1. Introduction
The treatment of zinc ferrite residues, generated during the acid leaching of zinc calcine, represents a critical stage for both the efficient recovery of non-ferrous metals and the mitigation of associated environmental risks. The primary phase in these residues – zinc ferrite (ZnFe₂O₄) – is a chemically stable spinel compound, exhibiting low solubility under conventional hydrometallurgical conditions. Therefore, overcoming its chemical inertness requires the application of various technological approaches, which are generally classified into four main groups: pyrometallurgical, combined (roasting–leaching), hydrometallurgical (including high-pressure processes), and bioleaching methods.
Pyrometallurgical processing of zinc ferrite residues involves high-temperature reduction of ZnFe₂O₄ followed by the capture of volatilized zinc. The most widely used method is the Waelz process [
1,
2,
3], in which a mixture of ferrite residue and a carbonaceous reductant (such as coal or coke) is treated in a rotary kiln at temperatures between 1000 and 1250 °C. Under these conditions, zinc is reduced and volatilized, then oxidized and captured as ZnO from the off-gases. Iron remains in the slag as stable oxides. Zinc recovery typically ranges between 85 % and 90 %. Industrial Waelz kilns are operated by companies such as Zhuzhou Smelter (China), Votorantim (Brazil), Glencore (Italy), and KCM Plovdiv (Bulgaria) [
4].
An alternative pyrometallurgical method is the Top-Submerged Lance (TSL) process, in which fine residues are injected directly into molten slag [
5,
6]. The intense mixing and high temperature promote rapid reduction and volatilization of zinc. The Ausmelt technology, based on this principle, is applied at plants in Whyalla (Australia), Onsan, and Sukpo (South Korea) [
4]. This process achieves recoveries of approximately 82 % zinc, 92 % lead, 86 % silver, and 61 % copper from the residues [
6].
Combined pyro-hydrometallurgical technologies for processing zinc ferrite residues typically involve roasting followed by leaching, aiming to convert zinc into water-soluble forms. In reductive roasting, ZnFe₂O₄ is transformed into ZnO and magnetite, after which acid leaching is applied. Laboratory tests conducted at 750 °C for 90 minutes, with 8 % CO and 90 g/L H₂SO₄, achieved recoveries of 61.38 % zinc and 80.9 % iron [
7]. Sulfatizing roasting using iron sulfate at 640 °C for 30 minutes leads to the conversion of various zinc forms into ZnSO₄, achieving up to 90.9 % zinc recovery with minimal soluble iron [
8,
9]. Roasting with ammonium sulfate in a three-step process results in the formation of zinc and iron sulfates, enabling selective metal extraction [
10]. Combined sulfatizing roasting and acid leaching (200 °C, 1 hour, H₂SO₄:solid = 1:1) can yield up to 90 % zinc extraction. Under milder conditions (95 °C, 2 hours, 200 g/L H₂SO₄), 51 % recovery of ferritic zinc and 82 % total zinc have been reported [
11,
12].
Hydrometallurgical technologies can be performed at atmosheric or elevated pressure. The most common method is hot sulfuric acid leaching followed by iron precipitation as jarosite, goethite, or hematite. This achieves high zinc and iron yields but makes impurity removal challenging [
13]. Reductive leaching improves extraction of zinc, iron, and indium by reducing Fe³⁺ to Fe²⁺, simplifying downstream processing. Reductants such as sphalerite, galena, and sulfur dioxide are effective in lab studies [
13,
14,
15]. For example, leaching with sphalerite (0.95 theoretical amount) at 150 g/L H₂SO₄, 90 °C, for 4 hours achieves 94.8 % indium, 96.1 % zinc, and 92.8 % iron recovery [
13]. Using galena under similar conditions yields 88 % indium, 87 % zinc and 91 % iron [
14]. Sulfur dioxide as reductant also effectively reduces Fe³⁺ to Fe²⁺, eliminating separation issues for indium [
15,
16].
Oxidative leaching with hydrogen peroxide or manganese dioxide lowers iron dissolution significantly while maintaining acceptable zinc extraction. Iron recovery drops from 70 % (without oxidants) to 0.4 % with MnO₂ and 5 % with H₂O₂, due to iron hydroxide or iron-manganese compound formation [
17].
Alkaline leaching using NaOH or Na₂CO₃ at pH >12 and 60–90 °C selectively dissolves zinc as zincates, leaving iron in the residue. However, this process is slower, with 70–85 % yields and limited industrial use [
18,
19,
20].
Pressure leaching (autoclave) uses elevated temperatures (up to 250 °C) and pressures (4–5 MPa) with oxygen or air to fully transform zinc ferrite into soluble zinc sulfate and insoluble iron precipitates. Extraction efficiency can exceed 95 %, but costs are higher than atmospheric leaching [
21,
22].
Bioleaching employs bacteria like Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans to oxidize iron and sulfur compounds, aiding zinc ferrite breakdown under acidic conditions. Though slower, this environmentally friendly method suits low-grade or finely dispersed residues and is under development worldwide [
23].
Choosing the right technology depends on residue composition, metal content, and economic and environmental considerations. Pyrometallurgical methods offer robustness and high productivity, while hydrometallurgical and combined approaches provide flexibility and better integration with circular economy goals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The initial zinc ferrite residue (ZFR) was supplied by the Bulgarian zinc production plant KCM. The material was subjected to a water washing process aimed at removing water-soluble zinc, conducted at a temperature of 60 °C with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:4 and continuous mechanical stirring. After this treatment, the resulting residue was dried, ground and homogenized using a knife mill. The chemical composition of the prepared material was subsequently determined using both conventional chemical methods and Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) with a Prodigy spectrometer. The results were summarized in
Table 1.
2.2. Leaching Experiments and Methods
The sulfuric acid leaching experiments of the ZFR under atmospheric conditions were performed in 1 L cylindrical reaction vessels (Lenz Laborglasinstrumente™), equipped with a thermostatic jacket and a withdrawal valve to maintain temperature control and facilitate sample extraction. For experiments conducted at elevated pressure, a 2 L glass autoclave (model TLA 30) was employed to ensure controlled pressure conditions during the leaching process. The acidity of the leach solution was measured using a combined pH electrode Aqua Lytic SD300, produced in Germany.
The filtrate obtained under the optimal conditions of the sulfuric acid leaching was neutralized with a 10 % solution of Ca(OH)2 to the desired pH value. The neutralized solution was used to perform studies on autoclave precipitation of iron in the form of hematite. The experiments were carried out in a laboratory novoclave from Büchi AG, with reactor (400 ml) constructed of stainless steel Hastelloy.
The chloride leaching experiments on lead cake were carried out using a 300 ml vessel in a thermostatically controlled water bath with mechanical stirring.
Upon completion of the experiments, the resulting pulp was filtered, and the insoluble residue was dried at 353 K for 24 hours and subsequently weighed using an analytical balance. The concentrations of the target metals in both the process solutions and the insoluble residues were determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Prodigy) and/or chemical methods.
The extraction degrees of the target metals were calculated based on the chemical composition of the insoluble residue remaining after the leaching process.
The phase composition of the insoluble residues was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a Philips PW 1050 diffractometer equipped with Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å), operating at 40 kV and 30 mA, with data collected over a 2θ range of 5° to 90°.
The morphology and phase composition of the ZFR and lead cakes were studied using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) from Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, coupled with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) from Oxford Instruments. SEM and EDS analyses of the hematite and the residue after chloride leaching were performed using an X-MaxN 50 mm² EDS detector by Oxford Instruments (20 kV accelerating voltage), mounted on a Tescan Vega 3 XMU electron microscope.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Sulfuric Acid Leaching of ZFR
The ZFR was subjected to both atmospheric and autoclave leaching to evaluate the most suitable processing method. Sulfuric acid, a cost-effective and widely available reagent, serves as an efficient leaching agent for a broad spectrum of metals. In Bulgaria, sulfuric acid is industrially produced from metallurgical SO₂ off-gases, which are generated during the processing of copper, lead, and zinc sulfide concentrates. The present study investigates the influence of key process parameters - namely temperature, sulfuric acid concentration, leaching duration, and solid-to-liquid ratio - on metal leaching degree and the phase composition of the resulting solid residues.
3.1.1. Effect of Temperature
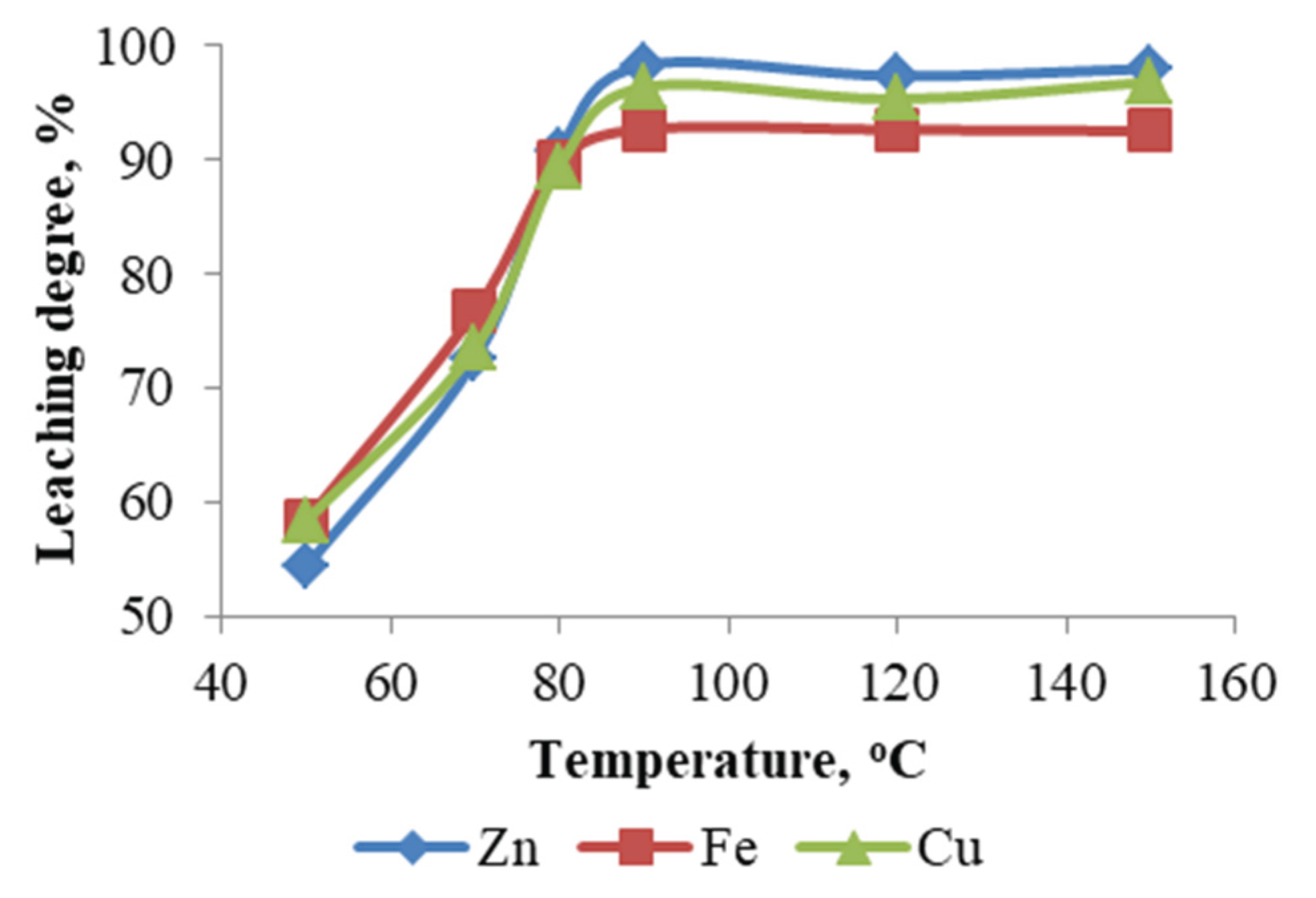
The influence of temperature on the sulfuric acid leaching of ZFR was systematically studied within the range of 50 to 150 °C, at a fixed sulfuric acid concentration of 200 g/L, a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, and a leaching duration of 3 hours. The data presented in
Figure 1 demonstrate a pronounced increase in the leaching efficiencies of zinc, iron, and copper with temperature elevation from 50 to 90 °C, achieving maximum extraction rates of 98.30 %, 92.72 %, and 96.40 %, respectively, at 90 °C. Further temperature increase under autoclave conditions (120 and 150 °C) did not yield any significant enhancement in the extraction of the target metals, indicating that 90 °C represents the optimal temperature for efficient metal recovery under the studied conditions.
