | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor |
| WAT | White Adipose Tissue |
| HMW | High Molecular Weight |
| ER | Endoplasmatic Reticulum |
| PPAR | Proliferator-Activated Receptor |
| TZD | Thiazolidinedione |
| TNF-α | Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kB |
| BBB | Blood Brain Barrier |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| IFN-α | Interferon Alpha |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| BAT | Brown Adipos Tissue |
| GLUT4 | Glucose Transporter Type 4 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| GLP1RA | Glucagone-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist |
References
- Tartt, A.N.; Mariani, M.B.; Hen, R.; Mann, J.J.; Boldrini, M. Dysregulation of Adult Hippocampal Neuroplasticity in Major Depression: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Mol Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Nie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Z.; Cai, M.; Wei, H.; Qin, P.; Dong, H.; Xiong, L. Recombinant Human Thioredoxin-1 Promotes Neurogenesis and Facilitates Cognitive Recovery Following Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsini, A.; Giacobbe, J.; Mandal, G.; Boldrini, M. Acute and Long-Term Effects of Adolescence Stress Exposure on Rodent Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis, Cognition, and Behaviour. Mol Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4124–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Preez, A.; Onorato, D.; Eiben, I.; Musaelyan, K.; Egeland, M.; Zunszain, P.A.; Fernandes, C.; Thuret, S.; Pariante, C.M. Chronic Stress Followed by Social Isolation Promotes Depressive-like Behaviour, Alters Microglial and Astrocyte Biology and Reduces Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Male Mice. Brain Behav Immun 2021, 91, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucassen, P.J.; Meerlo, P.; Naylor, A.S.; van Dam, A.M.; Dayer, A.G.; Fuchs, E.; Oomen, C.A.; Czéh, B. Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Stress, Sleep Disruption, Exercise and Inflammation: Implications for Depression and Antidepressant Action. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2010, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Underwood, M.D.; Hen, R.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Dwork, A.J.; John Mann, J.; Arango, V. Antidepressants Increase Neural Progenitor Cells in the Human Hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2376–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Hen, R.; Underwood, M.D.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Dwork, A.J.; Mann, J.J.; Arango, V. Hippocampal Angiogenesis and Progenitor Cell Proliferation Are Increased with Antidepressant Use in Major Depression. Biol Psychiatry 2012, 72, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Agostino, D.; Wu, Y.-T.; Daskalopoulou, C.; Hasan, M.T.; Huisman, M.; Prina, M. Global Trends in the Prevalence and Incidence of Depression:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders 2021, 281, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, T.S.; Thomas, D.M.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Earnest, C.P.; Rodarte, R.Q.; Martin, C.K.; Blair, S.N.; Bouchard, C. Trends over 5 Decades in U. S. Occupation-Related Physical Activity and Their Associations with Obesity. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.T.; Hamilton, D.G.; Zderic, T.W. Sedentary Behavior as a Mediator of Type 2 Diabetes. Med Sport Sci 2014, 60, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, A.L.; Hood, S.D.; Drummond, P.D. A Review of Lifestyle Factors That Contribute to Important Pathways Associated with Major Depression: Diet, Sleep and Exercise. J Affect Disord 2013, 148, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, S.-Y.; Lee, T.H.-Y.; Li, A.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F. Adiponectin Mediates Running-Restored Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes in Mice. Front Neurosci 2018, 12, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Stensel, D.J.; Lindley, M.R.; Mastana, S.S.; Nimmo, M.A. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Exercise: Mechanisms and Implications for the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2011, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Cao, L.; Zhou, D. The Impact of Physical Activities on Adolescents’ Rule Consciousness: The Chain Mediation Effect of Friendship Quality and Emotional Intelligence. Front Public Health 2025, 13, 1581016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.; Garcia, L.; Abbas, A.; Strain, T.; Schuch, F.B.; Golubic, R.; Kelly, P.; Khan, S.; Utukuri, M.; Laird, Y.; et al. Association Between Physical Activity and Risk of Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dishman, R.K.; McDowell, C.P.; Herring, M.P. Customary Physical Activity and Odds of Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 111 Prospective Cohort Studies. Br J Sports Med 2021, 55, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanaei-Moghaddam, B.; Katon, W.J.; Russo, J. The Longitudinal Effects of Depression on Physical Activity. General Hospital Psychiatry 2009, 31, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallance, J.K.; Winkler, E.A.H.; Gardiner, P.A.; Healy, G.N.; Lynch, B.M.; Owen, N. Associations of Objectively-Assessed Physical Activity and Sedentary Time with Depression: NHANES (2005–2006). Preventive Medicine 2011, 53, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, A.A.; Kop, W.J.; Deuster, P.A. Depressive Mood Symptoms and Fatigue After Exercise Withdrawal: The Potential Role of Decreased Fitness. Psychosomatic Medicine 2006, 68, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soini, E.; Rosenström, T.; Määttänen, I.; Jokela, M. Physical Activity and Specific Symptoms of Depression: A Pooled Analysis of Six Cohort Studies. Journal of Affective Disorders 2024, 348, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, G.R.; Royes, L.F.F. Peripheral to Brain and Hippocampus Crosstalk Induced by Exercise Mediates Cognitive and Structural Hippocampal Adaptations. Life Sci 2024, 352, 122799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.