Nearly four decades of research on copper oxide high-temperature superconductors (HTSCs) has produced a rich and complex phase diagram [
1]. Fundamentally, the primary distinction between cuprates and conventional superconductors lies in their doped nature [
2,
3]. Remarkably, subtle adjustments to the doped carrier concentration can trigger nearly all known condensed matter phase transitions [
4,
5]. These phenomena defy explanation within the framework of existing solid-state theories, presenting a severe challenge to traditional electron theory [
6,
7,
8]. Undoubtedly, there is an urgent need for a universal mechanism that enables both explanation and prediction. This mechanism must not only consistently describe the zero electrical resistance and Meissner effect of the superconducting state but also elucidate various anomalous phenomena in the normal state [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. It should account for not only copper-based superconductors but also emerging classes of superconducting materials [
17,
18].
Recent experimental insights enable a universal, self-consistent high-temperature superconductivity (HTS) theory with explanatory and predictive power, underpinned by four key observations:
(1) In correlated superconductors, the electron mean free path is subatomic (theoretically infinite), violating the Mott-Ioffe-Regel (MIR) limit and breaking well-defined quasiparticle excitations [
19,
20].
(2) Shot noise measurements in strange metals challenge discrete quasiparticle current models, showing electric and superconducting currents arise without quasiparticles [
21].
(3) In overdoped HTSCs and FeSe, the positive
-resistivity coefficient correlation [
22,
23] shows higher resistivity may enhance
, while overly low resistivity hinders it. This paradox implies superconductivity arises from an insulating (not metallic) background, consistent with good conductors (e.g., Au, Ag, Cu) lacking superconductivity, while HTS occurs in non-metallic cuprates.
(4) In topological insulator
, STM/STS studies reveal nanoscale coexistence of insulating and conducting domains [
24]. Analogous to charge-ordered structures in doped high-
superconductors (parented by Mott insulators), this coexistence further confirms that current/supercurrent is non-carrier-driven.
This paper defines the dissipation-free superconducting state as a Planck energy-quantized ground state, realized via the Planckian limit
[
25,
26]. Unlike conventional theories describing direct metal-superconductor transitions below
, our framework reveals a two-step pathway: (1) Metal-insulator transition at
, where ultralow temperatures localize electrons in polyhedral quantum wells via coherent condensation to form an insulating Wigner crystal; (2) Insulator-superconductor transition, where an external electric field induces collective electron micro-displacement relative to ionic lattices, forming a polarization capacitor (Coulomb-attractive electron-hole (e-h) pairing with the electric dipole vector as the order parameter, requiring no additional “glue" [
6]) that triggers symmetry breaking and Maxwell’s displacement current. This mechanism generates dissipation-free current without quasiparticle motion, consistent with the four key experimental findings above.
As a coherent condensed state, the superconducting state must satisfy the indistinguishability of electron states, which makes it possible to simplify complex quantum many-body problems into single-body ones. We derive the critical formula
, where
is the quantum well depth determined by the lattice constant, and
represents the electron–lattice correlation strength in quantum well states. This formula precisely predicts
for cuprate and iron-based superconductors using lattice constants, aligning excellently with experimental data and implying universal applicability. We uncover dualistic relationships between electron-ordered structures and doping [
27], as well as superconducting and pseudogap phases [
28]. Our analytical derivation of the HTSC phase diagram comprehensively accounts for all observed phase transitions. Remarkably, the theory resolves two enduring enigmas: the linear decline of pseudogap magnitude with doping in underdoped regions [
29] and the linear temperature dependence of resistivity in overdoped strange metals [
30].
Quantized polyhedral quantum-well and Planckian limit
