Submitted:
12 July 2025
Posted:
14 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
A. Research Questions, Technical Objectives and Expected Results
II. Methodology
Detailed Description of Research Methods and Conclusions
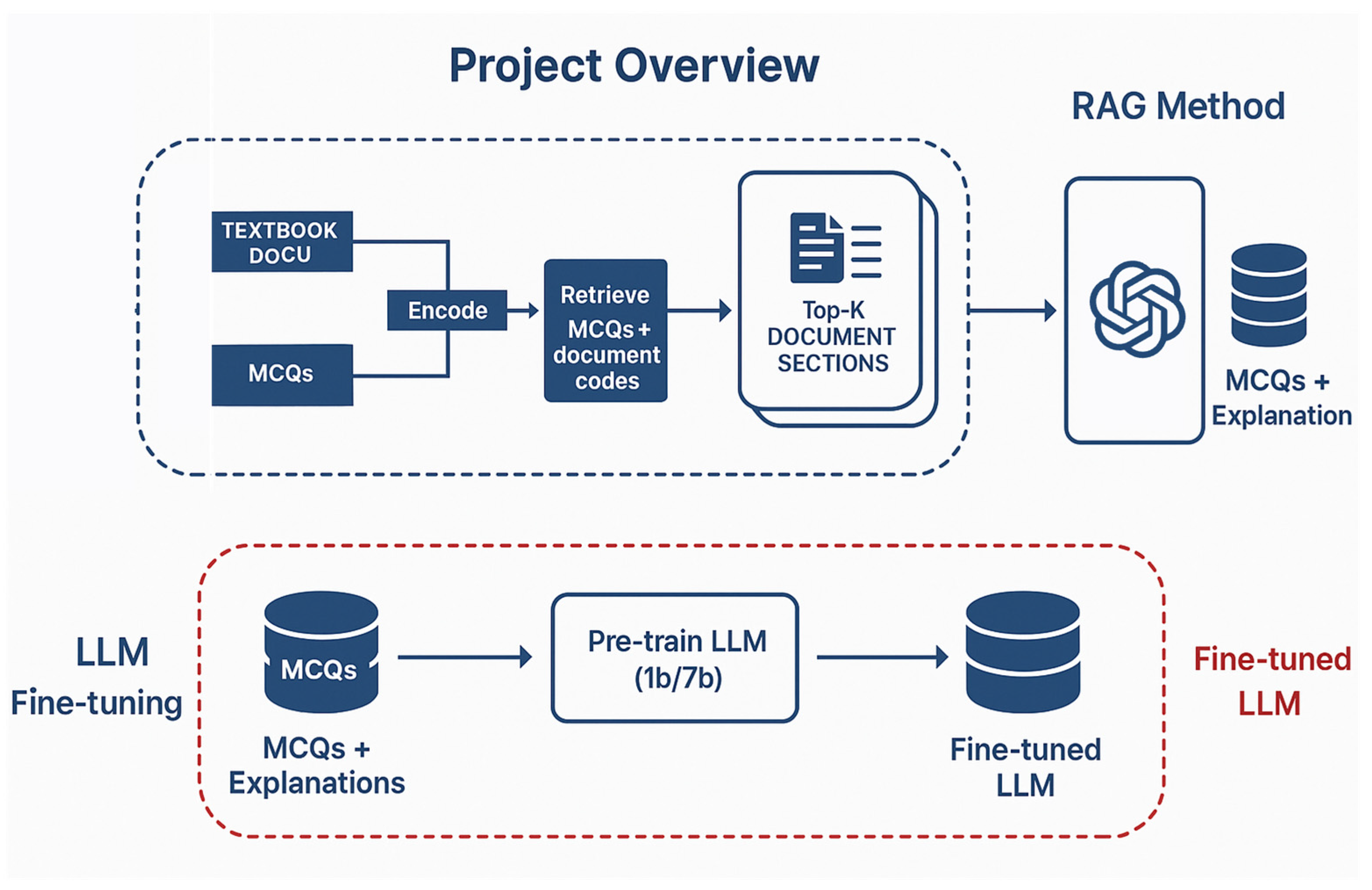
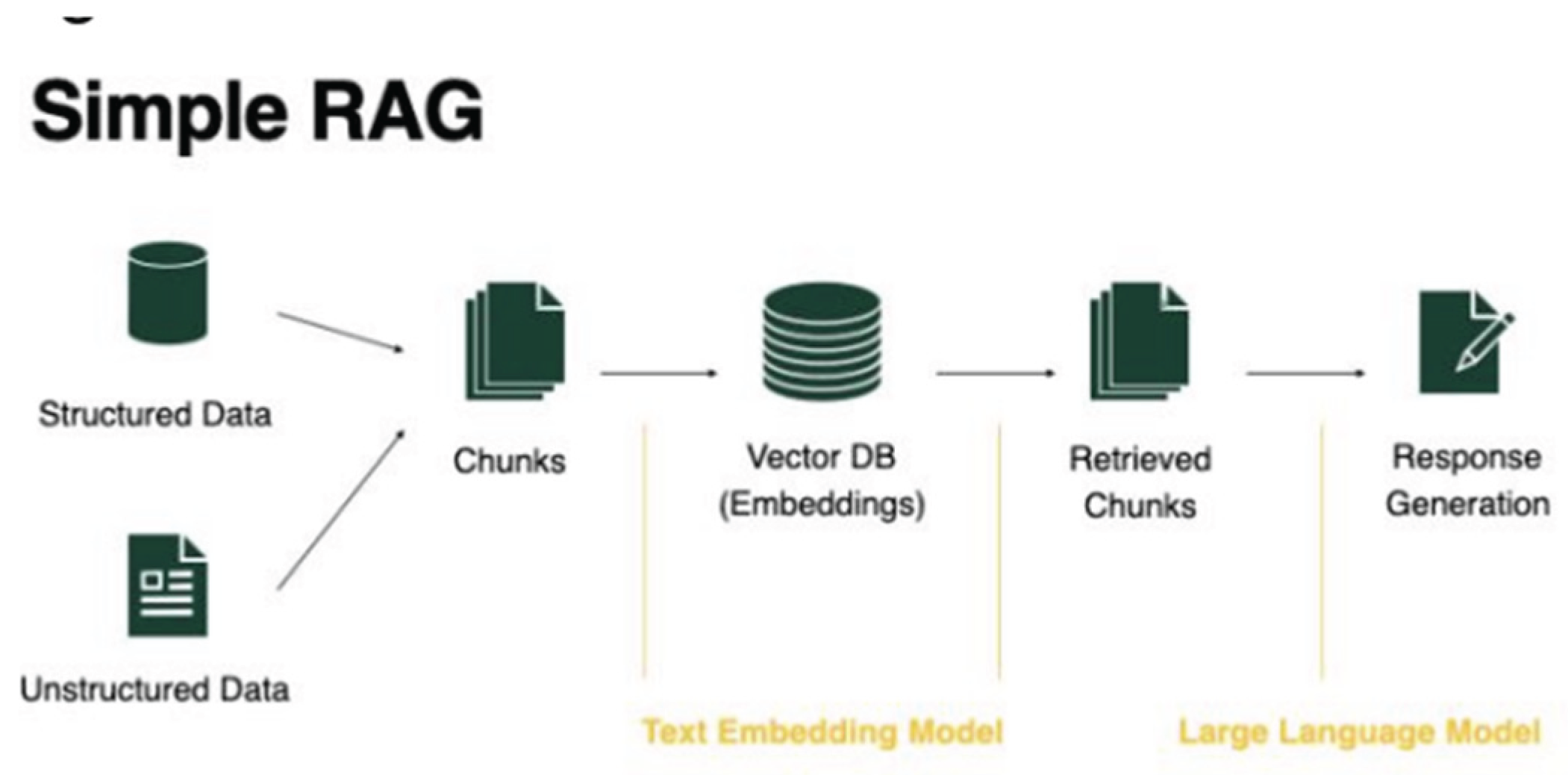
III. Result and Data Collection
