Submitted:
02 September 2025
Posted:
03 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Endpoints
- analyzing feature importance derived from the best-performing ML model, and
- conducting univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards analyses to determine the statistical association between individual features and survival outcomes.
2.3. Machine Learning
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. AI-Assisted Writing Statement
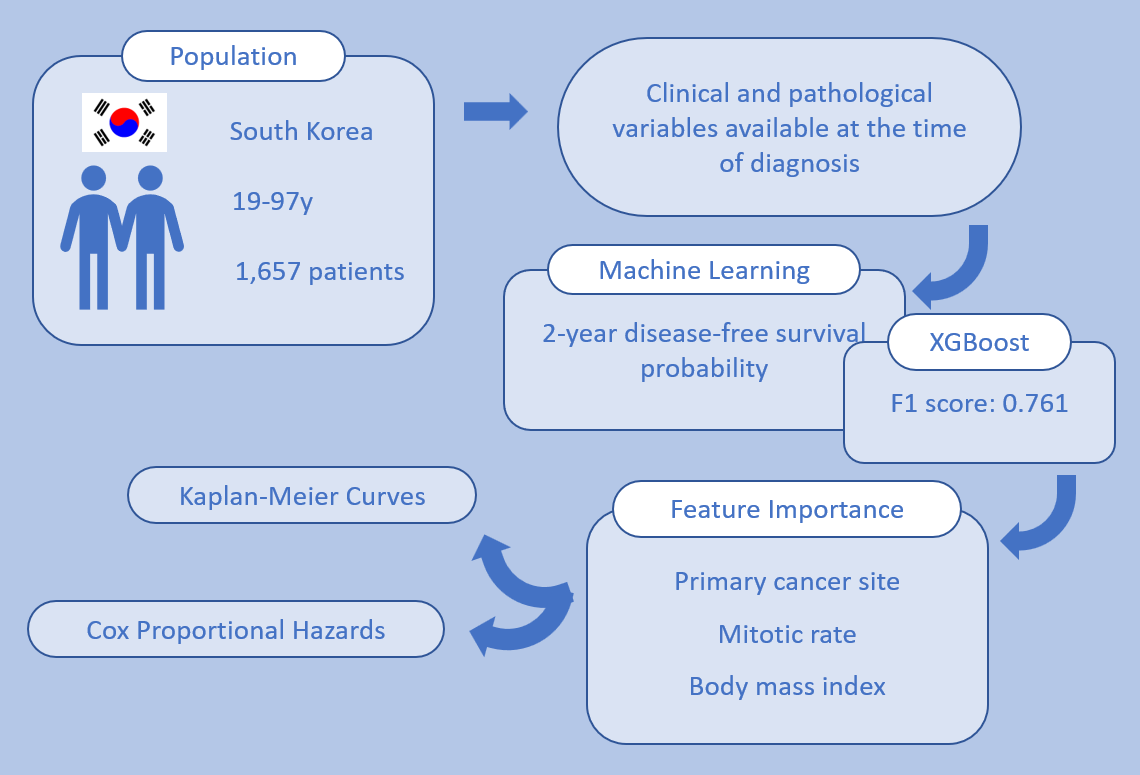
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Machine Learning Model Performance
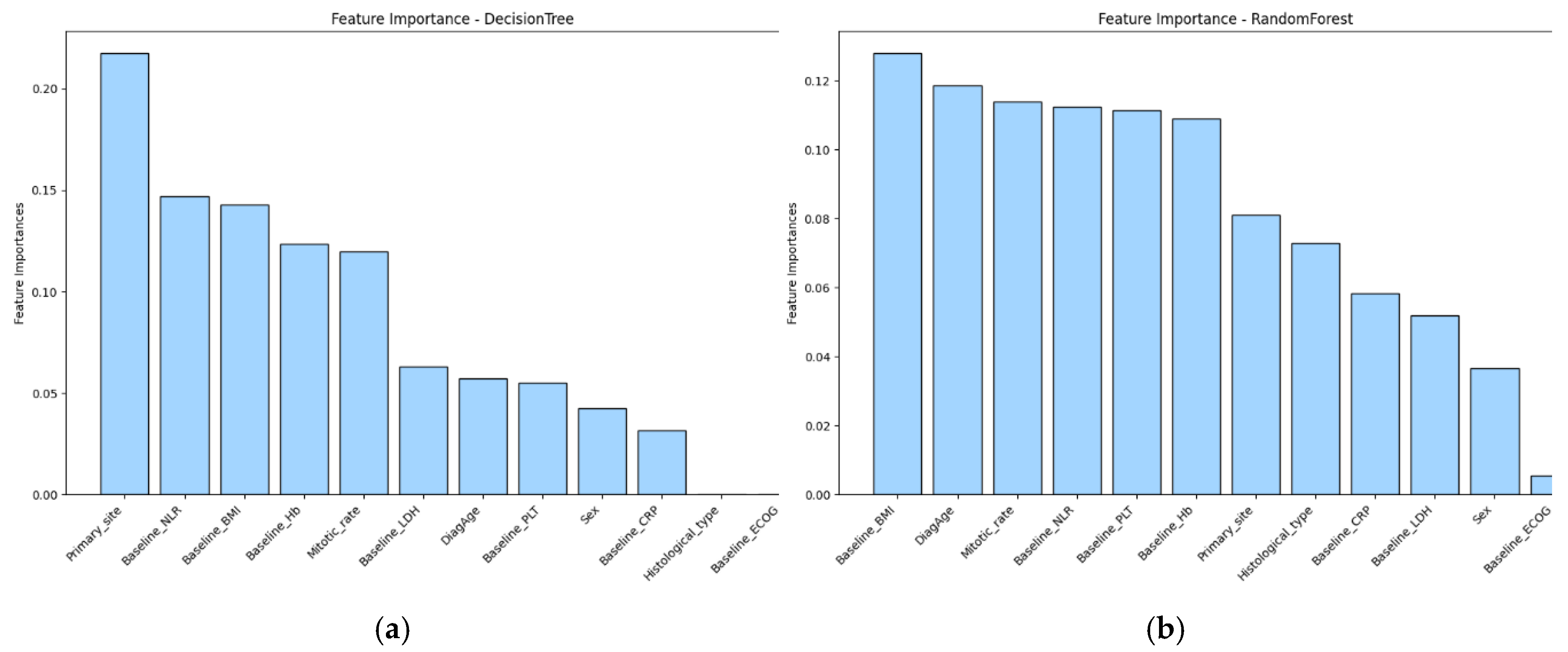
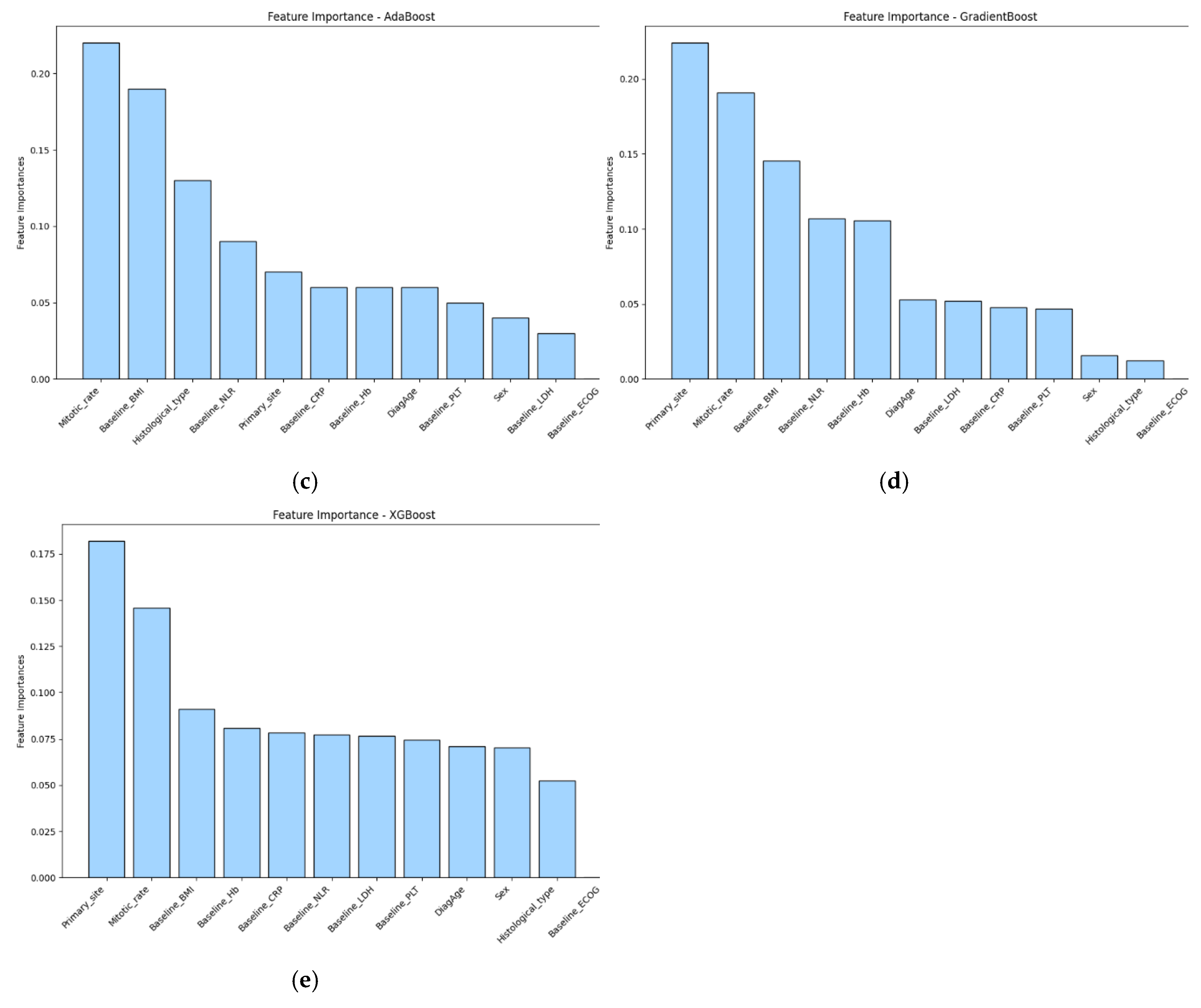
3.3. Feature Importance
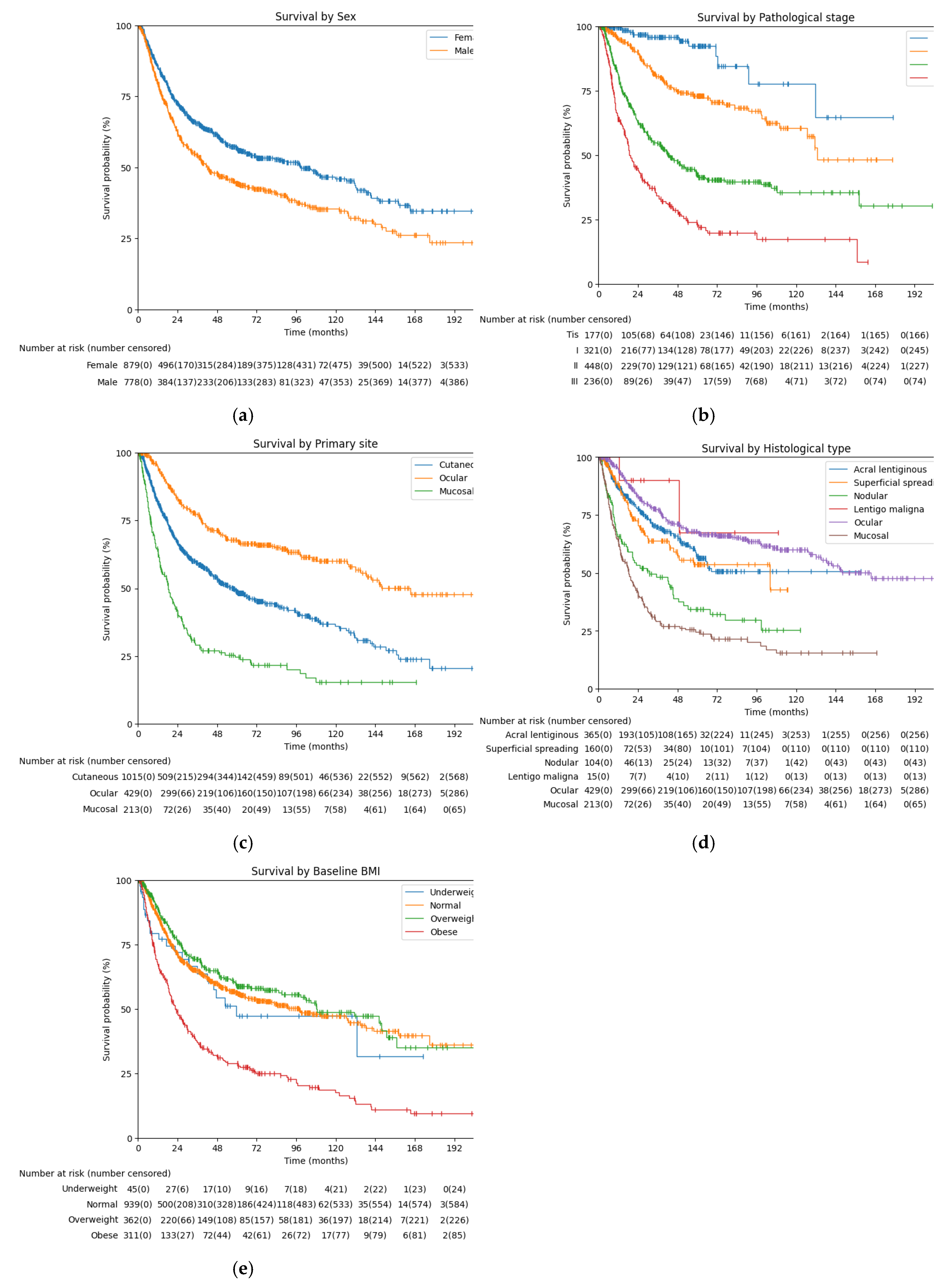
3.4. Survival Analysis Based on Key Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALM | Acral Lentiginous Melanoma |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CPH | Cox Proportional Hazards |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| DFS | Disease-Free Survival |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| EHR | Electronic Health Record |
