Submitted:
29 September 2025
Posted:
30 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
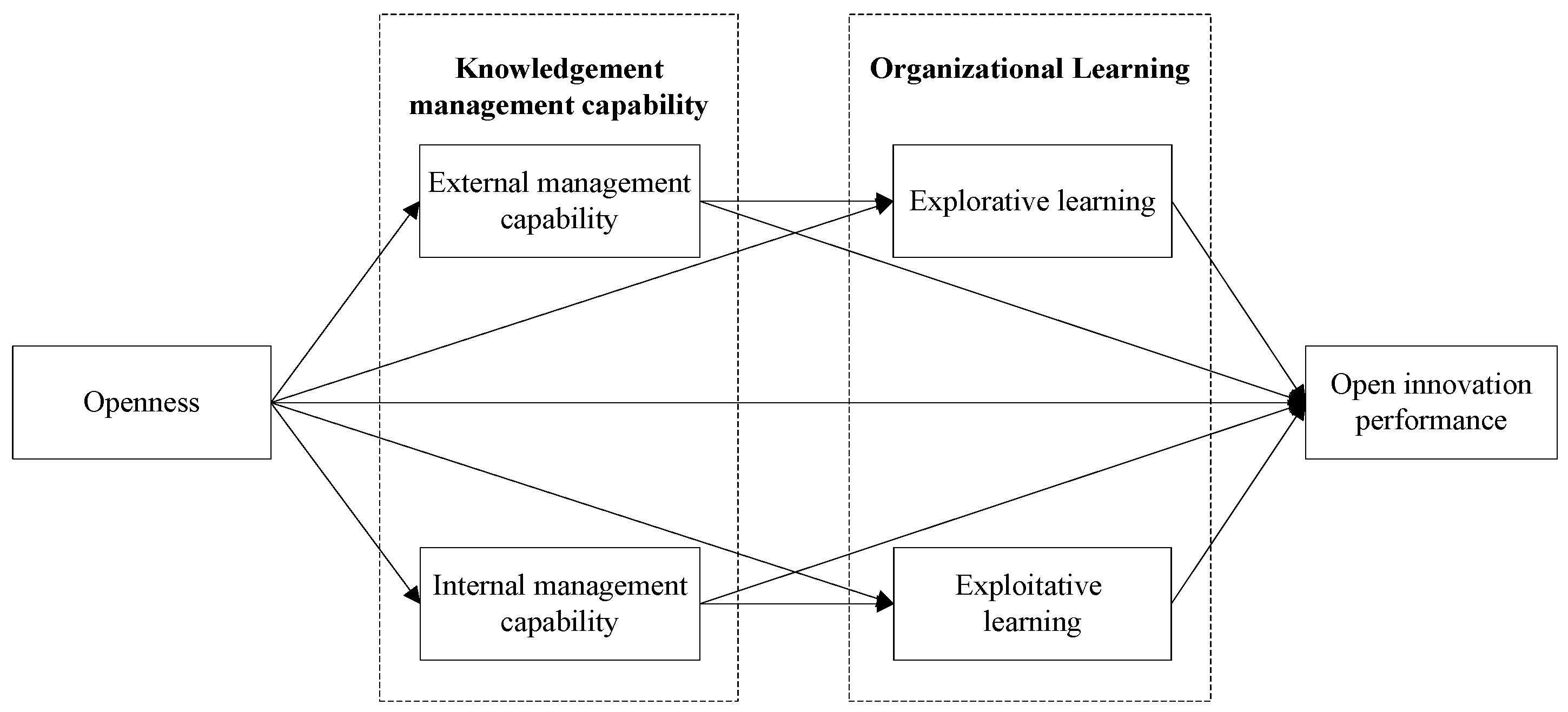
1. Theoretical Framework and Hypothesis Development
1.1. Openness and Open Innovation Performance
1.2. The Mediating Effect of Knowledge Management Capability
1.3. The Mediating Effect of Organizational Learning
1.4. The Serial Mediation of Knowledge Management Capability and Organizational Learning
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Sample
2.2. Measurement
3. Empirical Analysis and Results
3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.2. Reliability and Validity Test
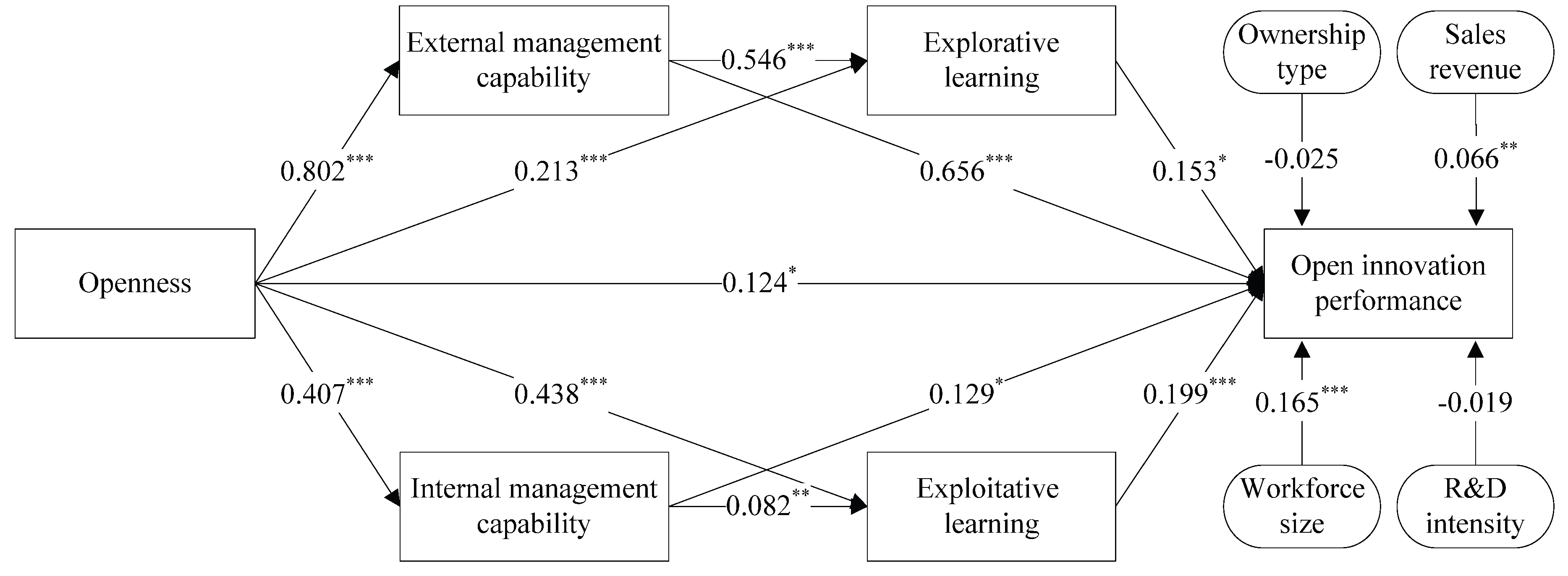
3.3. Hypothesis Test
3.3.1. Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
3.3.2. Mediating Effect Test
3.4. Robustness Test
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Research Implications and Limitations
5.1. Research Implications
5.2. Research Limitations and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Items (strongly disagree/1-strongly agree/7) |
| Openness |
| The firm has a culture encouraging collaborations with external organisations. |
| The firm has a willingness to share experiences through collaboration. |
| The top managers in the firm are proactive for collaboration with external organisations. |
| In general, the firm trusts external partners. |
| External knowledge management capability |
| We have the ability to identify and use relevant knowledge from external network. |
| We often analyze external knowledge. |
| We are able to integrate internal knowledge with external knowledge. |
| We are able to apply new knowledge to a specific application quickly. |
| The number of affiliates in our partnership network is considerable. |
| We have a close relationship with the affiliates in our partnership network. |
| We are able to identify knowledge that is transferred from us to external network. |
| The process of knowledge transfer from our company to external network is well organized. |
| We provide adequate support for the process of knowledge transfer to external network. |
| Internal knowledge management capability |
| Among all knowledge sources, our internal knowledge makes a major contribution. |
| Our internal team provides major knowledge. |
| Our new employees provide major knowledge. |
| We have the ability to retain the knowledge obtained from external sources. |
| We are able to integrate existing knowledge with new knowledge. |
| We have the ability to maintain the technology acquired from external sources. |
| We have the ability to expand our product range. |
| The percentage of our new product sales revenue is growing fast. |
| We have valuable knowledge in innovative manufacturing and technology processes. |
| Explorative learning |
| Team members were systematically searching for new possibilities during the project. |
| Team members offered new ideas and solutions to complicated problems (were inventive). |
| Team members experimented with new and creative ways for accomplishing work. |
| Team members evaluated diverse options regarding the course of the project. |
| The members of our team developed many new skills during the project. |
| Exploitative learning |
| The members of our team recombined existing knowledge for accomplishing work. |