3.1.2. Effect of Sulfuric Acid Concentration
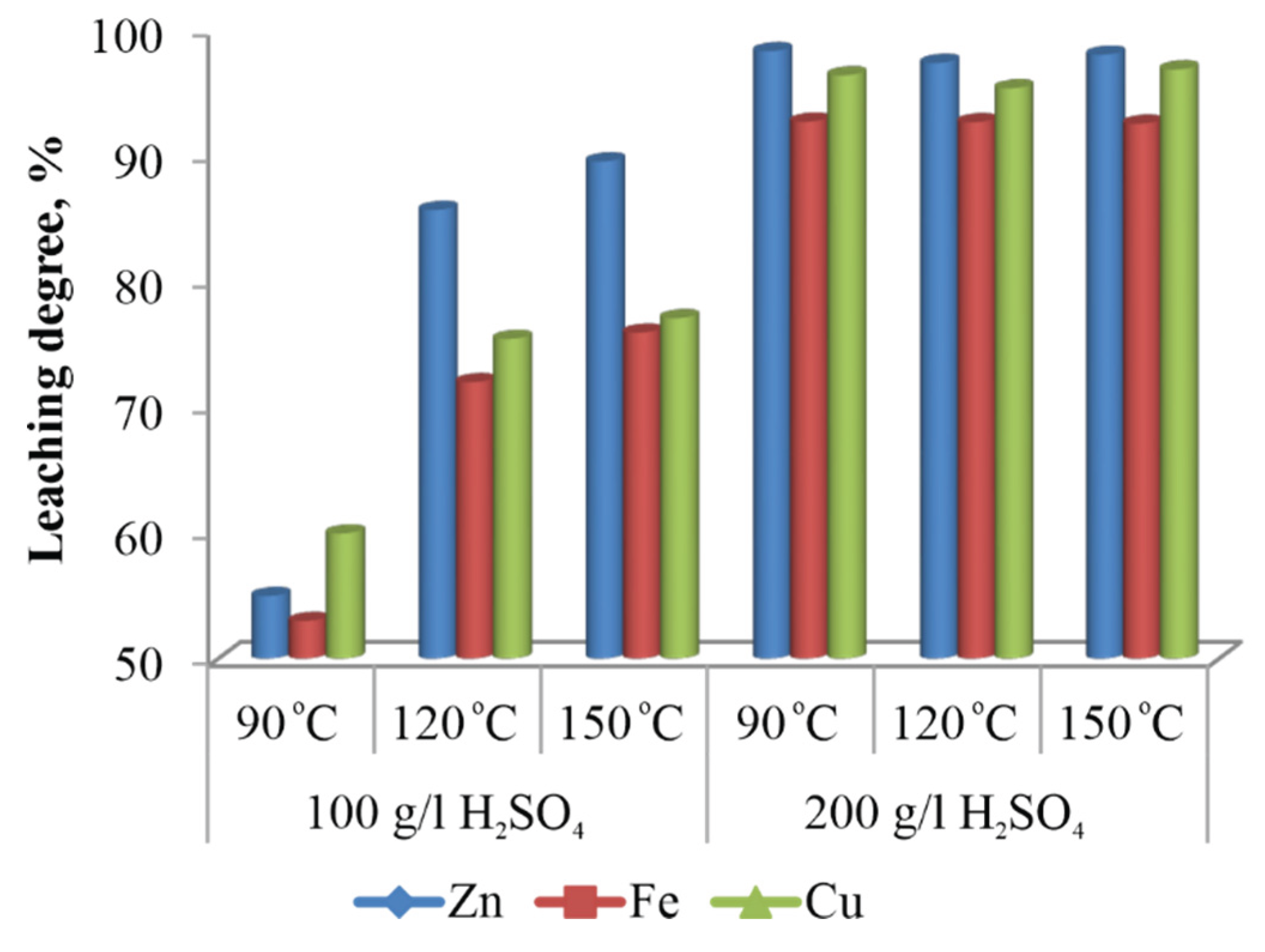
Experiments aimed at evaluating the influence of sulfuric acid concentration on the leaching process were conducted at initial acid concentrations of 100g/L and 200g/L, under three different temperatures - 90, 120, and 150 °C - while maintaining all other process parameters constant. The experimental results (
Figure 2) indicate that at an initial sulfuric acid concentration of 100g/L, the extraction efficiencies of zinc, iron, and copper remain low across all temperatures, with particularly poor performance observed under atmospheric leaching at 90 °C. Increasing the initial acid concentration to 200g/L led to a significant improvement in metal recovery across all studied temperatures, highlighting the critical role of acid concentration in enhancing leaching efficiency.
3.1.3. Effect of the Solid-to-Liquid Ratio
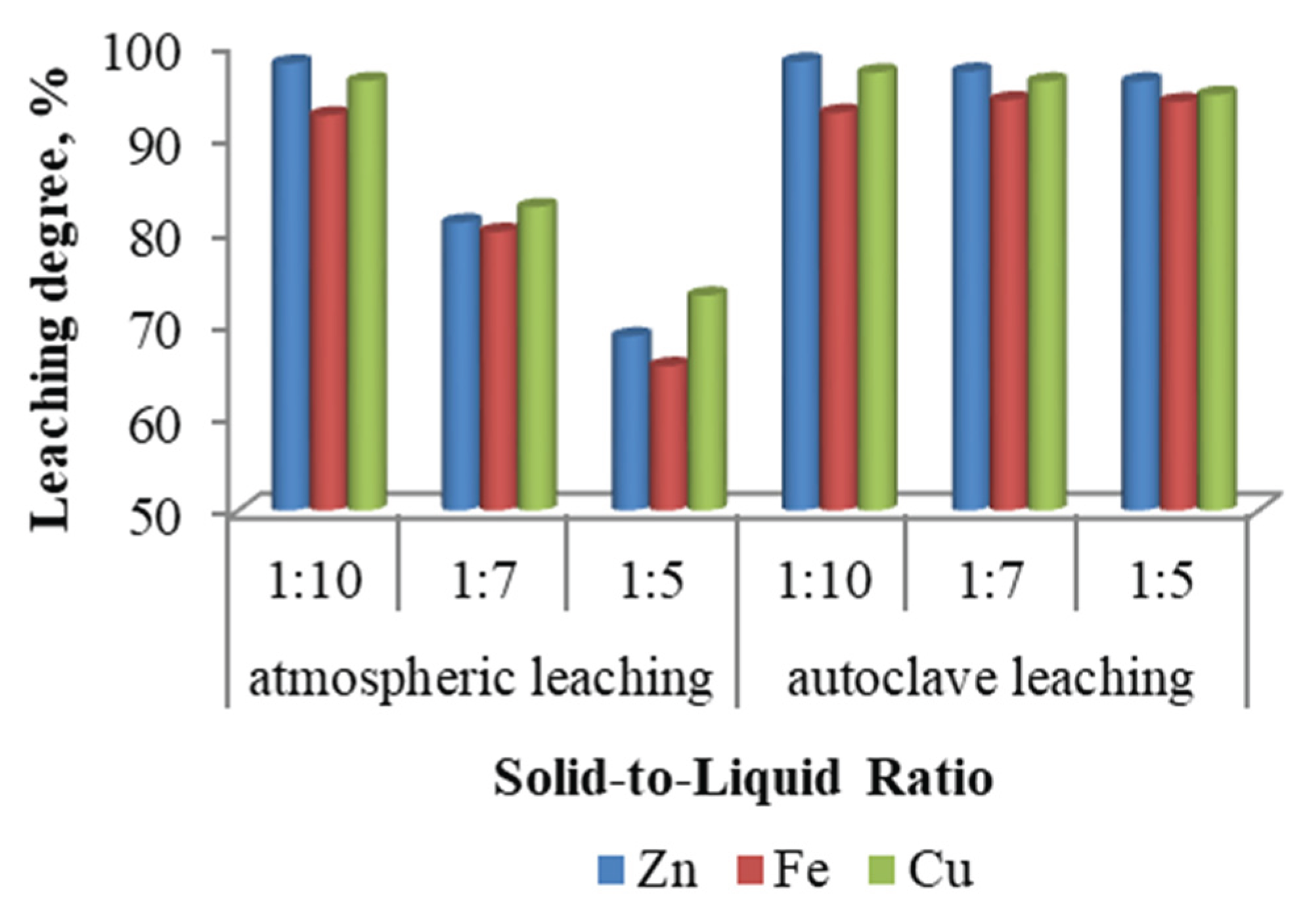
The solid-to-liquid ratio is a key parameter influencing the mass transfer processes occurring during the interaction between the solid phase and the leaching solution. Laboratory experiments to assess the effect of the solid-to-liquid ratio on metal extraction efficiency were conducted at ratios of 1:10, 1:7, and 1:5, with a leaching duration of 3 hours. Atmospheric leaching was carried out at 90 °C, while autoclave leaching of ZFR was performed at 150 °C.
As illustrated in
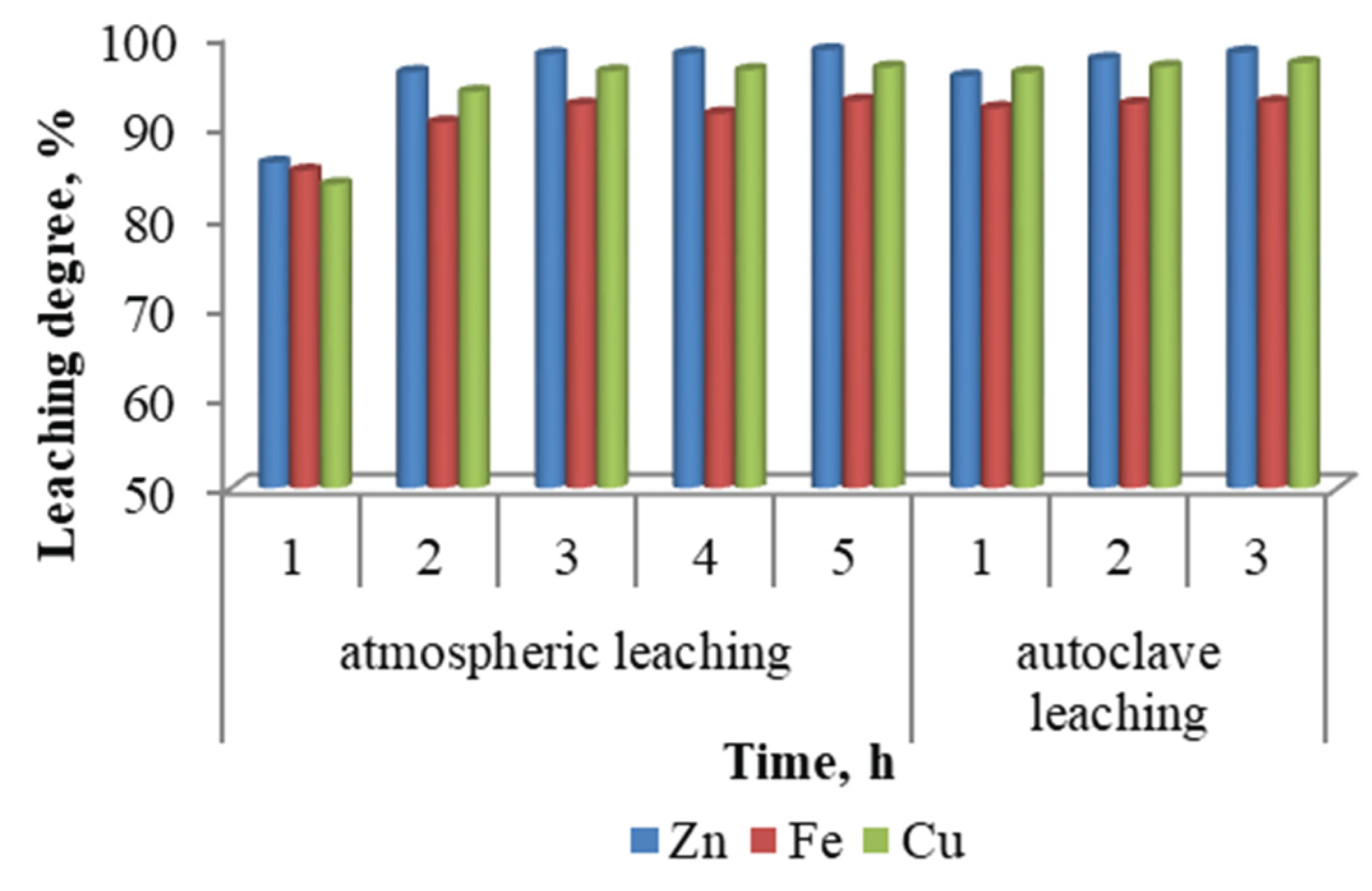
Figure 3, this parameter exerts a more pronounced influence under atmospheric leaching conditions, where a decrease in the solid-to-liquid ratio significantly enhances the extraction of zinc, iron, and copper. In contrast, under autoclave leaching conditions, increasing the solid content leads to only a slight reduction in extraction efficiencies. The optimal solid-to-liquid ratio for atmospheric leaching was found to be 1:10, at which the maximum leaching degrees for zinc, iron, and copper were achieved.
3.1.4. Effect of Reaction Time
The duration of the leaching experiments conducted under atmospheric conditions extended up to 5 hours, as shown in
Figure 4, whereas the autoclave leaching tests were limited to a maximum duration of 3 hours. Under atmospheric leaching, the metal extraction efficiencies increased markedly during the first 2 hours, after which only a marginal improvement was observed with further extension of the leaching time. In contrast, during autoclave leaching, the most significant increase in metal recovery occurred within the first hour. Subsequent increases in leaching duration had little to no effect on the extraction efficiencies. These findings indicate that the leaching kinetics are substantially faster under autoclave conditions, and prolonged treatment times offer diminishing returns in terms of metal recovery.
Based on the conducted investigation of the sulfuric acid leaching process of ZFR under both atmospheric and autoclave conditions, the following key conclusions can be drawn:
Sulfuric acid concentration is a critical factor determining the metal extraction efficiency. A minimum initial concentration of 200 g/L is required to achieve complete dissolution of copper, iron, and zinc.