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Data collection
3.1.2. Data processing
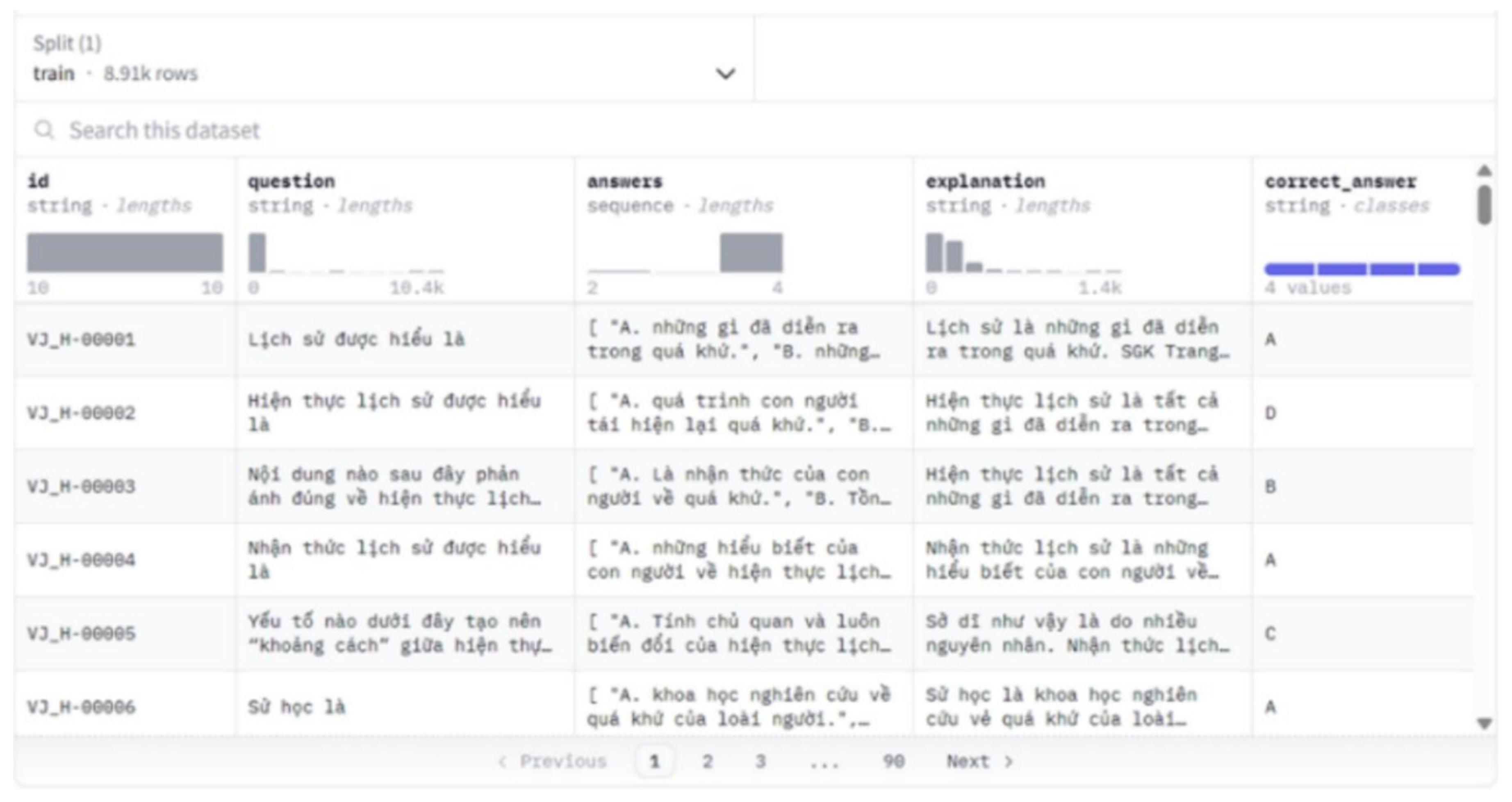
- 8912 samples