-Y. Adiponectin Exerts Neurotrophic Effects on Dendritic Arborization, Spinogenesis, and Neurogenesis of the Dentate Gyrus of Male Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2853–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, S.; Cazareth, J.; Zarif, H.; Guyon, A.; Heurteaux, C.; Chabry, J.; Petit-Paitel, A. Globular Adiponectin Limits Microglia Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype through an AdipoR1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front Cell Neurosci 2017, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liang, Y.; Chen, K.; Yau, S.-Y.; Sun, X.; Cheng, K.K.-Y.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F.; Li, A. Potential Involvement of Adiponectin Signaling in Regulating Physical Exercise-Elicited Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Dendritic Morphology in Stressed Mice. Front Cell Neurosci 2020, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Gage, F.H.; Aigner, L.; Song, H.; Curtis, M.A.; Thuret, S.; Kuhn, H.G.; Jessberger, S.; Frankland, P.W.; Cameron, H.A.; et al. Human Adult Neurogenesis: Evidence and Remaining Questions. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Yau, S.S.Y.; So, K.-F.; Zhang, L.; Ou, H. Exercise Preconditioning Alleviates Ischemia-Induced Memory Deficits by Increasing Circulating Adiponectin. Neural Regen Res 2025, 20, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Role of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Persistent Forms of Hippocampal Plasticity and Learning. Neuropharmacology 2013, 66, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minal, N.; Nilesh, W.; Akanksha, K. Epigenetic Regulation in Neuroplasticity: Key to Understanding and Treating Neurological Diseases. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2025, 41, e20250011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C.; Sur, M.; Dobkin, B.H.; O’Brien, C.; Sanger, T.D.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Rumsey, J.M.; Hicks, R.; Cameron, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Harnessing Neuroplasticity for Clinical Applications. Brain 2011, 134, 1591–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgal, S.K.; Nath, S.; Chaturvedi, J.; Sharma, S.K.; Joshi, J. Neuroplasticity in Depression: A Narrative Review with Evidence-Based Insights. Psychiatr Danub 2022, 34, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrarelli, F. Is Neuroplasticity Key to Treatment Response in Depression? Maybe So. Am J Psychiatry 2022, 179, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yang, B.; Rothschild, G.; Mann, J.J.; Sanford, L.D.; Tang, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W. Epigenetic Regulation in Major Depression and Other Stress-Related Disorders: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Relevance and Therapeutic Potential. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Bertelsen, A.B.; Holm, I.E.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Rosenberg, R.; Dorph-Petersen, K.-A. Hippocampal Volume and Cell Number in Depression, Schizophrenia, and Suicide Subjects. Brain Res 2020, 1727, 146546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, D.; Mackay, D.; Chana, G.; Beasley, C.; Landau, S.; Everall, I.P. Reduced Neuronal Size and Glial Cell Density in Area 9 of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Subjects with Major Depressive Disorder. Cereb Cortex 2002, 12, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, G.; O’Dwyer, G.; Teleki, Z.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J. GABAergic Neurons Immunoreactive for Calcium Binding Proteins Are Reduced in the Prefrontal Cortex in Major Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc-Ozcan, E.; Peng, C.-Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dunlop, S.R.; Contractor, A.; Kessler, J.A. Activating Newborn Neurons Suppresses Depression and Anxiety-like Behaviors. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surget, A.; Belzung, C. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Shapes Adaptation and Improves Stress Response: A Mechanistic and Integrative Perspective. Mol Psychiatry 2022, 27, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, S.; Veyssière, J.; Gandin, C.; Zsürger, N.; Pietri, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Glaichenhaus, N.; Petit-Paitel, A.; Chabry, J. Neurogenesis-Independent Antidepressant-like Effects of Enriched Environment Is Dependent on Adiponectin. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 57, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Zhai, M.; He, M.; Hu, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, C. Hyperactive Neuronal Autophagy Depletes BDNF and Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Corticosterone-Induced Mouse Model of Depression. