Submitted:
30 June 2025
Posted:
01 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- How do specific AI technologies (e.g., adaptive learning systems, AI-powered analytics, intelligent tutoring systems) contribute to advancing SDGs, particularly SDG 4 (Quality Education) and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities), within higher education?
- What are the primary challenges (ethical, infrastructural, cultural) and opportunities identified in the literature concerning the integration and governance of AI tools to effectively achieve sustainability objectives in higher education institutions?
- To what extent do AI-driven interventions reported in existing research promote measurable improvements in sustainability literacy, awareness, critical thinking, and actionable sustainability outcomes among higher education stakeholders, and what practical implications emerge from these findings?
Theoretical Framework
Methodology
Search String
| Topic | Search terms |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | ("artificial intelligence" OR "AI" OR "machine learning" OR "deep learning" OR "intelligent systems" OR "educational technology" OR "adaptive learning" OR "intelligent tutoring systems" OR "learning analytics" OR "chatbots" OR "generative AI") |
| AND Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) |
("sustainable development goals" OR "SDGs" OR "sustainability" OR "quality education" OR "reduced inequalities" OR "sustainable education" OR "equity in education" OR "gender equality" OR "innovation and infrastructure" OR "social justice" OR "inclusive education" |
| AND Education Level |
AND "higher education" OR "universities" OR "colleges" OR "tertiary education" OR "postsecondary education" OR "higher educational institutions" OR "academic institutions" |
Screening and Selection
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Interrater Reliability
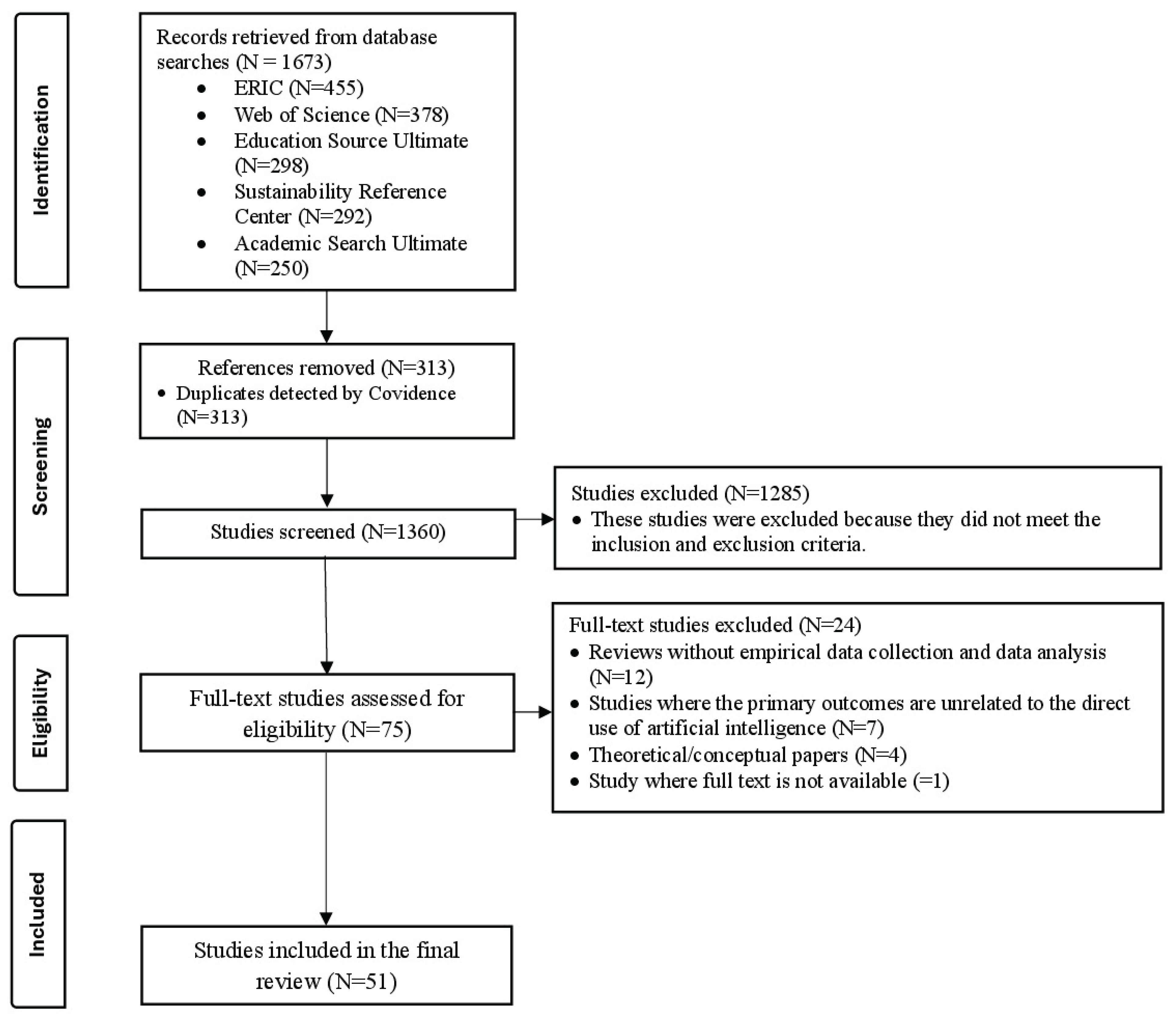
Data Extraction
Thematic Data Synthesis
Findings
- How do specific AI technologies contribute to advancing SDGs, particularly SDG 4 and SDG 10 within HEIs?
- AI-Driven Prediction and Analytics: Machine learning (ML) models and AI-based analytics tools are increasingly being used to predict student performance, identify dropout risks, and analyze factors influencing academic success (Agostini & Picasso, 2023; Albahl, 2025; Buenaño-Fernández et al., 2019; Villegas-Ch. et al., 2023; Soobramoney & Singh, 2019; Shilbayeh & Abonamah, 2021; Albahli, 2025; Jokhan et al., 2022).
- Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) and Adaptive Learning: ITS and adaptive instructional systems, which frequently leverage AI techniques, play a crucial role in personalizing instruction to meet individual student needs (Katsamakas et al., 2024; Savec & Jedrinovic, 2024; Tarisayi & Manhibi, 2024).
- AI in Curriculum Management: AI tools present promising opportunities to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of curriculum management in HEIs. These tools help institutions navigate complex challenges such as rapid technological advancement, evolving labor market demands, and increasing student diversity (Naldi et al., 2024; Airaj, 2022; Chiang, 2021; Lengyel et al., 2024).
- Support for Teachers: AI technologies offer teachers more efficient tools for focused and effective instruction (Niu et al., 2024). By automating aspects of traditional assessment practices, these tools reduce the manual workload and make large-scale evaluation more manageable. For example, AI can handle repetitive tasks such as grammar correction, freeing teachers to concentrate on higher-order instruction and creative pedagogical strategies (Agostini & Picasso, 2023; Iatrellis et al., 2024).
- Enhanced Accessibility: AI makes learning more inclusive; multimodal language models provide adaptive interfaces, speech-to-text, and multilingual support, aiding students with disabilities or diverse language backgrounds (Lin et al., 2024; Al-Dokhny et al., 2024).
- Support for Specific Groups: AI technologies are increasingly used to promote inclusive education, particularly for minority and underserved groups (Kalnina et al., 2024). In special education settings, tools like ChatGPT have proven valuable for supporting students' individualized learning and developmental needs, thereby contributing to the goals of SDG 10 (Ibrahim & Ajlouni, 2024).
- Addressing Equity: AI presents both opportunities and risks for promoting equity in HEIs. Stakeholder perspectives are vital for closing gaps (Zipf et al., 2025). AI-based distance learning can expand access in underserved regions and promote digital equity by sharing educational data more broadly (Savec & Jedrinovic, 2024)..
