1. Introduction
Gonorrhea caused by the bacterial pathogen
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Ng), is currently the second most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) world-wide with an incidence of >600,000 cases per year in the US and ~82 million globally. Ng colonizes the mucosa of men and women but disproportionately affects the health of women resulting in reduced fertility and other complications of the upper and lower genital tract. The general increase in the incidence of disease and emergence of multi-drug-resistant strains has increased concern for the potential of untreatable gonorrhea. While there is no vaccine specifically designed to prevent gonorrhea, epidemiological studies conducted by Petousis-Harris and co-workers in New Zealand revealed that a detergent-extracted outer membrane vesicle vaccine (dOMV) produced from closely related
Neisseria meningitidis bacteria (MeNZB) had 31% efficacy in preventing gonorrhea [
1]. The MeNZB vaccine was developed by Chiron, Corp. as a tailor-made vaccine to control a meningococcal disease epidemic caused by
Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B (MenB) [
2]. The effect of MeNZB on reducing gonorrhea in New Zealand was subsequently confirmed for other MenB OMV-containing vaccines [
3,
4,
5] including the current market leading MenB vaccine, 4CMenB (Bexsero®) [
6], and led to the development of several new vaccines for Ng based on Ng OMV [
7,
8,
9]. However, a recent Phase 2 clinical trial of an Ng OMV vaccine produced by Galaxo Smith Kline (GSK) failed to meet pre-defined efficacy criteria and it is unclear whether the vaccine will continue to be developed by the company [
10].
Currently there are two MenB vaccines licensed in the U.S, 4CMenB and MenB-FHbp (Trumenba®). Both MenB vaccines, however, provide incomplete meningococcal strain coverage, and elicit protection of relatively short duration [
11,
12]. In particular, 4CMenB was predicted to not provide protection against strains causing outbreaks in countries where it is used for routine vaccination of infants such as the UK, France, Spain, and Canada. Recently, MenB vaccine strain coverage in these countries was reported to be as little as 5.3% against emerging clonal complexes based on prediction by the genetic Meningococcal Antigen Typing System [
13].
Recognizing the limitations of current MenB vaccines, OMVax has developed a next generation MenB vaccine based on native outer membrane vesicles (NOMV) with over-expressed mutant Factor H binding proteins (FHbp) from subfamilies A and B with reduced Factor H binding [
14,
15]. In addition, the NOMV were made safer by eliminating sialic acid antigens that mimic host antigens and by deleting the acyl transferase LpxL1 resulting in penta-acyl lipooligosaccharide (LOS), which has reduced endotoxin activity [
7]. This latter modification eliminates the need for detergent extraction, which can remove important lipoprotein antigens such as FHbp from OMV and alter the structure of membrane protein epitopes that elicit protective antibodies [
7].
Recent studies have shown that antibodies elicited by 4CMenB that are reactive with diverse Ng strains are directed to the MenB porin protein, PorB, and lipooligosaccharide (LOS) [
16]. Since MenB OMV have been shown to have 30%-40% efficacy against Ng in fully vaccinated adults, OMVax considered whether protection against Ng by MenB OMV could be increased by also including an NOMV component produced from Ng strains that express porin proteins that are representative of each of the two sub-families of gonococcal porins, PorB.1a and PorB.1b (Ng NOMV). We show here that a combination MenB NOMV vaccine component (Nm NOMV) with overexpressed mutant FHbp from subfamilies A and B provide broader coverage and higher serum bactericidal activity (SBA) against MenB than existing MenB vaccines and, when combined with Ng NOMV components (Nm-Ng NOMV) elicit antibodies having broad SBA against MenB and Ng strains, inhibit colonization of Ng to human cervical and vaginal cell lines and in a transgenic mouse model of gonorrhea. Further, a combined MenB-Ng vaccine that protects against both pathogens may have greater acceptance than a stand-alone Ng vaccine since MenB vaccines are routinely administered to control meningococcal disease in schools, colleges, universities and the military in adolescents and young adults who have a higher risk of acquiring new Ng infections compared to other age groups [
17].
2. Materials and Methods
The MenB vaccine component was comprised of NOMV naturally blebbed from two mutant strains of
N. meningitidis. Each strain was derived from an H44/76 parent strain. Each strain has deletions of the wild-type
fhbp,
lpxL1, and
siaD-galE genes by insertion of DNA containing mutant
fhbp genes (Subfamily A containing three amino acid substitutions, or Subfamily B containing a single amino acid substitution), along with an engineered promoter, and drug resistance markers (erythromycin, kanamycin and spectinomycin, respectively). The Subfamily A and Subfamily B mutants of Factor H binding protein (FHbp) have reduced human Factor H (FH) binding [
14,
15]. Deletion of
lpxL1 results in penta-acylated lipooligosaccharide (LOS), which has attenuated endotoxin activity, compared with the wildtype hexa-acylated LOS [
18]. Interruption of the
siaD and
galE genes eliminates expression of the group B capsular polysaccharide and LOS derivatives, which may elicit antibodies cross-reactive with human tissues [
19,
20]. To enhance FHbp expression further, each strain also carries a modified version of a multi-copy plasmid containing a chloramphenicol resistance gene [
21] and coding for the respective mutant FHbp driven by the engineered promoter. Both
