Submitted:
05 July 2025
Posted:
07 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
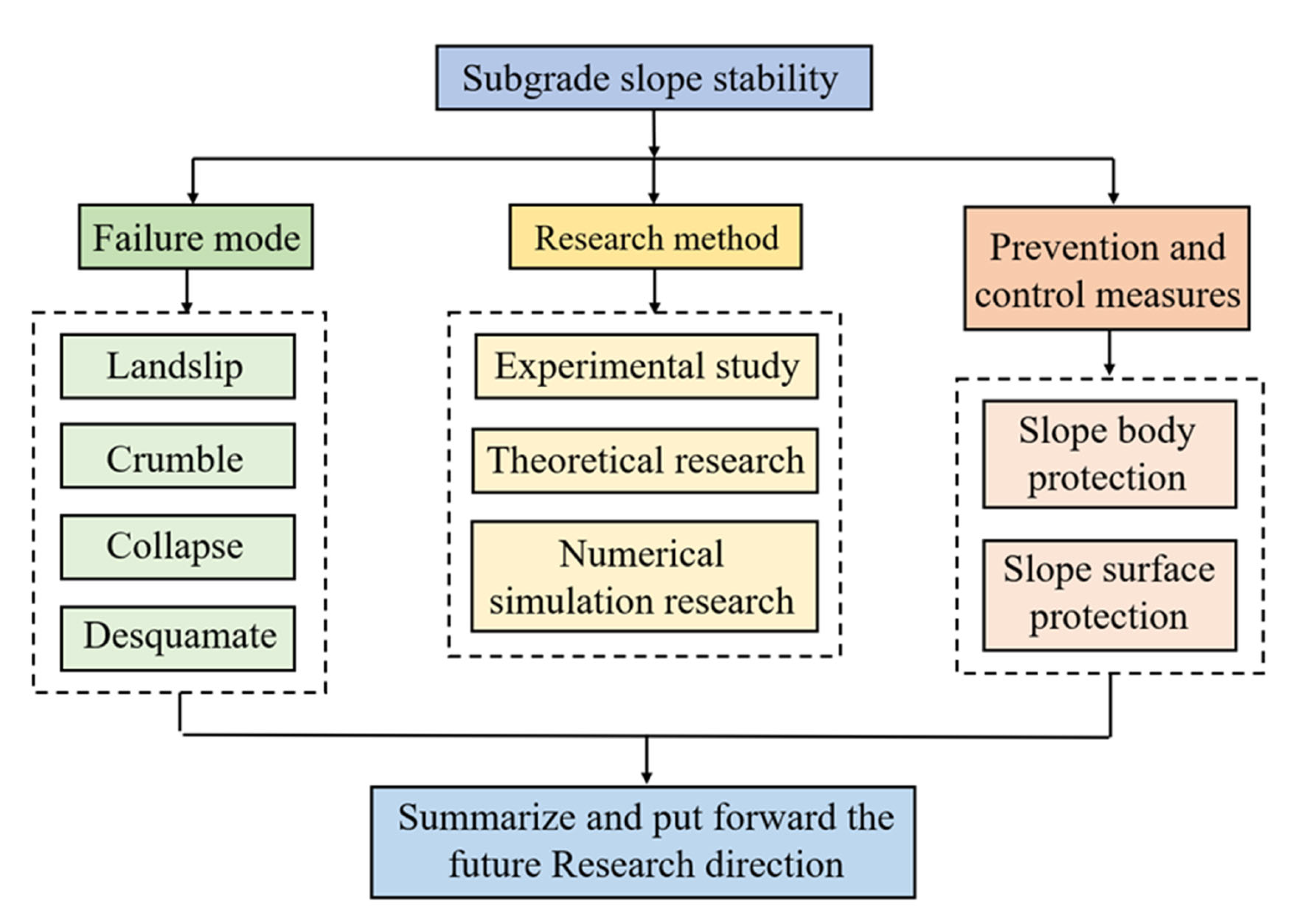
1. Introduction
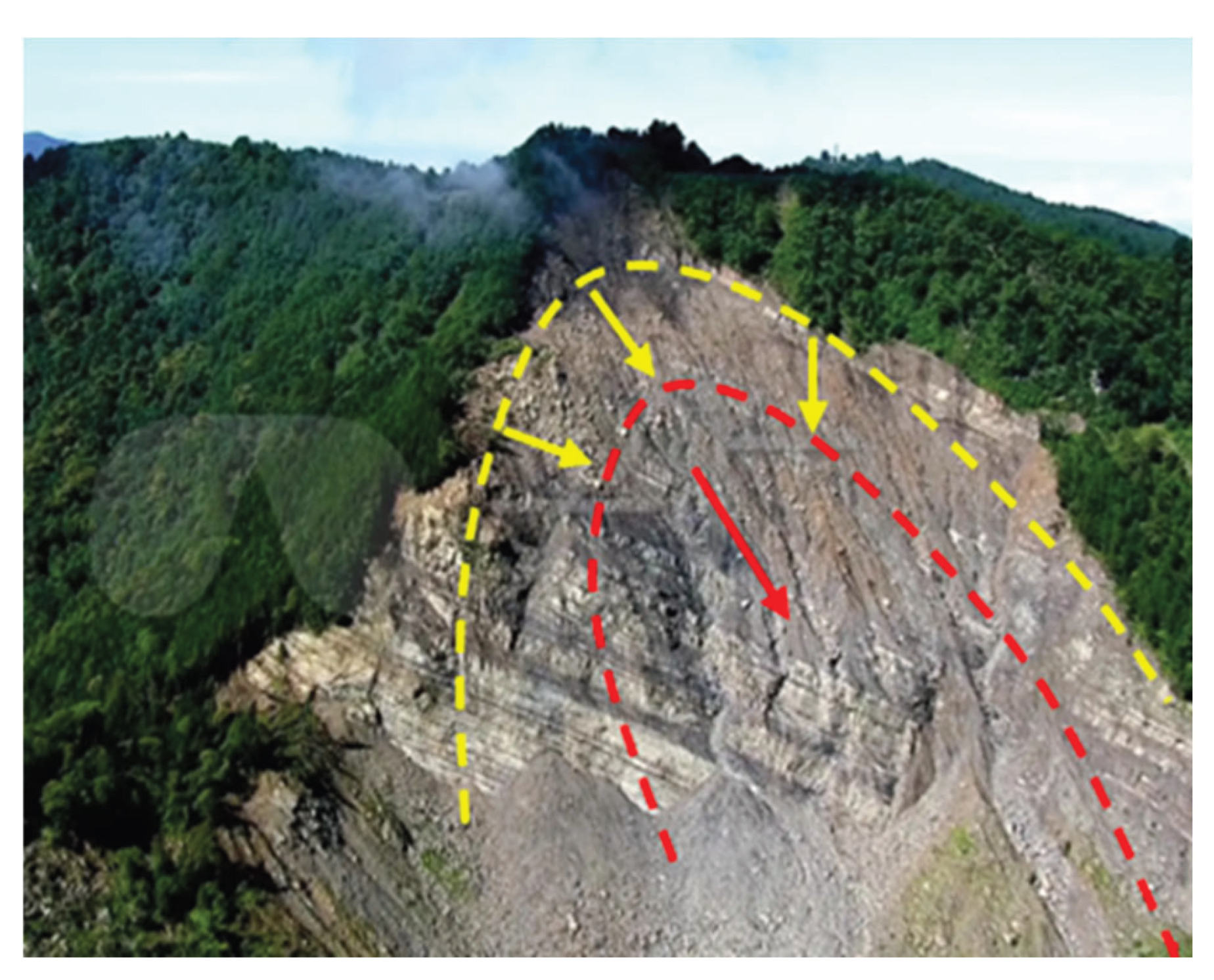
2. Forms of Slope Failure
2.1. Landslides
2.2. Crumble
2.3. Collapse
2.4. Flake
3. Slope Stability Research Methods
3.1. Pilot Study
3.1.1. Indoor Pilot Studies
2.1.2. Model Test Studies
2.1.3. Field Pilot Study
2.2. Theoretical Studies
2.3. Numerical Simulation Studies
3. Slope Damage Prevention and Control Measures
3.1. Slope Protection
3.1.1. Vegetation Cover
3.1.2. Engineering Protection
3.1.3. Flexible Protection
3.2. Slope Protection
3.2.1. Retaining Wall
3.2.2. Slope Stabilization
4. Conclusions and Outlook
References
- Yang, S.; Leshchinsky, B.; Cui, K.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y. Influence of failure mechanism on seismic bearing capacity factors for shallow foundations near slopes. Geotech. 2021, 71, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardani, N.; Zhou, A.; Nazem, M.; Shen, S.-L. Improved prediction of slope stability using a hybrid stacking ensemble method based on finite element analysis and field data. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 13, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SUMAN S, KHANS Z, DAS S K, et al. Slope stability analysis using artificial intelligence techniques. Natural Hazards, 2016, 84: 727-748.