- ‘id’, ‘question’, ‘answers’, ‘explanation’, ‘correct_answer’
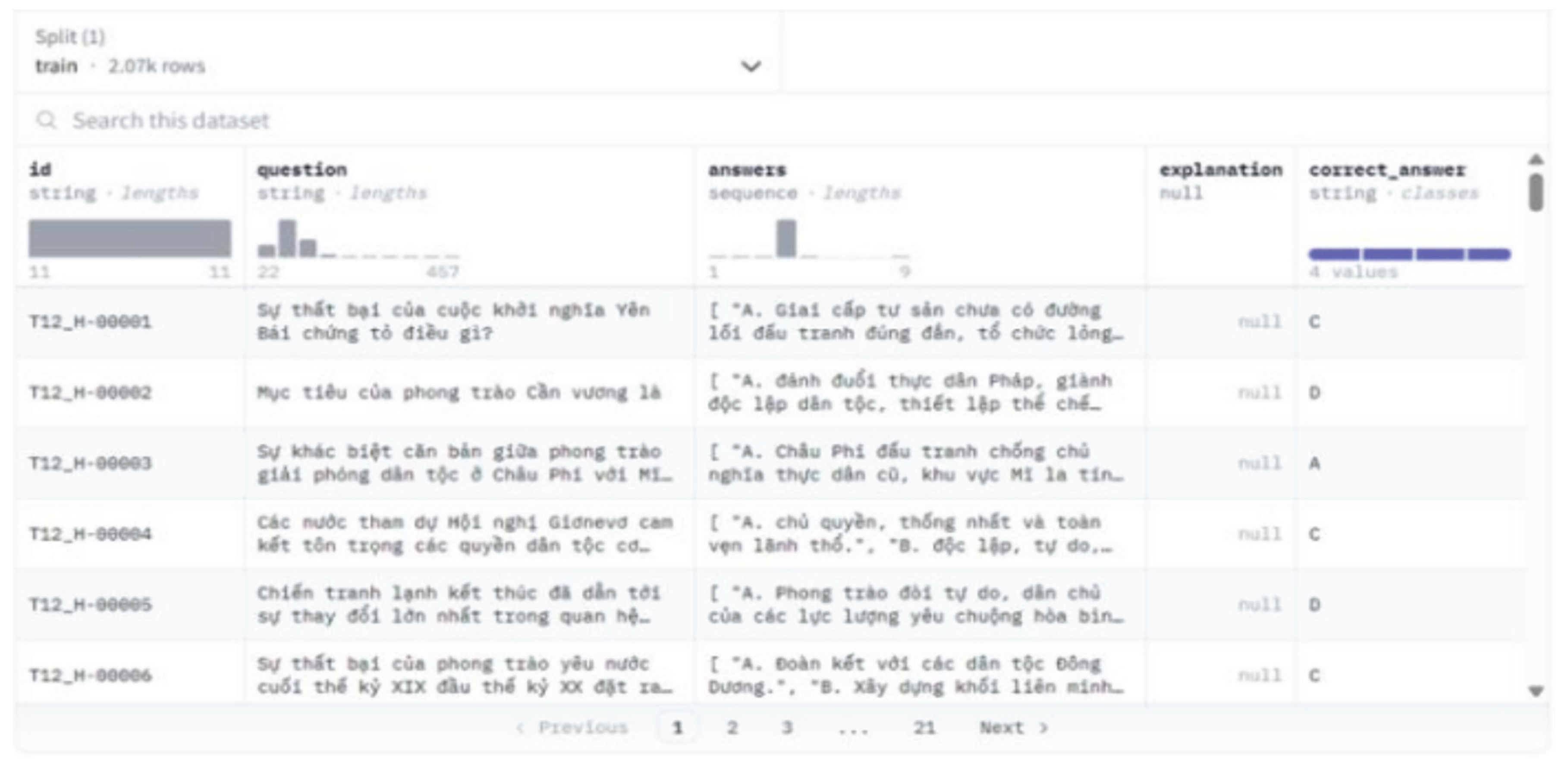
- 2069 samples
- ‘id’, ‘question’, ‘answers’, ‘explanation’, ‘correct_answer’
