Submitted:
22 July 2025
Posted:
23 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Subjects and Methods:
Subjects
Sequencing and Data Analysis
Gene Categorization
Variant Categorization
Results
Subject Characteristics
De Novo Variants Identified and Their Characteristics
Protein Functions and Pathways Related to the Identified DNV-PDVs
Tallying Inherited and De Novo Variants in Our Subjects
Discussion
Phenotypes in ASD
Genotypes in ASD
Silent Variants in Autism
ACMGG Criteria, Near Misses and Low Laboratory Yield
Mechanistic Pathways and Clinical Utility
Limitations
Potential Implications to an Increasing Prevalence of ASD
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Son, M.J.; Son, C.Y.; Radua, J.; Eisenhut, M.; Gressier, F.; Koyanagi, A.; Carvalho, A.F.; Stubbs, B.; Solmi, M.; et al. Environmental risk factors and biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder: an umbrella review of the evidence. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.; Friedman, E.; Jenkins, E.; Brooks, J.; Wisniewski, K.; Raguthu, S.; French, J. ASSOCIATION OF FRAGILE X SYNDROME WITH AUTISM. Lancet 1982, 319, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffenburg, S.; Gillberg, C.; Hellgren, L.; Andersson, L.; Gillberg, I.C.; Jakobsson, G.; Bohman, M. A Twin Study of Autism in Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1989, 30, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.; Le Couteur, A.; Gottesman, I.; Bolton, P.; Simonoff, E.; Yuzda, E.; Rutter, M. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol. Med. 1995, 25, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietert, R.R.; Dietert, J.M.; Dewitt, J.C. Environmental risk factors for autism. Emerg. Heal. Threat. J. 2011, 4, 7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.A. Prevalence and Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 and 8 Years — Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 16 Sites, United States, 2022. MMWR. Surveill. Summ. 2025, 74, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autism diagnosis on the rise, according to trends study,” autism speaks. Accessed: May 28, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.autismspeaks.org/science-news/why-autism-increasing.
- Leeb, R.T.; Danielson, M.L.; Claussen, A.H.; Robinson, L.R.; Lebrun-Harris, L.A.; Ghandour, R.; Bitsko, R.H.; Katz, S.M.; Kaminski, J.W.; Brown, J. Trends in Mental, Behavioral, and Developmental Disorders Among Children and Adolescents in the US, 2016–2021. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2024, 21, 240142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AutDB.” Accessed: May 29, 2025. [Online]. Available: http://www.mindspec.org/autdb.html.
- SFARI Gene.” Accessed: May 29, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://gene.sfari.org.
- De Rubeis, S.; Buxbaum, J.D. Genetics and genomics of autism spectrum disorder: embracing complexity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, R24–R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiman, B.L.; Boles, R.G. State of the Art of Genetic Testing for Patients With Autism: A Practical Guide for Clinicians. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2020, 34, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar, O.; Vahey, E.; Mintz, M.; Frye, R.E.; Boles, R.G. Reanalysis of Trio Whole-Genome Sequencing Data Doubles the Yield in Autism Spectrum Disorder: De Novo Variants Present in Half. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, F.; Shah, J.; Jain, D.; Shah, S.; Patel, H.; Patel, K.; I Solanki, D.; Iyer, A.S.; Menghani, B.; Mhatre, P.; et al. Comparative yield of molecular diagnostic algorithms for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis in India: evidence supporting whole exome sequencing as first tier test. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Kushima, I.; Kato, H.; Kimura, H.; Nawa, Y.; Aleksic, B.; Banno, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Uematsu, M.; Nagasaki, Y.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing analysis of Japanese autism spectrum disorder trios. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2024, 79, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Yuen, R.K.; Jin, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, N.; Wu, X.; Ju, J.; Mei, J.; Shi, Y.; He, M.; et al. Detection of Clinically Relevant Genetic Variants in Autism Spectrum Disorder by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.; Aliyev, E.; Trost, B.; Kohailan, M.; Aamer, W.; Syed, N.; Shaath, R.; Gandhi, G.D.; Engchuan, W.; Howe, J.; et al. Genomic architecture of autism spectrum disorder in Qatar: The BARAKA-Qatar Study. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerman, N.; Faust, G.; Meeks, N.; Modai, S.; Kalfon, L.; Falik-Zaccai, T.; Kaplun, A. A clinically validated whole genome pipeline for structural variant detection and analysis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, O.; Ebenau, L.; Weiner, K.; Mintz, M.; Boles, R.G. Whole exome/genome sequencing in cyclic vomiting syndrome reveals multiple candidate genes, suggesting a model of elevated intracellular cations and mitochondrial dysfunction. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of California Santa Cruz Genomic Institute UCSC Genome Browser. Available online: https://genome.ucsc.edu/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- GraphPad by Dotmatics.” Accessed: May 29, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/contingency1.cfm.
