Submitted:
24 August 2025
Posted:
25 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology and Disease Burden
3. Clinical Presentation
4. Pathophysiology
4.1. Histological features
4.2. Genetic contributions
4.3. Triggers
4.4. Pathogenesis
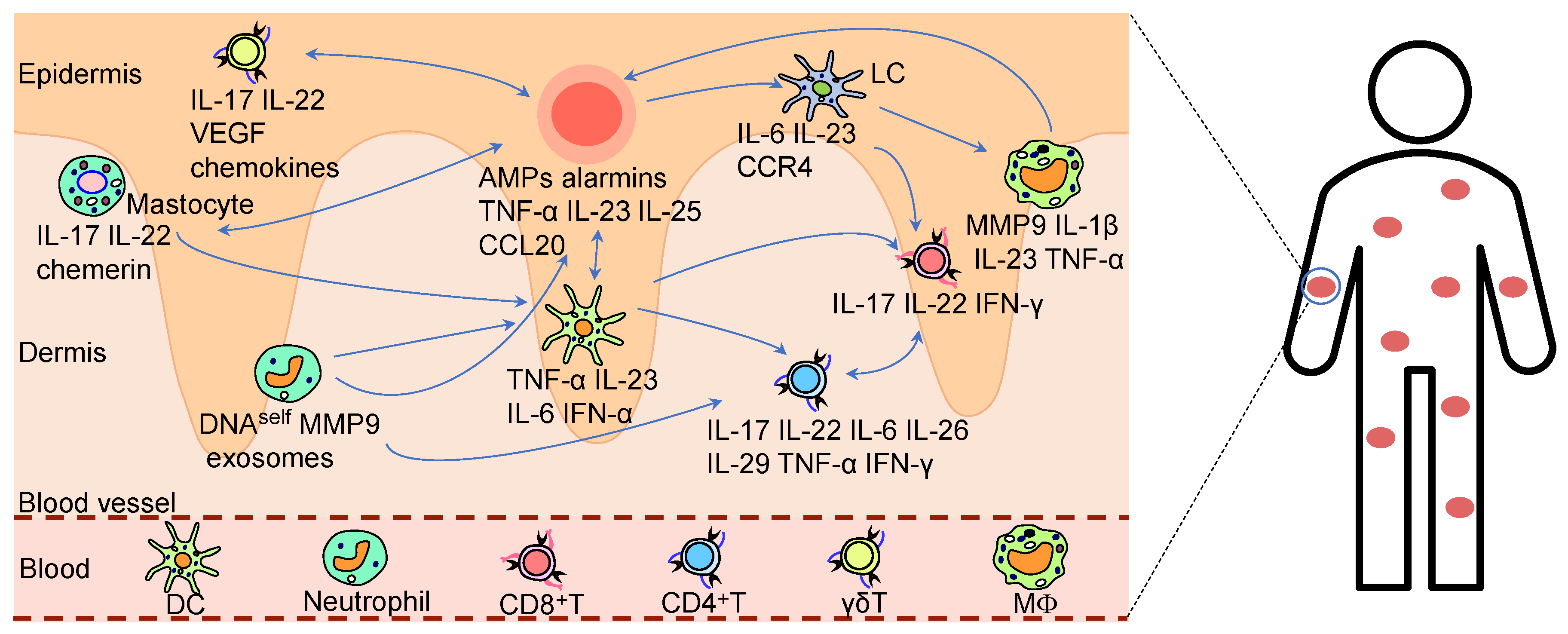
4.5. Innate Immunity
4.6. Adaptive Immunity
5. Management and Treatment
5.1. Conventional Topical Therapy
5.2. Conventional Systemic Therapy
| Category | Drug Name | Target/ Mechanism |
Efficacy Profile | Adverse Effects /Potential Risks |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Therapies |
Corticosteroids [178] | Suppression of Th17-mediated inflammation; modulation of dendritic and T-cell activity | Rapid symptom control; suitable for mild-to-moderate plaque psoriasis | hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression with prolonged use | Avoid continuous long-term application |
| Calcipotriol (Vitamin D3 analog) [194] | Regulation of keratinocyte proliferation/differentiation; immunomodulation | Improves hyperproliferation and differentiation; safe and effective | Local irritation (erythema, pruritus) | First-line for plaque psoriasis | |
| Tacrolimus ointment [195] | Calcineurin inhibition | High local tolerability | Burning sensation, infection risk | Suitable for mild cases or combination therapy | |
| Calcipotriol/betamethasone combo [196] | Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of Vitamin D3 analog + corticosteroid | Superior efficacy to monotherapy; reduced relapse | Reduced skin irritation vs. monotherapy | Indicated for moderate-to-thick plaques | |
| Tapinarof cream [183] | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, modulation; IL-17 suppression; skin barrier enhancement | Significant improvement in mild-to-severe plaque psoriasis | Folliculitis, local irritation | Favorable safety profile | |
| Systemic Therapies | NB-UVB [184] | local immunosuppression | First-line therapy with high safety | Frequent clinic visits; limited phototherapy center access | Suitable for pregnant patients and children |
| MTX [178] | Folate metabolism inhibition; anti-inflammatory | Effective for moderate-to-severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis | Hepatotoxicity myelosuppression, gastrointestinal disturbances | Requires regular liver function monitoring | |
| Cyclosporine [191] | Selective T-cell inhibition; IL-2 blockade | Rapid onset; used for acute flares | Nephrotoxicity, immunosuppression | renal monitoring | |
| Acitretin [189,197] | Keratinocyte differentiation modulation; anti-inflammatory | Controls hyperkeratosis; adjunct for severe psoriasis | Teratogenicity, xerosis, photosensitivity | Prohibited for pregnant women |
5.3. Biologicals
5.4. Small-Molecule Inhibitors
5.5. Alternative Therapy
6. Outlook
| Category | Drug Name | Target/Mechanism | Approval Status | Efficacy Profile | Adverse Effects/Potential Risks | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-17 monoclonal antibody | Secukinumab [201] | IL-17A neutralization; blocks IL-17A signaling | Approved (US, EU, CN, etc.) | PASI 90 response: 80–90%; rapid lesion clearance | Injection-site reactions, candidiasis | Requires infection monitoring |
| Vunakizumab (China-developed) [266] | Blocks IL-17A signaling | Approved (China) | Annual dosing: 14 injections; PASI 100 response: >70% | Low infection risk | Cost-effective domestic innovator | |
| Bimekizumab [202] | Dual IL-17A/F inhibition | Approved (EU, UK; US pending) | Superior to IL-17A monotherapy (higher PASI 100 rates) | Oral candidiasis, diarrhea | Synergistic dual-target action | |
| IL-23 monoclonal antibody | Guselkumab [267] | IL-23p19 blockade | Approved (US, EU, CN, etc.) | Q8W dosing; PASI 90 response >80% | Mild injection-site reactions, low Tuberculosis risk | Sustained long-term remission |
| Ustekinumab [198] | Dual IL-12/23p40 blockade; inhibits Th1/Th17 pathways | Approved (Global) | Long-term disease control in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis | Respiratory infections | First dual-target biologic for IL-12 and IL-23 | |
| TNF-α monoclonal antibody | Adalimumab [268] | TNF-α blockade | Approved (Global) | PASI 75 response: 70–80% in moderate-to-severe cases | Tuberculosis reactivation, potential malignancy risk | Preferred for psoriatic arthritis comorbidity |
| IL-36 monoclonal antibody | Spesolimab [204] | IL-36 blockade | Approved (US, EU, CN) | Rapid control of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) | Infections, infusion reactions | First-in-class IL-36 pathway inhibitor |
| Small-Molecule Inhibitors | Apremilast [243] | DE4 inhibitor; reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines | Approved in multiple countries | Suitable for mild-to-moderate cases; oral administration | Diarrhea, nausea, weight loss | Superior safety profile compared to traditional immunosuppressants |
| Tofacitinib [264] | JAK1/3 inhibition; blocks JAK-STAT signaling | Approved for PsA in multiple countries | Oral administration; rapid relief of articular symptoms | Infection risk, thromboembolic events | Requires long-term safety monitoring | |
| VTP-43742/PF-06763809 [242,269] | RORγt inhibition; reduces IL-17 production | Clinical trials | Novel Th17 pathway suppression with promising efficacy | Good tolerability/safety pending | First-in-class RORγt inhibitors | |
| Cell Therapies | CD19 CAR-T [173] | CD19-targeted B-cell depletion | Case reports only | Complete psoriasis remission sustained | CRS, B-cell aplasia-related infections | Mechanism unclear; target optimization needed |
| CAR-Tregs [214] | Engineered Tregs for enhanced immune suppression | Preclinical studies | Effective in experimental autoimmune models (exploratory for psoriasis) | Technical complexity, graft rejection risks | Potential tolerance-restoring approach | |
| Umbilical/Adipose MSCs [220,221,222] | Immunomodulation (paracrine effects) | Clinical trials | Good safety profile, preliminary evidence of sustained improvement in some patients | Transient fever, infusion-related reactions | Requires stringent quality control | |
| TCM Therapy | Compound Indigo Capsule [270] | Multi-target modulation | Approved (China) | Significant improvement in erythema and infiltration | Diarrhea, abdominal pain | Contraindicated in pregnancy |
| miRNA | miR-340 siRNA [206] | Downregulates IL-17A expression via RNA interference | Preclinical studies | Attenuates inflammation in murine models | Low delivery efficiency, poor stability | Requires nanocarrier optimization |
| Immunometabolic Modulator | GLS1 Inhibitor [233] | Glutamine metabolism blockade (Th17 differentiation) | Preclinical studies | Markedly improves IMQ-induced psoriasiform dermatitis in mice | Unknown | Targets metabolic reprogramming, avoids direct immunosuppression |
| Epigenetic Modulator | KAT8 Inhibitor [231] | Reduces H4K16ac (suppresses CXCL2/CCL3) | Preclinical studies | Ameliorates IMQ-induced murine model symptoms | Unknown | N/A |
| Other Investigative Drugs | CYnLIP(Nanocarrier) [210] | Co-delivers IL-36α siRNA + erlotinib | Preclinical studies | Significantly reduces murine PASI scores | Human safety unverified | Combines gene therapy + chemical drug |
| Ebosin(Streptomyces exopolysaccharide) [240] | Inhibits Th17 differentiation; modulates miR-155-TNFAIP3-IL-17 axis | Preclinical studies | Attenuates inflammation in murine models | Unclear toxicity profile | Natural product with multi-pathway modulation | |
| Antibody-Nanoparticle Conjugate [103] | Neutrophil-specific delivery of anti-inflammatory payload | Preclinical studies | Reduces systemic toxicity; site-specific action | Preclinical safety pending | Precision delivery technology prototype |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song Y, Li J, Wu Y: Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2024, 9.