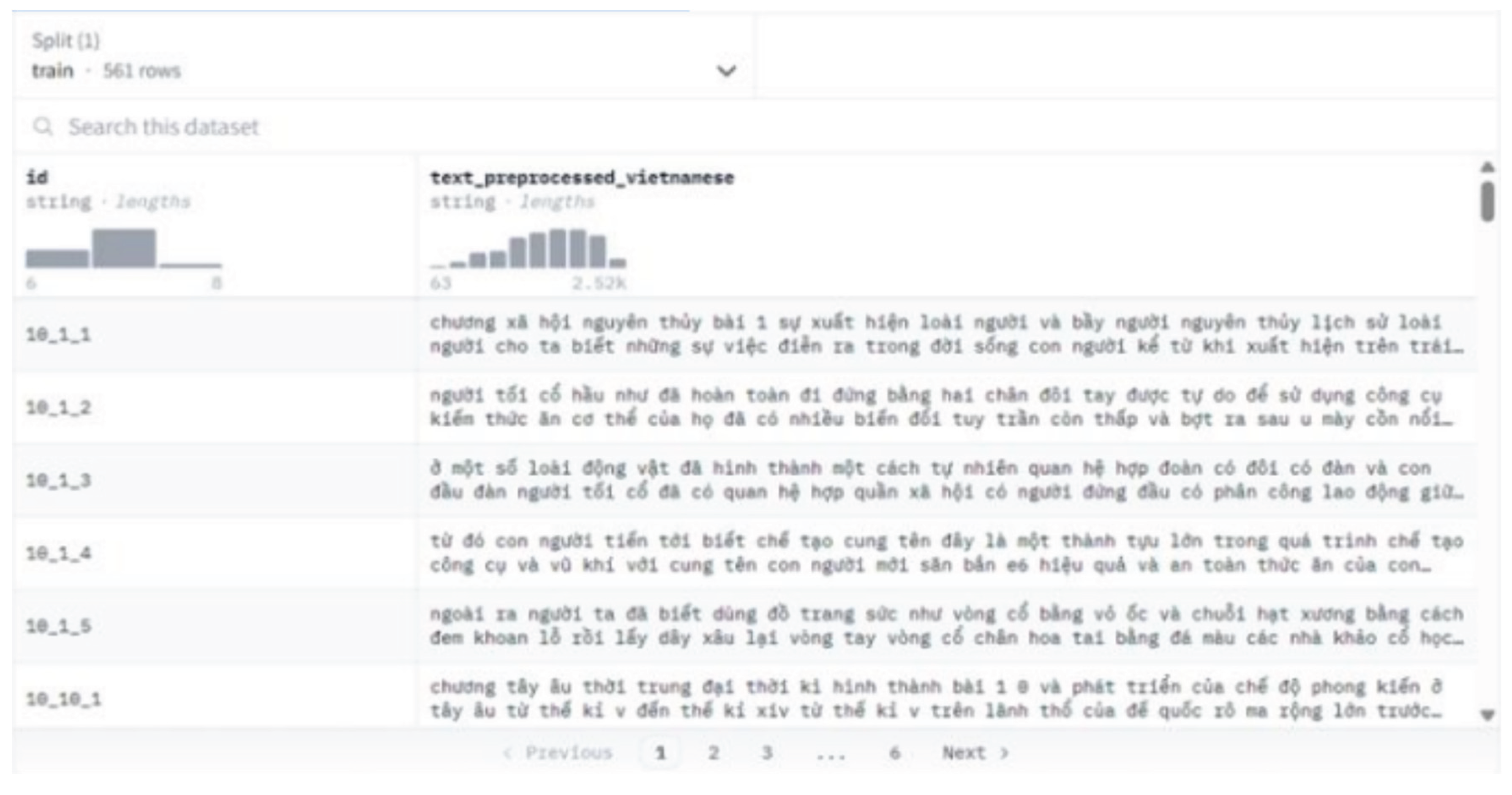
- 561 samples
- ‘id’, ‘text’
- Remove the characters ‘Sentence 1:‘, ‘Sentence 1.’, ‘Sentence 2:‘, ... at the beginning of the text.
