Submitted:
16 November 2025
Posted:
18 November 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
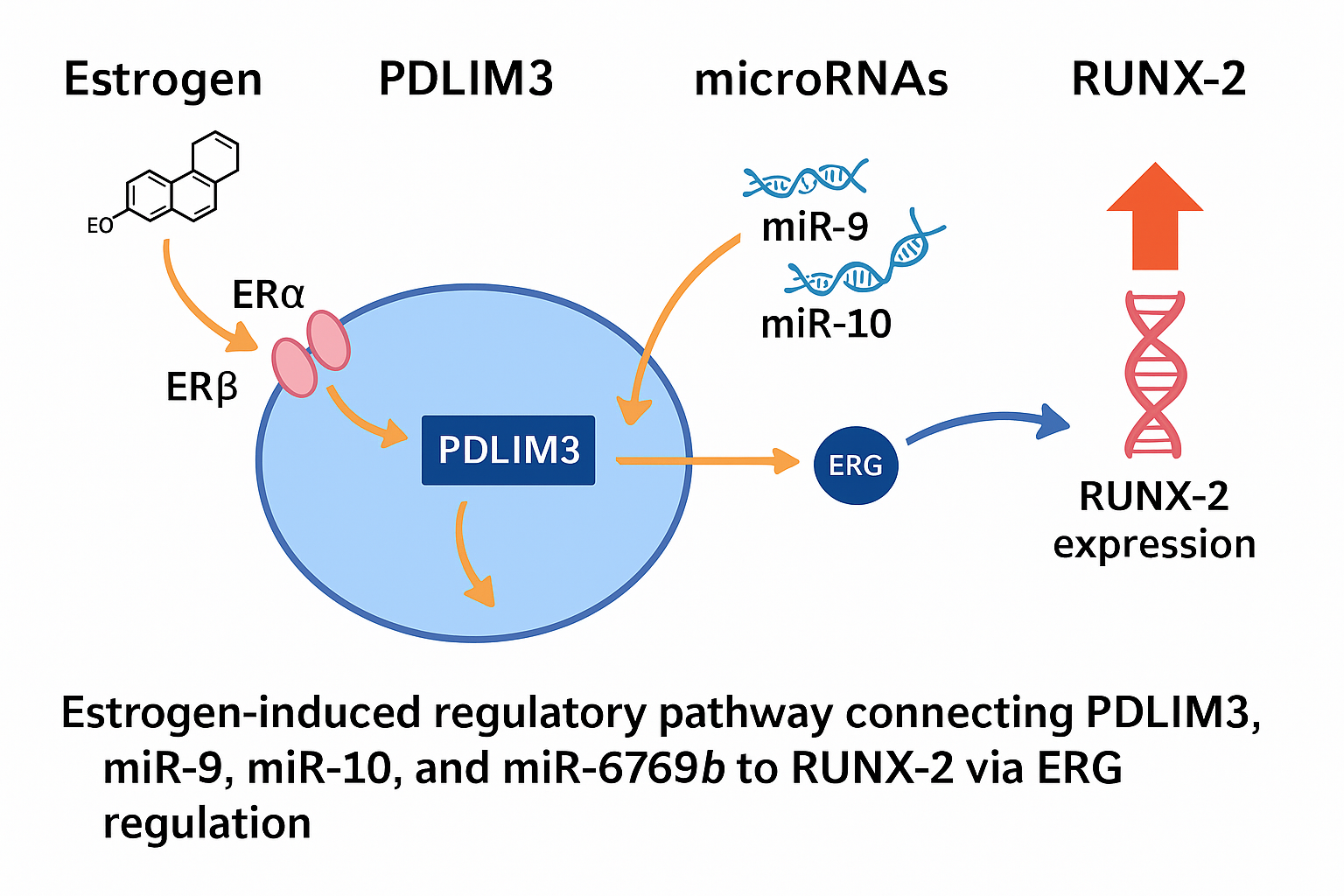
Estrogens govern the female reproductive cycle indefinitely. Estrogens, including estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), estriol (E3), and estetrol (E4), regulate the female life cycle since early embryonic stages and play a crucial role in development, metabolism, and cell function. Throughout evolution, estrogen has regulated reproduction by affecting reproductive organ development and behavior. Estrogen impacts all vertebrates, including fish, and has a role in physiological and pathological states in both genders. The RUNX-2 gene is a member of the RUNX family of transcription factors and encodes a nuclear protein with a Runt DNA-binding domain. This protein is essential for osteoblastic differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis and acts as a scaffold for nucleic acids and regulatory factors involved in skeletal gene expression. The protein can bind DNA both as a monomer or, with more affinity, as a subunit of a heterodimeric complex. In 2022, a study was conducted to characterize novel genes that are regulated by estrogen binding to its receptors (α or β). The PDLIM3 gene, with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 0.083, received the most stable CV score among other genes. Our integrative research uncovers a unique regulatory cascade in which estrogen binding to ERα/β enhances PDLIM3 expression, then modulating the expression of miR-9, miR-10, and the newly identified miR-6769b, finally activating RUNX2 transcription.
