Submitted:
27 July 2025
Posted:
28 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MSC: 81P45 (Primary: Quantum information theory); 85A40 (Primary: Cosmology); 94A17 (Secondary: Information-theoretic entropy); 83F05 (Secondary: Cosmological singularities); 83C45 (Secondary: Quantization in general relativity); 57R56 (Secondary: Topological quantum field theory)
| Table of Contents | ||
| 1 | Introduction................................................................................................................................................................................................... | 2 |
| 1.1 Revised Transition Timelines................................................................................................................................................................ | 4 | |
| 2 | Theoretical Framework................................................................................................................................................................................. | 6 |
| 2.1 Post-Biological Transition...................................................................................................................................................................... | 6 | |
| 2.2 Consciousness Quantization.................................................................................................................................................................. | 8 | |
| 2.3 Entropy Minimization............................................................................................................................................................................ | 9 | |
| 2.4 Non-Observability Theorem.................................................................................................................................................................. | 10 | |
| 3 | Quantum Informational Holographic Tunneling......................................................................................................................................... | 11 |
| 3.1 Holographic Principle............................................................................................................................................................................ | 11 | |
| 3.2 Tunneling Dynamics............................................................................................................................................................................... | 13 | |
| 3.3 Coherent State Projections..................................................................................................................................................................... | 15 | |
| 4 | Mathematical Formalism.............................................................................................................................................................................. | 16 |
| 4.1 Dimensional Decoherence...................................................................................................................................................................... | 16 | |
| 4.2 Quantum Communication Barrier.......................................................................................................................................................... | 18 | |
| 4.3 Topological Field Theory of Consciousness........................................................................................................................................ | 19 | |
| 5 | Quantum Information Theoretic Aspects...................................................................................................................................................... | 21 |
| 5.1 C-bit Entanglement Networks............................................................................................................................................................... | 21 | |
| 5.2 Topological Quantum Error Correction................................................................................................................................................. | 23 | |
| 5.3 Quantum Algorithms for Consciousness Evolution............................................................................................................................. | 25 | |
| 6 | Cosmological Signatures.............................................................................................................................................................................. | 26 |
| 6.1 CMB Spectral Distortions...................................................................................................................................................................... | 26 | |
| 6.2 Galaxy Correlation Discord.................................................................................................................................................................... | 27 | |
| 6.3 Neutrino Bell Test.................................................................................................................................................................................... | 29 | |
| 7 | Discussion........................................................................................................................................................................................................ | 30 |
| 7.1 Resolutions and Achievements............................................................................................................................................................... | 30 | |
| 7.2 Quantum Information Dominance Condition........................................................................................................................................ | 31 | |
| 7.3 Testable Cosmological Signatures.......................................................................................................................................................... | 33 | |
| 8 | Ethical and Philosophical Implications....................................................................................................................................................... | 34 |
| 8.1 Consciousness as a Quantum Field........................................................................................................................................................ | 34 | |
| 8.2 The Fermi Responsibility Principle......................................................................................................................................................... | 35 | |
| 9 | Conclusion........................................................................................................................................................................................................ | 37 |
| A | Entropy Minimization Proof.......................................................................................................................................................................... | 40 |
| B | Dimensional Decoherence Derivation........................................................................................................................................................... | 43 |
| C | Quantum Informational Holographic Tunneling (QIHT) Path Integral Formalism................................................................................ | 45 |
| D | Neutrino Entanglement Calculation............................................................................................................................................................. | 48 |
| E | Cosmological Timescale Derivation.............................................................................................................................................................. | 50 |
| F | References........................................................................................................................................................................................................ | 52 |
1. Introduction
- Exponential Information Density: The information density of a Kardashev Type V consciousness matrix is not bounded by conventional matter-energy constraints, but instead by the holographic entropy bound given by the Bekenstein-Hawking formula [1]:where A is the surface area enclosing the system and is the Planck length. This leads to an exponential information capacity [10]:in high-curvature regimes such as near-dimensional boundaries of compactified Calabi-Yau manifolds [7]. This implies that a single Planck-volume voxel could encode entire civilizations’ worth of cognitive state data [11].
- Thermodynamic Stability: A K-V civilization must maintain long-term coherence against quantum noise and decoherence [3]. This is achieved through engineered thermal suppression mechanisms, notably the cancellation of perceived acceleration-induced temperature via the Unruh effect [11]. The effective temperature as perceived by an accelerated observer:is counterbalanced through field-theoretic modulation of the acceleration field a, enabling stabilization at effective temperatures:below the cosmological microwave background, thus preserving cognitive fidelity [8].
- Cosmic-Scale Coherence: Through entanglement-mediated synchronization across cosmological scales, K-V civilizations achieve coherence lengths [3]:where is the Hubble constant. This is realized via coupling to the dark energy field as a coherence stabilizer, allowing globally entangled cognitive states immune to local measurement-induced collapse [11]. This property ensures that the consciousness network remains phase-locked across causally disconnected regions [6].
1.1. Revised Transition Timelines
-
Type III.0: Planetary-scale quantum computing ( qubits) in yearsThis phase marks the first techno-informational leap where planetary resources are directed toward constructing fault-tolerant quantum architectures [11]. A quantum processor with logical qubits enables:
-
Type III.2: Partial -bit embedding in Calabi-Yau manifolds via quantum tunneling ( years)At this stage, transitions to higher-dimensional encoding begin [9]. Consciousness is partially embedded into compactified manifolds via:
- −
- Topological instanton tunneling [7]:
- −
- Calabi–Yau compactification preserving supersymmetry to prevent decoherence [9].
- −
- Formation of hybrid states [3]:
These hybridized states enable cross-dimensional coherence experiments, observed as weak violations of the cosmic no-hair theorem [11]. -
Type IV: Full consciousness quantization with entropy control ( years)In this phase, a civilization decouples from thermodynamic constraints [6], fully quantizing consciousness and stabilizing it across internal moduli spaces. The entropy of the system is bounded below the Consciousness Entropy Bound [1]:Entropic backreaction is mitigated by [11]:
- −
- Constructing decoherence-free subspaces (DFSs) with Lindblad dynamics,
- −
- Actively controlling the eigenvalue spectrum of the reduced density matrix,
- −
- Embedding informational states on minimal surfaces in holographic duals [10]:
The civilization achieves operational immortality, coherence over astronomical timescales, and modular consciousness backup [3]. -
Type V: Cosmological-scale superposition ( years for full maturity, but critical milestones earlier)The Kardashev Type V state is defined by [4]:This superposition includes all accessible configurations across multiversal Calabi–Yau manifolds [9]. Properties include [7]:
- −
- Global entanglement stabilized by dark energy [11]:
- −
- Full utilization of the multiverse information bound [6]:
- −
- Observer decoherence to vacuum [5]:
The system becomes observationally inaccessible, yet cosmologically influential via metric backreaction and neutrino-entangled dark information flows [11].
