Submitted:
01 July 2025
Posted:
02 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
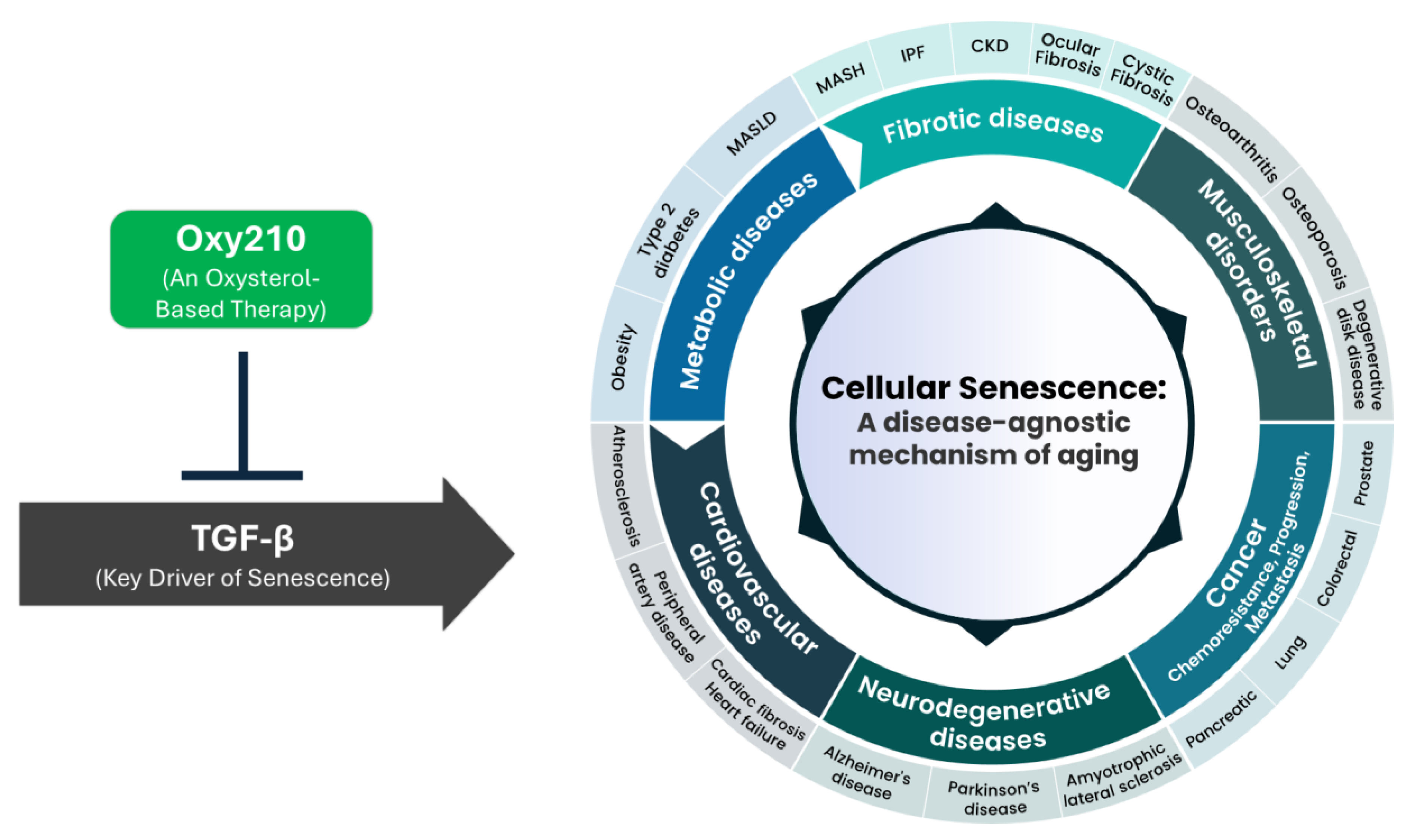
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. RNA isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.3. Animal Studies
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression in Liver Tissue of the APOE*3-Leiden.CETP Mice During MASH Development
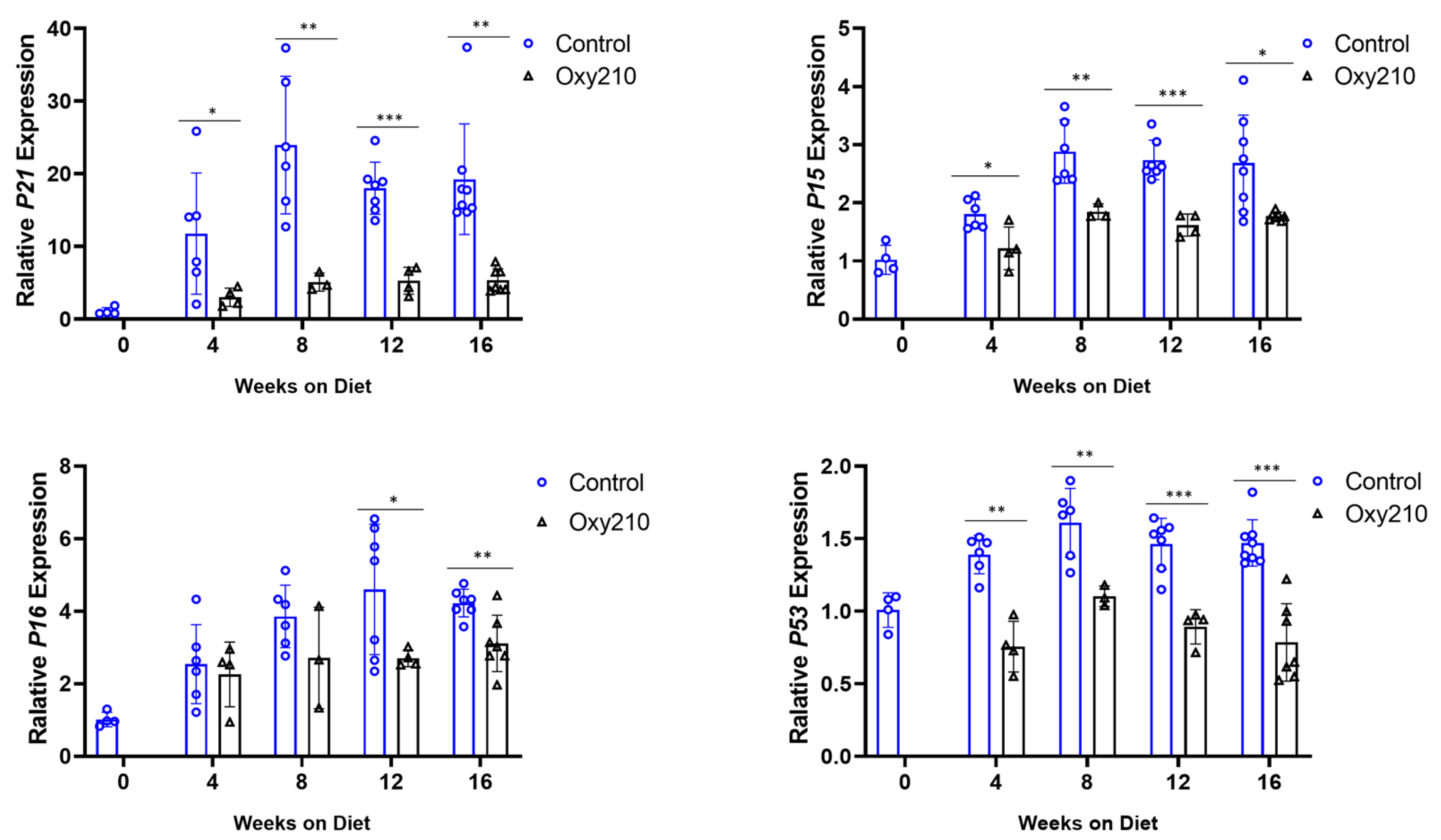
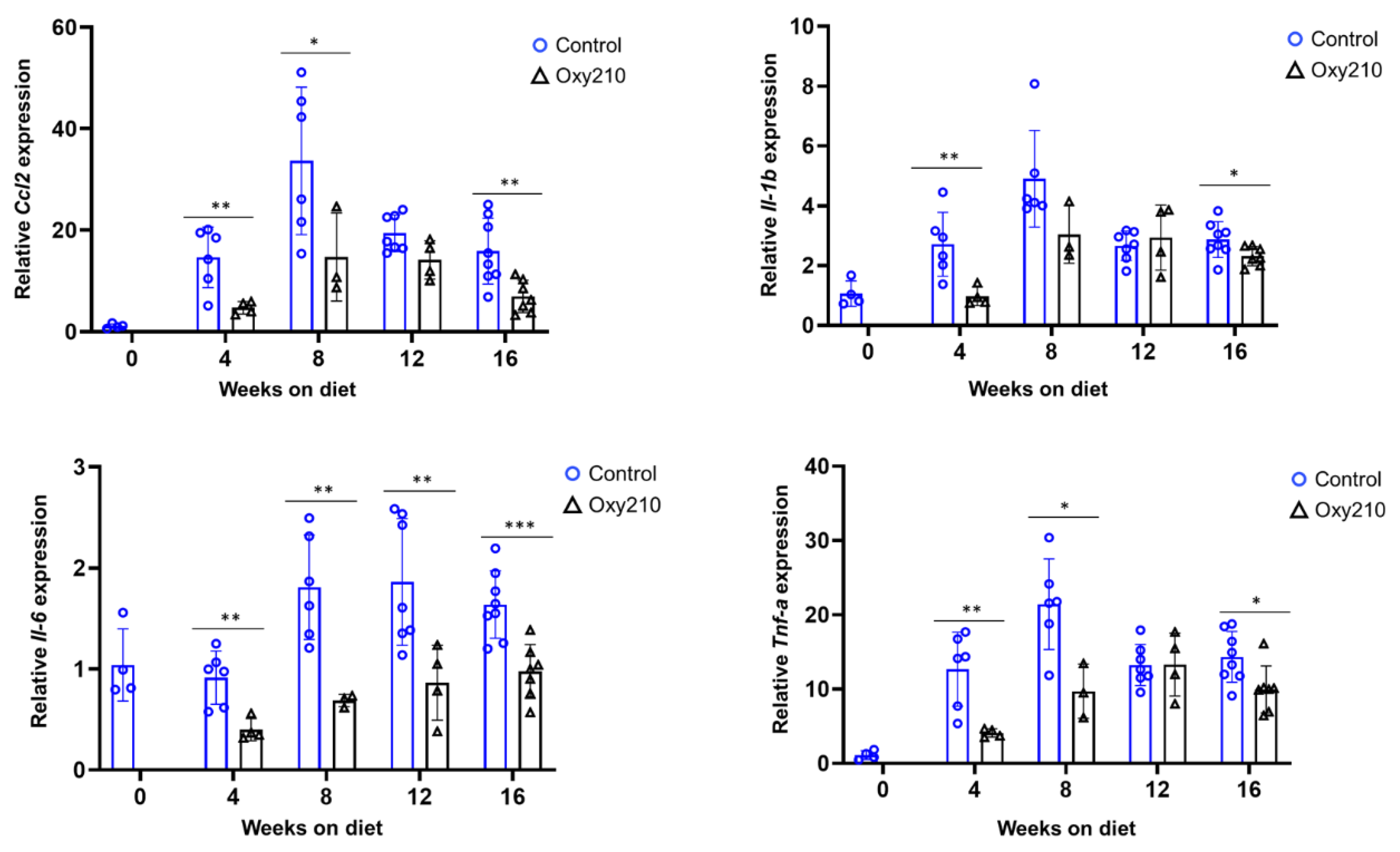
3.1.1. Senescence-Associated, SASP, and Pro-Inflammatory Genes (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3)
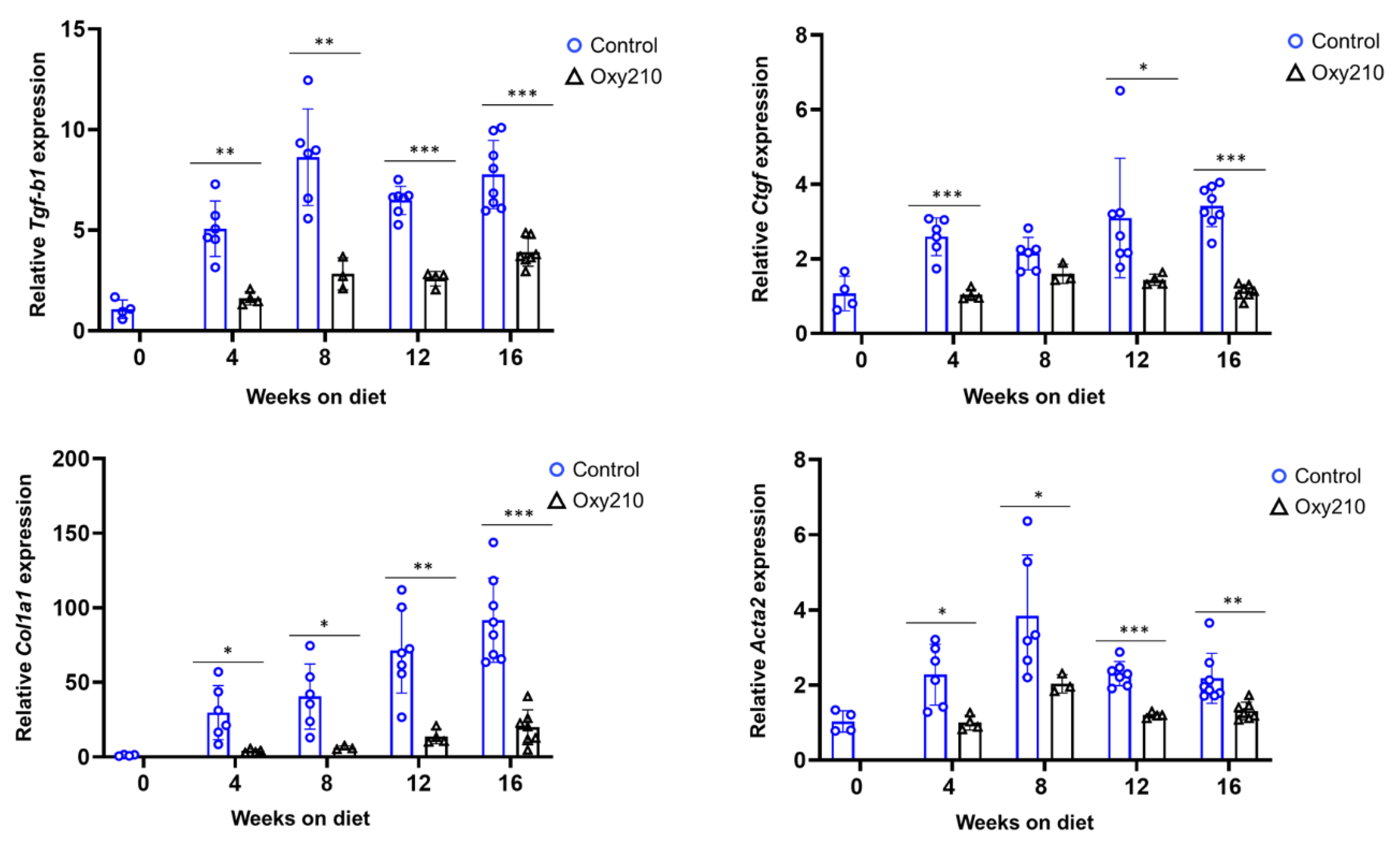
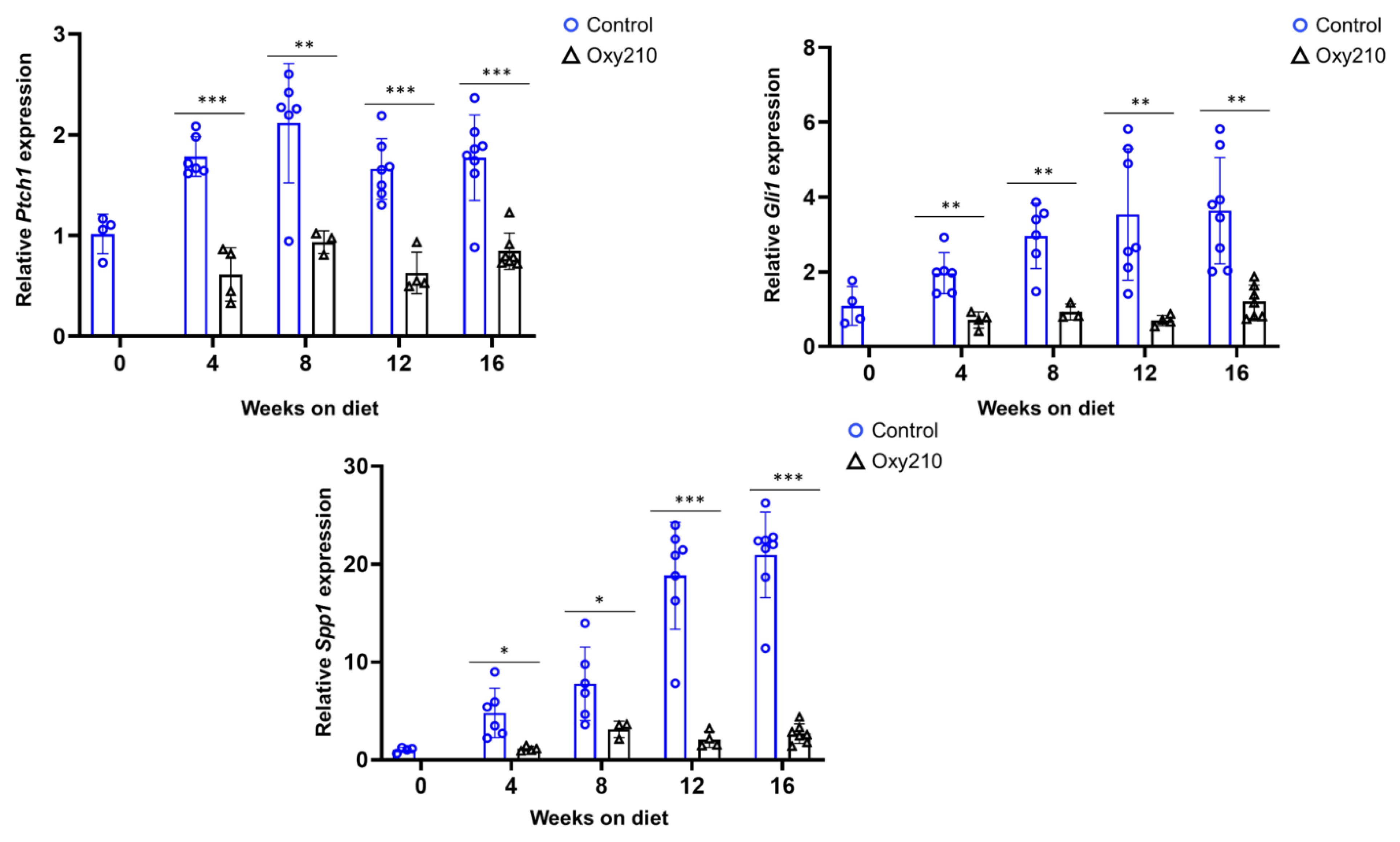
3.1.2. Pro-fibrotic TGF-β and Hh target genes (Figure 4 and Figure 5)
3.2. Effect of Oxy210 on the Expression of Senescence-Associated and Secretory Phenotype (SASP) Genes in Human HepG2 Cells (Figure 6).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, L.L.; Miao, H.; Wang, Y.N.; Liu, F.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.Y. TGF-β as A Master Regulator of Aging-Associated Tissue Fibrosis. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 1633–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iida, S.; Katsuyama, H. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-Its Pathophysiology, Association with Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease, and Treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Pitcher, L.E.; Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; Zhu, Y. Cellular senescence: a key therapeutic target in aging and diseases. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 132, e158450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-Montoya, M.; Pérez-Londoño, A.; Guatibonza-García, V.; Vargas-Villanueva, A.; Mendivil, C.O. Cellular Senescence as a Therapeutic Target for Age-Related Diseases: A Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, O.; Schosserer, M.; Grillari, J. Senopathies—Diseases Associated with Cellular Senescence. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, L.; Alexandersson, I.; Baboota, R.K.; Kroon, T.; Oscarsson, J.; Smith, U.; Boucher, J. Cellular Senescence in Hepatocytes Contributes to Metabolic Disturbances in NASH. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 957616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.C.; Haschak, M.J.; Popovic, B.; Brown, B.N. Macrophages in the Aging Liver and Age-Related Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashaswini, C.N.; Qin, T.; Bhattacharya, D.; Amor, C.; Lowe, S.; Lujambio, A.; Wang, S.; Friedman, S.L. Phenotypes and Ontogeny of Senescent Hepatic Stellate Cells in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodnik, M.; Miwa, S.; Tchkonia, T.; Tiniakos, D.; Wilson, C.L.; Lahat, A.; Day, C.P.; Burt, A.; Palmer, A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Grellscheid, S.N.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J.; Barnhoorn, S.; Mann, D.A.; Bird, T.G.; Vermeij, W.P.; Kirkland, J.L.; Passos, J.F.; Von Zglinicki, T.; Jurk, D. Cellular Senescence Drives Age-Dependent Hepatic Steatosis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Sakane, S.; Eguileor, A.; Yu, R.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. The Origin and Fate of Liver Myofibroblasts. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 17, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, H.; Maeda, H.; Noguchi, I.; Tanaka, M.; Wada, N.; Nagasaki, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Kanazawa, G.; Taguchi, K.