- What are the primary challenges and opportunities identified in the literature concerning the integration and governance of AI tools to effectively achieve sustainability objectives in HEIs?
- Ethical Concerns: Ethical challenges frequently arise in discussions about AI in HEIs. These include "bias in training data, which may focus disproportionately on certain demographics" (Lin et al., 2024, p.15) and "data privacy concerns" (Tarisayi & Manhibi, 2024, p.87). Academic integrity is a major concern, with increasing risks that students may plagiarize content or cheat on assignments and assessments using AI tools (Ballesteros et al., 2024; Espinoza Vidaurre et al., 2024; Perkins et al., 2024). These issues have sparked debates about restricting the use of generative AI in education.
- Infrastructural and Resource Constraints: Effective AI implementation demands "substantial investment in infrastructure and partnerships" (Tarisayi & Manhibi, 2024, p.92). Key challenges include securing computational power, memory capacity, and access to advanced software, all of which remain scarce in many regions. The high cost of deploying these systems, especially in resource-constrained environments, is a persistent barrier (Tarisayi & Manhibi, 2024).
- Cultural and Organizational Barriers: There can be "limited awareness and interest in AI usage despite the activeness of the student community" among facilitators and lecturers (Sendawula et al., 2024, p.176). There is also a "significant demand for support and training to help professors adapt sustainably to AI technologies" (Acosta-Enriquez et al., 2025, p.4). A shift in perception among educational stakeholders towards AI is needed, calling for "de-stigmatization of its use" (Lin et al., 2024).
- Opportunities – Infrastructure Partnerships
- Enhanced Learning and Teaching: AI can transform teaching by supporting instructors in designing courses, creating materials, delivering instruction, and assessing learning more creatively (Katsamakas et al., 2024; Conrad et al., 2024; Jiang, 2024). It also enables personalized learning, enhancing student engagement and motivation (Chadha, 2024; Man et al., 2023).
- Skill Development: AI education can promote students' understanding of innovative technologies by helping them apply "computational thinking" to solve problems, foster creativity and innovative ideas, and engage with ethical considerations in AI use (Kalnina et al., 2024, p. 11).
- Innovation and New Approaches: AI integration is propelling HEIs toward digital transformation and smart education (Buenaño-Fernández et al., 2019; Okulich-Kazarin et al., 2024). It facilitates data-driven strategies that enhance learning outcomes and optimize resource use (Albahl, 2025). Moreover, AI supports the development of innovative business models tailored to the needs of HEIs (Katsamakas et al., 2024).
- Preparation for the Future: Universities play a vital role in preparing students for an AI-driven workplace by equipping them with the skills to use AI responsibly, ethically, and effectively. This includes understanding AI’s role in professional settings, integrating it into workflows, and evaluating its effectiveness (Asad et al., 2024; Clark et al., 2024; Kalnina et al., 2024; Komatina et al., 2024).
- Effective integration requires clear guidelines (Adžić et al., 2024; Lin et al., 2024; Santiago-Ruiz, 2023) and regulatory frameworks (Espinoza Vidaurre et al., 2024; Chilicaus, 2024) defining appropriate student conduct and governing AI use.
- Universities should provide clear AI training to facilitators to bridge the knowledge gap (Sendawula et al., 2024).
- Policymakers should develop policies to regulate AI usage (Sendawula et al., 2024).
- Establishing ethical practices in AI ensures fairness (Mahade et al., 2025).
- Institutions need to develop educational policies that promote AI use and ensure its ethical implementation (Espinoza Vidaurre et al., 2024).
- Sustainability Literacy and Awareness: Integrating AI into education aligns with the broader goals of sustainable development, fostering awareness and action among students (Albahl, 2025; Bakry et al., 2024; Black & Tomlinson, 2025; Daniela et al., 2018; Vázquez-Verdera et al., 2021). AI can reshape how learners interact with curriculum content, including topics related to the SDGs (Prior et al., 2024; Ronaghi & Ronaghi, 2024). Tools such as ChatGPT can personalize learning and enable students to "engage more deeply with sustainability concerns" (Boustani et al., 2024, p.16).