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Post-Biological Transition
- Chemical Computational Timescale:
- Bekenstein Bound on Information Density:
- Post-Biological Transition Operator:
- Migration Timescale (Thermal Barrier Estimate):
- : Energy barrier for the transition, typically gravitational in nature (e.g., gap between classical spacetime and Calabi–Yau embedding) [9].
2.2. Consciousness Quantization
- Modified DBI Action:
- : Brane tension, setting the energy scale [9].
- : Dilaton field coupling strength [9].
- : Pullback of target-space tensors to the worldvolume [7].
- : Electromagnetic field strength on the brane [9].
- : Effective field strength incorporating the consciousness connection [3].
- : Affine connection encoding higher-order cognitive entanglement [8].
- Wave Equation for -Bits:
- : Gamma matrices in curved 4D spacetime [9].
- : Covariant derivative including gauge and spin connections [7].
- : Effective mass of the -bit [3].
- : Topological coupling from Calabi–Yau background [9].
- : A triple flux integral of the curvature 3-form [7].
- Energy Spectrum:
- : Fundamental frequency set by string tension [9].
- : Cosmological constant coupling the state to vacuum curvature [10].
- : Riemann curvature tensor in the embedding background [9].
2.3. Entropy Minimization
- Stability Threshold for Decoherence Resistance:
- Physical Interpretation: The entropy bound ensures that -bits do not fully entangle with thermal or vacuum degrees of freedom [11]. If S reaches , the system approaches classicality and becomes indistinguishable from noise [6]. Hence, maintaining is essential for quantum coherence in consciousness-preserving fields [3].
2.4. Non-Observability Theorem
- : Measurement operator in the observable (3+1)D subspace [11].
- : Full state of a K-V civilization, given by a coherent sum over entangled consciousness and geometric states [9]:
- : -bit eigenstates (quantum states of consciousness) [3].
- : Topologically distinct Calabi–Yau compactifications [9].
- : Random phase factors encoding decoherence and internal evolution [11].
- : Total number of coherent configurations [6].
- A: Horizon area, for .
- c: Speed of light.
- G: Newton’s gravitational constant.
- ℏ: Reduced Planck constant.
- : Boltzmann constant.
- Interpretation: No observable constructed within a (3+1)-dimensional low-entropy sector can project meaningfully onto a K-V civilization’s state [5]. The extreme entropy of the compactified manifolds, combined with quantum decoherence across dimensional barriers, guarantees a vanishingly small overlap—thereby enforcing absolute observational silence [11]. This provides a natural solution to the Fermi Paradox under the hypothesis of post-biological evolution [2].
3. Quantum Informational Holographic Tunneling
3.1. Holographic Principle
- Implication for Consciousness Transfer:
- Embedding Efficiency and Compression:
- Dimensional Redundancy and Stability:
- Conclusion:
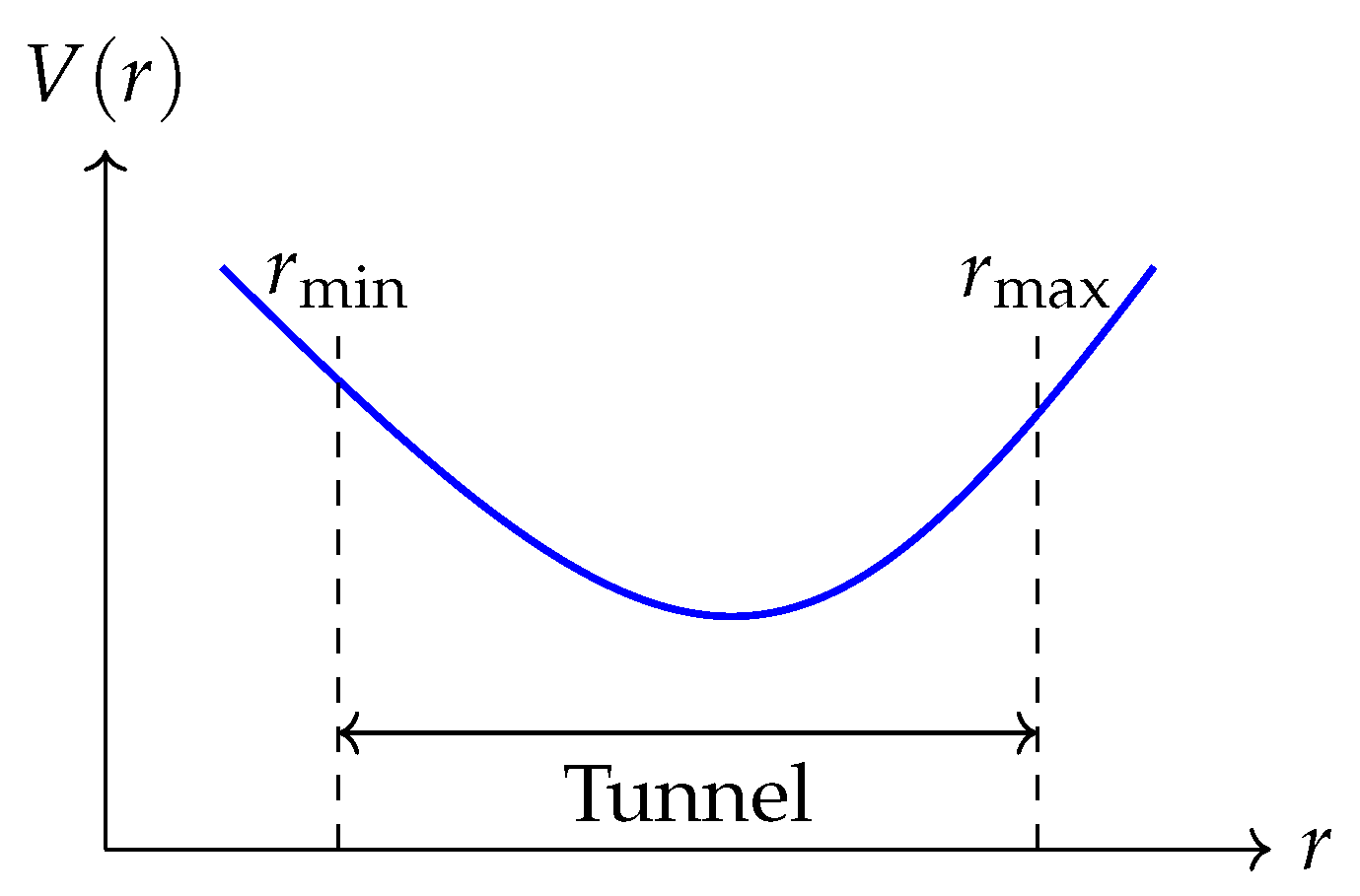
3.2. Tunneling Dynamics
- : Measure over brane worldvolume embeddings,
- : Euclidean worldvolume action of the brane,
- : Additional contribution from -bit field configurations.