Blackbody radiation, a foundational physics phenomenon that spurred the quantum revolution and reshaped understanding of the microcosm, may also resolve the HTS puzzle. Blackbody experiments show electrons emit radiation and dissipate energy at , yet superconductors exhibit zero energy dissipation for . Thus, superconducting research hinges on explaining how the thermodynamically stable superconducting state avoids spontaneous energy radiation in temperature fields.
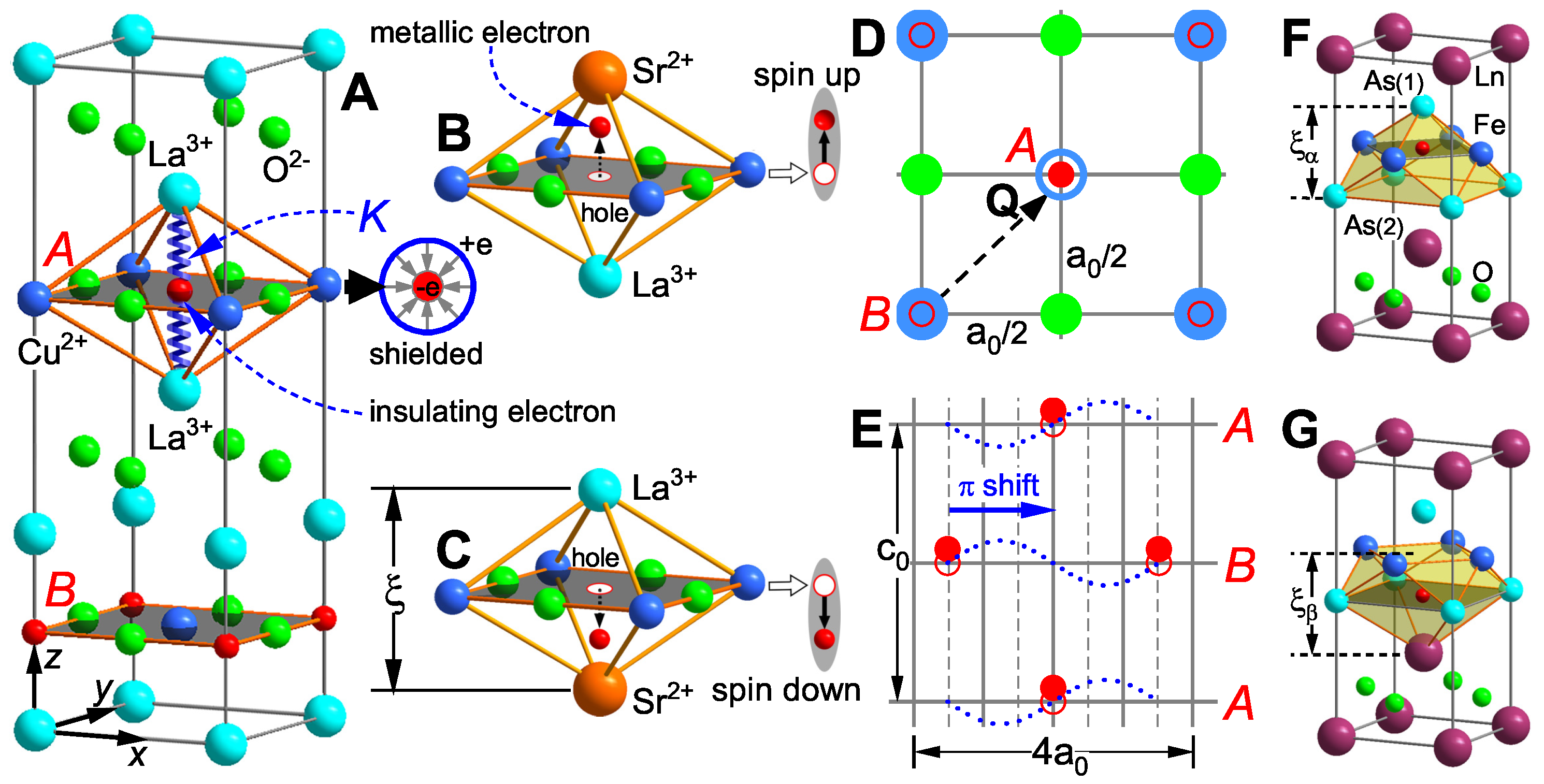
The first high-temperature superconductor was achieved by doping insulator
with Sr/Ba [
31]. In the undoped parent compound (
Figure 1A), quantum well ions show perfect
-directional symmetry, causing complete overlap of positive and negative charge centers. This fully shields localized octahedral electrons via the
shell (right inset) or renders them undetectable, making them unresponsive to external fields; these are termed insulating electrons. When Sr is doped,
substitutes
in two ways. Upper-position doping (
Figure 1B) breaks charge balance at the vertices and the octahedron’s mirror symmetry, pushing electrons upward from the
plane to a new equilibrium position above and leaving a hole at their original site. Lower-position doping (
Figure 1C) similarly pushes electrons downward from the
plane, forming a hole. Doping induces symmetry breaking, generating upward and downward e-h electric dipoles (right insets of
Figure 1B and C) that can be depicted by spin-up and spin-down states. These electrons, no longer shielded, respond to external fields and are called metallic or superconducting electrons.
Return to
Figure 1A again, according to Planck’s quantum hypothesis, the localized electron in the figure can be simplified as a quasi-one-dimensional harmonic oscillator. Here,
K represents the stiffness coefficient, which is determined by the Coulomb confinement strength of ions at the two vertices of the octahedral quantum well. The intrinsic frequency
of the harmonic oscillator can then be expressed as:
where
is the angular frequency and
is the effective mass of electron.
Eq. (
1) represents the minimum vibration frequency or the natural frequency of Planck’s quantization theory. For a given material, it has a definite value of
K and a definite Planck energy quantum
. An electron harmonic oscillator must absorb and radiate a complete energy quantum through resonance. However, if the thermal energy provided externally is less than the minimum energy quantum, the thermal vibrations of all electrons will be suppressed entirely. At this point, the electrons will condense into a insulating state with zero entropy and no energy consumption.
Based on the thermodynamic principle of energy equipartition, a superconductor with parameter
K may have a specific critical temperature
satisfying the following relationship:
where
is the Boltzmann constant and
represents the relaxation time of the harmonic oscillator or the scattering rate.
The relationship described by Eq. (
2) universally exists as the Planckian limit in various superconducting materials, with its physical significance readily interpretable. First,
embodies a quintessential quantum effect: were Planck’s constant
,
would necessarily vanish. Second,
serves as an intrinsic material property, precisely characterizing the inherent frequency of superconductors. Therefore, increasing the
K-value (stiffness constant) is the sole method to enhance
. Harder and more brittle materials (e.g., ceramics) with larger
K values are more likely to achieve higher
, while more ductile materials (e.g., good conductors like gold, silver, and copper) have smaller
K values, leading to low or no superconductivity. Based on the definition of resistivity, we can also derive the relationship between the intrinsic resistivity of superconducting materials and their corresponding
:
where
is a material-dependent constant.
As shown in Eq. (
3),
correlates positively with
: poorer conductivity implies stronger superconductivity or a higher transition temperature, contradicting conventional solid-state electron conduction theory. However, recent experiments found
[
22,
23], where
is the linear resistance coefficient, a finding that perfectly validates the physical meaning of Eq. (
3). Despite their apparent opposition, this relation reveals an intrinsic unity between the dissipationless superconducting transition temperature and dissipative resistance. This ubiquitous parameter relation in various systems suggests a universal mechanism underlies resistivity and unconventional superconductivity.