N. gonorrhoeae strains had LpxL1 and reduction modifiable protein knocked out.
NOMV were purified from culture supernatant of bacteria grown in chemically defined media, for
N. meningitidis, or GCLB [
22], for
N. gonorrhoeae with supplements that enable the bacteria to grow to high density. After reaching stationary phase, bacteria were harvested by centrifugation. The culture supernatant was filter sterilized using 0.2 µm filters and concentrated using 100 KDa filters (ThermoFisher Scientific). NOMV were collected by ultracentrifugation and further purified by size exclusion chromatography (ToyoPearl HW-55F; Sigma-Aldrich). Total protein concentration was measured by BCA (Pierce). The combination vaccine contained a 1:1 mixture of NOMV from
N. meningitidis and
N. gonorrhoeae. The combination vaccine referred to as Nm-Ng NOMV was combined with aluminum hydroxide adjuvant (Alhydrogel
® 2%, from Croda).
Five to six week old CD-1 mice were immunized I.P. on days 0, and 21 with Nm NOMV at 5 µg/dose, Ng NOMV at 5 µg/Dose, and Nm-Ng NOMV at 10 µg/dose, all adjuvanted with 50 µg/dose of Al(OH)3. Adjuvant alone was given at 50 µg/dose as negative control. Blood was collected by terminal cardiac puncture on day 35. Human CEACAM-1 and FH transgenic FVB-BALB/c hybrid mice were immunized I.P. on days 0, 21 and 42 with Ng NOMV at 5 µ/dose, and Nm-Ng NOMV at 10 µg/dose, both adjuvanted with 50 µg/Dose of Al(OH)3. Bexsero® was administered at 1/5 of the human dose. Blood was collected by terminal cardiac puncture on day 56.
Binding of the post immunization mouse sera to wild-type rFHbps and purified NOMV was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The wells of a microtiter plate (Immulon 2B; ThermoFisher Scientific) were coated with 2 µg/ml of rFHbp or NOMV in PBS and incubated overnight at 4°C. The plates were blocked with PBS containing 0.1% Tween-20 (Sigma) (PBST) and 1% (weight/volume) bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma). Concentration-dependent binding of the anti-FHbp and anti-NOMV Abs was measured at 1:100 to 1:200,000 dilution in PBST-BSA. After incubation (2 h at room temperature), the plates were washed and rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG)-alkaline phosphatase (Zymed; 1:5,000 diluted in PBST/BSA) was added. After 1 h at room temperature, alkaline phosphatase substrate (Sigma) was added, and the absorbance at 405 nm was measured after 30 min. ELISA titers were defined as the serum dilution giving an OD405nm of 1.
For serum bactericidal activity (SBA) assay, bacteria were grown to early log phase in liquid Frantz medium supplemented with 4 mM d,l-lactate (Sigma-Aldrich) and 2 mM cytidine 5′-monophospho-
N-acetylneuraminic acid (CMP-NANA; Carbosynth) to enhance the sialylation of lipooligosaccharide [
23]. Test sera were heated for 30 min at 56°C to inactivate endogenous complement. The 40-μl reaction mixture used to measure bactericidal activity contained 2-fold serial dilutions of the test serum sample, 300 to 400 CFU of bacteria, and 30% IgG-IgM depleted human complement (Pel-Freez Biologicals). The SBA titer was the interpolated dilution resulting in 50% survival of the bacteria after 60 minutes incubation at 37 °C and 5% CO
2 compared to the number of CFU per milliliter in negative-control sera and complement.
For Ng SBA assay, bacterial cultures were prepared the day prior to testing by streaking frozen stocks onto Chocolate II Agar (GC II Agar with Hemoglobin and IsoVitaleX™, Fisher Scientific) and re-passaged onto fresh Chocolate II Agar supplemented with CMP-NANA (50 µg/ml) on the day of assay. After 6 h at 37 °C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2, bacteria were then suspended in HBSS containing 1 mM MgCl2 and 0.15 mM CaCl2 and 2% BSA. Test sera were heated for 30 min at 56°C to inactivate endogenous complement. The 75-μl reaction mixture used to measure bactericidal activity contained 2-fold serial dilutions of the test serum sample, 800 to 1000 CFU of bacteria, and 20% (volume/volume) IgG-IgM depleted human complement (Pel-Freez Biologicals). The SBA titer was the interpolated dilution resulting in 50% survival of the bacteria after 60 minutes incubation at 37 °C and 5% CO2 compared to the number of CFU per milliliter in negative-control sera and complement.
