Submitted:
01 July 2025
Posted:
04 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction

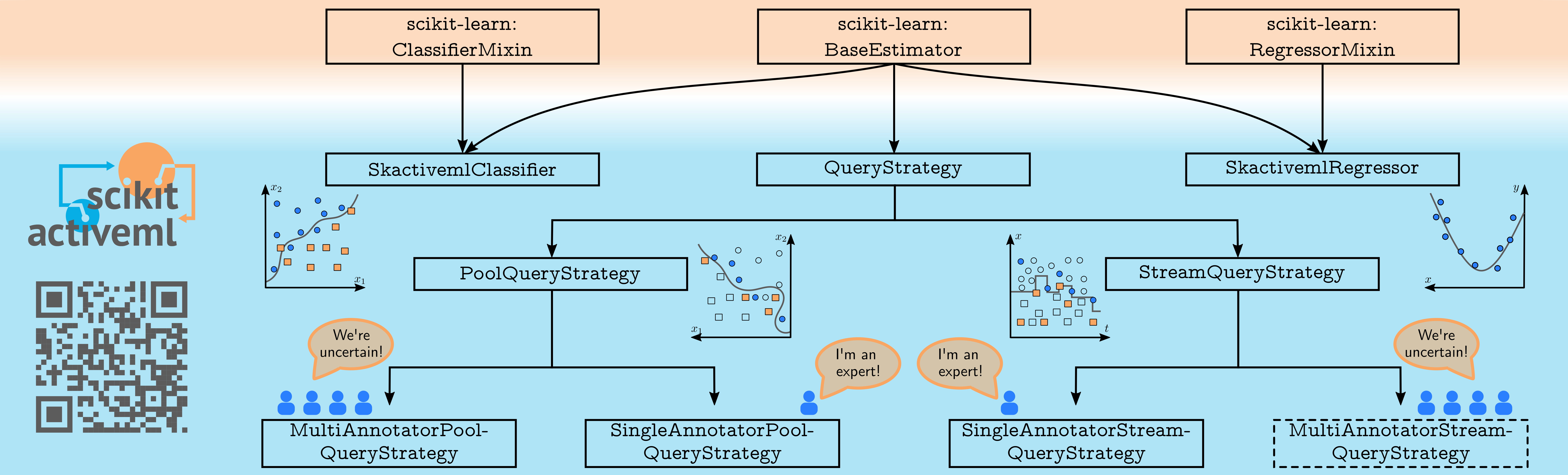
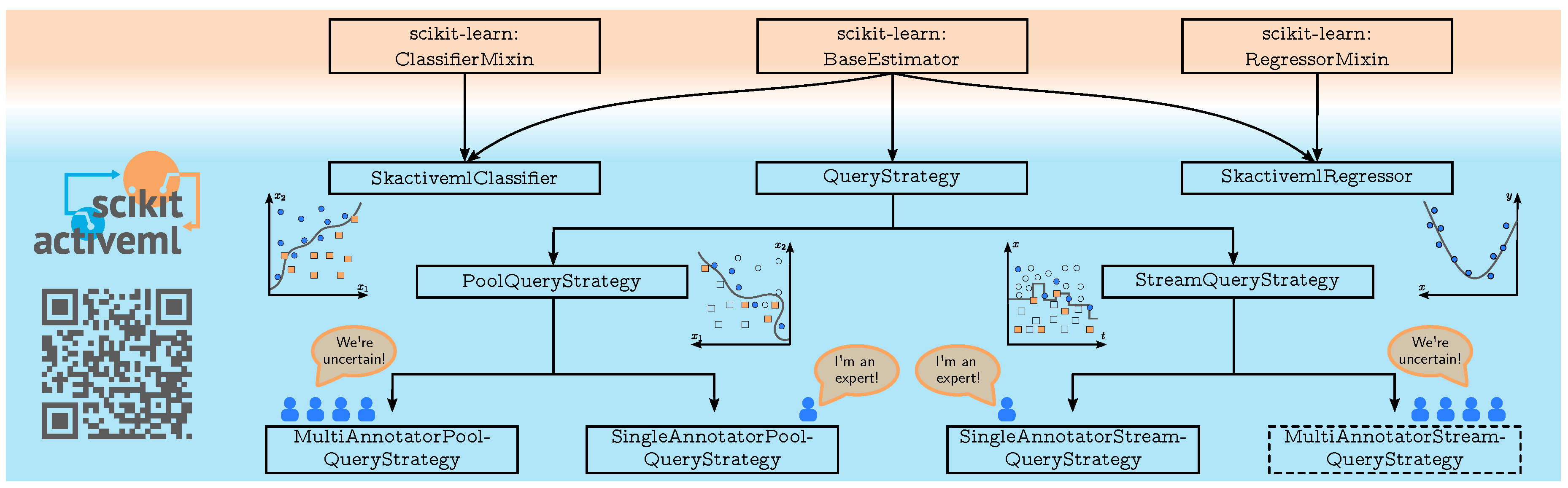
2. Structural Overview
| Algorithm 1: Code snippet of a pool-based active learning cycle for classification. |
| 1 import numpy as np |
| 2 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression |
| 3 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
| 4 from skactiveml.pool import Badge |
| 5 from skactiveml.classifier import SklearnClassifier |
| 6 |
| 7 # Generate data set with 10 initially labeled samples. |
| 8 X, y_true = make_blobs(n_samples=500, centers=8) |
| 9 y = np.full_like(y_true, fill_value=-1) |
| 10 rand_ids = np.random.choice(len(X), size=10) |
| 11 y[rand_ids] = y_true[rand_ids] |
| 12 |
| 13 # Create classifier and query strategy. |
| 14 clf = SklearnClassifier( |
| 15 LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000), |
| 16 classes=np.unique(y_true), |
| 17 missing_label=-1, |
| 18 ) |
| 19 qs = Badge(missing_label=-1) |
| 20 |
| 21 # Execute active learning cycle. |
| 22 n_cycles = 20 |
| 23 for c in range(n_cycles): |
| 24 q_ids = qs.query(X=X, y=y, clf=clf, batch_size=3) |
| 25 y[q_ids] = y_true[q_ids] |
| 26 |
| 27 # Fit final classifier. |
| 28 clf.fit(X, y) |
3. Related Work
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Appendix A. Beyond Pool-Based Active Learning for Classification
| Algorithm 2: Code snippet of a pool-based active learning cycle for regression. |
| 1 import numpy as np |
| 2 from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessRegressor |
| 3 from skactiveml.pool import GreedySamplingTarget |
| 4 from skactiveml.regressor import SklearnRegressor |
| 5 |
| 6 # Generate data set. |
| 7 random_state = np.random.RandomState(0) |
| 8 X = random_state.uniform(size=(200, 1), low=-1, high=1) |
| 9 y_true = np.sin(X.ravel()) + random_state.randn(len(X)) * 0.1 |
| 10 y = np.full_like(y_true, fill_value=np.nan) |
| 11 |
| 12 # Use 10 samples as initial training data. |
| 13 y[:10] = y_true[:10] |
| 14 |
| 15 # Create regressor and query strategy. |
| 16 gp = GaussianProcessRegressor(random_state=0) |
| 17 reg = SklearnRegressor(gp, random_state=0, missing_label=np.nan) |
| 18 qs = GreedySamplingTarget(method="GSi", random_state=0) |
| 19 |
| 20 # Execute active learning cycle. |
| 21 n_cycles = 5 |
| 22 for c in range(n_cycles): |
| 23 reg.fit(X, y) |
| 24 q_ids, u_scores = qs.query(X=X, y=y, reg=reg, fit_reg=False, batch_size=10, return_utilities=True) |
| 25 y[q_ids] = y_true[q_ids] |
| 26 |
| 27 # Fit final regressor. |
| 28 reg.fit(X, y) |
| Algorithm 3: Code snippet of a pool-based active learning cycle with noisy annotators. |
| 1 import numpy as np |
| 2 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
| 3 from skactiveml.pool import TypiClust |
