Submitted:
25 July 2025
Posted:
28 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Significance
1.2. Research Approach and Framework
1.3. Literature Review
1.3.1. Option Pricing Models
1.3.2. Deep Learning-Based Option Price Forecasting Models
2. Related Work
3. Fundamentals of Related Theories
3.1. B-S Option Pricing Theory
- The market is frictionless (no taxes or transaction costs).
- The market is complete; short selling is allowed, and arbitrage is absent.
- The price of the underlying follows a geometric Brownian motion with constant return and volatility.
- The underlying pays no dividends during the option life.
- The underlying can be traded continuously in any quantity.
- The risk-free rate is constant and continuous; borrowing and lending rates are equal.
3.2. Deep Learning Theories
3.2.1. BP Neural Network
- Random initialization of weights and biases.
- Forward propagation of inputs.
- Compute error by comparing output with target.
- Backpropagate errors through hidden layers.
- Update weights using gradient descent.
- Repeat until error falls below threshold.
3.2.2. LSTM Neural Network
- Forget gate: Decides what information to discard from the cell state.
- Input gate: Updates the cell state with new information.
- Output gate: Controls what information is output at each time step.
4. Model Construction for Option Price Prediction
4.1. Sample Selection
4.1.1. Sample Product Description
4.1.2. Sample Data Range
4.2. Variable Definition
4.2.1. Input and Output Variables
4.2.2. Data Preprocessing
- Time Conversion: Remaining time to maturity T is converted to years by:where is the number of trading days.
- Normalization: All input data, including risk-free rate and HV, are standardized using z-score normalization.
4.3. Option Price Prediction Model Construction
4.3.1. BP Neural Network Model
(1) Network Design and Parameters:
(2) Prediction Results Analysis:
4.3.2. LSTM Neural Network Model
(1) Network Design and Parameters:
(2) Prediction Results Analysis:
4.4. Experimental Analysis and Comparison
- Mean Squared Error (MSE):
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE):
- R-Squared ():
5. Conclusion
5.1. Summary of Findings
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
- Beyond the 9 input variables selected in this paper, there may be other influential features worth exploring, which could improve the predictive power of future models.
- The correlations among the 9 selected input features were not analyzed in depth. Future studies may investigate inter-variable correlations and their impact on model performance.
- The model uses historical volatility from the B-S formula as one of the input features. According to prior studies, using implied volatility instead of historical volatility may further reduce model error.
References
- Black, F., & Scholes, M. (1973). The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. Journal of Political Economy, 81(3), 637–654. [CrossRef]
- Bachelier, L. (1900). Théorie de la spéculation. Annales Scientifiques de l’École Normale Supérieure, 17(1), 21–86.
- Merton, R. C. (1973). Theory of rational option pricing. The Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science, 4(1), 141–183. [CrossRef]
- Merton, R. C. (1974). On the pricing of corporate debt: The risk structure of interest rates. The Journal of Finance, 29(2), 449–470. [CrossRef]
- Merton, R. C. (1976). Option pricing when underlying stock returns are discontinuous. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(1–2), 125–144. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J., Xie, Z., & Li, Q. (2020). Stackelberg game model of railway freight pricing based on option theory. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, Article 6436729. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Zhang, P., & Jiang, C. (2022). Option pricing and capacity allocation of China Railway Express considering capital constraint and spot market. In Proceedings of [Conference]. [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J., Lo, A., & Poggio, T. (1994). A nonparametric approach to pricing and hedging derivative securities via learning. The Journal of Finance, 49, 851–889. [CrossRef]
- Anders, U., Korn, O., & Schmitt, C. (1998). Improving the pricing of options: A neural network approach. Journal of Forecasting, 17(5–6), 369–388. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., Yang, Q., Xu, Y., et al. (2021). Attention-augmented neural network for option pricing. Neurocomputing, 454, 1–9.