- Theo Vos SSL, Cristiana Abbafati, Kaja M Abbas, Mohammad Abbasi, Mitra Abbasifard, Mohsen Abbasi-Kangevari, Hedayat Abbastabar. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD: Psoriatic Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2017, 376, 957–970. [CrossRef]
- Gelfand JM, Yeung H: Metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriatic disease. J Rheumatol Suppl 2012, 89, 24–28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robati RM, Partovi-Kia M, Haghighatkhah HR, Younespour S, Abdollahimajd F: Increased serum leptin and resistin levels and increased carotid intima-media wall thickness in patients with psoriasis: is psoriasis associated with atherosclerosis? J Am Acad Dermatol 2014, 71, 642–648. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampogna F, Tabolli S, Abeni D: Living with psoriasis: prevalence of shame, anger, worry, and problems in daily activities and social life. Acta Derm Venereol 2012, 92, 299–303. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO: The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2009, 129, 1339–1350. [CrossRef]
- Ghoreschi K, Balato A, Enerbäck C, Sabat R: Therapeutics targeting the IL-23 and IL-17 pathway in psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 754–766. [CrossRef]
- van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, Cornelissen F, Mus AM, Florencia E, Prens EP, Lubberts E: Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [CrossRef]
- Griffiths CEM, Armstrong AW, Gudjonsson JE, Barker J: Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Yao Q, Mariscal AG, Wu X, Hülse J, Pedersen E, Helin K, Waisman A, Vinkel C, Thomsen SF, et al: Epigenetic control of IL-23 expression in keratinocytes is important for chronic skin inflammation. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1420. [CrossRef]
- Dand N, Stuart PE, Bowes J, Ellinghaus D, Nititham J, Saklatvala JR, Teder-Laving M, Thomas LF, Traks T, Uebe S, et al.: GWAS meta-analysis of psoriasis identifies new susceptibility alleles impacting disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat Commun 2025, 16, 2051. [CrossRef]
- Mallon E, Bunce M, Savoie H, Rowe A, Newson R, Gotch F, Bunker CB: HLA-C and guttate psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 2000, 143, 1177–1182.
- Chen YL, Ng JSW, Ottakandathil Babu R, Woo J, Nahler J, Hardman CS, Kurupati P, Nussbaum L, Gao F, Dong T, et al.: Group A Streptococcus induces CD1a-autoreactive T cells and promotes psoriatic inflammation. Sci Immunol, 2023; 8, eadd9232.
- Yen YF, Chuang PH, Jen IA, Chen M, Lan YC, Liu YL, Lee Y, Chen YH, Chen YA: Incidence of autoimmune diseases in a nationwide HIV/AIDS patient cohort in Taiwan, 2000–2012. Ann Rheum Dis 2017, 76, 661–665. [CrossRef]
- Kim Alexander Papp WG, Charles W Lynde, Yves Poulin, David Adam, Benjamin Barankin, Kirk Barber, Marc Bourcier, Melinda Gooderham, Lyn C Guenther, Vincent C Ho, Andrei Metelitsa, Neil H Shear, Ronald B Vender, Norman Wasel, Marni C Wiseman: 2016 Addendum to the Canadian Guidelines for the Management of Plaque Psoriasis 2009. J Cutan Med Surg 2016, 20, 375–431.
- Khoroshun K, Bantel C, Hoffmann F, Jobski K: Methotrexate-related drug reactions on kidneys and liver in rheumatoid arthritis: an analysis of spontaneous reports in EudraVigilance. Arthritis Res Ther 2025, 27, 80. [CrossRef]
- Krupp P, Monka C: Side-effect profile of cyclosporin A in patients treated for psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 1990, 122 Suppl 36, 47–56.
- Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, Reich K, Griffiths CE, Papp K, Puig L, Nakagawa H, Spelman L, Sigurgeirsson B, et al: Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis--results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med 2014, 371, 326–338. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich K, Armstrong AW, Langley RG, Flavin S, Randazzo B, Li S, Hsu MC, Branigan P, Blauvelt A: Guselkumab versus secukinumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis (ECLIPSE): results from a phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 831–839. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, et al.: Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [CrossRef]
- Danielsen K, Olsen AO, Wilsgaard T, Furberg AS: Is the prevalence of psoriasis increasing? A 30-year follow-up of a population-based cohort. Br J Dermatol 2013, 168, 1303–1310. [CrossRef]
- Gibbs S: Skin disease and socioeconomic conditions in rural Africa: Tanzania. Int J Dermatol 1996, 35, 633–639. [CrossRef]
- Luo H: Global burden and cross-country inequalities in six major immune-mediated inflammatory diseases from 1990 to 2021: A systemic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Autoimmun Rev 2024, 23, 103639. [CrossRef]
- Wang K, Zhao Y, Cao X: Global burden and future trends in psoriasis epidemiology: insights from the global burden of disease study 2019 and predictions to 2030. Arch Dermatol Res 2024, 316, 114. [CrossRef]
- Wu J, Ma Y, Yang J, Tian Y: Exposure to Air Pollution, Genetic Susceptibility, and Psoriasis Risk in the UK. JAMA Netw Open 2024, 7, e2421665. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehncke WH, Schön MP: Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu Y, Lee CH, Chi CC: Association of Psoriasis With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol 2018, 154, 1417–1423. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan Z, Lu T, Chen Y, Yuan M, Yu H, Liu R, Xie X: Association Between Psoriasis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among Outpatient US Adults. JAMA Dermatol 2022, 158, 745–753. [CrossRef]
- Ramessur R, Saklatvala J, Budu-Aggrey A, Ostaszewski M, Möbus L, Greco D, Ndlovu M, Mahil SK, Barker JN, Brown S, et al.: Exploring the Link Between Genetic Predictors of Cardiovascular Disease and Psoriasis. JAMA Cardiol 2024, 9, 1009–1017. [CrossRef]
- Takeshita J, Grewal S, Langan SM, Mehta NN, Ogdie A, Van Voorhees AS, Gelfand JM: Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: Epidemiology. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017, 76, 377–390.
- Branisteanu DE, Pirvulescu RA, Spinu AE, Porumb EA, Cojocaru M, Nicolescu AC, Branisteanu DC, Branisteanu CI, Dimitriu A, Alexa AI, Toader MP: Metabolic comorbidities of psoriasis (Review). Exp Ther Med 2022, 23, 179.
- Pouplard C, Brenaut E, Horreau C, Barnetche T, Misery L, Richard MA, Aractingi S, Aubin F, Cribier B, Joly P, et al.: Risk of cancer in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2013; 27, (Suppl 3), 36–46.
- Ryan C, Sadlier M, De Vol E, Patel M, Lloyd AA, Day A, Lally A, Kirby B, Menter A: Genital psoriasis is associated with significant impairment in quality of life and sexual functioning. J Am Acad Dermatol 2015, 72, 978–983. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh S, Taylor C, Kornmehl H, Armstrong AW: Psoriasis and suicidality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017, 77, 425–440.e422. [CrossRef]
- Rompoti N, Tsiori S, Kontoangelos K, Kouzoupis A, Papageorgiou C, Gregoriou S, Stratigos A, Rigopoulos D: Psychopathological Profile of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis and Its Correlation to DLQI: Results from a Prospective, Monocentric Clinical Study. J Clin Med 2024, 13.
- Rendon A, Schäkel K: Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 1475. [CrossRef]
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN: Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 2007, 370, 263–271. [CrossRef]
- Mehta S, Singal A, Singh N, Bhattacharya SN: A study of clinicohistopathological correlation in patients of psoriasis and psoriasiform dermatitis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2009, 75, 100. [CrossRef]
- Dupire G, Droitcourt C, Hughes C, Le Cleach L: Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019, 3, Cd011571.
- Martin BA, Chalmers RJ, Telfer NR: How great is the risk of further psoriasis following a single episode of acute guttate psoriasis? Arch Dermatol 1996, 132, 717–718. [CrossRef]
- Singh RK, Lee KM, Ucmak D, Brodsky M, Atanelov Z, Farahnik B, Abrouk M, Nakamura M, Zhu TH, Liao W: Erythrodermic psoriasis: pathophysiology and current treatment perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl) 2016, 6, 93–104.
- Augustin M, Reich K, Blome C, Schäfer I, Laass A, Radtke MA: Nail psoriasis in Germany: epidemiology and burden of disease. Br J Dermatol 2010, 163, 580–585.
