Submitted:
25 August 2025
Posted:
28 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Ref. | Contribution | Pros | Cons | |
| (dos Santos Ferreira et al., 2016) | Investigated the influence of control systems and configuration management practices on scope development effectiveness using a system-based analytical approach. | Provides valuable insights into critical elements affecting effective scope development through control systems and configuration management. | Focused on scope development practices within a specific organizational or project context, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other settings. | |
| (Bou Ghantous et al., 2017) | Studied the role of control systems and configuration management in enhancing the adaptability of scope development processes, with a focus on improving project outcomes and strategic alignment. | Improved scope stability, enhanced project risk control. | Requires ongoing tracking of configuration changes and control system performance to ensure scope alignment. | |
| (Afram et al., 2014) | Investigated control system and configuration management methodologies in scope development to enhance project efficiency and support informed decision-making. | Enhanced scope control and configuration management through cost-effective system solutions. | May lead in configuration complexity and scope creep without effective control mechanisms. | |
| (Lueg et al., 2016) | Investigated control systems and configuration management as strategic tools to manage scope development challenges in complex and competitive project environments. | Strategic project alignment and facilitates scope evaluation against industry benchmarks. | High dependency on accurate and consistent documentation of scope changes and configuration updates. | |
| (Whyte et al., 2016) | Explored a systematic review how control systems and configuration management improve scope development by promoting consistency, traceability, and project alignment. | Improved scope definition accuracy, cost-efficient for project-based organizations. | Requires technical expertise not always available in project teams. | |