- Du, X. (2025, February). Financial text analysis using 1D-CNN: Risk classification and auditing support. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence (pp. 515–520). [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. (2025). Time-series nested reinforcement learning for dynamic risk control in nonlinear financial markets. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 5(1). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. (2025). Multimodal data-driven factor models for stock market forecasting. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 4(2). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Wang, J., Dai, L., Guo, F., & Cai, G. (2025). Federated learning for cross-domain data privacy: A distributed approach to secure collaboration. arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.00282. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y., Yang, L., Zhang, T., Song, Z., & Shao, F. (2025, March). Automated UI interface generation via diffusion models: Enhancing personalization and efficiency. In 2025 4th ISCAIT (pp. 780–783). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z., Bao, Q., Wang, Y., Feng, H., Du, J., & Sha, Q. (2025). Reinforcement learning in finance: QTRAN for portfolio optimization. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 4(3). [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y. (2024). Capsule network-based AI model for structured data mining with adaptive feature representation. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(9). [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q., Wang, J., Gong, H., Zhang, Y., Guo, X., & Feng, H. (2025, March). A deep learning approach to anomaly detection in high-frequency trading data. In 2025 ISCAIT (pp. 287–291). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Dai, L., Zhu, W., Quan, X., Meng, R., Chai, S., & Wang, Y. (2025). Deep probabilistic modeling of user behavior for anomaly detection via mixture density networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.08220. [CrossRef]
- Cui, W., & Liang, A. (2025). Diffusion-transformer framework for deep mining of high-dimensional sparse data. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 4(4). [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y. (2024). Temporal dependency modeling in loan default prediction with hybrid LSTM-GRU architecture. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(8). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. (2025). Reinforcement learning-controlled subspace ensemble sampling for complex data structures.
- Zhao, Y., Zhang, W., Cheng, Y., Tian, Y., & Wei, Z. (2025). Entity boundary detection in social texts using BiLSTM-CRF with integrated social features.
- Zhu, L., Guo, F., Cai, G., & Ma, Y. (2025). Structured preference modeling for reinforcement learning-based fine-tuning of large models. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 4(4). [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N., Zhu, W., Han, X., Huang, W., & Sun, Y. (2025). Joint graph convolution and sequential modeling for scalable network traffic estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.07674. [CrossRef]
- Yang, T. (2024). Transferable load forecasting and scheduling via meta-learned task representations. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 3(8). [CrossRef]
- Xin, H., & Pan, R. (2025). Unsupervised anomaly detection in structured data using structure-aware diffusion mechanisms. Journal of Computer Science and Software Applications, 5(5). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. (2024). Entity-aware graph neural modeling for structured information extraction in the financial domain. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(9). [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q. (2024). Hybrid deep learning for financial volatility forecasting: An LSTM-CNN-transformer model. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(11). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Graph-based discovery of implicit corporate relationships using heterogeneous network learning. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 3(7). [CrossRef]
- Gao, D. (2025). Deep graph modeling for performance risk detection in structured data queries. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 4(5). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W., Xu, Z., Tian, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, M., & Meng, X. (2025). Unified instruction encoding and gradient coordination for multi-task language models.
- Wang, S., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, R., & Song, Z. (2025). Capsule network-based semantic intent modeling for human-computer interaction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.00540. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. (2024). Internal knowledge adaptation in LLMs with consistency-constrained dynamic routing. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(5). [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y., Qi, N., Deng, Y., Xue, Z., Gong, M., & Zhang, W. (2025). Autonomous resource management in microservice systems via reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.12879. [CrossRef]
- Su, X. (2024). Forecasting asset returns with structured text factors and dynamic time windows. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(6). [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. (2024). Causal discriminative modeling for robust cloud service fault detection. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 3(7). [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. (2024). Deep contextual risk classification in financial policy documents using transformer architecture. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 3(8).
- Wei, M. (2024). Federated meta-learning for node-level failure detection in heterogeneous distributed systems. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 3(8). [CrossRef]
- Cui, W. (2024). Vision-oriented multi-object tracking via transformer-based temporal and attention modeling. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(11). [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y., & Xue, P. (2025). Multi-task learning for macroeconomic forecasting based on cross-domain data fusion. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, 4(6). [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Meng, R., Zhang, R., Wu, Q., & Wang, H. (2025). A deep Q-network approach to intelligent cache management in dynamic backend environments.
- Xing, Y. (2024). Bootstrapped structural prompting for analogical reasoning in pretrained language models. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, 4(11).
- Liu, X., Xu, Q., Ma, K., Qin, Y., & Xu, Z. (2025). Temporal graph representation learning for evolving user behavior in transactional networks.
- Fang, Z., Deng, Y., & Duan, Y. (2025). Dynamic portfolio optimization using multi-agent reinforcement learning in volatile markets.
- Sun, Q., Xue, Y., & Song, Z. (2024). Adaptive user interface generation through reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.16837. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N., Zhu, W., Han, X., Huang, W., & Sun, Y. (2025). Joint graph convolution and sequential modeling. [CrossRef]
- Xin, H., & Pan, R. (2025). Structure-aware diffusion mechanisms in anomaly detection.
- Wu, Y., Qin, Y., Su, X., & Lin, Y. (2025). Transformer-based risk monitoring for anti-money laundering with transaction graph integration.