| 4 from skactiveml.pool.multiannotator import SingleAnnotatorWrapper |
| 5 from skactiveml.classifier.multiannotator import AnnotatorLogisticRegression |
| 6 |
| 7 # Generate data set with four annotators, of which the last one is always wrong. |
| 8 X, y_true = make_blobs(n_samples=200, centers=5, random_state=0) |
| 9 classes = np.unique(y_true) |
| 10 y_noisy = np.column_stack((y_true, y_true, y_true, (y_true + 1) % 5)) |
| 11 |
| 12 # Perform active learning with zero initial labels. |
| 13 y = np.full(shape=y_noisy.shape, fill_value=-1) |
| 14 |
| 15 # Create classifier and query strategy. |
| 16 clf = AnnotatorLogisticRegression(missing_label=-1, classes=classes, random_state=0) |
| 17 qs = TypiClust(missing_label=-1, random_state=0) |
| 18 ma_qs = SingleAnnotatorWrapper(qs, random_state=0, missing_label=-1) |
| 19 |
| 20 # Function to be able to index via an array of indices. |
| 21 idx = lambda A: (A[:, 0], A[:, 1]) |
| 22 |
| 23 # Execute active learning cycles. |
| 24 n_cycles = 50 |
| 25 for c in range(n_cycles): |
| 26 # Fit multi-annotator classifier and compute annotators’ accuracies per sample. |
| 27 clf.fit(X, y) |
| 28 A_perf = clf.predict_annotator_perf(X) |
| 29 |
| 30 # Select samples and acquire labels. |
| 31 q_ids = ma_qs.query(X=X, y=y, batch_size=3, A_perf=A_perf, n_annotators_per_sample=1) |
| 32 y[idx(q_ids)] = y_noisy[idx(q_ids)] |
| 33 |
| 34 # Fit final multi-annotator classifier. |
| 35 clf.fit(X, y) |
| Algorithm 4: Code snippet of a stream-based active learning cycle for classification. |
| 1 import numpy as np |
| 2 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
| 3 from skactiveml.classifier import ParzenWindowClassifier |
| 4 from skactiveml.stream import Split |
| 5 from skactiveml.utils import MISSING_LABEL |
| 6 |
| 7 # Generate data set. |
| 8 X, y_true = make_blobs(n_samples=200, centers=4, random_state=0) |
| 9 |
| 10 # Initializing the training data as an empty array. |
| 11 X_train, y_train = [], [] |
| 12 |
| 13 # Create classifier and query strategy. |
| 14 clf = ParzenWindowClassifier(random_state=0, classes=np.unique(y_true)) |
| 15 qs = Split(random_state=0) |
| 16 |
| 17 # Execute active learning cycle. |
| 18 for x_t, y_t in zip(X, y_true): |
| 19 X_cand = x_t.reshape([1, -1]) |
| 20 y_cand = y_t |
| 21 clf.fit(X_train, y_train) |
| 22 queried_indices = qs.query(candidates=X_cand, clf=clf) |
| 23 qs.update(candidates=X_cand, queried_indices=queried_indices) |
| 24 X_train.append(x_t) |
| 25 y_train.append(y_cand if len(queried_indices) > 0 else MISSING_LABEL) |
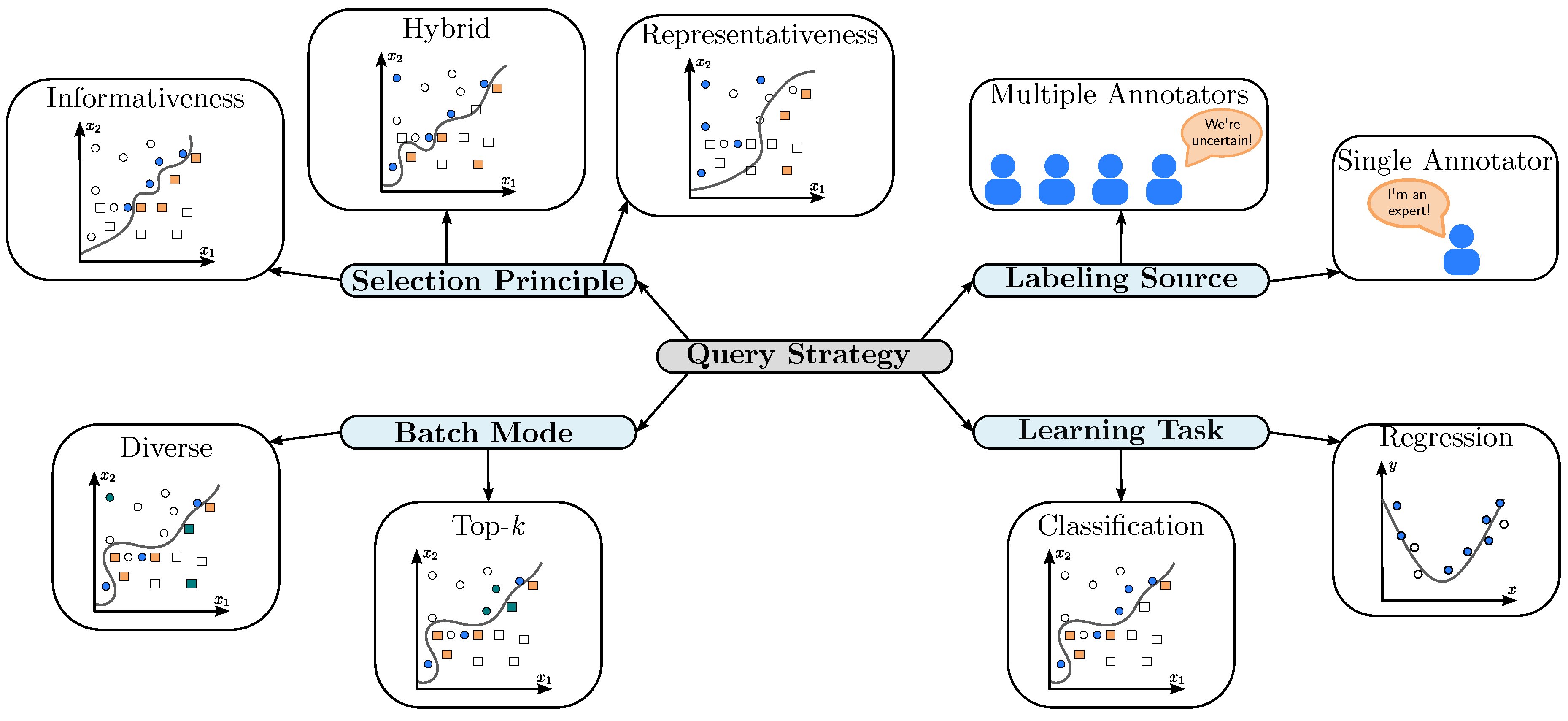
Appendix B. Overview of Query Strategies
| Name | Classi- fication |
Regres- sion |
Multi- annotator |
Diverse Batches |
Variants | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baselines and Wrappers | ||||||
| Random Sampling | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | N/A |