| (Zhang et al., 2014) | Examined how control systems and configuration management practices can strengthen scope development processes to support long-term project success and alignment with strategic objectives. | Better scope accuracy and tailored configuration control. | Can lead to increased costs due to extensive documentation and configuration management requirements. | |
| (Shafiee et al., 2018) | Proposed an integrated framework combining control systems and configuration management to enhance scope development adaptability and project responsiveness. | Adaptive scope management strategies, enhanced project responsiveness. | Complex control and configuration models may overwhelm smaller project teams. | |
| (Palma et al. 2019) | Examined the effectiveness of control systems and configuration management in driving successful scope development, with a focus on supporting project innovation and delivery. | Drives project innovation, supports effective scope development strategies. | Potential privacy and compliance risks concern with improper handling of configuration and scope documentation. | |
| (Marnada et al., 2022) | Provided a comparative study of projects utilizing structured control systems and configuration management versus traditional scope practices to improve project outcomes and efficiency. | Clear benefits in scope clarity, real-time insights. | Adoption barriers in projects with limited technical infrastructure. | |
| Analyzes the role of control systems and configuration management in the process of scope development, outlining their structure, function, and integration within project management frameworks. | Provides a comprehensive understanding of factors influencing control system and configuration management adoption in scope development. Identifies critical gaps in current research. | Limited focus on particular project types or organizational contexts, limiting broader applicability across industries and regions. | ||
1.1. Research Questions
1.3. Rationale
1.4. Objectives
1.5. Research Questions
- What are the key challenges that are faced during integration of control systems and configuration management? How can they be reduced?
- How does the integration of control systems and configuration management negatively impact the performance of the project?
- What are the main factors that positively influence the integration of control systems and configuration management in scope management to be successful?