| In our team, we primarily performed routine activities. |
| During the project, our team implemented standardized methodologies and regular work practices. |
| Team members improved and refined their existing knowledge and expertise during the project. |
| Team members mainly used their current knowledge and skills for performing their tasks. |
| Open innovation performance |
| Compared to major competitors, we develop more new products in the last three years. |
| Compared to major competitors, we develop new products faster in the last three years. |
| Compared to major competitors, we have a higher success rate of innovation projects in the last three years. |
| Compared to major competitors, we apply for more patents in the last three years. |
| Compared to major competitors, we have a higher proportion of new product sales revenue in the last three years. |
References
- Zhang, X.; Chu, Z.; Ren, L.; Xing, J. Open Innovation and Sustainable Competitive Advantage: The Role of Organizational Learning. Technol Forecast Soc Change 2023, 186, 122114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigliardi, B.; Ferraro, G.; Filippelli, S.; Galati, F. The Past, Present and Future of Open Innovation. Eur J Innov Manag 2021, 24, 1130–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid-Guijarro, A.; Martin, D.P.; García-Pérez-De-Lema, D. Capacity of Open Innovation Activities in Fostering Product and Process Innovation in Manufacturing Smes. Rev Managerial Sci 2021, 15, 2137–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Fan, X.; Zhang, B.; Shao, D. The Impact of Open Innovation on Innovation Performance: The Chain Mediating Effect of Knowledge Field Activity and Knowledge Transfer. Inf Technol Manag 2025, 26, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, K.; Salter, A. Open for Innovation: The Role of Openness in Explaining Innovation Performance among Uk Manufacturing Firms. Strateg Manag J 2006, 27, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.T.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Markovic, S.; Damnjanovic, V. Open Innovation Where It Really Matters: The U-Shaped Relationship between Relative Open Innovation and Innovation Performance in Developing Countries. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 2024, 71, 15540–15554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Liang, X.; Garrett, T.C. Antecedents and Outcomes of Open Innovation over the Past 20 Years: A Framework and Meta-Analysis. J Prod Innov Manag 2024, 41, 793–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, F.; Innocenti, N.; Baldetti, F.; Zampi, V. Firm's Openness and Innovation in Industry 4.0. Competitiveness Rev 2023, 34, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumanti, A.A.; Rizana, A.F.; Ramadhan, F.; Reynaldo, R. The Impact of Open Innovation Preparation on Or-ganizational Performance: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 126952–126966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhou, Y. Innovation Network, Knowledge Absorption Ability, and Technology Innovation Performance—an Empirical Analysis of China's Intelligent Manufacturing Industry. PLoS One 2023, 18, 0293429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.C.; Zo, H. Do R&D Resources Affect Open Innovation Strategies in Smes: The Mediating Effect of R&D Openness on the Relationship between R&D Resources and Firm Performance in South Korea's Innovation Clusters. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 2023, 35, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Tikas, G. Toward Measuring R&D Knowledge Management Capability: Scale Development and Empirical Validation. Vine J Inf Knowl Manag Syst, ahead-of-print. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, S.; Rasheed, M.; Khan, H.; Siddiqi, A. Human Resource Practices and Organizational Innovation Capability: Role of Knowledge Management. Vine J Inf Knowl Manag Syst 2021, 51, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.B.; Le, H.M. Stimulating Exploitative and Exploratory Innovation through Transformational Leadership and Knowledge Management Capability: The Moderating Role of Competitive Intensity. Leadership Organ Devel J 2023, 44, 1037–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaty, H.; Weiss, D. Coping with the Heterogeneity of External Knowledge Sources: Corresponding Openness Strategies and Innovation Performance. J Innov Knowl 2023, 8, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsono, T.W.; Hidayat, K.; Iqbal, M.; Abdillah, Y. Exploring the Effect of Transformational Leadership and Knowledge Management in Enhancing Innovative Performance: A Mediating Role of Innovation Capability. J Manuf Technol Manag 2025, 36, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K. The Impact of Knowledge Management Capabilities on Innovation Performance from Dynamic Capabilities Perspective: Moderating the Role of Environmental Dynamism. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Ju, X. How Does Enterprise Social Network Affects Open Innovation Performance? From the Dual Perspective of Inter- and Intra-Organisation. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 2023, 35, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdadi, M.M. Organizational Learning Capability, Innovation and Organizational Performance. Eur J Innov Manag 2021, 24, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.F.; Li, P.S.; Li, Y. The Relationship between Slack Resources and Organizational Resilience: The Moderating Role of Dual Learning. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.K.; Do, T.T.; Ho Nguyen, D.T. The Impact of Leadership Competences, Organizational Learning and Organizational Innovation on Business Performance. Bus Process Manag J 2022, 28, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Lim, H.; Song, J. The Influence of Leadership Style in China SMES on Enterprise Innovation Performance: The Mediating Roles of Organizational Learning. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Dogbe, C.S.K.; Pomegbe, W.W.K.; Sarsah, S.A.; Otoo, C.O.A. Organizational Learning Ambidexterity and Openness, as Determinants of Smes' Innovation Performance. Eur J Innov Manag 2021, 24, 414–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauter, R.; Globocnik, D.; Perl-Vorbach, E.; Baumgartner, R.J. Open Innovation and Its Effects on Economic and Sustainability Innovation Performance. J Innov Knowl 2019, 4, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, R.; Yang, X.; Hou, J. How Does the Innovation Openness of China's Sci-Tech Innovation Enterprises Support Innovation Quality: The Mediation Role of Structural Embeddedness. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, Z.a.; Zhou, Y. Optimal Degree of Openness in Open Innovation: A Perspective from Knowledge Acquisition & Knowledge Leakage. Technol Soc 2021, 67, 101756. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Chin, T.; Lin, J.H. Openness and Firm Innovation Performance: The Moderating Effect of Ambi-dextrous Knowledge Search Strategy. J Knowl Manag 2020, 24, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yu, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D. Effects of Open Innovation Strategies on Innovation Performance of Smes: Evidence from China. Chinese Manag Stud 2021, 15, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippakoon, P.; Sang-Arun, N.; Vishuphong, P. External Knowledge Sourcing, Knowledge Management Capacity and Firms' Innovation Performance: Evidence from Manufacturing Firms in Thailand. J Asia Bus Stud 2021, 17, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Qi, Y. Fostering Knowledge Creation through Network Capability Ambidexterity with the Moderation of an Innovation Climate. J Knowl Manag 2023, 27, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.M.; Mortara, L.; Minshall, T. Dynamic Capabilities and Economic Crises: Has Openness Enhanced a Firm's Performance in an Economic Downturn? Ind Corp Chang 2018, 27, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Unleashing the Dynamics of Triple-a Capabilities: A Dynamic Ambidexterity View. Ind Manag Data Syst 2021, 121, 2595–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Guo, J.e.; Chen, T.; Murong, R. Configuration Research on Innovation Performance of Digital Enterprises: Based on an Open Innovation and Knowledge Perspective. Front Environ Sci 2023, 10, 953902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongmahesak, K.; Wongsuwan, N.; Akkaya, B.; Palazzo, M. Impact of Knowledge Management Process on Organizational Performance: The Mediating Role of Technological Innovation. Knowl Process Manag 2025, 32, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Yu, D.K. Exploring the Impact of Knowledge Management Capability on Firm Performance: The Mediating Role of Business Model Innovation. Kybernetes 2024, 53, 3591–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, U.; Lichtenthaler, E. A Capability-Based Framework for Open Innovation: Complementing Absorptive Capacity. J Manag Stud 2009, 46, 1315–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. Moderating Effect of Structural Holes on Absorptive Capacity and Knowledge-Innovation Performance: Empirical Evidence from Chinese Firms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Krenz, A.; Moffat, J. The Effects of Absorptive Capacity on Innovation Performance: A Cross-Country Perspective*. Jcms-Journal of Common Market Studies 2021, 59, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; Geng, Q.; Zhao, Q. Understanding the Efforts of Cross-Border Search and Knowledge Co-Creation on Manufacturing Enterprises' Service Innovation Performance. Systems 2023, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Lin, B.-W.; Chen, C.