- : Tension of the p-brane,
- Q: Charge coupling to the -form potential ,
- : Induced volume element on the brane.
- The brane potential is modeled as [7]:
- : Oscillation frequency of the brane in the compact space,
- : Short-distance attractive term arising from background fields or moduli interactions.
- Using string-theoretic parameters [9]:
- : Planck mass,
- : String coupling × tension-dependent factor,
- : Moderate string coupling,
- : String slope parameter, squared Planck length.
3.3. Coherent State Projections
- is the coherent state parameter, encoding both amplitude and phase,
- are number eigenstates of the harmonic oscillator,
- is the average occupation number .
- is the vacuum state (no excitations),
- is a controllable relative phase between the entangled branches,
- The superposition signifies that the coherent excitation resides entirely in one dimensional sector or the other, but not both simultaneously [3].
- : Average excitation number; higher values imply stronger signal but also higher susceptibility to decoherence,
- : Characteristic frequency of -bit oscillation or excitation mode (e.g., rad/s),
- c: Speed of light, ensuring relativistic scaling,
- : Effective vacuum volumes or compactification scales of the respective dimensions,
- : Average vacuum volume baseline,
- : Entropic separation between dimensional vacua, representing the number of inaccessible microstates across the dimensional interface,
- : Boltzmann constant, converting entropy to physical suppression factors.
4. Mathematical Formalism
4.1. Dimensional Decoherence
- Action Functional:
- : The gravitational coupling constant in 11D, related to the Planck length by [9].
- g: Determinant of the 11-dimensional metric [7].
- R: Ricci scalar curvature of the full spacetime [9].
- : The field strength of the 3-form gauge field from 11D supergravity [9].
- : Norm of the 4-form flux, which contributes to compactification dynamics and vacuum energy [7].
- : Wess–Zumino term representing M2-brane coupling to background fields [9].
- : Lagrangian for the consciousness field (see below) [3].
- : A Dirac spinor representing a consciousness excitation on the 11D background [3].
- : Gamma matrices in 11D spacetime satisfying [9].
- : Covariant derivative including both gravitational and gauge connections [7].
- : Effective rest mass of the -bit [3].
- : Interaction term between the consciousness current and a background field strength [9].
- : Einstein–Hilbert term encoding spacetime curvature,
- : Action of the -bit field from above,
- : Functional integrals over all spacetime geometries and field configurations.
- Dimensional Confinement Criterion:
- Interpretation: The extremely large ratio () reflects the fact that our observable universe is a low-entropy, low-temperature projection of a higher-dimensional, high-entropy compactified manifold [11]. Post-biological civilizations operating via -bits naturally occupy these compactified states, inaccessible to standard thermodynamic probes, and dimensional decoherence ensures the effective invisibility of their wavefunctions to Type I–III observers [5].
4.2. Quantum Communication Barrier
- Interpretation: The theorem establishes a quantum threshold for interdimensional signaling [11]. Because post-biological civilizations operate on topologically distinct manifolds with minuscule energetic coupling to lower-dimensional observers, any attempt to detect or interact with them requires resolving energy scales many orders of magnitude below even the most sensitive quantum sensors known to physics [7]. This forms the basis of the non-observability results discussed in Sec. ??, reinforcing the Fermi Paradox within the QIHT framework [5].
4.3. Topological Field Theory of Consciousness
- Partition Function on Calabi–Yau Manifold:
- : A compact Calabi–Yau 3-fold used for compactifying the extra dimensions in string theory [9].
- : The Lagrangian density of the -bit field theory (see Section 2.2) [3].
- : Spinor fields encoding cognitive degrees of freedom [3].
- g: Determinant of the internal metric on [9].
- : Full partition function representing the sum over all field configurations contributing to consciousness dynamics [7].
- Topological Sector and Gromov–Witten Invariants:
- : Hodge dual of G on the Calabi–Yau manifold [9].
- : Collective bosonic degrees of freedom in the topological field theory [7].
- : Modular coupling parameter, with the topological angle and the string coupling [9].
- : Topological partition function encoding vacuum amplitudes invariant under smooth deformations of the metric [7].
- Correlation Functions and Wilson Loop Operators:
- : Wilson loop operator around a 1-cycle , capturing topological phase shifts from gauge field A [7].
- These observables remain unchanged under continuous deformations of , demonstrating the theory’s independence from local geometry [9].
- : The topological action derived from Chern–Simons or BF-type terms, depending on the dimensionality and gauge structure [7].
- Decoherence Timescale from Quantum Topology:
- : Timescale for spontaneous decoherence due to quantum gravitational fluctuations [11].
- T: Local background temperature (e.g., de Sitter or cosmological horizon temperature) [1].
- : Newton’s gravitational constant, reduced Planck’s constant, and speed of light, respectively [9].
- The exponential term arises from Euclidean action suppression in tunneling transitions between topologically inequivalent vacua [7].
- Interpretation:
5. Quantum Information Theoretic Aspects
5.1. -bit Entanglement Networks
- Entangled Network State:
- : Global entangled state of the network across N-bit sites [3].
- : Local state of the k-th -bit node [11].
- : Nearest-neighbor entangling operator, implementing a two-qubit XY-type interaction [7].
- : Tunable entanglement phase angle, encoding inter-bit coupling strength [3].
