Submitted:
06 July 2025
Posted:
08 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
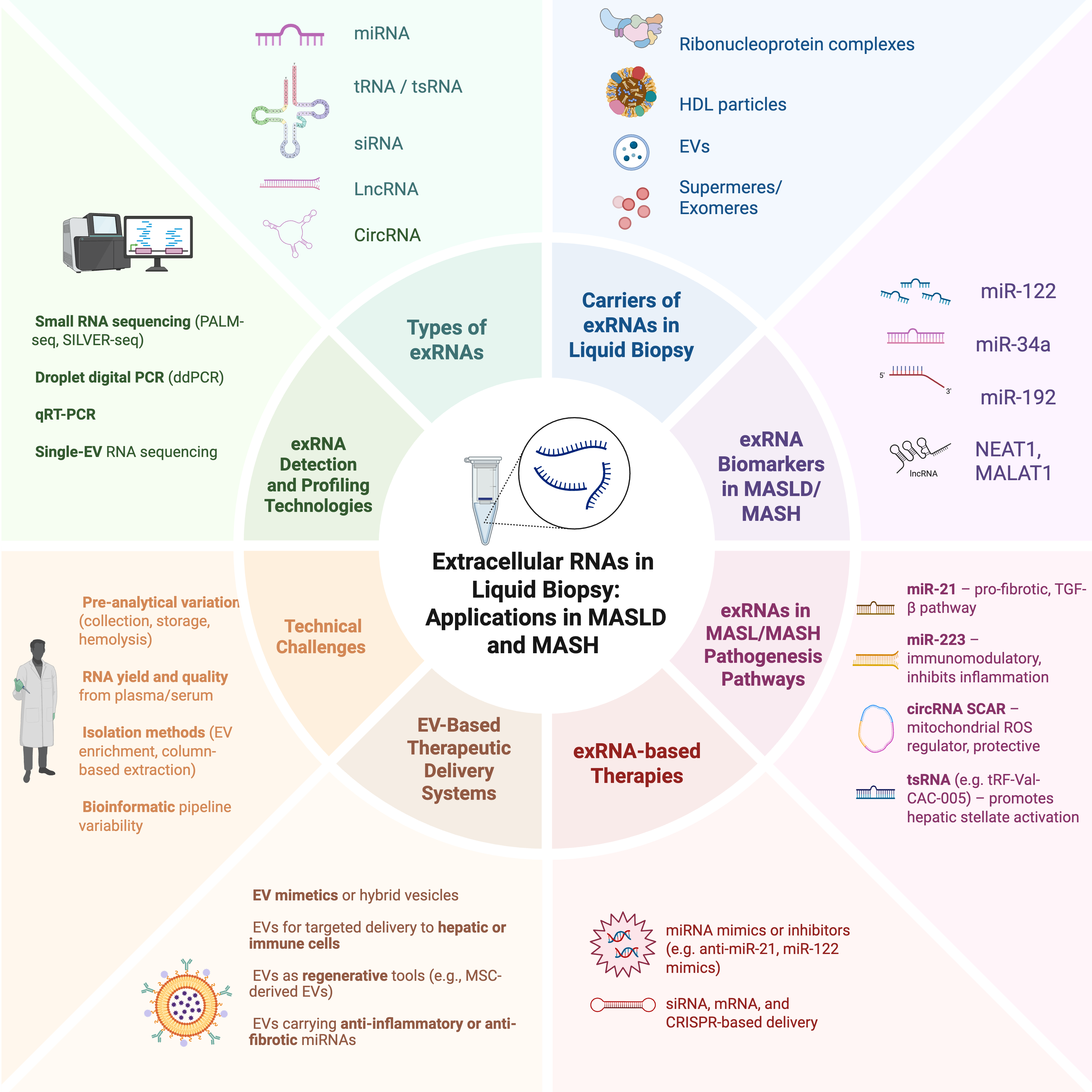
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Extracellular RNA as Carrier of Circulating Biomarkers
II.1 Types of Extracellular RNAs
II.2 Sources of exRNA in Liquid Biopsies
II.3 exRNA Detection and Analysis Methods
II.4 Other Technical Considerations
III. ExRNAs in MASLD and MASH
III.1 Correlation with Disease Severity and Progression
III.2 exRNA Changes with Treatment Response
III.3 Diagnostic Accuracy of exRNAs Versus Traditional Biomarkers
III.4 Mechanistic Roles of exRNA in MASLD Pathophysiology
IV. Current Status of Liquid Biopsy in MASLD and MASH Management
V. Comparison of Liquid Biopsy with Traditional Diagnostic Methods
VI. Future Perspectives for exRNA Diagnostics in MASLD and MASH
VII. Challenges and Limitations
VIII. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Conflict of Interest
Abbreviations
| ExRNAs | Extracellular RNAs |
| MASLD | Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease |
| MASH | Metabolic Associated Steatohepatitis |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| circRNA | circular RNA |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| tRNA | Transfer RNA |
| tsRNA | tRNA-derived Small RNA |
| cfDNA | Circulating Free DNA |
| RNA-seq | RNA Sequencing |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| MRE | Magnetic Resonance Elastography |
| MRI-PDFF | Magnetic Resonance Imaging Proton Density Fat Fraction |
| TE | Transient Elastography |
| NFS | NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) Fibrosis Score |
| APR | Aspartate Aminotransferase to Platelet Ratio |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ddPCR | Droplet Digital PCR |
| MRS | Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy |
| UV-vis | Ultraviolet-Visible Spectrophotometry |
| NPV | Negative Predictive Value |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
References
- Chan WK, Chuah KH, Rajaram RB, Lim LL, Ratnasingam J, Vethakkan SR. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2023;32(3):197-213. [CrossRef]
- Younossi ZM, Kalligeros M, Henry L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025;31(Suppl):S32-S50. [CrossRef]
- Sato-Espinoza K, Chotiprasidhi P, Liza E, Placido-Damian Z, Diaz-Ferrer J. Evolution of liver transplantation in the metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease era: Tracking impact through time. World J Transplant. 2024;14(4):98718. [CrossRef]
- Maurice J, Manousou P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical Medicine. 2018;18(3):245. [CrossRef]
- Castagneto-Gissey L, Bornstein SR, Mingrone G. Can liquid biopsies for MASH help increase the penetration of metabolic surgery? A narrative review. Metabolism. 2024;151:155721. [CrossRef]
- Torre E, Di Matteo S, Martinotti C, et al. Economic Impact of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in Italy. Analysis and Perspectives. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2024;16:773-784. [CrossRef]
- Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J, et al. MAFLD: a consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(7):1999-2014.e1. [CrossRef]
- Dale K, Fallouh ,Yasmeen, and Alkhouri N. MASLD and MASH: how a change of nomenclature may impact our approach in treating liver disease. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2024;33(11):1095-1097. [CrossRef]
- Targher G, Byrne CD, Tilg H. MASLD: a systemic metabolic disorder with cardiovascular and malignant complications. Gut. 2024;73(4):691-702. [CrossRef]
- Zhang YN, Fowler KJ, Ozturk A, et al. Liver fibrosis imaging: A clinical review of ultrasound and magnetic resonance elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;51(1):25-42. [CrossRef]
- Zoncapè M, Liguori A, Tsochatzis EA. Non-invasive testing and risk-stratification in patients with MASLD. Eur J Intern Med. 2024;122:11-19. [CrossRef]
- Hsu C, Caussy C, Imajo K, et al. Magnetic resonance vs transient elastography analysis of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and pooled analysis of individual participants. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2018;17(4):630. [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj EA, Mózes FE, Jayaswal ANA, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of elastography and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with NAFLD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2021;75(4):770-785. [CrossRef]