- MedCalc®.” Accessed: May 29, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.medcalc.org/calc/odds_ratio.php.
- Leblond, C.S.; Rolland, T.; Barthome, E.; Mougin, Z.; Fleury, M.; Ecker, C.; Bonnot-Briey, S.; Cliquet, F.; Tabet, A.-C.; Maruani, A.; et al. A Genetic Bridge Between Medicine and Neurodiversity for Autism. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2024, 58, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblond, C.S.; Rolland, T.; Barthome, E.; Mougin, Z.; Fleury, M.; Ecker, C.; Bonnot-Briey, S.; Cliquet, F.; Tabet, A.-C.; Maruani, A.; et al. A Genetic Bridge Between Medicine and Neurodiversity for Autism. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2024, 58, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, A.; Ionita-Laza, I.; Gogos, J.A.; Xu, B.; Karayiorgou, M. De Novo Synonymous Mutations in Regulatory Elements Contribute to the Genetic Etiology of Autism and Schizophrenia. Neuron 2016, 89, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhine, C.L.; Neil, C.; Wang, J.; Maguire, S.; Buerer, L.; Salomon, M.; Meremikwu, I.C.; Kim, J.; Strande, N.T.; Fairbrother, W.G.; et al. Massively parallel reporter assays discover de novo exonic splicing mutants in paralogs of Autism genes. PLOS Genet. 2022, 18, e1009884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupp, D.R.; Barnard, R.A.; Duffourd, Y.; Evans, S.A.; Mulqueen, R.M.; Bernier, R.; Rivière, J.-B.; Fombonne, E.; O’rOak, B.J. Exonic Mosaic Mutations Contribute Risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Chen, F.; Qin, Z.; Yi, S.; Huang, L.; Huang, L.; Feng, Y.; Wei, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Novel Synonymous and Frameshift Variants in the TRIP12 Gene Identified in 2 Chinese Patients With Intellectual Disability. Neurol. Genet. 2022, 8, e200025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuto, M.; Cesarini, S.; Severi, G.; Ambrosini, E.; Russo, A.; Seri, M.; Palumbo, P.; Palumbo, O.; Castori, M.; Panza, E.; et al. Phenotypic Description of A Patient with ODLURO Syndrome and Functional Characterization of the Pathogenetic Role of A Synonymous Variant c.186G>A in KMT2E Gene. Genes 2024, 15, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhong, H.; Wu, B.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Yu, C.; Li, D.; Shu, J.; Cai, C. Identification of the synonymous variant c.3141G > A in TNRC6B gene that altered RNA splicing by minigene assay. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hours, C.; Recasens, C.; Baleyte, J.-M. ASD and ADHD Comorbidity: What Are We Talking About? Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 837424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, D.P.; Behan, N.A.; O'Brien, J.M.; Marchetti, F.; MacFarlane, A.J.; Gollapudi, B. Folate deficiency increases chromosomal damage and mutations in hematopoietic cells in the transgenic mutamouse model. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2018, 59, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Leydier, L.; Sharma, S.; Katwala, J.; Sahu, A. A quest for genetic causes underlying signaling pathways associated with neural tube defects. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copp, A.J.; DE Greene, N. Genetics and development of neural tube defects. J. Pathol. 2009, 220, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