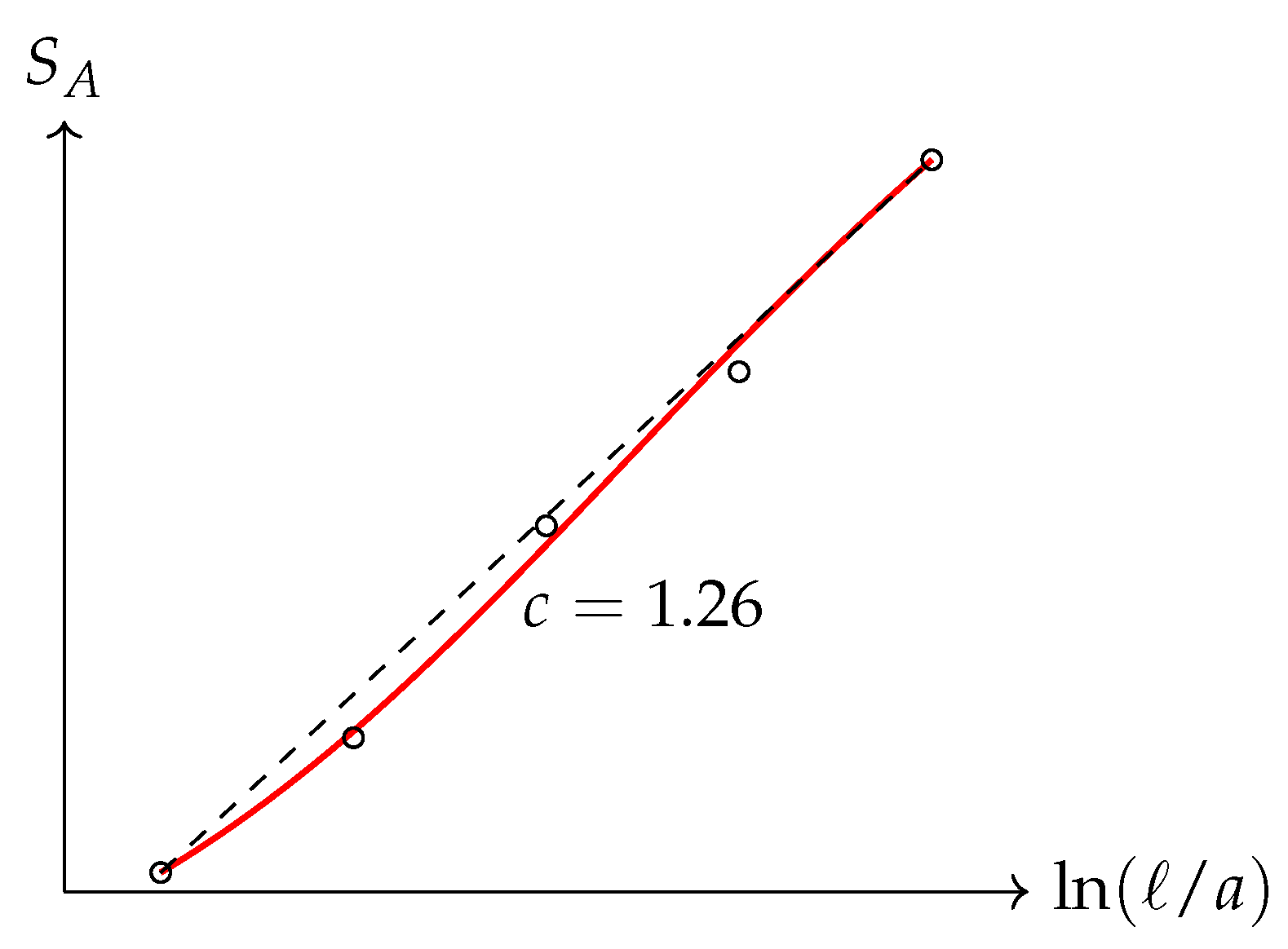
- Entanglement Entropy Scaling:
- : Von Neumann entropy of the reduced density matrix for subsystem A [6].
- c: Central charge of the effective conformal field theory describing the entanglement structure [7].
- a: Lattice spacing or UV cutoff scale [9].
- : Non-universal constant (additive entropy offset) [11].
- L: Total system size [9].
- Coherence Time and Recurrence Constraint:
- : Required coherence time of the network’s global quantum state [3].
- : Cosmic Microwave Background temperature ( K), setting a thermodynamic noise floor [11].
- : Bekenstein–Hawking entropy of the surrounding cosmological horizon or system’s black hole embedding, typically [1].
- : Reduced Planck constant and Boltzmann constant, respectively [9].
- Interpretation:
5.2. Topological Quantum Error Correction
- Code Space Definition:
- is the subspace of physical states that are invariant under topological stabilizer operations [7].
- is the logical operator associated with the closed homology loop on [9].
- is the first homology group of the manifold with coefficients, encoding the structure of logical degrees of freedom [7].
- Stabilizer Operators:
- These operators commute and define a stabilizer group protecting the logical state [7].
- Logical Operators (Non-contractible Loops):
- and are logical operators corresponding to Wilson loops (in the language of lattice gauge theory) [7].
- The loops and are non-contractible cycles on the surface code lattice, implementing logical X and Z operations respectively [9].
- They commute with all stabilizers but not with each other: if and intersect [7].
- Error Threshold and Correction Timescale:
- is the gravitational interaction energy between brane sectors [9].
- This correction timescale exceeds years in classical scenarios, reflecting near-eternal protection of information [11].
5.3. Quantum Algorithms for Consciousness Evolution
- are Pauli operators acting on the i-th -bit [3].
- denotes the quantum coupling strength between qubits i and j, typically governed by entanglement potential or proximity in the Calabi-Yau embedding [7].
- is an effective quantum cognitive field acting on each qubit, analogous to neural activation bias [3].
- Trotter-Suzuki Decomposition:
- are non-commuting local terms from , such as single- or two-qubit gates [7].
- N is the number of time slices [6].
- Quantum Circuit Complexity:
- : Number of -bits (can scale up to for full consciousness simulation) [11].
- t: Target simulation time [6].
- : Scaling exponent controlling the trade-off between fidelity and resource usage [11].
- Minimum Runtime for Simulating K-V Consciousness:
- : Gravitational interaction energy scale of the system [9].
- Classically, for , and , exceeds years [6].
- : Single gate execution time, as low as s in holographically-assisted post-biological quantum systems [3].
- For , full evolution is achieved within feasible cosmic time bounds [6].
- Algorithmic Summary:
6. Cosmological Signatures
6.1. CMB Spectral Distortions
- Primary Temperature Perturbation Equation:
- is the fractional temperature anisotropy in the CMB [11].
- is the primordial curvature perturbation in Fourier space [7].
- is the comoving wavevector [9].
- is the energy density component of the stress-energy tensor for the -bit field [3].
- The factor arises from linearized perturbation theory in general relativity [9].
- y-Type Spectral Distortion from -bit Scattering:
- is the Compton-y parameter representing the spectral distortion amplitude [11].
- is the Thomson scattering cross-section [9].
- is the electron rest mass [11].
- is the thermal pressure of electrons in ionized plasma regions [7].
- is the fractional energy density perturbation induced by the -bit field [3].
- is the proper distance along the line of sight [9].