- Karlas T, Weise L, Kuhn S, et al. Correlation of cell-free DNA plasma concentration with severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Transl Med. 2017;15(1):106. [CrossRef]
- Buzova D, Braghini MR, Bianco SD, et al. Profiling of cell-free DNA methylation and histone signatures in pediatric NAFLD: A pilot study. Hepatology Communications. 2022;6(12):3311. [CrossRef]
- Buzova D, Maugeri A, Liguori A, et al. Circulating histone signature of human lean metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Clin Epigenetics. 2020;12(1):126. [CrossRef]
- Sookoian S, Pirola CJ. Cell-free DNA methylation as liquid biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a gap between innovation and implementation. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2017;6(2):117-121. [CrossRef]
- Yiğit B, Boyle M, Özler O, et al. Plasma cell-free DNA methylation: a liquid biomarker of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 2018;67(10):1907-1908. [CrossRef]
- Howell LS, Ireland L, Park BK, Goldring CE. MiR-122 and other microRNAs as potential circulating biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2018;18(1):47-54. [CrossRef]
- Mikulski D, Kościelny K, Dróżdż I, et al. Serum Levels of miR-122-5p and miR-125a-5p Predict Hepatotoxicity Occurrence in Patients Undergoing Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(8):4355. [CrossRef]
- Polyzos SA, Aronis KN, Kountouras J, Raptis DD, Vasiloglou MF, Mantzoros CS. Circulating leptin in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2016;59(1):30-43. [CrossRef]
- Tobaruela-Resola AL, Milagro FI, Elorz M, et al. Circulating miR-122-5p, miR-151a-3p, miR-126-5p and miR-21-5p as potential predictive biomarkers for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease assessment. J Physiol Biochem. Published online August 14, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Liu XL, Pan Q, Zhang RN, et al. Disease-specific miR-34a as diagnostic marker of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in a Chinese population. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(44):9844-9852. [CrossRef]
- Salvoza NC, Klinzing DC, Gopez-Cervantes J, Baclig MO. Association of Circulating Serum miR-34a and miR-122 with Dyslipidemia among Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLOS ONE. 2016;11(4):e0153497. [CrossRef]
- Turchinovich A, Baranova A, Drapkina O, Tonevitsky A. Cell-free circulating nucleic acids as early biomarkers for NAFLD and NAFLD-associated disorders. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1256. [CrossRef]
- Atic AI, Thiele M, Munk A, Dalgaard LT. Circulating miRNAs associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023;324(2):C588-C602. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee B, Sarkar M, Bose S, et al. MicroRNAs: Key modulators of inflammation-associated diseases. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 2024;154:364-373. [CrossRef]
- Huang X, Yuan T, Tschannen M, et al. Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:319. [CrossRef]
- Yamada H, Suzuki K, Ichino N, et al. Associations between circulating microRNAs (miR-21, miR-34a, miR-122 and miR-451) and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;424:99-103. [CrossRef]
- Coppin L, Leclerc J, Vincent A, Porchet N, Pigny P. Messenger RNA life-cycle in cancer cells: emerging role of conventional and non-conventional RNA-binding proteins? Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):650. [CrossRef]
- Mattick JS, Amaral PP, Carninci P, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(6):430-447. [CrossRef]
- Spanos M, Gokulnath P, Chatterjee E, Li G, Varrias D, Das S. Expanding the horizon of EV-RNAs: LncRNAs in EVs as biomarkers for disease pathways. Extracell Vesicle. 2023;2:100025. [CrossRef]
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. From RNA to Protein. In: Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th Edition. Garland Science; 2002. Accessed June 19, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26829/.
- Li G, Manning AC, Bagi A, et al. Distinct Stress-Dependent Signatures of Cellular and Extracellular tRNA-Derived Small RNAs. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(17):e2200829. [CrossRef]
- Thompson DM, Parker R. Stressing out over tRNA cleavage. Cell. 2009;138(2):215-219. [CrossRef]