- Park JH, Park YJ, Kim SK, Kwon JE, Kang HY, Lee ES, Choi JH, Kim YC: Histopathological Differential Diagnosis of Psoriasis and Seborrheic Dermatitis of the Scalp. Ann Dermatol 2016, 28, 427–432. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi LC, Stuart PE, Tian C, Gudjonsson JE, Das S, Zawistowski M, Ellinghaus E, Barker JN, Chandran V, Dand N, et al.: Large scale meta-analysis characterizes genetic architecture for common psoriasis associated variants. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 15382. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang H, Jin X, Li Y, Jiang H, Tang X, Yang X, Cheng H, Qiu Y, Chen G, Mei J, et al.: A large-scale screen for coding variants predisposing to psoriasis. Nat Genet 2014, 46, 45–50. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun LD, Cheng H, Wang ZX, Zhang AP, Wang PG, Xu JH, Zhu QX, Zhou HS, Ellinghaus E, Zhang FR, et al.: Association analyses identify six new psoriasis susceptibility loci in the Chinese population. Nat Genet 2010, 42, 1005–1009. [CrossRef]
- Lønnberg AS, Skov L, Skytthe A, Kyvik KO, Pedersen OB, Thomsen SF: Heritability of psoriasis in a large twin sample. Br J Dermatol 2013, 169, 412–416. [CrossRef]
- Antonatos C, Grafanaki K, Asmenoudi P, Xiropotamos P, Nani P, Georgakilas GK, Georgiou S, Vasilopoulos Y: Contribution of the Environment, Epigenetic Mechanisms and Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis. Biomedicines 2022, 10.
- Della Bella C, Corrà A, Mantengoli E, Galano A, Benagiano M, Bonciani D, Mariotti EB, Pratesi S, Quintarelli L, Aimo C, et al. : Skin IL-17A and IFN-γ Production Correlate with Disease Severity in Patients with Psoriasis and Streptococcal Infection. J Invest Dermatol 2023, 143, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa A, Siewert K, Stöhr J, Besgen P, Kim SM, Rühl G, Nickel J, Vollmer S, Thomas P, Krebs S, et al.: Melanocyte antigen triggers autoimmunity in human psoriasis. J Exp Med 2015, 212, 2203–2212. [CrossRef]
- Arakawa A, Reeves E, Vollmer S, Arakawa Y, He M, Galinski A, Stöhr J, Dornmair K, James E, Prinz JC: ERAP1 Controls the Autoimmune Response against Melanocytes in Psoriasis by Generating the Melanocyte Autoantigen and Regulating Its Amount for HLA-C*06:02 Presentation. J Immunol 2021, 207, 2235–2244.
- Shen Z, Wang G, Fan JY, Li W, Liu YF: HLA DR B1*04, *07-restricted epitopes on Keratin 17 for autoreactive T cells in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci 2005, 38, 25–39. [CrossRef]
- Cargill M, Schrodi SJ, Chang M, Garcia VE, Brandon R, Callis KP, Matsunami N, Ardlie KG, Civello D, Catanese JJ, et al.: A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am J Hum Genet 2007, 80, 273–290. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu H, Lou F, Yin Q, Gao Y, Sun Y, Bai J, Xu Z, Liu Z, Cai W, Ke F, et al.: RIG-I antiviral signaling drives interleukin-23 production and psoriasis-like skin disease. EMBO Mol Med 2017, 9, 589–604. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi M, Hirota T, Saeki H, Nakagawa H, Ishiuji Y, Matsuzaki H, Tsunemi Y, Kato T, Shibata S, Sugaya M, et al.: Genetic polymorphism in the TRAF3IP2 gene is associated with psoriasis vulgaris in a Japanese population. J Dermatol Sci 2014, 73, 264–265. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden JL, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM: The immunogenetics of Psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 2015, 64, 66–73. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng Y, Xie W, Tao X, Liu N, Yu Y, Huang Y, Xu D, Fan Y: Infection-provoked psoriasis: Induced or aggravated (Review). Exp Ther Med 2021, 21, 567. [CrossRef]
- Assarsson M, Söderman J, Seifert O: Significant Correlation Between Cutaneous Abundance of Streptococcus and Psoriasis Severity in Patients with FBXL19 Gene Variants. Acta Derm Venereol, 2024; 104, adv34892.
- Gudmundsdottir AS, Sigmundsdottir H, Sigurgeirsson B, Good MF, Valdimarsson H, Jonsdottir I: Is an epitope on keratin 17 a major target for autoreactive T lymphocytes in psoriasis? Clin Exp Immunol 1999, 117, 580–586.
- Johnston A, Gudjonsson JE, Sigmundsdottir H, Love TJ, Valdimarsson H: Peripheral blood T cell responses to keratin peptides that share sequences with streptococcal M proteins are largely restricted to skin-homing CD8(+) T cells. Clin Exp Immunol 2004, 138, 83–93. [CrossRef]
- Morar N, Willis-Owen SA, Maurer T, Bunker CB: HIV-associated psoriasis: pathogenesis, clinical features, and management. Lancet Infect Dis 2010, 10, 470–478. [CrossRef]
- Fuchs D, Hausen A, Reibnegger G, Werner ER, Dierich MP, Wachter H: Psoriasis, gamma-interferon, and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med 1987, 106, 165. [CrossRef]
- Liu S, He M, Jiang J, Duan X, Chai B, Zhang J, Tao Q, Chen H: Triggers for the onset and recurrence of psoriasis: a review and update. Cell Communication and Signaling 2024, 22.
- Aram K, Patil A, Goldust M, Rajabi F: COVID-19 and exacerbation of dermatological diseases: A review of the available literature. Dermatol Ther 2021, 34, e15113. [CrossRef]
- Chen ML, Kao WM, Huang JY, Hung YM, Wei JC: Human papillomavirus infection associated with increased risk of new-onset psoriasis: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 2020, 49, 786–797. [CrossRef]
- Rousset L, Halioua B: Stress and psoriasis. Int J Dermatol 2018, 57, 1165–1172. [CrossRef]
- Woźniak E, Owczarczyk-Saczonek A, Placek W: Psychological Stress, Mast Cells, and Psoriasis-Is There Any Relationship? Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22.
- Kanda N, Watanabe S: Regulatory roles of sex hormones in cutaneous biology and immunology. J Dermatol Sci 2005, 38, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Adachi A, Honda T: Regulatory Roles of Estrogens in Psoriasis. J Clin Med 2022, 11.
- Cemil BC, Cengiz FP, Atas H, Ozturk G, Canpolat F: Sex hormones in male psoriasis patients and their correlation with the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index. J Dermatol 2015, 42, 500–503. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi K, Chikazawa S, Chen Y, Suzuki S, Ichimasu N, Katagiri K: Oestrogen inhibits psoriasis-like dermatitis induced by imiquimod in mice in relation to increased IL-10 producing cells despite elevated expression of IL-22, IL-23, IL-17 mRNA. Exp Dermatol 2023, 32, 203–209. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terán-Pérez G, Arana-Lechuga Y, Esqueda-León E, Santana-Miranda R, Rojas-Zamorano J, Velázquez Moctezuma J: Steroid hormones and sleep regulation. Mini Rev Med Chem 2012, 12, 1040–1048.
- Paus R, Theoharides TC, Arck PC: Neuroimmunoendocrine circuitry of the ‘brain-skin connection’. Trends Immunol 2006, 27, 32–39. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei J, Zhu J, Xu H, Zhou D, Elder JT, Tsoi LC, Patrick MT, Li Y: Alcohol consumption and smoking in relation to psoriasis: a Mendelian randomization study. Br J Dermatol 2022, 187, 684–691. [CrossRef]
- Brenaut E, Horreau C, Pouplard C, Barnetche T, Paul C, Richard MA, Joly P, Le Maître M, Aractingi S, Aubin F, et al.: Alcohol consumption and psoriasis: a systematic literature review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2013; 3, (Suppl 3), 30–35.
- Murzaku EC, Bronsnick T, Rao BK: Diet in dermatology: Part II. Melanoma, chronic urticaria, and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014, 71, 1053.e1051–1053.e1016.
