1. Introduction
PharmVR is an innovative digital platform for Computer Aided Learning (CAL) that transforms the understanding and practice of experimental pharmacology in India. PharmVR employs Virtual Reality (VR) technology to create a 3D environment in which animal experiments are simulated through a highly interactive and immersive environment. It is a tool that has been specifically designed for those who are training for a career in the fields of pharmacy, medicine, and veterinary sciences. The solution gives the students a completely virtual and yet true-to-nature solution to live animal testing. One of the main advantages in the traditional way of learning is that the teaching mode is two-dimensional. Learners normally find themselves having to rely on out-of-date 2D animations or theoretical demonstrations for the understanding of complex pharmacological procedures. PharmVR comes in handy in a classroom by getting the recording process, which was inactive to be replaced with active, experiential training [
1,
2,
3,
4].
By means of its gaming system imitations of the real-world, the learners will be able to engage in virtual experiments, drug administration, physiology observation, and lab equipment interaction, yet they remain in a safe, ethical, and entertaining environment. Furthermore, PharmVR does not stop its innovation with its usage of AI-driven intelligent tutoring systems with real-time feedback, guidance, and performance tracking of students [
5,
6,
7].
Figure 1.
Concept of VR Based Animal Simulator.
Figure 1.
Concept of VR Based Animal Simulator.
The system is able to automatically catch up to the learner’s pace to deliver one-on-one instruction catered to develop personalized learning experiences such that the assistant really understands the way the student wants to learn. Still, the PharmVR system is not based on the English language technology but is also providing complete support in many Indian regional languages which can be easily understood by children of various linguistic communities. Therefore, this very platform tackles modules as those the Pharmacy Council of India (PCI) and National Medical Commission (NMC) has, to remove the burden of animal testing and at the same time keep the academic records straight. Therefore, it involves not only AI education tools, VR technology, and gamification but also combines that with one’s deep understanding, apart from the positive effects it generates in terms of thought, and the noble side of a student. The PharmVR digital platform is not just meant for simulation purposes. It is a complete e-learning system that could serve various purposes in pharmacology education. It has been designed with features to cater for both teachers and students. The features include lab manuals, virtual experiments, performance analytics, downloadable observation sheets and exam-mode simulations, and all the base stations and networking details are carefully planned to support both the students as well as the instructors. PharmVR as a product of leading-edge EdTech in India‘s spirits of innovation and humane science, is not only the next generation of pharmacology education but it is a comprehensive and a 360-degree solution — immersive, inclusive, interactive, and intelligent [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15].
Table 1.
Unique Features of PharmVR (Compared to Ex Pharm).
Table 1.
Unique Features of PharmVR (Compared to Ex Pharm).
| Feature |
Ex Pharm |
PharmVR |
| Simulation Type |
2D Animation |
3D VR-based immersive environment |
| Interaction |
Click-based |
Gamified real-time actions (e.g., inject, dissect, administer drugs) |
| Teaching Model |
Static content |
AI-driven personalized tutor |
| Language |
English only |
All major Indian languages |
| Scoring |
No live feedback |
Live test scores, performance tracking & adaptive feedback |
| Student Experience |
Linear modules |
Mission-style tasks, rewards & badges |
| Accessibility |
Desktop only |
VR Headset, Desktop, Tablet, Mobile |
1.1. Modules Planned in PharmVR
Each module in PharmVR is designed in alignment with the PCI, NMC, and Veterinary Council curriculum. These immersive simulations aim to provide practical understanding in a safe, ethical, and engaging virtual environment.