- Qing, Lv. Study on Prevention and Treatment Technology of Slope Engineering Disasters. Zhejiang University, 2006.
- Gordan, B.; Armaghani, D.J.; Hajihassani, M.; Monjezi, M. Prediction of seismic slope stability through combination of particle swarm optimization and neural network. Eng. Comput. 2015, 32, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QI C C, TANG X L. Slope stability prediction using integrated metaheuristic and machine learning approaches: a comparative study. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2018, 118: 112-122.
- Bishop, A.W. The use of the Slip Circle in the Stability Analysis of Slopes. Geotech. 1955, 5, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell.R. Some Landslide Risk Zoning Schemes in Use in Easter. Australia and Their Application(C).Sixth Australian New Zealand Conference on Geomachanics, Christchurch,1992:505-512.
- A.Uromeihy, M.R. A.Uromeihy, M.R.Mahdavifar. Landslide Hazard Zonation of the Khorshrostam Area,Iran. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment.2000,58(3):207-213.
- Yunlong Fan,Yuanshuai Dong,Yun, Hou,; et al. Failure mode and treatment measures of high soil slope in highway cutting. Engineering technology research.2020,5(18):36-38.
- van Westen, C.J.; Rengers, N.; Soeters, R. Use of Geomorphological Information in Indirect Landslide Susceptibility Assessment. Nat. Hazards 2003, 30, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Fernández-Merodo, J.; Mulas, J.; Pastor, M.; Luzi, G.; Monserrat, O. A landslide forecasting model using ground based SAR data: The Portalet case study. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, C. Parameter inversion and deformation mechanism of Sanmendong landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir region under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall. Eng. Geol. 2016, 205, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hu, B.; Yan, E.; Xu, X.; Yi, Q. Research on the creep mechanism of Huangniba landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of China considering the seepage–stress coupling effect. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 78, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Xu, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Iqbal, J.; Fu, X.; Huang, X.; Cheng, W. Activity law and hydraulics mechanism of landslides with different sliding surface and permeability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Eng. Geol. 2019, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paronuzzi P, Rigo E, Bolla A. Influence of filling-drawdown cycles of the Vajont reservoir on Mt. Toc slope stability. Geomorphology, 2013,191:75-93.
- Application of finite difference method in stability analysis of high rock slope; Qiang Ren;. Liaoning Normal University,2018.
- Richard E, Goodman, D Scott Kieffer. Behavior of Rock in Slopes. 2: Journal of Geotechnical and Geo-environmental engineering, 2000,(8), 2000.