- Dai YX, Wang SC, Chou YJ, Chang YT, Chen TJ, Li CP, Wu CY: Smoking, but not alcohol, is associated with risk of psoriasis in a Taiwanese population-based cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2019, 80, 727–734. [CrossRef]
- Nestle FO, Di Meglio P, Qin JZ, Nickoloff BJ: Skin immune sentinels in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009, 9, 679–691. [CrossRef]
- Perera GK, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO: Psoriasis. Annu Rev Pathol 2012, 7, 385–422. [CrossRef]
- Zhang LJ, Sen GL, Ward NL, Johnston A, Chun K, Chen Y, Adase C, Sanford JA, Gao N, Chensee M, et al.: Antimicrobial Peptide LL37 and MAVS Signaling Drive Interferon-β Production by Epidermal Keratinocytes during Skin Injury. Immunity 2016, 45, 119–130. [CrossRef]
- Zhou X, Chen Y, Cui L, Shi Y, Guo C: Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: from keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 81. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanesi C, Madonna S, Gisondi P, Girolomoni G: The Interplay Between Keratinocytes and Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 1549. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan S, Xu Z, Lou F, Zhang L, Ke F, Bai J, Liu Z, Liu J, Wang H, Zhu H, et al: NF-κB-induced microRNA-31 promotes epidermal hyperplasia by repressing protein phosphatase 6 in psoriasis. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 7652. [CrossRef]
- Silva de Melo BM, Veras FP, Zwicky P, Lima D, Ingelfinger F, Martins TV, da Silva Prado D, Schärli S, Publio G, Hiroki CH, et al: S100A9 Drives the Chronification of Psoriasiform Inflammation by Inducing IL-23/Type 3 Immunity. J Invest Dermatol 2023, 143, 1678–1688.e1678. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homey B, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Wiesenborn A, Massacrier C, Pin JJ, Oldham E, Catron D, Buchanan ME, Müller A, deWaal Malefyt R, et al: Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha/CCL20 and CC chemokine receptor 6 in psoriasis. J Immunol 2000, 164, 6621–6632. [CrossRef]
- Müller A, Hennig A, Lorscheid S, Grondona P, Schulze-Osthoff K, Hailfinger S, Kramer D: IκBζ is a key transcriptional regulator of IL-36-driven psoriasis-related gene expression in keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, 10088–10093. [CrossRef]
- Ekman AK, Bivik Eding C, Rundquist I, Enerbäck C: IL-17 and IL-22 Promote Keratinocyte Stemness in the Germinative Compartment in Psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2019, 139, 1564–1573.e1568. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes MA, Suárez-Fariñas M, Krueger JG: Immunology of psoriasis. Annu Rev Immunol 2014, 32, 227–255. [CrossRef]
- Lou F, Sun Y, Xu Z, Niu L, Wang Z, Deng S, Liu Z, Zhou H, Bai J, Yin Q, et al: Excessive Polyamine Generation in Keratinocytes Promotes Self-RNA Sensing by Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis. Immunity 2020, 53, 204–216.e210. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Rosales YA, Langereis JD, Gorris MAJ, van den Reek J, Fasse E, Netea MG, de Vries IJM, Gomez-Muñoz L, van Cranenbroek B, Körber A, et al.: Immunomodulatory aged neutrophils are augmented in blood and skin of psoriasis patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2021, 148, 1030–1040. [CrossRef]
- Katayama H: Development of psoriasis by continuous neutrophil infiltration into the epidermis. Exp Dermatol 2018, 27, 1084–1091. [CrossRef]
- Schön MP, Krahn T, Schön M, Rodriguez ML, Antonicek H, Schultz JE, Ludwig RJ, Zollner TM, Bischoff E, Bremm KD, et al.: Efomycine M, a new specific inhibitor of selectin, impairs leukocyte adhesion and alleviates cutaneous inflammation. Nat Med 2002, 8, 366–372. [CrossRef]
- Senra L, Mylonas A, Kavanagh RD, Fallon PG, Conrad C, Borowczyk-Michalowska J, Wrobel LJ, Kaya G, Yawalkar N, Boehncke WH, Brembilla NC: IL-17E (IL-25) Enhances Innate Immune Responses during Skin Inflammation. J Invest Dermatol 2019, 139, 1732–1742.e1717. [CrossRef]
- Lin AM, Rubin CJ, Khandpur R, Wang JY, Riblett M, Yalavarthi S, Villanueva EC, Shah P, Kaplan MJ, Bruce AT: Mast cells and neutrophils release IL-17 through extracellular trap formation in psoriasis. J Immunol 2011, 187, 490–500. [CrossRef]
- Herster F, Bittner Z, Archer NK, Dickhöfer S, Eisel D, Eigenbrod T, Knorpp T, Schneiderhan-Marra N, Löffler MW, Kalbacher H, et al.: Neutrophil extracellular trap-associated RNA and LL37 enable self-amplifying inflammation in psoriasis. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 105. [CrossRef]
- Shao S, Fang H, Dang E, Xue K, Zhang J, Li B, Qiao H, Cao T, Zhuang Y, Shen S, et al.: Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Inflammatory Responses in Psoriasis via Activating Epidermal TLR4/IL-36R Crosstalk. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 746. [CrossRef]
- Ma F, Plazyo O, Billi AC, Tsoi LC, Xing X, Wasikowski R, Gharaee-Kermani M, Hile G, Jiang Y, Harms PW, et al: Single cell and spatial sequencing define processes by which keratinocytes and fibroblasts amplify inflammatory responses in psoriasis. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3455. [CrossRef]
- Hu SC, Yu HS, Yen FL, Lin CL, Chen GS, Lan CC: Neutrophil extracellular trap formation is increased in psoriasis and induces human β-defensin-2 production in epidermal keratinocytes. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 31119. [CrossRef]
- Shao S, Fang H, Zhang J, Jiang M, Xue K, Ma J, Zhang J, Lei J, Zhang Y, Li B, et al.: Neutrophil exosomes enhance the skin autoinflammation in generalized pustular psoriasis via activating keratinocytes. Faseb j 2019, 33, 6813–6828. [CrossRef]
- Liu XT, Shi ZR, Lu SY, Hong D, Qiu XN, Tan GZ, Xiong H, Guo Q, Wang L: Enhanced Migratory Ability of Neutrophils Toward Epidermis Contributes to the Development of Psoriasis via Crosstalk With Keratinocytes by Releasing IL-17A. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 817040. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen J, Zhu Z, Li Q, Lin Y, Dang E, Meng H, Sha N, Bai H, Wang G, An S, Shao S: Neutrophils Enhance Cutaneous Vascular Dilation and Permeability to Aggravate Psoriasis by Releasing Matrix Metallopeptidase 9. J Invest Dermatol 2021, 141, 787–799. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin CY, Yu HP, Chang YT, Lin ZC, Alalaiwe A, Hwang TL, Fang JY: Targeting anti-inflammatory immunonanocarriers to human and murine neutrophils via the Ly6 antigen for psoriasiform dermatitis alleviation. Biomater Sci 2023, 11, 873–893. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes MA, Chamian F, Abello MV, Fuentes-Duculan J, Lin SL, Nussbaum R, Novitskaya I, Carbonaro H, Cardinale I, Kikuchi T, et al.: Increase in TNF-alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressing dendritic cells in psoriasis and reduction with efalizumab (anti-CD11a). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 19057–19062. [CrossRef]
- Terhorst D, Chelbi R, Wohn C, Malosse C, Tamoutounour S, Jorquera A, Bajenoff M, Dalod M, Malissen B, Henri S: Dynamics and Transcriptomics of Skin Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in an Imiquimod-Induced, Biphasic Mouse Model of Psoriasis. J Immunol 2015, 195, 4953–4961. [CrossRef]
- Cheng JB, Sedgewick AJ, Finnegan AI, Harirchian P, Lee J, Kwon S, Fassett MS, Golovato J, Gray M, Ghadially R, et al: Transcriptional Programming of Normal and Inflamed Human Epidermis at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Rep 2018, 25, 871–883. [CrossRef]
- Zaba LC, Fuentes-Duculan J, Eungdamrong NJ, Abello MV, Novitskaya I, Pierson KC, Gonzalez J, Krueger JG, Lowes MA: Psoriasis is characterized by accumulation of immunostimulatory and Th1/Th17 cell-polarizing myeloid dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol 2009, 129, 79–88. [CrossRef]
- Rebane A, Zimmermann M, Aab A, Baurecht H, Koreck A, Karelson M, Abram K, Metsalu T, Pihlap M, Meyer N, et al.: Mechanisms of IFN-γ-induced apoptosis of human skin keratinocytes in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012, 129, 1297–1306. [CrossRef]
- Nestle FO, Conrad C, Tun-Kyi A, Homey B, Gombert M, Boyman O, Burg G, Liu YJ, Gilliet M: Plasmacytoid predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-alpha production. J Exp Med 2005, 202, 135–143. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou Y, Xu F, Chen XY, Yan BX, Wang ZY, Chen SQ, Zheng M, Man XY: The epidermal immune microenvironment plays a dominant role in psoriasis development, as revealed by mass cytometry. Cell Mol Immunol 2022, 19, 1400–1413. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borek I, Köffel R, Feichtinger J, Spies M, Glitzner-Zeis E, Hochgerner M, Sconocchia T, Krump C, Tam-Amersdorfer C, Passegger C, et al.: BMP7 aberrantly induced in the psoriatic epidermis instructs inflammation-associated Langerhans cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020, 145, 1194–1207.e1111. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiki R, Kabashima K, Honda T, Nakamizo S, Sawada Y, Sugita K, Yoshioka H, Ohmori S, Malissen B, Tokura Y, Nakamura M: IL-23 from Langerhans cells is required for the development of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis by induction of IL-17A-producing γδ T cells. J Invest Dermatol 2014, 134, 1912–1921.
- Zheng T, Zhao W, Li H, Xiao S, Hu R, Han M, Liu H, Liu Y, Otsu K, Liu X, Huang G: p38α signaling in Langerhans cells promotes the development of IL-17-producing T cells and psoriasiform skin inflammation. Sci Signal 2018, 11.
- Martini E, Wikén M, Cheuk S, Gallais Sérézal I, Baharom F, Ståhle M, Smed-Sörensen A, Eidsmo L: Dynamic Changes in Resident and Infiltrating Epidermal Dendritic Cells in Active and Resolved Psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2017, 137, 865–873. [CrossRef]
- Fujita H, Shemer A, Suárez-Fariñas M, Johnson-Huang LM, Tintle S, Cardinale I, Fuentes-Duculan J, Novitskaya I, Carucci JA, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E: Lesional dendritic cells in patients with chronic atopic dermatitis and psoriasis exhibit parallel ability to activate T-cell subsets. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011, 128, e571–e512.