IgG from postimmunization serum pools from mice immunized with each vaccine and adjuvant control were purified using Protein G HP SpinTrap columns (Cytiva Lifesciences). The concentrations of the purified mouse serum IgG were determined by a capture ELISA in which a goat anti-mouse κ chain specific antibody (Biosource) was adsorbed to the wells of a microtiter plate and used to capture the Abs. The bound Abs were detected with goat anti-mouse κ chain specific antibody conjugated with alkaline phosphatase (Biosource). The concentrations of the mouse IgG Abs were assigned by comparison with binding of a purified mouse IgG standard (BioRad).
For colonization assays, bacterial cultures were prepared the day prior to testing by streaking frozen stocks onto Chocolate II Agar (GC II Agar with Hemoglobin and IsoVitaleX™, Fisher Scientific). Bacteria were then suspended in PBS to an OD620nm of 0.3 and 10 µM CellTrace™ CFSE Cell Proliferation dye (Invitrogen) was added to the solution. The labeling reaction was stopped after 30 minutes with fetal bovie serum (FBS), and free label removed with two washes. Labeled bacteria were spun down and respuspended in PBS supplemented with CMP-NANA (50 µg/ml) to an OD620nm of 0.3. Bacteria were further diluted in cell culture media to reach ∼1 × 105 CFU/mL. For the adherence assays, monolayers of human cervical (ME-180, ATCC #HTP-33) and vaginal epithelial (VK2/E6E7, ATCC #CRL-2616) cells were incubated at 37 °C, 5 % CO2 for four hours with ∼1 × 105 CFU sialylated N. gonorrhoeae strains that had been pre-incubated with 25 µg/ml purified mouse IgG for 15 min in cell culture media. Following infection, cells were washed three times with PBS to remove non-adherent bacteria, the cells were detached using Gibco™ StemPro™ Accutase™, and transferred to microcentrifuge tubes. Cells were washed twice with PBS and fixed with 4% Paraformaldehyde. Labeled adherent bacteria were quantitated using ImageStreamX (Cytek Biosciences). Data are presented as percentage of inhibition of adherent bacteria relative to adjuvant only antibody control.
Transgenic mice were screened for the human CEACAM1 gene and human FH protein expression as described elsewhere [
24]. MenB strain 8047 and Ng strain WHO F were grown as described as for the SBA assay protocol above. After reaching an OD
620nm of 0.6 for Nm and after being resuspended to an OD of 0.3 for Ng, bacteria were diluted to get to the targeted inoculum of 10
3 CFU/animal for 8047, and 10
7 CFU/animal for WHO F. Immediately after the challenge, a sample of the bacteria preparation was plated on an agar plate to confirm the inoculum. Mice were challenged intranasally and euthanized after 48 hours for Nm challenge and 72 hours for Ng challenge. Tracheal wash and tissue samples were collected for each animal and plated on GC agar plates (REF) supplemented with IsoVitalex and VCNT inhibitor. Colonies were visible after 16-24 hours incubation at 37˚C with 5% CO
2. The tracheal wash was performed using an insulin syringe filled with 500µL of PBS, 1 mM Mg buffer inserted into the trachea, and the wash was collected from the nares into a 1.5mL microtube. To obtain bacteria adhering to the nasal pharynx mucosal surfaces, the lower jaw of the mouse was removed. The soft palette was collected into a tube filled with 500µL of 0.05% trypsin-EDTA or Accutase™ (ThermoFisher Scientific). The hard palette and nasal passages were swabbed with an ultrafine aluminum shaft applicator with a calcium alginate fiber tip (Puritan), which was resuspended into the tube with soft palette tissue sample. The soft palette and fiber tip were incubated at 37°C for 10 minutes before plating the entire solution on a chocolate agar plate. The tracheal wash was plated on a separate plate. CFU were counted the following day after overnight incubation at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO
2. Statistical comparison between the results for mice given adjuvant only with mice immunized with the Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine was performed using a Welch’s two tailed t test with Prism (GraphPad).