- Friedrich M, Aigner A. Therapeutic siRNA: state-of-the-art and future perspectives. BioDrugs. 2022;36(5):549-571. [CrossRef]
- Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(11):675-691. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Q, Liu CH, Ampuero J, et al. Circular RNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Functions and clinical significance. RNA Biol. 2024;21(1):1-15. [CrossRef]
- Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, et al. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(4):466-477. [CrossRef]
- Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [CrossRef]
- Hu W, Liu C, Bi ZY, et al. Comprehensive landscape of extracellular vesicle-derived RNAs in cancer initiation, progression, metastasis and cancer immunology. Molecular Cancer. 2020;19(1):102. [CrossRef]
- Brandes F, Meidert AS, Kirchner B, et al. Identification of microRNA biomarkers simultaneously expressed in circulating extracellular vesicles and atherosclerotic plaques. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024;11:1307832. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(12):5003-5008. [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Yang B feng, Ai J. MicroRNA transport: A new way in cell communication. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2013;228(8):1713-1719. [CrossRef]
- LaPlante EL, Stürchler A, Fullem R, et al. exRNA-eCLIP intersection analysis reveals a map of extracellular RNA binding proteins and associated RNAs across major human biofluids and carriers. Cell Genom. 2023;3(5):100303. [CrossRef]
- Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM, Shamburek RD, Remaley AT. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(4):423-433. [CrossRef]
- Tabet F, Vickers KC, Cuesta Torres LF, et al. HDL-transferred microRNA-223 regulates ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Nat Commun. 2014;5(1):3292. [CrossRef]
- Scicali R, Di Pino A, Pavanello C, et al. Analysis of HDL-microRNA panel in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia subjects with LDL receptor null or defective mutation. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):20354. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Freitas D, Kim HS, et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):332-343. [CrossRef]
- Anand S, Samuel M, Mathivanan S. Exomeres: A New Member of Extracellular Vesicles Family. Subcell Biochem. 2021;97:89-97. [CrossRef]
- Clancy JW, Boomgarden AC, D’Souza-Schorey C. Profiling and promise of supermeres. Nat Cell Biol. 2021;23(12):1217-1219. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Q, Jeppesen DK, Higginbotham JN, et al. Supermeres are functional extracellular nanoparticles replete with disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat Cell Biol. 2021;23(12):1240-1254. [CrossRef]
- Al Amir Dache Z, Otandault A, Tanos R, et al. Blood contains circulating cell-free respiratory competent mitochondria. The FASEB Journal. 2020;34(3):3616-3630. [CrossRef]
- Stephens OR, Grant D, Frimel M, et al. Characterization and origins of cell-free mitochondria in healthy murine and human blood. Mitochondrion. 2020;54:102-112. [CrossRef]
- Park JH, Hayakawa K. Extracellular Mitochondria Signals in CNS Disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:642853. [CrossRef]
- Vikramdeo KS, Anand S, Khan MA, et al. Detection of mitochondrial DNA mutations in circulating mitochondria-originated extracellular vesicles for potential diagnostic applications in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):18455. [CrossRef]
- Spanos M, Gokulnath P, Whittaker OR, et al. Circulating Extracellular Mitochondria in Cardiometabolic Disease: Harnessing the Potential for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Physiologia. 2024;4(4):341-362. [CrossRef]
- Extracellular Mitochondria in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Neurological Recovery After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | Stroke. Accessed June 18, 2025. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017758.
- Sadik N, Cruz L, Gurtner A, et al. Extracellular RNAs: A New Awareness of Old Perspectives. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1740:1-15. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Z, Wu Q, Yan Z, et al. Extracellular RNA in a single droplet of human serum reflects physiologic and disease states. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2019;116(38):19200-19208. [CrossRef]