- Wang Y, Edelmayer R, Wetter J, Salte K, Gauvin D, Leys L, Paulsboe S, Su Z, Weinberg I, Namovic M, et al.: Monocytes/Macrophages play a pathogenic role in IL-23 mediated psoriasis-like skin inflammation. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 5310. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang H, Peters T, Kess D, Sindrilaru A, Oreshkova T, Van Rooijen N, Stratis A, Renkl AC, Sunderkötter C, Wlaschek M, et al.: Activated macrophages are essential in a murine model for T cell-mediated chronic psoriasiform skin inflammation. J Clin Invest 2006, 116, 2105–2114. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratis A, Pasparakis M, Rupec RA, Markur D, Hartmann K, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Peters T, van Rooijen N, Krieg T, Haase I: Pathogenic role for skin macrophages in a mouse model of keratinocyte-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Clin Invest 2006, 116, 2094–2104. [CrossRef]
- Erbel C, Akhavanpoor M, Okuyucu D, Wangler S, Dietz A, Zhao L, Stellos K, Little KM, Lasitschka F, Doesch A, et al.: IL-17A influences essential functions of the monocyte/macrophage lineage and is involved in advanced murine and human atherosclerosis. J Immunol 2014, 193, 4344–4355. [CrossRef]
- Sieminska I, Pieniawska M, Grzywa TM: The Immunology of Psoriasis-Current Concepts in Pathogenesis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2024, 66, 164–191. [CrossRef]
- Kolkhir P, Elieh-Ali-Komi D, Metz M, Siebenhaar F, Maurer M: Understanding human mast cells: lesson from therapies for allergic and non-allergic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2022, 22, 294–308. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli SJ, Gaudenzio N, Tsai M: Mast Cells in Inflammation and Disease: Recent Progress and Ongoing Concerns. Annu Rev Immunol 2020, 38, 49–77. [CrossRef]
- Cheung KL, Jarrett R, Subramaniam S, Salimi M, Gutowska-Owsiak D, Chen YL, Hardman C, Xue L, Cerundolo V, Ogg G: Psoriatic T cells recognize neolipid antigens generated by mast cell phospholipase delivered by exosomes and presented by CD1a. J Exp Med 2016, 213, 2399–2412. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou T, Du X, Zhang L, Zheng Y, Jia T, Song X, Che D, Geng S: Suprabasin-derived polypeptides: SBSN(50–63) induces inflammatory response via TLR4-mediated mast cell activation. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1329–1339. [CrossRef]
- Ji YZ, Liu SR: Koebner phenomenon leading to the formation of new psoriatic lesions: evidences and mechanisms. Biosci Rep 2019, 39.
- Ribot JC, Lopes N, Silva-Santos B: γδ T cells in tissue physiology and surveillance. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 221–232. [CrossRef]
- Cai Y, Xue F, Quan C, Qu M, Liu N, Zhang Y, Fleming C, Hu X, Zhang HG, Weichselbaum R, et al.: A Critical Role of the IL-1β-IL-1R Signaling Pathway in Skin Inflammation and Psoriasis Pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 2019, 139, 146–156. [CrossRef]
- Laggner U, Di Meglio P, Perera GK, Hundhausen C, Lacy KE, Ali N, Smith CH, Hayday AC, Nickoloff BJ, Nestle FO: Identification of a novel proinflammatory human skin-homing Vγ9Vδ2 T cell subset with a potential role in psoriasis. J Immunol 2011, 187, 2783–2793. [CrossRef]
- Peng P, Lou Y, Wang S, Wang J, Zhang Z, Du P, Zheng J, Liu P, Xu LX: Activated NK cells reprogram MDSCs via NKG2D-NKG2DL and IFN-γ to modulate antitumor T-cell response after cryo-thermal therapy. J Immunother Cancer 2022, 10.
- Choi Y, Saron WA, O’Neill A, Senanayake M, Wilder-Smith A, Rathore AP, St John AL: NKT cells promote Th1 immune bias to dengue virus that governs long-term protective antibody dynamics. J Clin Invest 2024, 134.
- Venken K, Jacques P, Mortier C, Labadia ME, Decruy T, Coudenys J, Hoyt K, Wayne AL, Hughes R, Turner M, et al.: RORγt inhibition selectively targets IL-17 producing iNKT and γδ-T cells enriched in Spondyloarthritis patients. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu Y, Chen Y, Chen Z, Zhang X, Guo C, Yu Z, Xu P, Sun L, Zhou X, Gong Y, et al: Dysregulated Peripheral Invariant Natural Killer T Cells in Plaque Psoriasis Patients. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 799560.
- Liu P, Peng C, Chen X, Wu L, Yin M, Li J, Qin Q, Kuang Y, Zhu W: Acitretin Promotes the Differentiation of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Treatment of Psoriasis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 625130.
- Sarkar D, Pramanik A, Das D, Bhattacharyya S: Shifting phenotype and differentiation of CD11b(+)Gr1(+) immature heterogeneous myeloid derived adjuster cells support inflammation and induce regulators of IL17A in imiquimod induced psoriasis. Inflamm Res 2024, 73, 1581–1599. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic DV, Di Battista JA, Martel-Pelletier J, Jolicoeur FC, He Y, Zhang M, Mineau F, Pelletier JP: IL-17 stimulates the production and expression of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-beta and TNF-alpha, by human macrophages. J Immunol 1998, 160, 3513–3521. [CrossRef]
- Albanesi C, Cavani A, Girolomoni G: IL-17 is produced by nickel-specific T lymphocytes and regulates ICAM-1 expression and chemokine production in human keratinocytes: synergistic or antagonist effects with IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. J Immunol 1999, 162, 494–502. [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi M, Kokubu F, Odaka M, Watanabe S, Suzuki S, Ieki K, Matsukura S, Kurokawa M, Adachi M, Huang SK: Induction of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by a new cytokine, ML-1 (IL-17F), via Raf I-MEK-ERK pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004, 114, 444–450. [CrossRef]
- Johnston A, Fritz Y, Dawes SM, Diaconu D, Al-Attar PM, Guzman AM, Chen CS, Fu W, Gudjonsson JE, McCormick TS, Ward NL: Keratinocyte overexpression of IL-17C promotes psoriasiform skin inflammation. J Immunol 2013, 190, 2252–2262. [CrossRef]
- Yeste A, Mascanfroni ID, Nadeau M, Burns EJ, Tukpah AM, Santiago A, Wu C, Patel B, Kumar D, Quintana FJ: IL-21 induces IL-22 production in CD4+ T cells. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 3753. [CrossRef]
- Hammer AM, Morris NL, Cannon AR, Khan OM, Gagnon RC, Movtchan NV, van Langeveld I, Li X, Gao B, Choudhry MA: Interleukin-22 Prevents Microbial Dysbiosis and Promotes Intestinal Barrier Regeneration Following Acute Injury. Shock 2017, 48, 657–665. [CrossRef]
- Bunte K, Beikler T: Th17 Cells and the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in the Pathogenesis of Periodontitis and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20.
- Chang HW, Yan D, Singh R, Liu J, Lu X, Ucmak D, Lee K, Afifi L, Fadrosh D, Leech J, et al: Alteration of the cutaneous microbiome in psoriasis and potential role in Th17 polarization. Microbiome 2018, 6, 154.
- Zheng Y, Danilenko DM, Valdez P, Kasman I, Eastham-Anderson J, Wu J, Ouyang W: Interleukin-22, a T(H)17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature 2007, 445, 648–651. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifari S, Kaplan CD, Tran EH, Crellin NK, Spits H: Identification of a human helper T cell population that has abundant production of interleukin 22 and is distinct from T(H)-17, T(H)1 and T(H)2 cells. Nat Immunol 2009, 10, 864–871. [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach C, Gehad A, Yang C, Watanabe R, Guenova E, Teague JE, Campbell L, Yawalkar N, Kupper TS, Clark RA: Human TH9 cells are skin-tropic and have autocrine and paracrine proinflammatory capacity. Sci Transl Med 2014, 6, 219ra218.
- Singh TP, Schön MP, Wallbrecht K, Gruber-Wackernagel A, Wang XJ, Wolf P: Involvement of IL-9 in Th17-associated inflammation and angiogenesis of psoriasis. PLoS One, 2013; 8, e51752.
- Niu J, Song Z, Yang X, Zhai Z, Zhong H, Hao F: Increased circulating follicular helper T cells and activated B cells correlate with disease severity in patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2015, 29, 1791–1796. [CrossRef]
- Austin LM, Ozawa M, Kikuchi T, Walters IB, Krueger JG: The majority of epidermal T cells in Psoriasis vulgaris lesions can produce type 1 cytokines, interferon-gamma, interleukin-2, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, defining TC1 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) and TH1 effector populations: a type 1 differentiation bias is also measured in circulating blood T cells in psoriatic patients. J Invest Dermatol 1999, 113, 752–759.
- Guenova E, Skabytska Y, Hoetzenecker W, Weindl G, Sauer K, Tham M, Kim KW, Park JH, Seo JH, Ignatova D, et al: IL-4 abrogates T(H)17 cell-mediated inflammation by selective silencing of IL-23 in antigen-presenting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, 2163–2168. [CrossRef]
- Huang C, Sun P-Y, Jiang Y, Liu Y, Liu Z, Han S-L, Wang B-S, Huang Y-X, Ren A-R, Lu, J.-F, et al.: Sensory ASIC3 channel exacerbates psoriatic inflammation via a neurogenic pathway in female mice. Nature Communications, 2024; 15.
- Baker BS, Laman JD, Powles A, van der Fits L, Voerman JS, Melief MJ, Fry L: Peptidoglycan and peptidoglycan-specific Th1 cells in psoriatic skin lesions. J Pathol 2006, 209, 174–181. [CrossRef]
- Baker BS, Powles A, Fry L: Peptidoglycan: a major aetiological factor for psoriasis? Trends Immunol 2006, 27, 545–551. [CrossRef]
- Menssen A, Trommler P, Vollmer S, Schendel D, Albert E, Gürtler L, Riethmüller G, Prinz JC: Evidence for an antigen-specific cellular immune response in skin lesions of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Immunol 1995, 155, 4078–4083. [CrossRef]
- Lin WJ, Norris DA, Achziger M, Kotzin BL, Tomkinson B: Oligoclonal expansion of intraepidermal T cells in psoriasis skin lesions. J Invest Dermatol 2001, 117, 1546–1553. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelyushin S, Haak S, Ingold B, Kulig P, Heppner FL, Navarini AA, Becher B: Rorγt+ innate lymphocytes and γδ T cells initiate psoriasiform plaque formation in mice. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, 2252–2256. [CrossRef]
- Zhang YY, Lin YT, Wang L, Sun XW, Dang EL, Xue K, Zhang WG, Zhang KM, Wang G, Li B: CD8αα(+)T cells exert a pro-inflammatory role in patients with psoriasis. Skin Health Dis, 2021; 1, e64.