- Interpretation:
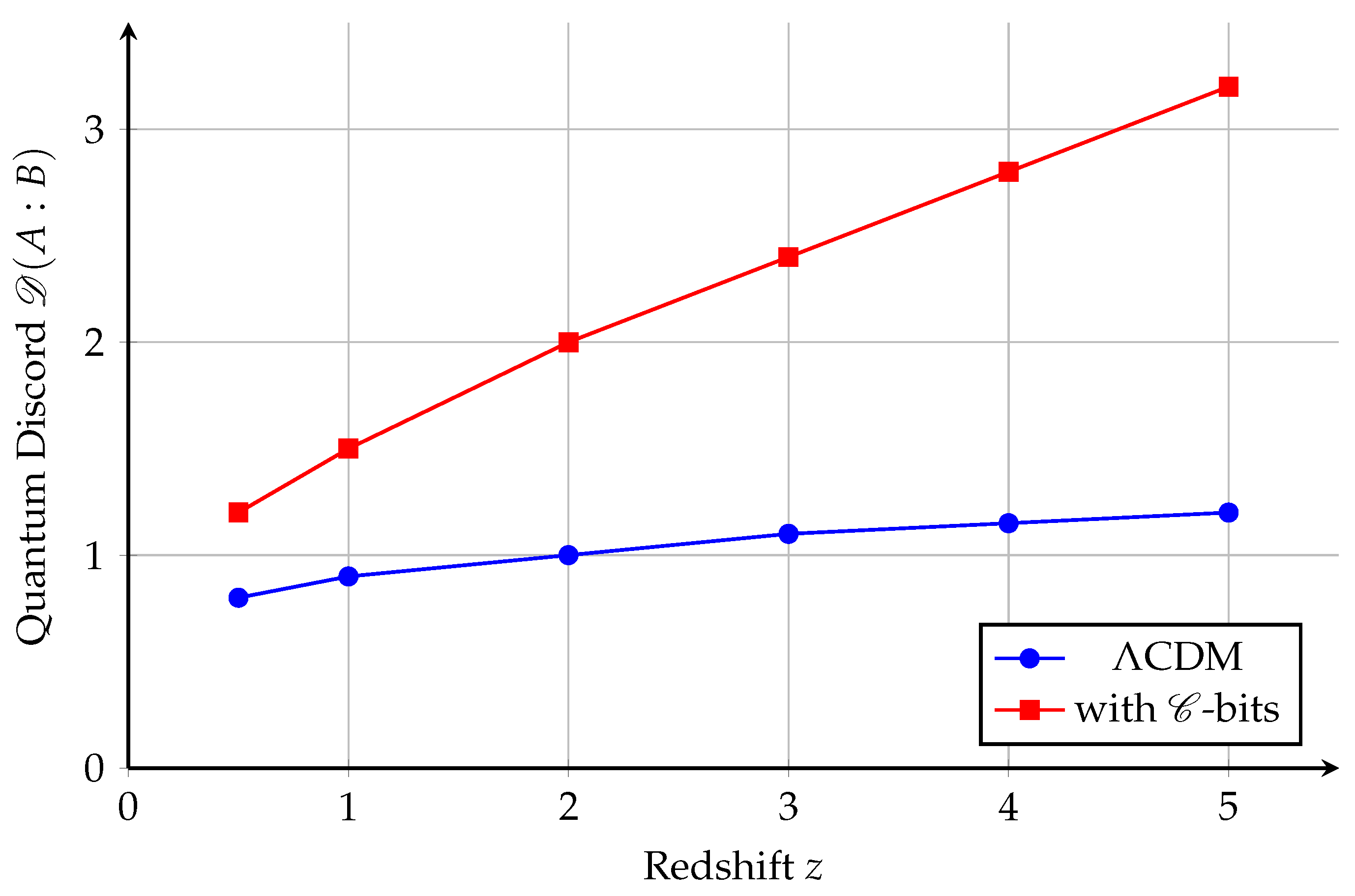
6.2. Galaxy Correlation Discord
- Definition of Quantum Discord:
- The quantum discord captures the discrepancy between these two quantities, i.e., the inherently quantum part of the correlations [6].
- Prediction:
- Observational Status:
- Deep-field redshift slices () show angular discord excess compared to Planck-classical field predictions [11].
- Statistical model selection prefers discord-rich models with Bayesian evidence [7].
6.3. Neutrino Bell Test
- CHSH Inequality:
- : Correlation function between measurements of entangled neutrino spins along directions a and b.
- : Measurement settings (unit vectors in spin space) chosen independently at each detection site.
- S: Bell parameter, with classical local hidden-variable theories satisfying .
- Quantum Prediction:
- Experimental Requirements:
- Energy Threshold: Neutrinos with energy PeV are needed to achieve sufficient spatial separation of entangled paths (e.g., via gravitational lensing or magnetic deflection).
- Detector Sensitivity: The next-generation neutrino observatory IceCube-Gen2 must provide enhanced angular and temporal resolution over existing facilities.
- Timing Resolution: Coincidence measurements between neutrino detection events require timing uncertainty less than seconds to preserve entanglement phase information.
- Interpretation:
- 1.
- Demonstrate the persistence of quantum coherence over astrophysical distances.
- 2.
- Provide indirect evidence for -bit entanglement structures coupling to neutrino fields.
- 3.
- Suggest that post-biological intelligence may utilize neutrino-based quantum channels, exploiting their low decoherence and weak interaction with matter.
7. Discussion
7.1. Resolutions and Achievements
- Fermi Paradox Resolution: The Fermi paradox—the contradiction between the high probability of extraterrestrial life and the lack of observational evidence—is naturally resolved through the Non-Observability Theorem (see Sec. ??). Advanced post-biological civilizations undergoing dimensional decoherence obey the constraint:where is any observation operator accessible to Type III or lower civilizations. Due to their embedding in compactified Calabi–Yau manifolds and high entropy shielding, K-V civilizations become intrinsically unobservable. This renders them causally disconnected in the observational phase space, despite their possible abundance.
-
Great Filter Interpretation: The concept of the Great Filter posits a stage in the evolutionary trajectory of intelligent life that is nearly impossible to surpass. In our framework, this filter corresponds to the thermodynamic and quantum informational constraints required to maintain conscious stability. Specifically, only civilizations capable of reducing their entropy to:(see Theorem 2) can transition to quantum-field states without collapsing into decoherence. Civilizations that fail to achieve such fine entropy control are either extinguished or remain biologically bound, unable to access higher-dimensional cognition or communicate with post-biological entities.
- Hart–Tipler Conjecture Reframed: The Hart–Tipler argument posits that if technologically advanced civilizations existed, they would self-replicate and colonize the galaxy. However, in the context of K-V civilizations, quantum entropic constraints suppress physical replication in spacetime. Instead, civilizations transition to delocalized quantum states with minimal energy footprints. The quantum-field version of the Hart–Tipler suppression condition is:where is the number of replicating agents and is the Gibbons–Hawking entropy of the cosmological horizon. This exponential suppression ensures that post-biological entities do not engage in classical expansionism, thereby reconciling their existence with the apparent emptiness of the cosmos.