-J. How Do Internal Openness and External Openness Affect Innovation Capabilities and Firm Performance? IEEE Trans Eng Manag 2013, 60, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N. Knowledge Management Capability and Outbound Open Innovation: Unpacking the Role of Desorptive Capacity. Knowl Process Manag 2023, 30, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braojos, J.; Benitez, J.; Llorens, J.; Ruiz, L. Impact of It Integration on the Firm's Knowledge Absorption and Desorption. Inf Manag 2020, 57, 103290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashosi, G.D.; Wu, Y.; Getele, G.K.; Bianca, E.M.; Irakoze, E. The Role of Absorptive Capacity and Firm Openness Strategies on Innovation Performance. Inf Resour Manag J 2020, 33, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medase, S.K.; Abdul-Basit, S. External Knowledge Modes and Firm-Level Innovation Performance: Empirical Evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa. J Innov Knowl 2020, 5, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGahan, A.M.; Bogers, M.L.A.M.; Chesbrough, H.; Holgersson, M. Tackling Societal Challenges with Open Innovation. California Manag Rev 2021, 63, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Knowledge Management Capability and Technology Uncertainty: Driving Factors of Dual Innovation. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 2021, 33, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Sarfraz, M.; Khawaja, K.F.; Shaheen, H.; Mariam, S. The Influence of Knowledge Management Capacities on Pharmaceutical Firms Competitive Advantage: The Mediating Role of Supply Chain Agility and Moderating Role of Inter Functional Integration. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 953478. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, K.; Kim, E.; Jeong, E. Structural Relationship and Influence between Open Innovation Capacities and Performances. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, H. How Internal It Capability Affects Open Innovation Performance: From Dynamic Capability Perspective. Sage Open 2022, 12, 21582440211069389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraishi, A.; Paulraj, A.; Huq, F.; Seepana, C. Knowledge Management in Offshoring Innovation by Smes: Role of Internal Knowledge Creation Capability, Absorptive Capacity and Formal Knowledge-Sharing Routines. Supply Chain Manag-an Int J 2023, 28, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nuaimi, F.M.S.; Singh, S.K.; Ahmad, S.Z. Open Innovation in Smes: A Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. J Knowl Manag 2024, 28, 484–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwary, A.K.; Alwi, M.K.; Rchman, S.U.; Rabiul, M.K.; Babatunde, A.Y.; Alam, M.M.D. Knowledge Management Practices on Innovation Performance in the Hotel Industry: Mediated by Organizational Learning and Organizational Crea-tivity. Global Knowl Memory Commun 2024, 73, 662–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceptureanu, S.I.; Ceptureanu, E.G. Learning Ambidexterity and Innovation in Creative Industries. The Role of Enabling Formalisation. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 2024, 36, 3385–3399. [Google Scholar]