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Erchinger, V.J.; Ousdal, O.T.; Oltedal, L.; Tanaka, K.F.; Takamiya, A. Neurobiological Mechanisms of Electroconvulsive Therapy for Depression: Insights into Hippocampal Volumetric Increases from Clinical and Preclinical Studies. J Neurochem 2024, 168, 1738–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Feng, Y.; Hong, Z.; Yin, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X. High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Promotes Neural Stem Cell Proliferation after Ischemic Stroke. Neural Regen Res 2024, 19, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Tian, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, B. Aerobic Exercise Restores Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Cognitive Function by Decreasing Microglia Inflammasome Formation Through Irisin/NLRP3 Pathway. Aging Cell 2025, e70061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Cooke, S.F. Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression: A Clinical Perspective. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2011, 66 Suppl 1, 3–17. [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Aghajanian, G.K. Synaptic Dysfunction in Depression: Potential Therapeutic Targets. Science 2012, 338, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, W.N. Synaptic Plasticity in Depression: Molecular, Cellular and Functional Correlates. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013, 43, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Ibrahim, M.Z.; Benoy, A.; Sajikumar, S. Long-term Plasticity in the Hippocampus: Maintaining within and ‘Tagging’ between Synapses. The FEBS Journal 2022, 289, 2176–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Gu, T.; Luo, Q.; Sha, S.; Du, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, L. Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 Impairs Long-Term Depression in Nucleus Accumbens and Induces Depressive-like Behavior. Neuropharmacology 2025, 273, 110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W.C.; Jones, O.D.; Glanzman, D.L. Is Plasticity of Synapses the Mechanism of Long-Term Memory Storage? npj Sci. Learn. 2019, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, L.R.; Wang, Y.T.; Phillips, A.G. Evaluation of the Wistar-Kyoto Rat Model of Depression and the Role of Synaptic Plasticity in Depression and Antidepressant Response. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2019, 105, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csabai, D.; Wiborg, O.; Czéh, B. Reduced Synapse and Axon Numbers in the Prefrontal Cortex of Rats Subjected to a Chronic Stress Model for Depression. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahati, K.; Bhagya, V.; Christofer, T.; Sneha, A.; Shankaranarayana Rao, B.S. Enriched Environment Ameliorates Depression-Induced Cognitive Deficits and Restores Abnormal Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2016, 134, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, B.A.; Nguyen, T.N.B.; Tobe, R.H.; Walker, A.M.; Gabbay, V. Multimodal Investigations of Reward Circuitry and Anhedonia in Adolescent Depression. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12, 678709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ge, T.; Leng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, R. The Role of Neural Plasticity in Depression: From Hippocampus to Prefrontal Cortex. Neural Plasticity 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygvold, T.W.; Hatlestad-Hall, C.; Elvsåshagen, T.; Moberget, T.; Andersson, S. Long Term Potentiation-like Neural Plasticity and Performance-Based Memory Function. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2022, 196, 107696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltaci, S.B.; Mogulkoc, R.; Baltaci, A.K. Molecular Mechanisms of Early and Late LTP. Neurochem Res 2019, 44, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Dudai, Y.; Mayford, M.R. The Molecular and Systems Biology of Memory. Cell 2014, 157, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowiański, P.; Lietzau, G.; Czuba, E.; Waśkow, M.; Steliga, A.; Moryś, J. BDNF: A Key Factor with Multipotent Impact on Brain Signaling and Synaptic Plasticity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2018, 38, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panja, D.; Bramham, C.R. BDNF Mechanisms in Late LTP Formation: A Synthesis and Breakdown. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Begni, V.; Pariante, C.M.; Riva, M.A. The Human BDNF Gene: Peripheral Gene Expression and Protein Levels as Biomarkers for Psychiatric Disorders. Transl Psychiatry 2016, 6, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, D.; Moretti, F.; Bartoccetti, A.; Mauro, S.; Crocamo, C.; Carrà, G.; Bartoli, F. The Role of BDNF in Major Depressive Disorder, Related Clinical Features, and Antidepressant Treatment: Insight from Meta-Analyses. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2023, 149, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.S.; Cardoso, A.; Vale, N. BDNF Unveiled: Exploring Its Role in Major Depression Disorder Serotonergic Imbalance and Associated Stress Conditions. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, T.; Yoshimura, R.; Ikuta, T.; Iwata, N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Major Depressive Disorder: Evidence from Meta-Analyses. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molendijk, M.L.; Spinhoven, P.; Polak, M.; Bus, B.A.A.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Elzinga, B.M. Serum BDNF Concentrations as Peripheral Manifestations of Depression: Evidence from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses on 179 Associations (N=9484). Mol Psychiatry 2014, 19, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaira, T.; Nakagawasai, O.; Takahashi, K.; Nemoto, W.; Sakuma, W.; Lin, J.