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Sakai, H.; Nakashima, H.; Kinoshita, M.; Kitagishi, H.; Iwakiri, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Watanabe, H.; Maruyama, T. Carbon Monoxide-Loaded Red Blood Cells Ameliorate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis Progression via Enhancing AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Activity and Inhibiting Kupffer Cell Activation. Redox Biol. 2024, 76, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Kluwe, J.; Osawa, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Schwabe, R.F. TLR4 Enhances TGF-β Signaling and Hepatic Fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Brenner, D.A. Recent Advancement of Molecular Mechanisms of Liver Fibrosis. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2015, 22, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.T.; Kurt, Z.; Tuominen, I.; Norheim, F.; Davis, R.C.; Pan, C.; Dirks, D.L.; Magyar, C.E.; French, S.W.; Chella Krishnan, K.; Sabir, S.; Campos-Pérez, F.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Macías-Kauffer, L.; León-Mimila, P.; Canizales-Quinteros, S.; Yang, X.; Beaven, S.W.; Huertas-Vazquez, A.; Lusis, A.J. The Genetic Architecture of Diet-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2182–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, S.T.; Wang, F.; Stappenbeck, F.; French, S.W.; Magyar, C.E.; Parhami, F.; Lusis, A.J. Oxy210, a Novel Inhibitor of Hedgehog and TGF-β Signalling, Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis and Hypercholesterolemia in Mice. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stappenbeck, F.; Wang, F.; Sinha, S.K.; Hui, S.T.; Farahi, L.; Mukhamedova, N.; Fleetwood, A.; Murphy, A.J.; Sviridov, D.; Lusis, A.J.; Parhami, F. Anti-Inflammatory Oxysterol, Oxy210, Inhibits Atherosclerosis in Hyperlipidemic Mice and Inflammatory Responses of