- March, J.G. Exploration and Exploitation in Organizational Learning. Organ Sci 1991, 2, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Qiang, Q.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.Q. How Knowledge Sharing Affects Business Model Innovation: An Empirical Study from the Perspective of Ambidextrous Organizational Learning. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.L. Learning Ambidexterity and Technology Innovation: The Moderating Effect of Knowledge Network Modularity. J Eng Technol Manag 2024, 72, 101812. [Google Scholar]
- Öberg, C.; Alexander, A.T. The Openness of Open Innovation in Ecosystems - Integrating Innovation and Management Literature on Knowledge Linkages. J Innov Knowl 2019, 4, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Seo, E.-H.; Kim, C.Y. The Relationships between Environmental Dynamism, Absorptive Capacity, Organizational Ambidexterity, and Innovation Performance from the Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. Sustainability 2025, 17, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Y. The Impact of Enterprise Niche on Dual Innovation Performance: Moderating Role of Innovation Openness. Eur J Innov Manag 2023, 26, 1547–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M. Examining the Linkage among Open Innovation, Customer Knowledge Management and Radical Innovation: The Multiple Mediating Effects of Organizational Learning Ability. Baltic J Manag 2018, 29, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, S.; Mahmood, A.; Waqar, H. The Interplay of Open Innovation and Strategic Innovation: Unpacking the Role of Organizational Learning Ability and Absorptive Capacity. Int J Eng Bus Manag 2022, 14, 18479790211069745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginja Antunes, H.d.J.; Pinheiro, P.G. Linking Knowledge Management, Organizational Learning and Memory. J Innov Knowl 2020, 5, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Zamora, R.; Hernandez-Perlines, F.; Pena-Garcia, I.; Gutierrez-Broncano, S. The Impact of Absorptive Capacity on Innovation: The Mediating Role of Organizational Learning. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.K.; Fatima, T.; Sarwar, A.; Amin, S. Knowledge Management Capabilities and Organizational Outcomes: Contemporary Literature and Future Directions. Kybernetes 2022, 51, 2814–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Mackenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J Appl Psychol 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.M.; Ju, Y.; Moon, T.H.; Minshall, T.; Probert, D.; Sohn, S.Y.; Mortara, L. Beyond Absorptive Capacity in Open Innovation Process: The Relationships between Openness, Capacities and Firm Performance. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 2016, 28, 1009–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forés, B.; Camisón, C. Does Incremental and Radical Innovation Performance Depend on Different Types of Knowledge Accumulation Capabilities and Organizational Size? J Bus Res 2016, 69, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudambi, S.M.; Tallman, S. Make, Buy or Ally? Theoretical Perspectives on Knowledge Process Outsourcing through Alliances. J Manag Stud 2010, 47, 1434–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Lai, M.-C.; Huang, W.