- Diani M, Casciano F, Marongiu L, Longhi M, Altomare A, Pigatto PD, Secchiero P, Gambari R, Banfi G, Manfredi AA, et al: Increased frequency of activated CD8(+) T cell effectors in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10870. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meglio P, Villanova F, Navarini AA, Mylonas A, Tosi I, Nestle FO, Conrad C: Targeting CD8(+) T cells prevents psoriasis development. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016, 138, 274–276.e276.
- Cheuk S, Wikén M, Blomqvist L, Nylén S, Talme T, Ståhle M, Eidsmo L: Epidermal Th22 and Tc17 cells form a localized disease memory in clinically healed psoriasis. J Immunol 2014, 192, 3111–3120. [CrossRef]
- Migayron L, Merhi R, Seneschal J, Boniface K: Resident memory T cells in nonlesional skin and healed lesions of patients with chronic inflammatory diseases: Appearances can be deceptive. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2024, 153, 606–614. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng G, Zhang Y, Song J, Zhang Y, Zheng Q, Luo Y, Fei X, Yang Y, Kuai L, Li B, Luo Y: The role and therapeutic strategies for tissue-resident memory T cells, central memory T cells, and effector memory T cells in psoriasis. Immunology 2024, 173, 470–480. [CrossRef]
- Matos TR, O’Malley JT, Lowry EL, Hamm D, Kirsch IR, Robins HS, Kupper TS, Krueger JG, Clark RA: Clinically resolved psoriatic lesions contain psoriasis-specific IL-17-producing αβ T cell clones. J Clin Invest 2017, 127, 4031–4041. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee BH, Bang YJ, Lim SH, Kang SJ, Kim SH, Kim-Schulze S, Park CG, Kim HJ, Kim TG: High-dimensional profiling of regulatory T cells in psoriasis reveals an impaired skin-trafficking property. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104985.
- Sugiyama H, Gyulai R, Toichi E, Garaczi E, Shimada S, Stevens SR, McCormick TS, Cooper KD: Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation. J Immunol 2005, 174, 164–173. [CrossRef]
- Yang L, Li B, Dang E, Jin L, Fan X, Wang G: Impaired function of regulatory T cells in patients with psoriasis is mediated by phosphorylation of STAT3. J Dermatol Sci 2016, 81, 85–92. [CrossRef]
- Sivasami P, Elkins C, Diaz-Saldana PP, Goss K, Peng A, Hamersky Mt, Bae J, Xu M, Pollack BP, Horwitz EM, et al: Obesity-induced dysregulation of skin-resident PPARγ(+) Treg cells promotes IL-17A-mediated psoriatic inflammation. Immunity 2023, 56, 1844–1861.e1846. [CrossRef]
- Lu J, Ding Y, Yi X, Zheng J: CD19+ B cell subsets in the peripheral blood and skin lesions of psoriasis patients and their correlations with disease severity. Braz J Med Biol Res 2016, 49, e5374.
- Jones DA, Yawalkar N, Suh KY, Sadat S, Rich B, Kupper TS: Identification of autoantigens in psoriatic plaques using expression cloning. J Invest Dermatol 2004, 123, 93–100. [CrossRef]
- Guarneri C, Aguennouz M, Guarneri F, Polito F, Benvenga S, Cannavò SP: Autoimmunity to heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 in psoriatic patients and correlation with disease severity. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2018, 16, 1103–1107. [CrossRef]
- Yunusbaeva M, Valiev R, Bilalov F, Sultanova Z, Sharipova L, Yunusbayev B: Psoriasis patients demonstrate HLA-Cw*06:02 allele dosage-dependent T cell proliferation when treated with hair follicle-derived keratin 17 protein. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 6098. [CrossRef]
- Lande R, Botti E, Jandus C, Dojcinovic D, Fanelli G, Conrad C, Chamilos G, Feldmeyer L, Marinari B, Chon S, et al.: The antimicrobial peptide LL37 is a T-cell autoantigen in psoriasis. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 5621. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbai AM, Fiorentino D, Perin J, Darrah E, Yang Q, Gutierrez-Alamillo L, Bingham CO, Petri M, Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L: SOX-5 Transcription Factor: a Novel Psoriatic Autoantigen Preferentially Found in Women. ACR Open Rheumatol 2024, 6, 807–819. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang SY, An WH, Wang ZS, Wang WL, Zhang B, Xu KL, Guo SL, Gao M, Li B, Huang L, et al: Incidentally cured psoriasis in a patient with refractory/relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving CD19 CAR-T cell therapy: a case report. Front Immunol 2024, 15, 1418768. [CrossRef]
- Mizumaki K, Horii M, Kano M, Komuro A, Matsushita T: Suppression of IL-23-mediated psoriasis-like inflammation by regulatory B cells. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 2106. [CrossRef]
- Mavropoulos A, Zafiriou E, Simopoulou T, Brotis AG, Liaskos C, Roussaki-Schulze A, Katsiari CG, Bogdanos DP, Sakkas LI: Apremilast increases IL-10-producing regulatory B cells and decreases proinflammatory T cells and innate cells in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019, 58, 2240–2250.
- Mavropoulos A, Varna A, Zafiriou E, Liaskos C, Alexiou I, Roussaki-Schulze A, Vlychou M, Katsiari C, Bogdanos DP, Sakkas LI: IL-10 producing Bregs are impaired in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis and inversely correlate with IL-17- and IFNγ-producing T cells. Clin Immunol 2017, 184, 33–41.
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, Feldman SR, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, Gottlieb A, Koo JY, Lebwohl M, Leonardi CL, et al: Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 6. Guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: case-based presentations and evidence-based conclusions. J Am Acad Dermatol 2011, 65, 137–174.
- Nast A, Boehncke WH, Mrowietz U, Ockenfels HM, Philipp S, Reich K, Rosenbach T, Sammain A, Schlaeger M, Sebastian M, et al.: S3—Guidelines on the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris (English version). Update. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges, 2012; 10, (Suppl 2), S1–95.
- Jones SA, Perera DN, Fan H, Russ BE, Harris J, Morand EF: GILZ regulates Th17 responses and restrains IL-17-mediated skin inflammation. J Autoimmun 2015, 61, 73–80. [CrossRef]
- Koo J, Cuffie CA, Tanner DJ, Bressinck R, Cornell RC, DeVillez RL, Edwards L, Breneman DL, Piacquadio DJ, Guzzo CA, Monroe EW: Mometasone furoate 0.1%-salicylic acid 5% ointment versus mometasone furoate 0.1% ointment in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis: a multicenter study. Clin Ther 1998, 20, 283–291. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason A, Mason J, Cork M, Hancock H, Dooley G: Topical treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: an abridged Cochrane systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol 2013, 69, 799–807. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segaert S, Duvold LB: Calcipotriol cream: a review of its use in the management of psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat 2006, 17, 327–337. [CrossRef]
- Lebwohl MG, Stein Gold L, Strober B, Papp KA, Armstrong AW, Bagel J, Kircik L, Ehst B, Hong HC, Soung J, et al: Phase 3 Trials of Tapinarof Cream for Plaque Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 2219–2229. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA, Feldman SR, Gelfand JM, Gordon KB, Gottlieb A, Koo JYM, Lebwohl M, Lim HW, et al: Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 5. Guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy and photochemotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010, 62, 114–135.
- Rim JH, Park JY, Choe YB, Youn JI: The efficacy of calcipotriol + acitretin combination therapy for psoriasis: comparison with acitretin monotherapy. Am J Clin Dermatol 2003, 4, 507–510. [CrossRef]
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, Van Voorhees AS, Leonardi CL, Gordon KB, Lebwohl M, Koo JY, Elmets CA, Korman NJ, et al: Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 1. Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol 2008, 58, 826–850. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisondi P, Del Giglio M, Cotena C, Girolomoni G: Combining etanercept and acitretin in the therapy of chronic plaque psoriasis: a 24-week, randomized, controlled, investigator-blinded pilot trial. Br J Dermatol 2008, 158, 1345–1349. [CrossRef]
- Katz HI, Waalen J, Leach EE: Acitretin in psoriasis: an overview of adverse effects. J Am Acad Dermatol, 1999; 41, S7–s12.
- Goldfarb MT, Ellis CN, Gupta AK, Tincoff T, Hamilton TA, Voorhees JJ: Acitretin improves psoriasis in a dose-dependent fashion. J Am Acad Dermatol 1988, 18, 655–662. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Eusebio E, Armario-Hita JC, de Miquel VA: Treatment of psoriasis: focus on clinic-based management with infliximab. Am J Clin Dermatol, 2014; 15, (Suppl 1), S5–16.