- Critical Thinking: AI tools can promote critical thinking and problem-solving, which are "important for resolving sustainability concerns" (Boustani et al., 2024, p.16). An effective learning environment supported by AI fosters “critical engagement that encourages students’ active, reflective, and informed participation in the learning process” (Lin et al., 2024, p.14). On the other hand, some researchers caution that AI could potentially restrict students' creative thinking (Sendawula et al., 2024).
- Actionable Sustainability Outcomes: AI contributes to institutional sustainability by enhancing efficiency and optimizing resource use, and it can also support broader outreach initiatives aligned with the SDGs (Borsatto et al., 2024). "Using smart tools and making effective decisions will lead to time and energy savings and productivity enhancement," which are key factors in achieving sustainability goals in HEIs (Ronaghi & Ronaghi, 2024, p.167). AI adoption has been linked to improved sustainability scores and better control of environmental performance (Ronaghi & Ronaghi, 2024).
Practical Implications:
- Invest in AI Infrastructure and Training: Universities must ensure the availability of necessary software, infrastructure, and funding to support the deployment of AI (Ronaghi & Ronaghi, 2024). Equally important are comprehensive training programs that enhance faculty members' understanding of AI applications and their integration into pedagogy (Tarisayi & Manhibi, 2024).
- Promote AI Literacy and Thoughtful Engagement: Students should be guided to examine AI tools carefully, assess their outputs, and understand their limitations along with associated ethical risks (Adžić et al., 2024; Black & Tomlinson, 2025). Integrating AI literacy into the curriculum is crucial for enabling learners to engage with technology in a responsible and informed manner (Adžić et al., 2024; Espinoza Vidaurre et al., 2024).
- Leverage AI for Operational Efficiency and Resource Management: AI integration can enhance HRM practices and decision-making processes by improving efficiency, productivity, and the effective use of resources (Mahade et al., 2025; Ronaghi & Ronaghi, 2024).
Discussion
Educational Quality and Equity through AI Integration
Challenges, Opportunities, and Governance of AI for Sustainability
AI’s Role in Advancing Sustainability Literacy, Critical Thinking, and Institutional Outcomes
Limitations of the Study
Recommendations for Future Research
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- Acosta-Enriquez, B. G.; Reyes-Perez, M. D.; Huamani Jordan, O.; Carreño Saucedo, L.; Padilla-Caballero, J. E. A.; Fernández-Altamirano, A. E. F.; García Vovera, A. J.; Briceño-Hernandez, R. N.; Alarcón Bustíos, J. M. Exploring the determinants of the sustainable use of artificial intelligence in Peruvian university teachers: A structural equation modeling analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17(7), 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, M. M.; Ngulube, P. Surge of data analytics in postgraduate education and methodological plurality: A systematic review. Discover Education 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adžić, S.; et al. Understanding student attitudes toward GenAI tools: A comparative study of Serbia and Austria. International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education (IJCRSEE) 2024, 12(3), 583–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Sharma, D.; Saxena, A. B. Adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) for development of smart education as the future of a sustainable education system. Journal of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Neural Network 2023, 3(6), Article 23.28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, D.; Picasso, F. Large language models for sustainable assessment and feedback in higher education: Towards a pedagogical and technological framework. In In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on High-performance Artificial Intelligence Systems in Education CEUR Workshop Proceedings, Rome, Italy (Vol. 3605); 2023. Available online: http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3605/.