3. Results
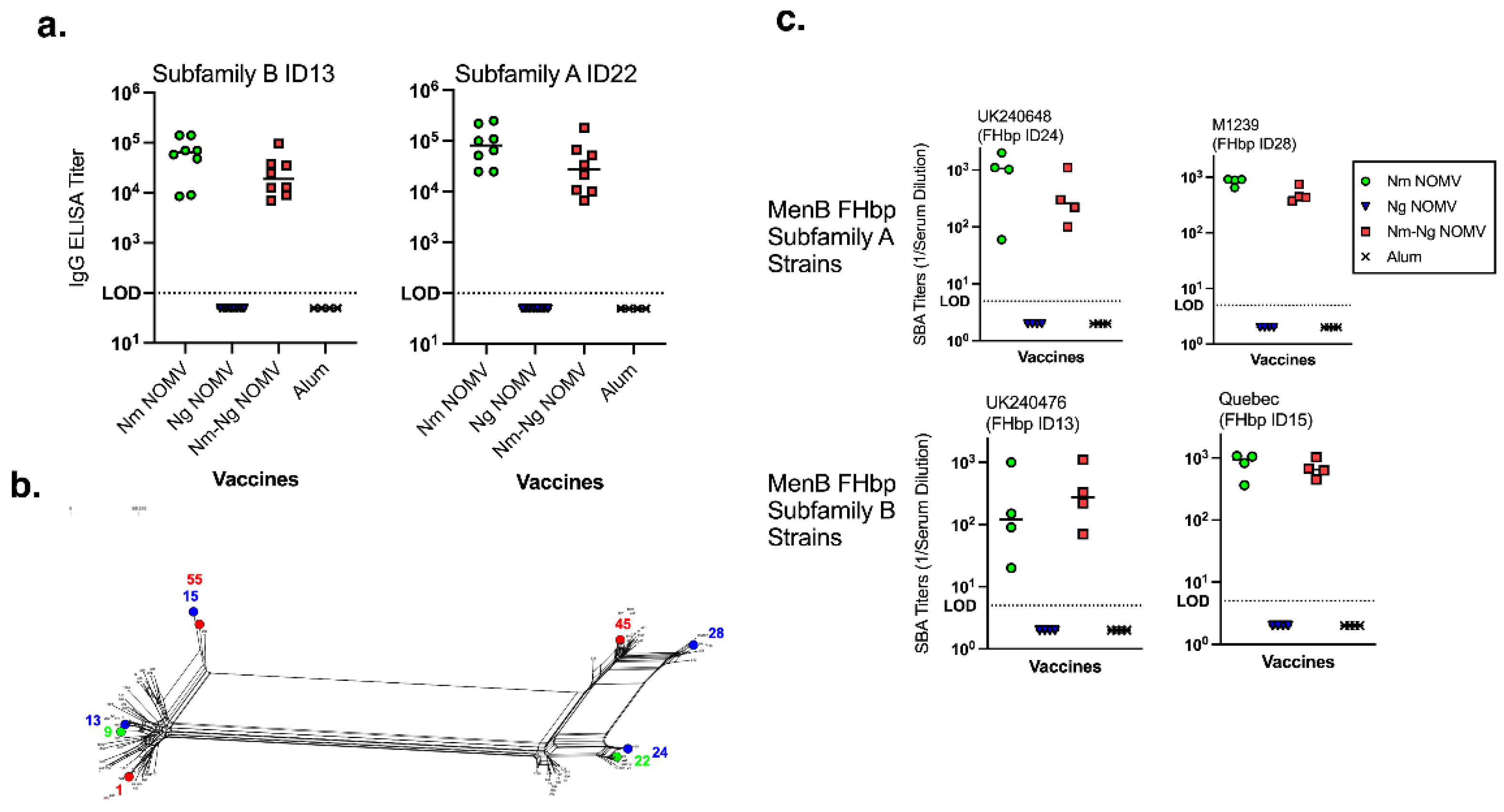
The IgG anti-FHbp titers of all CD1 WT mice before vaccination were below the lowest serum dilution tested (<1:100). At two weeks after dose 2, the IgG titers remained below 1:100 in the adjuvant negative-control group and Ng NOMV vaccine group. IgG titers increased in both vaccine groups (
Figure 1a) where the Nm NOMV component was present (alone and in combination with the Ng NOMV vaccine). The anti-FHbp IgG titers elicited by the Nm-Ng NOMV combination were not significantly reduced compared to Nm NOMV alone. To test the breadth of SBA activity, MenB strains were chosen to represent both close (FHbp IDs 13 and 24) and distant (ID15 and ID28) homology to the FHbp antigens present in the vaccines (
Figure 1b) for FHbp subfamilies B and A, respectively. The SBA titers using IgG/IgM-depleted human complement are shown in
Figure 1c. There was no significant difference between titers elicited by the combination Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine or Nm NOMV alone. The Ng NOMV component and adjuvant alone antisera had no SBA against the four MenB test strains.