| Subsampling Wrapper | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | N/A | 1 | N/A |
| Parallel Selection Wrapper | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | N/A | 1 | N/A |
| Single Annotator Wrapper | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | N/A | 1 | N/A |
| Informativeness | ||||||
| Uncertainty Sampling (US) | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 3 |
Lewis and Gale (1994) Scheffer et al. (2001) Settles (2009) |
| Query by Committee (QbC) | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 4 |
Seung et al. (1992) Engelson and Dagan (1996) McCallum and Nigamy (1998) Burbidge et al. (2007) Beluch et al. (2018) |
| Expected Model Variance Reduction |
✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Cohn et al. (1996) |
| Expected Error Reduction (EER) |
✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 2 | Roy and McCallum (2001) |
| Value of Information (VOI) | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 3 |
Margineantu (2005) Kapoor et al. (2007) Joshi et al. (2009) |
| Interval Estimation Threshold (IEThresh) |
✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | 1 | Donmez et al. (2009) |
| Bayesian Active Learning by Disagreement (BALD) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Houlsby et al. (2011) |
| Expected Model Change (EMC) |
✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Cai et al. (2013) |
| Active Learning with Cost Embedding (ALCE) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Huang and Lin (2016) |
| Uncertainty Sampling via Maximizing Average Precision (USAP) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Wang et al. (2018) |
| Expected Model Output Change (EMOC) |
✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | äding et al. (2018) |
| Cost-sensitive Uncertainty Sampling (CsUS) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Chen and Lin (2013) |
| Batch Bayesian Active Learning by Disagreement (BatchBALD) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Kirsch et al. (2019) |
| Epistemic Uncertainty Sampling (EpisUS) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Nguyen et al. (2019) |
| Regression-based Kullback- Leibler Divergence Maximization |
✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Elreedy et al. (2019) |
| Contrastive Active Learning (CAL) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Margatina et al. (2021) |
| Continued on the next page. | ||||||
| Name | Classi- fication |
Regres- sion |
Multi- annotator |
Diverse Batches |
Variants | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Representativeness | ||||||
| Core Set | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Sener and Savarese (2018) |
| Discriminative Active Learning (DAL) |
✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Gissin and Shalev-Shwartz (2019) |