Temperature plays a major role in the leaching process. Practically complete leaching of the ZFR requires a minimum temperature of 90 °C.
The solid-to-liquid ratio significantly affects metal extraction only under atmospheric leaching conditions, with lower ratios favouring higher extraction rates.
The optimal leaching duration under atmospheric conditions is approximately 3 hours while under autoclave conditions, 1 hour is sufficient to achieve high extraction rates. Beyond this timeframe, only marginal improvements in metal recovery are observed.
Autoclave leaching offers higher process rates and allows operation at higher pulp densities, increasing overall efficiency. However, it requires specialized pressure-resistant equipment, which raises the cost of implementation.
These findings provide a solid basis for selecting optimal leaching conditions depending on available resources and desired process efficiency.
3.1.5. Characterization of the Products of Sulfuric Acid Leaching
Table 2 presents the chemical composition of the leachate and the solid residue obtained under optimal conditions of atmospheric and autoclave sulfuric acid leaching of ZFR. The data showed that the compositions of the pregnant solutions and the undissolved residues obtained under both atmospheric and autoclave conditions are similar. This provides additional evidence that atmospheric leaching is the more favourable option for the treatment of ZFR.
The concentrations of iron, copper, and zinc in the pregnant solution after atmospheric leaching were 27.64 g/L, 17.81 g/L, and 1.25 g/L, respectively. Lead and silver were found to be fully concentrated in the undissolved residue, with slightly higher concentrations observed in the residue from autoclave leaching. Lead is the predominant element in the undissolved residues.
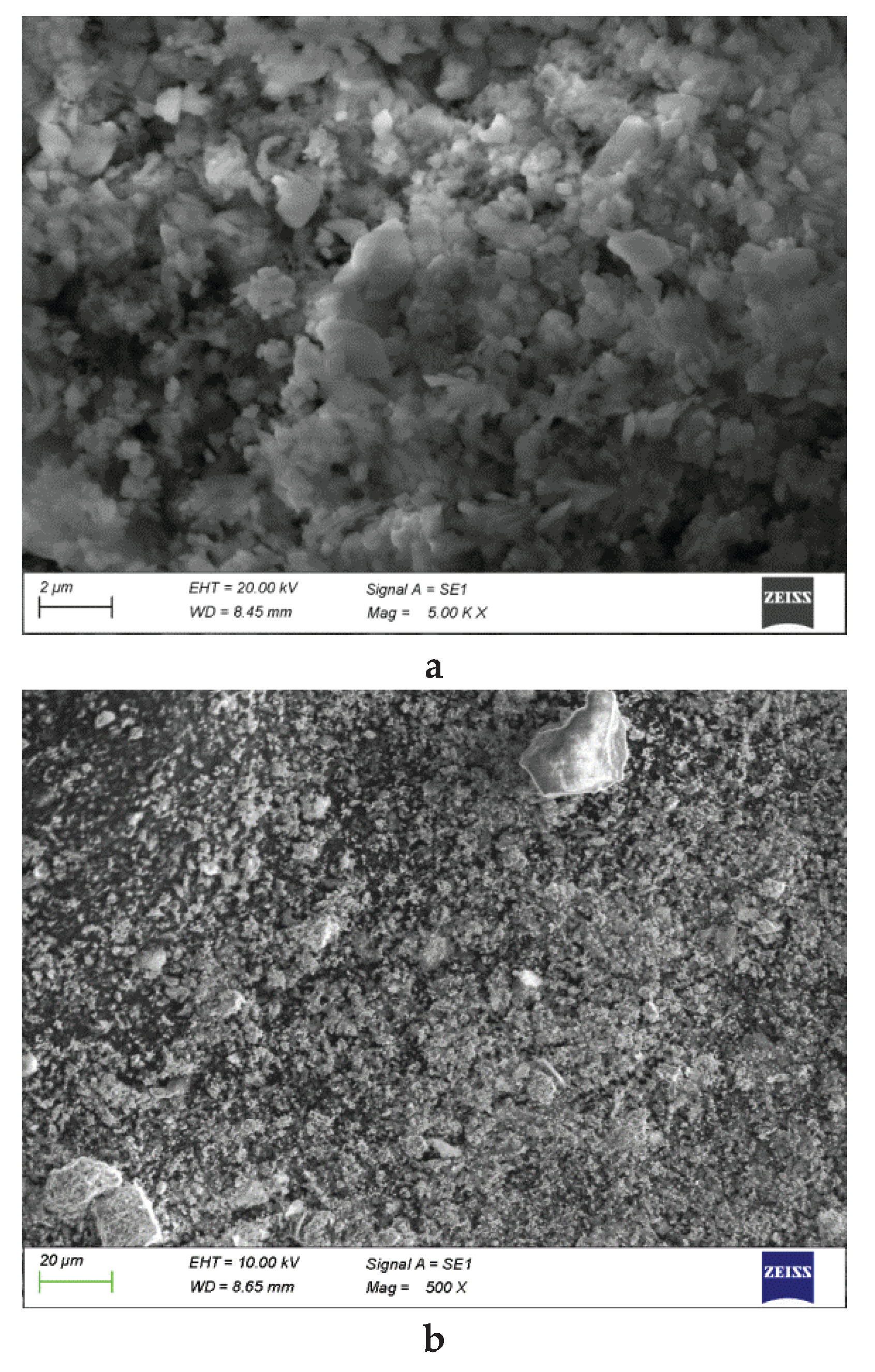
The phase composition, morphology, and elemental distribution of the undissolved residues were characterized by XRD and SEM-EDX analyses.
Figure 5 presents SEM micrographs of the lead cake obtained after atmospheric (a) and autoclave leaching (b), respectively.
A Map Sum Spectrum of selected areas of the lead residue, given in
Table 3 and
Figure 5, showed that in addition to lead, there are elevated levels of silicon, iron, and sulfur. The compositions of the analyzed regions are similar.
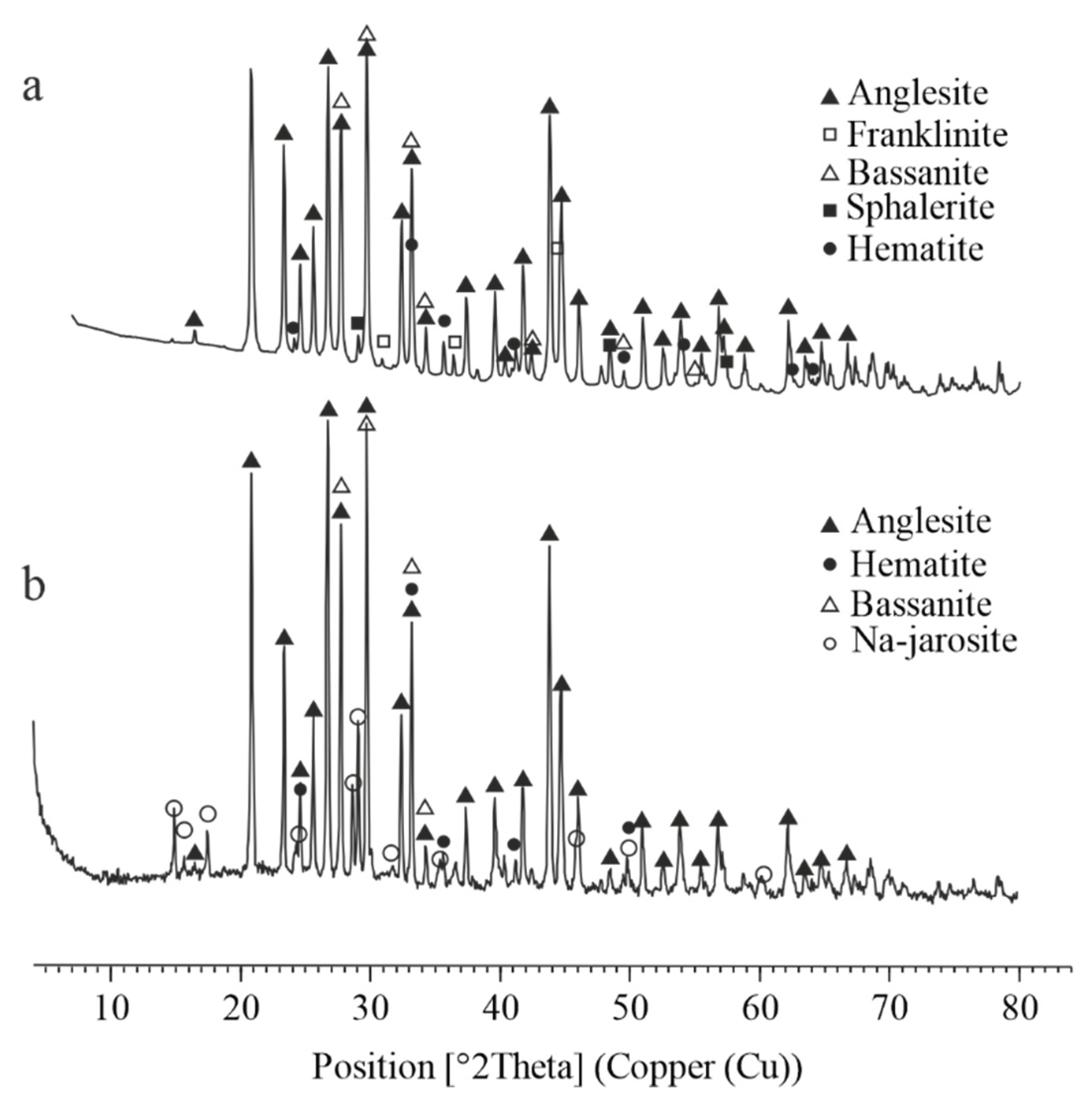
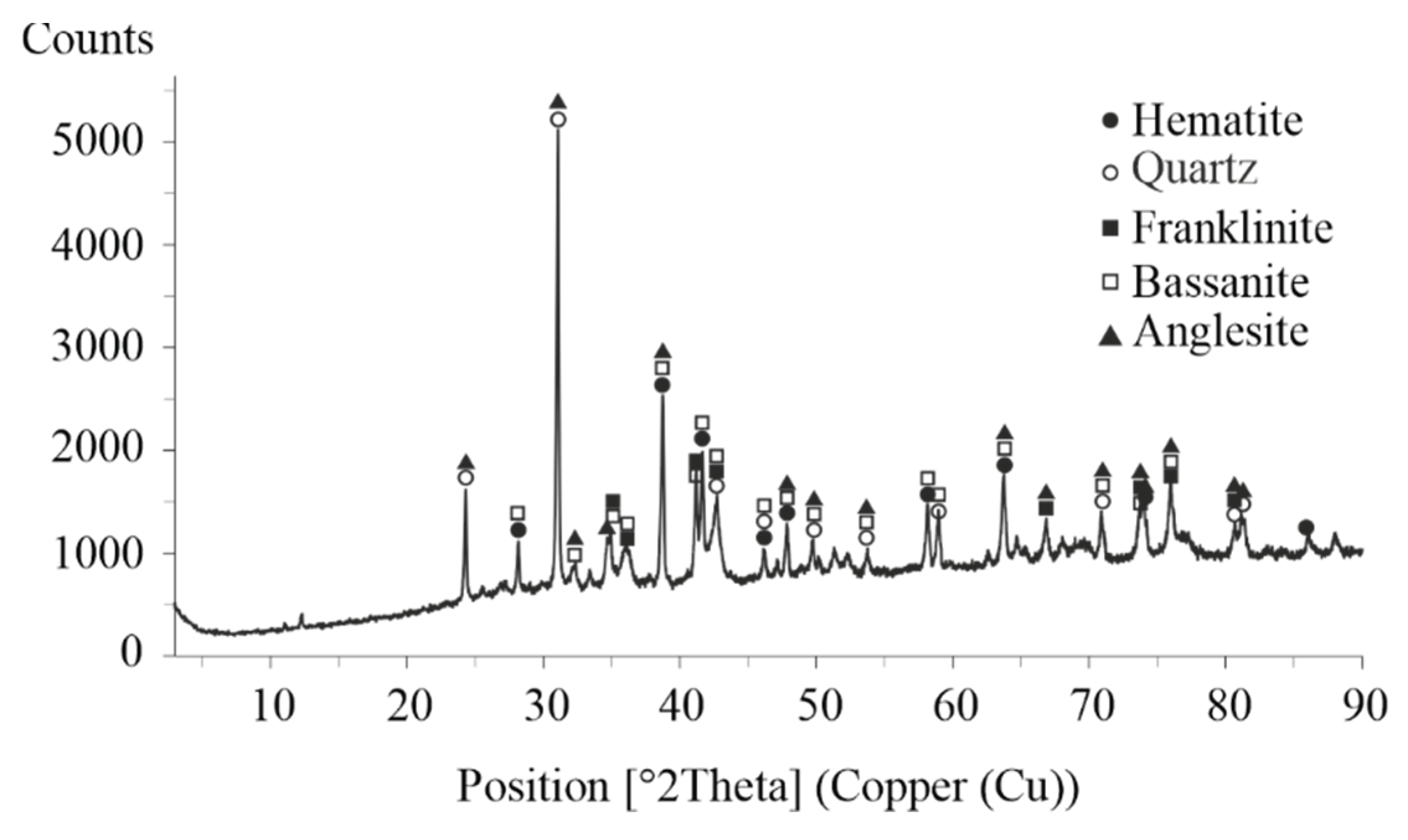
The XRD patterns shown in
Figure 6 reveal that the crystalline phases present in the lead residue after atmospheric leaching include anglesite, bassanite, franklinite, hematite, and sphalerite. In contrast, the lead residue obtained after autoclave leaching contains anglesite, bassanite, sodium jarosite, and hematite.