| F1 | F1 Score (harmonic mean of precision and recall) |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PLT | Platelet Count |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanations |
| SSM | Superficial Spreading Melanoma |
| TNM | Tumor–Node–Metastasis |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J Clin 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Central Cancer Registry, Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2024.
- Gershenwald, J.E.; Scolyer, R.A.; Hess, K.R.; Sondak, V.K.; Long, G.V.; Ross, M.I.; Lazar, A.J.; Faries, M.B.; Kirkwood, J.M.; McArthur, G.A.; et al. Melanoma staging: Evidence-based changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin 2017, 67, 472–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, C.M.; Whiteman, D.C. Risk stratification for melanoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1868–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, C.M.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Soong, S.J.; Thompson, J.F.; Atkins, M.B.; Byrd, D.R.; Buzaid, A.C.; Cochran, A.J.; Coit, D.G.; Ding, S.; et al. Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and classification. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27, 6199–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yun, S.J. Cutaneous Melanoma in Asians. Chonnam Med J 2016, 52, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, P.T.; Goldstein, A.M.; McMaster, M.L.; Tucker, M.A. Acral lentiginous melanoma: incidence and survival patterns in the United States, 1986-2005. Arch Dermatol 2009, 145, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Kweon, S.S.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, S.C.; Yun, S.J. A clinicopathologic analysis of 177 acral melanomas in Koreans: relevance of spreading pattern and physical stress. JAMA Dermatol 2013, 149, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravaioli, G.M.; Dika, E.; Lambertini, M.; Chessa, M.A.; Fanti, P.A.; Patrizi, A. Acral melanoma: correlating the clinical presentation to the mutational status. G Ital Dermatol Venereol 2019, 154, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.M.; Shen, L.; Sokil, M.M.; Yeh, I.; Jorgenson, E. Prognostic factors and survival in acral lentiginous melanoma. Br J Dermatol 2017, 177, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, P.; Ayyappan, G.; Jayagopal, P.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Mallik, S.; Al-Rasheed, A.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Soufiene, B.O. Detection for melanoma skin cancer through ACCF, BPPF, and CLF techniques with machine learning approach. BMC Bioinformatics 2023, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, H.; Thiers, B.H.; Wang, J.Z. Automatic diagnosis of melanoma using machine learning methods on a spectroscopic system. BMC Med Imaging 2014, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa-Silva, O.; Pastur Romay, L.A.; Viruez Roca, R.D.; Rojas, M.; Suarez-Penaranda, J.M. Machine Learning Techniques in Predicting BRAF Mutation Status in Cutaneous Melanoma From Clinical and Histopathologic Features. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2022, 30, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibault, J.E.; Giraud, P.; Burgun, A. Big Data and machine learning in radiation oncology: State of the art and future prospects. Cancer Lett 2016, 382, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, 2016.