- Airaj, M. Cloud computing technology and PBL teaching approach for a qualitative education in line with SDG4. Sustainability 2022, 14(23), 15766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahli, S. Advancing sustainable educational practices through AI-driven prediction of academic outcomes. Sustainability 2025, 17(3), 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dokhny, A.; Alismaiel, O.; Youssif, S.; Nasr, N.; Drwish, A.; Samir, A. Can multimodal large language models enhance performance benefits among higher education students? An investigation based on the task–technology fit theory and the artificial intelligence device use acceptance model. Sustainability 2024, 16(23), 10780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ally, M.; Perris, K. Artificial intelligence in the Fourth Industrial Revolution to educate for sustainable development. Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apata, O. E.; Ajamobe, J. O.; Ajose, S. T.; Oyewole, P. O.; Olaitan, G. I. The role of artificial intelligence in enhancing classroom learning: Ethical, practical, and pedagogical considerations. In In Proceedings of the 2025 ASEE Gulf-Southwest Annual Conference, University of Texas at Arlington; American Society for Engineering Education, 2025. Available online: https://peer.asee.org/49594.
- Asad, M.; Fryan, L. H. A.; Shomo, M. I. Sustainable entrepreneurial intention among university students: Synergetic moderation of entrepreneurial fear and use of artificial intelligence in teaching. Sustainability 2025, 17(1), 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, H. E. S.; Ismail, R. F.; Khalil, M. T. Artificial intelligence (AI) knowledge generation between acceptance and rejection as a tool to enhance project-based learning and professors’ performance in private higher education sector in Egypt. Cybrarians Journal 73 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, M. A. A.; Acosta Enríquez, B. G.; Ramos Farroñán, E. V.; García Juárez, H. D.; Cruz Salinas, L. E.; Blas Sánchez, J. E.; Arbulú Castillo, J. C.; Licapa-Redolfo, G. S.; Farfán Chilicaus, G. C. The sustainable integration of AI in higher education: Analyzing ChatGPT acceptance factors through an extended UTAUT2 framework in Peruvian universities. Sustainability 2024, 16(4), Article 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera Castro, G. P.; Chiappe, A.; Becerra Rodríguez, D. F.; Sepulveda, F. G. Harnessing AI for Education 4.0: Drivers of personalized learning. Electronic Journal of e-Learning 2024, 22(5), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, K. A.; Castleman, B. L.; Song, Y. Are algorithms biased in education? Exploring racial bias in predicting community college student success. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management 2024, 44(2), 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R. W.; Tomlinson, B. University students describe how they adopt AI for writing and research in a general education course. Scientific Reports 15 2025, 8799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsatto, J. M. L. S.; Marcolin, C. B.; Abdalla, E. C.; Amaral, F. D. Aligning community outreach initiatives with SDGs in a higher education institution with artificial intelligence. Cleaner and Responsible Consumption 12 2024, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustani, N. M.; Sidani, D.; Boustany, Z. Leveraging ICT and generative AI in higher education for sustainable development: The case of a Lebanese private university. Administrative Sciences 2024, 14(4), 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenaño-Fernández, D.; Gil, D.; Luján-Mora, S. Application of machine learning in predicting performance for computer engineering students: A case study. Sustainability 2019, 11(10), 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, A. Transforming higher education for the digital age: Examining emerging technologies and pedagogical innovations. Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies in Education 2024, 13(S1), 53–70. Available online: https://ojed.org/jise. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Lin, J. Does ChatGPT play a double-edged sword role in the field of higher education? An in-depth exploration of the factors affecting student performance. Sustainability 2023, 15(24), 16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T. Estimating the artificial intelligence learning efficiency for civil engineer education: A case study in Taiwan. Sustainability 2021, 13(21), 11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomiak-Orsa, I.; Smolag, K. Nowaczyk et al., S., et al., Eds.; Remote learning technologies in achieving the fourth Sustainable Development Goal. In ECAI 2023 Workshops CCIS 1948; Springer, 2024; pp. 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M. J.; Reynders, M.; Holme, T. A. Students’ experience of a ChatGPT enabled final exam in a non-majors chemistry course. Journal of Chemical Education 2024, 101(4), 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, E. J.; White, A.; Ramirez, J. M.; Alvara, A.; Rees, L. K. Acceptability, feasibility, and effectiveness of an artificial intelligence chatbot in an asynchronous epidemiology course. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Perspectives in Higher Education 2024, 9(2), 1–20. Available online: https://ojed.org/jimphe/article/view/6220/3088.