3.2. Precipitation of Hematite
Hematite (Fe₂O₃) is a widely occurring iron oxide with diverse industrial applications, including iron and steel production, use as a pigment, and in catalytic processes. In conventional zinc industry practice, hematite precipitation involves an initial reduction of ferric ions (Fe³⁺) to ferrous ions (Fe²⁺), followed by neutralization. The resulting ferrous solution is then subjected to oxidative hydrothermal treatment at elevated temperatures (170–200 °C), where oxygen is introduced to oxidize Fe²⁺ back to Fe³⁺, which subsequently hydrolyzes to form hematite [
24,
25].
From a theoretical standpoint, hematite precipitation is governed by the hydrolysis of trivalent iron, as described by the following reaction [
26]:
This reaction leads to acid generation, thereby increasing the acidity of the solution during the precipitation process. Under certain conditions, instead of direct hematite formation, metastable iron hydroxysulfate phases - such as hydronium jarosite and basic ferric sulfate - may precipitate. These phases are pH-dependent and typically transform into hematite upon prolonged hydrothermal treatment or increased temperature, following the sequence [
27]:
In the present study, a method for direct hematite precipitation from ferric sulfate solutions was investigated, omitting the reduction step commonly used in industrial processes. Analysis confirmed that the concentration of ferrous iron (Fe²⁺) remained below 100 mg/L, indicating that the iron present was predominantly in the trivalent form. The ferric sulfate solutions were initially neutralized to pH 1.5 using milk of lime. After removal of the resulting gypsum phase, the solutions underwent hydrothermal treatment to facilitate hematite formation.
The effects of temperature (ranging from 150 to 200 °C) and the addition of hematite seed material were systematically studied to evaluate their influence on the degree of iron precipitation, the morphology and crystallinity of the resulting precipitate, and the incorporation of impurities were analyzed.
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature and Seeds Concentration
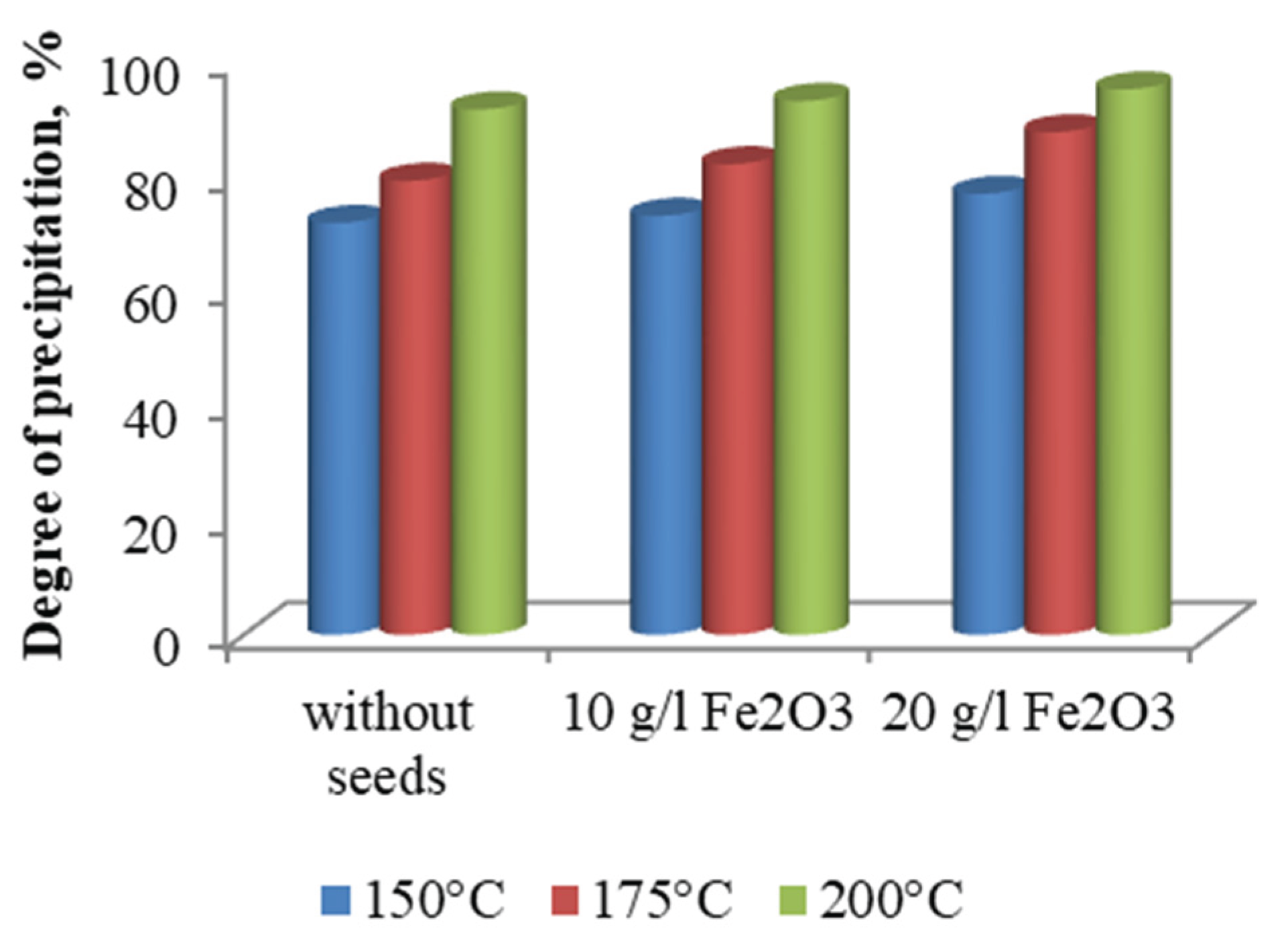
The hydrothermal precipitation of iron was investigated at temperatures of 150, 175, and 200 °C, at a solution pH of 1.5, an initial iron concentration of 17.7g/L, and a reaction time of 2 hours. The experimental results, presented in
Figure 7, indicate a clear trend of increasing iron precipitation efficiency with rising temperature. In the absence of hematite seed material, the precipitation degree increased from 71.75 % at 150 °C to 91.52 % at 200 °C. This enhancement is attributed to the accelerated kinetics of ferric hydrolysis and nucleation processes at elevated temperatures, which favour the formation of well-crystallized hematite phases.
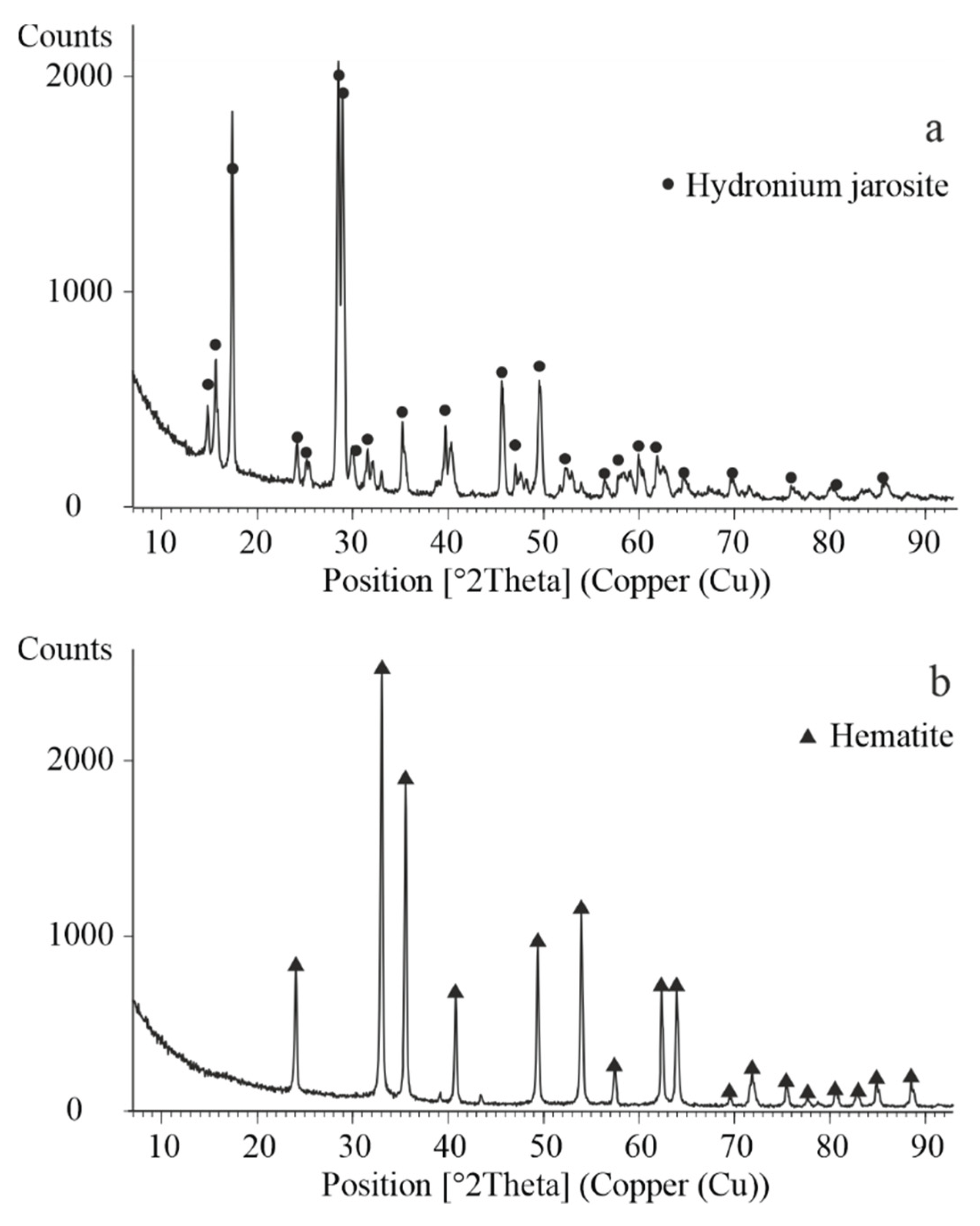
The precipitate obtained at 150 °C was characterized by XRD analysis. As shown in
Figure 8a, the only crystalline phase identified was jarosite, indicating that under these conditions and in the absence of hematite seeds, the hydrolysis of ferric iron favours the formation of intermediate iron hydroxysulfate compounds rather than hematite.
The effect of temperature in the presence of hematite seed material at concentrations of 10 and 20g/L is also illustrated in
Figure 7. The experimental data show that the degree of iron precipitation increased from 76.83 % to 95.02 % as the temperature rose within the studied range, when 20 g/L of hematite seeds were used. Reducing the seed concentration to 10g/L resulted in a decrease in precipitation efficiency by approximately 3–4 %, highlighting the catalytic role of hematite seeds in promoting nucleation and accelerating crystallization processes.
The precipitate formed at a temperature of 200 °C in the presence of 20 g/L hematite seeds was subjected to detailed characterization using XRD analysis (
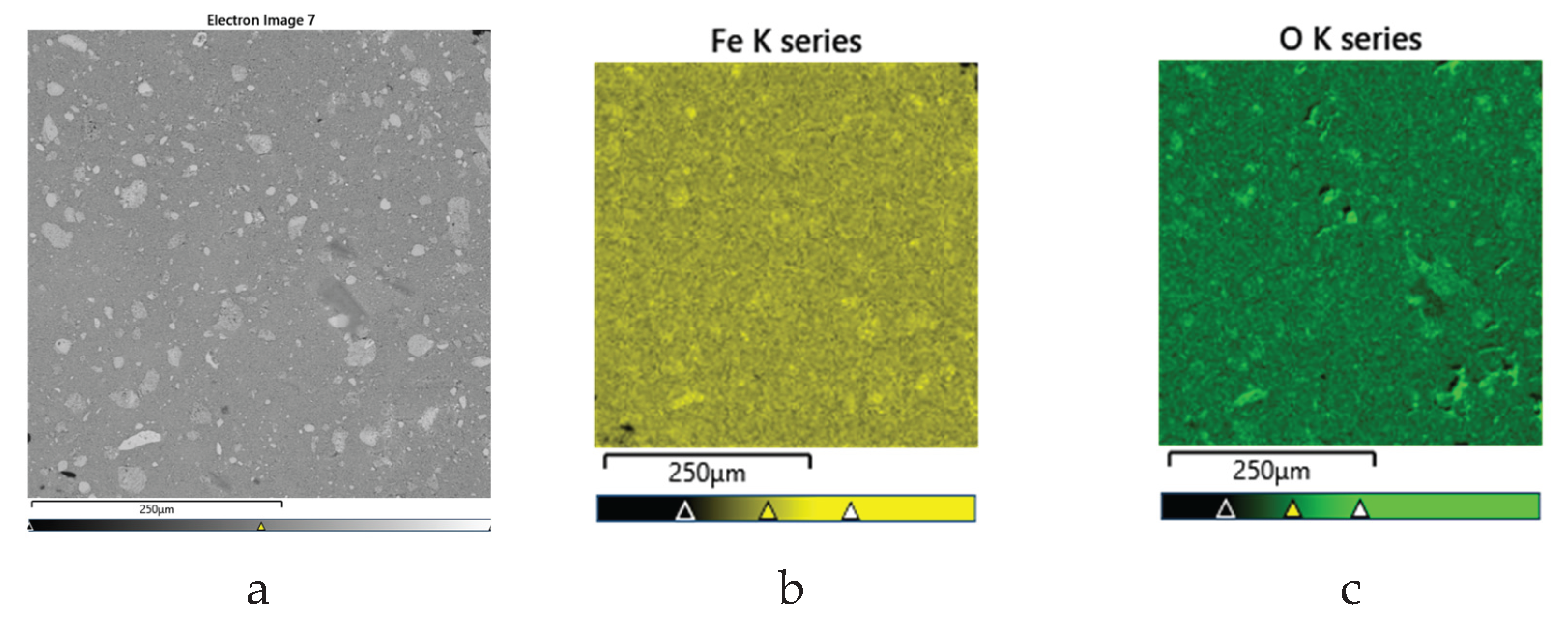
Figure 8b). In addition, the morphology of the precipitate was investigated by SEM. Representative SEM images, along with elemental mapping for iron and oxygen, are shown in
Figure 9, and the corresponding chemical composition of a selected particle is presented in
Table 4.