- Noninvasive preeclampsia prediction using plasma cell–free RNA signatures - ClinicalKey. Accessed June 18, 2025. https://www.clinicalkey.com/#!/content/playContent/1-s2.0-S000293782300323X?returnurl=https:%2F%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%2Fretrieve%2Fpii%2FS000293782300323X%3Fshowall%3Dtrue&referrer=.
- Zhong P, Bai L, Hong M, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Circulating cfRNA in Plasma: Implications for Disease Diagnosis and Beyond. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024;14(10):1045. [CrossRef]
- Rozowsky J, Kitchen RR, Park JJ, et al. exceRpt: A Comprehensive Analytic Platform for Extracellular RNA Profiling. Cell Syst. 2019;8(4):352-357.e3. [CrossRef]
- Murillo OD, Thistlethwaite W, Rozowsky J, et al. ExRNA atlas analysis reveals distinct extracellular RNA cargo types and their carriers present across human biofluids. Cell. 2019;177(2):463-477.e15. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee E, Rodosthenous RS, Kujala V, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles in human cardiorenal syndrome promote renal injury in a kidney-on-chip system. JCI Insight. 2023;8(22):e165172. [CrossRef]
- Gokulnath P, Spanos M, Lehmann HI, et al. Distinct Plasma Extracellular Vesicle Transcriptomes in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Subtypes: A Liquid Biopsy Approach. Circulation. 2024;149(14):1147-1149. [CrossRef]
- Happel C, Ganguly A, Tagle DA. Extracellular RNAs as potential biomarkers for cancer. jcmt. 2020;6(0):N/A-N/A. [CrossRef]
- Tang R, Zhang Z, Xu J, et al. Integration of single-nucleus and exosome RNA sequencing dissected inter-cellular communication and biomarkers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024;23:1689-1704. [CrossRef]
- Luo T, Chen SY, Qiu ZX, et al. Transcriptomic Features in a Single Extracellular Vesicle via Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Small Methods. 2022;6(11):2200881. [CrossRef]
- Kojabad AA, Farzanehpour M, Galeh HEG, et al. Droplet digital PCR of viral DNA/RNA, current progress, challenges, and future perspectives. J Med Virol. 2021;93(7):4182-4197. [CrossRef]
- Wang C, Ding Q, Plant P, et al. Droplet digital PCR improves urinary exosomal miRNA detection compared to real-time PCR. Clin Biochem. 2019;67:54-59. [CrossRef]
- Campomenosi P, Gini E, Noonan DM, et al. A comparison between quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR technologies for circulating microRNA quantification in human lung cancer. BMC Biotechnol. 2016;16(1):60. [CrossRef]
- Del Re M, Biasco E, Crucitta S, et al. The Detection of Androgen Receptor Splice Variant 7 in Plasma-derived Exosomal RNA Strongly Predicts Resistance to Hormonal Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients. European Urology. 2017;71(4):680-687. [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann K, Cieselski M, Schumann J. Relative versus absolute RNA quantification: a comparative analysis based on the example of endothelial expression of vasoactive receptors. Biol Proced Online. 2021;23(1):6. [CrossRef]
- Huang Z, Fang J, Zhou M, Gong Z, Xiang T. CRISPR-Cas13: A new technology for the rapid detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:1011399. [CrossRef]
- Grölz D, Hauch S, Schlumpberger M, et al. Liquid biopsy preservation solutions for standardized pre-analytical workflows—venous whole blood and plasma. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2018;6(4):275-286. [CrossRef]
- Asleh K, Dery V, Taylor C, Davey M, Djeungoue-Petga MA, Ouellette RJ. Extracellular vesicle-based liquid biopsy biomarkers and their application in precision immuno-oncology. Biomark Res. 2023;11:99. [CrossRef]
- De Sousa KP, Rossi I, Abdullahi M, Ramirez MI, Stratton D, Inal JM. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles and future directions in diagnosis and therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023;15(1):e1835. [CrossRef]
- Konoshenko MYu, Lekchnov EA, Vlassov AV, Laktionov PP. Isolation of extracellular vesicles: general methodologies and latest trends. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8545347. [CrossRef]
- Lone SN, Nisar S, Masoodi T, et al. Liquid biopsy: a step closer to transform diagnosis, prognosis and future of cancer treatments. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:79. [CrossRef]
- Zhu L, Sun HT, Wang S, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:152. [CrossRef]