- Hatzor, Y.; Talesnick, M.; Tsesarsky, M. Continuous and discontinuous stability analysis of the bell-shaped caverns at Bet Guvrin, Israel. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2002, 39, 867–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavers, D.S. Simple methods to analyze buckling of rock slopes. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 1981, 14, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek E,and Bray J, W. Rock slope engineering,3rd Ed. Inst. 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hunan Water conservancy and hydropower survey and design Institute. Slope engineering geology. 2: Beijing: Water Resources and Electric Power Press, 1983, 1983.
- Goodman R E, Gen-hua Shi. Block Theory and its Application to Rock Engineering. P: New York, 1985.
- Shi Gen-hua. Discontinuous deformationanalysis: A new numerical model for the static and dynamics of block systems. Berkely: Dep. of Civil Eng., University of Calif. 19 August; 88.
- Clough, A.K. Variable factor of safety in slopes stability analysis by limit equilibrium method.J.,1stEng. India Part Ⅱ1988,69(3):149-155.
- Bishop, A.W. The use of the slip circle in the stability analysis of slopes Geotichnique,London,1955,5(1):7-17.
- Gao, W.; Ge, S. A comprehensive review of slope stability analysis based on artificial intelligence methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugang Zhao,Bo An, Kaiyang Wang, et al. Study on suitable length of transition section of slope rate based on control of highway slope collapse disaster. Highways & Automotive Applications, 2023, (03): 73-75. [CrossRef]
- Fang Qiang. A brief discussion on the formation of highway subgrade slope collapse and its prevention measures. Building Materials and Decoration, 2020, (17): 267-268.
- Baolong Zhang. The influence of hydrologic conditions on highway high slope collapse is analyzed based on finite element method. Highways & Transportation in Inner Mongolia, 2015, (06): 39-41. [CrossRef]
- Shujuan Qin. Design analysis of slope collapse repair and reinforcement in mountainous areas. Traffic world, 2023, (09): 90-92. [CrossRef]
- Wanjun Ye, Zhipeng Zhao, Gengshe Yang, et al. Influence of soil moisture state on the spalling disease of loess slope. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28 (07): 18-24. [CrossRef]
- Jian Xu, Xiang Zheng, Hui Zhang. Analysis on mechanism and stability of freeze-thaw spalling disease for slope in loess area. J. Xi’an Univ. of Arch. & Tech. (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 50 (04): 477-484. [CrossRef]
- Ting Yao. Study on Stability of Silty Clay Slope in Alpine Region. Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2019.
- Asteris, P.G.; Rizal, F.I.M.; Koopialipoor, M.; Roussis, P.C.; Ferentinou, M.; Armaghani, D.J.; Gordan, B. Slope Stability Classification under Seismic Conditions Using Several Tree-Based Intelligent Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, P. Numerical analysis of evaluation methods and influencing factors for dynamic stability of bedding rock slope. J. Vibroengineering 2017, 19, 1937–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, C.; Zhao, Z. Influence of the Slope Shape on Seismic Stability of a Slope. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain E J, Gow A J. Effect of freezing and thawing on the permeability and structure of soils. Engineering Geology, 1979, 13(1):73-92.
- Song, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, B.; Zhao, J. Large-scale triaxial compression tests of geocell-reinforced sand. Geosynth. Int. 2019, 26, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konrad, J.-M. Physical processes during freeze-thaw cycles in clayey silts. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1989, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrod K D, Knutsson S, Sheng D. Pore-Water Pressures in Freezing and Thawing FineGrained Soils. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering, 1996, 10(2):77-92. Chunjun Gao. Study on the Drainage Pipe Blocking Mechanism Caused by Groundwater Crystallization and its Influences on the High Slope Stability. Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2020.
- Chunjun Gao. Study on the Drainage Pipe Blocking Mechanism Caused by Groundwater Crystallization and its Influences on the High Slope Stability. Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2020.
- Yan Wang. Study on Performance of Geocell to Protect Highway Embankment Slope. Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2022.