The results show that iron and oxygen are the predominant elements, confirming the hematite phase. Minor impurities detected include sulfur, silicon, lead, and calcium, present in trace amounts. The low concentration of impurities suggests high purity of the obtained hematite, indicating its potential suitability for commercial applications.
The solution obtained after sulfuric acid leaching of the cake and removal of iron is low in zinc content (17 g/L). It can be recycled for the leaching of subsequent portions of cake until the zinc concentration increases to 150 g/L, at which point it becomes appropriate to purify the solution from impurities, a process traditionally carried out using zinc powder.
The solution, purified from iron and other impurities, is then subjected to electrowinning for zinc recovery. The spent electrolyte resulting from this process is returned to the beginning of the cycle.
3.3. Chloride Leaching of Pb Cake
As indicated by the analyses of the lead cake obtained after sulfuric acid leaching of ZFR, lead is present predominantly in the form of anglesite (PbSO₄), with a concentration of approximately 27 %. According to the literature [
28,
29,
30,
31], the most suitable method for extracting lead from this residue is chloride leaching, during which the following reactions take place:
The influence of several process parameters on lead extraction efficiency was investigated, along with the leaching behavior of other metals such as silver, zinc, iron, and copper.
3.3.1. Effect of NaCl Concentration
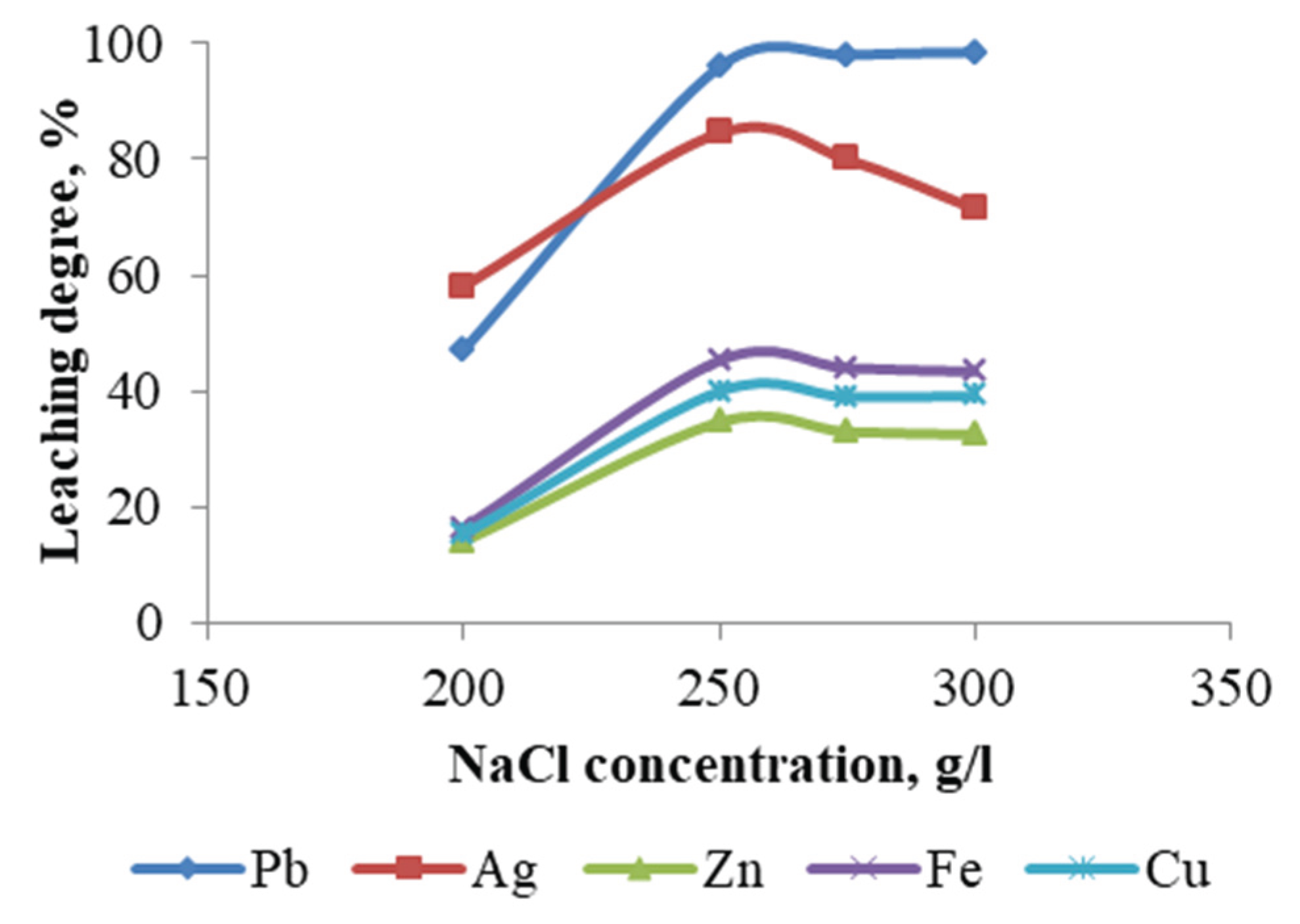
The impact of varying NaCl concentrations (200–300 g/L) on the metal leaching was examined under constant parameters. The constant parameters included HCl concentration (1 M), temperature (60 °C), pulp density (10 %), and duration (1 hour). The recovery of the metals under consideration increased with increasing NaCl concentration above 100 g/L (
Figure 10), with some showing a higher rate of increase (lead and silver) and others a lower rate.
The obtained results indicate that the concentration of chloride ions is a significant parameter influencing lead and silver recovery.
With increasing chloride ion concentration, the insoluble PbCl₂ is converted into soluble complexes such as PbCl₃⁻ and PbCl₄²⁻. The maximum lead extraction efficiency of 98.51 % was achieved at a NaCl concentration of 300 g/L. At the same NaCl concentration, the extraction efficiency of silver was reduced to 71.5 %. The leaching degrees for the remaining metals, including copper, zinc, and iron, were found to be considerably lower.
It should be noted that in some of the experiments, secondary precipitation of Pb was observed when the temperature was lowered or when the pulp was washed during filtration, since the solubility of PbCl2 was significantly reduced when the temperature was lowered and when the solution was diluted.
3.3.2. Effect of HCl Concentration
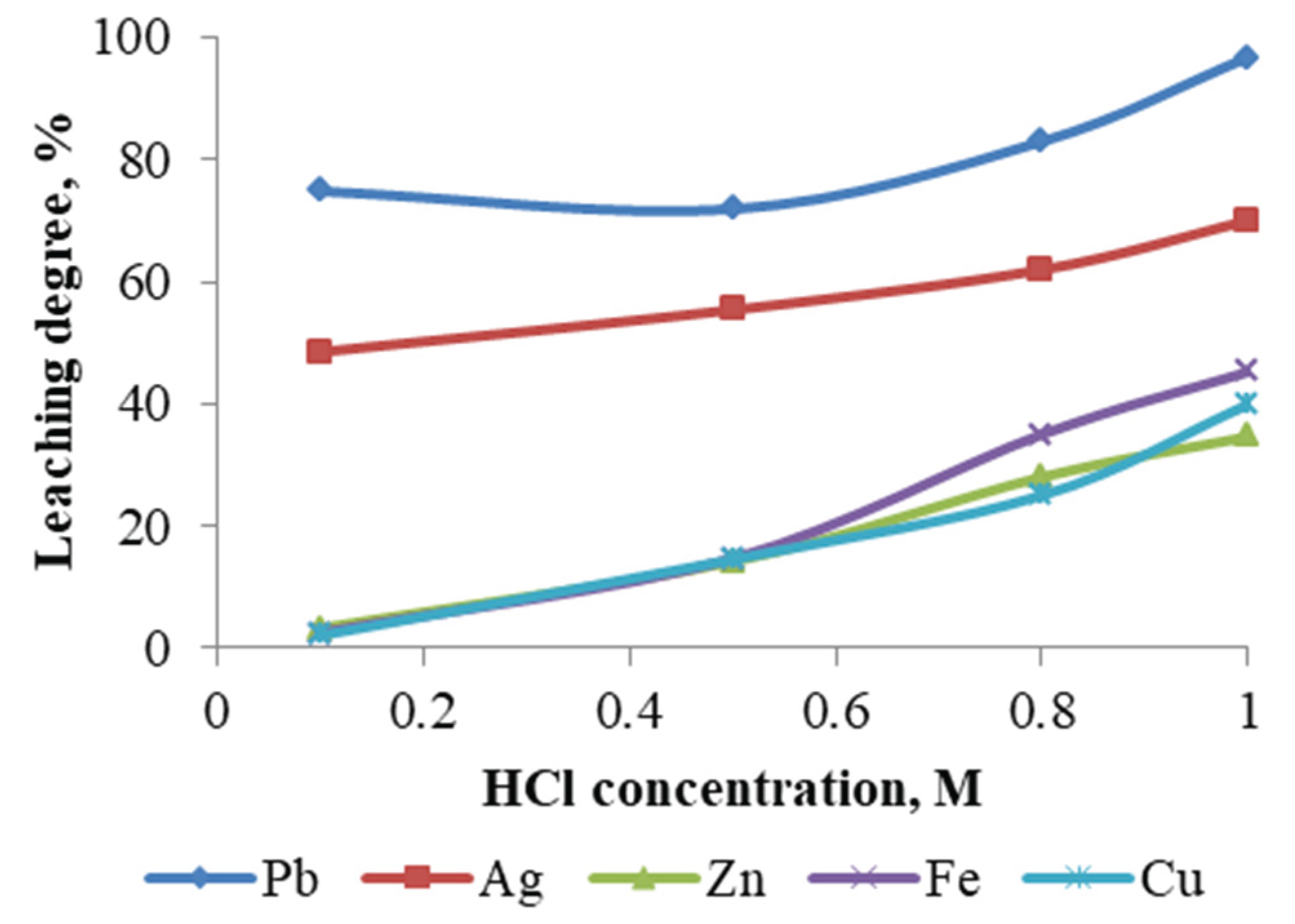
Experiments were conducted to evaluate the effect of HCl concentration, within the range of 0.1–1 M, on the metal leaching efficiency (
Figure 11), while maintaining the following parameters constant: temperature – 60 °C; leaching duration – 1 hour; NaCl concentration – 250 g/L; and pulp density – 10 %.
As the acid concentration is increased, a corresponding increase in the mass reduction rate of the cake is observed. This, in turn, leads to an elevated metal recovery rate. Utilizing a 1M HCl solution, a maximum lead recovery of 96.70 % was attained, accompanied by a 55 % reduction in the initial material mass. It is important to note that increasing the acid concentration above 1M will result in production solutions with very low pH values, which complicates the subsequent extraction process of lead and silver from solution.