- Hartjes TA, Mytnyk S, Jenster GW, van Steijn V, van Royen ME. Extracellular vesicle quantification and characterization: common methods and emerging approaches. Bioengineering (Basel). 2019;6(1):7. [CrossRef]
- Masago K, Fujita S, Oya Y, et al. Comparison between fluorimetry (Qubit) and spectrophotometry (NanoDrop) in the quantification of DNA and RNA extracted from frozen and FFPE tissues from lung cancer patients: A real-world Use of genomic tests. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(12):1375. [CrossRef]
- Conesa A, Madrigal P, Tarazona S, et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016;17(1):13. [CrossRef]
- Brown J, Pirrung M, McCue LA. FQC Dashboard: integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics. 2017;33(19):3137-3139. [CrossRef]
- Babraham Bioinformatics - FastQC A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Accessed December 14, 2024. https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- Raplee ID, Evsikov AV, Marín de Evsikova C. Aligning the aligners: comparison of RNA sequencing data alignment and gene expression quantification tools for clinical breast cancer research. J Pers Med. 2019;9(2):18. [CrossRef]
- Everaert C, Luypaert M, Maag JLV, et al. Benchmarking of RNA-sequencing analysis workflows using whole-transcriptome RT-qPCR expression data. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1559. [CrossRef]
- Patro R, Duggal G, Love MI, Irizarry RA, Kingsford C. Salmon: fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression using dual-phase inference. Nat Methods. 2017;14(4):417-419. [CrossRef]
- Kolberg L, Raudvere U, Kuzmin I, Adler P, Vilo J, Peterson H. g:Profiler—interoperable web service for functional enrichment analysis and gene identifier mapping (2023 update). Nucleic Acids Research. 2023;51(W1):W207-W212. [CrossRef]
- Brouard JS, Bissonnette N. Variant calling from RNA-seq data using the GATK joint genotyping workflow. In: Ng C, Piscuoglio S, eds. Variant Calling: Methods and Protocols. Springer US; 2022:205-233. [CrossRef]
- Hochreuter MY, Dall M, Treebak JT, Barrès R. MicroRNAs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Progress and perspectives. Mol Metab. 2022;65:101581. [CrossRef]
- Panella R, Petri A, Desai BN, et al. MicroRNA-22 is a key regulator of lipid and metabolic homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(16):12870. [CrossRef]
- Carpi S, Daniele S, de Almeida JFM, Gabbia D. Recent advances in miRNA-based therapy for MASLD/MASH and MASH-associated HCC. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(22):12229. [CrossRef]
- Raptis DD, Mantzoros CS, Polyzos SA. Fibroblast growth factor-21 as a potential therapeutic target of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023;19:77-96. [CrossRef]
- Gim JA, Bang SM, Lee YS, et al. Evaluation of the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through analysis of serum exosomal miRNA expression. PLOS ONE. 2021;16(8):e0255822. [CrossRef]
- Cheung O, Puri P, Eicken C, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic MicroRNA expression. Hepatology. 2008;48(6):1810-1820. [CrossRef]
- Becker PP, Rau M, Schmitt J, et al. Performance of Serum microRNAs -122, -192 and -21 as Biomarkers in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. PLOS ONE. 2015;10(11):e0142661. [CrossRef]
- Povero D, Eguchi A, Li H, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles with specific proteome and liver micrornas are potential biomarkers for liver injury in experimental fatty liver disease. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e113651. [CrossRef]
- Pirola CJ, Fernández Gianotti T, Castaño GO, et al. Circulating microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: from serum non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut. 2015;64(5):800-812. [CrossRef]
- Kim TH, Lee Y, Lee YS, et al. Circulating miRNA is a useful diagnostic biomarker for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2021;11:14639. [CrossRef]
- Ando Y, Yamazaki M, Yamada H, et al. Association of circulating miR-20a, miR-27a, and miR-126 with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in general population. Sci Rep. 2019;9:18856. [CrossRef]
- Huang P, Tu B, Liao HJ, et al. Elevation of plasma tRNA fragments as a promising biomarker for liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5886. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Q, Liu CH, Wu D, Jiang W, Zhang N, Tang H. LncRNA and circRNA in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. Biomolecules. 2023;13(3):560. [CrossRef]