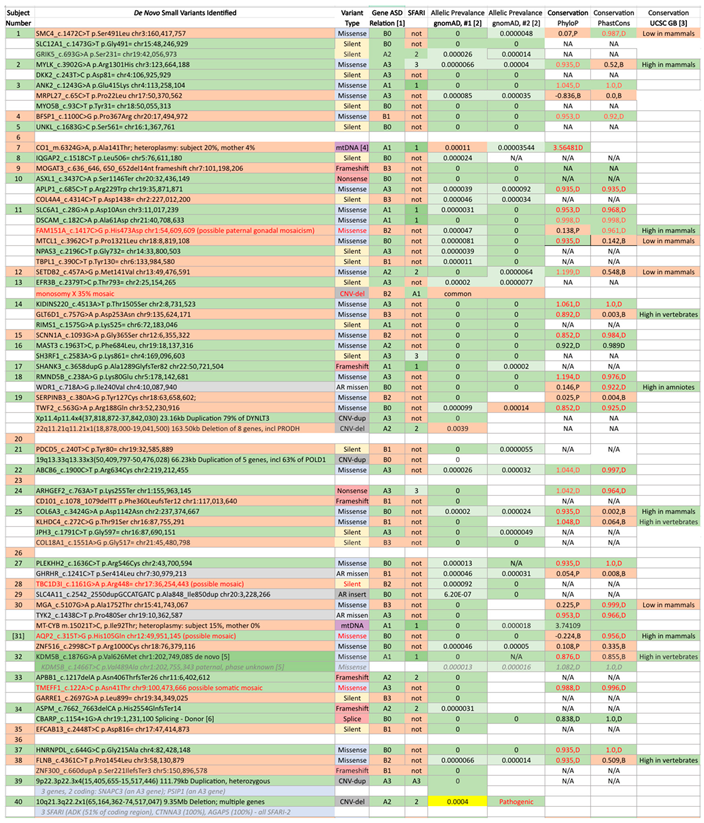 |
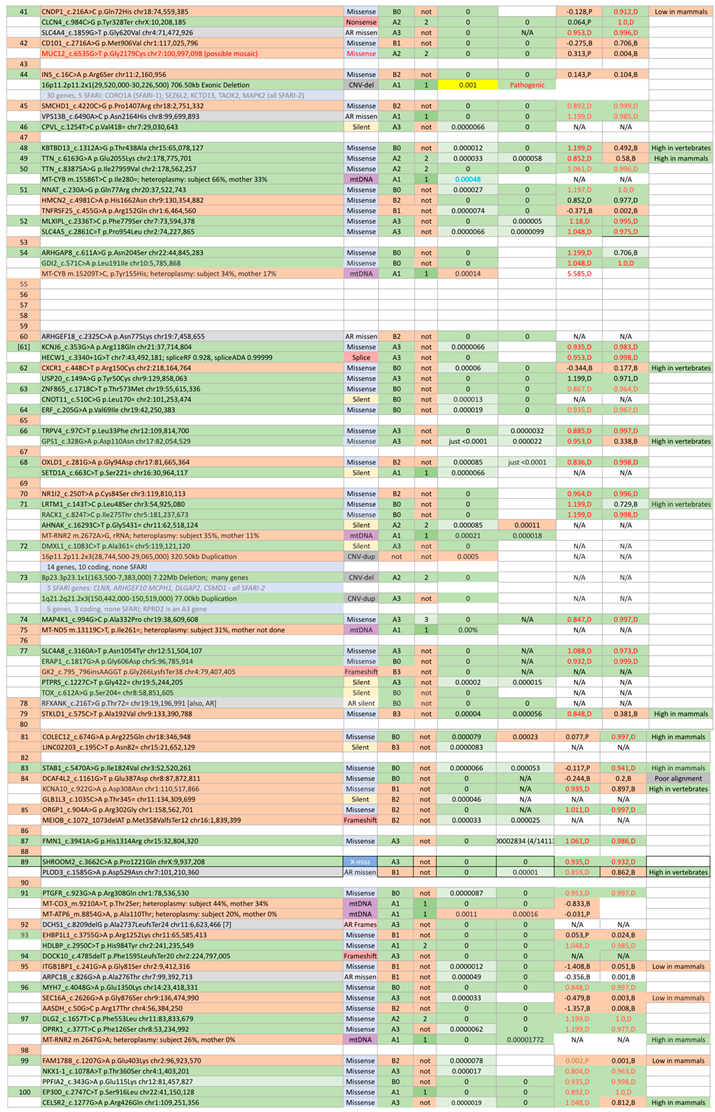 |
| Subject # 1 | Gene(s) with De Novo Variant 2 | Designation on Report 3 | Disease Status 4 | Case Reports (individuals, families, publications) 5 | NDD per HGMD 6 | Protein Function 7 | IonTransp | Red OxMito |
Immune | Ubiquitin | Synapse | Express | NeuroGen | CytoSkel | Cell -Cell |
Signal ing |
Danger |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | ANK2 | Other Variants | Known | 36, 30, 10 | 64 | Spectrin-actin cytoskeleton | |||||||||||
| 10 | ASXL1 | Positive | Known | 135, 134, 121 | 6 | Gene silencing, developmental roles | |||||||||||
| 11 | SLC6A1 | Other Variants | Known | 18, 18, 15 | 53 | GABA transporter | |||||||||||
| 11 | DSCAM | Other Variants | Very rare | 7, 6, 6 | 38 | Neural cell adhesion molecule | |||||||||||
| 16 | MAST3 | Other Variants | Known | 13, 7, 2 | 1 | Serine/threonine kinase | |||||||||||
| 17 | SHANK3 | Positive | Known | 188, 206, 64 | 91 | Synaptic scaffolding protein | |||||||||||
| 32 | KDM5B | Uncertain | Very rare | 4, 3, 3 | 31 | Demethylase, gene repression | |||||||||||
| 33 | APBB1 | Likely Negative | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | Transcription coregulator | |||||||||||
| 34 | ASPM | Other Variants | Known | 85, 75, 24 | 13 | Mitotic spindle function in embryonic neuroblasts | |||||||||||
| 37 | HNRNPDL | Negative | Known | 118, 78, 24 | 0 | mRNA splicing and nuclear export | |||||||||||
| 40 | 10q21.3q22.2x1 (65,164,362-74,517,047) 9.35Mb deletion [>170/many/3 genes] | Positive | Known | ADK: 50, 45, 36 CTNNA3: 4, 4, 4 AGAP5: 2, 1, 1 |
ADK: 3 CTNNA3: 30 AGAP5: Not reported |
ADK (51%): Adenosine kinase, regulator of extracellular and intracellular adenine/ adenosine; anti-inflammatory agents CTNNA3: Catenin family, cell-cell adhesion; roles in blood-brain barrier and immune cell transmigration AGAP5: Possibly GTPase activator. |
|||||||||||
| 41 | CLCN4 | Positive | Known | 62, 25, 8 | 18 | Voltage-gated chloride channel | |||||||||||
| 44 | 16p11.2p11.2x1 (29,520,000-30,226,500) 706.50kb deletion [39/31/5] |
Positive | Very rare | CORO1A: 7, 5, 5 SEZ6L2: 9, 9, 6 KCTD13: 0, 0, 0 TAOK2: 1, 1, 1 MAPK3: 9, 9, 5 |
CORO1A: 1 SEZ6L2: 1 KCTD13: 11 TAOK2: 3 MAPK3: 5 |
CORO1A: possibly cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation SEZ6L2: May contribute to specialized endoplasmic reticulum functions in neurons KCTD13: ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process, signal transduction TAOK2: focal adhesion assembly, intracellular signal transduction MAPK3: Kinase, signaling cascade regulating cellular processes including differentiation |