3.3.3. Effect of Temperature
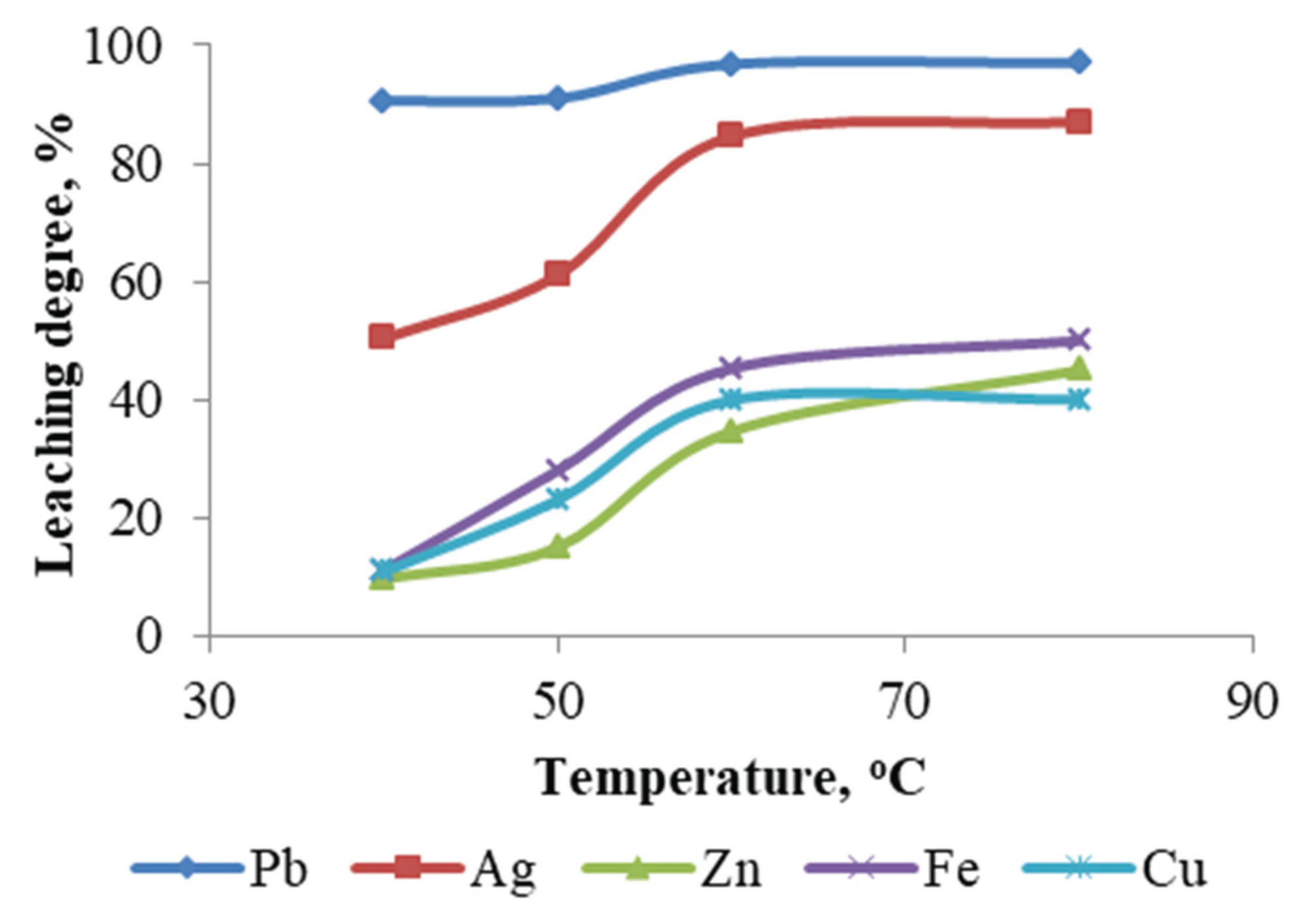
To investigate the effect of temperature on metal leaching efficiency, four experiments were conducted at 40, 50, 60, and 80 °C, while maintaining the following parameters constant: NaCl concentration – 250 g/L; HCl concentration – 1 M; pulp density – 10 %; and leaching duration – 1 hour. The results of these experiments are presented in
Figure 12.
As demonstrated in the figure, the temperature has a significant impact on the solubility of metals, including Ag, Cu, Zn, and Fe. However, the extraction rate of Pb remains relatively constant regardless of temperature variations.
3.3.4. Effect of Time
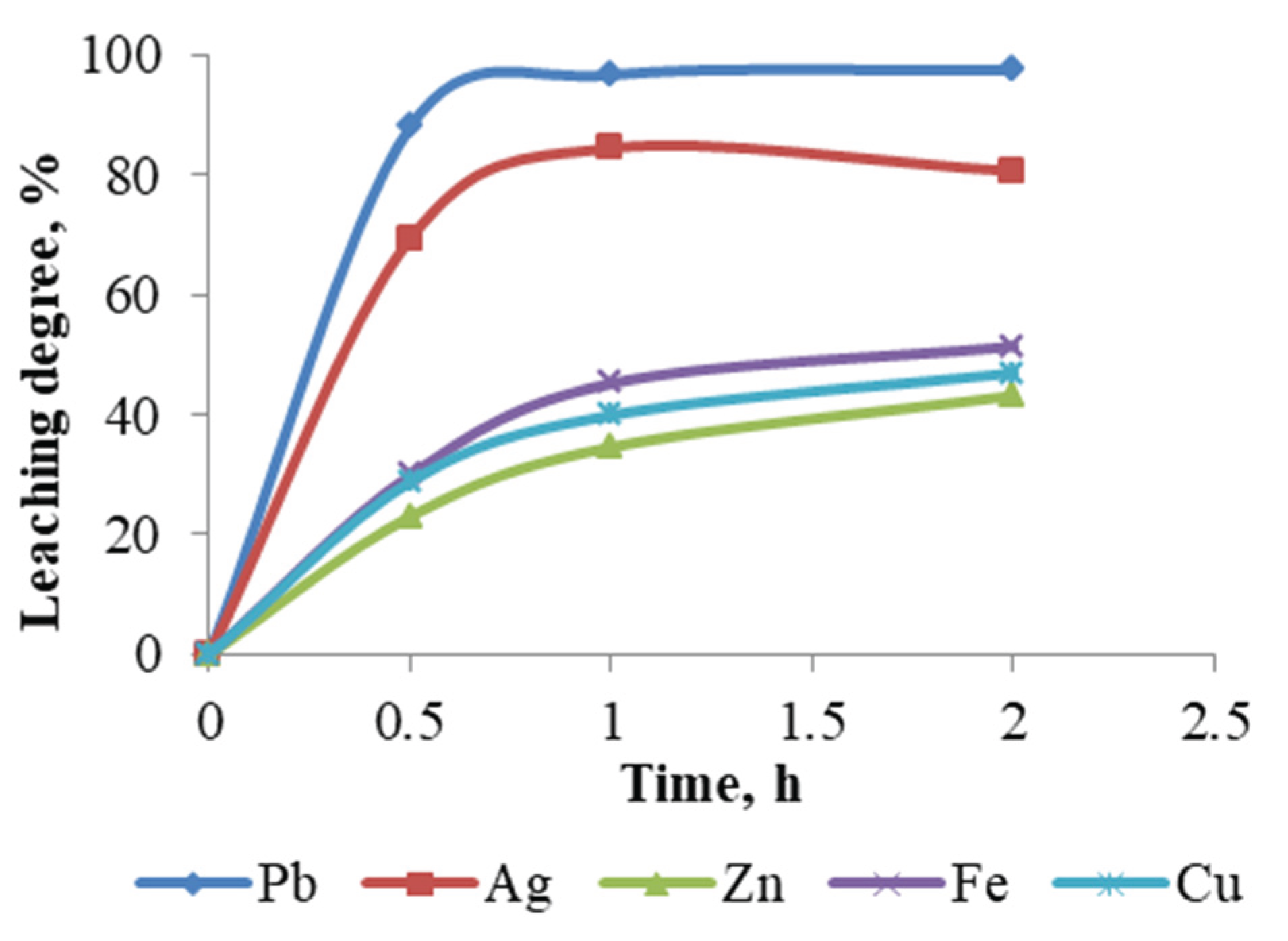
A series of experiments were conducted in which the duration of leaching was varied while maintaining constant conditions. The experimental setup included a sodium chloride concentration of 250 g/L, a hydrochloric acid concentration of 1 M, a pulp density of 10 %, and a temperature of 60 °C.
The experimental results (
Figure 13) demonstrate that during the initial hour, there is significant dissolution of the lead cake, followed by a slight increase in the rate of extraction of copper, iron, and zinc. In contrast, the extraction of lead remains relatively unchanged, while that of silver leaching degree has decreased slightly. The maximum recoveries of lead and silver under these conditions are 97.62 % and 84.55 %, respectively.
3.3.5. Effect of Solid:Liquid Ratio
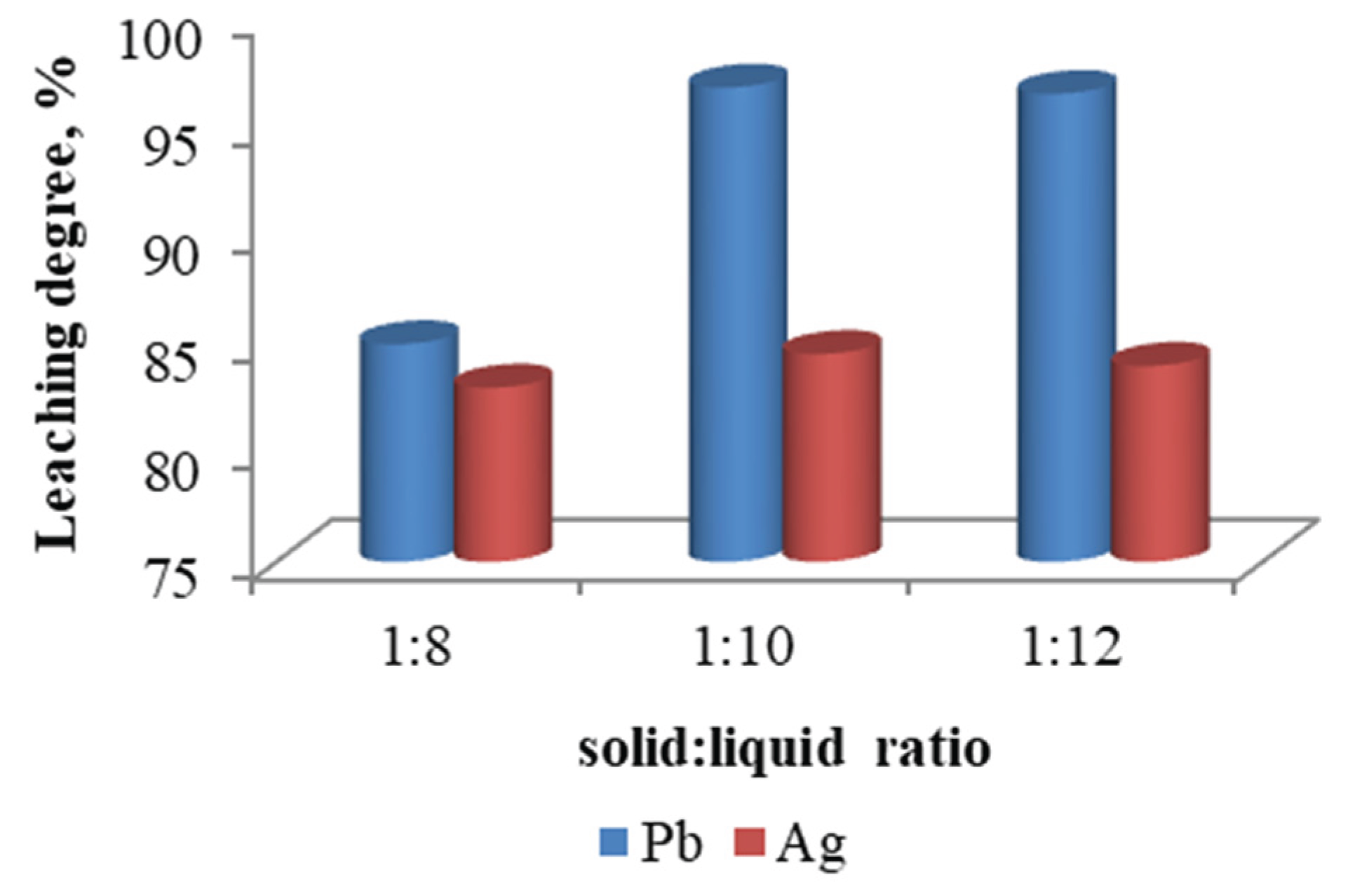
The effect of pulp density on the recovery rate of lead and silver was investigated, and the results are presented in
Figure 14. As the solid-liquid ratio increases above 1:10, the leaching degree of lead and silver remains constant.
In accordance with the conducted experiments and the obtained results, the optimal conditions for chloride leaching of the lead cake can be determined:
- NaCl concentration - 250 g/L
- HCl concentration - 1M;
- Process duration - 1 hour;
- Temperature 60oC.
Consequently, a production solution and insoluble residue with chemical compositions outlined in
Table 5 were obtained at the specified optimal conditions.
It has been demonstrated that, within the established optimal parameters for chloride leaching, a mass reduction of 54.75 % was reached for the initial lead cake. Furthermore, the leaching rates for lead and silver were found to be 96.79 % and 84.55 %, respectively.