- Zhou W, Qiu K. The correlation between lncRNA NEAT1 and serum hepcidin in the peripheral blood of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(4):2593-2599.
- Shen X, Guo H, Xu J, Wang J. Inhibition of lncRNA HULC improves hepatic fibrosis and hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2019;234(10):18169-18179. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Q, Liu J, Deng H, et al. Targeting Mitochondria-Located circRNA SCAR Alleviates NASH via Reducing mROS Output. Cell. 2020;183(1):76-93.e22. [CrossRef]
- Akuta N, Kawamura Y, Suzuki F, et al. Impact of circulating miR-122 for histological features and hepatocellular carcinoma of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japan. Hepatol Int. 2016;10(4):647-656. [CrossRef]
- Tobaruela-Resola AL, Riezu-Boj JI, Milagro FI, et al. Circulating microRNA panels in subjects with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease after following a 2-year dietary intervention. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025;48(4):987-1003. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Yang D, Wang B, Zeng Y, Li W. The value of miRNAs in the prognosis of obese patients receiving bariatric surgery. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(4):1905-1914.
- Li YJ, Baumert BO, Stratakis N, et al. Circulating microRNA expression and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents with severe obesity. World J Gastroenterol. 2024;30(4):332-345. [CrossRef]
- Aspichueta P, Zeisel MB. miR-21p-5p coordinates biological pathways to promote MASLD progression. Liver International. 2023;43(11):2343-2345. [CrossRef]
- Tan Y, Ge G, Pan T, Wen D, Gan J. A pilot study of serum microRNAs panel as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105192. [CrossRef]
- Park JG, Kim G, Jang SY, et al. Plasma Long Noncoding RNA LeXis is a Potential Diagnostic Marker for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Life (Basel). 2020;10(10):230. [CrossRef]
- Xiang J, Deng YY, Liu HX, Pu Y. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes PPARα/CD36-Mediated Hepatic Lipogenesis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating miR-206/ARNT Axis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:858558. [CrossRef]
- Leti F, Legendre C, Still CD, et al. Altered expression of MALAT1 lncRNA in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis fibrosis regulates CXCL5 in hepatic stellate cells. Translational Research. 2017;190:25-39.e21. [CrossRef]
- Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, et al. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(8):2884-2897. [CrossRef]
- Hsu SH, Wang B, Kota J, et al. Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(8):2871-2883. [CrossRef]
- Paluschinski M, Kordes C, Vucur M, et al. Differential Modulation of miR-122 Transcription by TGFβ1/BMP6: Implications for Nonresolving Inflammation and Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cells. 2023;12(15):1955. [CrossRef]
- Colaianni F, Zelli V, Compagnoni C, et al. Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122. Genes. 2024;15(10):1313. [CrossRef]
- Wen J, Friedman JR. miR-122 regulates hepatic lipid metabolism and tumor suppression. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(8):2773-2776. [CrossRef]
- Xu Y, Zhu Y, Hu S, et al. Hepatocyte miR-34a is a key regulator in the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Metab. 2021;51:101244. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Sun M, Cao Y, et al. miR-34a regulates lipid metabolism by targeting SIRT1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with iron overload. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2020;695:108642. [CrossRef]
- Liu RH, Ning B, Ma XE, Gong WM, Jia TH. Regulatory roles of microRNA-21 in fibrosis through interaction with diverse pathways (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports. 2016;13(3):2359-2366. [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi-Yorimoto A, Yamaura Y, Kanki M, et al. MicroRNA-21 is associated with fibrosis in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and serves as a plasma biomarker for fibrotic liver disease. Toxicol Lett. 2016;258:159-167. [CrossRef]