Our research, based entirely on the single-electron approximation, posits that indistinguishability of electron states is prerequisite for the superconducting electron state as a stable thermodynamic system free from thermal fluctuations. That is, clarifying one local electron’s properties reveals all electrons’ behavior. This assumption simplifies the quantum many-body problem to a single-particle one and addresses coherent condensation in the superconducting state. Achieving this requires accounting for structural specifics of high-temperature superconductor crystals. As
Figure 1A shows, each unit cell typically contains two copper oxide planes (
A and
B) with
-plane projections differing by vector
(
Figure 1D). This enables superconducting electrons to form a
-shifted honeycomb-shaped stable Wigner symmetric structure in the non-superconducting
-plane (
Figure 1E), which is also the root of the pinned triangular vortex lattices commonly found in type-II superconductors [
32]. Notably, many high-quality copper oxide superconductors have lattice constants with
, e.g.,
(Bi2201,
[
33]) and
(CCOC,
[
34]). Subsequent sections will further show that all observed charge-ordered phases, exotic phase transitions (especially STM results with four-unit-cell periodicity) derive fundamentally from
Figure 1E.
Universal inverse-square law of
From Eqs. (
1) and (
2), the magnitude of
K directly determines that of
. The parameter
K, characterizing material ductility or brittleness, is fundamentally determined by lattice structure. This explains why doping, pressure, etc., affect
in superconductors by altering lattice parameters. As shown in
Figure 1C, the depth
of the polyhedral quantum well is the key factor influencing
: smaller
enhances Coulomb confinement of local electrons by ions at both vertices, leading to synchronous increases in
K and
. For simplification, assuming the effective charge of polyhedral vertex ions is
and the electric field energy density at the electron’s position is
P, we have:
where
is an undetermined constant related to the properties of the material. Substituting Eq. (
4) into Eq. (
2) , we can immediately obtain:
where
represents the coupling strength between electrons and quantum wells, which is called the correlation strength factor.
Table 1 shows the experimentally measured superconducting transition temperature
of cuprate and iron-based superconductors versus the depth
of polyhedral quantum wells, both following the inverse-square relationship in Eq. (
5). The difference lies in the correlation strength factors, with average values of
and
, three times higher for cuprates, indicating stronger electron correlation and higher
. Notably, the record
of cuprates (164 K) [
35] is also three times that of iron-based superconductors (55 K) [
36]. It has been revealed that the same superconductor can typically form two quantum well structures, corresponding to the frequently observed two superconducting domes with distinct
values, such as in cuprates [
37] and iron-based compounds [
38]. In particular, two groups independently identified superconducting phases at 43 K and 55 K in SmFeAsOF (Rows 10-11 of
Table 1) in 2008 [
36,
39], and our theory predicted
values of 42.2 K and 54.3 K, which are in close agreement with the experiments. Sun et al. observed dual transitions at 32 K and 48.7 K in high-pressure KFeSe [
38], and our model predicted 32.1 K and 49 K (last two rows of
Table 1). Additionally, quantum wells act as quantum resonators where the resonance energy of localized electrons follows the same inverse-square law. For iron-based superconductors,
(meV). Xie et al. found three resonance peaks at 9.5, 13.0, and 18.3 meV in
via neutron spin scattering [
40], while our calculations based on the three resonator heights (fourth last row of
Table 1) yield 9.9, 13.4, and 17.6 meV, consistent with the experimental results.
Superconductivity in
with
80 K under pressures above 14 GPa [
18] has reignited global interest in Ni-based superconductors [
41,
42,
43]. A pivotal question remains: Can Ni-based materials exceed Cu-based
limits? Theories suggest Ni-based
may surpass Cu-based values and even approach room temperature [
41]. Our analysis shows Ni- and Cu-based superconductors share octahedral quantum well structures (
Figure 1A,
). Using
Å [
18] in Eq. (
5), we predict a maximum
K for Ni-based systems. Recent work by Wang et al. confirms this trend:
exhibits
K (2.5 K higher than
) due to Pr-induced lattice contraction (
pm,
pm). The theoretical
K aligns well with experimental results [
43].
To the best of our knowledge, Eq. (
5) represents the first formula capable of accurately predicting the superconducting transition temperature exclusively from crystal structure parameters. This theoretical framework not only enhances our mechanistic understanding of superconducting phenomena but also paves the way for unraveling the enigmatic behavior of matter at the microscale.
Charge order, symmetry breaking, order parameter and superconducting transition
Increasing evidence suggests that layered superconductors exhibit striped superconductivity, where the charge stripe phase is quasi-one-dimensional. Experiments further indicate that superconductivity originates from charge stripes extending along the crystal’s
b-axis, with significantly higher superfluid density than in the
a-axis direction [
44]. As shown in
Figure 1E, the charge
-shift structure on the non-superconducting
-plane is fixed, confining doping concentration changes to the
b-axis direction. Based on the indistinguishability of superconducting electrons and electron crystal stability, the quasi-one-dimensional doping along the
b-axis is assumed periodically uniform, such that the doping concentration can be expressed as:
where
m, the doping principal quantum number, determines many critical properties, including high-temperature superconducting charge order, pseudogap, strange metal behavior, and phase diagrams.
The physical meaning of Eq. (
6) is straightforward: the numerator 2 denotes two types of
planes (
A and
B) along the
c-axis, the denominator 4 represents the charge stripe spacing along the
a-axis, and
m can be written as
(where
p is the number of undoped vacancies and
q is the number of doped sites in quasi-one-dimensional stripes).