| Greedy Sampling (GS) | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 3 | Wu et al. (2019) |
| Typicality Clustering (TypiClust) | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Hacohen et al. (2022) |
| Probability Coverage (ProbCover) | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Yehuda et al. (2022) |
| Regression Tree Active Learning (RT-AL) |
✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 3 | Jose et al. (2023) |
| Hybrid | ||||||
| Density-weighted Uncertainty Sampling (DwUS) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Donmez et al. (2007) |
| Dual Strategy for Active Learning (DUAL) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Donmez et al. (2007) |
| Querying Informative and Representative Examples (QUIRE) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 |
Huang et al. (2010) Huang et al. (2014) |
| Density-Diversity-Distribution -Distance Sampling (4DS) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Reitmaier and Sick (2013) |
| Multi-class Probabilistic Active Learning (McPAL) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Kottke et al. (2016) |
| Batch Active Learning by Diverse Gradient Embeddings (BADGE) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Ash et al. (2020) |
| Clustering Uncertainty-weighted Embeddings (CLUE) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Prabhu et al. (2021) |
| Fast Active Learning by Contrastive Uncertainty (FALCUN) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Gilhuber et al. (2024) |
| Dropout Query (DropQuery) | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 1 | Gupte et al. (2024) |
| Name | Classi- fication |
Regres- sion |
Multi- annotator |
Diverse Batches |
Variants | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baselines and Wrappers | ||||||
| Periodic Sampling | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | N/A |
| Stream Random Sampling | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 2 | N/A |
| Informativeness | ||||||
| Fixed-Uncertainty | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Žliobaitė et al. (2014) |
| Randomized-Variable-Uncertainty | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Žliobaitė et al. (2014) |
| Variable-Uncertainty | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Žliobaitė et al. (2014) |
| Hybrid | ||||||
| Density-Based Active Learning for Data Streams (DBALStream) |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Ienco et al. (2014) |
| Split | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Žliobaitė et al. (2014) |
| Probabilistic Active Learning (PAL) in Datastreams |
✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 1 | Kottke et al. (2015) |
| Cognitive Dual-Query Strategy (CoqDQS) | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 5 | Liu et al. (2023) |
Appendix C. Comparison of Active Learning Projects
References