- DeVries, Z.; Locke, E.; Hoda, M.; Moravek, D.; Phan, K.; Stratton, A.; Kingwell, S.; Wai, E.K.; Phan, P. Using a national surgical database to predict complications following posterior lumbar surgery and comparing the area under the curve and F1-score for the assessment of prognostic capability. Spine J 2021, 21, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, J.; BenTaieb, A.; Hamarneh, G. Deep features to classify skin lesions. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 13th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI); 2016; pp. 1397–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, C.; Buja, A.; Rugge, M.; Miatton, A.; Zorzi, M.; Vecchiato, A.; Del Fiore, P.; Tropea, S.; Brazzale, A.; Damiani, G. Machine learning to predict overall short-term mortality in cutaneous melanoma. Discover Oncology 2023, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Nguyen, N.; Liu, F.; DeSimone, M.S.; Leung, B.W.; Rajeh, A.; Collier, M.R.; Choi, M.S.; Amadife, M.; Tang, K.; et al. Prediction of early-stage melanoma recurrence using clinical and histopathologic features. NPJ Precis Oncol 2022, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.M.; Lee, K.G.; Choi, W.; Cheong, S.H.; Myung, K.B.; Hahn, H.J. An updated review of mucosal melanoma: Survival meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol 2019, 11, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, K.D.; Olszewski, A.J. Epidemiology and survival outcomes of ocular and mucosal melanomas: a population-based analysis. Int J Cancer 2014, 134, 2961–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.L.Y.; Hong, J.; Goh, W.L.; Chang, E.W.Y.; Yang, V.S.; Poon, E.; Somasundaram, N.; Farid, M.; Chan, A.S.Y.; Chan, J.Y. Clinical features and survival outcomes of ocular melanoma in a multi-ethnic Asian cohort. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.M.; Jung, C.J.; Won, C.H.; Chang, S.E.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, W.J. Different progression pattern between acral and nonacral melanoma: A retrospective, comparative, clinicoprognostic study of 492 cases of primary cutaneous melanoma according to tumor site. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 2021, 87, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandala, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Galli, F.; Patuzzo, R.; De Giorgi, V.; Rulli, E.; Gianatti, A.; Valeri, B.; Merelli, B.; Szumera-Cieckiewicz, A.; et al. Acral lentiginous melanoma histotype predicts outcome in clinical stage I-II melanoma patients: an International multicenter study. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kwak, M.-J.; Yi, C.C.; Bae, Y.C. Epidemiology and prognostic factors of malignant melanoma among 200 Asian patients from a single medical center. Indian Journal of Surgery 2024, 86, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.F.; Soong, S.J.; Balch, C.M.