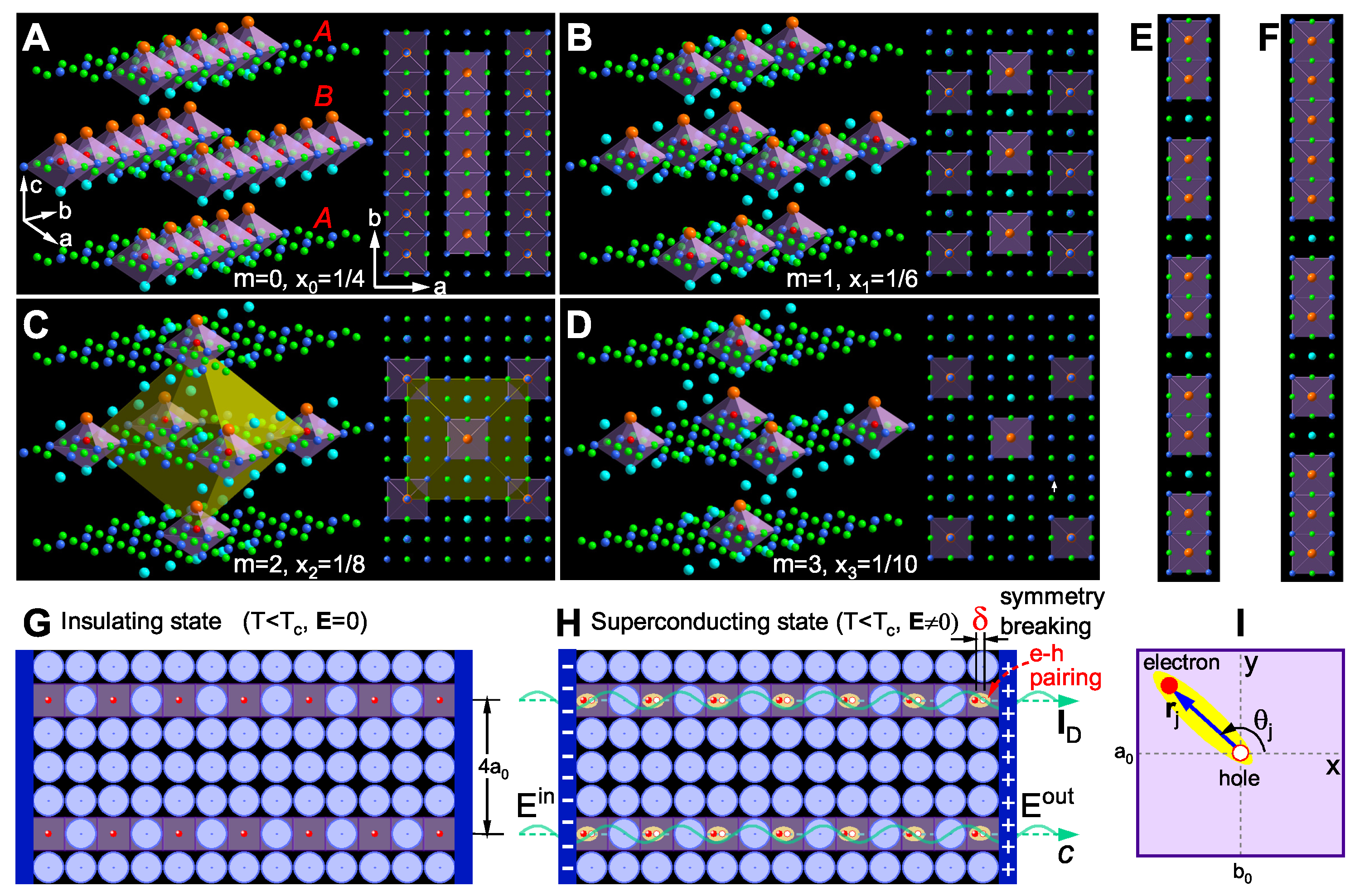
Figure 2, A to D depicts four characteristic real-space charge-ordered patterns in cuprate superconductors governed by Eq. (
6).
Figure 2A depicts the overdoped regime (
,
,
) with complete filling of doping sites (see the top view on the right); any additional doping destabilizes the charge order and quenches superconductivity.
Figure 2B illustrates optimal doping
,
,
), where one-dimensional superconducting chains reach half-filling to maximize
.
Figure 2C demonstrates the 1/8 anomaly [
45] at
(
), where equal charge stripe periodicities along the
a- and
b-axes trigger an LTO→ LTT phase transition. This transition pins electrons into stable yellow octahedra, forming an isotropic checkerboard pattern. The resulting structure exhibits insulating behavior, suppressing the superconducting phase transition. Finally,
Figure 2D shows the underdoped state (
,
), where sparse carriers reduce interelectronic coupling, weakening ordered-state stiffness and
K values, thus lowering
.
It should be noted that
Figure 2, A to D show the ideal theoretical results of long-range charge-ordered structures with integer doping. In experiments, fractional doping (
Figure 2E), disordered doping (
Figure 2F), mixed doping, and local inhomogeneous doping occur due to variations in doping concentration, temperature, etc. Different dopings induce commensurate/incommensurate and long/short-range electron orders, jointly forming the rich high-temperature superconducting phase diagram [
1]. Regarding the relationship between
Figure 2 A to D charge ordering structures and superconductivity: Traditional views suggest that superconducting phase transition occurs spontaneously at
. However, we propose a different perspective: Superconducting phase transition must be accompanied by symmetry breaking, while cooling alone does not induce macroscopic symmetry breaking. Take
as an example: Below
, all half-doped quasi-1D electrons in the
plane freeze at equilibrium positions (
Figure 2G). Due to the lattice field symmetry shielding effect, electrons condense into a rigid insulating state. Despite coherent condensation, the superconducting phase transition has not yet occurred.
Figure 2H shows that an external electric field induces collective electron displacement
and symmetry breaking, which microscopically resembles e-h pairing (requiring no additional “glue" [
6]) or the generation of quantized capacitance (yellow ellipse). These structures act as capacitive elements in large-scale integrated circuits, and their superposition forms macroscopic polarized charges and total capacitance at the ends of the superconductor. According to Maxwell’s hypothesis, a displacement current
arises within the superconductor. The superconducting current, essentially an electromagnetic wave that requires no directional electron motion, can propagate noiselessly and unimpeded during transmission even when the confined quasi-1D quantum channels are not fully doped (with spatially segregated conducting (doped) and insulating (undoped) regions) [
21]. Notably, quasi-1D electronic structures serve as a universal guarantee for maintaining superconductivity in various monolayer 2D superconductors [
46,
47,
48].