- Caviglia JM, Yan J, Jang MK, et al. MicroRNA-21 and Dicer are dispensable for hepatic stellate cell activation and the development of liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2018;67(6):2414-2429. [CrossRef]
- Markovic J, Sharma AD, Balakrishnan A. MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury. Cells. 2020;9(8):1767. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Al A, El-Ahwany E, Zoheiry M, et al. miRNA-221 and miRNA-222 are promising biomarkers for progression of liver fibrosis in HCV Egyptian patients. Virus Research. 2018;253:135-139. [CrossRef]
- Calvente CJ, Tameda M, Johnson CD, et al. Neutrophils contribute to spontaneous resolution of liver inflammation and fibrosis via microRNA-223. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(10):4091-4109. [CrossRef]
- Gu J, Xu H, Chen Y, Li N, Hou X. MiR-223 as a Regulator and Therapeutic Target in Liver Diseases. Front Immunol. 2022;13. [CrossRef]
- Chen K, Lin T, Yao W, Chen X, Xiong X, Huang Z. Adipocytes-derived exosomal miR-122 promotes non-alcoholic fat liver disease progression via targeting Sirt1. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;46(7):531-541. [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Xiao F, Sun J, et al. Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles miR-122-5p promotes hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by regulating Kupffer cell polarization. International Immunopharmacology. 2023;119:110060. [CrossRef]
- Hu MJ, Long M, Dai RJ. Acetylation of H3K27 activated lncRNA NEAT1 and promoted hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via regulating miR-212-5p/GRIA3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(1):191-203. [CrossRef]
- Sun Y, Song Y, Liu C, Geng J. LncRNA NEAT1-MicroRNA-140 axis exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver through interrupting AMPK/SREBP-1 signaling. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2019;516(2):584-590. [CrossRef]
- Hussein MA, Valinezhad K, Adel E, Munirathinam G. MALAT-1 Is a Key Regulator of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Metastasis. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(1):234. [CrossRef]
- Lu J, Guo J, Liu J, Mao X, Xu K. Long Non-coding RNA MALAT1: A Key Player in Liver Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:734643. [CrossRef]
- Sallam T, Jones MC, Gilliland T, et al. Feedback modulation of cholesterol metabolism by the lipid-responsive non-coding RNA LeXis. Nature. 2016;534(7605):124-128. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J, Cheng M, Zhao X. A tRNA-derived fragment (tRF-3001b) aggravates the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting autophagy. Life Sci. 2020;257:118125. [CrossRef]
- Sohail AM, Khawar MB, Afzal A, Hassan A, Shahzaman S, Ali A. Multifaceted roles of extracellular RNAs in different diseases. Mil Med Res. 2022;9(1):43. [CrossRef]
- Yamada H, Ohashi K, Suzuki K, et al. Longitudinal study of circulating miR-122 in a rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;446:267-271. [CrossRef]
- Chai C, Rivkin M, Berkovits L, et al. Metabolic circuit involving free fatty acids, microRNA 122, and triglyceride synthesis in liver and muscle tissues. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(5):1404-1415. [CrossRef]
- Chouik Y, Aubin A, Maynard-Muet M, et al. The grade of obesity affects the noninvasive diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in individuals with MASLD. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024;32(6):1114-1124. [CrossRef]
- Angelini G, Panunzi S, Castagneto-Gissey L, et al. Accurate liquid biopsy for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Gut. 2022;72(2):392. [CrossRef]
- Sanyal AJ, Williams SA, Lavine JE, et al. Defining the serum proteomic signature of hepatic steatosis, inflammation, ballooning and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2023;78(4):693-703. [CrossRef]
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328-357. [CrossRef]
- Younossi ZM, Loomba R, Anstee QM, et al. Diagnostic Modalities for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, and Associated Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2018;68(1):349-360. [CrossRef]
- Castera L, Vilgrain V, Angulo P. Noninvasive evaluation of NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10(11):666-675. [CrossRef]