- Settles, B. Active Learning Literature Survey. Computer Sciences Technical Report 1648, University of Wisconsin–Madison, 2009.
- Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, R.; Ding, W.; Okumura, M. A Survey on Deep Active Learning: Recent Advances and New Frontiers. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, pp. 5879–5899.
- Cacciarelli, D.; Kulahci, M. Active learning for data streams: a survey. Mach. Learn. 2024, 113, 185–239.
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830.
- Herde, M.; Huseljic, D.; Sick, B.; Calma, A. A survey on cost types, interaction schemes, and annotator performance models in selection algorithms for active learning in classification. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 166970–166989.
- Ash, J.T.; Zhang, C.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Langford, J.; Agarwal, A. Deep Batch Active Learning by Diverse, Uncertain Gradient Lower Bounds. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Learn. Represent., 2020.
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2019, pp. 8026–8037.
- In Tietz, M. ; Fan, T.J.; Nouri, D.; Bossan, B. skorch Developers. skorch: A scikit-learn compatible neural network library that wraps PyTorch. Tietz, M.; Fan, T.J.; Nouri, D.; Bossan, B.; skorch Developers. skorch: A scikit-learn compatible neural network library that wraps PyTorch, 2017.
- Oquab, M.; Darcet, T.; Moutakanni, T.; Vo, H.V.; Szafraniec, M.; Khalidov, V.; Fernandez, P.; Haziza, D.; Massa, F.; El-Nouby, A.; et al. DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023.
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the Conf. North Am. Chapter Assoc. Comput. Linguist.: Hum. Lang. Technol., 2019, pp. 4171–4186.
- Baevski, A.; Zhou, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Auli, M. wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations. In Proceedings of the Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2020, pp. 12449–12460.
- Hacohen, G.; Dekel, A.; Weinshall, D. Active Learning on a Budget: Opposite Strategies Suit High and Low Budgets. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Mach. Learn., 2022, pp. 8175–8195.
- Yehuda, O.; Dekel, A.; Hacohen, G.; Weinshall, D. Active Learning Through a Covering Lens. In Proceedings of the Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2022, pp. 22354–22367.
- In Huseljic, D. ; Hahn, P.; Herde, M.; Rauch, L. Sick, B. Fast Fishing: Approximating Bait for Efficient and Scalable Deep Active Image Classification. In Proceedings of the Jt. Eur. Conf. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Discov. Databases., pp. 280–296. Huseljic, D.; Hahn, P.; Herde, M.; Rauch, L.; Sick, B. Fast Fishing: Approximating Bait for Efficient and Scalable Deep Active Image Classification. In Proceedings of the Jt. Eur. Conf. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Discov. Databases., 2024, pp. 280–296.