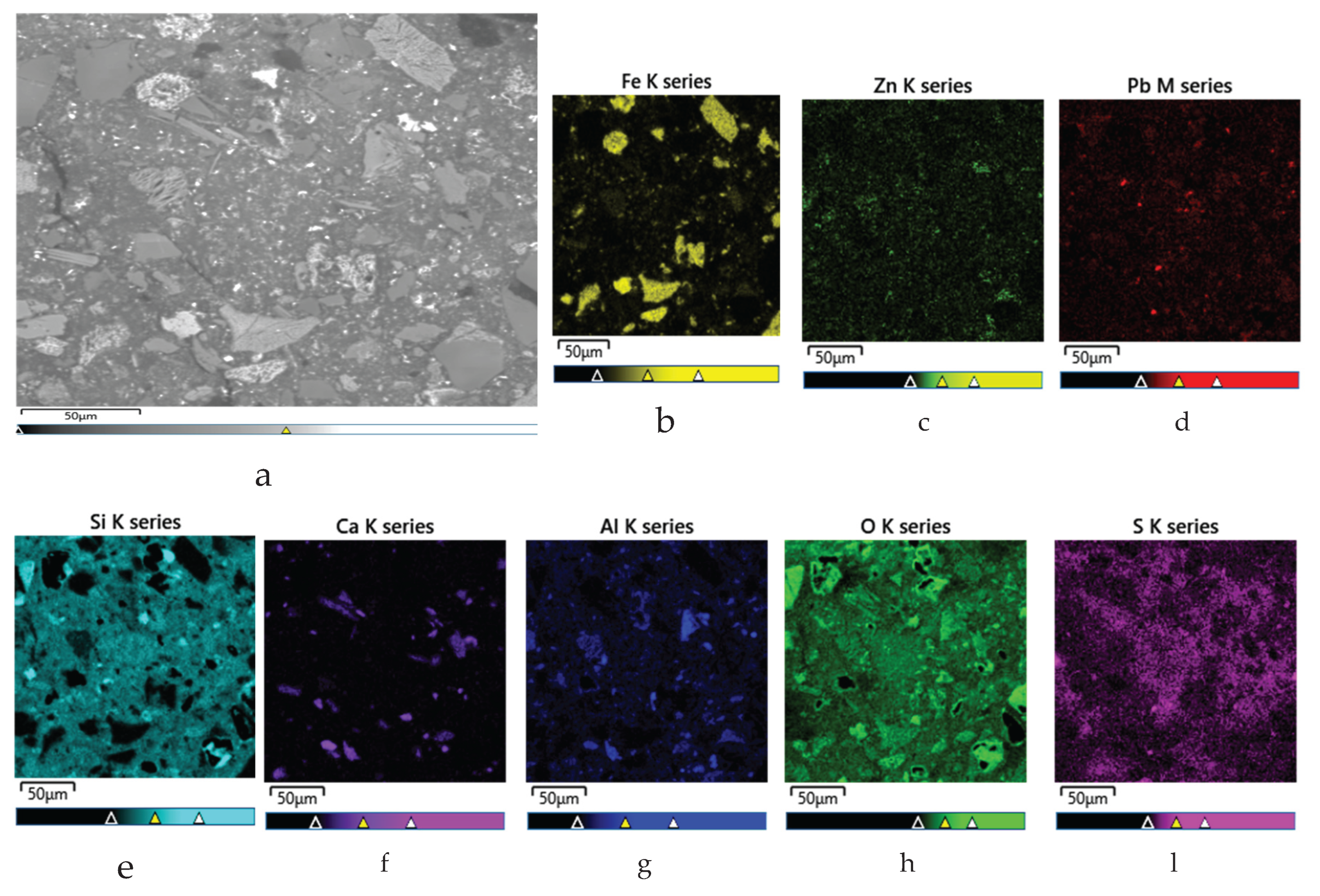
After chloride leaching, the solid residue was examined using SEM–EDS. The SEM image (
Figure 15a) revealed a heterogeneous morphology, with angular grains (likely ferritic phases), fibrous PbCl₂/PbSO₄ structures, and a porous matrix possibly composed of silicate minerals.
EDS analysis (
Table 6) showed that oxygen (44.33 %), silicon (25.57 %), and iron (14.68 %) were dominant, indicating silicate and iron oxide phases.
XRD (
Figure 16) identified the crystalline phases in the residue as: hematite, quartz, franklinite, albite, and anglesite. The detection of PbSO₄ in the solid residue suggests incomplete extraction of lead during the chloride leaching process. This observation is further corroborated by the results of ICP analysis, as presented in
Table 6.
3.3. Cementation of Lead and Silver from Chloride Leachate
Based on previous experience [
32], an effective method for recovering lead and silver from the chloride leachate is the cementation process using zinc powder. This method allows selective precipitation of target metals through redox reactions, exploiting the more negative standard electrode potential of zinc.
In the conducted experiment, the production solution was first neutralized to a pH of 2.4 using a 10 % NaOH solution at room temperature. Cementation was then performed by adding zinc powder in a 200 % stoichiometric excess relative to the amount required to reduce all soluble lead and silver. The reaction proceeded for 1 hour under constant stirring.
The chemical composition of the resulting cementation precipitate is summarized in
Table 7, confirming efficient selective recovery of lead and silver, with lead content reaching 84.75 % and silver 0.1740 %. The low levels of residual zinc, iron, and copper indicate effective separation and minimal contamination.
3.4. Hydrometallurgical Process Scheme for ZFR Treatment
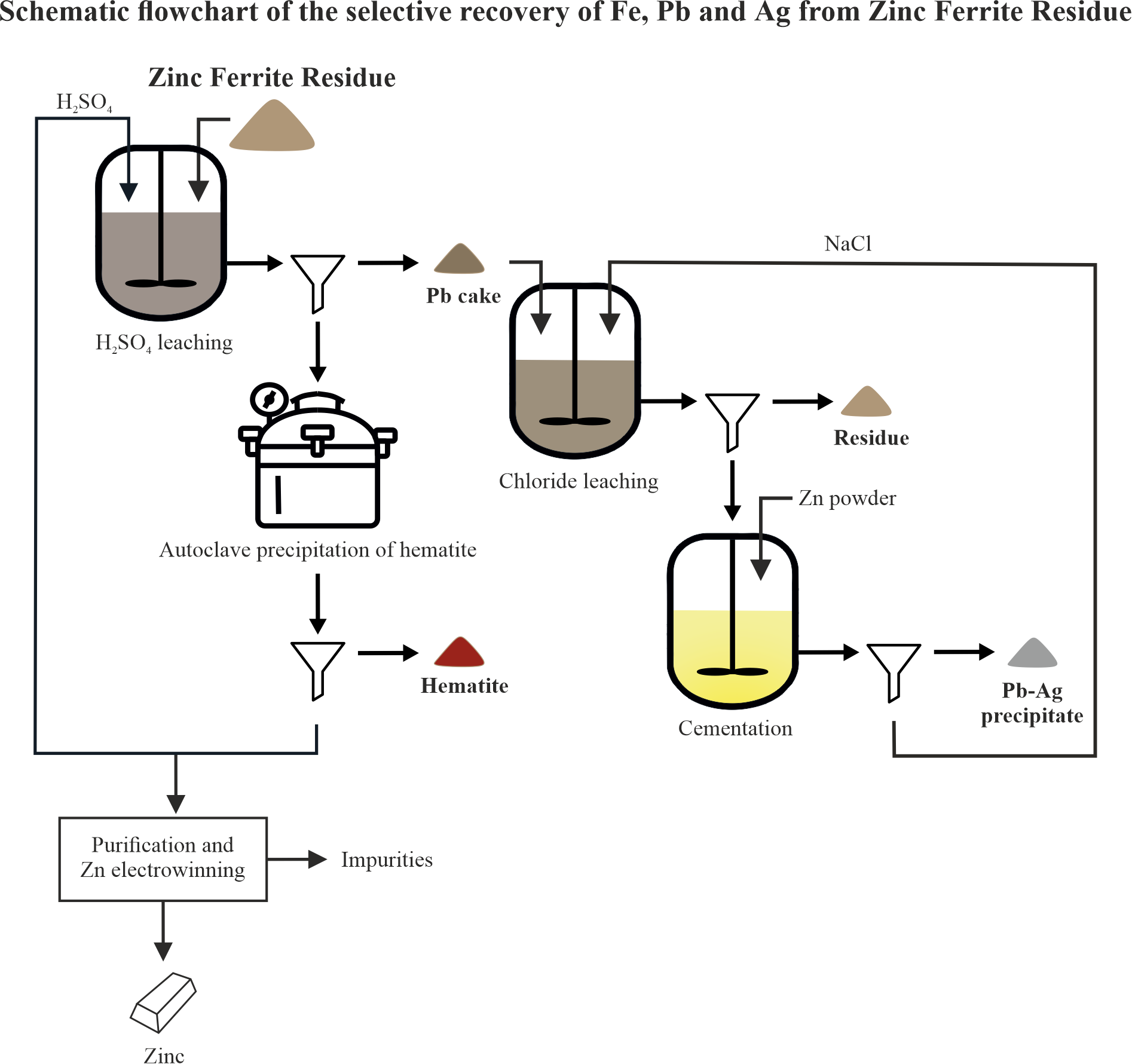
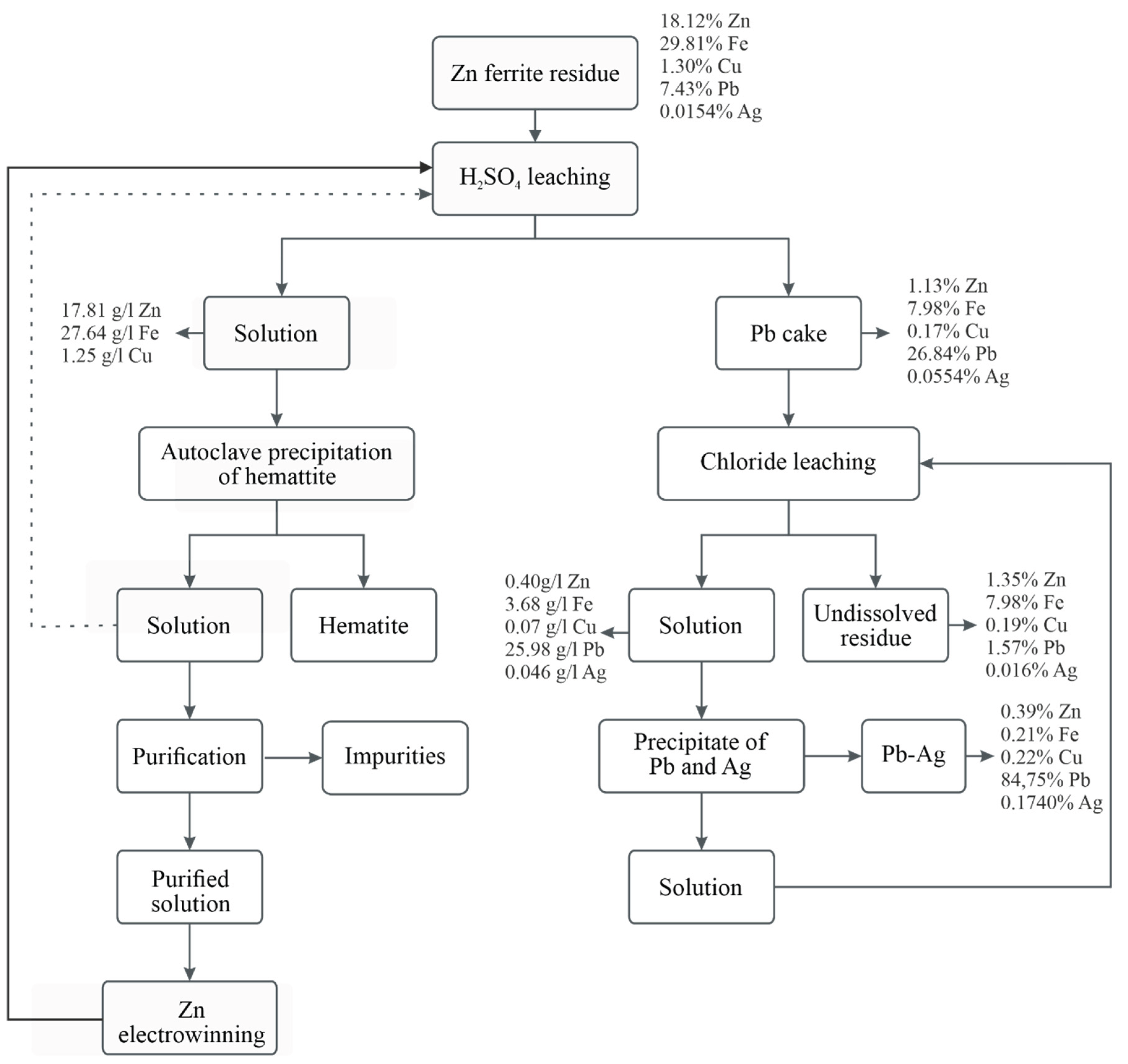
The
Figure 17 presents the overall technological scheme for the hydrometallurgical treatment of ZFR. It visualizes the sequence of the main stages through which the primary valuable metals - zinc, iron, lead, and silver - are extracted and separated. The entire scheme demonstrates an efficient, stepwise approach for the recovery of valuable components from ZFR. It is characterized by selectivity of the processes, good separation of the fractions, and potential for application under industrial conditions.
It is important to note that the final insoluble residue obtained after chloride leaching still contains traces of non-ferrous and precious metals, particularly lead, rendering it a hazardous material. This underscores the need for further research focused on either enhanced metal recovery or the safe disposal/stabilization of the residue to meet environmental regulations.
3. Conclusions
Sulfuric acid leaching under atmospheric conditions (90 °C, 200 g/L H₂SO₄) provides a high extraction degree of zinc (98.3 %), copper (96.4 %), and iron (92.72 %) from the ZFR, with temperature and acid concentration identified as determining factors for process efficiency.
Autoclave processing of the production solution leads to effective precipitation of iron in the form of hematite, especially when hematite seeds are used. The resulting product has high purity and low impurity content.