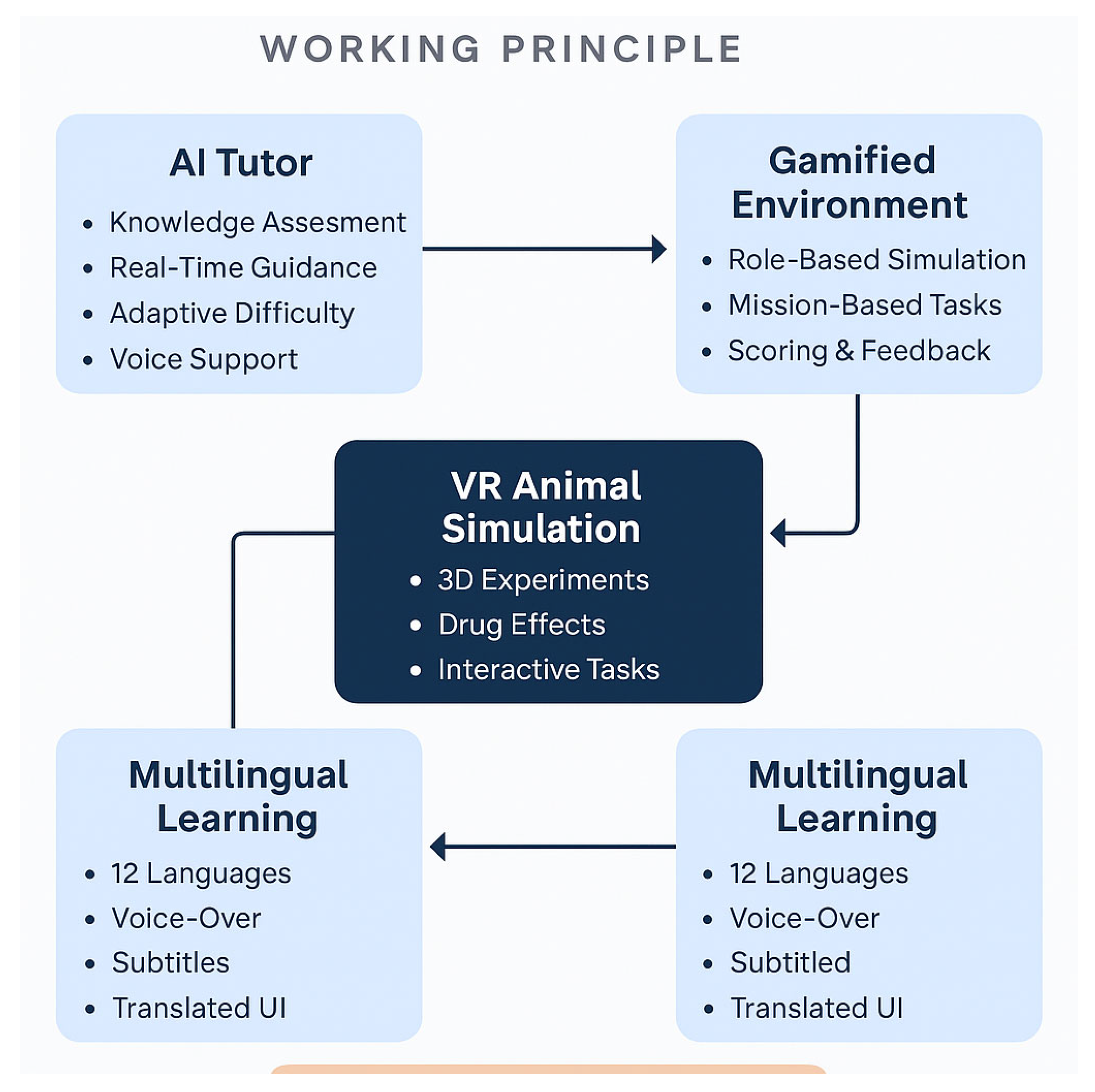
Figure 2.
Concept Map and Working Principle.
Figure 2.
Concept Map and Working Principle.
1. Ocular Pharmacology
This module demonstrates the effects of mydriatics, miotics, and local anesthetics on a virtual rabbit eye. Students can simulate drug administration and observe changes in pupil diameter and reflexes, helping them understand autonomic control of ocular function.
2. Analgesic Activity
Students can evaluate the effectiveness of analgesic drugs using virtual tail flick, hot plate, and writhing tests. These methods help in understanding pain perception and the role of various analgesic agents in managing pain.
3. Anti-Anxiety & CNS Drugs
This module includes behavioral tests such as the elevated plus maze, open field, and actophotometer. It allows learners to study the actions of anxiolytics, CNS stimulants, and depressants on animal behavior.
4. Muscle Relaxant Activity
Simulated rota-rod and grip strength tests help students analyze the muscle relaxant properties of drugs. These activities demonstrate how coordination and muscle tone are affected by centrally acting agents.
5. Anticonvulsant Studies
The PTZ-induced seizure model allows users to assess the anticonvulsant activity of various drugs. Students can visualize seizure patterns and evaluate the effectiveness of protective agents.
