1. Introduction
Clonazepam is a drug that belongs to the group of benzodiazepines. Its mechanism of action involves allosteric interactions between central benzodiazepine receptors and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the brain, enhancing the effects of GABA. In Spain it is indicated in most of the clinical forms of epileptic disease and seizures in infants, children and adults. In the last group it is used in status epilepticus too [
1,
2].
The INSST and the American Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the United States (NIOSH) classify it as a group 3 non-antineoplastic drug that primarily has adverse reproductive effects [
3,
4]. The FDA classified clonazepam as a category “D” pregnancy risk drug prior to 2015 [
5].
A pre-filled syringe is a ready-to-use system that decreases the hazards of drug manipulation and also saves nursing time. Nevertheless, currently the lack of stability studies of clonazepam in pre-filled syringes prevents the pharmacy services from preparing and storing it. Therefore, this study investigates the physicochemical stability of clonazepam in pre-filled syringes in several different conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation of Pre-Filled Syringes
Oral clonazepam 2.5 mg/mL solution syringes: Amber polypropylene 1 ml light protected oral syringes (Becton DickinsonTM, Madrid –Spain-) with a tip cap were pre-filled with 0.4 mL of clonazepam 2.5 mg/mL oral solution drops (Rivotril®, Roche Farma, S.A., Madrid, -Spain-). Each syringe contained 1 mg of clonazepam (
Figure 1). Two groups of syringes were stored at either controlled room temperature (25ºC) exposed to ambient light, or under refrigerated conditions (2-8ºC) protected from light.
Parenteral clonazepam 1 mg/mL solution syringes: Luer lock polypropylene syringes (Nipro Europe Group Companies, Madrid –Spain-) for parental use were pre-filled with 1 mL of clonazepam 1 mg/mL parenteral solution (Rivotril® powder 1 mg + 1 mL solvent, Roche Farma, S.A., Madrid, -Spain-), connected to a closed safety system (TexiumTM, Becton Dickinson España, S.A., Madrid, -Spain-) as shown in
Figure 2. Two groups of syringes were stored at either controlled room temperature (25ºC) protected or unprotected from light, or under refrigerated conditions (2-8ºC) protected from light.
2.2. Chemical Stability
The chemical stability of oral and parenteral clonazepam in pre-filled syringes was studied over 30 days of storage (day 0; days 1 to 4; days: 7, 9, 11, 14, 17, 21, 24, 28 and 30).
The chemical stability was studied on the selected days by withdrawing an aliquot of each syringe that was then diluted with the mobile phase to a concentration of 25 µg/mL. Three different batches of each preparation were analyzed in triplicate by HPLC within 10 minutes of dilution.
If the drug concentration remained between 90 and 110% of the initial concentration during the 30 days of storage, the preparation was considered stable [
6,
7,
8].
2.3. Chromatographic Method
Conditions: A Waters Breeze HPLC system (Waters Cromatography, S.A., Barcelona, -Spain-) and a XBridge 5 µm C18 (130 Å pore size, 4.6 x 150 mm) reversed-phase column (Waters Cromatography, S.A., Barcelona, -Spain-) were used. The chromatographic conditions were: isocratic mobile phase composed of ultrapure water/acetonitrile/methanol (40/30/30 v/v) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min, ultraviolet detector at 254 nm, 30 °C column temperature, injection volume of 20 μL and run time of 5 minutes [
9,
10]. The HPLC reagents acetonitrile (HPLC-grade) and methanol (HPLC-grade) were purchased from Panreac Química S.L.U. (Barcelona, -Spain-). The reference drug clonazepam was obtained from Roche Farma, S.A. (Madrid, -Spain-).
Validation of the method: The HPLC method was validated in terms of linearity, precision and accuracy according to the ICH guidelines [
11].
Linearity: Linearity between the peak area and the clonazepam concentration was evaluated by performing five measurements in a concentration range of 6-45 μg/mL (6, 15, 24, 30 and 45 μg/mL). A calibration curve and the corresponding linear regression analysis were performed, obtaining the results of the coefficient of determination (R
2), the slope (a) and the Y intercept (b) [
6].
Precision: Precision was verified by repeatability in intra and inter-day studies. The intra-day study consisted of analyzing five times, on the same day, the samples at 80, 100 and 120% of the target concentration (25 µg/mL). In the inter-day study the samples were analyzed five times during four different days, at 80, 100 and 120% of the target concentration. The mean, the standard deviation and the coefficient of variation were calculated, with less than 1% variation being accepted for intra-day repeatability, and less than 2% for inter-day repeatability [
6,
12].
Accuracy: Accuracy was determined by recovery studies in triplicate at 20, 25 and 30 μg/mL concentrations of clonazepam. Recovery was expressed as a percentage, and the mean value was compared with the theoretical value (100%), using Student’s t test [6, 12,13].