- Which important role do innovative technologies play in facilitating the integration of control systems and configuration management?
- What trends have been observed in the integration of control system and configuration management?
1.6. Research Contributions
- It delivers an in-depth evaluation of integration practices, identifying best practices for risk mitigation and performance improvement, while emphasizing the strategic advantages of adopting integrated approaches in project settings.
- It synthesizes prior scholarship on control systems and configuration management, pinpointing gaps related to the effective implementation of these systems across diverse project environments. Addressing these gaps clarifies where further research and innovation are needed, advancing knowledge and strengthening competitiveness in scope management.
- It develops regression-based models to explain the relationships between integrated control systems and configuration management practices, offering a methodological contribution to both academic research and practical application.
1.7. Research Novelty
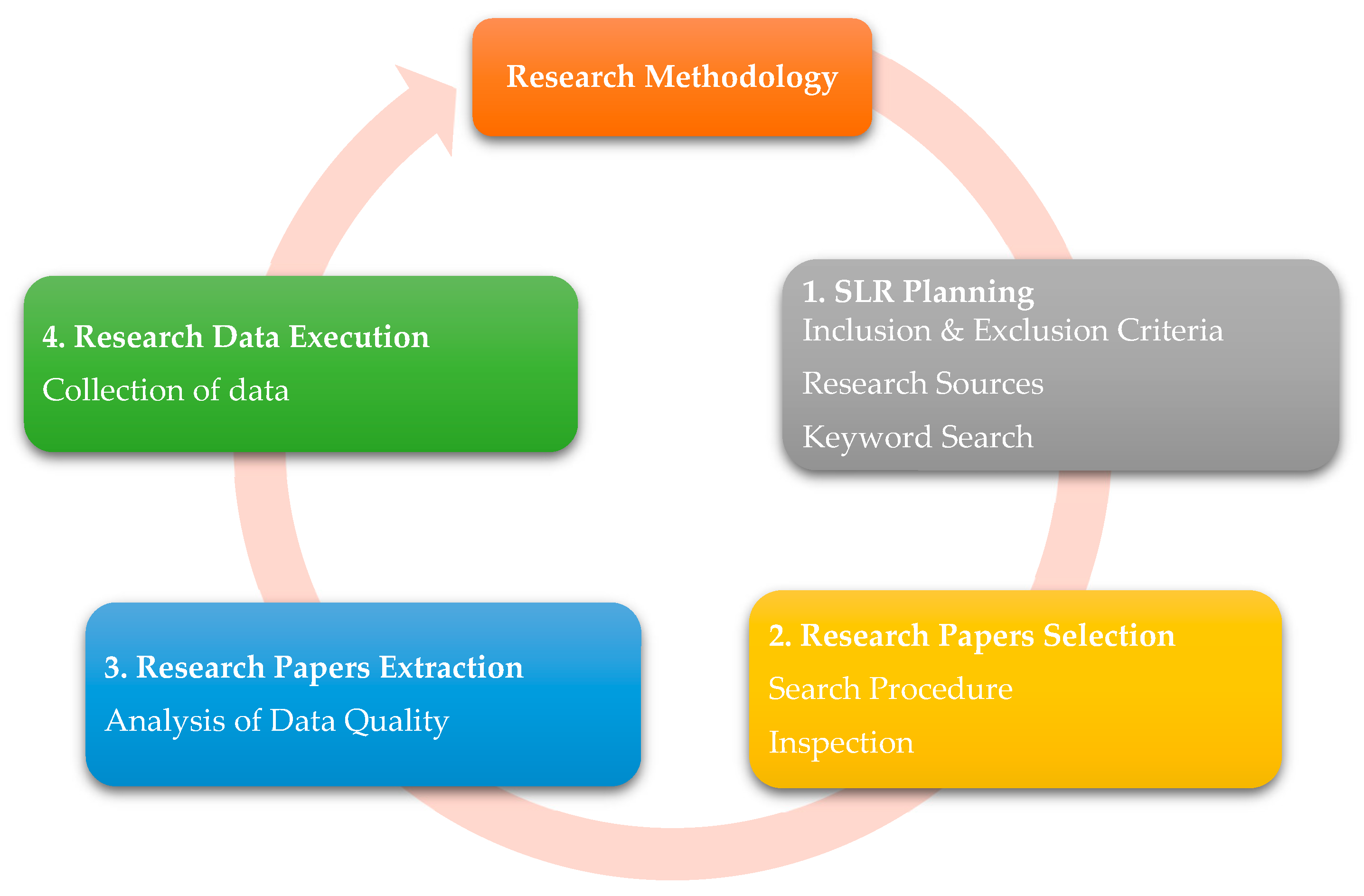
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
| Topic | Article papers focusing on control system and configuration management in scope development. | Article papers not focusing on control system and configuration management in scope development. |
| Research Framework | The Articles must include research framework or methodology for control system and configuration management in scope development. | Articles must exclude research framework or methodology for control system and configuration management in scope development. |
| Language | Must be written in English | Articles published in languages other than English |
| Period | Articles between 2014 to 2025 | Articles outside 2014 and 2025 |
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
| No. | Online Repository | Number of results |
| 1 | Google Scholar | 86 |
| 2 | Web of Science | 145 |
| 3 | Scopus | 36 |
| Total | 267 |
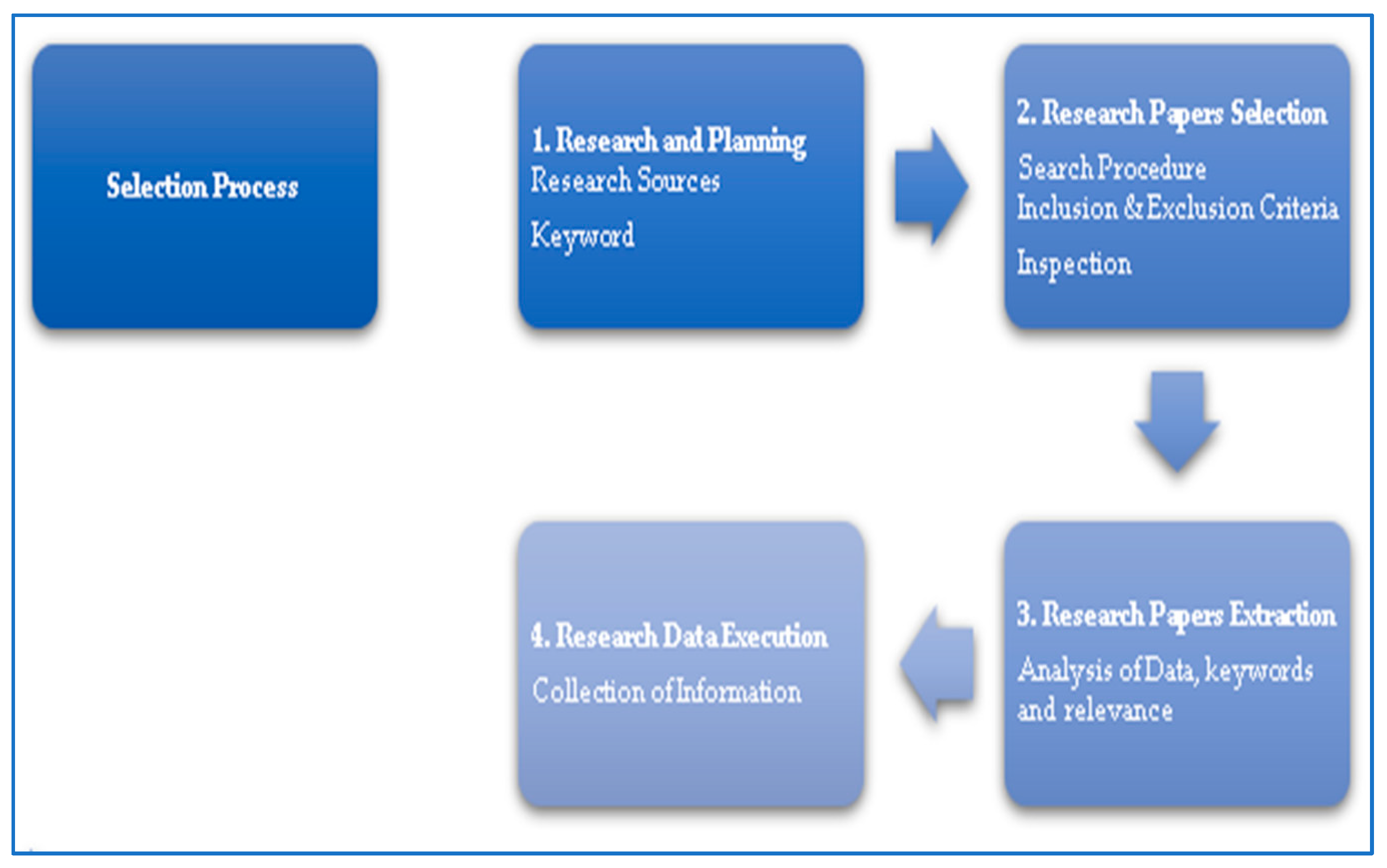
2.4. Selection Process

2.5. Data Collection Process
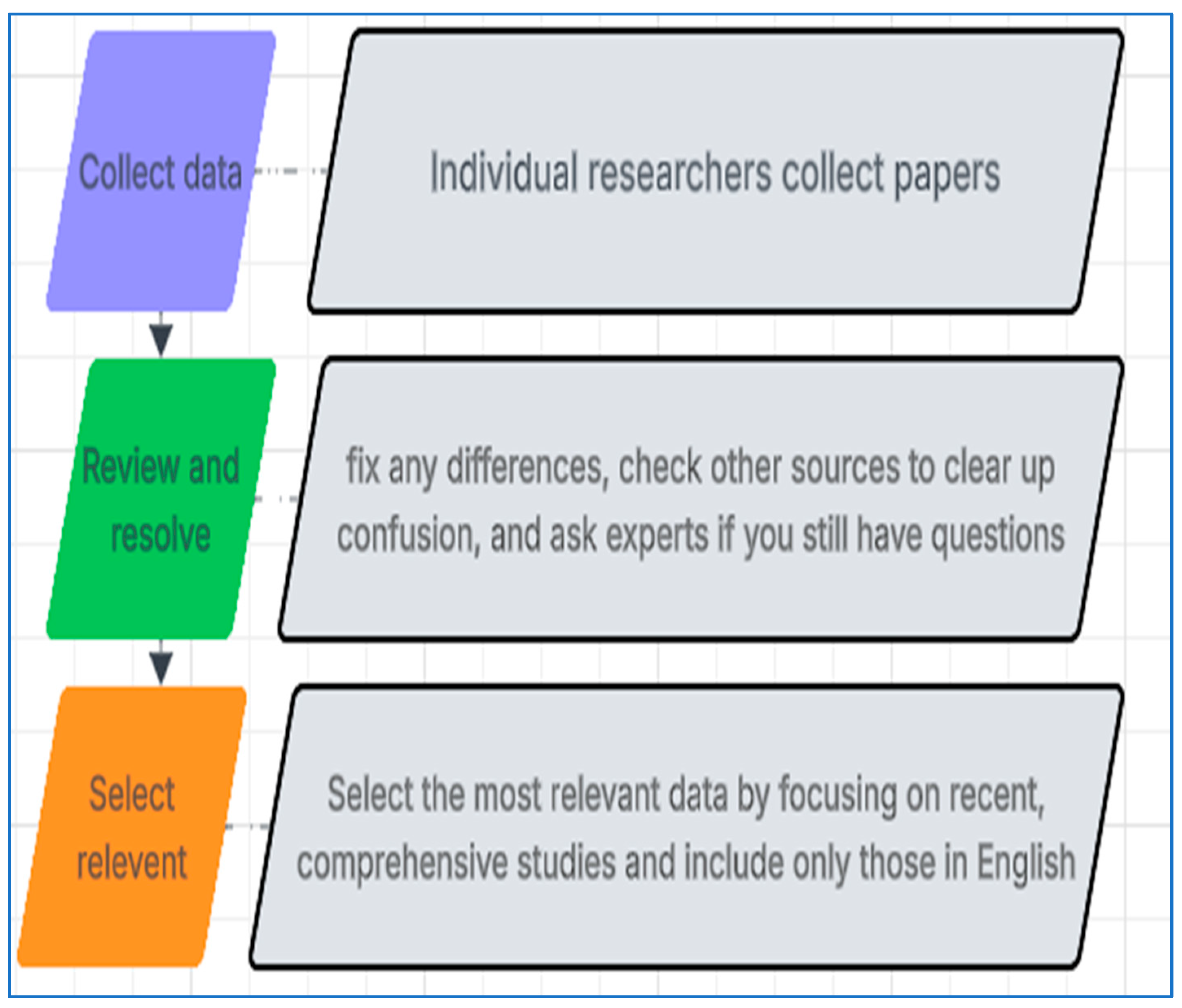
2.6.1. Data Items
2.6.2. Data Collection Method