- Daniela, L.; Visvizi, A.; Gutiérrez-Braojos, C.; Lytras, M. D. Sustainable higher education and technology-enhanced learning (TEL). Sustainability 2018, 10(10), 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza Vidaurre, S. M.; Velásquez Rodríguez, N. C.; Gambetta Quelopana, R. L.; Martinez Valdivia, A. N.; Leo Rossi, E. A.; Nolasco-Mamani, M. A. Perceptions of artificial intelligence and its impact on academic integrity among university students in Peru and Chile: An approach to sustainable education. Sustainability 2024, 16(19), 9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T. L.; Stevenson, R. B.; Lasen, M.; Ferreira, J.-A.; Davis, J. M. Approaches to embedding sustainability in teacher education: A synthesis of the literature. Teaching and Teacher Education 63 2017, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, F.; Ninduwezuor-Ehiobu, N.; Adanma, U. M.; Solomon, N. O. AI-powered waste management: Predictive modeling for sustainable landfill operations. Comprehensive Research and Reviews in Science and Technology 2024, 2(1), 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, Á.; Rodríguez-Fórtiz, M. J.; Rodríguez-Almendros, M. L.; Martínez-Segura, M. J. Mobile learning technology based on iOS devices to support students with special education needs. Computers & Education 61 2013, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, M. AI tools in society: Impacts on cognitive offloading and the future of critical thinking. Societies 2025, 15(1), 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P. Enhancing educational outcomes by boosting artificial intelligence application in personalized learning. Science Insights Education Frontiers 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatrellis, O.; Samaras, N.; Kokkinos, K.; Panagiotakopoulos, T. Leveraging generative AI for sustainable academic advising: Enhancing educational practices through AI-driven recommendations. Sustainability 2024, 16(17), 7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A. H.; Ajlouni, A. O. Exploring ChatGPT in supporting special education undergraduates in achieving CEC standards: Students’ perception. Journal of Social Studies Education Research 2024, 15(5), 87–119. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1457498.pdf.
- Jiang, Y. Interaction and dialogue: Integration and application of artificial intelligence in blended mode writing feedback. The Internet and Higher Education 64 2024, 100975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokhan, A.; Chand, A. A.; Singh, V.; Mamun, K. A. Increased digital resource consumption in higher educational institutions and the artificial intelligence role in informing decisions related to student performance. Sustainability 2022, 14(4), 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalniņa, D.; Nimante, D.; Baranova, S. Artificial intelligence for higher education: Benefits and challenges for pre-service teachers. Frontiers in Education 9 2024, 1501819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsamakas, E.; Pavlov, O. V.; Saklad, R. Artificial intelligence and the transformation of higher education institutions: A systems approach. Sustainability 2024, 16(14), 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komasawa, N.; Yokohira, M. Simulation-based education in the artificial intelligence era. Cureus 15 2023, e40940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatina, D.; Miletić, M.; Mosurović Ružičić, M. Embracing artificial intelligence (AI) in architectural education: A step towards sustainable practice? Buildings 2024, 14(8), 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainjo, B. Mitigating academic institution dropout rates with predictive analytics algorithms. International Journal of Education, Teaching, and Social Sciences 2023, 3(1), 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J. R.; Koch, G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33(1), 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, P.; Felvégi, E.; Füzesí, I. Integrating Artificial Intelligence in agricultural higher education: Transforming learning and research. Journal of Agricultural Informatics 2024, 15(2), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M. P.