Limit of detection and limit of quantification: To determine the limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ) of clonazepam, the independent term “b” and the slope “a” were used in the equations LOD = 3 b/a and LOQ = 10 b/a [
6,
14].
2.4. Physical Stability
Physical stability was studied checking visual aspects, determining pH and observing crystal formation. 1 mL samples of each preparation were obtained on the selected evaluation days and were checked for visual aspects such as particle formation, crystals, turbidity, precipitation or color changes during storage. The pH was measured with a calibrated SevenMultiTM pH meter (Mettler Toledo, Cornellà de Llobregat, -Spain-). A visual inspection booth with both a black/white background [
15] and bright-field, and a SediMAX2TM phase contrast microscope (77 Elektronika, Budapest, -Hungary-), were used to determine the presence of particles and crystals.
3. Results
3.1. Validation of the Analytical Method
The method demonstrated excellent linearity, with a R
2 greater than 0.9996. The regression equation was calculated as y = 127436x + 8625. The results were highly satisfactory regarding the intra-day and inter-day repeatability of the three clonazepam quality control solutions. Accuracy ranged from 98.34% to 101.62%, while precision, expressed as relative standard deviation (RSD%), fell within the range of 0.094% to 0.682% for intra-day precision and 0.232% to 0.713% for inter-day precision. These RSD% values comfortably meet the ICH (International Conference on Harmonisation) standards, which stipulate a maximum RSD of 1% and 2% respectively. Likewise, the accuracy was between 98% and 102%. The LOD and the LOQ were calculated as 0.20 µg/mL and 0.68 µ/mL respectively (
Table 1 and
Table 2).
3.2. Stability Study
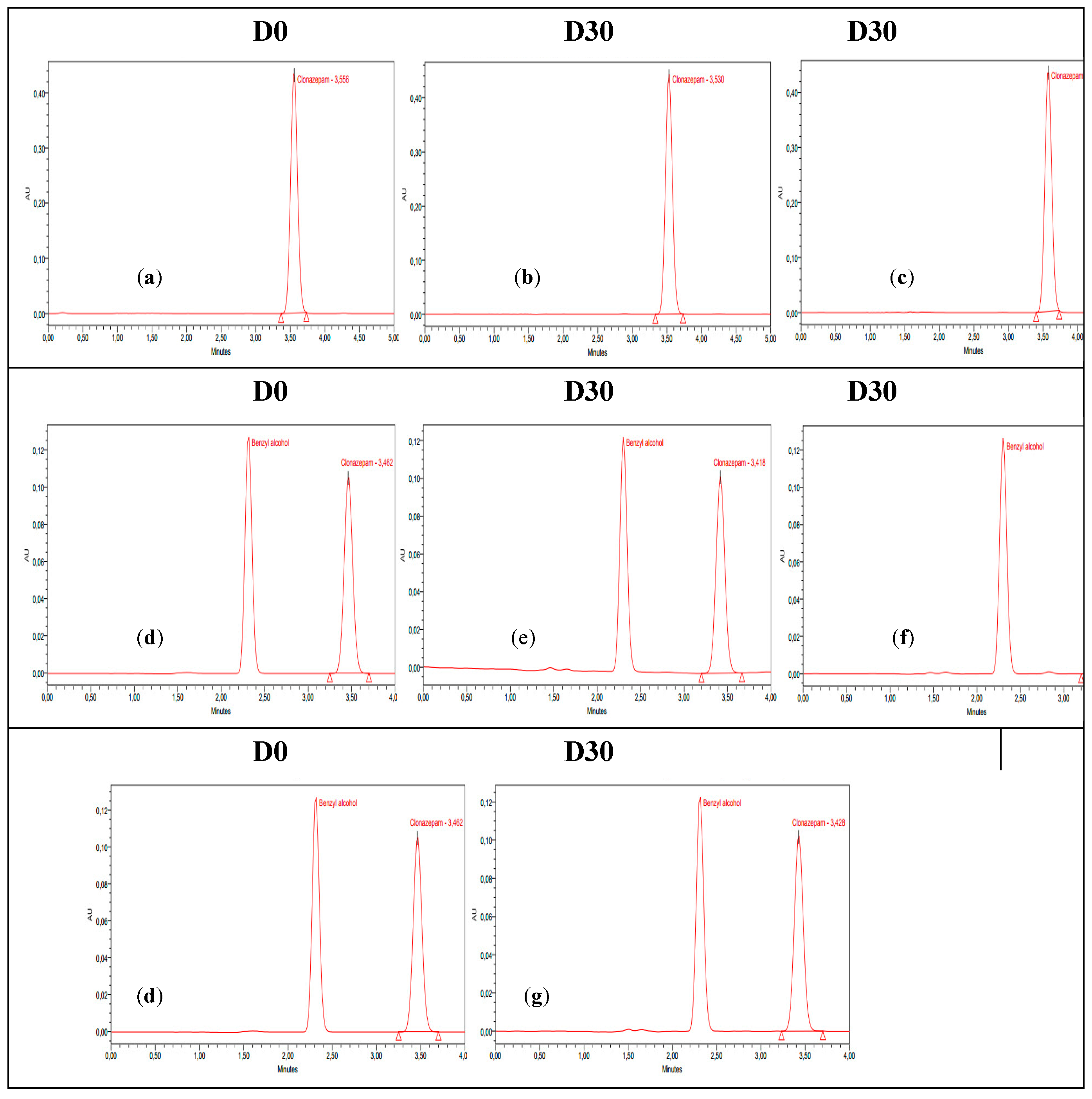
The stability study was carried out by measuring the concentration of clonazepam in pre-filled syringes on each day of the analysis, as described previously. The mean concentrations were calculated and expressed as recovery percentage with respect to the measurement on the first day (D0 = 100%). The chromatograms of D0 and D30 (day 30 of the study) for each preparation under the specified storage conditions are presented in
Figure 1. The clonazepam 1 mg/mL parenteral solution contains benzyl alcohol as a preservative agent. This compound exhibits absorption at 254 nm, which accounts for the appearance of a corresponding peak in the chromatograms.
Figure 1.
Chromatograms of clonazepam. Oral clonazepam 2.5 mg/mL solution in pre-filled syringes: (a) D0; (b) D30 room temperature; (c) refrigeration condition protected from de light. Parenteral clonazepam 1 mg/mL solution in pre-filled syringes: (d) D0; (e) room temperature; (f) room temperature protected from light; (g) refrigeration condition protected from de light. .
Figure 1.
Chromatograms of clonazepam. Oral clonazepam 2.5 mg/mL solution in pre-filled syringes: (a) D0; (b) D30 room temperature; (c) refrigeration condition protected from de light. Parenteral clonazepam 1 mg/mL solution in pre-filled syringes: (d) D0; (e) room temperature; (f) room temperature protected from light; (g) refrigeration condition protected from de light. .
The results show that the concentrations remained stable for 30 days in all of the storage conditions used for the oral clonazepam 2.5 mg/mL solution syringes (
Table 3) and the parenteral clonazepam 1 mg/mL solution syringes (
Table 4).
No significant variation was observed with regards to visual aspects (color changes, turbidity) and pH throughout the study (
Table 3 and
Table 4).
4. Discussion