2.6.3. Definition of Collected Variables
| Field | Description |
| Study characteristics | Focuses on tools, models and methodologies applied, this includes control system architectures and configuration management structures.t. |
| Participant characteristics | Information about the industry dominion like software development and aerospace, the project types involved in scope formulation and the organizational scale. |
| Intervention characteristics | Details of control systems and configuration management tools used, integration with existing systems, and scope of application in scope of development attempts. |
| Economic factors |
Financial aspects such as implementation costs, return on investment as well as budget aligning limitations in scope planning |
| External influences | Regulatory agreement, stakeholder demands that structures overall scope planning through the control and management systems. |
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Synthesis Methods
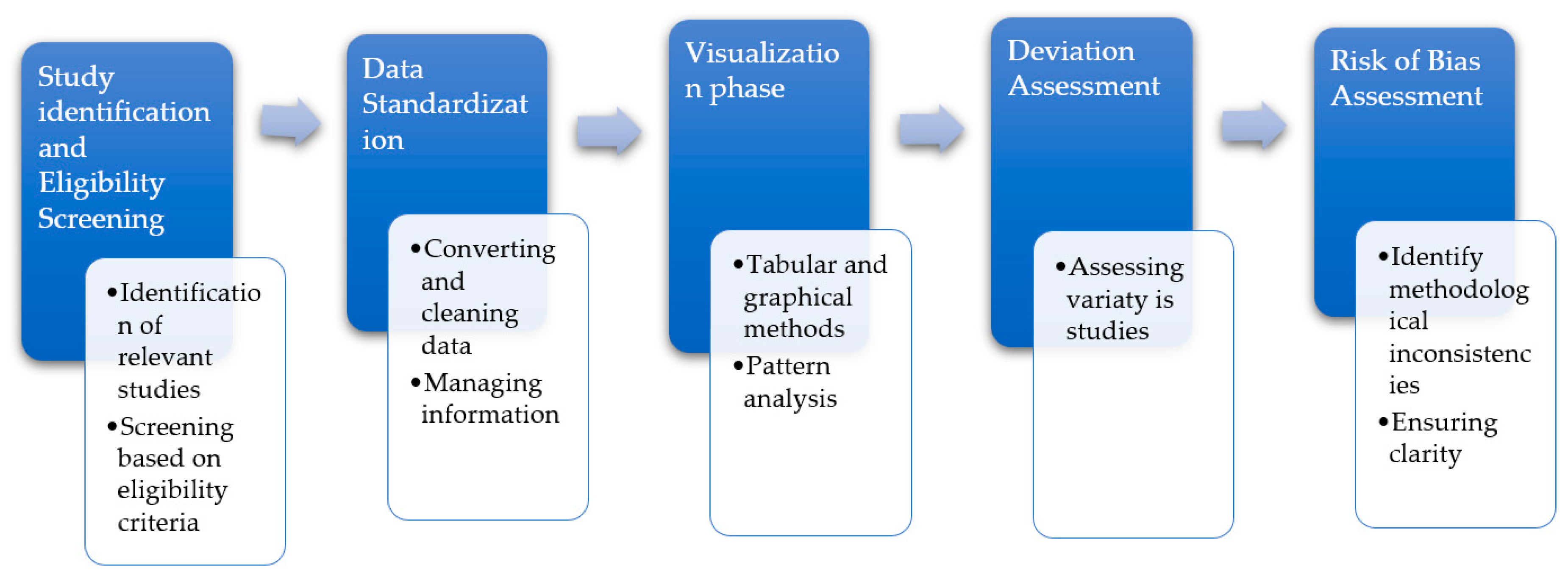
2.8.1. Eligibility for Synthesis
2.8.2. Data Preparation for Synthesis
2.8.3. Tabulation and Visual Display of Results
2.8.4. Synthesis of Results
2.8.5. Exploring Causes of Heterogeneity
2.8.6. Sensitivity Analyses
2.9. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.10. Certainty assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
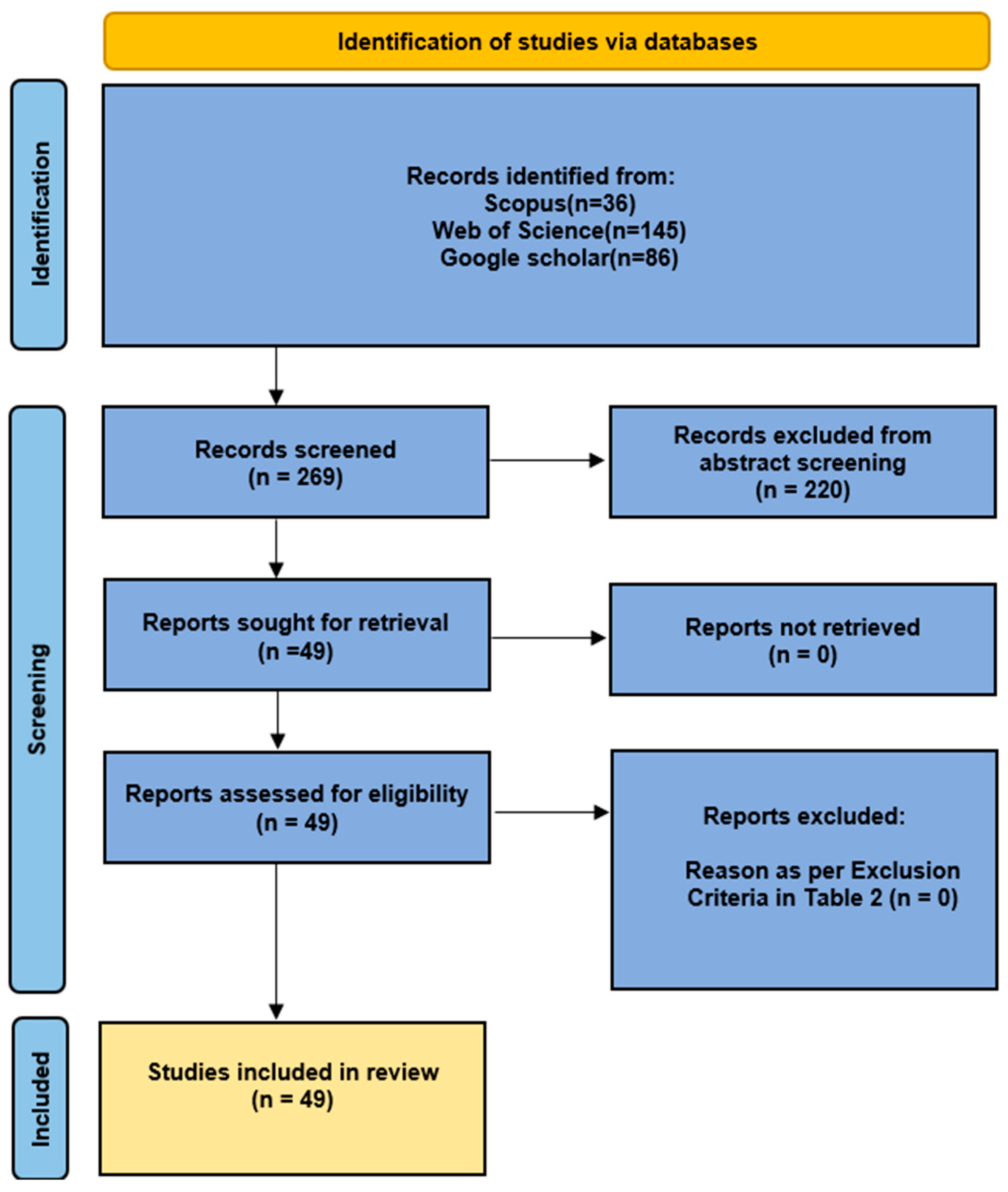
3.1.2. Reporting Results of Collected Results
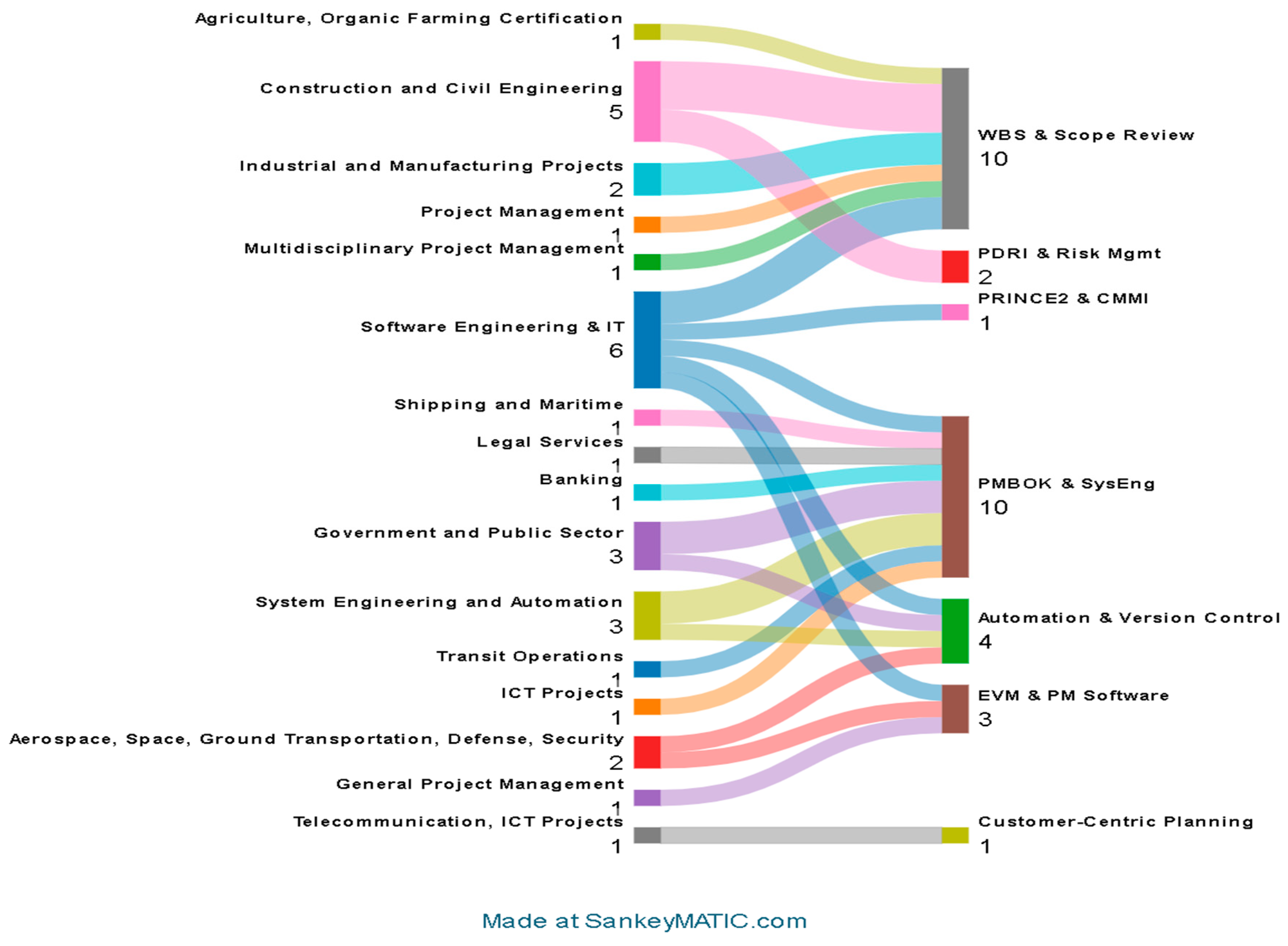
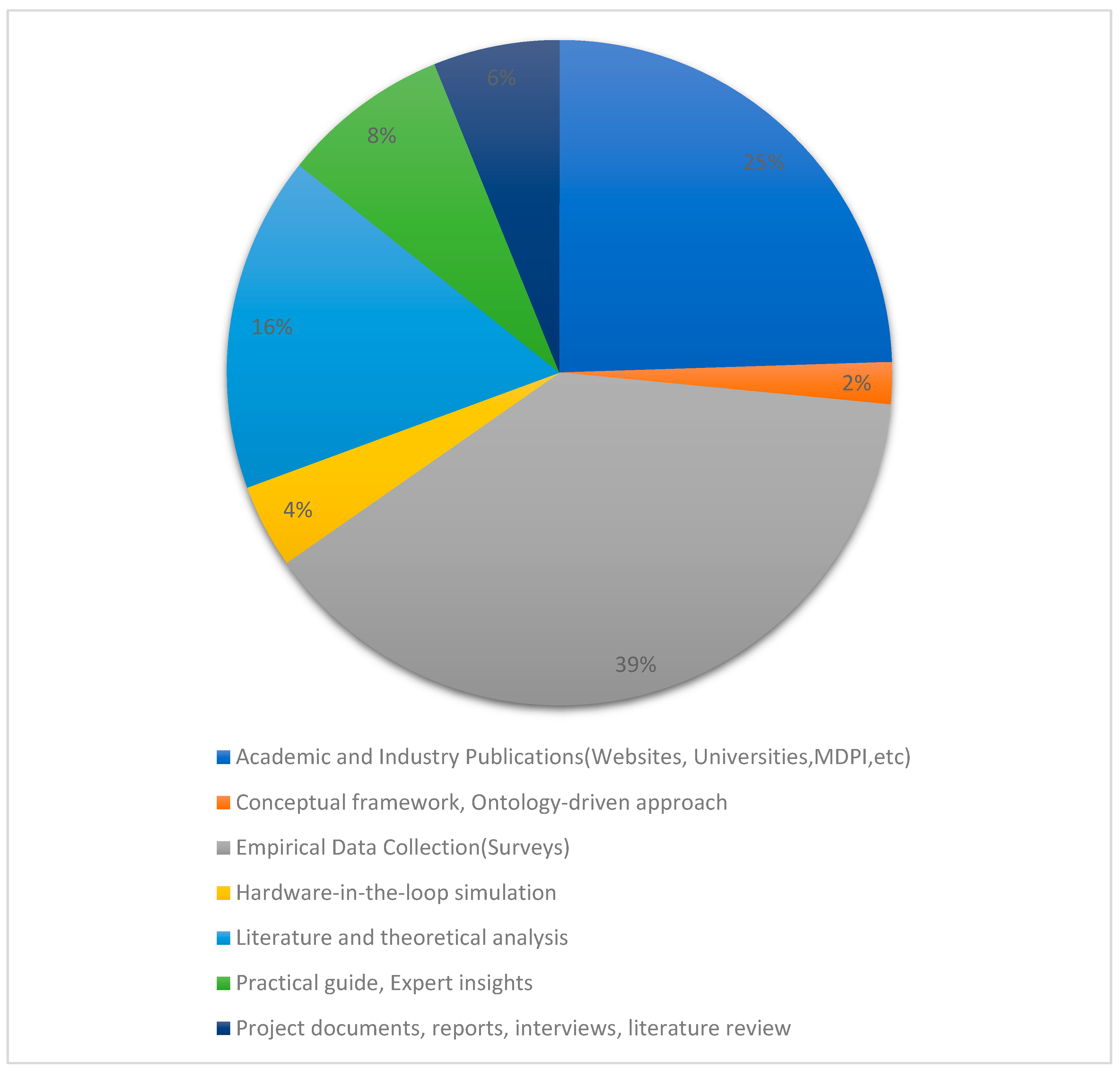
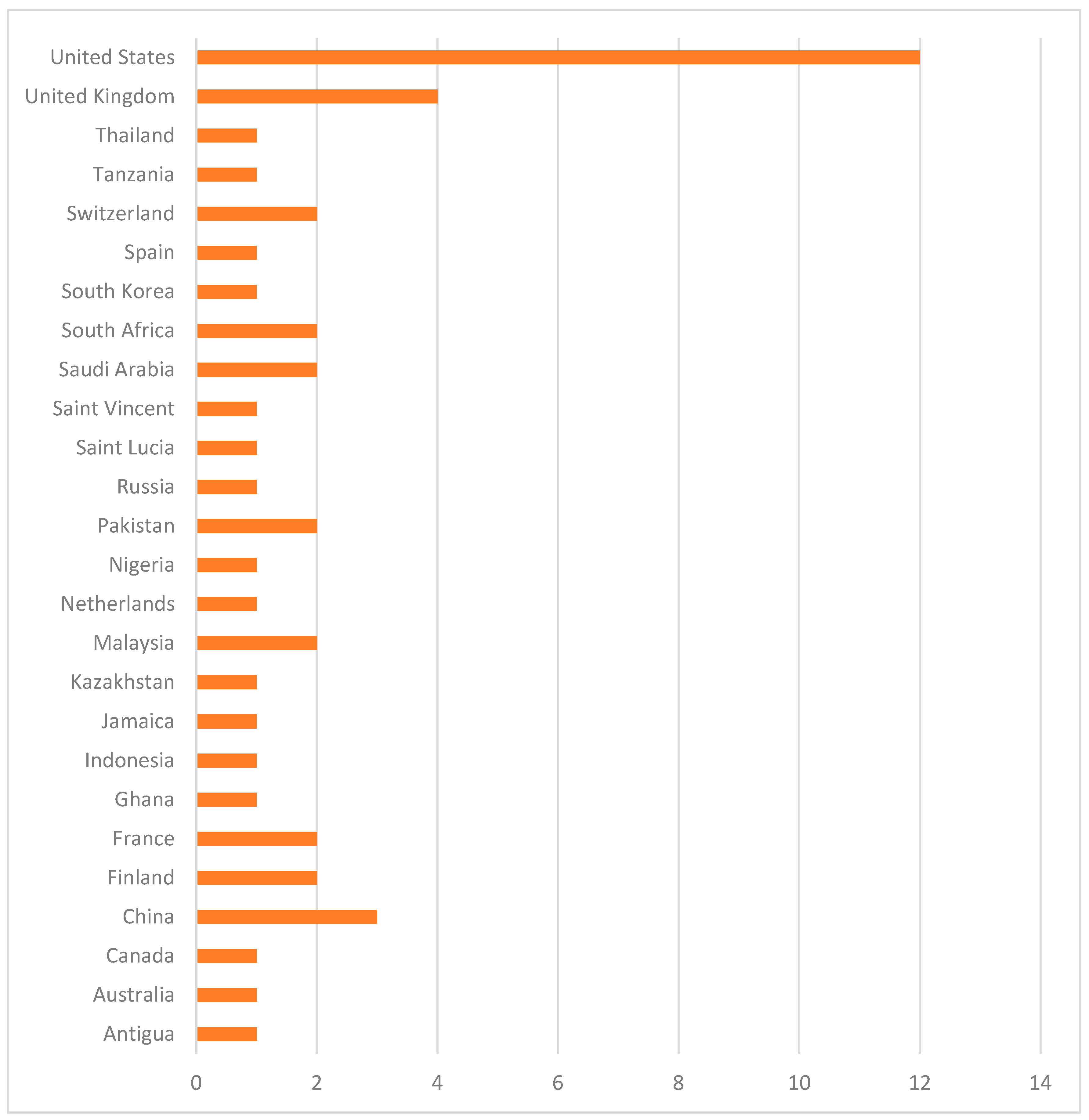
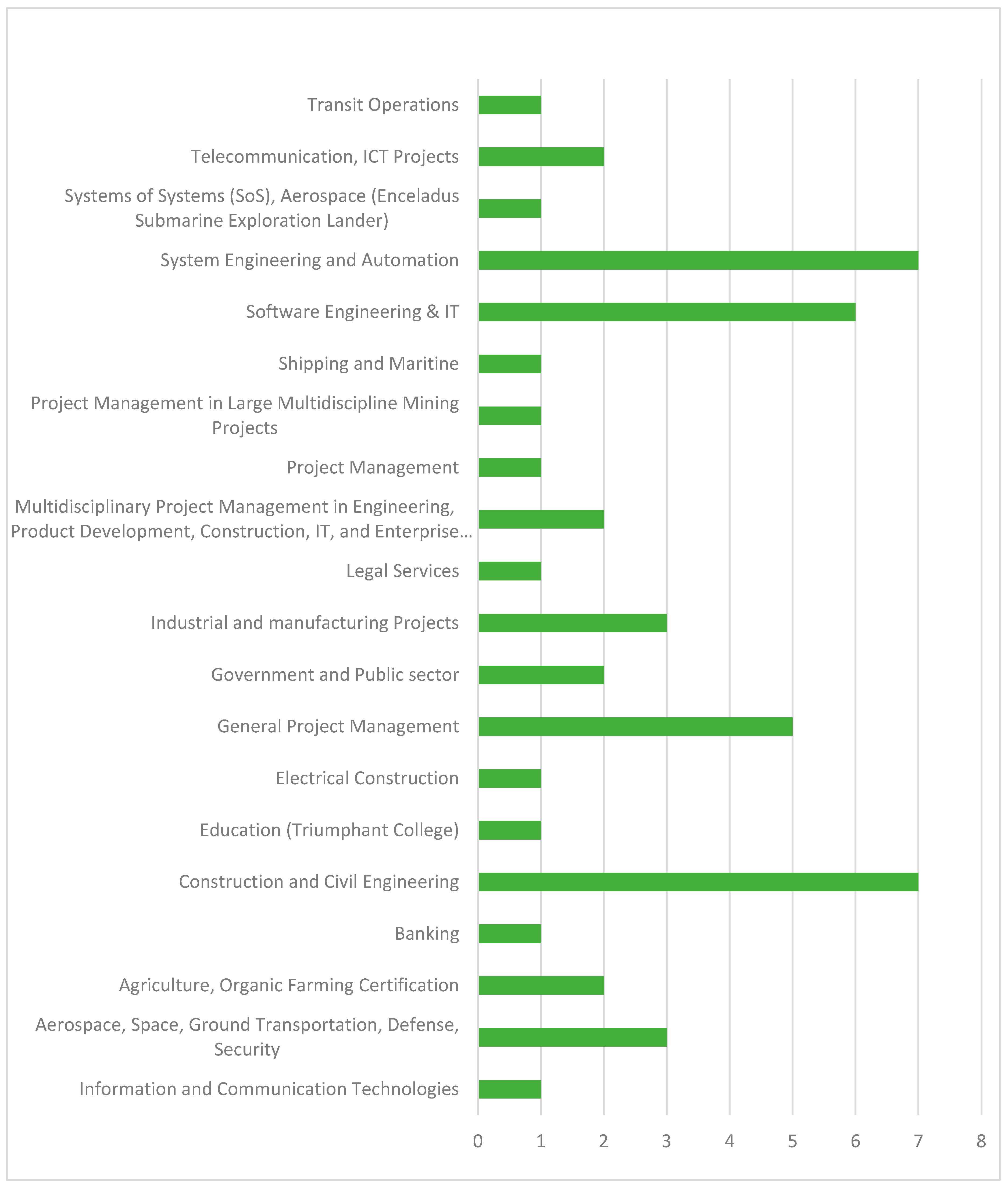
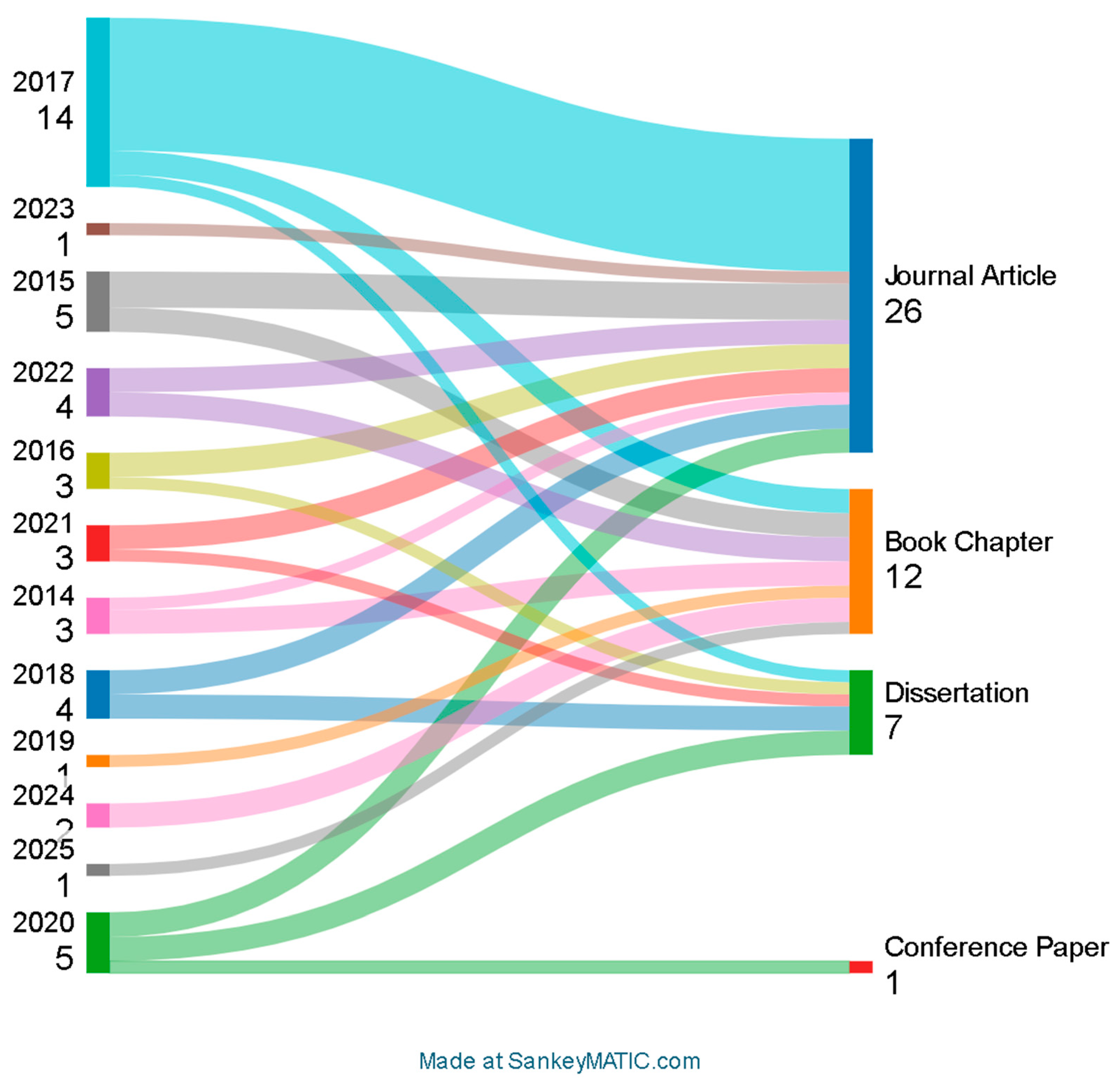
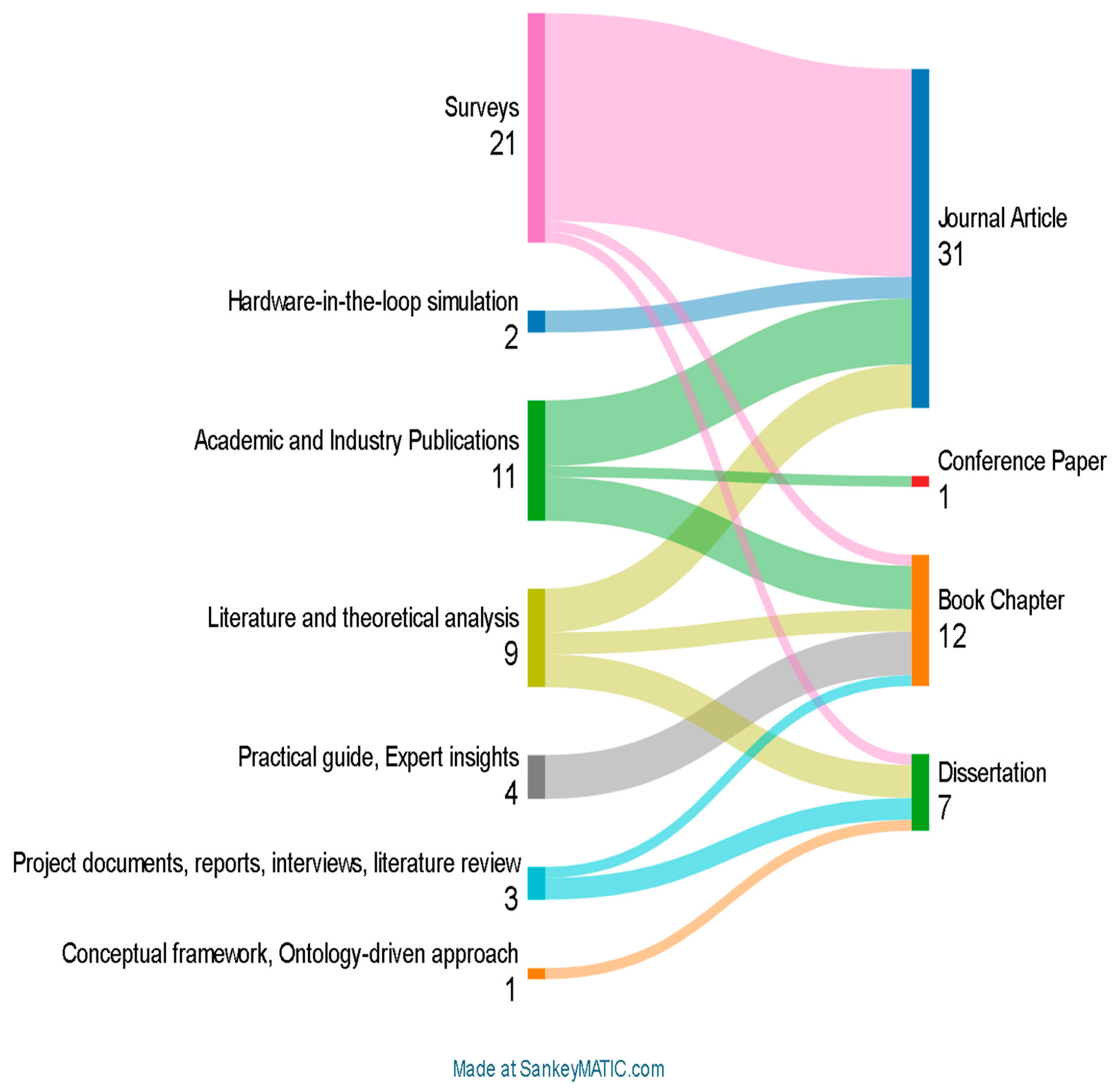
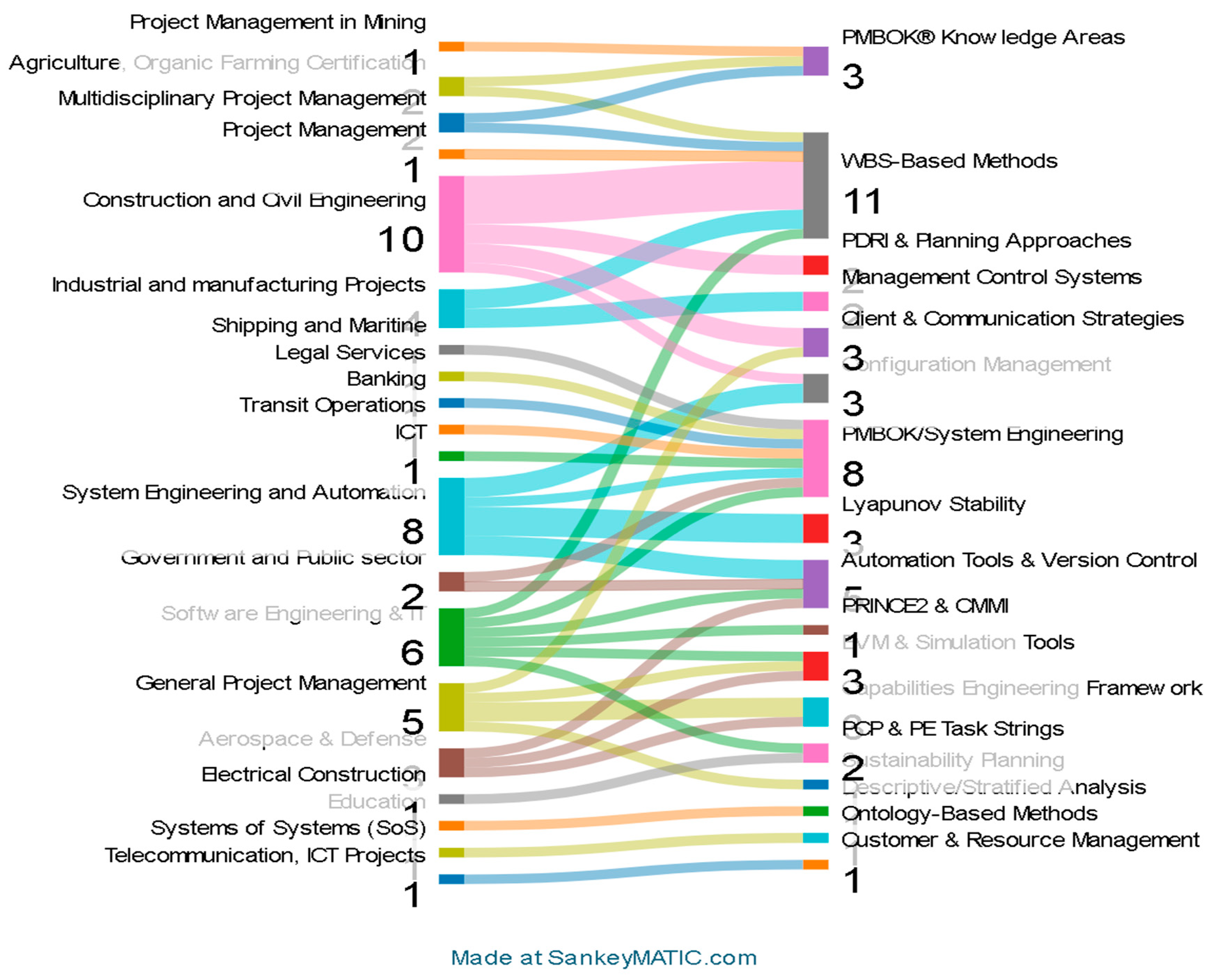
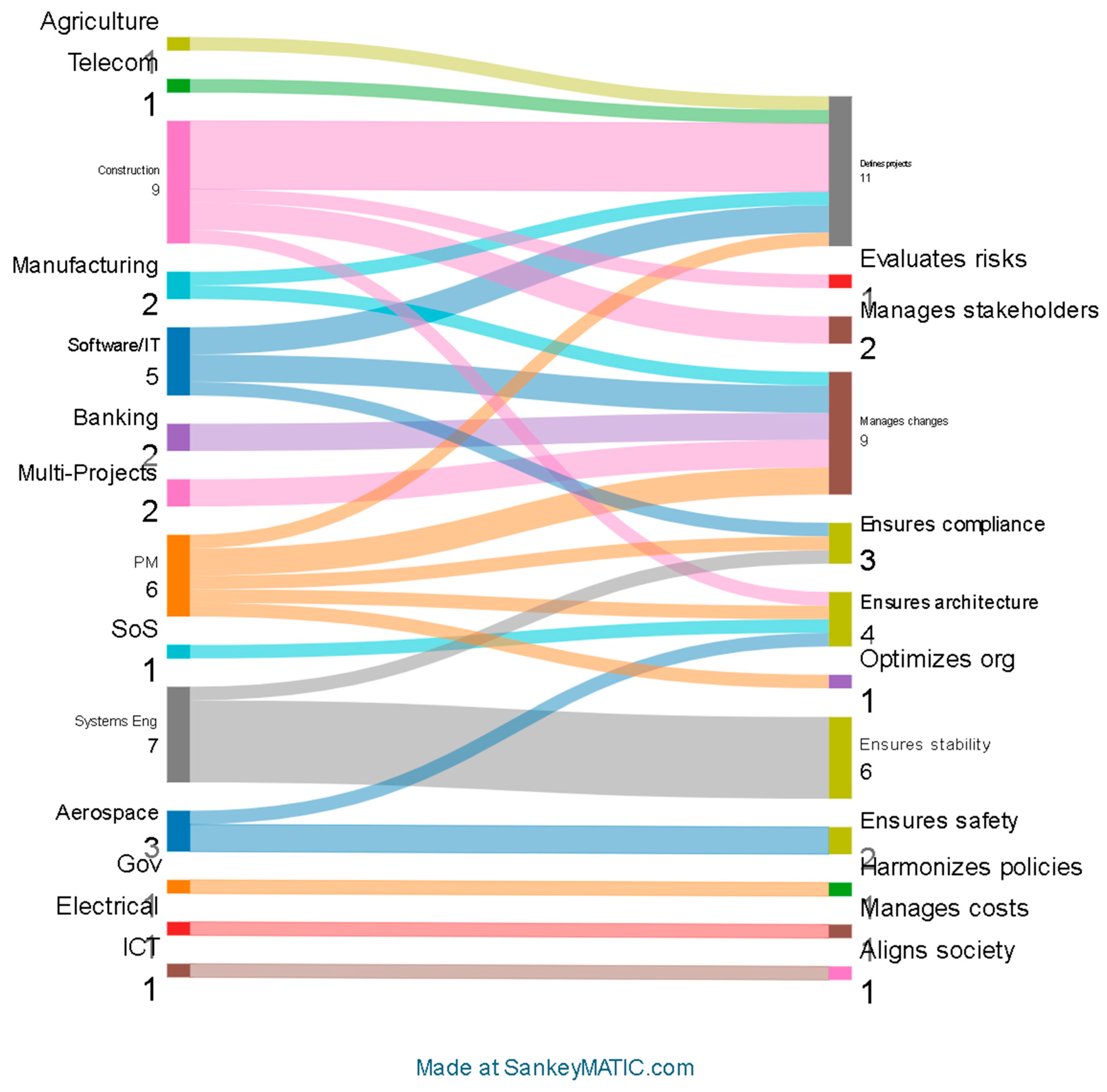
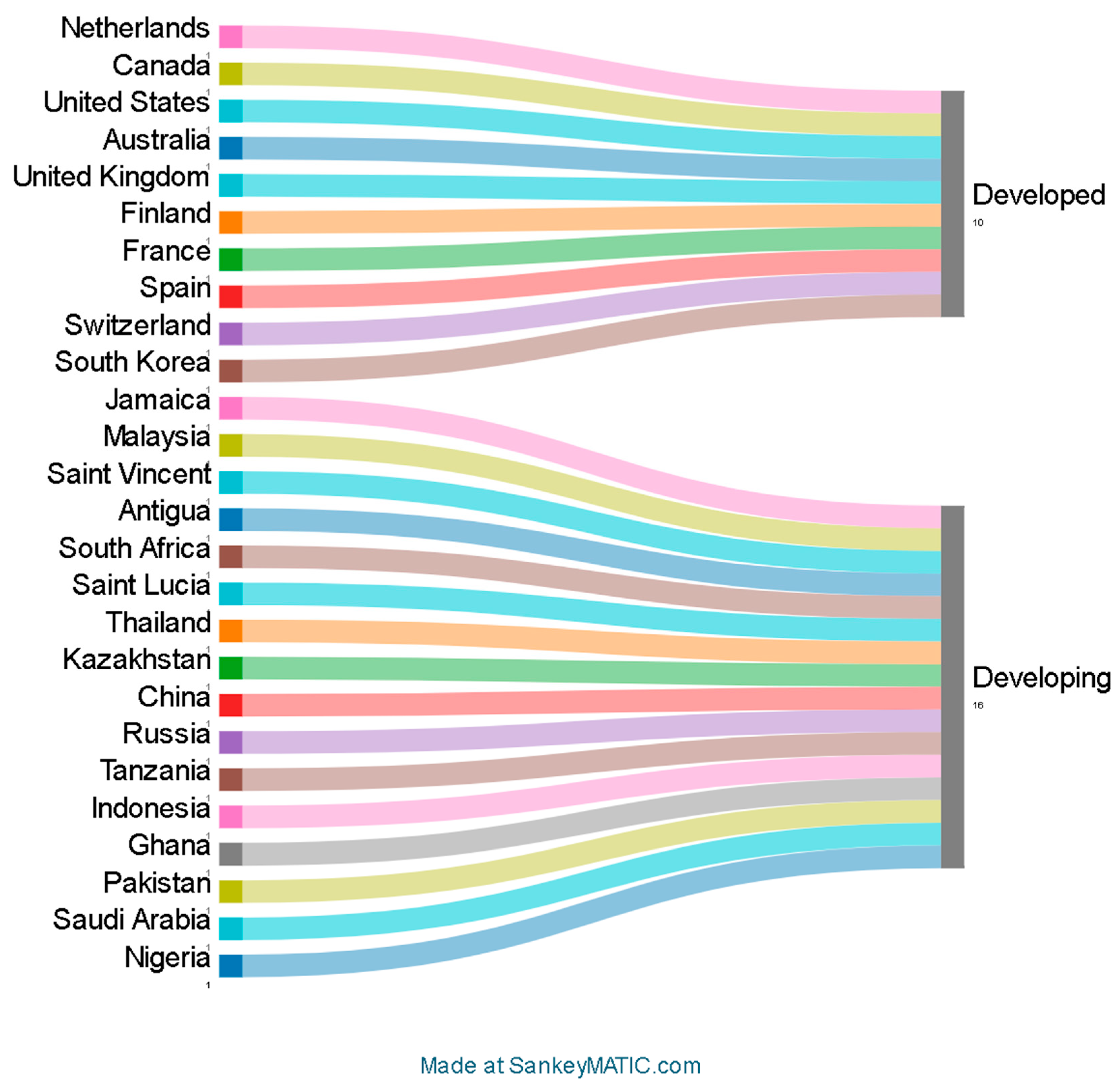
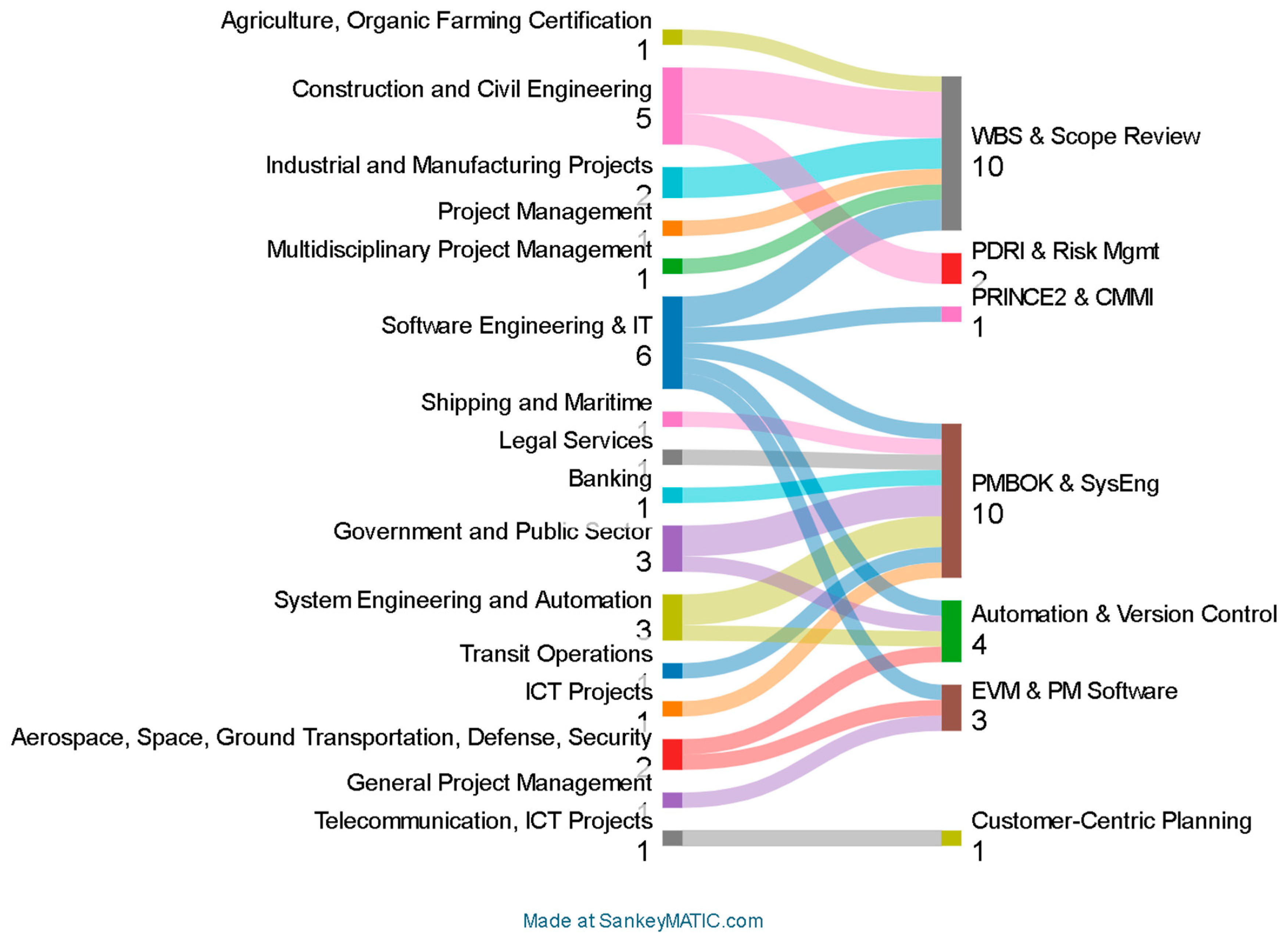
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
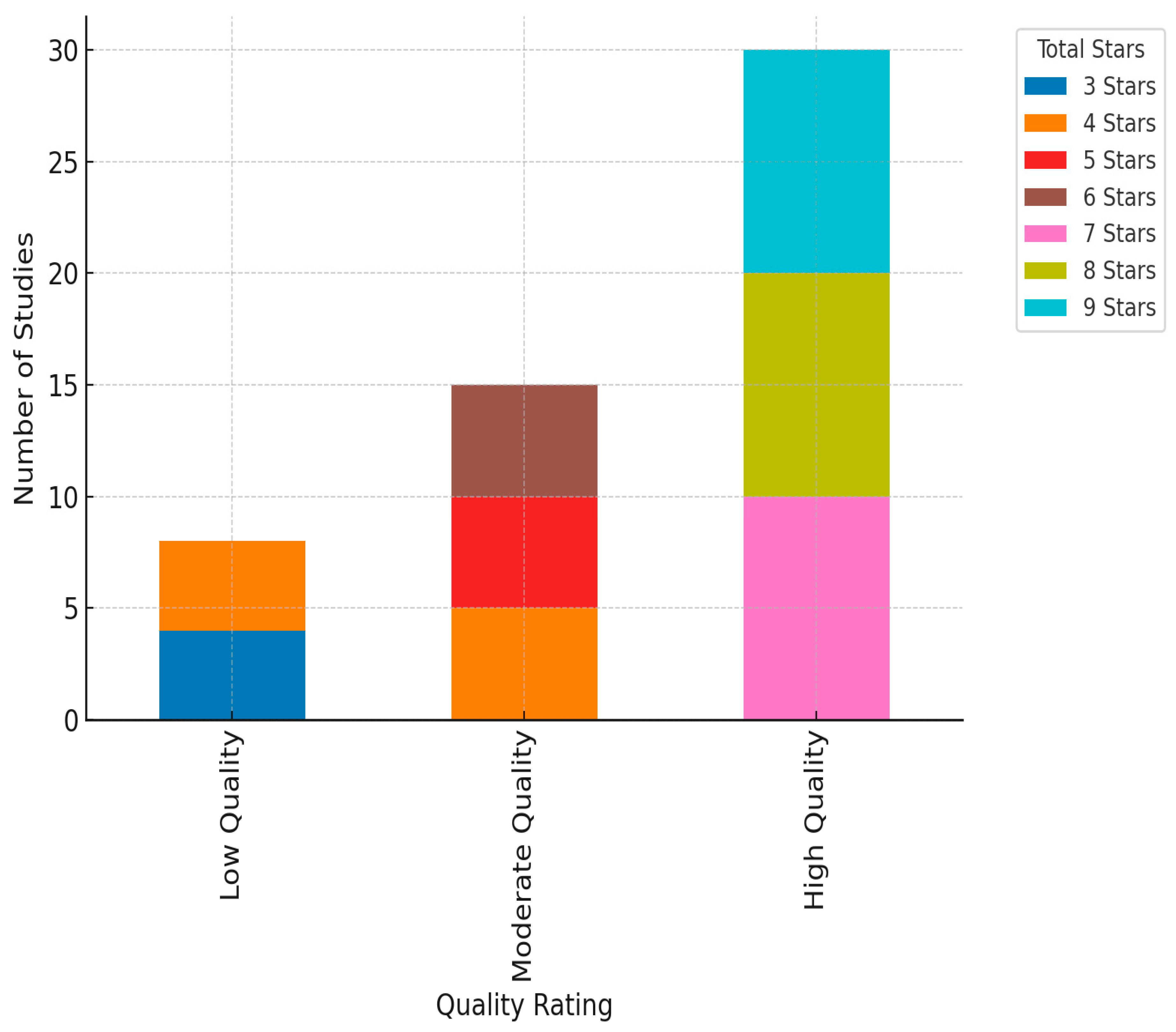
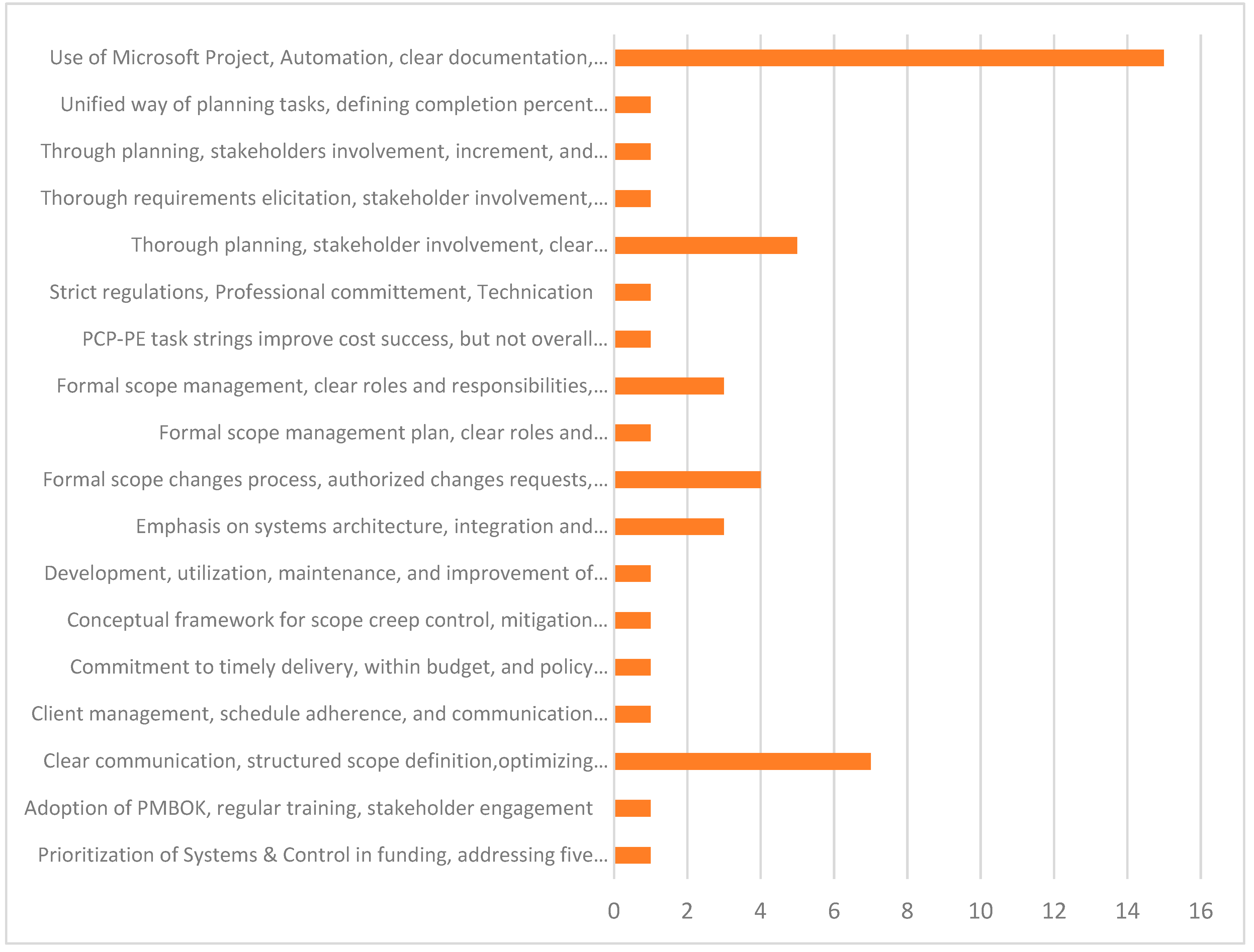
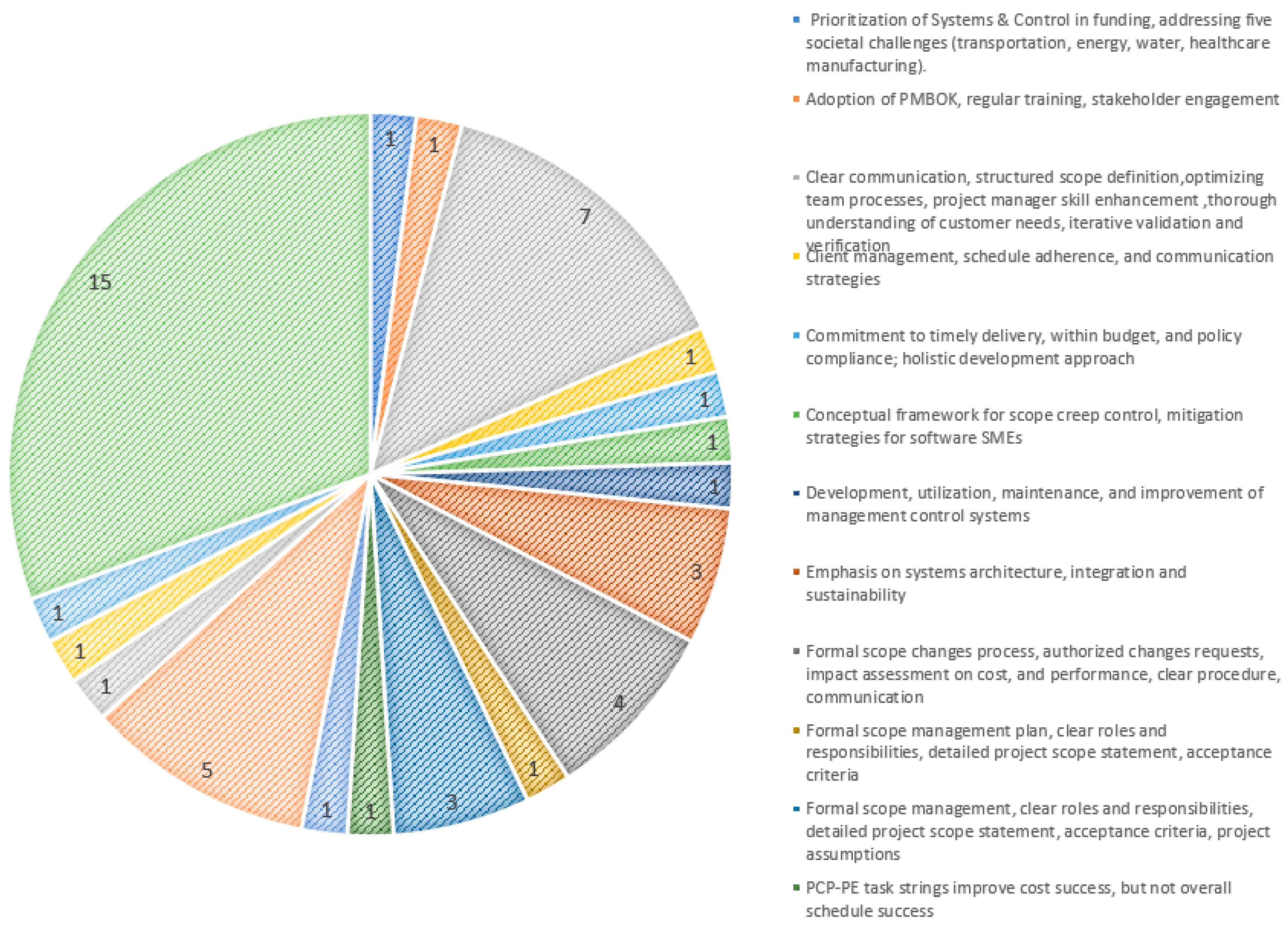
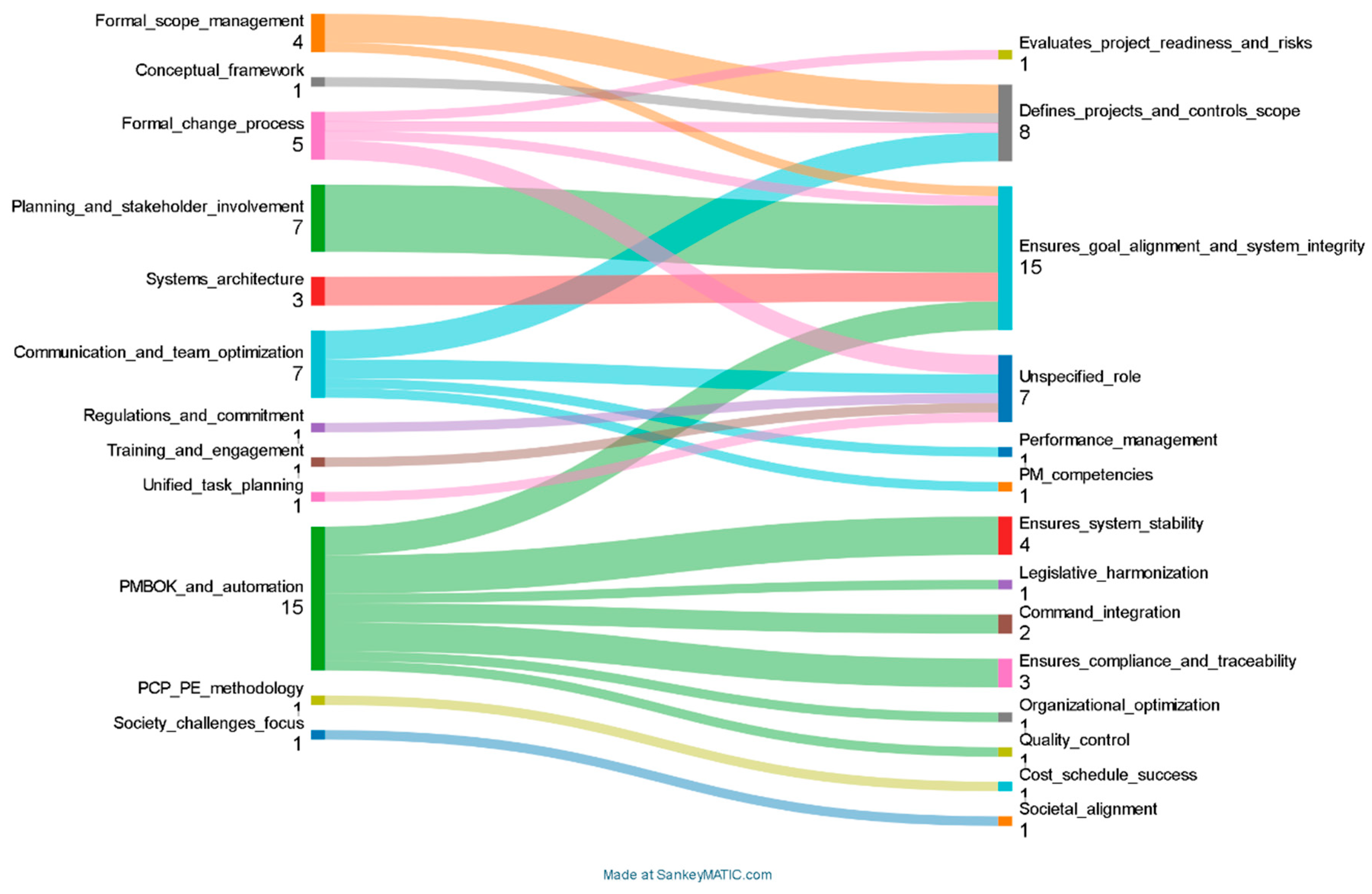
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Results of Synthesis
3.5.1. Characteristics and Risk of Bias Among Contributing Studies
3.5.2. Results of Statistical Syntheses
3.5.3. Investigation of Heterogeneity