|||||||||||
| 73 | 8p23.3p23.1x1 (163,500-7,383,000) 7.22Mb deletion [88/26/5] | Positive | Known | CLN8: 65, 52, 33 ARHGEF10: 4, 4, 4 MCPH1: 38, 22, 19 DLGAP2: 7, 7, 4 CSMD1: 10, 8, 8 |
CLN8: 4 ARHGEF10: 6 MCPH1: 10 DLGAP2: 17 CSMD1: 27 |
CLN8: Possibly lipid related, neuronal differentiation, protection against cell death ARHGEF10: Guanine nucleotide exchange; possibly role in neural morphogenesis MCPH1: DNA damage response protein, G2/M checkpoint arrest DLGAP2: Synapse organization and signaling in neuronal cells CSMD1: Likely involved in learning or memory |
|||||||||||
| 97 | DLG2 | Supplementary | Very rare | 6, 4, 3 | 11 | Membrane-associated guanylate kinase, scaffold for the clustering of receptors, ion channels, and associated signaling proteins | |||||||||||
| 97 | OPRK1 | Supplementary | Known | 2241, 546, 2 | 0 | Opioid receptor | |||||||||||
| 100 | EP300 | Uncertain | Known | 316, 313, 85 | 9 | Histone acetyltransferase | |||||||||||
| 1 | SLC12A1 | Known | 57, 51, 30 | 0 | Na-K-Cl cotransporter | ||||||||||||
| 2 | MYLK | Known | 117, 117, 8 | 0 | Myosin light chain kinase | ||||||||||||
| 3 | MYOSB | Known | 18, 7, 4 | Not reported | Myoglobin | ||||||||||||
| 5 | UNKL | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | Ubiquitination | ||||||||||||
| 8 | IQGAP2 | Very rare | 1, 1, 1 | 2 | GTPase binding, interacts with cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, and signaling molecules to regulate cell morphology and motility | ||||||||||||
| 10 | APLP1 | Very rare | 7, 2, 2 | 1 | Transcriptional activator, synaptic maturation | ||||||||||||
| 11 | NPAS3 | Very rare | 4, 3, 3 | 2 | Transcription factor, neurogenesis | ||||||||||||
| 13 | EFR3B | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | Localize phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase to the plasma membrane | ||||||||||||
| 14 | KIDINS220 | Known | 15, 12, 12 | 4 | Controls neuronal cell survival, differentiation into exons and dendrites, synaptic plasticity; interacts with membrane, cytosolic signaling, and cytoskeletal components | ||||||||||||
| 14 | RIMS1 | Very rare | 6, 5, 5 | 13 | Regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis, regulates voltage-gated calcium channels during neurotransmitter and insulin release | ||||||||||||
| 16 | SH3RF1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | E3 ubiquitin ligase, cell death response, calcium homeostasis | ||||||||||||
| 19 | Xp11.4p11.4x2 (37,818,872-37,842,030) 23.16kb intragenic 2-copy-duplication (on X-chromosome in XY male) [1/1/0] | Very rare | DYNLT3: 1, 1, 1 | DYNLT3: Not reported | DYNLT3 (79%): A dynein light chain – a motor protein - intracellular retrograde motility of vesicles and organelles along microtubules; transcriptional modulator | ||||||||||||
| 21 | 19q13.33q13.33x3 (50,409,797-50,476,028) 66.23kb 3-copy-duplication of 5 genes, incl 35% of POLD1 [4/4/0] | Known | POLD1: 40, 34, 30 FAM71E1: 0, 0, 0 SPIB: 0, 0, 0 MYBPC2: 0, 0, 0 |
POLD1: 0 FAM71E1: 0 SPIB: 0 MYBPC2: 0 |