Vascular Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Stappenbeck, F.; Tang, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.E.; Hui, S.T.; Lusis, A.J.; Parhami, F. Oxy210, a Semi-Synthetic Oxysterol, Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Macrophages via Inhibition of Toll-like Receptor (TLR) 4 and TLR2 Signaling and Modulation of Macrophage Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, B.; Kamath, A.J.; Pradeep, G.; Devan, A.R.; Sethi, G.; Nath, L.R. Unveiling the Role of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Chronic Liver Disease: Therapeutic Insights and Strategies. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Murata, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, K. TGF-β/Smad Signaling during Hepatic Fibro-carcinogenesis (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Stappenbeck, F.; Parhami, F. Oxy210, a Semi-Synthetic Oxysterol, Inhibits Profibrotic Signaling in Cellular Models of Lung and Kidney Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Suzuki, H.I. TGF-β Signaling in Cellular Senescence and Aging-Related Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, P.; Millar, F.R.; Tarrats, N.; Rink, C.J.; Finch, A.J.; Brunton, V.G.; Passos, J.F.; Morton, J.P. The Innate Immune Sensor Toll-Like Receptor 2 Controls the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw0254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Chen, S.; Yi, Z.; Shi, H.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Z. The Role of p21 in Cellular Senescence and Aging-Related Diseases. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; Nehme, J.; Demaria, M. Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safwan-Zaiter, H.; Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.D. P16INK4A—More Than a Senescence Marker. Life 2022, 12, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijit, M.; Caracciolo, V.; Melillo, A.; Amicarelli, F.; Giordano, A. Role of p53 in the Regulation of Cellular Senescence. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Jat, P. Mechanisms of Cellular Senescence: Cell Cycle Arrest and Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 645593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, R.; Sadaie, M.; Hoare, M.; Narita, M. Cellular Senescence and Its Effector Programs. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilborg, A.; Wilhelm, M.T.; Wiman, K.G. Regulation of Tumor Suppressor p53 at the RNA Level. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chen, X. Senescence Regulation by the p53 Protein Family. In Methods in Molecular Biology, Vol. 965; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, K.D.; Wagner, N. The Senescence Markers p16INK4A, p14ARF/p19ARF, and p21 in Organ Development and Homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Rai, R.; Khan, S.S.; Eren, M.; Ghosh, A.K. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Is a Marker and a Mediator of Senescence. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Naik, I.; Braunstein, Z.; Zhong, J.; Ren, B. Transcription Factor C/EBP Homologous Protein in Health and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, G. NADPH Oxidases and Mitochondria in Vascular Senescence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lener, B.; Kozieł, R.; Pircher, H.; Kratochwil, M.; Hermann, M.; Dencher, N.A.; Jansen-Dürr, P. The NADPH Oxidase Nox4 Restricts the Replicative Lifespan of Human Endothelial Cells. Biochem. J. 2009, 423, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Tacke, F.; Sugimoto, A.; Friedman, S.L. Antifibrotic Therapies for Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease. JHEP Rep. 2025, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenić, K.; Lenartić, M.; Marinović, S.; Polić, B.; Wensveen, F.M. The "Domino effect" in MASLD: The inflammatory cascade of steatohepatitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 54, e2149641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Transforming Growth Factor-β in Tissue Fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, S.; ten Dijke, P. TGF-β in Progression of Liver Disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L. Navigating the Complex Role of Senescence in Liver Disease. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2024, 137, 3061–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, G.M.; Chan, I.S.; Swiderska, M.; Schroder, V.T.; Guy, C.; Karaca, G.F.; Moylan, C.; Venkatraman, T.; Feuerlein, S.; Syn, W.-K.; Jung, Y.; Witek, R.P.; Choi, S.; Michelotti, G.A.; Rangwala, F.; Merkle, E.; Lascola, C.; Diehl, A.M. Hedgehog Signaling Antagonist Promotes Regression of Both Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Murine Model of Primary Liver Cancer. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Roh, Y.S.; Song, J.; Li, S.; Seki, E.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Karin, G.; Loomba, R.; Glaser, S.; Alpini, G.; Torok, N.J. Transforming Growth Factor beta Signaling in Hepatocytes Participates in Steatohepatitis Through Regulation of Cell Death and Lipid Metabolism in Mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijnikman, A.S.; Herrema, H.; Scheithauer, T.P.M.; Kroon, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Groen, A.K. Evaluating Causality of Cellular Senescence in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Sharpless, N.E. Senescence in Health and Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the p53 Tumor Suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaib, S.