- Dulai PS, Sirlin CB, Loomba R. MRI and MRE for non-invasive quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in NAFLD and NASH: Clinical trials to clinical practice. J Hepatol. 2016;65(5):1006-1016. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Glaser KJ, Sanderson SO, Ehman RL. Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology. 2011;259(3):749-756. [CrossRef]
- Imajo K, Kessoku T, Honda Y, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging more accurately classifies steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease than transient elastography. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(3):626-637.e7. [CrossRef]
- Yin M, Venkatesh SK. Ultrasound or MR elastography of liver: which one shall I use? Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018;43(7):1546-1551. [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli G, Tinelli C, Dal Bello B, et al. Accuracy of real-time shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a pilot study. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2125-2133. [CrossRef]
- Cui J, Heba E, Hernandez C, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography is superior to acoustic radiation force impulse for the Diagnosis of fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study. Hepatology. 2016;63(2):453-461. [CrossRef]
- Verma S, Jensen D, Hart J, Mohanty SR. Predictive value of ALT levels for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and advanced fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Liver Int. 2013;33(9):1398-1405. [CrossRef]
- Anty R, Iannelli A, Patouraux S, et al. A new composite model including metabolic syndrome, alanine aminotransferase and cytokeratin-18 for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in morbidly obese patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(11-12):1315-1322. [CrossRef]
- Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45(4):846-854. [CrossRef]
- Shah AG, Lydecker A, Murray K, et al. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(10):1104-1112. [CrossRef]
- McPherson S, Hardy T, Dufour JF, et al. Age as a confounding factor for the accurate non-invasive diagnosis of advanced NAFLD fibrosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(5):740-751. [CrossRef]
- Angulo P, Bugianesi E, Bjornsson ES, et al. Simple noninvasive systems predict long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(4):782-789.e4. [CrossRef]
- Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, et al. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 2017;35(2):180-188. [CrossRef]
- Sato Y, Hatakeyama H, Sakurai Y, Hyodo M, Akita H, Harashima H. A pH-sensitive cationic lipid facilitates the delivery of liposomal siRNA and gene silencing activity in vitro and in vivo. J Control Release. 2012;163(3):267-276. [CrossRef]
- Baldari S, Di Rocco G, Magenta A, Picozza M, Toietta G. Extracellular vesicles-encapsulated microRNA-125b produced in genetically modified mesenchymal stromal cells inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Cells. 2019;8(12):1560. [CrossRef]
- Anthiya S, Griveau A, Loussouarn C, et al. MicroRNA-based drugs for brain tumors. Trends Cancer. 2018;4(3):222-238. [CrossRef]
- Mishra S, Webster P, Davis ME. PEGylation significantly affects cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of non-viral gene delivery particles. Eur J Cell Biol. 2004;83(3):97-111. [CrossRef]
- Yang J, Hendricks W, Liu G, et al. A nanoparticle formulation that selectively transfects metastatic tumors in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(36):14717-14722. [CrossRef]
- Huang X, Kong N, Zhang X, Cao Y, Langer R, Tao W. The landscape of mRNA nanomedicine. Nat Med. 2022;28(11):2273-2287. [CrossRef]
- Ito D, Kawaguchi Y, Inagaki Y, et al. Assessment of liver function-related mRNA expression and fluorescence imaging in outflow-obstructed regions in rats. Surg Today. 2023;53(4):513-521. [CrossRef]
- Bose R, Ain R. Regulation of Transcription by Circular RNAs. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:81-94. [CrossRef]
- Hudson D, Afzaal T, Bualbanat H, et al. Modernizing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease diagnostics: the progressive shift from liver biopsy to noninvasive techniques. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024;17:17562848241276334. [CrossRef]
- Talwalkar JA, Kurtz DM, Schoenleber SJ, West CP, Montori VM. Ultrasound-based transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5(10):1214-1220. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