The superconducting phase transition is a two-step process, with the intermediate insulating state being crucial. Strictly speaking, superconductivity is impossible without the insulating state. In metals like gold, silver, and copper, electrons cannot completely freeze into an insulating state under existing low-temperature conditions, hence no superconductivity is exhibited. Everything has two sides, though: if the insulating property (locality) is too strong, as in the undoped parent compounds of high-temperature superconductors, an external field cannot drive the symmetry breaking of electron states as shown in
Figure 2H, preventing the superconducting phase transition from occurring.
Two-step phase transitions can be well described by order parameters. In the presence of both temperature field
T and electric field
E, the e-h pairs can be described by the electric dipole vector (
Figure 2I). For a superconductor with
N doped valence electrons, the phase transition order parameter can be defined based on the electric dipole as follows:
In the metallic state (
,
), the order parameter has components both along the electric field’s
x-direction (contributing to current) and the perpendicular
y-direction (contributing to resistance). In the insulating state (
,
), with random thermal motion fully quelled (i.e.,
), the order parameter in Eq. (
7) vanishes in both
x- and
y-directions, where electrons and holes are completely overlapped with full electron screening. In the superconducting state (
,
), thermal vibrations are fully suppressed, so electric field-induced symmetry breaking occurs solely along the
x-direction (no
y-direction breaking). The corresponding order parameter in Eq. (
7) thus reaches its maximum
, resulting in zero resistance.
It is well-known that stripe phases with 4-fold lattice periodicity widely exist in cuprate superconductors, though theoretical interpretations of their origin remain controversial. Here, we propose a plausible explanation: these phases arise from intrinsic double
layers (
) and
-shift stability in high-
materials (
Figure 1E). In extreme underdoping (
), sparse charge carriers fail to form long-range order due to weak interactions/competition, driving electrons to form short-range
near-cube incommensurate clusters. Recently, two teams independently observed via STM local nematic states of typical size
in (Bi2201) [
33] and (CCOC) [
34] systems, providing new experimental support for our mechanism.
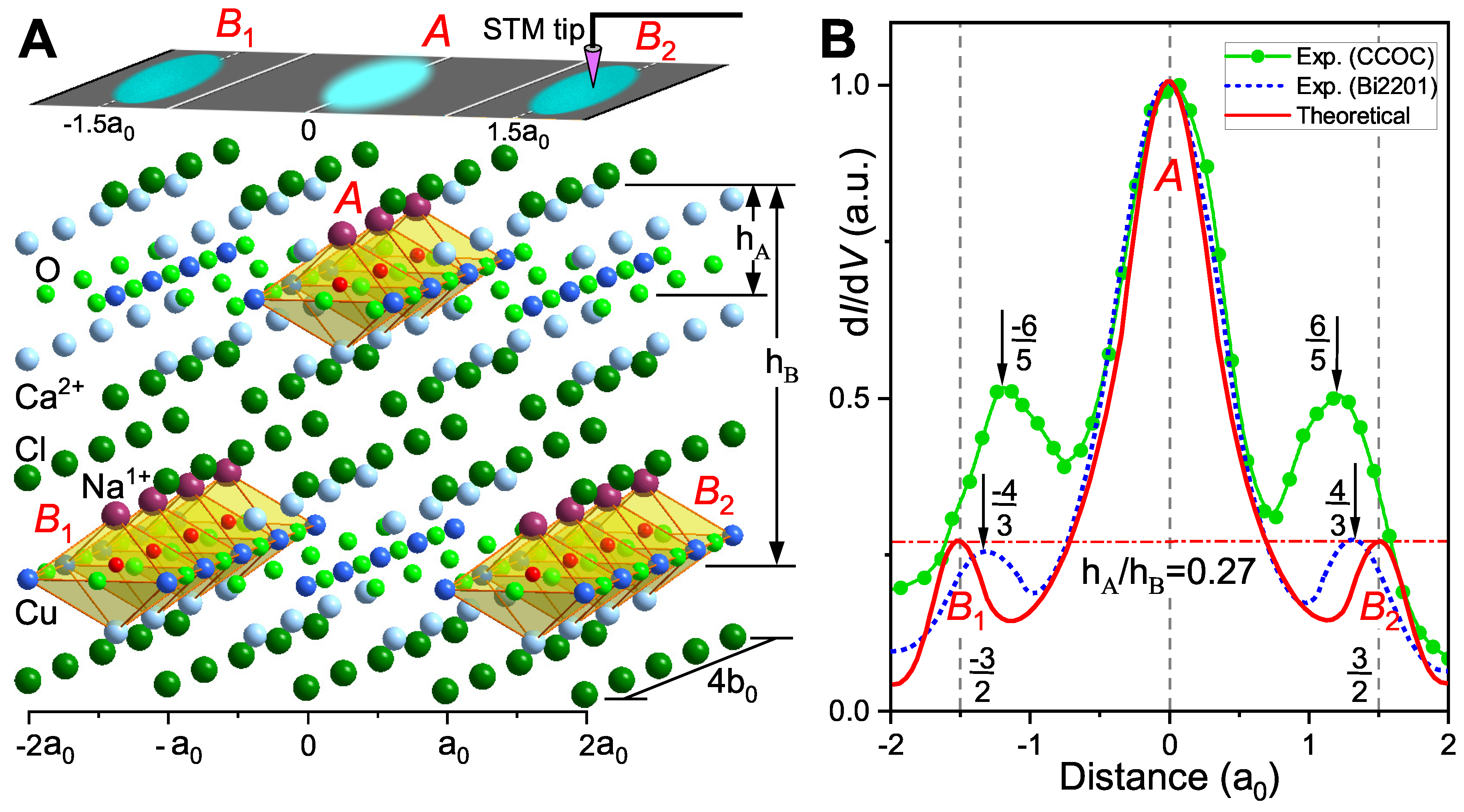
Figure 3A shows the
plaquette cluster in CCOC, where
replaces
, breaking mirror symmetry and inducing hole doping in octahedral quantum wells. From stability and symmetry, doping at the central position of the upper
layer forms three connected octahedral quantum wells (
A), whose electrons correspond to the brightest central bar in STM experiments. Doping at
in the lower
plane forms symmetrically arranged four-connected octahedral quantum wells (
and
). As the lower
plane (
B) is farther from the cleavage plane (
), its STM bars appear darker. Based on
Figure 3A, the theoretical DOS peak result is qualitatively shown as the red line in
Figure 3B. The intensity ratio of the central peak to secondary peaks is quantitatively determined by
. Taking the central peak as 1, secondary peaks equal
. For CCOC and Bi2201,
and
are (2.742 Å, 10.263 Å) and (4.662 Å, 17.175 Å), giving
k values of 0.267 and 0.271, respectively. Then, the value of the two secondary peaks is approximately 0.27 (red dotted line in
Figure 3B). Experimental results for CCOC (green) and Bi2201 (blue) show good agreement for Bi2201, while CCOC has secondary peak position/intensity errors, likely due to scanning speed and probe-sample distance.