- Yonghui Cheng,Zhanlin Cheng,Yuanbin Zhang. Centrifugal model test study on the instability mechanism of expansive soil slope under rainfall conditions. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering.2011,33(S1):416-421.
- Wanfu Zeng. Test of influence of water level fall in front of slope on slope stability. Water Technology and Economy.2021,27(09):68-73.
- Jiale Cai, Law of water infiltration in macroscopic cracks of loess And its influence on slope failure. Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2023.
- Songyu Liu, Guojun Cai, Wei Zhang, et al. Progress in Geotechnical Investigation, Testing and Evaluation. China Civil engineering Journal.:1-18.
- Jingyun Gu,Yulong Luo,Xingjie, Zhang,; et al. A visual test device for subsurface erosion based on planar laser induced fluorescence and its preliminary application. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering. 2021,40(06):1287-1296.
- Yaonan Li: Study on slope stability under rainfall infiltration. Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2020.
- Guangshuai: Research on Application of Electrokinetic Consolidation for Open-pit Coal Mine Slope in Inner Mongolia. Shenyang Jianzhu University, 2022.
- Dongdong Liu: Study on the influence of anti slide pile on the stability of high slope reinforced by tunnel crossing slope. Central South University, 2022.
- SHAN W, ZHANG C C, GUO Y. Mechanism of shallow slide on soil road cutting slope during spring in seasonal frozen region; proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Civil Engineering, Architecture and Building Materials (CEABM 2012), Yantai, PEOPLES R CHINA, F -27, 2012. 2012. 25 May.
- Gao, W. Stability analysis of rock slope based on an abstraction ant colony clustering algorithm. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 7969–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIU K, WANG Y Q. Influence of Soil Heterogeneity on the Behavior of Frozen Soil Slope under Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Cmes-Computer Modeling In Engineering and Sciences, 2022, 131(1): 119-135.
- Azarafza M, Asghari-KaljahiE, Ghazifard A, et al. Application of fuzzy expert decision a king system for rock slope block top pling modeling and assessment: a case study.Modeling Earth Systems and Environment.2021(1):7.
- Lei Sun. Study of the slope failure evolution and the slope stability analysis under water-rock coupling with the combined finite-discrete element method. Wuhan University, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Kalatehjari, R.; A Rashid, A.S.; Hajihassani, M.; Kholghifard, M.; Ali, N. Determining the unique direction of sliding in three-dimensional slope stability analysis. Eng. Geol. 2014, 182, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Y K, Gao YF, Zhang F. A simplified approach to determine the unique direction of sliding in 3D slopes. Engineering Geology, 2016, 211: 179-183.
- Griffiths D V, Lane P A. Slope stability analysis by finite elements. 3: Geotechnique, 1999, 49(3), 1999.
- Li, A.; Merifield, R.; Lyamin, A. Stability charts for rock slopes based on the Hoek–Brown failure criterion. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2008, 45, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.W. The use of the Slip Circle in the Stability Analysis of Slopes. Geotech. 1955, 5, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janbu, N. Slop stability computations, Embankment Dam Engineering, John Wiley and Sons, New York. 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Humpheson, C.; Lewis, R.W. Associated and non-associated visco-plasticity and plasticity in soil mechanics. Geotech. 1975, 25, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim J Y,Lee S R. An improved search strategy for the critical slip surface using finite element stress fields. Computers and Geotechnies,1997,21(4):295-313.
- Su H, Hu J, Yang M. Evaluation method for slope stability under multianchor support. Natural Hazards Review, 2015, 16(4):04014034.1-04014034.7.
- Rui Wang.Instability analysis of soil cutting slope induced by rainfall in Linxia area. Chang ‘an University, 2020.
- Juan Xiang: The Cut Slope Stability Analysis and Governance Research inTong Ping highway. Central South University, 2011.