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Ding, S.; Coit, D.G.; Flaherty, K.T.; Gimotty, P.A.; Johnson, T.; Johnson, M.M.; et al. Prognostic significance of mitotic rate in localized primary cutaneous melanoma: an analysis of patients in the multi-institutional American Joint Committee on Cancer melanoma staging database. J Clin Oncol 2011, 29, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckers, E.A.; Kruijff, S.; Bastiaannet, E.; van Ginkel, R.J.; Hoekstra-Weebers, J.E.; Hoekstra, H.J. Obesity is not associated with disease-free interval, melanoma-specific survival, or overall survival in patients with clinical stage IB-II melanoma after SLNB. Journal of surgical oncology 2021, 124, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.; Garmyn, M.; Guvenc, C. The Effect of Body Mass Index on Melanoma Biology, Immunotherapy Efficacy, and Clinical Outcomes: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shwartz-Ziv, R.; Armon, A. Tabular data: Deep learning is not all you need. Information Fusion 2022, 81, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary site | Total | Cutaneous | Ocular | Mucosal | ||||
| Histological type | Total | Acral lentiginous | Superficial spreading | Nodular | Lentigo maligna | |||
| N (%) | 1657 | 1015 (61.26) | 365 (22.03) | 160 (9.66) | 104 (6.28) | 15 (0.91) | 429 (25.89) | 213 (12.85) |
| Median age | ||||||||
| Year (range) | 59 (19-97) | 60 (19-95) | 63 (21-93) | 58 (19-87) | 58 (24-87) | 70 (42-86) | 56 (19-90) | 62 (28-97) |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 778 (46.95) | 469 (46.21) | 171 (46.85) | 70 (43.75) | 52 (50.00) | 10 (66.67) | 206 (48.02) | 103 (48.36) |
| Female | 879 (53.05) | 546 (53.79) | 194 (53.15) | 90 (56.25) | 52 (50.00) | 5 (33.33) | 223 (51.98) | 110 (51.64) |
| ECOG PS* | ||||||||
| 0 | 841 (50.75) | 575 (56.65) | 254 (69.59) | 121 (75.62) | 68 (65.38) | 12 (80.00) | 173 (40.33) | 93 (43.66) |
| 1 | 90 (5.43) | 18 (1.77) | 3 (0.82) | 2 (1.25) | 1 (0.96) | 0 (0.00) | 54 (12.59) | 18 (8.45) |
| 2 | 7 (0.42) | 4 (0.39) | 1 (0.27) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.23) | 2 (0.94) |
| 3 | 2 (0.12) | 1 (0.10) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.47) |
| Pathological stage | ||||||||
| In situ | 177 (10.68) | 174 (17.14) | 96 (26.30) | 17 (10.62) | 0 (0.00) | 6 (40.00) | 0 (0.00) | 3 (1.41) |
| I | 321 (19.37) | 242 (23.84) | 102 (27.95) | 66 (41.25) | 13 (12.50) | 6 (40.00) | 66 (15.38) | 13 (6.10) |
| II | 448 (27.04) | 274 (27.00) | 111 (30.41) | 43 (26.88) | 47 (45.19) | 1 (6.67) | 153 (35.66) | 21 (9.86) |
| III | 236 (14.24) | 177 (17.44) | 48 (13.15) | 29 (18.12) | 40 (38.46) | 0 (0.00) | 30 (6.99) | 29 (13.62) |
| Baseline BMI** | ||||||||
| Underweight | 45 (2.72) | 25 (2.46) | 6 (1.64) | 5 (3.12) | 2 (1.92) | 0 (0.00) | 15 (3.50) | 5 (2.35) |
| Normal | 939 (56.67) | 554 (54.58) | 217 (59.45) | 109 (68.12) | 50 (48.08) | 12 (80.00) | 279 (65.03) | 106 (49.77) |
| Overweight | 362 (21.85) | 209 (20.59) | 92 (25.21) | 30 (18.75) | 26 (25.00) | 2 (13.33) | 104 (24.24) | 49 (23.00) |
| Obese | 311 (18.77) | 227 (22.36) | 50 (13.70) | 16 (10.00) | 26 (25.00) | 1 (6.67) | 31 (7.23) | 53 (24.88) |
| Relapse | ||||||||
| No | 1102 (66.51) | 658 (64.83) | 270 (73.97) | 116 (72.50) | 46 (44.23) | 13 (86.67) | 334 (77.86) | 110 (51.64) |