6. In-Vitro Tissue Bath Setup
This simulation mimics real-time responses in guinea pig ileum, frog heart, and rat fundus setups. Students can perform dose-response curves (DRCs) and understand drug-receptor interactions in isolated tissues.
7. Dog Blood Pressure Simulation
Learners can simulate the effect of drugs like epinephrine, acetylcholine, and histamine on dog BP and heart rate. This module offers a virtual cardiovascular setup to observe drug-induced changes in hemodynamic parameters.
8. Bioassay Modules
Students are introduced to matching, interpolation, three-point, and four-point bioassays. These simulations provide hands-on experience in determining drug potency using tissue responses.
9. Toxicity Testing
This module replicates skin and eye irritation tests in a virtual setup, adhering to ethical standards. It helps students learn how to evaluate acute toxicity without harming live animals.
10. Endocrine System
Simulations include studying the effects of insulin, thyroid hormones, and anti-thyroid drugs. Students can observe virtual changes in metabolism, weight, and biochemical parameters related to hormonal balance.
1.2. AI-Powered Learning Engine
PharmVR integrates an intelligent AI tutor module that personalizes the learning experience for every student. Before each experiment, the AI conducts a quick knowledge check to assess the learner’s baseline understanding. Based on this, it customizes the teaching approach, offering real-time suggestions, step-by-step guidance, and automated corrections during simulations. The system dynamically adjusts the difficulty level of content based on student performance, helping slow learners catch up and challenging advanced users further. With voice guidance available in over 12 Indian languages, PharmVR ensures that no student is left behind, regardless of their native language or learning pace.
1.3. Gamified Environment
To make learning engaging and effective, PharmVR transforms the virtual lab into a gamified ecosystem. Students take on role-based simulations, acting as virtual pharmacologists or researchers conducting experiments. Each module presents mission-based challenges that must be completed to unlock subsequent levels, keeping learners motivated through continuous achievement. A real-time scoring system evaluates performance based on accuracy, speed, and decision-making. Learners earn points, badges, and virtual promotions, turning their progress into a rewarding experience. The live feedback system ensures learners immediately understand their mistakes, helping reinforce concepts effectively.
1.4. Languages Supported
Recognizing the linguistic diversity of India, PharmVR has been built with multilingual accessibility at its core. The platform supports the following 12 Indian languages in addition to English: Hindi, Tamil, Telugu, Bengali, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, Gujarati, Punjabi, Urdu, and Assamese. Each module features voice-over narration, translated subtitles, and localized interface elements. This ensures that students from all regions can learn complex pharmacological concepts in their preferred language, reducing cognitive barriers and promoting inclusivity in professional education.
1.5. Academic Compliance
PharmVR is designed in strict alignment with national academic and ethical standards. The simulation modules are developed to match the Pharmacy Council of India (PCI) and National Medical Commission (NMC) curriculum frameworks, ensuring relevance and acceptability across academic institutions. Furthermore, PharmVR adheres to PETA-endorsed guidelines for animal-free education, promoting ethical and humane teaching practices. The platform also supports the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 objectives, particularly in digital transformation and equitable access to quality education.
1.6. Additional Highlights
PharmVR includes a range of features designed to enhance usability and institutional integration. The platform is accessible in both offline and online modes, catering to institutions with limited internet infrastructure. A secure login system allows institutions and students to manage accounts and track academic progress seamlessly. After each virtual experiment, students can download detailed lab reports that include graphs, observations, and space for self-assessment. An integrated lab manual and MCQ bank prepares learners for real-world examinations. Additionally, educators can access an admin dashboard to monitor individual and class-level performance, making PharmVR a complete teaching and learning solution.
1.7. About the Company: PharmVR Pvt. Ltd.
PharmVR Pvt. Ltd. is a registered MSME startup under the Government of India, recognized for its innovation in healthcare and education technology. The company was founded by a multidisciplinary team of clinical pharmacists, software developers, and education specialists, united by a shared mission to revolutionize pharmacology education through technology. PharmVR is fully trademark protected and has filed patents covering its virtual simulation engine and AI-powered tutoring framework. As an emerging leader in digital learning for health sciences, PharmVR is committed to building ethical, inclusive, and tech-forward solutions that enhance professional competency across India’s diverse educational landscape.