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Su, L. Initiation and Displacement Analysis of Cohesive Soil Slopes by Discrete Element Modelling. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 35, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihua Luo. Stability analysis method of expressway slope under static and dynamic loads. Hunan University, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Pei, X.; Wei, R.; Yang, B.; Lei, N.; Zhang, X.; Yin, D.; Wang, S.; Tao, Q. Ecological Restoration of Engineering Slopes in China—A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Wang J, Duan Q, et al. The Investigation and3D Numerical Simulation of Herb Rootsin Rein forcing Soiland Stabilizing Slope. KSCE JOURNAL OF CIVILENG INEERING. 2018,22(12):4909-4921.
- Fan, J.-C.; Huang, C.-L.; Yang, C.-H.; Liao, K.-W.; Liao, W.-W. Effect evaluation of shotcrete vegetation mulching technique applied to steep concrete-face slopes on a highway of Taiwan. Paddy Water Environ. 2011, 11, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, Y.; Kitahara, H.; Ochiai, H.; Sammori, T.; Kawanami, A. Landslide fluidization process by flume experiments. Eng. Geol. 2002, 66, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz H J, Griswold F S. The influence of tree roots on soil morphology. 1939.
- Sawangsuriya, A.; Jotisankasa, A.; Sukolrat, J.; Dechasakulsom, M.; Mahatumrongchai, V.; Milindalekha, P.; Anuvechsirikiat, S. Comparison of Erosion Susceptibility and Slope Stability of Repaired Highway Embankment. Geo-Congress 2013, United States.
- Mehdipour, I.; Ghazavi, M.; Moayed, R.Z. Numerical study on stability analysis of geocell reinforced slopes by considering the bending effect. Geotext. Geomembranes 2013, 37, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Yong, W.; Jun-Long, H.; Jing, W.; Qing-Jun, Z. Experimental study on anti-eroding effect of slope protected by degradable geocell; p. 01 2026. [CrossRef]
- Vedpathak, S. Dalmia G. & Bagli S. Protecting Slopes Through Geocells — An Innovative Paradigm[C]. International Symposium “Geosynthetics—The Road Ahead”. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wuxing Liang, Zhanhui Qu, Shiqiang Xu. Research on protection technology of highway slope. Journal of Xi ‘an Institute of Technology. 2006(05): 649-651.
- Nadim F, Whitman R V. Seismically induced movement of retaining walls. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, ASCE, 1983, 109(7), 915~931.
- Buklje, L. “ltheological aspects in soil mechanics.”. Wiley-Interscience, London.1969.
- Fathipour, H.; Siahmazgi, A.S.; Payan, M.; Chenari, R.J. Evaluation of the lateral earth pressure in unsaturated soils with finite element limit analysis using second-order cone programming. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan C C, Fang Y S. Numerical solution of active earth pressures on rigid retaining walls built near rock faces. Computers and Geotechnics, 2010, 37(7-8): 1023- 1029.
- Wörden, F.T.; Achmus, M. Numerical modeling of three-dimensional active earth pressure acting on rigid walls. Comput. Geotech. 2013, 51, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimin Wang,Hui Zhang,Huan, Li,; et al. Dynamic analysis of reinforced earth retaining wall considering earthquake time history. Vibration and Shock.2013,32(24):187-191.
- Huafeng Lou,Ze liu,Huan, Liu,; et al. Analysis of the influence of wall Angle on the structure of modular reinforced earth retaining wall. Industrial building. 2023,53(04):141-147.
- Stamatopoulos Constantine A, Bassanou Maria. Mitigation of the seismic motion near the edge of cliff-type topographies using anchors and piles. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 2009, 7(1): 221-253.
- Ma Ning, Wu Honggang, Ma Huimin, et al. Examining dynamic soil pressures and the effectiveness of different pile structures inside reinforced slopes using shaking table tests. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2019, 116:293-303.
- Chen Wai-Fah, Liu Xl. Limit analysis in soil mechanics. Elsevier, 2012.