Chloride leaching of the lead cake shows that under optimal conditions, high extraction rates of lead (96.79 %) and silver (84.55 %) are achieved, with a reduction in residue mass by about 55 %.
Cementation with zinc powder is an effective method for precipitating lead and silver from the chloride solution. Yields of 98.72 % for Pb and 97.27 % for Ag were achieved, and the precipitate contains 84.75 % Pb and silver 0.174 % Ag.
Despite the efficient extraction of the target metals, the residual material after chloride leaching still contains non-ferrous and precious metals, most likely embedded in stable mineral phases. The presence of lead in the residue classifies it as hazardous waste.
The proposed scheme is technologically justified, demonstrates high selectivity, and can be implemented for treating ZFR. Further development is needed for effective treatment of the final insoluble residue.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization P.I. and B.L.; methodology P.I. and B.L.; software P.I., B.L., N.K. and V.S.; validation P.I. and B.L.; formal analysis N.K.; investigation P.I., B.L., N.K., V.S.; resources P.I. and B.L.; data curation P.I. and B.L.; writing - original draft preparation P.I., B.L. and V.S; writing - review and editing P.I., B.L. and V.S.; visualization P.I. and B.L.; supervision P.I. and B.L.; project administration P.I.; funding acquisition P.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Union Next Generation EU, through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project №BG-RRP-2.004-0002, “BiOrgaMCT”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not relevant
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting reported results have been included in the manuscript in the form of graphs.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support from KCM for the samples of ZFR.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ZFR |
Zinc Ferrite Residue |
| SEM |
Scanning electron microscope |
| EDS |
Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| ICP-OES |
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy |
| XRD |
X-ray diffraction |
References
- Kozlov, P. The Waelz Process; Ore and Metals Publishing House: Moscow, Russia, 2003; pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Berdiyarov, B.T. Analysis of the possibility of increasing the degree of zinc Waelz and reducing metal losses during Waelz. Tech. Sci. Innov. 2021, 2021, Article 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoychev, S.; Minchev, E.; Kyurkchiev, A.; Radonov, G. Technologies for treatment of zinc-containing waste from metallurgy in KCM AD. In PbZn 2020: 9th International Symposium on Lead and Zinc Processing; Siegmund, A., Alam, S., Grogan, J., Kerney, U., Shibata, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinin, A.; Nikolic, M.; Kleppinger, R.; Oeters, F. Outotec® Ausmelt technology for treating zinc residues. World Metall.–Erzmetall 2013, 66, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, S.; Reuter, M.A.; Baxter, R.; Kaye, A. Ausmelt technology for lead and zinc processing. In Proceedings of the Lead and Zinc 2008 Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 25–27 February 2008; The Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, J.; Reuter, M.A.; Matusewicz, R.; Hughes, S.; Piret, N. Top submerged lance direct zinc smelting. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chai, L.; Peng, B.; Li, M.; Peng, N.; Hou, D. A novel method to recover zinc and iron from zinc leaching residue. Miner. Eng. 2014, 55, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Peng, B.; Chai, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, N.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, D. High-zinc recovery from residues by sulfate roasting and water leaching. JOM 2015, 67, 2333–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Peng, B.; Liang, Y.; Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Hu, M. Recovery of valuable metals from zinc leaching residue by sulfate roasting and water leaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, B.; Min, X.; Hu, M.; Peng, N.; Yuan, Y. Study on separating of zinc and iron from zinc leaching residues by roasting with ammonium sulphate. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Seyrankaya, A.; Çoçen, İ. Hydrometallurgical evaluation of zinc leach plant residue. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 4565–4570. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, M.D.; Altundoğan, H.S.; Tümen, F. Recovery of zinc and lead from zinc plant residue. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 75, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, C.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, M. Reductive leaching of indium-bearing zinc residue in sulfuric acid using sphalerite concentrate as reductant. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z. Reductive leaching of indium from zinc-leached residue using galena as reductant. Miner. Eng. 2021, 163, 106777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, L.P.; Jing, T.L.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhang, T.A. Reductive leaching of indium-bearing zinc ferrite in sulfuric acid using sulfur dioxide as a reductant. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Min, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Fei, J.; Li, Y. Enhanced cadmium extraction from zinc neutral leaching residue using sulfur dioxide. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, R.; Rashchi, F.; Vahidi, E. Recovery of zinc from leach residues with minimum iron dissolution using oxidative leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 188, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silwamba, M.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N.; Tabelin, C.B.; Hashizume, R.; Fukushima, T.; Park, I.; Jeon, S.; Igarashi, T.; Sato, T.; et al. Alkaline leaching and concurrent cementation of dissolved Pb and Zn from zinc plant leach residues. Minerals 2022, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, M.; Yurten, M. Kinetics of Pb and Zn leaching from zinc plant residue by sodium hydroxide. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2015, 15, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, P.; Pourghahramani, P. Selective mechanochemical alkaline leaching of zinc from zinc plant residue. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, K.; Ma, H.; Qin, S. The behavior of zinc and iron in neutralized residue during pressure leaching. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, C. Study on the improvement of the zinc pressure leaching process. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethurajan, M.; Lens, P.N.L.; Rene, E.R.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Huguenot, D.; Horn, H.A.; Figueiredo, L.H.A.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Bioleaching and selective biorecovery of zinc from zinc metallurgical leach residues from the Três Marias zinc plant (Minas Gerais, Brazil). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Zapata, J.; Padilla, R. Effect of variables on the quality of hematite precipitated from sulfate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozberk, E.; Collins, M.J.; Makwana, M.; Masters, I.M.; Pulenberg, R.; Bahl, W. Zinc pressure leaching at the Ruhr-Zink refinery. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 39, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wei, C.; Yi, S.; Fan, G.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Li, M. Formation of iron hydroxysulphate phases in the hematite process by hydrolysis of ferric sulphate. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C. Production of hematite in acidic zinc sulphate media. Can. J. Mater. Eng. 2002, 1–10, p–36. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, R.; Mohanan, P.K.; Swarnkar, S.R. Hydrometallurgical processing of lead-bearing materials for the recovery of lead and silver as lead concentrate and lead metal. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 58, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, F.; Moradkhani, D.; Safarzadeh, M.S.; Rashchi, F. Brine leaching of lead-bearing zinc plant residues: Process optimization using orthogonal array design methodology. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedizadeh, M.; Azizi, A.; Bahri, Z. Recycling lead from a zinc plant residue (ZPR) using brine leaching and cementation with aluminum powder. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42121–42134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, B.; Moghaddam, J. Chloride leaching of lead and silver from refractory zinc plant residue. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2011, 15, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Kazakova, N.; Lucheva, B.; Iliev, P. A study on the cementation process of non-ferrous metals from a brine leaching solution. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2020, 55, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Effect of temperature.
Figure 1.
Effect of temperature.
Figure 2.
Effect of sulfuric acid concentration.
Figure 2.
Effect of sulfuric acid concentration.
Figure 3.
Effect of the Solid-to-Liquid Ratio.
Figure 3.
Effect of the Solid-to-Liquid Ratio.
Figure 4.
Effect of Reaction Time.
Figure 4.
Effect of Reaction Time.
Figure 5.
SEM micrographs of the Pb cake. (a) - atmospheric leaching, (b) autoclave leaching.
Figure 5.
SEM micrographs of the Pb cake. (a) - atmospheric leaching, (b) autoclave leaching.
Figure 6.
XRD pattern of the lead cake, obtained at atmospheric and autoclave leaching of ZFR. (a) – atmospheric leaching, (b) – autoclave leaching.
Figure 6.
XRD pattern of the lead cake, obtained at atmospheric and autoclave leaching of ZFR. (a) – atmospheric leaching, (b) – autoclave leaching.
Figure 7.
Effect of temperature and seeds dosage on the iron precipitation degree.
Figure 7.
Effect of temperature and seeds dosage on the iron precipitation degree.
Figure 8.
XRD pattern of the obtained precipitate. (а) - without seeds, (b) in the presence of 20 g/L seeds.
Figure 8.
XRD pattern of the obtained precipitate. (а) - without seeds, (b) in the presence of 20 g/L seeds.
Figure 9.
SEM micrographs and EDS element mapping of hematite. (a) SEM image; (b) Fe distribution; (c) O distribution.
Figure 9.
SEM micrographs and EDS element mapping of hematite. (a) SEM image; (b) Fe distribution; (c) O distribution.
Figure 10.
Metal leaching degree depending on NaCl concentration.
Figure 10.
Metal leaching degree depending on NaCl concentration.
Figure 11.
Metal leaching degree depending on HCl concentration.
Figure 11.
Metal leaching degree depending on HCl concentration.
Figure 12.
Metal leaching degree depending on temperature.
Figure 12.
Metal leaching degree depending on temperature.
Figure 13.
Metal leaching degree depending on time.
Figure 13.
Metal leaching degree depending on time.
Figure 14.
Metal leaching degree depending on solid:liquid ratio.
Figure 14.
Metal leaching degree depending on solid:liquid ratio.
Figure 15.
SEM micrograph of insoluble residue, obtained at chloride leaching of Pb cake (a) and EDS elemental mapping in the insoluble residue after chloride leaching of Pb cake (b) –Fe; (c) – Zn; (d) – Pb; (e)- Si; (f) – Ca; (g) – Al; (h) – O; (l) - S.
Figure 15.
SEM micrograph of insoluble residue, obtained at chloride leaching of Pb cake (a) and EDS elemental mapping in the insoluble residue after chloride leaching of Pb cake (b) –Fe; (c) – Zn; (d) – Pb; (e)- Si; (f) – Ca; (g) – Al; (h) – O; (l) - S.
Figure 16.
XRD pattern of the insolble residue, obtained at chloride leaching of Pb cake.
Figure 16.
XRD pattern of the insolble residue, obtained at chloride leaching of Pb cake.
Figure 17.
Hydrometallurgical process flowchart for the treatment of ZFR.
Figure 17.
Hydrometallurgical process flowchart for the treatment of ZFR.
Table 1.
Main chemical composition of ZFR (mass fraction, %).
Table 1.
Main chemical composition of ZFR (mass fraction, %).
| Zn |
Fe |
Cu |
Pb |
Ag |
Mn |
S |
Si |
Ca |
Al |
| 18.12 |
29.81 |
1.30 |
7.43 |
0.0154 |
1.84 |
3.52 |
3.27 |
2.21 |
1.11 |
Table 2.
Chemical composition of the Pb cake by ICP-OES (mass %).
Table 2.
Chemical composition of the Pb cake by ICP-OES (mass %).
| Type of leaching |
Products |
Chemical composition, mass % |
| |
Fe |
Zn |
Pb |
Cu |
Ag |
| Atmospheric leaching |
Solution g/L |
27.64 |
17.81 |
- |
1.25 |
- |
| Insoluble residue % |
7.98 |
1.13 |
26.84 |
0.17 |
0.0554 |
| Autoclave leaching |
Solution g/L |
27.59 |
17.76 |
- |
1.26 |
- |
| Insoluble residue % |
9.12 |
1.47 |
30.53 |
0.168 |
0.0634 |
Table 3.
EDS Analysis of Pb cake.
Table 3.
EDS Analysis of Pb cake.
| Element |
Weight %
(Atmospheric leaching) |
Weight %
(Autoclave leaching) |
| Pb |
29.48 |
25.77 |
| Fe |
7.51 |
9.78 |
| Zn |
2.03 |
1.86 |
| S |
5.46 |
5.42 |
| O |
38.59 |
40.78 |
| Si |
12.42 |
11.15 |
| Al |
1.32 |
1.47 |
| Ca |
0.43 |
1.22 |
| K |
0.00 |
0.66 |
| Na |
0.32 |
0.63 |
| Mg |
0.12 |
0.58 |
| Mn |
1.99 |
0.36 |
| Cu |
0.33 |
0.33 |
Table 4.
EDS Analysis of hematite.
Table 4.
EDS Analysis of hematite.
| Element |
Weight % |
| Fe |
75.28 |
| O |
23.28 |
| S |
0.90 |
| Si |
0.29 |
| Pb |
0.21 |
| Ca |
0.04 |
Table 5.
Chemical composition of the chloride leaching products (mass fraction, %).
Table 5.
Chemical composition of the chloride leaching products (mass fraction, %).
| |
Zn |
Fe |
Cu |
Pb |
Ag |
| Insoluble residue, % |
1.35 |
7.98 |
0.19 |
1.57 |
0.016 |
| Solution, g/L |
0.40 |
3.61 |
0.07 |
25.98 |
0.046 |
Table 6.
EDS Analysis of the residue after chloride leaching.
Table 6.
EDS Analysis of the residue after chloride leaching.
| Element |
Weight % |
| Fe |
15.70 |
| Pb |
1.50 |
| Zn |
4.82 |
| S |
1.67 |
| Si |
25.57 |
| Al |
3.58 |
| O |
44.33 |
| Ti |
1.02 |
| Mg |
0.87 |
| Ca |
0.76 |
| Na |
0.19 |
Table 7.
Chemical composition of the cementation precipitate, (mass fraction, %).
Table 7.
Chemical composition of the cementation precipitate, (mass fraction, %).
| Zn |
Fe |
Cu |
Pb |
Ag |
| 0.39 |
0.21 |
0.22 |
84.75 |
0.1740 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).