-W. Resource Complementarity, Transformative Capacity, and Inbound Open Innovation. J Bus Ind Mark 2015, 30, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zong, B.; Zhang, L. Explorative and Exploitative Learning in Teams: Unpacking the Antecedents and Consequences. Front Psychol 2020, 11, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Liang, L. How Open Innovation Performance Responds to Partner Heterogeneity in China. Management Decision 2018, 56, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golafshani, N. Understanding Reliability and Validity in Qualitative Research. Qual Rep 2003, 8, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis. A Global Perspective, 7th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- Kline, R.B.; Little, T.D. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guilford Press: New York, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, D.W.M.; Sarvari, H.; Golestanizadeh, M.; Saka, A. Evaluating the Impact of Organizational Learning on Organizational Performance through Organizational Innovation as a Mediating Variable: Evidence from Iranian Construction Companies. Int J Constr Manag 2024, 24, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuks, O. It Capability, Organisational Learning and Innovation Performance of Firms in Kenya. J Knowl Econ 2023, 14, 3489–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Rawashdeh, A.M.; Almasarweh, M.S.; Alhyasat, E.B.; Rawashdeh, O.M. The Relationsip between the Quality Knowledge Management and Organizational Performance Via the Mediating Role of Organizational Learning. Int J Qual Res 2021, 15, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Number | Percent(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise ownership type | State-owned enterprise | 316 | 42.5 |
| Private enterprise | 247 | 33.2 | |
| Joint Ventures | 128 | 17.2 | |
| Foreign-owned enterprise | 53 | 7.1 | |
| Sales revenue | <5 million CNY | 48 | 6.5 |
| 5 million-50 million CNY | 229 | 30.8 | |
| 50 million -300 million CNY | 373 | 50.1 | |
| >300 million CNY | 94 | 12.6 | |
| Workforce size | < 50 | 78 | 10.5 |
| 50-300(including) | 192 | 25.8 | |
| 300-1000(including) | 318 | 42.7 | |
| >1000 | 156 | 21.0 | |
| R&D intensity | <1% | 139 | 18.7 |
| 1%-2%(including) | 217 | 29.2 | |
| 2-5%(including) | 296 | 39.8 | |
| >5% | 92 | 12.4 |
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Openness | 0.854 | |||||
| 2.External knowledge management capability | 0.602*** | 0.849 | ||||
| 3.Internal knowledge management capability | 0.340** | 0.370** | 0.805 | |||
| 4.Explorative learning | 0.576** | 0.557** | 0.282* | 0.865 | ||
| 5.Exploitative learning | 0.466** | 0.531** | 0.206* | 0.546** | 0.884 | |
| 6.Open innovation performance | 0.590*** | 0.615*** | 0.334** | 0.571** | 0.507** | 0.867 |
| Mean | 4.550 | 4.694 | 5.158 | 4.762 | 4.152 | 4.997 |
| Standard deviation | 1.300 | 1.592 | 1.312 | 1.469 | 1.609 | 1.630 |
| Variable | Items | Factor loading | CR | AVE | Cronbach’s α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Openness (OPN) |
OPN1 | 0.761 | 0.915 | 0.730 | 0.880 |
| OPN2 | 0.827 | ||||
| OPN3 | 0.911 | ||||
| OPN4 | 0.910 | ||||
| External knowledge management capability(EKM) | EKM1 | 0.852 | 0.958 | 0.720 | 0.913 |
| EKM2 | 0.826 | ||||
| EKM3 | 0.899 | ||||
| EKM4 | 0.784 | ||||
| EKM5 | 0.899 | ||||
| EKM6 | 0.761 | ||||
| EKM7 | 0.913 | ||||
| EKM8 | 0.835 | ||||
| EKM9 | 0.852 | ||||
| Internal knowledge management capability(IKM) | IKM1 | 0.793 | 0.943 | 0.648 | 0.830 |
| IKM2 | 0.724 | ||||
| IKM3 | 0.770 | ||||