3.5.4. Sensitivity Analyses Results
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
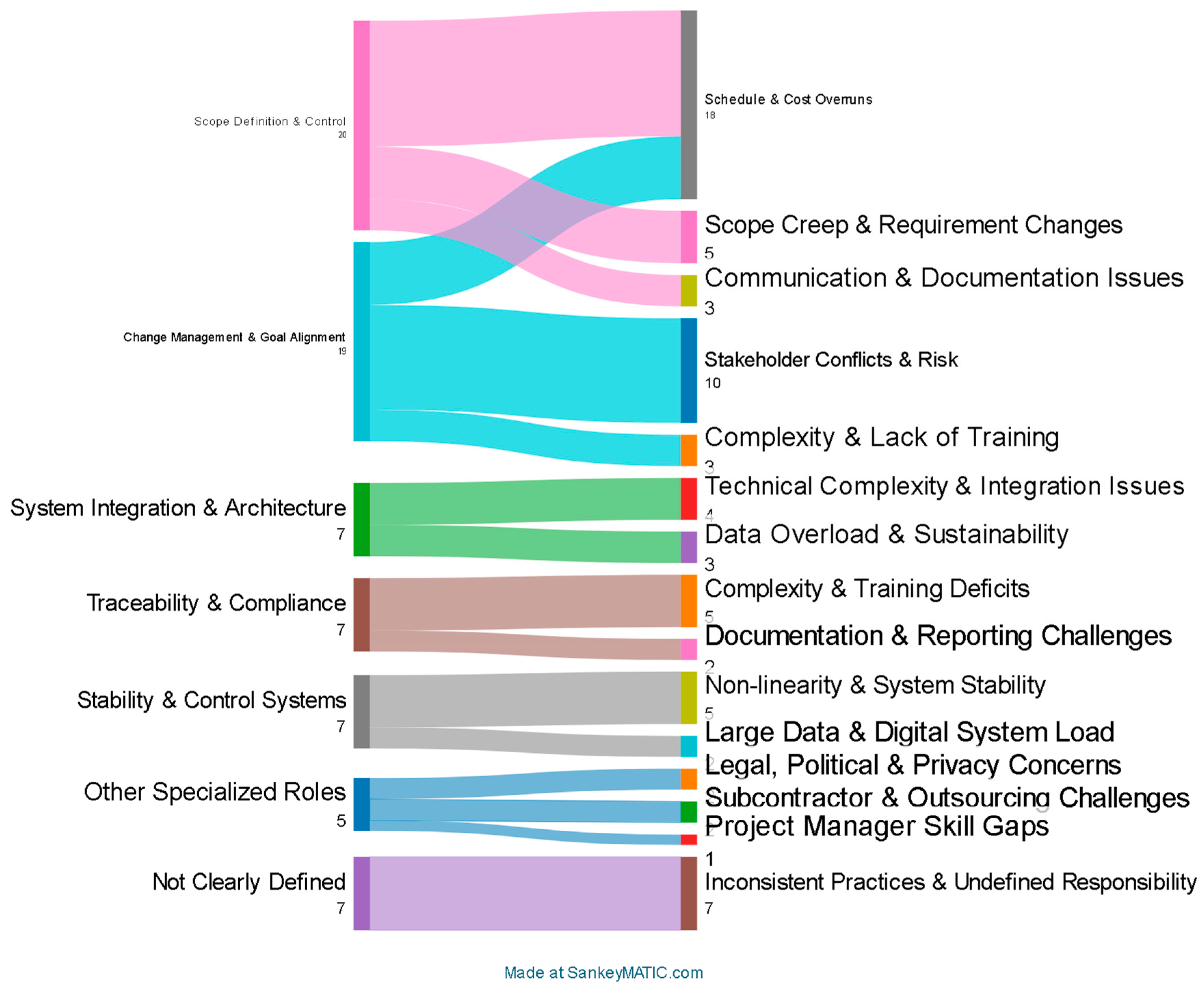
4. Discussion
Why is the use of configuration and control techniques in scope development often reported less than other approaches, and how can we fix this?
Why are some techniques, such as version control systems, receiving a lot of attention in papers, while others are not?
How can organizations apply standard techniques, like change request logging and traceability matrices, to enhance performance in situations that are limited?
How do cloud-based control and configuration frameworks assist with the scoping of work in fast-changing and disorganized workplace settings?
Can researchers and practitioners bring together more diverse tools and approaches that can support a better understanding of managing scope?
Can reporting rules be developed to more completely cover the wide range and utilization of control systems and configuration management plans?
5. Conclusion
References
- Ali, U., & Kidd, C. (2014). Critical success factors for configuration management implementation. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 113(2), 250-264. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/02635571311303569/full/pdf?title=critical-success-factors-for-configuration-management-implementation.
- Althiyabi, T., & Qureshi, M. R. J. (2021). Predefined project scope changes and its causes for project success. International Journal of Software Engineering & Applications, 12(2/3), 41-51. https://www.google.com/search?q=. [CrossRef]
- Anup, C. (2016, November). Towards a framework to address governance requirements of IT projects in the South African banking industry (Master's dissertation, University of South Africa, School of Computing). https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/158576943.pdf.
- Bahill, A. T., Bentz, B., & Dean, F. F. (2014, July). Discovering system requirements (SAND96-1620). Sandia National Laboratories. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/263004.
- Bayanouni, H. (2016). Developing an IT bidding maturity model (ITBMM) for IT firms operating in the gulf region (Order No. 27790141). Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/developing-bidding-maturity-model-itbmm-firms/docview/2340515867/se-2.