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L. Cellular Senescence and Senolytics: The Path to the Clinic. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhanovsky, V.; Yon, M.; Dickins, R.A.; Hearn, S.; Simon, J.; Miething, C.; Yee, H.; Zender, L.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence of Activated Stellate Cells Limits Liver Fibrosis. Cell 2008, 134, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Gonzalez, S.; Rodrigo-Torres, D.; Gadd, V.L.; Forbes, S.J. Cellular Senescence in Liver Disease and Regeneration. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Weiskirchen, R.; Ehrlich, M.; Henis, Y.I. Dual Signaling Pathways of TGF-β Superfamily Cytokines in Hepatocytes: Balancing Liver Homeostasis and Disease Progression. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1580500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Lee, Y.A.; Fujiwara, N.; Ybanez, M.; Allen, B.; Martins, S.; Fiel, M.I.; Goossens, N.; Chou, H.-I.; Hoshida, Y.; Friedman, S.L. A Simple Diet- and Chemical-Induced Murine NASH Model with Rapid Progression of Steatohepatitis, Fibrosis and Liver Cancer. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Xia, L.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Qin, W. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Advances. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli, G.; Villa, E.; Lahn, M. Transforming Growth Factor-β as a Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1890–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Vaquero, J.; Férnandez-Barrena, M.G.; Lasarte, J.J.; Avila, M.A.; Sarobe, P.; Reig, M.; Calvo, M.; Fabregat, I. The TGF-β Pathway: A Pharmacological Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Cancers 2021, 13(13), 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, B.; Ying, W.; Qian, X. Identification of Hedgehog Signaling as a Potential Oncogenic Driver in an Aggressive Subclass of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Reanalysis of the TCGA Cohort. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. Hedgehog Signaling, a Critical Pathway Governing the Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2021, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Viscardi, G.; Papaccio, F.; D'Amodio, M.; Esposito, C.; Cennamo, G.; Ciardiello, F.; Martinelli, E. Implication of the Hedgehog Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.H.; Du, K.; Dutta, R.K.; Maeso-Diaz, R.; Oh, S.H.; Wang, L.; Gao, G.; Ferreira, A.; Hill, J.; Pullen, S.S.; Diehl, A.M. The senescence-associated secretome of Hedgehog-deficient hepatocytes drives MASLD progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2024, 134, e180310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Friedman, S.L. Found in Translation—Fibrosis in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH). Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadi0759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, N.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L. Lipids and Lipid Metabolism in Cellular Senescence: Emerging Targets for Age-Related Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 97, 102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stappenbeck, F.; Wang, F.; Tang, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.E.; Parhami, F. Inhibition of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Oxy210, an Oxysterol-Derivative that Antagonizes TGFβ and Hedgehog Signaling. Cells 2019, 8, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.Y.; Spezia, M.; Chen, T.; Stappenbeck, F.; Wang, F.; Parhami, F. Oxysterol Derivatives Oxy186 and Oxy210 Inhibit WNT Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