Since the publication of the document on hazardous drugs and preventive measures for their preparation and administration, Hospital Pharmacy Services have been involved in implementing measures to adapt practices to the recommendations given by the INSST and European Agency for Safety and Health at Work in its guidance document for the safe management of hazardous medicinal products at work [
16]. Among the adaptation options is the possibility of direct delivery of the drug from the Pharmacy Service in a standardized dose and container, ready for administration. If stability studies of the drug in standardized containers are available, it is possible to prepare and store the drug in the Pharmacy Service, depending on consumption, to avoid the need for shift or daily preparation.
There are currently only two studies published that evaluate the stability of oral clonazepam solutions. One of them assessed the stability of clonazepam 0.2 mg/mL oral solution stored under refrigeration (2-8ºC) and at room temperature, using clonazepam in powder form, concluding that the solution was stable for 90 days. The other analyzed the stability of clonazepam 0.1 mg/mL oral solution prepared from commercial tablets, both stored under refrigeration (2-8ºC) and at room temperature protected from light, observing that the solution remained stable for 60 days under both storage conditions. Unlike the previous cases, this study has evaluated the stability of commercialized clonazepam drugs in the presentations of 2.5 mg/mL oral drops and 1 mg/mL injectable solution, repackaged in pre-filled polypropylene syringes. Both concentrations are significantly higher than the concentrations mentioned in the studies beforehand, a condition that does not seem to affect the stability observed in the current work.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, clonazepam 2.5 mg/mL oral solution in light-protected pre-filled polypropylene syringes, both at room temperature and under refrigeration (2-8ºC), and clonazepam 1 mg/mL parenteral solution in pre-filled polypropylene syringes at room temperature with and without light protection, and under refrigeration (2-8ºC) with light protection, are observed to be physically and chemically stable for at least 30 days. This has allowed for preparation of ready-to-use stock of this hazardous drug, minimizing drug manipulation by nursing staff and therefore reducing the risk of occupational exposure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.R.R.; methodology: J.C.R.R., I.T.H. and L.B.G.; validation, J.C.R.R., J.M.A.H. and A.C.V.; formal analysis, J.C.R.R., I.T.H. and L.B.G.; investigation: I.T.H. and L.B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.R.R., I.T.H. and L.B.G.; writing—review and editing, J.C.R.R., J.M.A.H. and A.C.V.; supervision, J.C.R.R., J.M.A.H. and A.C.V.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GABA |
Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| HPLC |
High-performance liquid chromatography |
| ICH |
International Conference on Harmonisation |
| INSST |
Spanish National Institute for Safety and Health at Work |
| LOD |
Limit of detection |
| LOQ |
Limit of quantification |
| NIOSH |
Health of the United States |
| R2 |
Correlation coefficient |
| RSD% |
Relative standard deviation |
| SD |
Standard deviation |
| SEFH |
Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacy |
References
- Spanish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency. Datasheet of Rivotril 1 mg/mL concentrate and solvent for injectable solution. [Internet]. Datasheet of Rivotril 1 mg/mL concentrate and solvent for injectable solution [cited 2024 Aug 12];Available from: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/ft/52332/FT_52332.