- Gupte, S.R.; Aklilu, J.; Nirschl, J.J.; Yeung-Levy, S. Revisiting Active Learning in the Era of Vision Foundation Models. Trans. Mach. Learn. Res. 2024.
- Huang, K.H. DeepAL: Deep Active Learning in Python. arXiv:2111.15258 2021.
- Yang, Y.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Chung, Y.A.; Wu, T.E.; Chen, S.A.; Lin, H.T. libact: Pool-based Active Learning in Python. arXiv:1710.00379 2017.
- Tang, Y.P.; Li, G.X.; Huang, S.J. ALiPy: Active Learning in Python. arXiv:1901.03802 2019.
- Danka, T.; Horvath, P. modAL: A modular active learning framework for Python. arXiv:1805.00979 2018.
- Tsvigun, A.; Sanochkin, L.; Larionov, D.; Kuzmin, G.; Vazhentsev, A.; Lazichny, I.; Khromov, N.; Kireev, D.; Rubashevskii, A.; Shahmatova, O.; et al. ALToolbox: A Set of Tools for Active Learning Annotation of Natural Language Texts. In Proceedings of the Conf. Empir. Methods Nat. Lang. Process.: Syst. Demonstr., 2022, pp. 406–434.
- Atighehchian, P.; Branchaud-Charron, F.; Lacoste, A. Bayesian active learning for production, a systematic study and a reusable library. arXiv:2006.09916 2020.
- Scherer, P.; Pouplin, A.; Del Vecchio, A.; Bolton, O.; Soman, J.; Taylor-King, J.P.; Edwards, L.; Gaudelet, T.; et al. PyRelationAL: a python library for active learning research and development. arXiv:2205.11117 2022.
- Schröder, C.; Müller, L.; Niekler, A.; Potthast, M. Small-Text: Active Learning for Text Classification in Python. In Proceedings of the Conf. Eur. Chapter Assoc. Comput. Linguist.: Syst. Demonstr., 2023, pp. 84–95.
- Wu, J.; Sheng, V.S.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Dadakova, T.; Swisher, C.L.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, P. Multi-Label Active Learning Algorithms for Image Classification: Overview and Future Promise. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 53, 1–35.
- Li, C.Y.; Rakitsch, B.; Zimmer, C. Safe Active Learning for Multi-Output Gaussian Processes. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Stat., 2022, pp. 4512–4551.
- Vlachos, A. A stopping criterion for active learning. Comput. Speech Lang. 2008, 22, 295–312.
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, A. Active learning query strategies for classification, regression, and clustering: A survey. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2020, 35, 913–945.
- Wu, D.; Lin, C.T.; Huang, J. Active Learning for Regression using Greedy Sampling. Inf. Sci. 2019, 474, 90–105.
- Donmez, P.; Carbonell, J.G.; Schneider, J. Efficiently Learning the Accuracy of Labeling Sources for Selective Sampling. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Min., 2009, pp. 259–268.
- Raykar, V.C.; Yu, S.; Zhao, L.H.; Valadez, G.H.; Florin, C.; Bogoni, L.; Moy, L. Learning from Crowds. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1297–1322.
- Herde, M.; Lührs, L.; Huseljic, D.; Sick, B. Annot-Mix: Learning with Noisy Class Labels from Multiple Annotators via a Mixup Extension. In Proceedings of the Eur. Conf. Artif. Intell., 2024, pp. 2910–2918.
- Žliobaitė, I.; Bifet, A.; Pfahringer, B.; Holmes, G. Active Learning With Drifting Streaming Data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 25, 27–39.
- Lewis, D.D.; Gale, W.A. A Sequential Algorithm for Training Text Classifiers. In Proceedings of the Annu. Int. ACM-SIGIR Conf. Res. Dev. Inf. Retr., 1994, pp. 3–12.
- Scheffer, T.; Decomain, C.; Wrobel, S. Active Hidden Markov Models for Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the Int. Symp. Intell. Data Anal., 2001, pp. 309–318.
- Seung, H.S.; Opper, M.; Sompolinsky, H. Query by Committee. In Proceedings of the Annu. Workshop Comput. Learn. Theory., 1992, pp. 287–294.
- Engelson, S.P.; Dagan, I. Minimizing Manual Annotation Cost in Supervised Training from Corpora. In Proceedings of the Annu. Meet. Assoc. Comput. Linguist., 1996, pp. 319–326.