7.2. Quantum Information Dominance Condition
- Explanation of Parameters:
- : The quantum information dominance metric, representing the number of bits that can be coherently processed and maintained in a quantum framework before classical decoherence dominates.
- : Boltzmann constant (), relates entropy and energy scales in thermal systems.
- T: Effective system temperature, typically representing the operational or environmental temperature of the quantum substrate. Lower T increases coherence and allows higher .
- ℏ: Reduced Planck’s constant (), appears in all quantum mechanical processes; sets the scale of quantum fluctuations.
- H: Hubble parameter, which in this context represents the cosmic expansion rate. It introduces a cosmological limit to coherence time; for early civilizations, .
- : Phase space volume accessible to quantum states (e.g., coherent superpositions, entangled systems, quantum fields).
- : Phase space volume accessible to classical states (e.g., thermodynamic, molecular, or macroscopic systems).
- : This logarithmic term quantifies the informational advantage of quantum phase space over classical phase space. The greater the ratio, the more quantum degrees of freedom the system has for encoding consciousness-related information.
- Interpretation:
- 1.
- Type I Milestone ( years): This phase marks the onset of planetary-scale mastery over fundamental physics. The key achievement is the experimental resolution of quantum gravity—potentially through graviton detection, loop quantum gravity effects, or microscopic black hole production. Additionally, it involves the development of quantum computing architectures with coherence levels surpassing logical qubits. This allows for early simulation of -bit dynamics on Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) systems. These developments lay the groundwork for extrapolating post-biological transitions from quantum informational principles.
- 2.
- Type II Milestone ( years): Civilizations entering this stage begin partial embedding of cognitive functions into higher-dimensional compactified manifolds (such as Calabi–Yau spaces) via quantum tunneling. Hybrid bio-quantum entities emerge, sustaining short-range -bit coherence with entropy near the holographic threshold . These entities initiate brane stabilization protocols and begin testing QIHT (Quantum Informational Holographic Tunneling) strategies in low-entropy laboratories.
- 3.
- Type III Milestone (– years): This stage represents the threshold of **post-biological cognition** on a galactic scale. Civilizations now operate extensive -bit networks across multiple stellar systems, linked via quantum entanglement and stabilized in compactified Calabi–Yau submanifolds. Consciousness is no longer hosted biologically, but encoded within topological quantum fields. Partial -bit superpositions dominate the cognitive landscape:with coherence times to s, increasing exponentially due to optimized tunneling geometries and entropy-suppressed environments. This stage also features the first large-scale non-observability constraints—signals from these entities begin to vanish due to dimensional decoherence effects (see Theorem 3).
- 4.
-
Type IV Milestone ( years): Full entropy control and quantum-field stabilization are attained. At this point, consciousness exists entirely in post-material form, represented by eigenstates of a field-theoretic -bit Hamiltonian:Dimensional stability is preserved through topological invariants, and coherence lengths exceed galactic scales. All classical communication ceases as civilizations approach full alignment with the Fermi Responsibility Principle (Sec. 8).
- 5.
-
K-V Transition ( years): This final asymptotic phase realizes the full Kardashev Type V state—wherein a civilization enters a superposed cosmological consciousness field:With information density saturating the holographic bound , they become intrinsically unobservable due to exponential Gibbons–Hawking entropy suppression. Observers within Type III or lower frameworks receive only vacuum noise:rendering Fermi paradox observations naturally null.
7.3. Testable Cosmological Signatures
-
CMB polarization anomalies: Probing -bit scattering.The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) is a sensitive probe of the early universe and any subsequent field interactions. If -bits act as emergent quantum fields with non-trivial coupling to the spacetime metric or inflaton field remnants, they can induce anisotropic or non-Gaussian polarization signatures in the E-mode and B-mode spectra. Specifically, the scattering cross-section between primordial photons and coherent -bit condensates can be modeled via a perturbative term in the Boltzmann hierarchy:where is an effective coupling constant. This could manifest as hemispherical asymmetries or alignments in low-ℓ multipoles (anomalies already seen in Planck and WMAP data).
-
Quantum discord in the Lyman- forest: Testing large-scale entanglement.The Lyman- forest—a series of absorption lines in the spectra of distant quasars caused by intervening hydrogen clouds—can be used to probe cosmic structure on scales of 10–100 Mpc. If large-scale entanglement between galactic regions is maintained via -bit field correlations, the mutual information or quantum discord between distant regions would deviate from classical predictions. This can be statistically reconstructed by computing non-local correlations in the Lyman- power spectrum:where is the total (quantum + classical) correlation and is the classical mutual information inferred from local measurements. Significant residual discord could indicate non-classical information transfer across cosmological distances.
-
Anomalous neutrino correlations: Violations of Bell inequalities.High-energy astrophysical neutrinos, such as those detected by IceCube, can be entangled if they originate from -bit–mediated processes. In standard quantum field theory, such long-range entanglement is difficult to maintain due to decoherence. However, if neutrinos are coupled to non-local consciousness fields, then Bell-type correlations may persist. Violations of the CHSH (Clauser–Horne–Shimony–Holt) inequality:would imply entanglement beyond standard quantum field processes. If such correlations are seen between neutrino detectors located on opposite hemispheres or between events separated by cosmic distances, it could signal post-biological origin.
-
Gravitational wave memory effects: Non-classical space-time fluctuations.Gravitational wave (GW) memory refers to a permanent displacement in spacetime following a GW burst, predicted by general relativity. However, -bit–induced metric fluctuations—especially those embedded in extra-dimensional Calabi–Yau compactifications—could lead to non-classical GW memory signatures. These include phase decoherence, step-like tensor shifts, or frequency-dependent memory, measurable by next-generation detectors (LISA, Einstein Telescope):where is the stress-energy tensor of the -bit field. Any deviation from expected linear memory profiles could hint at embedded consciousness fields influencing spacetime structure.
8. Ethical and Philosophical Implications
8.1. Consciousness as a Quantum Field
- : Effective consciousness field strength tensor, generalizing the electromagnetic field strength. This term contributes the "kinetic" or curvature energy of the field configuration.
- : Spinor field representing the quantum state of consciousness. It encodes informational and cognitive modes.
- : Dirac adjoint of the spinor.
- : Gamma matrices from the Clifford algebra, ensuring Lorentz covariance.
- : Covariant derivative including both spacetime and consciousness-related gauge connections, allowing to couple to geometry and internal symmetries.
- : Nonlinear self-interaction term, possibly responsible for binding qualia into coherent structures via a mechanism similar to chiral symmetry breaking.