- Ho VC, Griffiths CE, Albrecht G, Vanaclocha F, León-Dorantes G, Atakan N, Reitamo S, Ohannesson A, Mørk NJ, Clarke P, et al: Intermittent short courses of cyclosporin (Neoral(R)) for psoriasis unresponsive to topical therapy: a 1-year multicentre, randomized study. The PISCES Study Group. Br J Dermatol 1999, 141, 283–291. [CrossRef]
- Ho VC, Griffiths CE, Berth-Jones J, Papp KA, Vanaclocha F, Dauden E, Beard A, Puvanarajan L, Paul C: Intermittent short courses of cyclosporine microemulsion for the long-term management of psoriasis: a 2-year cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001, 44, 643–651. [CrossRef]
- Lin VW, Ringold S, Devine EB: Comparison of Ustekinumab With Other Biological Agents for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Bayesian Network Meta-analysis. Arch Dermatol 2012, 148, 1403–1410. [CrossRef]
- Ortonne JP, van de Kerkhof PC, Prinz JC, Bieber T, Lahfa M, Rubins A, Wozel G, Lorette G: 0.3% Tacrolimus gel and 0.5% Tacrolimus cream show efficacy in mild to moderate plaque psoriasis: Results of a randomized, open-label, observer-blinded study. Acta Derm Venereol 2006, 86, 29–33. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remitz A, Reitamo S, Erkko P, Granlund H, Lauerma AI: Tacrolimus ointment improves psoriasis in a microplaque assay. Br J Dermatol 1999, 141, 103–107. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas WS, Poulin Y, Decroix J, Ortonne JP, Mrowietz U, Gulliver W, Krogstad AL, Larsen FG, Iglesias L, Buckley C, Bibby AJ: A new calcipotriol/betamethasone formulation with rapid onset of action was superior to monotherapy with betamethasone dipropionate or calcipotriol in psoriasis vulgaris. Acta Derm Venereol 2002, 82, 131–135.
- Elias KM, Laurence A, Davidson TS, Stephens G, Kanno Y, Shevach EM, O’Shea JJ: Retinoic acid inhibits Th17 polarization and enhances FoxP3 expression through a Stat-3/Stat-5 independent signaling pathway. Blood 2008, 111, 1013–1020. [CrossRef]
- Jairath V, Acosta Felquer ML, Cho RJ: IL-23 inhibition for chronic inflammatory disease. Lancet 2024, 404, 1679–1692. [CrossRef]
- Mease PJ, Chohan S, Fructuoso FJG, Luggen ME, Rahman P, Raychaudhuri SP, Chou RC, Mendelsohn AM, Rozzo SJ, Gottlieb A: Efficacy and safety of tildrakizumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis: results of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose, 52-week phase IIb study. Ann Rheum Dis 2021, 80, 1147–1157.
- Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Langley RG, Luger T, Ohtsuki M, Reich K, Amato D, Ball SG, Braun DK, et al: Phase 3 Trials of Ixekizumab in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 345–356. [CrossRef]
- Reich K, Sullivan J, Arenberger P, Jazayeri S, Mrowietz U, Augustin M, Elewski B, You R, Regnault P, Frueh JA: Secukinumab shows high and sustained efficacy in nail psoriasis: 2.5-year results from the randomized placebo-controlled TRANSFIGURE study. Br J Dermatol 2021, 184, 425–436. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren RB, Blauvelt A, Bagel J, Papp KA, Yamauchi P, Armstrong A, Langley RG, Vanvoorden V, De Cuyper D, Cioffi C, et al.: Bimekizumab versus Adalimumab in Plaque Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 130–141. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich K, Warren RB, Lebwohl M, Gooderham M, Strober B, Langley RG, Paul C, De Cuyper D, Vanvoorden V, Madden C, et al.: Bimekizumab versus Secukinumab in Plaque Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 142–152. [CrossRef]
- Morita A, Strober B, Burden AD, Choon SE, Anadkat MJ, Marrakchi S, Tsai TF, Gordon KB, Thaçi D, Zheng M, et al.: Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous spesolimab for the prevention of generalised pustular psoriasis flares (Effisayil 2): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 1541–1551. [CrossRef]
- Yang W, Bai X, Jia X, Li H, Min J, Li H, Zhang H, Zhou J, Zhao Y, Liu W, et al: The binding of extracellular cyclophilin A to ACE2 and CD147 triggers psoriasis-like inflammation. J Autoimmun 2024, 148, 103293. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian J, Liu R, Fan T, Liao L, Wang S, Geng W, Wang T, Shi W, Ruan Q: miR-340 Alleviates Psoriasis in Mice through Direct Targeting of IL-17A. The Journal of Immunology 2018, 201, 1412–1420. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen L, Huang D, Huang Z, Liu X, He M, Luo M, Tang Z, Tan G, Guo Q, Xiong H: Decreased HMGCS1 inhibits proliferation and inflammatory response of keratinocytes and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis via the STAT3/IL-23 axis. Int Immunopharmacol 2024, 133, 112033. [CrossRef]
- Whitehead KA, Langer R, Anderson DG: Knocking down barriers: advances in siRNA delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009, 8, 129–138. [CrossRef]
- Tang Q, Khvorova A: RNAi-based drug design: considerations and future directions. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2024, 23, 341–364. [CrossRef]
- Boakye CHA, Patel K, Doddapaneni R, Bagde A, Marepally S, Singh M: Novel amphiphilic lipid augments the co-delivery of erlotinib and IL36 siRNA into the skin for psoriasis treatment. J Control Release 2017, 246, 120–132. [CrossRef]
- Song Y, Li J, Wu Y: Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 263. [CrossRef]
- Zhang A, Zhang G, Yang H, Gong B, Li S, Wei N, Xue H, Wei H, Wang J, Qiu S: Treatment of pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia and severe plaque psoriasis with anti-CD19 CAR T cells: a case report. Frontiers in Immunology 2025, 16.
- Wang X, Wu X, Tan B, Zhu L, Zhang Y, Lin L, Xiao Y, Sun A, Wan X, Liu S, et al: Allogeneic CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy in patients with severe myositis and systemic sclerosis. Cell 2024, 187, 4890–4904.e4899. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransson M, Piras E, Burman J, Nilsson B, Essand M, Lu B, Harris RA, Magnusson PU, Brittebo E, Loskog AS: CAR/FoxP3-engineered T regulatory cells target the CNS and suppress EAE upon intranasal delivery. J Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 112.
- Zhang W, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Zheng H, Wang S, Liao Z, Sheng T, Zhao S, Hou W, Yu X, et al.: Adoptive T(reg) therapy with metabolic intervention via perforated microneedles ameliorates psoriasis syndrome. Sci Adv, 2023; 9, eadg6007.
- Rosenzwajg M, Lorenzon R, Cacoub P, Pham HP, Pitoiset F, El Soufi K, C RI, Bernard C, Aractingi S, Banneville B, et al: Immunological and clinical effects of low-dose interleukin-2 across 11 autoimmune diseases in a single, open clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2019, 78, 209–217. [CrossRef]
- Chen W, Ren G, Zuo K, Huang X: Complete remission of both immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis and psoriasis after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018; 97, e13589.
- Kaffenberger BH, Wong HK, Jarjour W, Andritsos LA: Remission of psoriasis after allogeneic, but not autologous, hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. J Am Acad Dermatol 2013, 68, 489–492. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn H, Lee SY, Jung WJ, Pi J, Lee KH: Psoriasis treatment using minimally manipulated umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2021, 9, 6798–6803. [CrossRef]
- Cheng L, Wang S, Peng C, Zou X, Yang C, Mei H, Li C, Su X, Xiao N, Ouyang Q, et al: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for psoriasis: a phase 1/2a, single-arm study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 263. [CrossRef]
- Yao D, Ye S, He Z, Huang Y, Deng J, Wen Z, Chen X, Li H, Han Q, Deng H, et al.: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs) in the treatment for psoriasis: results of a single-arm pilot trial. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 1653. [CrossRef]
- Tang L, Yao D, He Z, Ye S, Chen X, Huang Y, Han Q, Zeng X, Zheng X, Liu T, et al: Distinct adaptive immune receptor feature of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs) treatment of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 2024, 316, 542. [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman R, Mahmood A, Kshatriya P, Patel D, Srivastava A: Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Media Ameliorate Psoriasis Vulgaris: A Case Study. Case Rep Dermatol Med 2019, 2019, 8309103.
- Shao H, Chen J: Extracellular Vesicles from miR-146a Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis by Regulating Cytokine Expression. Iran J Immunol 2025, 22, 119–130.
- Mohseni Meybodi MA, Nilforoushzadeh MA, KhandanDezfully N, Mansouri P: The safety and efficacy of adipose tissue-derived exosomes in treating mild to moderate plaque psoriasis: A clinical study. Life Sci 2024, 353, 122915. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou M, Cao J, Luo R, Zhu B, Miao R, Yu L, Wang X, Li W, Fu Y, Zhang J, et al.: Drug-loaded microneedle patches containing regulatory T cell-derived exosomes for psoriasis treatment. Acta Biomater 2025, 198, 452–466. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran NS, Bhupendrabhai MN, Tan TT, Zhang B, Lim SK, Choo ABH, Lai RC: A phase 1, open-label study to determine safety and tolerability of the topical application of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (MSC) exosome ointment to treat psoriasis in healthy volunteers. Cytotherapy 2025, 27, 633–641.
- Bucci L, Hagen M, Rothe T, Raimondo MG, Fagni F, Tur C, Wirsching A, Wacker J, Wilhelm A, Auger JP, et al: Bispecific T cell engager therapy for refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med 2024, 30, 1593–1601. [CrossRef]
- Gao C, Cai Y, Wu X, Song J, Zheng Q, Wang M, Luo Y, Luo Y, Fei X, Zhang Y, et al.: CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout and Overexpression Studies Unveil the Role of PD-L1 in Immune Modulation in a Psoriasis-like Mouse Model. Inflammation, 2025.
- Tan E, Wan T, Pan Q, Duan J, Zhang S, Wang R, Gao P, Lv J, Wang H, Li D, et al: Dual-responsive nanocarriers for efficient cytosolic protein delivery and CRISPR-Cas9 gene therapy of inflammatory skin disorders. Sci Adv 2024, 10, eadl4336. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang Y, Jiang Y, Wang Z, Wang X, Ma L, Ding Y, Rui B, Zhao C, Li X, Xu M, et al.: Targeting KAT8 alleviates self-RNA-driven skin inflammation by modulating histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation in psoriasis. Cell Death Differ, 2025.