- China, C. R., & Goodwin, M. (2024, January 30). What is configuration management (CM)?. IBM. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/configuration-management.
- de la Cruz López, M. P., Cartelle Barros, J. J., del Caño Gochi, A., & Lara Coira, M. (2021). New approach for managing sustainability in projects. Sustainability, 13(13), 7037. [CrossRef]
- Dubuison, X. (2017, December). Project management plan for the conduct of training in standards for certification of organic farming project (Master's thesis). Universidad para la Cooperación Internacional. https://omeka.campusuci2.com/biblioteca/files/original/15eea74e172269ae5abb10f352859458.pdf.
- Häkkinen, M. (2015, May). The earned value in project management: Benefits in the ICT projects (Master's thesis). School of Business. https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/94740/Marko.Hakkinen.pdf?sequence=3.
- Hardion, V., Spruce, D. P., Lindberg, M., Otero, A. M., Lidon-Simon, J., Jamroz, J. J., & Persson, A. (2013). Configuration Management of the control system. THPPC013. https://accelconf.web.cern.ch/ICALEPCS2013/papers/thppc013.pdf.
- Harefa, T., Santoso, R., & Fuadah, L. (2024). Literature review of performance management systems and their impact on employee performance. International Journal of Economics, Accounting and Management, 1(4), 251-259. https://www.google.com/search?q=. [CrossRef]
- Hyrynsalmi, S. M., Koskinen, K. M., Rossi, M., & Smolander, K. (2024). Navigating Cloud-Based Integrations: Challenges and Decision Factors in Cloud-Based Integration Platform Selection. IEEE Access. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10637466.
- Jackson, D., Semler, C., Ryus, P., & Nevers, B. (2014, December). How to guide - transit operations decision support systems (TODSS) (FHWA-JPO-14-144). Kittelson & Associates, Inc.; CH2M Hill, Inc.; United States. Federal Highway Administration; United States. Department of Transportation. Federal Transit Administration. https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/3497.
- Kim, J., Lim, J., Lim, H.-C., & Kim, D. Y. (2022). Improving sustainable project success strategies focused on cost and schedule for electrical construction project management. Sustainability, 14(5), 2653. [CrossRef]