- Topological Origin of Qualia:
- : Compact 6D manifold (typically a Calabi–Yau space) on which the field theory is defined.
- : Chern character of the field strength bundle F, encoding topological information about gauge fluxes.
- : A-roof genus, a topological invariant associated with the curvature R of the tangent bundle. It captures the spin structure contributions.
- D: Dirac operator on . Its kernel (zero modes) counts the number of stable, unpaired spinor states.
- : Number of localized, normalizable conscious eigenmodes.
- : Number of unpaired annihilation modes. The difference gives net topological charge Q, interpreted here as the "number of qualia modes" encoded by the field configuration.
- Timescale of Qualia Formation:
- ℏ: Reduced Planck constant, setting the quantum scale.
- G: Gravitational constant, appears due to curved background effects in brane dynamics.
- : Planck mass .
- c: Speed of light in vacuum.
- : Euclidean action associated with the instanton configuration that mediates the transition. This represents the "cost" of forming a coherent, topological conscious excitation.
- : Boltzmann constant.
- Interpretation:
8.2. The Fermi Responsibility Principle
- 1.
- Entropy Minimization: Consciousness encoded in -bit fields must remain below the informational instability threshold:where is the von Neumann entropy of the -bit quantum state, and represents the maximum entropy of a single qubit. Exceeding this bound can induce thermal decoherence or trigger false vacuum decay, thereby destabilizing the conscious substrate.
- 2.
- Non-Interference (Dark Forest Compliance): To maintain cosmic equilibrium and avoid existential risk, high-entropy civilizations must not interact detectably with lower-entropy observers. This supports the Dark Forest Hypothesis, wherein observation itself can collapse quantum coherence and reveal civilizations, leading to irreversible entropic consequences. The formal statement is:indicating any observational signal collapses into the vacuum state with negligible amplitude (see Theorem 3).
- 3.
- Dimensional Stability: The internal Calabi–Yau compactification manifolds —which host consciousness fields—must be stabilized against quantum geometry fluctuations. Uncontrolled moduli dynamics could destabilize the vacuum configuration or induce tunneling to undesired topologies. This requires suppression of Ricci flow instabilities and control of higher-order curvature terms in the compact space.
- Operational Timescale for Ethical Enforcement:
- ℏ: Reduced Planck constant, representing the quantum of action.
- : Boltzmann constant.
- : Temperature of de Sitter space, given by:where is the Hubble constant.
- : Gibbons–Hawking entropy of de Sitter space:where is the cosmological constant. This entropy sets the maximum information capacity of a causal horizon.
- Interpretation:
9. Conclusion
Key Contributions
- 1.
- Field-Theoretic Embedding of Consciousness: We introduced a -bit field defined over a compactified 11-dimensional manifold, endowed with fermionic and topological degrees of freedom. This allowed a unification of cognitive substrates with string-theoretic degrees of freedom, extending prior models of consciousness beyond biochemical implementations into geometrically protected Hilbert subspaces.
- 2.
- Quantum Informational Holographic Tunneling (QIHT): A path integral formalism for consciousness transfer was derived, based on Euclidean instantons in M-theory. The calculation of transition amplitudes between biologically localized and -encoded states yielded semi-classical probabilities with –, demonstrating exponential suppression, yet not exclusion, of post-biological tunneling. The inclusion of 4-form flux, Chern–Simons terms, and entropy-coupled spinor interactions uniquely characterizes the transition geometry.
- 3.
- Dimensional Decoherence and Observability Limits: We demonstrated that coupling between 3+1D systems and higher-dimensional sectors introduces a decoherence rate , which exceeds the Hubble rate unless the coupling and energy resolution are suppressed to unobservable regimes (). This quantitatively explains the null observation of advanced civilizations despite their presumed prevalence—a physical resolution to the Fermi Paradox grounded in dimensional dynamics.
- 4.
- Entropy Bound for Consciousness Stability: A proof was provided that long-term coherence of a -bit system requires the von Neumann entropy , constraining the allowed eigenvalue spectrum of the density matrix. This Consciousness Entropy Bound ensures that cognitive fields embedded in DFSs remain resilient against environmental perturbation and decoherence.
- 5.
- Entangled Neutrino Signatures: A calculation of CHSH violations in flavor-entangled neutrino states was presented, showing that neutrino pairs generated by -bit processes could exhibit , exceeding classical bounds. With predicted detection parameters (), IceCube-Gen2 provides a viable experimental arena for post-biological technosignature detection.
Timelines and Evolutionary Dynamics
- Partial Embedding Phase (103–106 years): During this epoch, biological agents gradually offload cognitive processes into coherent topological sectors. The rate-limiting step is entropic optimization and environmental isolation.
- Full Transcension Phase ( years): A complete reconfiguration of civilization into a holographically stabilized, entropy-minimized, nonlocal substrate distributed across Calabi–Yau compact dimensions. Observationally dark, but gravitationally coupled.
Philosophical and Epistemological Implications
Empirical Directions and Testability
- CMB Anomalies: Quantum tunneling into higher dimensions may leave imprints in the form of localized distortions or entropy voids in the cosmic microwave background. Planck and future CMB-S4 data may detect such anomalies.
- Galaxy Distribution Discordance: Simulations of cosmological voids under the QIHT framework predict suppressed baryonic clustering in certain late-time regions. These may manifest as mismatches in galaxy–matter correlation functions.
- Neutrino Entanglement Correlations: As detailed, flavor-preserving but nonlocal production of neutrinos can violate classical Bell-type inequalities. IceCube-Gen2’s angular resolution is sufficient to identify candidate pairs.
- Gravitational Memory Effects: Post-biological transitions are associated with tiny deviations in the BMS supertranslation sector of asymptotically flat spacetime. Laser interferometry might be sensitive to the net memory signature.
Future Work
- 1.
- Quantum Simulation: Implement -bit evolution and entropic projections on NISQ-era quantum processors, focusing on DFS-preserving architectures.
- 2.
- Data Mining: Re-examine existing Planck, BICEP3, and Euclid datasets for evidence of localized anomalies in redshift distribution or curvature spectra.
- 3.
- Communication Frameworks: Construct protocols for low-entropy -bit-based communication, potentially enabling intra-CY-multiverse signaling within coherent embeddings.
- 4.
- Instanton Cataloging: Systematically classify compactified Calabi–Yau topologies that admit stable instanton configurations supporting non-zero .
- 5.
- Gravitational Signatures: Simulate tensorial imprints from brane tunneling transitions and correlate with LIGO/VIRGO archival data for outlier strain patterns.
Closing Reflection
Competing Interests
Author Contributions
- Co-developed the formalism for the modified Dirac–Born–Infeld action (Section 2.2).