- Remove special characters and non-Vietnamese characters.
- Keep the samples containing all 4 answers ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’.
- Format the answers in the ‘answers’ column starting with a letter (A, B, C or D) and a ‘.’.
- Remove special characters and non-Vietnamese characters.
- Check and format data into 1 of 4 characters ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’.
- If there is no explanation data, replace it with the value ‘null’.
- If there is explanation data, remove special characters and non-Vietnamese characters.
- Unicode Normalization: Function using unicodedata.normalize (‘NFC’, text) to normalize text to a composite Unicode format.
- Standardize Vietnamese accents: Standardize Vietnamese accents, including converting exclamation marks and tone marks from typing style 1 and 2 to the old typing style.
- Convert text to lowercase: Convert all characters in text to lowercase.
- Sentence normalization: Remove unnecessary characters and extra spaces in the text.
3.1.3. Result
3.2. Students Explain Multiple Choice Answers Using the RAG Method
3.2.1. Text Encoding (Embedding)
- -
- This problem aims to find the optimal embedding method for extracting relevant text. This process is very important for the ability of RAG to retrieve the most relevant information from the knowledge base for the query.
- -
- The nature of the problem is Vietnamese language, so fine-tuned embedding models will be more suitable. However, the team will still test other optimization models to compare the results. The group got the following results:
| Model | Result |
| All-MiniLM-L6-v2 | 15.62% |
| sup-SimCSE-Vietnamese-phobert-base | 35.83% |
| vietnamese-bi-encoder | 33.94% |
| Doc2Vec | 4.07% |
3.2.2. Passage Retrieval
| Evaluation Method | Result |
| Cosine similarity | 26.21% |
| Okapi BM25 | 33.52% |
| Semantic search | 28.04% |
| Okapi BM25 and Semantic search (coefficient = 0.5) | 35.80% |
3.2.3. Generation
- -
- From top-k text segments after the text extraction process, combine into a complete applied knowledge text.
- -
- Use OpenAI’s application programming interfaces (APIs) to support the process of generating explanations from the above questions and texts. Explanations are only used with information in the applicable knowledge text, if there is no relevant information, no results are returned, this helps ensure historical content is accurate.