-R.; Tan-No, K. Mechanisms Underpinning AMP-Activated Protein Kinase-Related Effects on Behavior and Hippocampal Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Depression. Neuropharmacology 2019, 150, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Cao, J.; Liu, X.; Meng, F.; Li, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J. AMPK Plays a Dual Role in Regulation of CREB/BDNF Pathway in Mouse Primary Hippocampal Cells. J Mol Neurosci 2015, 56, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, F.; Rossetti, A.C.; Racagni, G.; Gass, P.; Riva, M.A.; Molteni, R. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Bridge between Inflammation and Neuroplasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 2014, 8, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Macchi, F.; Plazzotta, G.; Veronica, B.; Bocchio-Chiavetto, L.; Riva, M.A.; Pariante, C.M. Inflammation and Neuronal Plasticity: A Link between Childhood Trauma and Depression Pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraz-Petrozzi, B.; Insan, S.; Spangemacher, M.; Reinwald, J.; Lamadé, E.K.; Gilles, M.; Deuschle, M.; Sartorius, A. Association between rTMS-Induced Changes in Inflammatory Markers and Improvement in Psychiatric Diseases: A Systematic Review. Ann Gen Psychiatry 2024, 23, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Tan, H. Fluoxetine Mitigates Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice via Anti-Inflammation and Enhancing Neuroplasticity. Brain Research 2024, 1825, 148723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Luo, Y.; Liang, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P.; Yang, H.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Running Exercise on Hippocampal Microglia and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depression Model Rats. Transl Psychiatry 2021, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.E.; Scheinost, D.; Finnema, S.J.; Naganawa, M.; Davis, M.T.; DellaGioia, N.; Nabulsi, N.; Matuskey, D.; Angarita, G.A.; Pietrzak, R.H.; et al. Lower Synaptic Density Is Associated with Depression Severity and Network Alterations. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, M.; James, R.; Marks, J.; Zhao, S.; Szabo, A.; Kidambi, S. Adiposity Distribution Influences Circulating Adiponectin Levels. Translational Research 2014, 164, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.; Álvarez-Indo, J.; Cifuentes, M.; Morselli, E.; Kerr, B.; Burgos, P.V. Enhancing Adipose Tissue Functionality in Obesity: Senotherapeutics, Autophagy and Cellular Senescence as a Target. Biol Res 2024, 57, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Uchida, S.; Kita, S.; Hara, K.; Hada, Y.; Vasseur, F.; Froguel, P.; et al. Impaired Multimerization of Human Adiponectin Mutants Associated with Diabetes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2003, 278, 40352–40363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, F. Regulation of Adiponectin Multimerization, Signaling and Function. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2014, 28, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, Oxidative Stress, Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, and the Associated Health Risks: Causes and Therapeutic Strategies. Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders 2015, 13, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, Y.B.; Pandey, V. Obesity and Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stresses. Front. Immun. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, Y.; Hong, Y.A.; Choi, S.R.; Chung, S.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Resveratrol Increases AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 Expression in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy. J Transl Med 2016, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcome of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Asia, 1999–2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Feng, S.; Covinsky, K.E.; Hayssen, H.; Zhou, L.-Q.; Yeh, B.M.; Lai, J.C. A Comparison of Muscle Function, Mass, and Quality in Liver Transplant Candidates: Results From the Functional Assessment in Liver Transplantation Study. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Shao, H.; Liu, S.; Niu, Y.; Fu, L. Globular Adiponectin Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle by Enhancing the LKB1-Mediated AMPK Activation via SESN2. Sports Medicine and Health Science 2023, 5, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandin, A.; Amosse, J.; Froger, J.; Hilairet, G.; Durcin, M.; Fizanne, L.; Ghesquière, V.; Prieur, X.; Chaigneau, J.; Vergori, L.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Are Carriers of Adiponectin with Insulin-Sensitizing and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Cell Reports 2023, 42, 112866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinova, L.; Atochin, D.; Vasilenko, M.; Fattakhov, N.; Zatolokin, P.; Vaysbeyn, I.; Kirienkova, E. Role of Adiponectin and Proinflammatory Gene Expression in Adipose Tissue Chronic Inflammation in Women with Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2014, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin as an Anti-Inflammatory Factor. Clinica Chimica Acta 2007, 380, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Ramírez, P.; Malmhäll, C.; Tliba, O.; Rådinger, M.; Bossios, A. Adiponectin/AdipoR1 Axis Promotes IL-10 Release by Human Regulatory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 677550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Murmu, A.; Matore, B.W.; Roy, P.P.; Singh, J. Thiazolidinedione an Auspicious Scaffold as PPAR-γ Agonist: Its Possible Mechanism to Manoeuvre against Insulin Resistant Diabetes Mellitus. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports 2024, 11, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Lam, K.S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Xu, A. Adiponectin and Cardiovascular Health: An Update. British J Pharmacology 2012, 165, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Tsuboi, A.; Minato, S.; Kitaoka, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Yano, M.; Kurata, M.; Wu, B.; Kazumi, T.; Fukuo, K. Association of Age and Anemia With Adiponectin Serum Levels in Normal-Weight Japanese Women. J Clin Med Res 2019, 11, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Hileman, S.M.; Patel, H.R.; Berg, A.H.; Pajvani, U.B.; Scherer, P.E.; Ahima, R.S. Adiponectin Acts in the Brain to Decrease Body Weight. Nat Med 2004, 10, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, S.Y.; Li, A.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Ching, Y.P.; Christie, B.R.; Lee, T.M.C.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F. Physical Exercise-Induced Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Antidepressant Effects Are Mediated by the Adipocyte Hormone Adiponectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 15810–15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, M.; Weigert, J.; Buettner, R.; Wanninger, J.; Schäffler, A.; Müller, A.M.; Killian, S.; Sauerbruch, S.; Schlachetzki, F.; Steinbrecher, A.; et al. Detection of Adiponectin in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007, 293, E965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusminski, C.M.; McTernan, P.G.; Schraw, T.; Kos, K.; O’Hare, J.P.; Ahima, R.; Kumar, S.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin Complexes in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid: Distinct Complex Distribution from Serum. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clain, J.; Couret, D.; Planesse, C.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Meilhac, O.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Viranaicken, W.; Diotel, N. Distribution of Adiponectin Receptors in the Brain of Adult Mouse: Effect of a Single Dose of the Adiponectin Receptor Agonist, AdipoRON, on Ischemic Stroke. Brain Sci 2022, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemer, J.; Pinky, P.D.; Smith, W.D.; Bhattacharya, D.; Chauhan, A.; Govindarajulu, M.; Hong, H.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Judd, R.; Amin, R.H.; et al. Adiponectin Knockout Mice Display Cognitive and Synaptic Deficits. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorska-Ciebiada, M.; Ciebiada, M. Adiponectin and Inflammatory Marker Levels in the Elderly Patients with Diabetes, Mild Cognitive Impairment and Depressive Symptoms. IJMS 2024, 25, 10804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehto, S.M.; Huotari, A.; Niskanen, L.; Tolmunen, T.; Koivumaa-Honkanen, H.; Honkalampi, K.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Herzig, K.-H.; Viinamäki, H.; Hintikka, J. Serum Adiponectin and Resistin Levels in Major Depressive Disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2010, 121, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, R.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Tesauro, M.; Cola, C.; Fortuna, E.; Zanasi, M.; Troisi, A.; Siracusano, A.; Lauro, R.; Romeo, F. Decreased Plasma Adiponectin Concentration in Major Depression. Neurosci Lett 2006, 407, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugmann, S.; Quante, A.; Heuser, I.; Schwarzer, R.; Anghelescu, I. Inflammatory Biomarkers in 70 Depressed Inpatients with and without the Metabolic Syndrome. J Clin Psychiatry 2010, 71, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábregas, B.C.; Vieira, É.L.M.; Moura, A.S.; Carmo, R.A.; Ávila, R.E.; Abreu, M.N.S.; Prossin, A.R.; Teixeira, A.L. A Follow-Up Study of 50 Chronic Hepatitis C Patients: Adiponectin as a Resilience Biomarker for Major Depression. Neuroimmunomodulation 2016, 23, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Lei, Y.; You, J.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Garza, J.; Zhang, D.; Guo, M.; Scherer, P.E.; Lodge, D.; et al. Adiponectin Modulates Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Neuron Activity and Anxiety-Related Behavior through AdipoR1. Mol Psychiatry 2019, 24, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aprile, I.; Petrillo, G.; Zonca, V.; Mazzelli, M.; De Cillis, F.; Di Benedetto, M.G.; Riva, M.A.; Cattaneo, A. Sex-Specific Metabolic and Inflammatory Alterations in Adult Animals Vulnerable to Prenatal Stress Exposure. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2025, 138, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, M.; Qin, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Running Exercise Alleviates Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Shifts the Balance of Microglial M1/M2 Polarization through Adiponectin/AdipoR1 Pathway Activation in Mice Exposed to Chronic Unpredictable Stress. Mol Psychiatry 2024, 29, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousti, F.; Ahmadi, R.; Mirahmadi, F.; Hosseinmardi, N.; Rohampour, K. Adiponectin Modulates Synaptic Plasticity in Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus. Neuroscience Letters 2018, 662, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Fasano, R.; Paolisso, G. Adiponectin and Cognitive Decline. IJMS 2020, 21, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, J.L.; Soyombo, A.; Czysz, A.H.; Jha, M.K.; Carmody, T.J.; Mason, B.L.; Scherer, P.E.; Trivedi, M.H. Adiponectin Moderates Antidepressant Treatment Outcome in the Combining Medications to Enhance Depression Outcomes Randomized Clinical Trial. Pers Med Psychiatry 2018, 9–10, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Machado-Vieira, R.; Gold, P.W.