-C.; Liu, A. L.; Poitras, E.; Chang, M.; Chang, D. H. An exploratory study on the efficacy and inclusivity of AI technologies in diverse learning environments. Sustainability 2024, 16(20), 8992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, M.; Snyder-Duch, J.; Bracken, C. C. Content analysis in mass communication: Assessment and reporting of intercoder reliability. Human Communication Research 2002, 28(4), 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Ch’ng, L. K. Construction of a teaching strategy model for cultivating higher-order thinking skills in college students. International Journal of Social Science and Business Management 2024, 2(1), Article 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahade, A.; Elmahi, A.; Alomari, K. M.; Abdalla, A. A. Leveraging AI-driven insights to enhance sustainable human resource management performance: Moderated mediation model: Evidence from UAE higher education. Discover Sustainability 2025, 6(267). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S. C.; Matei, O.; Faragau, T.; Andreica, L.; Daraba, D. The innovative use of intelligent chatbot for sustainable health education admission process: Learnt lessons and good practices. Applied Sciences 2023, 13(3), 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, D. Artificial intelligence in the Industry 4.0, and its impact on poverty, innovation, infrastructure development, and the Sustainable Development Goals: Lessons from emerging economies? Sustainability 2021, 13(11), 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, Y.; Yarime, M. Education for sustainable development and sustainability science: Re-purposing higher education and research. Higher Education Policy 2015, 28(4), 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldi, A.; Nurkadri, N.; Srisudarso, M.; Cahyono, D.; Suyitno, S. Evaluation of the effectiveness of artificial intelligence system in higher education curriculum management. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Education 2023, 2(2), 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, D.; Watkinson, A.; Jamali, H.; Herman, E.; Tenopir, C.; Volentine, R.; Allard, S.; Levine, K. Peer review: Still king in the digital age; Learned Publishing, 2015; Volume 28, 1, pp. 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X. The role of artificial intelligence autonomy in higher education: A uses and gratification perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolet, V. Educating for sustainability: Principles and practices for teachers; Routledge, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Okulich-Kazarin, V.; Artyukhov, A.; Skowron; Artyukhova, N.; Wołowiec, T. When artificial intelligence tools meet “non-violent” learning environments (SDG 4.3): Crossroads with smart education. Sustainability 2024, 16(17), 7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okulich-Kazarin, V.; Artyukhov, A.; Skowron; Artyukhova, N.; Dluhopolskyi, O.; Cwynar, W. Sustainability of higher education: Study of student opinions about the possibility of replacing teachers with AI technologies. Sustainability 2024, 16(1), 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J.; McKenzie, J. E.; Bossuyt, P. M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T. C.; Mulrow, C. D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J. M.; Akl, E. A.; Brennan, S. E.; Chou, R.; Glanville, J.; Grimshaw, J. M.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Lalu, M. M.; Li, T.; Loder, E. W.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; McDonald, S.; Moher, D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, M.; Roe, J.; Vu, B. H.; Postma, D.; Hickerson, D.; McGaughran, J.; Khuat, H. Q. Simple techniques to bypass GenAI text detectors: Implications for inclusive education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 21 2024, Article 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, D. D.; Seshadrinath, S. M.; Zhang, M.; McCormack, M. Measuring sustainable development goals (SDGs) in higher education through semantic matching. Studies in Higher Education 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaghi, M. H.; Ronaghi, M. How does the use of artificial intelligence affect sustainability rating in Middle Eastern universities? Asian Education and Development Studies 2025, 14(2), 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.; Bonfield, C. Making human learning visible in a world of invisible generative AI: An international perspective. In ASCILITE 2024 Conference Companion Materials; 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ruiz, E. Writing with ChatGPT in a context of educational inequality and digital divide. International Journal of Education and Development using Information and Communication Technology 2023, 19(3), 28–38. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1413385.pdf.