| IKM4 | 0.829 | ||||
| IKM5 | 0.834 | ||||
| IKM6 | 0.862 | ||||
| IKM7 | 0.837 | ||||
| IKM8 | 0.781 | ||||
| IKM9 | 0.806 | ||||
| Explorative learning (ERL) |
ERL1 | 0.865 | 0.937 | 0.749 | 0.896 |
| ERL2 | 0.879 | ||||
| ERL3 | 0.909 | ||||
| ERL4 | 0.845 | ||||
| ERL5 | 0.827 | ||||
| Exploitative learning(EIL) | EIL1 | 0.875 | 0.947 | 0.781 | 0.879 |
| EIL2 | 0.886 | ||||
| EIL3 | 0.912 | ||||
| EIL4 | 0.905 | ||||
| EIL5 | 0.839 | ||||
| Open innovation performance (OIP) |
OIP1 | 0.866 | 0.938 | 0.751 | 0.939 |
| OIP2 | 0.908 | ||||
| OIP3 | 0.862 | ||||
| OIP4 | 0.824 | ||||
| OIP5 | 0.870 |
| Path | Estimate | p-value | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Direct effect | Openness→Open innovation performance | 0.124 | 0.058 | 0.049 | 0.162 |
| Indirect effect | Openness→External knowledge management capability→Open innovation performance | 0.526 | 0.000 | 0.443 | 0.609 |
| Openness→Internal knowledge management capability→Open innovation performance | 0.053 | 0.079 | 0.026 | 0.061 | |
| Openness→Explorative learning→Open innovation performance | 0.033 | 0.086 | 0.012 | 0.067 | |
| Openness→Exploitative learning→Open innovation performance | 0.087 | 0.000 | 0.047 | 0.127 | |
| Openness→External knowledge management capability→Explorative learning→Open innovation performance | 0.067 | 0.077 | 0.005 | 0.096 | |
| Openness→Internal knowledge management capability→Exploitative learning→Open innovation performance | 0.007 | 0.028 | 0.001 | 0.012 | |
| Total indirect effect | - | 0.773 | 0.000 | 0.65 | 0.794 |
| Total effect | - | 0.897 | 0.000 | 0.738 | 0.915 |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise ownership type | -0.195*** | -0.059*** | -0.073*** | -0.158*** | -0.060** | -0.071*** |
| Sales revenue | 0.035 | 0.103 | 0.065*** | 0.014 | 0.022 | 0.024 |
| Workforce size | 0.265*** | 0.191 | 0.171*** | 0.231*** | 0.142*** | 0.217*** |
| R&D intensity | 0.127*** | 0.033 | 0.015 | 0.082*** | 0.013 | 0.036 |
| Openness | 0.663*** | |||||
| External knowledge management capability | 0.762*** | |||||
| Internal knowledge management capability | 0.290*** | |||||
| Explorative learning | 0.637*** | |||||
| Exploitative learning | 0.578*** | |||||
| R2 | 0.104 | 0.503 | 0.649 | 0.184 | 0.469 | 0.413 |
| F | 30.024*** | 209.973*** | 382.378*** | 46.725*** | 182.691*** | 145.994*** |
| Variables | Model 7 | Model 8 | Model 9 | Model 10 | Model 11 | Model 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise ownership type | -0.058*** | -0.053** | -0.022 | -0.013 | -0.037* | -0.008 |
| Sales revenue | 0.077*** | 0.093*** | 0.073*** | 0.080*** | 0.064*** | 0.071*** |
| Workforce size | 0.168*** | 0.184*** | 0.142*** | 0.179*** | 0.142*** | 0.172*** |
| R&D intensity | 0.010 | 0.022 | -0.005 | -0.002 | -0.009 | -0.011 |
| Openness | 0.168*** | 0.632*** | 0.447*** | 0.505*** | 0.121*** | 0.479*** |
| External knowledge management capability | 0.635*** | 0.532*** | ||||
| Internal knowledge management capability | 0.097*** | 0.087*** | ||||
| Explorative learning | 0.381*** | 0.225*** | ||||
| Exploitative learning | 0.363*** | 0.360*** | ||||
| R2 | 0.659 | 0.511 | 0.591 | 0.603 | 0.686 | 0.609 |
| F | 333.610*** | 180.612*** | 249.581*** | 261.593*** | 322.299*** | 230.153*** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