| Case | Syntax | Example |
| With relevant text | ###System Message Applicable knowledge: {Applicable Knowledge} Only use the info in the applicable knowledge section and do not use any other knowledge to explain. If there is no data related to the question, print “null explanation”. ###User Message Question: {Question} {Choices} Correct Answer: {Correct Answer} ###Explanation (max 2 sentences): |
###System Message Applicable knowledge: (Applicable Knowledge) Only use the info in the applicable knowledge section and do not use any other knowledge to explain. If there is no data related to the question, print “null explanation”. ###User Message Question: The difference in skin color among races around the world reflects differences in: [‘A. level of civilization’ ‘B. social class’ ‘C. economic level’ ‘D. biological characteristics’] Correct Answer: D ###Explanation (max 2 sentences): |
| No relevant text | ###User Message ###Question: {Question} {Choices} ###Correct Answer: {Correct Answer} ###Explanation (max 2 sentences): |
###User Message ###Question: The difference in skin color among races around the world reflects differences in: [‘A. level of civilization’ ‘B. social class’ ‘C. economic level’ ‘D. biological characteristics’] ###Correct Answer: D ###Explanation (max 2 sentences): |
- -
- Both results are obtained using knowledge from the top-k text segments after segmentation, where k = 4 and the segmentation uses chunk-size = 200 and overlap = 15, respectively.
- -
- Explanation: The difference in skin color between races in the world is a manifestation of human’s long-term adaptation to different natural conditions, not a difference in civilization level, social class or economic level. This reflects the biological diversity of humans in the process of evolution and adaptation to the living environment.
3.2.4. Results of Generating Explanations for Multiple Choice Questions in History Using the RAG Method
- -
- First execution with gpt-3.5-turbo and related documentation on the entire dataset (10981 questions) resulted in 7719 generated explanations, achieving 70.29%.
- -
- Continued execution with ungenerated questions explained with gpt-4 and related documents, resulting in 1902 generated explanations corresponding to 58.31%.
- -
- The remaining questions are continued to be executed with gpt-3.5-turbo but without the relevant documentation to achieve maximum results.
3.3. Refining the LLM Model for History Multiple Choice Questions
3.3.1. Overview
- -
- From the data generated by the RAG method, the multiple choice question data with answers and explanations will be refined on large language models (LLM) using the Quantized LoRA (QLoRA) method. QLoRA is a method that combines quantization and LoRA (Learnable ReLU Activation) networks to reduce the memory burden and accelerate computation for deep learning models. This technique helps to lighten the Transformer model and improve performance on devices that support 16-bit computing. This topic provides practical results, refining LLM models (1 billion parameters and 7 billion parameters) to perform the task of answering and explaining history test questions.
3.3.2. Implementation Work
- -
- Set up environmental parameters to fine-tune the model.
- -
- Test prompts to improve model results.
- -
- Compare the results from the refined LLM model.
3.3.3. Implementation method
| QLoRA Parameters | BitsandBytes Parameters | Training Arguments |
| lora_r: 64 lora_alpha: 16 lora_dropout: 0.1 |
use_4bit = True bnb_4bit_quant_type: nf4 bnb_4bit_compute_dtype: float16 use_nested_quant: False |
per_device_train_batch_size: 1 gradient_accumulation_steps: 1 max_grad_norm: 0.3 learning_rate: 2e-4 weight_decay: 0.001 optim: paged_adamw_32bit lr_scheduler_type: cosine max_steps: 1 warmup_ratio: 0.03 logging_steps: 25 |
| Prompt | Syntax | Example |