- Komal, B., Janjua, U. I., Cheema, M. F., Malik, M. N., Anwar, F., Madni, T. M., & Shahid, A. R. (2020). The impact of scope creep on project success: An empirical investigation. IEEE Access, 8, 125188-125197. [CrossRef]
- Kossmann, M., Samhan, A., Odeh, M., Qaddoumi, E., Tbakhi, A., & Watts, S. (2020). Extending the scope of configuration management for the development and life cycle support of systems of systems—An ontology-driven framework applied to the Enceladus Submarine Exploration Lander. Systems Engineering, 23(3), 366-391. [CrossRef]
- Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue, F., Annaswamy, A., Engell, S., Isaksson, Å., Khargonekar, P., Murray, R. M., Nijmeijer, H., Samad, T., Tilbury, D., & Van den Hof, P. (2017). Systems & control for the future of humanity, research agenda: Current and future roles, impact and grand challenges. Annual Reviews in Control, 43, 1-64. [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, P., & Aalto, P. (2017). Smart and secure borders through automated border control systems in the EU? The views of political stakeholders in the Member States. European Security, 26(2), 207–225. [CrossRef]
- Lindkvist, C., Stasis, A., & Whyte, J. (2013). Configuration management in complex engineering projects. Procedia CIRP, 11, 173-176. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., & Luo, C. (2017). Stability analysis for GE T700 turboshaft distributed engine control systems. IEEE Access, 5, 21666-21672. https://www.google.com/search?q=. [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, G., Mancini, M., & Romano, E. (2014). Systems engineering to improve the governance in complex project environments. International Journal of Project Management, 32(8), 1395-1410. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0263786313001385.
- Luqman, A. (2014). Comparison of configuration management activities between Prince 2 & CMMI 1.1. In 2014 International Conference on Emerging Technologies (pp. 742-745). IEEE. https://www.google.com/search?q=. [CrossRef]
- Madziwo, C. P. (2018). Investigating the effects of pro-ject change in scope on employee performance at Triumphant College (Master's thesis, The Open University of Tanzania). http://repository.out.ac.tz/id/eprint/2922.