Pseudogap, strange metal, linear dependence and phase diagram
Two perfect linearities represent two major puzzles in condensed matter physics. In cuprate superconductors, experiments such as tunneling spectroscopy and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) have shown that the pseudogap decreases linearly with hole-doping concentration, deviating from the -shaped evolution of
[
29]. In the overdoped regime of HTSCs (the strange metal state), the normal-state resistivity exhibits auniversal linear dependenceon temperature [
30]. We propose a theoretical framework to explain these two phenomena within our current model.
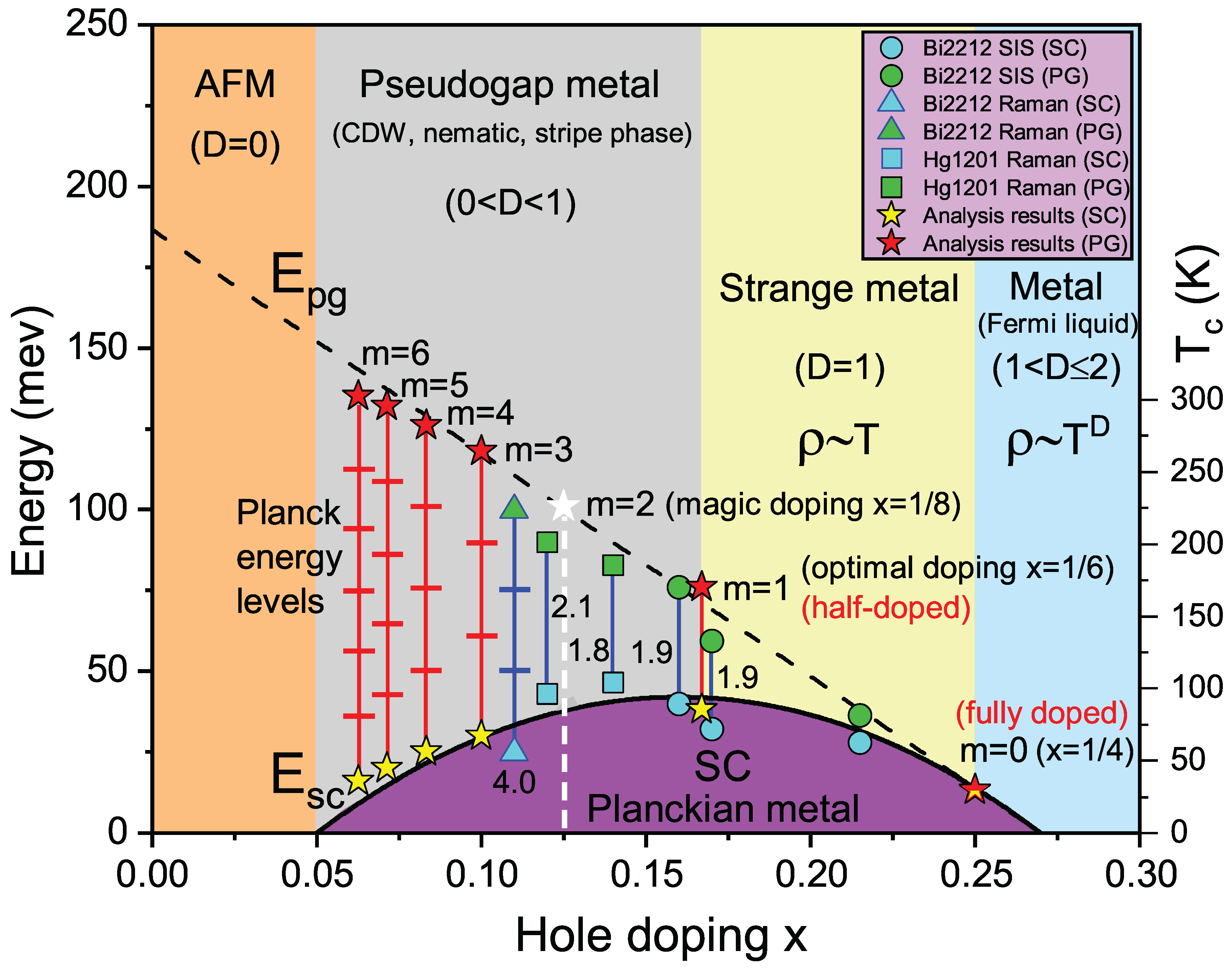
The peculiar pseudogap exhibited by HTSCs in the normal state has been extensively verified by experiments. However, its origin and relationship with the superconducting mechanism remain controversial. Notably, the pseudogap strongly depends on the doping concentration. Through analyzing extensive experimental data, Hüfner et al. concluded the coexistence of two energy scales in HTSCs [
29], as shown in
Figure 4. They found that the superconducting energy scale follows a dome-shaped curve (denoted as
meV), while the pseudogap can be represented by a linear relationship
meV.