- homas, C. Simplified Trial Wedge Method for Soil Nailed Wall Analysis. GeotechGeolEng, 2010, 28:299-309.
- Natoli, E.; Admiraal, B.; de Wit, D.; Yahyaoui, A.; de Vos, W.J. River embankment strengthening by non-metallic nails: overview on a permanent soil nailing for flood protection. Innov. Infrastruct. Solutions 2017, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calors D M, Jose Ricardo Cameiro, Lopes M D. Effect of Different Aggregates on the Mechanical Damages Suffered by Geotextiles. Materials, 2019, 12(24):4229.
- Ahmadi, M.M.; Borghei, A. Numerical investigation into the static behavior of stepped soil nail walls. Sci. Iran. 2018, 25, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang C, Tong X, Wu D, et al. A new model form echaical Clulation Of h-type an tislidepiles. TRUCTURES.2023,56.
- Sawwaf M, A. Strip footing behavior on pile and sheet pile-stabilized sand slope. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2015,131(6):705-715.
- Yang, S.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J. Study on embedded length of piles for slope reinforced with one row of piles. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 3, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| method | Scope of application | advantage | shortcoming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative analysis [62] | A slope with relatively simple geology | The landslide mode and deformation mechanism can be determined | It is often empirical and subjective |
| Quantitative analysis [63] | Slope with single influence factor and simple model | The calculation formula is simple and can solve nonlinear problems | The applied mathematical method takes into account too simple factors, which leads to errors in calculation results |
| Uncertainty analysis [64] | When there is uncertainty | More considerations and more comprehensive analysis | Most random factors cannot refine parameters, resulting in deviations in mechanical and mathematical models, and it is difficult to accurately determine the probability of each factor |
| Numerical method | Solution method | Advantage | Shortcoming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finite element method(FEM) | The stress field and displacement field of rock and soil media are solved by matrix displacement method or force method | It can be used to solve the problems of elasticity, elastoplasticity, viscoelastoplasticity and viscoplasticity | The solution ideal for large deformation, discontinuous displacement, infinite field, stress concentration and so on |
| Boundary element method(BEM) | The medium boundary is discretized into boundary elements, the boundary differential equations are transformed into linear algebraic equations, and the boundary stress and displacement solutions are solved | Only the boundaries of the study area are discretized. With less data input, it is ideal for dealing with unbounded and semi-unbounded problems | The fundamental solution of the governing differential equation must be known; It is inferior to finite element in dealing with nonlinearity, non-uniformity and simulating step by step excavation |
| Discrete element method(DEM) | Discrete regions into units; The force between elements is determined by the relation between force and displacement, and the motion of individual elements is determined by Newton’s law of motion | Considering the characteristics of heterogeneity, discontinuity and large deformation, the blocks can be translated, rotated and even separated from each other | It is only suitable for rock mass with block, stratified fracture or general cataclastic structure |
| Unbounded element method | It is widely used to solve nonlinear problems, dynamic problems, discontinuous problems, and is the extension of finite element method | Effectively solve the “boundary effect” of finite element and the shortcomings of artificial boundary determination | Generally, it should be combined with other methods, such as finite element method |
| FLAC method | Finite difference principle | The characteristics of rock and soil discontinuity and large deformation are fully considered, and the solution speed is fast | The division of computing boundary and cell grid has great arbitrariness |
| Block theory (BT) | Principles of geometry and analytical methods | The geometric features, using the principles of topology and group theory, are suitable for rock mass stability analysis | Only shear strength is considered, regardless of joint deformation and force moment action |
| Type | Applicable condition |
| Coating protection | Soft rock formation |
| Mortar or concrete shotcrete protection | Soft rock prone to weathering, lack of slope flatness, crushing heavy rock slope |
| Dry piece protection | Slopes susceptible to weathering and severe damage |
| Slurry masonry revetment | Soil slope which is severely scoured by water |
| Wall protection | Slopes with soft rock formations or excavated slopes are more broken |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