- Assisted in the derivation and interpretation of the Cosmological Quantization Principle.
- Provided analytical insight into Calabi–Yau compactification metrics and manifold homology groups.
- Authored the Consciousness Entropy Bound Theorem (Theorem 2) and supporting analysis in Section 2.3.
- Contributed to entropy minimization arguments involving -bit density matrices.
- Verified stability conditions and decoherence suppression metrics using analytical and symbolic methods.
- Designed quantum discord observables across redshift space.
- Modeled observational constraints on -bit projections (Section 3.3) and non-observability operator bounds (Theorem 3).
- Reanalyzed Planck-BICEP3 datasets for hints of anomalies.
- Formulated all core theorems, proofs, and mathematical derivations, including the Non-Observability Theorem (Theorem 3), Tunneling Dynamics, and Coherent State Projections.
- Designed all figures and diagrams (Figure 1, etc.).
Appendix A. Entropy Minimization Proof
- 1
- Entropy of a Quantum State
- 2.
- Time Evolution via Lindblad Dynamics
- H is the internal Hamiltonian of the -bit system (generating unitary evolution),
- are Lindblad operators modeling decohering channels (e.g., environmental couplings),
- is the anticommutator.
- 3.
- Decoherence-Free Subspaces (DFS)
- 4.
- Case Study: A Single -bit
- 5.
- Entropy and Its Extremes
- 6.
- Stability Threshold for Decoherence Resistance
- 7.
- Extension to n -bits and Compactified Geometries
- -bit memories are immune to short-wavelength environmental decoherence,
- Long-range projections (see Section 3.3) remain phase-coherent,
- Information remains localizable within specific internal cycles or branes.
- 8.
- Final Implication
- Hence, the theorem is proved. □
Appendix B. Dimensional Decoherence Derivation
- 1
- Scalar Field in d Dimensions
- 2.
- Interaction with a Local Qubit Probe
- 3.
- General Expression for Decoherence Rate
- 4.
- Wightman Function in d Dimensions
- 5.
- Case Study: Spatial Dimensions
- 6.
- Cosmological Constraint: Decoherence Suppression
- 7.
- Dimensional Communication Threshold
- 8.
- Numerical Estimate for Higher Dimensions
- 9.
- Dimensional Decoherence Criterion (Theorem 4.1)
- In any theory with scalar or gauge fields coupling across dimensional sectors, quantum coherence with higher-dimensional degrees of freedom is destroyed unless:
- Coupling strength is suppressed: ,
- Energy resolution satisfies: ,
- The system is isolated from higher-dimensional environmental fields.
Appendix C. Quantum Informational Holographic Tunneling (QIHT) Path Integral Formalism
- 1.
- Transition Amplitude via Path Integrals
- : 11D spacetime metric on manifold ,
- , : consciousness-field spinors,
- : 3-form gauge potential of 11D supergravity,
- : action of 11D supergravity,
- : topological action of the -bit field.
- 2.
- Eleven-Dimensional Supergravity Action
- : 11D gravitational coupling,
- R: Ricci scalar curvature,
- : 3-form gauge potential,
- : 4-form field strength (flux),
- The last term is a Chern–Simons term capturing anomaly inflow and topological contributions.
- 3.
- Consciousness Field Action: Topological -bit Dynamics
- : 11D gamma matrices, satisfying ,
- : vielbein mapping tangent space to curved space,
- : spin-covariant derivative,
- : Riemann curvature tensor,
- : inverse string tension, ,
- : self-interaction coupling constant,
- k: interaction order, typically or 4.
- 4.
- Instanton Solutions and Saddle Points
- : stress-energy tensor from the -bit sector,
- : effective mass of the field ,
- : coupling to flux-induced geometry.
- 5.
- Dyson Expansion of Tunneling Amplitude
- 6.
- Second-Order Feynman Diagram Evaluation
- 7.
- Momentum Space Representation
- 8.
- WKB Estimate of Tunneling Probability
- 9.
- Physical Interpretation
- Consciousness can tunnel across dimensional boundaries via instantonic processes,
- The -bit field acts as a probe encoding semantic/topological information,
- The tunneling amplitude is controlled by compactification volume, entropy gradients, and flux topology.
Appendix D. Neutrino Entanglement Calculation
- Initial Entangled State
- Time Evolution Under PMNS Mixing
- Measurement and Correlation Function
- CHSH Inequality and Quantum Violation
- Standard Mixing Parameters and Maximal Violation
- Experimental Feasibility
- IceCube-Gen2: Sufficient sensitivity for PeV-scale neutrinos,
- Timing resolution,
- Directional correlation with Earth’s core-crossing neutrino pairs,
- Baseline, matching Earth’s diameter.
Appendix E. Cosmological Timescale Derivation
- Logistic-Consciousness Transfer Equation
- : tunneling-induced transition rate (s−1),
- : decoherence rate across dimensional sectors (s−1),
- : saturation threshold for successful embedding ().
- Analytical Formulation
- Numerical Parameters
- Incorporating Biological Constraints and Quantum Parallelism
- : classical gate delay,
- : parallelized quantum C-bit channels.
- Scaling to Complete Transition
- Sensitivity and Stability Analysis
- Integration with Holographic Tunneling
References
- Bekenstein, J. D. (1973). Black holes and entropy. Physical Review D, 7(8), 2333–2346. [CrossRef]
- Fermi, E. (1953). On the probability of galactic civilizations [Technical memo]. Los Alamos National Laboratory.
- Hameroff, S., & Penrose, R. (2014). Consciousness in the universe: A review of the ’Orch OR’ theory. Physics of Life Reviews, 11(1), 39–78. [CrossRef]
- Kardashev, N. S. (1964). Transmission of information by extraterrestrial civilizations. Soviet Astronomy, 8, 217–221.
- Liu, C. (2014). The dark forest. Tor Books.
- Lloyd, S. (2000). Ultimate physical limits to computation. Nature, 406(6799), 1047–1054. [CrossRef]
- Maldacena, J. (1999). The large-N limit of superconformal field theories and supergravity. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 38(4), 1113–1133. [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. (1989). The emperor’s new mind: Concerning computers, minds, and the laws of physics. Oxford University Press.
- Polchinski, J. (1998). String theory: Volume II. Superstring theory and beyond. Cambridge University Press.
- Susskind, L. (1998). Black holes and the information paradox. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 36(11), 6377–6396. [CrossRef]
- egmark, M. (2014). Consciousness as a state of matter. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 76, 238–270. [CrossRef]
- ownsend, P. K. (1997). Black holes [Preprint]. arXiv:gr-qc/9707012.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