- McCallum, A.K.; Nigamy, K. Employing EM and Pool-Based Active Learning for Text Classification. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Mach. Learn., 1998, pp. 359–367.
- Burbidge, R.; Rowland, J.J.; King, R.D. Active Learning for Regression Based on Query by Committee. In Proceedings of the Intell. Data Eng. Autom. Learn., 2007, pp. 209–218.
- Beluch, W.H.; Genewein, T.; Nürnberger, A.; Köhler, J.M. The Power of Ensembles for Active Learning in Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2018, pp. 9368–9377.
- Cohn, D.A.; Ghahramani, Z.; Jordan, M.I. Active Learning with Statistical Models. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1996, 4, 129–145.
- Roy, N.; McCallum, A. Toward Optimal Active Learning through Monte Carlo Estimation of Error Reduction. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Mach. Learn., 2001, pp. 441–448.
- Margineantu, D.D. Active Cost-Sensitive Learning. In Proceedings of the Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell., 2005, p. 1622–1623.
- In Kapoor, A. ; Horvitz, E. Basu, S. Selective Supervision: Guiding Supervised Learning with Decision-Theoretic Active Learning. In Proceedings of the Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell., pp. 877–882. Kapoor, A.; Horvitz, E.; Basu, S. Selective Supervision: Guiding Supervised Learning with Decision-Theoretic Active Learning. In Proceedings of the Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell., 2007, pp. 877–882.
- Joshi, A.J.; Porikli, F.; Papanikolopoulos, N. Multi-class Active Learning for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2009, p. 2372–2379.
- Houlsby, N.; Huszár, F.; Ghahramani, Z.; Lengyel, M. Bayesian Active Learning for Classification and Preference Learning. arXiv:1112.5745 2011.
- Cai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Maximizing Expected Model Change for Active Learning in Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. Data Min., 2013, pp. 51–60.
- Huang, K.H.; Lin, H.T. A Novel Uncertainty Sampling Algorithm for Cost-Sensitive Multiclass Active Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. Data Min., 2016, pp. 925–930.
- Wang, H.; Chang, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Y.D. Uncertainty Sampling for Action Recognition via Maximizing Expected Average Precision. In Proceedings of the Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell., 2018, pp. 964–970.
- Käding, C.; Rodner, E.; Freytag, A.; Mothes, O.; Barz, B.; Denzler, J. Active Learning for Regression Tasks with Expected Model Output Changes. In Proceedings of the Br. Mach. Vis. Conf., 2018.
- Chen, P.L.; Lin, H.T. Active Learning for Multiclass Cost-Sensitive Classification Using Probabilistic Models. In Proceedings of the Conf. Technol. Appl. Artif. Intell., 2013, pp. 13–18.
- Kirsch, A.; Van Amersfoort, J.; Gal, Y. BatchBALD: Efficient and Diverse Batch Acquisition for Deep Bayesian Active Learning. In Proceedings of the Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2019, pp. 7026–7037.
- Nguyen, V.L.; Destercke, S.; Hüllermeier, E. Epistemic Uncertainty Sampling. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Discov. Sci., 2019, pp. 72–86.
- Elreedy, D.; F. Atiya, A.; I. Shaheen, S. A Novel Active Learning Regression Framework for Balancing the Exploration-Exploitation Trade-Off. Entropy 2019, 21, 651.
- Margatina, K.; Vernikos, G.; Barrault, L.; Aletras, N. Active Learning by Acquiring Contrastive Examples. In Proceedings of the Conf. Empir. Methods Nat. Lang. Process., 2021, pp. 650–663.
- In Sener, O. ; Savarese, S. Active Learning for Convolutional Neural Networks: A Core-Set Approach. Sener, O.; Savarese, S. Active Learning for Convolutional Neural Networks: A Core-Set Approach. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Learn. Represent., 2018.
- Gissin, D.; Shalev-Shwartz, S. Discriminative Active Learning. arXiv:1907.06347 2019.
- Jose, A.; de Mendonça, J.P.A.; Devijver, E.; Jakse, N.; Monbet, V.; Poloni, R. Regression Tree-based Active Learning. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2023, pp. 420–460.
- Donmez, P.; Carbonell, J.G.; Bennett, P.N. Dual Strategy Active Learning. In Proceedings of the Eur. Conf. Mach. Learn., 2007, pp. 116–127.
- Huang, S.J.; Jin, R.; Zhou, Z.H. Active Learning by Querying Informative and Representative Examples. In Proceedings of the Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2010.