- Spanish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency. Datasheet of Rivotril 2,5 mg/mlL oral drops solution [Internet]. Datasheet of Rivotril 2,5 mg/mlL oral drops solution [cited 2024 Aug 12];Available from: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/ft/52333/FT_52333.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Hazardous drugs. Preventive measures for their preparation and administration [Internet]. Medicam. Peligr. Medidas Prev. Para Su Prep. Adm.2016 [cited 2024 Aug 12];Available from: https://www.insst.es/documentacion/catalogo-de-publicaciones/medicamentos-peligrosos.
- Connor TH, MacKenzie, BA, DeBord DG, Trout DB, O’Callaghan JP, Ovesen JL, Whittaker C. Cincinnati, OH, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. NIOSH [2020]. NIOSH list of hazardous drugs in healthcare settings 2020 [Internet]. [cited 2024 Aug 5];Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docket/review/docket233c/pdfs/DRAFT-NIOSH-Hazardous-Drugs-List-2020.
- Lal, R. Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation: Improved Benefit-Risk Information [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2024 Aug 27];Available from: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/%22Drugs-in-Pregnancy-and-Lactation--Improved-Benefit-Risk-Information%22-January-22--2015-Issue.
- Asociación Española de Farmacéuticos de la Industria (AEFI). Validación de métodos analíticos. Monografía. Comisión de normas de buena fabricación y control de calidad. Barcelona: Edicion Hewlett Packard; 2001.
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare. European Pharmacopoeia. 11th ed. Estrasburgo: European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare; 2022.
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary (USP-NF). 2022nd ed. Rockville: US Pharmacopeia Convention, Inc; 2022.
- Allen LV, Erickson MA. Stability of acetazolamide, allopurinol, azathioprine, clonazepam, and flucytosine in extemporaneously compounded oral liquids. Am J Health-Syst Pharm AJHP Off J Am Soc Health-Syst Pharm 1996, 53, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Polonini HC, Loures S, Lima LC, Ferreira AO, Brandão MAF. Stability of Atenolol, Clonazepam, Dexamethasone, Diclofenac Sodium, Diltiazem, Enalapril Maleate, Ketoprofen, Lamotrigine, Penicillamine-D, and Thiamine in SyrSpend SF PH4 Oral Suspensions. Int J Pharm Compd 2016, 20, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, J. International Conference On Harmonisation Of Technical Requirements For Registration Of Pharmaceuticals For Human Use [Internet]. In: Brouder A, Tietje C, editors. Handbook of Transnational Economic Governance Regimes. Brill; 2009 [cited 2018 Jun 6]. page 1041–54. Available from: http://booksandjournals.brillonline.com/content/books/10.1163/ej.9789004163300.i-1081.
- Sagar Baliram, PM. A Validated Stability–Indicating HPLC Method estimation of Clonazepam In the bulk drug and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. Pharm Anal Acta [Internet] 2015 [cited 2018 ];06(02). Available from: https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/a-validated-stabilityindicating-hplc-method-estimation-of-clonazepam-in-the-bulk-drug-and-pharmaceutical-dosage-form-2153-2435.1000332.php? 20 May 4032. [Google Scholar]
- Statistical validation: Quantitative determination (General Explanations). Basle: Hoffman F. La Roche, 1987:1-9.
- N. Miller James, C. N. Miller James, C. Miller Jane. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry. 5a. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited; 2005.
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios. Contaminación por partículas: particulas visibles. Real Farmacopea Española [Internet]. [cited 2024 Sep 10];Available from: https://extranet.boe.es/farmacopea/doc.php? 2092.
- European Agency for Safety and Health at Work. Guidance for the safe management of hazardous medicinal products at work | Safety and health at work EU-OSHA [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2024 Aug 28];Available from: https://osha.europa.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).