POLD1 (35%): Catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase delta; plays a critical role in DNA replication and repair FAM71E1 (69%): Innate immune response SPIB: Transcriptional activator, acts as a lymphoid-specific enhancer MYBPC2: Modifies the activity of actin-activated myosin ATPase |
||||||||||||
| 22 | ABCB6 | Known | 79, 4, 14 | 1 | Heavy metal importer, mitochondrial porphyrin uptake | ||||||||||||
| 24 | ARHGEF2 | Very rare | 2, 2, 2 | 2 | Rho GTPase, transcriptional factor binding; involvement in cell motility and polarization, dendritic spine morphology, antigen presentation, innate immune response, cell cycle regulation, and microtubule stability | ||||||||||||
| 25 | COL6A3 | Known | 609, 590, 41 | 1 | Alpha-3 chain of type VI collagen | ||||||||||||
| 25 | JPH3 | Known | 13, 11, 7 | 1 | Junctional complexes between the plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum, mediates cross talk between cell surface and intracellular ion channels. | ||||||||||||
| 27 | PLEKHH2 | Known | 17, 17, 7 | 0 | Predicted to enable actin binding activity, including cytoskeleton | ||||||||||||
| 31 | AQP2 | Known | 88, 61, 50 | 0 | Aquaporin-2 water channel prominent in renal collecting tubules | ||||||||||||
| 33 | TMEFF1 | Very rare | 1, 1, 1 | 0 | Blocks viruses from entering neurons | ||||||||||||
| 34 | CBARP | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | Regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis and voltage-gated calcium channel activity. | ||||||||||||
| 39 | 9p22.3p22.3x4 (15,405655-15,517,446) 111.79kb 4-copy-duplication [3/2/0] | Known | SNAPC3: 0, 0, 0 PSIP1: 10, 10, 7 |
SNAPC3: 1 PSIP1: Not reported |
SNAPC3: Transcription of both RNA polymerase II and III small-nuclear RNA genes PSIP1: Transcriptional coactivator involved in neuroepithelial stem cell differentiation and neurogenesis |
||||||||||||
| 46 | CPVL | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | Carboxypeptidase likely involved in lysosomal phagocytosis, inflammatory protease cascade, and antigen presentation. | ||||||||||||
| 49 | TTN | Known | 215, 165, 116 | 14 | Assembly and functioning of cardiac and striated myocytes | ||||||||||||
| 50 | TTN | Known | 215, 165, 116 | 14 | Assembly and functioning of cardiac and striated myocytes | ||||||||||||
| 50 | MT-CYB | Known | 21, 21, 11 | Not reported | mtDNA-encoded subunit of respiratory complex III | ||||||||||||
| 51 | NNAT | Very rare | 2, 2, 1 | Not reported | May regulate ion channels during brain development | ||||||||||||
| 52 | MLXIPL | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | Transcription factor for triglyceride synthesis genes | ||||||||||||
| 52 | SLC4A5 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | Sodium bicarbonate cotransporter involved in intracellular pH regulation | ||||||||||||
| 54 | ARHGAP8 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | GTPase activator for the Rho-type GTPases. Involved in signaling pathways that regulate cell processes involved in cytoskeletal changes | ||||||||||||