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Ballard, E.D.; Richards, E.M.; Henter, I.D.; De Sousa, R.T.; Niciu, M.J.; Yuan, P.; Zarate, C.A. The Role of Adipokines in the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine. Mol Psychiatry 2017, 22, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permoda-Pachuta, A.; Malewska-Kasprzak, M.; Skibińska, M.; Rzepski, K.; Dmitrzak-Węglarz, M. Changes in Adipokine, Resitin, and BDNF Concentrations in Treatment-Resistant Depression after Electroconvulsive Therapy. Brain Sci 2023, 13, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.S.; Gerszten, R.E.; Taylor, J.M.; Pedersen, B.K.; Van Praag, H.; Trappe, S.; Febbraio, M.A.; Galis, Z.S.; Gao, Y.; Haus, J.M.; et al. Exerkines in Health, Resilience and Disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2022, 18, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirico, F.; Bianco, A.; D’Alicandro, G.; Castaldo, C.; Montagnani, S.; Spera, R.; Di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D. Effects of Physical Exercise on Adiponectin, Leptin, and Inflammatory Markers in Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Child Obes 2018, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, J.M.; Helge, J.W.; Richelsen, B.; Stallknecht, B. Diet and Exercise Reduce Low-Grade Inflammation and Macrophage Infiltration in Adipose Tissue but Not in Skeletal Muscle in Severely Obese Subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2006, 290, E961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, T.R.; Mendes, T.T.; Ramos, G.P.; Cabido, C.E.T.; Morandi, R.F.; Ferraz, F.O.; Miranda, A.S.; Mendonça, V.A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Silami-Garcia, E.; et al. Aerobic Training Modulates the Increase in Plasma Concentrations of Cytokines in Response to a Session of Exercise. J Environ Public Health 2021, 2021, 1304139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürimäe, J.; Purge, P.; Jürimäe, T. Adiponectin and Stress Hormone Responses to Maximal Sculling after Volume-Extended Training Season in Elite Rowers. Metabolism 2006, 55, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, R.R.; Aboudehen, K.S.; Carruth, A.K.; Durand, R.T.J.; Acevedo, E.O.; Hebert, E.P.; Johnson, L.G.; Castracane, V.D. Adiponectin Responses to Continuous and Progressively Intense Intermittent Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003, 35, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, M.A.; White, L.J.; McCoy, S.; Kim, H.-W.; Petty, T.; Wilsey, J. Plasma Adiponectin Response to Acute Exercise in Healthy Subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 2004, 91, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamurtas, A.Z.; Theocharis, V.; Koukoulis, G.; Stakias, N.; Fatouros, I.G.; Kouretas, D.; Koutedakis, Y. The Effects of Acute Exercise on Serum Adiponectin and Resistin Levels and Their Relation to Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Males. Eur J Appl Physiol 2006, 97, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Wei, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhou, F.; Chen, J.; Han, Q.; Huang, M.; Tan, X.; Liu, Q.; et al. Exercise Ameliorates the FGF21-Adiponectin Axis Impairment in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Endocr Connect 2019, 8, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Montoya, J.; Bentes, A.; Pavez, Y.; Rubilar, P.; Lavoz, C.; Ehrenfeld, P.; Sandoval, V.; Martínez-Huenchullán, S. Metabolic Response After a Single Maximal Exercise Session in Physically Inactive Young Adults (EASY Study): Relevancy of Adiponectin Isoforms. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, P.H.; von Ah Morano, A.E.; Agostinete, R.R.; Werneck, A.O.; Giannopoulos, A.J.; Bell, M.; Antunes, B.M.; Lira, F.S.; Fernandes, R.A.; Klentrou, P. Cytokine and Adipokine Response Following High-Intensity Interval Running and Cycling in Female Adolescents. Eur J Appl Physiol 2025. [CrossRef]
- Vidal, P.; Stanford, K.I. Exercise-Induced Adaptations to Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, S.; Aiello, G.; Mansilla Di Martino, E.; Campaci, D.; Muthanna, F.M.S.; Lombardo, M. The Role of Adipose Tissue and Nutrition in the Regulation of Adiponectin. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Soriano, E.; Sáinz, N.; Gil-Iturbe, E.; Castilla-Madrigal, R.; Celay, J.; Fernández-Galilea, M.; Pejenaute, Á.; Lostao, M.P.; Martínez-Climent, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J. Differential Remodeling of Subcutaneous White and Interscapular Brown Adipose Tissue by Long-Term Exercise Training in Aged Obese Female Mice. J Physiol Biochem 2023, 79, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, B.J.; Schleh, M.W.; Ahn, C.; Ludzki, A.C.; Gillen, J.B.; Varshney, P.; Van Pelt, D.W.; Pitchford, L.M.; Chenevert, T.L.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; et al. Moderate-Intensity Exercise and High-Intensity Interval Training Affect Insulin Sensitivity Similarly in Obese Adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020, 105, e2941–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blümer, R.M.E.; van Roomen, C.P.; Meijer, A.J.; Houben-Weerts, J.H.P.M.; Sauerwein, H.P.; Dubbelhuis, P.F. Regulation of Adiponectin Secretion by Insulin and Amino Acids in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Metabolism 2008, 57, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, T.; Tao, H.; Wattacheril, J.; Marks-Shulman, P.; Abumrad, N.N. Regulation of Adiponectin Production by Insulin: Interactions with Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-6. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2011, 300, E350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerbacka, J.; Cornér, A.; Kannisto, K.; Kolak, M.; Makkonen, J.; Korsheninnikova, E.; Nyman, T.; Hamsten, A.; Fisher, R.M.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Acute in Vivo Effects of Insulin on Gene Expression in Adipose Tissue in Insulin-Resistant and Insulin-Sensitive Subjects. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, V.F.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-DE-Lacerda, C.A. High-Intensity Interval Training (Swimming) Significantly Improves the Adverse Metabolism and Comorbidities in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2016, 56, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Pala, R.; Genc, E.; Tuzcu, M.; Orhan, C.; Sahin, N.; Er, B.; Cinar, V.; Sahin, K. L-Carnitine Supplementation Increases Expression of PPAR-Î3 and Glucose Transporters in Skeletal Muscle of Chronically and Acutely Exercised Rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2018, 64, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, H.; Mirnejad, R.; Soleimani, M.; Arabzadeh, E. Swimming Exercise Improves Gene Expression of PPAR-γ and Downregulates the Overexpression of TLR4, MyD88, IL-6, and TNF-α after High-Fat Diet in Rat Skeletal Muscle Cells. Gene 2021, 775, 145441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M. Self-Regulation of the Inflammatory Response by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Inflamm Res 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Gao, X.; Ge, Q.; Tai, W.; Hao, X.; Shao, Q.; Fang, Z.; Chen, M.; Song, Y.; Gao, W.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Reduces Adiponectin Production by Decreasing Transcriptional Activity of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ in Calf Adipocytes. J Dairy Sci 2023, 106, 5182–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalve, F.A.; Pyarasani, R.D.; Delgado-Lopez, F.; Moore-Carrasco, R. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Targets for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases. Mediators Inflamm 2013, 2013, 549627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Hawkins, M.; Combs, T.P.; Rajala, M.W.; Doebber, T.; Berger, J.P.; Wagner, J.A.; Wu, M.; Knopps, A.; Xiang, A.H.; et al. Complex Distribution, Not Absolute Amount of Adiponectin, Correlates with Thiazolidinedione-Mediated Improvement in Insulin Sensitivity. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 12152–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, X.; Yu, A.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Enhances Adiponectin Secretion via up-Regulating DsbA-L Expression. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2015, 411, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Yau, M.; Xu, A. Post-Translational Modifications of Adiponectin: Mechanisms and Functional Implications. Biochemical Journal 2008, 409, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Gholamhoseinian, A.; Fallah, H. Zataria Multiflora Increases Insulin Sensitivity and PPARγ Gene Expression in High Fructose Fed Insulin Resistant Rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2014, 17, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, M.; Spriet, L.L. Skeletal Muscle Energy Metabolism during Exercise. Nat Metab 2020, 2, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Mechanisms of Cellular Energy Sensing and Restoration of Metabolic Balance. Mol Cell 2017, 66, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. Compr Physiol 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tishinsky, J.M.; Dyck, D.J.; Robinson, L.E. Lifestyle Factors Increasing Adiponectin Synthesis and Secretion. Vitam Horm 2012, 90, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Christie, B.R.; van Praag, H.; Lin, K.; Siu, P.M.-F.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F.; Yau, S.-Y. AdipoRon Treatment Induces a Dose-Dependent Response in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, F.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Fan, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, C.; et al. Role of Adiponectin-Notch Pathway in Cognitive Dysfunction Associated with Depression and in the Therapeutic Effect of Physical Exercise. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.-G.; Liu, C.-L.; Yan, H.-J. AdipoRon Improves Cognitive Dysfunction of Alzheimer’s Disease and Rescues Impaired Neural Stem Cell Proliferation through AdipoR1/AMPK Pathway. Exp Neurol 2020, 327, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, R.H.; Cook, J.G. Stress Relief Techniques: P38 MAPK Determines the Balance of Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Pathways. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.-Y. Adiponectin Stimulates Proliferation of Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells through Activation of P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (p38MAPK)/Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β (GSK-3β)/β-Catenin Signaling Cascade. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 44913–44920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, E.; Kim, C.-H.; Song, H.