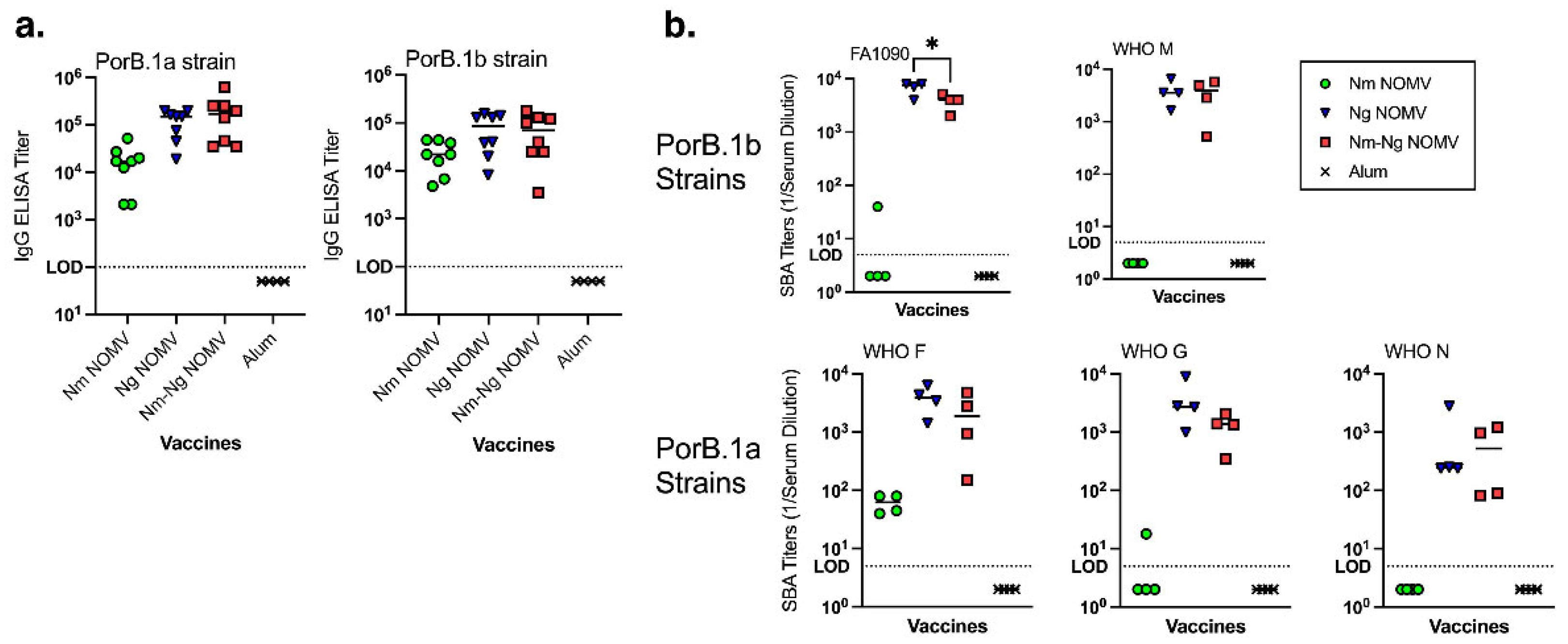
The IgG titers against NOMV from two Ng strains, WHO M (PorB.1a) and WHO N (PorB.1b) that are heterologous to the vaccine NOMV are shown in
Figure 2a. The titers of mice given Ng NOMV alone or in combination are approximately 10-fold higher than for mice given the Nm NOMV vaccine only and there was no significant difference between the titers of mice immunized with Ng NOMV or the Nm-Ng NOMV combination vaccine.
The Nm NOMV antisera had little or no SBA against the Ng test strains. Ng NOMV and Nm-Ng NOMV antisera had high SBA titers against strains expressing PorB.1a and PorB.1b. The difference in Ng NOMV SBA titers were not significantly different from those of the Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine except for Ng strain FA1090, which is homologous to the strains used to prepare the Ng NOMV component. PorB.1b and PorB.1a in the strains used to prepare the NOMV vaccine were heterologous to PorB in WHO M, WHO G and WHO N.
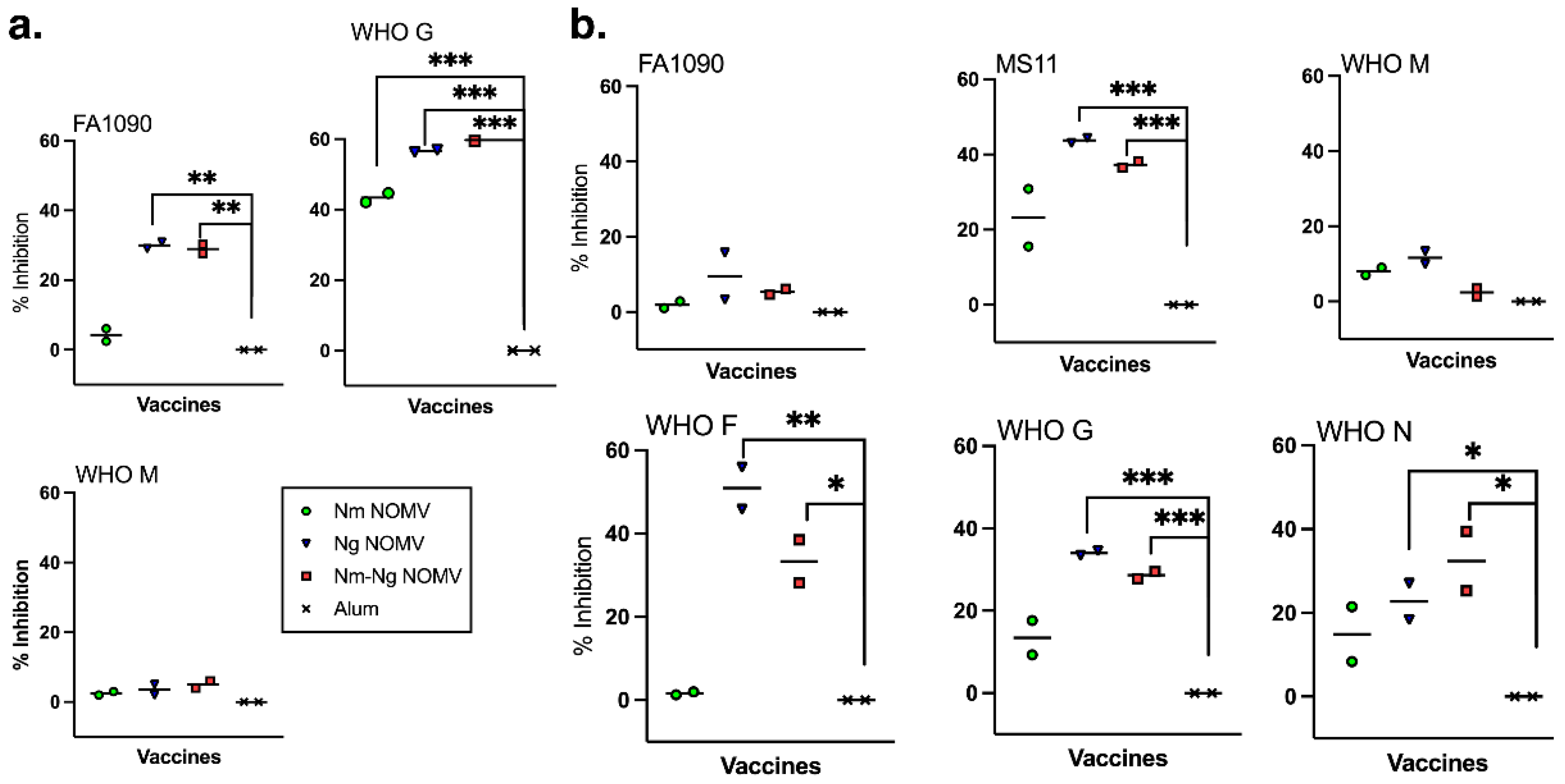
Currently, there is no in vitro correlate of protection against Ng infection. However, for N. gonorrhoeae to cause an infection, it must adhere to mucosal epithelium. Therefore, we investigated whether purified IgG antibodies from mice immunized with the NOMV vaccines was able to inhibit adherence to VK2/E6E7 vaginal and ME-180 cervical epithelial cells using sialylated, fluorescently labeled bacteria from Ng strains expressing PorB.1a (WHO F, WHO G, WHO M) and PorB.1b (FA1090, MS11, and WHO M). The data were obtained and analyzed using an ImageStreamX Mark II flow cytometer that combines flow cytometry with