| Yes | 555 (33.49) | 357 (35.17) | 95 (26.03) | 44 (27.50) | 58 (55.77) | 2 (13.33) | 95 (22.14) | 103 (48.36) |
| Death | ||||||||
| No | 1098 (66.26) | 689 (67.88) | 293 (80.27) | 130 (81.25) | 66 (63.46) | 14 (93.33) | 315 (73.43) | 94 (44.13) |
| Yes | 559 (33.74) | 326 (32.12) | 72 (19.73) | 30 (18.75) | 38 (36.54) | 1 (6.67) | 114 (26.57) | 119 (55.87) |
| ROC AUC* | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 score | |
| Decision tree | 0.533 | 0.507 | 0.781 | 0.328 | 0.462 |
| Random forest | 0.664 | 0.630 | 0.750 | 0.638 | 0.689 |
| Bagging | 0.629 | 0.607 | 0.693 | 0.701 | 0.697 |
| AdaBoost | 0.616 | 0.630 | 0.740 | 0.655 | 0.695 |
| GradientBoost | 0.668 | 0.681 | 0.797 | 0.678 | 0.733 |
| XGBoost | 0.652 | 0.630 | 0.652 | 0.914 | 0.761 |
| DNN** | 0.605 | 0.641 | 0.718 | 0.730 | 0.724 |
| Features | Hazards ratio (95% CI) | p-value |
| Age | 1.014 (1.008-1.019) | < 0.005 |
| Sex (reference: female) | ||
| Male | 1.419 (1.227-1.641) | < 0.005 |
| ECOG PS* | 1.104 (0.855-1.426) | 0.447 |
| Baseline Hb | 0.976 (0.921-1.034) | 0.412 |
| Baseline PLT | 1.001 (1.000-1.002) | 0.139 |
| Baseline LDH | 1.003 (1.002-1.005) | < 0.005 |
| Baseline CRP | 1.005 (1.002-1.009) | 0.005 |
| Baseline NLR | 1.173 (1.110-1.240) | < 0.005 |
| Histological type (reference: acral lentiginous) | ||
| Superficial spreading | 0.846 (0.635-1.129) | 0.256 |
| Nodular | 1.700 (1.307-2.211) | < 0.005 |
| Lentigo maligna | 0.365 (0.091-1.464) | 0.155 |
| Ocular | 0.442 (0.367-0.533) | < 0.005 |
| Mucosal | 2.564 (2.139-3.074) | < 0.005 |
| Baseline BMI (reference: normal) | ||
| Underweight | 0.993 (0.643-1.532) | 0.973 |
| Overweight | 0.694 (0.575-0.837) | < 0.005 |
| Obese | 2.323 (1.984-2.719) | < 0.005 |
| Features | Median DFS (months) (95% CI) | 2-year DFS rate (%) (95% CI) | Log-rank p-value |
| Total | 63.93 (52.93-85.33) | 67.65 (65.16-70.00) | |
| Sex | < 0.005 | ||
| Female | 98.97 (71.23-131.27) | 72.50 (69.03-75.39) | |
| Male | 42.13 (36.53-54.53) | 62.19 (58.40-65.73) | |
| Primary site | < 0.005 | ||
| Cutaneous | 57.67 (48.03-68.33) | 66.80 (63.54-69.84) | |
| Ocular | 165.23 (134.93-inf) | 82.94 (78.76-86.37) | |
| Mucosal | 18.37 (13.90-22.40) | 40.77 (33.75-47.66) | |
| Histological type | < 0.005 | ||
| Acral lentiginous | Not reached | 77.75 (72.54-82.09) | |
| Superficial spreading | 103.93 (45.47-inf) | 72.45 (61.42-77.73) | |
| Nodular | 30.70 (17.57-45.40) | 53.34 (41.61-61.71) | |
| Lentigo maligna | Not reached | 90.00 (47.30-98.53) | |
| Ocular | 165.23 (134.93-inf) | 82.94 (78.76-86.37) | |
| Mucosal | 18.37 (13.90-22.40) | 40.77 (33.75-47.66) | |
| Pathological stage | < 0.005 | ||
| In situ | Not reached | 96.82 (91.70-98.80) | |
| I | 132.80 (126.50-inf) | 89.35 (85.01-92.49) | |
| II | 43.07 (33.13-52.93) | 62.76 (57.78-67.33) | |
| III | 19.37 (17.23-24.83) | 44.60 (37.86-51.11) | |
| Baseline BMI | < 0.005 | ||
| Underweight | 59.60 (30.87-inf) | 71.98 (55.88-83.05) | |
| Normal | 97.57 (68.90-127.80) | 71.06 (67.75-74.09) | |
| Overweight | 108.70 (85.33-150.60) | 75.81 (70.68-80.17) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