- Dhillon-LaBrooy A, Braband KL, Tantawy E, Rampoldi F, Kao YS, Boukhallouk F, Velasquez LN, Mamareli P, Silva L, Damasceno LEA, et al: Inhibition of Mitochondrial Translation Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation by Targeting Vγ4+ γδ T Cells. J Invest Dermatol 2024, 144, 844–854.e842. [CrossRef]
- Xia X, Cao G, Sun G, Zhu L, Tian Y, Song Y, Guo C, Wang X, Zhong J, Zhou W, et al: GLS1-mediated glutaminolysis unbridled by MALT1 protease promotes psoriasis pathogenesis. J Clin Invest 2020, 130, 5180–5196. [CrossRef]
- He X, Liu R, Fan T, Huang X, Wu C, Su W, Wang T, Ruan Q: Treating Autoimmune Diseases by Targeting IL-23 with Gene-Silencing Pyrrole-Imidazole Polyamide. J Immunol 2020, 204, 2053–2063. [CrossRef]
- Hossen MM, Ma Y, Yin Z, Xia Y, Du J, Huang JY, Huang JJ, Zou L, Ye Z, Huang Z: Current understanding of CTLA-4: from mechanism to autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1198365. [CrossRef]
- Yu C, Sonnen AF, George R, Dessailly BH, Stagg LJ, Evans EJ, Orengo CA, Stuart DI, Ladbury JE, Ikemizu S, et al.: Rigid-body ligand recognition drives cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) receptor triggering. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 6685–6696. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini A, Gharibi T, Marofi F, Babaloo Z, Baradaran B: CTLA-4: From mechanism to autoimmune therapy. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 80, 106221. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner HI, Tzaribachev N, Vega-Cornejo G, Louw I, Berman A, Calvo Penadés I, Antón J, Ávila-Zapata F, Cuttica R, Horneff G, et al.: Subcutaneous Abatacept in Patients With Polyarticular-Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Results From a Phase III Open-Label Study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018, 70, 1144–1154. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee WS, Nam KH, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Kim JE, Shin EC, Kim GR, Choi JM: Alleviating psoriatic skin inflammation through augmentation of Treg cells via CTLA-4 signaling peptide. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1233514. [CrossRef]
- Guo W, Xu F, Zhuang Z, Liu Z, Xie J, Bai L: Ebosin Ameliorates Psoriasis-Like Inflammation of Mice via miR-155 Targeting tnfaip3 on IL-17 Pathway. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 662362. [CrossRef]
- Stenderup K, Rosada C, Dam TN, Salerno E, Belinka BA, Kachlany SC: Resolution of psoriasis by a leukocyte-targeting bacterial protein in a humanized mouse model. J Invest Dermatol 2011, 131, 2033–2039. [CrossRef]
- Gege C: RORγt inhibitors as potential back-ups for the phase II candidate VTP-43742 from Vitae Pharmaceuticals: patent evaluation of WO2016061160 and US20160122345. Expert Opin Ther Pat 2017, 27, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong AW, Read C: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. Jama 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [CrossRef]
- Schaper-Gerhardt K, Rossbach K, Nikolouli E, Werfel T, Gutzmer R, Mommert S: The role of the histamine H(4) receptor in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Br J Pharmacol 2020, 177, 490–502.
- Zhu J, Yang T, Tang M, Yang Z, Pei H, Ye H, Tang Y, Cheng Z, Lin P, Chen L: Studies on the anti-psoriasis effects and its mechanism of a dual JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor flonoltinib maleate. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 137, 111373.
- Armstrong AW, Gooderham M, Warren RB, Papp KA, Strober B, Thaçi D, Morita A, Szepietowski JC, Imafuku S, Colston E, et al.: Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 POETYK PSO-1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 2023, 88, 29–39. [CrossRef]
- Deng BX, Jiang, C.Y, Wang P, Liu, W.L, Qu X, Zhao, Y.M, Chen K, Cai, N.N, & Tao, Y: Distribution and evolution patterns of TCM syndromes in psoriasis. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2006; 770–772.
- Liu AM, Zhang, BX, Zhao W, & Xu, S. D: Discussion on etiology and pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2021, 44, 266–271.
- Huang G, Yuan X, Hu, C.X, Fu, J.J, Shi, H.Y, Xin Q, Yang M, & Gong, L. P: Study on the effect of Xijiao Dihuang Decoction on intestinal Th17/Treg imbalance in psoriasis mice based on the gut-immune-skin axis. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine 2023, 35, 1569–1572.
- Chen H, & Wang, S. P: Therapeutic effect of Compound Indigo Naturalis Capsule on psoriasis vulgaris and its influence on serum IL-2 and IL-8 levels. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials 2004, 885–886.
- Feng J, Xu, H.Q, & Su, B. S: Effect of Compound Qingdai Capsule on c-myc expression in epidermal keratinocytes of psoriasis patients. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 1996, 146–148.
- Lei M, Liu R, Yao B, Hu, Y.J, Wang, W.J, & Zhang, X. J: Expression of p38MAPK/Th17 signaling pathway-related cytokines in psoriasis vulgaris patients and the regulatory effect of Modified Gentian Liver-Draining Decoction. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research 2020, 31, 1342–1347.
- Chen LH: Clinical observation on Compound Indigo Naturalis Ointment for treating psoriasis vulgaris. Journal of Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2010, 27, 45–47.
- Zou JH, Gong LP, Huang G, Hu, C.X, Yan J, & Zhang, F. Y: Meta-analysis of acupuncture efficacy for psoriasis vulgaris. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2020, 36, 127–130.
- Li B, Li Z, Chen Q, Fang, W.H, & Zhang, C. H: Effects of moving cupping therapy on peripheral blood CD4+ T lymphocyte subsets in plaque psoriasis patients with blood stasis syndrome. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy 2021, 36, 1769–1772.
- Zhou Y, Yang M, Bai, X.P, Gao Y, Han H, & Guan, H. W: Efficacy of NB-UVB phototherapy combined with self-prepared Cool-Blood Anti-Itching decoction herbal bath for psoriasis vulgaris and its effects on hemorheology. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2017, 26, 3023–3026.
- Feng F, Wang Y, Zhao, J.X, Di, T.T, Meng, Y.J, Chen, Z.X, Qi C, Hu, X.Q, Wang, Y.Z, & Li, P: Effects of fire needle therapy on psoriasiform skin lesions and STAT3 pathway in imiquimod-induced mice. Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion 2022, 42, 541–548.
- Song X, Tang, S.W, Jiang, W.C, Yang Y, Wang, Q.L, & Xie, S. Q: Chinese herbal bath combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for stable plaque psoriasis and its impact on patients’ quality of life. Chinese Journal of Dermatovenereology 2017, 31, 757–759.
- Guang YJ: Clinical observation of NB-UVB combined with Chinese herbal fumigation for psoriasis vulgaris. Medical Diet and Health 2020, 18, 28–30.
- Chen CF, Zheng, YZ, Jia, L.Y, & Yu, T. G: Clinical study of Shugan Jieyu Capsule in treating psoriasis vulgaris. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2017, 33, 222–225.
- Dai XR, Peng, FF, Miao, Y.X, Dong M, & Jiang, G. F: Nursing observation on the interventional effects of Five-Element Jue-tone music therapy for psoriasis patients with Qi-stagnation constitution. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine 2018, 38, 715–718.
- Langley RG, Krueger GG, Griffiths CE: Psoriasis: epidemiology, clinical features, and quality of life. Ann Rheum Dis, 2005; 64, (Suppl. 2), ii18–23; discussion ii24–15.
- Chen L, Su M, Jin Q, Wang CG, Assani I, Wang MX, Zhao SF, Lv SM, Wang JW, Sun B, et al.: Discovery of N-(2-benzyl-4-oxochroman-7-yl)-2-(5-(ethylsulfonyl) pyridin-2-yl) acetamide (b12) as a potent, selective, and orally available novel retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor γt inverse agonist. Bioorg Chem 2022, 119, 105483.
- Mease P, Hall S, FitzGerald O, van der Heijde D, Merola JF, Avila-Zapata F, Cieślak D, Graham D, Wang C, Menon S, et al.: Tofacitinib or Adalimumab versus Placebo for Psoriatic Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2017, 377, 1537–1550. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang A, Zhang G, Yang H, Gong B, Li S, Wei N, Xue H, Wei H, Wang J, Qiu S: Treatment of pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia and severe plaque psoriasis with anti-CD19 CAR T cells: a case report. Front Immunol 2025, 16, 1529745. [CrossRef]
- Yan K, Li F, Bi X, Han L, Zhang Z, Chen R, Li Y, Zhang L, Wang X, Li L, et al: Efficacy and safety of vunakizumab in moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 2025, 92, 92–99. [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt A, Papp KA, Griffiths CE, Randazzo B, Wasfi Y, Shen YK, Li S, Kimball AB: Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the continuous treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: Results from the phase III, double-blinded, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 1 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017, 76, 405–417.
- Gordon KB, Langley RG, Leonardi C, Toth D, Menter MA, Kang S, Heffernan M, Miller B, Hamlin R, Lim L, et al: Clinical response to adalimumab treatment in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: double-blind, randomized controlled trial and open-label extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006, 55, 598–606. [CrossRef]
- Berstein G, Zhang Y, Berger Z, Kieras E, Li G, Samuel A, Yeoh T, Dowty H, Beaumont K, Wigger-Alberti W, et al.: A phase I, randomized, double-blind study to assess the safety, tolerability and efficacy of the topical RORC2 inverse agonist PF-06763809 in participants with mild-to-moderate plaque psoriasis. Clin Exp Dermatol 2021, 46, 122–129. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen L, Zhao W: Compound Indigo Naturalis Ointment in the Treatment of 60 Cases of Plaque Psoriasis. Guangming Journal of Chinese Medicine 2014, 29, 1413–1414.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