| Fine-tune | ###QUESTION: {Question} {Choices} ###ANSWER: {Correct answer} EXPLAIN: {Explanation} |
###QUESTION: History helps us understand… Choices: A, B, C, D ###ANSWER: D EXPLAIN: Explanation in max 2 sentences |
| Model | Param | Data | Repeats | Time (h) | Train Val(%) | Test (%) |
| Bloomz | 1B | TRAIN | 10 | 5 | 31 | 26 |
| Bloomz | 1B | TEST | 20 | 2.5 | 34 | 32 |
| Bloomz | 1B | TRAIN | 5 | 2.5 | 32 | 26 |
| Bloomz | 1B | TRAIN | 1 | 0.5 | 36 | 25 |
| Bloomz | 1B | TRAIN/10 | 1 | 0.2 | 28 | 25 |
| Bloomz | 7B1 | TRAIN/10 | 1 | 0.5 | 33 | 28 |
| Bloomz | 7B1 | TRAIN | 1 | 2.5 | 49 | 42 |
| Llama | 7B | TRAIN/10 | 1 | 0.5 | 65 | 27 |
| Llama | 7B | TRAIN | 1 | 2.5 | 52 | 43 |
| VinaLlama | 7B | TRAIN | 1 | 2.5 | 50 | 30 |
| PhoGPT | 4B | TRAIN/10 | 1 | 6 | 28 | 23 |
| PhoGPT-Chat | 4B | TRAIN/10 | 1 | 6 | 29 | 24 |
| Qwen | 7B | TRAIN | 1 | 2.5 | 70 | 55 |
3.4. Website Building
3.4.1. Back-End
3.4.2. Front End
3.4.3. Server Configuration

3.5. Finished Product

IV. Conclusion
4.1. Novelty
4.2. Creativity
4.3. Replicability
4.4. Product Existence
4.5. Development Direction
4.6. Conclusion
References
- Vailaya, A. (2002). Automatic image orientation detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 11. [CrossRef]
- Dang, A. T. , Huynh, T. M. T., & Tran, V. L. (n.d.). A method for building an intelligent assistant application based on self-instruction techniques for fine-tuning LLMs. (Source not publicly available online—citation incomplete).
- Ngo, V. T. H. , Dao, D. T., & Tran, T. M. H. (2023). The application of federated learning with FedBN algorithm for breast cancer detection. In Proceedings of the 16th National Conference on Fundamental and Applied Information Technology Research (FAIR’2023). https://vap.ac.vn/Portals/0/TuyenTap/2024/2/21/64e13532907845ed9f5a2547dfec276f/15BB_FAIR2023_paper_4435.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- Ninh, K. C. , Tu, K. N., Vo, T. H., & Ninh, K. D. (2023). Applications of recurrent neural network in fake news classification. In Proceedings of the 16th National Conference on Fundamental and Applied Information Technology Research (FAIR’2023). https://elib.vku.udn.vn/handle/123456789/4138. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.-V. , & Nguyen, Q. -N. (2023). Evaluating the symbol binding ability of large language models for multiple-choice questions in Vietnamese general education. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology (pp. 177–183). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyễn, T. T. N. , Bùi, T. L., & Nguyễn, Đ. D. (2017). Một phương pháp phân đoạn ký tự cho bài toán nhận dạng chữ viết tay online. In FAIR - Nghiên cứu cơ bản và ứng dụng công nghệ thông tin. (Source not found online—citation incomplete).
- Võ, D. N. , & Đinh, Đ. (2020). Các tiêu chí ngôn ngữ trong việc xây dựng kho ngữ liệu tiếng Việt. In Proceedings of the 13th National Conference on Fundamental & Applied Information Technology Research. https://vap.ac.vn/Portals/0/TuyenTap/2021/6/18/363b8d0087164f4ca9882cae5d2230d0/4_FAIR2020_paper_118_637596274935007124.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- Dương, T. L. (2023). Ứng dụng ChatGPT thúc đẩy dạy và học bậc đại học trong kỷ nguyên trí tuệ nhân tạo. Tập san Khoa học và Kỹ thuật Trường Đại học Bình Dương, 6. [CrossRef]
- Daly, C. (2023). Learning to rank: Performance and practical barriers to deployment in enterprise search. In 2023 3rd Asia Conference on Information Engineering (ACIE). IEEE. https://www.computer. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Vietjack | Tech12h | Total |
| Quantity | 8912 | 2069 | 10981 |
| Percentage | 81.2% | 18.8% | 100% |
| Answer Ratio (A:B:C:D) | 25:26:26:23 | 23:26:24:27 | 25:26:26:23 |
| Grade | 10 | 11 | 12 | Total |
| Pages | 197 | 155 | 209 | 561 |
| Percentage | 35.1% | 27.6% | 37.3% | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