Interestingly, it will be shown that the integer
m in Eq. (
6) governs the superconducting properties and exhibits a remarkably close correlation with the pseudogap. We find that the pseudogap
and the superconducting energy scale
satisfy the following quantization relationship:
Figure 4 shows
exhibits a dome-shaped dependence on doping concentration
x (yellow stars), while
decreases linearly with
x (red stars). This gap discrepancy stems from their origins:
originates from the Planck ground state, and
from Planck excited states. As in
Figure 2A, when
(saturation occupancy), all polyhedral quantum wells in the 1D chain are occupied, closing the pseudogap. Reducing doping creates vacancies, gradually opening the pseudogap. At optimal doping (
, half-filling in
Figure 2B),
completely opens to twice
, corresponding to electron transitions from the ground to first excited state. Four sets of experimental data near optimal doping confirm
, indicating half-filling dominance. The 1/8 anomaly suppresses superconductivity in the underdoped region, preventing
(white stars). At
, three vacancies between quantum wells (
Figure 2D) induce a third excited-state pseudogap with
, matching the quadruple
signal (triangles) near
. Asmincreases, excited-state energy levels rise, driving the pseudogap to depend linearly on doping. As shown in
Figure 2A to D and Eq. (
8), the superconducting phase arises from doped quantum well electrons (conducting domains), while undoped vacancies (insulating domains) form the pseudogap phase. These two phases are a contradictory unity of competition and unity [
28], with their proportions summing to one.
As illustrated in
Figure 4, besides the purple superconducting region (referred to here as the Planck metallic state), the high-temperature superconducting phase diagram can be divided into four areas based on doping: orange for undoped antiferromagnetic Mott insulator, gray for underdoped pseudogap metal, yellow for strange metal, and blue for Fermi liquid. The dimension
D in the phase diagram represents the charge-ordered phase and measures electron behavior in the normal state. Our research focuses on the anomalous resistivity behavior of strange metals, which corresponds to the mixed state between full doping (
Figure 2A) and half-doping (
Figure 2B), with the doping concentration expressed as:
where
and
are the proportions of the two states, satisfying
.
The most critical feature of the mixed state defined by Eq. (
9) is that it can ensure the
-shift stability in
Figure 1E and the quasi-one-dimensional charge order and conductivity characteristics (
Figure 2, A and B). Consequently, the strange metal arising from this mixed state necessarily satisfies
. Generally, the temperature-dependent resistivity can be expressed as:
. For the strange metal’s mixed state (
), naturally leading to the universal linear temperature dependence of electrical resistivity
. When
(saturation doping concentration), excess doping disrupts the
-shift stability and quasi-one-dimensional charge order, in this case
; as doping increases, the
component emerges and increases, and the resistivity exhibits the conventional Fermi liquid behavior of metals.
Concluding remarks
This study proposes a novel framework for HTSCs, where superconductivity stems from localized electrons in polyhedral quantum wells, and the order parameter of the superconducting phase transition is essentially the electric dipole vector of e-h pairs. It redefines the superconducting state as symmetry breaking of an external field-induced Planck metal, linking crystal structures intrinsically to the dissipationless Planck ground state. A key derivation, , accurately predicts for cuprate and iron-based superconductors, matching experimental data. No additional quasiparticle glue is required. The theory addresses several long-standing puzzles in high-temperature superconductivity (HTS), including the Planckian limit of critical temperatures, the linear decay of the pseudogap with hole doping, the competition between pseudogap and superconducting phases, strange metal resistivity, nematic phase, and checkerboard anomaly. Leveraging electron indistinguishability in the superconducting state, it simplifies quantum many-body problems to single-electron models, by passing challenges like pairing mechanisms. It reinterprets the superconducting transition as an insulator transition below , superconductivity emerges under external fields when Wigner crystals (Planck metals) undergo symmetry-breaking displacements, forming polarization capacitors for lossless Maxwell displacement current transmission without quasiparticles. Applications cover Fermi surface topology, d-wave symmetry, spin resonance, and pressure-induced transitions. Current research spans kagome lattices, , hydrogen-rich compounds, twisted bilayer graphene, and the quantum Hall effect, advancing understanding of superconductivity and quantum many-body theory in strongly correlated systems.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available in the main text or the supplementary.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Haihu Wen, Yayu Wang, Liling Sun, and Ningning Wang for sharing and the helpful discussion of their experimental results. The author would like to acknowledge Duan Feng for his invaluable suggestions and helpful discussions at the early stage of this research. The author is grateful to Shusheng Jiang, Changde Gong, and Dingyu Xing for their unwavering encouragement and support of the research process during his stay at Nanjing University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- B. Keimer, S. A. Kivelson, M. R. Norman, S. Uchida, J. Zaanen. From quantum matter to high-temperature superconductivity in copper oxides. Nature 518, 179–186 (2015). [CrossRef]
- P. A. Lee, N. Nagaosa, X. G. Wen. Doping a mott insulator: physics of high-temperature superconductivity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 17–85 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Y. He, et al. Fermi Surface and Pseudogap Evolution in a Cuprate Superconductor. Science 344, 608–611 (2014). [CrossRef]
- P. W. Phillips, et al. Stranger than metals. Science 377, eabh4273 (2022).
- P. Giraldo-Gallo, et al. Scale-invariant magnetoresistance in a cuprate superconductor. Science 361, 479–481 (2018). [CrossRef]
- P. W. Anderson. Is there glue in cuprate superconductors? Science 316, 1705–1707 (2007).
- S. Dal Conte, et al. Disentangling the Electronic and Phononic Glue in a High-Tc Superconductor. Science 335, 1600–1603 (2012).
- J. Zaanen. Why the temperature is high. Nature 430, 512–513 (2004).