fluorescence microscopy to identify and count individual cells with adherent bacteria. Purified IgG from mice immunized with Nm NOMV had significant inhibition activity against WHO G to VK2/E6E7 vaginal cells compared to the adjuvant only control but not any other Ng strain or any strain to ME-180 cervical cells (
Figure 3a,b). In contrast, IgG from mice immunized with Ng NOMV and the combination Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine inhibited adherence of all Ng strains to both cell lines except for WHO M on VK2/E6E7 cells and to FA1090 and WHO M on ME-180 cells (
Figure 3a,b). The differences in inhibitory activity between purified IgG from Ng NOMV and Nm-Ng NOMV-immunized mice was not significant.
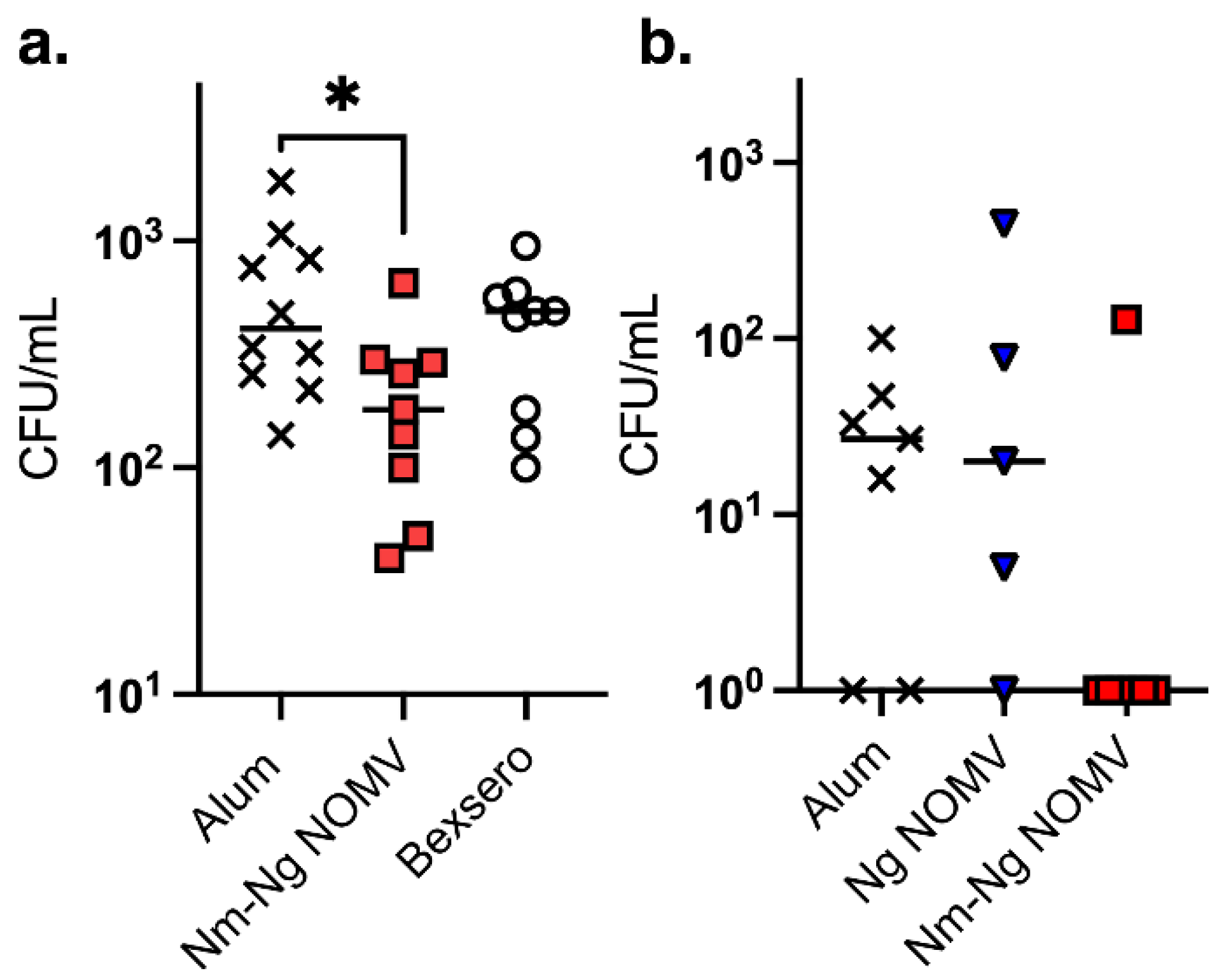
Ng is a human restricted pathogen. Although a wild-type mouse Ng challenge model is commonly used to test whether vaccine elicited antibodies can inhibit vaginal colonization by Ng strains, the wild-type mice used lack human-specific receptors and immune shielding mechanisms and, therefore, do not replicate Ng colonization of human mucosal tissues. To determine whether mice immunized with NOMV vaccines can inhibit colonization in an animal model, we constructed a transgenic (Tg) mouse line that expresses human CEACAM1 for adhesion through Opa proteins and Factor H to provide immune shielding. The human CEACAM1/FH Tg mice were challenged intranasally with MenB strain 8047 or Ng strain WHO F after immunization with two doses of each NOMV vaccine or adjuvant only. The Nm 8047 strain was heterologous to the strains used to prepare the NOMV used in the vaccines. For MenB colonization, an additional control included 4CMenB, which provides protection against MenB disease but does not appear to affect colonization in humans [