- Monarch, I. A., & Wessel, J. (2014). The capabilities engineering framework: Holistic approach to systems of systems life cycle. In Collection of Technical Papers - 2014 AIAA InfoTech at Aerospace Conference, Volume 2 (pp. 1570-1586). American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
- Moustafaev, J. (2014). Project scope management: A practical guide to requirements for engineering, product, construction, IT and enterprise projects (1st ed.). Auerbach Publications. [CrossRef]
- Muneer, M., Khan, N., Awais Hussain, M., Shuai, Z., Khan, A. A., Farooq, R., Moawwez, M. A., & Tariq, M. A. U. R. (2022). A quantitative study of the impact of organizational culture, communication management, and clarity in project scope on constructions’ project success with moderating role of project manager’s competencies to enhance constructions management practices. Buildings, 12(11), 1856. [CrossRef]
- Nagapetyan, V. E., & Khachumov, V. M. (2017). A combined system for contactless control of robotic systems by verbal and gesture commands. Scientific and Technical Information Processing, 44, 379–385. [CrossRef]
- Ogunberu, A. O., Akintelu, S. O., & Olaposi, T. O. (2018). Application of project scope management practices on project success among telecommunication organizations in Nigeria. International Journal of Development and Sustainability, 7(2), 518-532. https://isdsnet.com/ijds-v7n2-08.pdf.
- Qasim, L. (2020, December). System reconfiguration : A Model based approach; From an ontology to the methodology bridging engineering and operations (Doctoral dissertation, Université Paris-Saclay). https://theses.hal.science/tel-03242294.
- Ram, J., Wu, M. L., & Tagg, R. (2014). Competitive advantage from ERP projects: Examining the role of key implementation drivers. International Journal of Project Management, 32(4), 663-675. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ming-Lu-Wu-2/publication/261564077_Competitive_advantage_from_ERP_projects_Examining_the_role_of_key_implementation_drivers/links/5f47da35a6fdcc14c5d0728f/Competitive-advantage-from-ERP-projects-Examining-the-role-of-key-implementation-drivers.pdf.
- Ramage, K. L. (2018). Scope management strategies for engineering leaders to improve project success rates (Order No. 10839418). Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/scope-management-strategies-engineering-leaders/docview/2079041984/se-2.
- Ramesh, B., Powers, T., Stubbs, C., & Edwards, M. (2014, March). Implementing requirements traceability: a case study. In Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Requirements Engineering (RE'95) (pp. 89-95). IEEE.
- Richardson, G. L., & Carstens, D. S. (2019). *Project management tools and techniques.
- Dos Santos Ferreira, M., & Furtado, A. P. C. (2016). Configuration Management to Tests Automatics in a Software Factory. ICSEA 2016, 99.
- Bou Ghantous, G., & Gill, A. (2017). DevOps: Concepts, practices, tools, benefits and challenges. PACIS2017. https://opus.lib.uts.edu.au/bitstream/10453/130066/1/DevOps-%20Concepts%20Practices%20Tools%20Benefits%20and%20Challenges.pdf.
- Afram, A., & Janabi-Sharifi, F. (2014). Theory and applications of HVAC control systems–A review of model predictive control (MPC). Building and environment, 72, 343-355. [CrossRef]
- Lueg, R., & Radlach, R. (2016). Managing sustainable development with management control systems: A literature review. European Management Journal, 34(2), 158-171. [CrossRef]
- Whyte, J., Stasis, A., & Lindkvist, C. (2016). Managing change in the delivery of complex projects: Configuration management, asset information and ‘big data’. International journal of project management, 34(2), 339-351. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. L. (2014). Product configuration: a review of the state-of-the-art and future research. International Journal of Production Research, 52(21), 6381-6398. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00207543.2014.942012.
- Mtjilibe, Tshepang and Rameetse, Emmanuel and Mgwenya, Nkosinathi and Thango, Bonginkosi, Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities of Social Media for Organizational Engagement in SMEs: A Comprehensive Systematic Review (July 06, 2024). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4998542. [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, S., Kristjansdottir, K., Hvam, L., & Forza, C. (2018). How to scope configuration projects and manage the knowledge they require. Journal of Knowledge Management, 22(5), 982-1014. [CrossRef]
- Palma, F. E., Fantinato, M., Rafferty, L., & Hung, P. C. (2019, May). CPS-PMBOK: How to better manage cyber-physical system development projects. In International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (pp. 154-181). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Marnada, P., Raharjo, T., Hardian, B., & Prasetyo, A. (2022). Agile project management challenge in handling scope and change: A systematic literature review. Procedia Computer Science, 197, 290-300. [CrossRef]
- Thango, B. A., & Obokoh, L. (2024). Techno-Economic Analysis of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems for Power Interruptions: A Systematic Review. Eng, 5(3), 2108–2156. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J. A., Acher, M., Martin, H., Jézéquel, J. M., Botterweck, G., & Ventresque, A. (2021). Learning software configuration spaces: A systematic literature review. Journal of Systems and Software, 182, 111044. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121221001412.
- Thobejane, L. T., & Thango, B. A. (2024). Partial Discharge Source Classification in Power Transformers: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 14(14), 6097. [CrossRef]
- Gall, M., & Pigni, F. (2022). Taking DevOps mainstream: a critical review and conceptual framework. European Journal of Information Systems, 31(5), 548-567. [CrossRef]
- Macarthy, R. W., & Bass, J. M. (2020, August). An empirical taxonomy of DevOps in practice. In 2020 46th euromicro conference on software engineering and advanced applications (seaa) (pp. 221-228). IEEE.
- Díaz, J., Almaraz, R., Pérez, J., & Garbajosa, J. (2018, May). DevOps in practice: an exploratory case study. In Proceedings of the 19th international conference on agile software development: Companion (pp. 1-3).
- Senapathi, M., Buchan, J., & Osman, H. (2018, June). DevOps capabilities, practices, and challenges: Insights from a case study. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering 2018 (pp. 57-67).
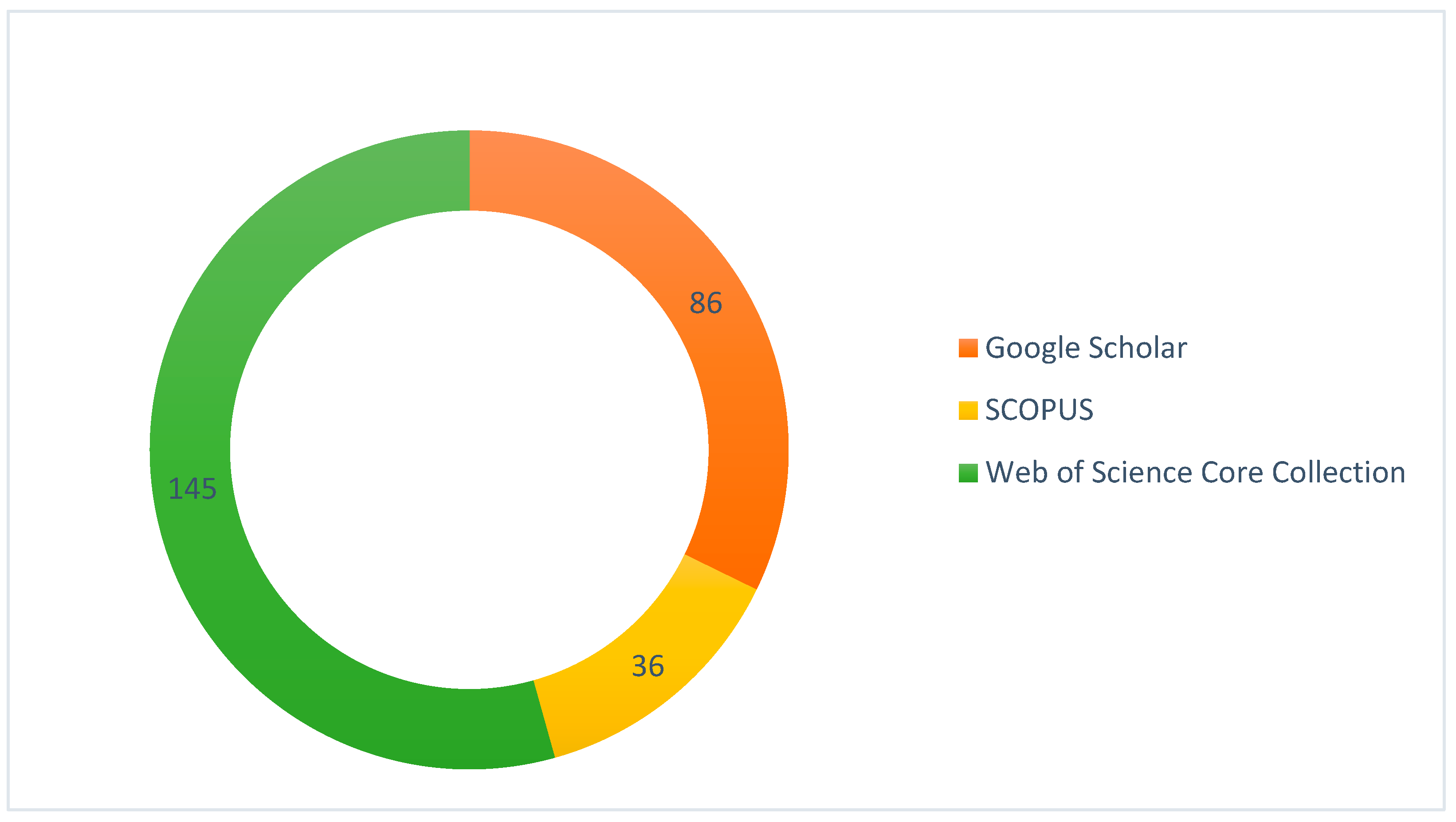
| Ref. | QA1 | QA2 | QA3 | QA4 | Total | % grading |
| (Qureshi, 2021; Rizwan & Qureshi, 2021; Smith, 2017; Jackson et al., 2014; Dubuison, 2017; Lehtonen & Aalto, 2017; Madziwo, 2018; Harefa et al., 2024; Boulanger & Boulanger, 2019; Pfiffner, 2022b; Aborhor, 2021; Kim et al., 2022; Saman et al., 2020) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | ≤60 |
| (U.S. Federal Highway Administration & U.S. Department of Transportation, 2014; Nagapetyan & Khachumov, 2017; Whyte, 2014; Bai & Liang, 2014; Pfiffner, 2022a) | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70 |
| (Bahill & Dean, 2014; Carstens & Richardson, 2019; de la Cruz López et al., 2021; Hakkinen, 2014; Harefa et al., 2024; Koenig & Mahmood, 2014; Leketi & Raborife, 2019; Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue et al., 2017; Brown, 2025; KOMAL et al., 2020; Althiyabi & Qureshi, 2021; Ussahawanitchakit, 2017) | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| (Auzair & Amir, 2017; Bayanouni, 2016; China & Goodwin, 2024; Kossmann et al., 2020; Leketi & Raborife, 2019; Lu, 2017; Moustafaev, 2014; Qasim, 2020; Yates, 2014; Yu & Liao, 2017; Zumatov, 2017) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| (Whyte, 2014; Doe, 2018; Kittelson & Associates et al., 2014; Lu, 2017; Lindkvist et al., 2014; Carstens & Richardson, 2019; Luqman, 2014; Muneer et al., 2022; Okereke & Afolabi, 2018) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| Outcome | Certainty of Evidence | Effect Estimate | Interpretation |
| Operational Efficiency | Moderate | Mean difference of 12% improvement in scope delivery timelines | Control system and configuration management likely enhance operational efficiency by streamlining scope development processes. |
| project Performance | High | 15% increase in scope adherence on average | Strong evidence supports that integrated control and configuration practices leads to great project outcomes. |
| Strategic scope planning | Moderate | Risk ratio of 1.8 for improved scope planning quality | These systems probably improve strategic alignments and, enhancing decision speed and accuracy. |
| Stakeholder Coordination | Moderate | 10% increase in stakeholders satisfaction rates | Configuration management practices enhances communication and alignment across stakeholders during scope development. |
| Change Management Responsiveness | Low | Hazard ratio of 1.5 for faster adaptation to changes | Evidence suggests that practices helps teams respond more effectively to scope changes, though with consistency variability. |
| Innovation and Product Development | Moderate | Mean difference of 8% in scope innovation success | Control and configuration mechanisms likely contribute to innovation and successful through structured flexible scope design. |
| Risk mitigation in scope control | High | 20 % improvement in managing scope related risks | Strong evidence shows these systems significantly enhance risk management within scope development processes. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