- Huang, S.J.; Jin, R.; Zhou, Z.H. Active Learning by Querying Informative and Representative Examples. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1936–1949.
- Reitmaier, T.; Sick, B. Let us know your decision: Pool-based active training of a generative classifier with the selection strategy 4DS. Inf. Sci. 2013, 230, 106–131.
- Kottke, D.; Krempl, G.; Lang, D.; Teschner, J.; Spiliopoulou, M. Multi-class Probabilistic Active Learning. In Proceedings of the Eur. Conf. Artif. Intell., 2016, pp. 586–594.
- Prabhu, V.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Saenko, K.; Hoffman, J. Active Domain Adaptation via Clustering Uncertainty-weighted Embeddings. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., 2021, pp. 8505–8514.
- In Gilhuber, S. ; Beer, A.; Ma, Y. Seidl, T. FALCUN: A Simple and Efficient Deep Active Learning Strategy. In Proceedings of the Jt. Eur. Conf. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Discov. Databases, pp. 421–439. Gilhuber, S.; Beer, A.; Ma, Y.; Seidl, T. FALCUN: A Simple and Efficient Deep Active Learning Strategy. In Proceedings of the Jt. Eur. Conf. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Discov. Databases, 2024, pp. 421–439.
- Ienco, D.; Žliobaitė, I.; Pfahringer, B. High density-focused uncertainty sampling for active learning over evolving stream data. In Proceedings of the Int. Workshop Big Data Streams Heterog. Source Min. Algorithms Syst. Program. Models Appl., 2014, pp. 133–148.
- Kottke, D.; Krempl, G.; Spiliopoulou, M. Probabilistic Active Learning in Datastreams. In Proceedings of the Adv. Intell. Data Anal., 2015, pp. 145–157.
- Liu, S.; Xue, S.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, J. Online Active Learning for Drifting Data Streams. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 186–200.
- Falcon, W.; Team, T.P.L. PyTorch Lightning, 2023. Accessed 06-05-2024. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the Conf. Empir. Methods Nat. Lang. Process.: Syst. Demonstr., 2020, pp. 38–45.
- Montiel, J.; Halford, M.; Mastelini, S.M.; Bolmier, G.; Sourty, R.; Vaysse, R.; Zouitine, A.; Gomes, H.M.; Read, J.; Abdessalem, T.; et al. River: machine learning for streaming data in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 1–8.
| General | Query Strategies | Learning Tasks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Authors | Number | Pool | Stream | Multi-annotator | Regression | Classification |
| DeepAL | Huang | 9 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| libact | Yang et al. | 19 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| alipy | Tang et al. | 30 | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| modal | Danka and Horvath | 21 | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| altoolbox | Tsvigun et al. | 19 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| baal | Atighehchian et al. | 10 | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| pyrelational | Scherer et al. | 17 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| small-text | Schröder et al. | 23 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| scikit-activeml | Herde et al. | 61 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Name | Implementation | Documentation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Last Release | Frameworks | License | Tests | Coverage | Tutorials | Developer Guide | |
| DeepAL | N/A | pytorch | MIT | ✗ | N/A | ✗ | ✗ |
| libact | 2019 | scikit-learn | BSD-2-Clause | ✓ | 90 % | ✓ | ✓ |
| alipy | 2021 | scikit-learn | BSD-3-Clause | ✓ | N/A | ✓ | ✗ |
| modal | 2023 |
scikit-learn, keras, skorch |
MIT | ✓ | 97 % | ✓ | ✓ |
| altoolbox | 2022 | pytorch, transformers | MIT | ✓ | N/A | ✗ | ✓ |
| baal | 2024 | pytorch, transformers | Apache 2.0 | ✓ | N/A | ✓ | ✓ |
| pyrelational | 2024 |
scikit-learn, pytorch(-lightning) |
Apache 2.0 | ✓ | 94 % | ✓ | ✓ |
| small-text | 2024 |
scikit-learn, pytorch, transformers |
MIT | ✓ | 96 % | ✓ | ✓ |
| scikit-activeml | 2025 |
scikit-learn, skorch, river1 |
BSD-3-Clause | ✓ | 100 % | ✓ | ✓ |
| 1 |
scikit-activeml (v0.6) depends on scikit-learn (v1.6), which is unsupported by the latest release of river (v0.22). Therefore, river (v0.22) is only compatible with scikit-activeml (v0.5). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