| 54 | GDI2 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | GDP-dissociation inhibitor, regulates intracellular membrane trafficking | ||||||||||||
| 61 | KCNJ6 | Known | 12, 12, 7 | 1 | G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel; may be involved in the regulation of insulin secretion by glucose and/or neurotransmitters. | ||||||||||||
| 61 | HECW1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | E3 ubiquitin protein ligase | ||||||||||||
| 62 | USP20 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 2 | Deubiquitinating enzyme that plays a role in many cellular processes including autophagy, cellular antiviral response | ||||||||||||
| 63 | ZNF865 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | Transcription factor | ||||||||||||
| 63 | CNOT11 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | Involved in nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening | ||||||||||||
| 64 | ERF | Known | 32, 26, 26 | 1 | Transcription factor; involved in development, apoptosis, and the regulation of telomerase | ||||||||||||
| 66 | TRPV4 | Known | 115, 85, 48 | 3 | Ca2+-permeable, nonselective cation channel; regulation of systemic osmotic pressure. | ||||||||||||
| 66 | GPS1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | Suppresses G-protein and mitogen-activated signal transduction; essential regulator of the ubiquitin conjugation pathway | ||||||||||||
| 68 | SETD1A | Very rare | 9, 7, 6 | 12 | Histone lysine methyltransferase; involved in RNA processing and the DNA damage response | ||||||||||||
| 71 | LRTM1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | Axon guidance and negative chemotaxis, synapse assembly | ||||||||||||
| 71 | RACK1 | Very rare | 1, 1, 1 | 0 | Regulation of signal transduction; and vesicle-mediated transport; present in phagocytic cup | ||||||||||||
| 71 | AHNAK | Very rare | 3, 3, 2 | 6 | Large structural scaffold protein involved in blood-brain barrier formation, cell structure and migration, cardiac calcium channel regulation, and neuronal cell differentiation | ||||||||||||
| 72 | DMXL1 | Very rare | 2, 2, 2 | 6 | WD repeat protein, regulatory functions | ||||||||||||
| 73 | 1q21.2q21.2x3 (150,442,000-150,519,000) 77.00kb 3-copy-duplication [5/3/0] | Known | RPRD2: 0, 0, 0 TARS2: 3, 3, 3 ECM1: 84, 74, 59 |
RPRD2: 1 TARS2: 0 ECM1: 0 |
RPRD2 (88%): Involved in mRNA 3'-end processing TARS2: Mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase – mitochondrial translation ECM1: Negative regulator of endochondral bone mineralization |
||||||||||||
| 74 | MAP4K1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase; involved in several processes: response to environmental stress, cell signaling, promoting apoptosis, hematopoietic lineage decisions and growth regulation, IL2 production | ||||||||||||
| 77 | SLC4A8 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | Sodium and bicarbonate cotransporter, important for pH regulation in neurons | ||||||||||||