-T.; Lee, J.E. Adiponectin Receptor-Mediated Signaling Ameliorates Cerebral Cell Damage and Regulates the Neurogenesis of Neural Stem Cells at High Glucose Concentrations: An in Vivo and in Vitro Study. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampada, A.; Taylor, V. Notch Signaling as a Master Regulator of Adult Neurogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1179011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Yoon, G.H.; Chung, S.S.; Abid, M.N.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, M.O. Novel Osmotin Inhibits SREBP2 via the AdipoR1/AMPK/SIRT1 Pathway to Improve Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathological Deficits. Mol Psychiatry 2017, 22, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, S.; Chen, S.; Zou, J.; Zeng, P.; Tan, S. Neurological Mechanism-Based Analysis of the Role and Characteristics of Physical Activity in the Improvement of Depressive Symptoms. Rev Neurosci 2025. [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Hou, W.; Yao, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, S. Adiponectin Promotes Neurogenesis After Transient Cerebral Ischemia Through STAT3 Mediated BDNF Upregulation in Astrocytes. Neurochem Res 2023, 48, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, S.; Debayle, D.; Béchade, C.; Maroteaux, L.; Gay, A.-S.; Bayer, P.; Heurteaux, C.; Guyon, A.; Chabry, J. Adiporon, an Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Acts as an Antidepressant and Metabolic Regulator in a Mouse Model of Depression. Transl Psychiatry 2018, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabry, J.; Nicolas, S.; Cazareth, J.; Murris, E.; Guyon, A.; Glaichenhaus, N.; Heurteaux, C.; Petit-Paitel, A. Enriched Environment Decreases Microglia and Brain Macrophages Inflammatory Phenotypes through Adiponectin-Dependent Mechanisms: Relevance to Depressive-like Behavior. Brain Behav Immun 2015, 50, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.-H.; Ou, H.-N.; Yu, J.-S.; Yau, S.-Y.; Tsang, H.W.-H. Pharmacological Blocking of Adiponectin Receptors Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Neuropathology and Impairs Hippocampal Function. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Branchi, I.; Poletti, S.; Lorenzi, C.; Bigai, G.; Colombo, C.; Zanardi, R. Adiponectin Predicts Poor Response to Antidepressant Drugs in Major Depressive Disorder. Human Psychopharmacology 2021, 36, e2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houminer-Klepar, N.; Dopelt, K. Associations Between Mediterranean Diet, Processed Food Consumption, and Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression: Cross-Sectional Study Among Israeli Adults. Foods 2025, 14, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Cuenca, J.A.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.E.; Pineda-Juárez, J.A.; Mendoza-Mota, A.G.; Valencia-Aldana, O.D.; Núñez-Angeles, S.; Vera-Gómez, E.; Hernández-Patricio, A.; Loeza-Magaña, P.; Lara-Vargas, J.A.; et al. Effect of Mediterranean Diet in Combination with Isokinetic Exercise Therapy on Body Composition and Cytokine Profile in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2025, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, H.A.; Aziz, H.M.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M. The Potential Effects of Metformin and/or Sitagliptin on Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio in Diabetic Obese Patients: A New Therapeutic Effect. J Pak Med Assoc 2024, 74, S241–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, S.A.; Elmelgy, A.A.; El-Kharashi, O.A.; Abd-Alkhalek, H.A.; Louka, M.L.; Sallam, H.A.; Aboul-Fotouh, S. Metformin Potentiates Cognitive and Antidepressant Effects of Fluoxetine in Rats Exposed to Chronic Restraint Stress and High Fat Diet: Potential Involvement of Hippocampal c-Jun Repression. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2018, 391, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femminella, G.D.; Frangou, E.; Love, S.B.; Busza, G.; Holmes, C.; Ritchie, C.; Lawrence, R.; McFarlane, B.; Tadros, G.; Ridha, B.H.; et al. Evaluating the Effects of the Novel GLP-1 Analogue Liraglutide in Alzheimer’s Disease: Study Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial (ELAD Study). Trials 2019, 20, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, C.B.G.; Lu, T.T.-H.; Gabery, S.; Marstal, K.; Alanentalo, T.; Mercer, A.J.; Cornea, A.; Conradsen, K.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Dahl, A.B.; et al. Integrated Brain Atlas for Unbiased Mapping of Nervous System Effects Following Liraglutide Treatment. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, N.; Hölscher, C. The Neuroprotective Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease: An in-Depth Review. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 970925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Guo, L.; Pan, Q. The Antidepressant Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2024, 32, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Hayes, M.R.; Skibicka, K.P. GLP-1 and Weight Loss: Unraveling the Diverse Neural Circuitry. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2016, 310, R885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metabolism 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, Mortality, and Kidney Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badulescu, S.; Gill, H.; Shah, H.; Brudner, R.; Phan, L.; Di Vincenzo, J.D.; Tabassum, A.; Armanyous, M.; Llach López, C.-D.; Rosenblat, J.D.; et al. Semaglutide for the Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomised, Phase 2 Clinical Trial 2025.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