- S. Badoux, et al. Change of carrier density at the pseudogap critical point of a cuprate superconductor. Nature 531, 210–214 (2016). [CrossRef]
- C. C. Tsui, J. R. Kirtley. Pairing symmetry in cuprate superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 969–1016 (2000). [CrossRef]
- D. Fausti, et al. Light-induced superconductivity in a stripe-ordered cuprate. Science 331, 189–191 (2011). [CrossRef]
- R. Comin, et al. Charge Order Driven by Fermi-Arc Instability in Bi2Sr2-xLaxCuO6+ffi. Science 343, 390–392 (2014).
- E. Dagotto. Correlated electrons in high-temperature superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 763 (1994). [CrossRef]
- Fischer, et al. Scanning tunneling spectroscopy of high-temperature superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys.79, 353–419 (2007).
- D. N. Basov, T. Timusk. Electrodynamics of high-Tc superconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 721–779 (2005).
- C. M. Varma. Colloquium: Linear in temperature resistivity and associated mysteries including high temperature superconductivity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 031001 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Y. Kamihara, T. Watanabe, M. Hirano, H. Hosono. Iron-based layered superconductor La[O1-xFx]FeAs (x= 0.05-0.12) with Tc=26 K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 3296-3297 (2008).
- H. L. Sun, et al. Signatures of superconductivity near 80 K in a nickelate under high pressure. Nature 621, 493–498 (2023). [CrossRef]
- S. Martin, et al. Normal-state transport properties of Bi2+xSr2-yCuO6+ffi crystals. Phys. Rev. B 41, 846 (1990).
- O. Gunnarsson, M. Calandra, J. E. Han. Colloquium: Saturation of electrical resistivity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 1085–1099 (2003). [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, et al. Shot noise in a strange metal. Science 382, 907–911 (2023). [CrossRef]
- J. Yuan, et al. Scaling of the strange-metal scattering in unconventional superconductors. Nature 602, 431–436 (2022). [CrossRef]
- X. Jiang, et al. Interplay between superconductivity and the strange-metal state in FeSe. Nat. Phys. 19, 365–371 (2023). [CrossRef]
- A. Coe, et al. Nanoscale Conducting and Insulating Domains on YbB6. Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 236205 (2025).
- S. A. Hartnoll, A. P. Mackenzie. Colloquium: Planckian dissipation in metals. Rev. Mod. Phys. 94, 041002 (2022). [CrossRef]
- G. Grissonnanche, et al. Linear-in temperature resistivity from an isotropic Planckian scattering rate. Nature 595, 667–672 (2021). [CrossRef]
- T. Hanaguri, et al. A checkerboard electronic crystal state in lightly hole-doped Ca2-xNaxCuO2Cl2. Nature 430, 1001–1005 (2004).
- M. R. Norman, D. Pines, C. Kallin. The pseudogap: friend or foe of high Tc? Adv. Phys. 54, 715–733 (2005).
- S. Hüfner, et al. Two gaps make a high-temperature superconductor? Rep. Prog. Phys. 71, 062501 (2008). [CrossRef]
- A. Legros, et al. Universal T-linear resistivity and Planckian dissipation in overdoped cuprates. Nat. Phys. 15, 142–147 (2019). [CrossRef]
- J. G. Bednorz, K. A. Müller. Possible high-Tc superconductivity in the Ba-La-Cu-O system. Z. Phys. B 64, 189–193 (1986). [CrossRef]
- A. A. Abrikosov. Nobel Lecture: Type-II superconductors and the vortex lattice. Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 975–979 (2004). [CrossRef]
- S. S. Ye, et al. Visualizing the Zhang-Rice singlet, molecular orbitals and pair formation in cuprate. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.09260 (2023).
- H. Li, et al. Low-energy gap emerging from confined nematic states in extremely underdoped cuprate superconductors. npj Quantum Mater. 8, 18 (2023).
- L. Gao, et al. Superconductivity up to 164 K in HgBa2Cam-1CumO2m+2+δ (m=l, 2, and 3) under quasihydrostatic pressures. Phys. Rev. B 50, 4260–4263 (1994).
- Z. A. Ren, et al. Superconductivity at 55 K in iron-based F-doped layered quaternary compound Sm[O1-xFx]FeAs. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 2215–2216 (2008).
- R. A. Cooper et al. Anomalous Criticality in the Electrical Resistivity of La2-xSrxCuO4. Science 323, 603–607 (2009).
- L. Sun, et al. Re-emerging superconductivity at 48 kelvin in iron chalcogenides. Nature 483, 67–69 (2012). [CrossRef]
- X. H. Chen, et al. Superconductivity at 43 K in SmFeAsO1-xFx. Nature 453, 761–762 (2008). [CrossRef]
- T. Xie, et al. Odd and even modes of neutron spin resonance in the bilayer iron-based superconductor CaKFe4As4. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 267003 (2018).
- B. Geisler, et al. Structural transitions, octahedral rotations, and electronic properties of A3Ni2O7 rare-earth nickelates under high pressure. npj Quantum Mater. 9, 38 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhu, et al. Superconductivity in pressurized trilayer La4Ni3O10-ffi single crystals. Nature 631, 531–536 (2024).
- N. Wang, et al. Bulk high-temperature superconductivity in pressurized tetragonal La2PrNi2O7. Nature 634, 579–584 (2024). [CrossRef]
- T. Wu, et al. Magnetic-field-induced charge-stripe order in the high-temperature superconductor YBa2Cu3Oy. Nature 477, 191–194 (2011). [CrossRef]
- S. Komiya, H. D. Chen, S. C. Zhang, Y. Ando. Magic doping fractions for high-temperature superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 207004 (2005). [CrossRef]
- D. Qiu, et al. Recent advances in 2D superconductors. Adv. Phys. 33, 2006124 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Y. Yu, et al. High-temperature superconductivity in monolayer Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+ffi. Nature 575, 156–163 (2019). [CrossRef]
- V. Fatemi, et al. Electrically tunable low-density superconductivity in a monolayer topological insulator. Science 362, 926–929 (2018). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).