| 77 | ERAP1 | Very rare | 3, 3, 1 | 0 | Aminopeptidase involved in trimming HLA class I-binding precursors so that they can be presented on MHC class I molecules | ||||||||||||
| 77 | PTPRS | Known | 13, 13, 8 | 0 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase signaling protein involved in cell-cell interaction, primary axonogenesis, and axon guidance during embryogenesis; down-regulates activation of NF-kappa-B, TNF, interferon alpha, and interferon beta | ||||||||||||
| 77 | TOX | Known | 603, 520, 1 | 0 | Transcriptional regulator, involved in chromatin assembly, transcription and replication, may function to regulate T-cell development | ||||||||||||
| 83 | STAB1 | Known | 0, 0, 0 | 2 | Roles in tissue homeostasis and remodeling, intracellular sorting and recycling, cell adhesion, receptor scavenging; possible roles in angiogenesis, defense against bacterial infection | ||||||||||||
| 87 | FMN1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 2 | Roles in adherens junction formation, polymerization of linear actin cables; transcriptional activity | ||||||||||||
| 89 | SHROOM2 | Very rare | 3, 2, 1 | 0 | Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel activity; regulates cytoskeletal organization and architecture of endothelial cells; roles in migration and angiogenesis | ||||||||||||
| 91 | PTGFR | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | G-protein coupled receptor for prostaglandin F2-alpha which activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system | ||||||||||||
| 93 | HDLBP | Very rare | 4, 4, 4 | 2 | Binds high density lipoprotein; removes excess cholesterol levels in cells; binds RNA and can induce heterochromatin formation | ||||||||||||
| 94 | DOCK10 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 0 | Guanosine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases; involved in cytokinesis; essential for dendritic spine morphogenesis in Purkinje cells and in hippocampal neurons; sustains B-cell lymphopoiesis. | ||||||||||||
| 96 | MYH7 | Known | 797, 699, 155 | 1 | Myosin heavy chain 7; interacts with actin for force generation; abundant in muscle but present ubiquitously including in brain | ||||||||||||
| 99 | NKX1-1 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | Not reported | Transcription factor homeobox protein; embryonic development | ||||||||||||
| 99 | PPFIA2 | Novel | 0, 0, 0 | 1 | Liprin, scaffold for recruitment and anchoring of LAR family PTPases; binds to calcium-calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase; important for axon guidance; scaffolding protein in the dendritic spines | ||||||||||||
| 100 | CELSR2 | Very rare | 1, 1, 1 | 2 | Belongs to the flamingo subfamily of non-classic-type cadherins; likely a receptor involved in cell adhesion and receptor-ligand interactions; cell/cell signaling during nervous system formation |
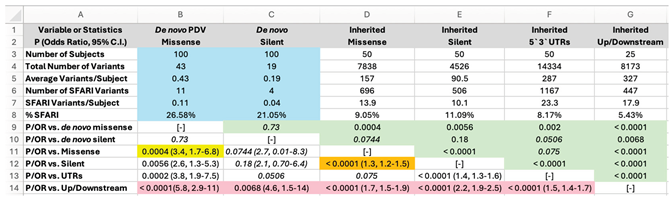 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