25]. As shown in
Figure 4, mice given NOMV-NmNg vaccine inhibited colonization of MenB strain 8047 that was significant compared to the adjuvant only control but not to 4CMenB. Also, Tg mice immunized with NOMV-NmNg inhibited colonization of WHO F compared to mice immunized with adjuvant or NOMV-Ng (p>0.0001).
4. Discussion
To date, the only vaccines shown to have efficacy in preventing gonorrhea are vaccines containing vesicles isolated from the closely related bacterial species
Neisseria meningitidis. Building upon this data, we constructed a novel vaccine, Nm-Ng NOMV, that combines a next generation NOMV MenB vaccine with NOMV produced from Ng strains that express PorB.1a and PorB.1b. We focused on PorB for both Nm and Ng strains since PorB is a major component of OMV from both Nm and Ng. Further support for this approach comes from a recent study of human monoclonal antibodies produced from subjects vaccinated with 4CMenB that were reactive with Nm and Ng PorB epitopes as well as LOS [
16]. The anti-PorB antibodies had SBA against Ng strains and provided cross-protection in a wild-type mouse vaginal challenge model of gonococcal infection. The PorB amino acid sequence from the production strain for Nm NOMV is identical to PorB in the OMV component of 4CMenB. The two Ng strains used for production of NOMV were chosen based on PorB.1a and PorB.1b sequences where the surface exposed variable loops were among the most common for Ng isolates of each PorB subfamily circulating world-wide [
26].