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Material and Methods
Ingenuity Pathway Analysis Software.
III. Results and Outcomes, all the figures and tables are provided as supplementary materials
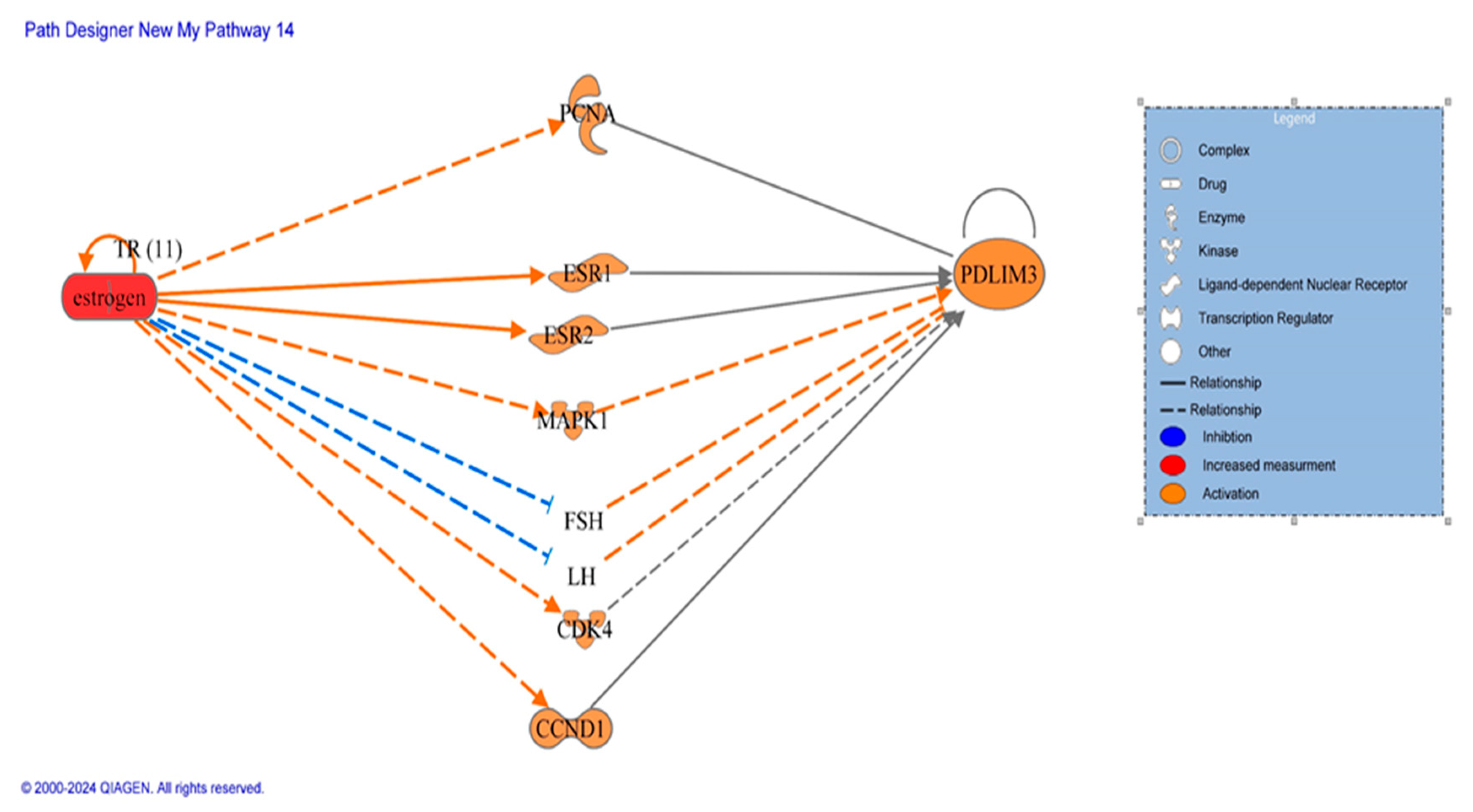
1. Molecular Pathway Analysis of Molecules Mediating the Relationship Between Estrogen and PDLIM3
| Symbol | Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCND1 | cyclin D1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
| CDK4 | cyclin dependent kinase 4 | Nucleus | kinase |
| ESR1 | estrogen receptor 1 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
| ESR2 | estrogen receptor 2 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