- Savec, V. F; Jedrinović, S. The role of AI implementation in higher education in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals: A case study from Slovenia. Sustainability 2025, 17(1), 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, R.; Ames, K.; Leichtweis, S. 2024 governance of artificial intelligence and data in Australasian higher education: A snapshot of policy and practice (An ACODE Whitepaper) 2024. [CrossRef]
- Sendawula, K.; Kimuli, N. S.; Kimuli, N. N.; Kirugga, A.; Noordin, S. Guralnick et al., D., et al., Eds.; Beyond potential: Exploring the lived experiences of artificial intelligence usage in Ugandan universities for quality education. In TLIC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer, 2024; Vol. 1166, pp. 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Ogunola, A. A.; Ishaq, S. M.; Khawaji, T.; Mowafaq, F.; Arafat, Y. Revolutionizing education: The transformative power of artificial intelligence in shaping a brighter future for humanities. Library Progress International 2024, 44(3), 21898–21912. Available online: https://bpasjournals.com/library-science/index.php/journal/article/view/2834.
- Shilbayeh, S.; Abonamah, A. Predicting student enrolments and attrition patterns in higher educational institutions using machine learning. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology 2021, 18(4), 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaway, A. P.; Wood, A. M.; Hedges, L. V. How to do a systematic review: A best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annual Review of Psychology 70 2019, 747–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, M. B.; dos Santos, V. M.; Diniz, E. H.; Cruz, A. P. A. Artificial intelligence for sustainability: A systematic literature review in information systems. Revista de Gestão Social e Ambiental 2024, 18(3), Article 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobramoney, R.; Singh, A. Identifying students at-risk with an ensemble of machine learning algorithms. In 2019 Conference on Information Communications Technology and Society (ICTAS); IEEE, 2019; pp. 1–6. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8703616.
- Sterling, S. Transformative learning and sustainability: Sketching the conceptual ground. Learning and Teaching in Higher Education 5 2010, 17–33. Available online: https://dl.icdst.org/pdfs/files3/ce3bd9b5c8a4133cd2d81b507badbd85.pdf.
- Tarisayi, K. S.; Manhibi, R. Revolutionizing education in Zimbabwe: Stakeholder perspectives on strategic AI integration. Journal of Learning and Teaching in Digital Age 2025, 10(1), 87–93. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1459941.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, B. Exploring the philosophy and practice of AI literacy in higher education in the Global South: A scoping review. Cybrarians Journal Special Issue: ICIL Conference 2024, (73). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Verdera, V.; Domingo, J.; Dura, E.; Gabaldón-Estevan, D.; López-Baeza, E.; Machause López, S.; Meco-Tébar, F.; Rueda, S.; Serrano-Lara, J.; Signes-Soler, I.; Vázquez de Ágredos Pascual, M. L.; Martínez-García, E. The future we want: A learning experience to promote SDGs in higher education from the United Nations and University of Valencia. Sustainability 2021, 13(15), 8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Arias-Navarrete, A.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Proposal of an architecture for the integration of a chatbot with artificial intelligence in a smart campus for the improvement of learning. Sustainability 2020, 12(4), 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Govea, J.; Revelo-Tapia, S. Improving student retention in institutions of higher education through machine learning: A sustainable approach. Sustainability 2023, 15(19), 14512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walshe, R.; Koene, A.; Baumann, S.; Panella, M.; Maglaras, L.; Medeiros, F. Artificial intelligence as an enabler for sustainable development. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC); 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Pyng, H. S.; Ayub, A. F. M.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, J.; Qing, Z. University students’ usage of generative artificial intelligence for sustainability: A cross-sectional survey from China. Sustainability 17 2025, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Bello, S.; Pervin, N.; Tukur, A. K. Implementing a proposed framework for enhancing critical thinking skills in synthesizing AI-generated texts. Thinking Skills and Creativity 53 2024, 101619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J. The paradox of self-efficacy and technological dependence: Unraveling generative AI’s impact on university students’ task completion. The Internet and Higher Education 65 2024, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, S.; Wu, C.; Petricini, T. Using the information inequity framework to study GenAI equity: Analysis of educational perspectives. Information Research 2025, 30(iConf), Article 47284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