OMVax’s Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine elicited antibodies that had SBA against diverse Ng strains. In our SBA assay, the bacteria were grown in the presence of CMP-NANA, which is scavenged from the human host and used by the bacteria to sialylate LOS. Sialylation of LOS results in bacteria that are considerably more resistant to SBA than strains grown without CMP-NANA [
27]. SBA assays were performed using IgG/IgM-depleted human complement, which more closely replicates SBA activity in humans compared to SBA done with non-human complement [
28]. SBA activity confirms that Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine elicits antibodies that recognize antigens on the bacterial surface of the strains tested that are present in amounts sufficient for robust SBA activity. SBA has not been established as a surrogate of protection against disease but is likely to be important in preventing gonorrhea.
Nm and Ng are obligate human pathogens that use mechanisms for attachment (CEACAMs, CD46), invasion [
29], and immune shielding (FH [
30], TspB [
31], Opa
CEA [
32]) that specifically interact with human receptors. Antibodies elicited by vaccines (e.g., IgA and IgG) are present in secretions enveloping epithelial cells that are in direct contact with Nm and Ng during the earliest stages of infection and can prevent colonization and invasion [
33]. Antibodies that interfere with the mechanisms of colonization protect the host during the initial stages of infection from more advanced stages of disease and potentially limit transmission between vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals (i.e., community immunity). The most cost effective and widely used vaccines provide both individual and community protection.
Purified IgG from mice immunized with Ng NOMV or Nm-Ng NOMV were able to inhibit adherence of 5 out of 6 Ng strains to human vaginal and/or cervical cell lines. Interestingly, antibodies elicited by both vaccines inhibited adherence of Ng strain FA1090 to vaginal cells but not cervical cells and did not inhibit adherence of Ng strain WHO M to either cell line even though both vaccines produced high titers of bactericidal antibodies against WHO M (
Figure 3a,b). Inhibiting adherence is also likely important for protection, but adherence mediated by bacterial Opa protein binding to host CEACAM receptors is complicated by expression of different CEACAMs (e.g., CEACAM1 in cervical tissues and CEACAM5 in vaginal tissues) and expression of different Opa proteins by the bacteria, which also vary depending on environmental factors [
34]. Although we did not quantitate antibodies to Opa proteins elicited by Ng NOMV or Nm-Ng NOMV, it is possible that presence of multiple Opa proteins in the mixture of NOMVs may be important for eliciting antibodies that can inhibit adherence by diverse strains in the vaginal and cervical cell culture models of Ng adherence.
To evaluate ability to inhibit Ng colonization in a live animal, we used a transgenic mouse model of Ng colonization that replicates some aspects of pathogenesis in humans in expressing human CEACAM1, a receptor specific for Opa proteins expressed by Nm and Ng that mediates adhesion, and human FH to provide immune protection. The mice were challenged intranasally, which enabled testing both male and female mice. Although the results were not statistically significant in this under powered preliminary experiment, 6 of 7 mice vaccinated with Nm-Ng NOMV and challenged intranasally with Ng strain WHO F had no colonizing bacteria compared to only 2 of 7 mice given adjuvant alone or 1 of 6 given Ng NOMV alone (
Figure 4). The trend suggests the combination vaccine that included the MenB NOMV component provided superior protection compared to the Ng NOMV component alone and are consistent with the results of the epidemiological studies showing vaccines with a MenB OMV provide some protection against gonorrhea in humans [
1,
3,
4,
5,
6].
Although there are two MenB vaccines approved for use in humans in multiple countries, neither 4CMenB or MenB-FHbp is broadly protective or able to protect against disease caused by an increasing number of strains currently causing outbreaks in several European countries and Canada [
11,
12,
13]. The situation calls for development of a next generation MenB vaccine that can provide broader coverage. The Nm NOMV component of Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine, contains mutant FHbps from subfamilies A and B with reduced FH binding overexpressed in NOMV such that epitope structure and native environment is preserved. As a result, the FHbp antigens elicit high titers of antibodies that bind to FHbp and mediate complement-dependent bactericidal activity but can also block FH binding, which further enhances SBA [
35]. SBA is a surrogate of protection in humans against meningococcal disease [
36]. As shown in
Figure 1c, the ability of Nm NOMV to elicit antibodies with broad SBA activity was not diminished by combining with Ng NOMV in the Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine. Similarly, Nm-Ng NOMV elicited antibodies with high SBA titers against diverse Ng strains compared to Ng NOMV alone (
Figure 2) and inhibited colonization of a heterologous MenB strain in a mouse model of meningococcal disease (
Figure 4a).
Finally, a combination MenB-Ng vaccine may be advantageous with respect to acceptance and potential to control the spread of gonorrhea. Adolescents and young adults are commonly vaccinated for protection against MenB and this age group is also of greatest risk of acquiring new gonorrhea infections [
17]. The Nm-Ng NOMV vaccine has the potential to address both problems since a vaccine with potential to prevent life-threatening meningococcal disease and gonorrhea in a population of sexually active subjects at highest risk of Ng infections may be more acceptable to the public than a vaccine specifically for prevention of a sexually transmitted infection.