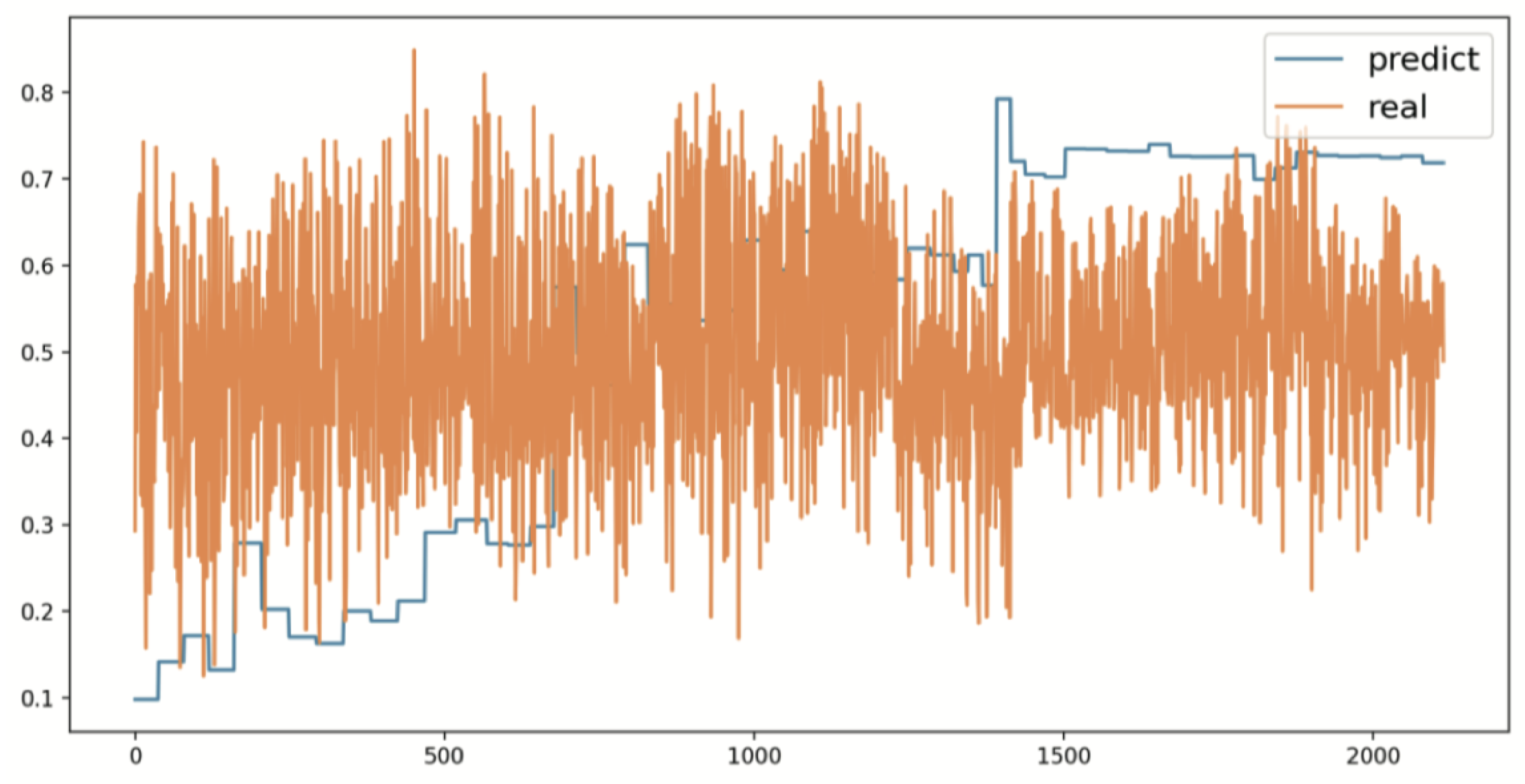

| Index | True Price | BP Predicted Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.459045 | 0.651990 |
| 2 | 0.262803 | 0.329410 |
| 3 | 0.150352 | 0.112909 |
| 4 | 0.012373 | 0.026878 |
| 5 | 0.028034 | 0.097869 |
| Index | True Price | LSTM Predicted Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.459045 | 0.485363 |
| 2 | 0.262803 | 0.236087 |
| 3 | 0.150352 | 0.136311 |
| 4 | 0.012373 | 0.014152 |
| 5 | 0.028034 | 0.069612 |
| Metric | BP Network | LSTM Network |
|---|---|---|
| MSE | 0.088528 | 0.035709 |
| MAE | 0.372881 | 0.053793 |
| 0.6409727 | 0.8516187 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