| Estrogen | estrogen | Other | chemical drug |
| FSH | Follicle stimulating hormone | Plasma Membrane | complex |
| LH | Luteliizng hormone | Plasma Membrane | Complex |
| MAPK1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Cytoplasm | Kinase |
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen | Nucleus | Enzyme |
| PDLIM3 | PDZ and LIM domain 3 | Cytoplasm | Other |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
regulation of binding | Estrogen |
|
chemical-protein interactions | Estrogen |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
activation | CDK4 |
|
activation | ESR1 |
|
activation | ESR2 |
|
activation | MAPK1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
expression | CCND1 |
|
expression | ESR1 |
|
expression | ESR2 |
|
expression | FSH |
|
expression | LH |
|
expression | PCNA |
|
localization | FSH |
|
localization | LH |
|
molecular cleavage | ESR1 |
|
phosphorylation | ESR1 |
|
phosphorylation | ESR2 |
|
phosphorylation | MAPK1 |
|
regulation of binding | CCND1 |
|
regulation of binding | CDK4 |
|
regulation of binding | ESR1 |
|
regulation of binding | ESR2 |
|
transcription | CCND1 |
|
translocation | ESR1 |
|
translocation | ESR2 |
|
translocation | estrogen |
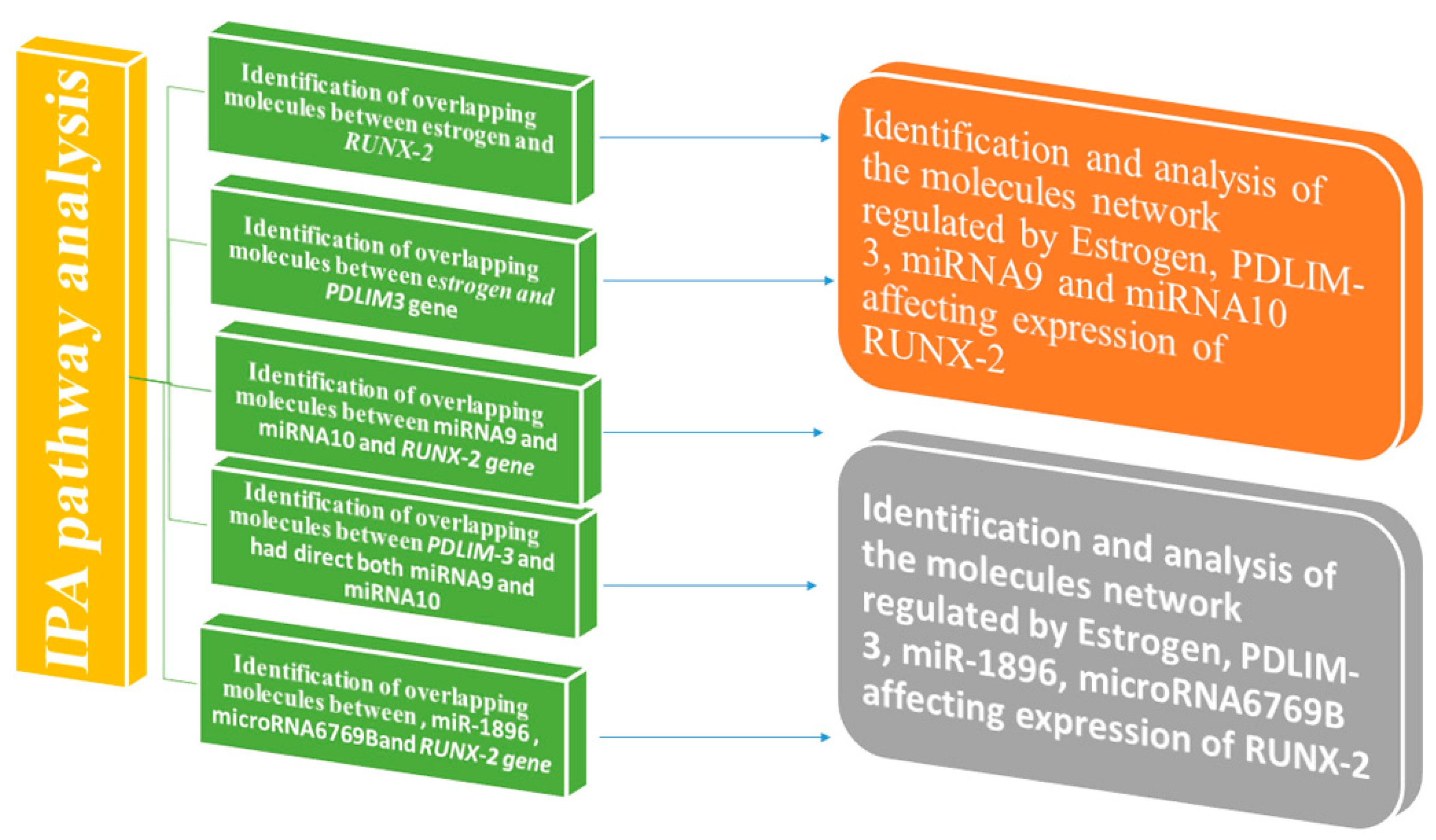
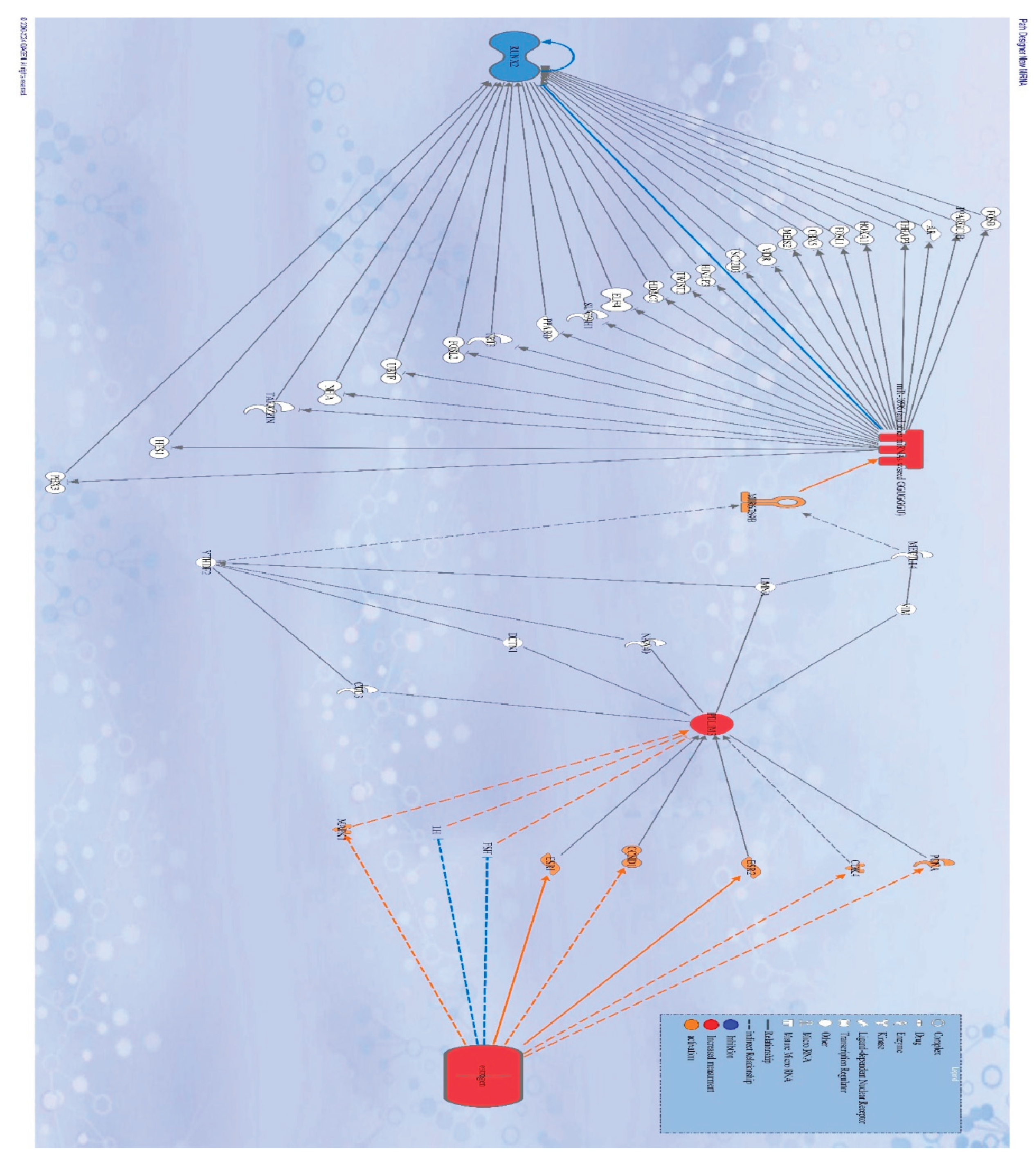
2. Molecular Pathway Analysis of Molecules Mediating the Relationship Between Estrogen and Affect Expression of RUNX-2
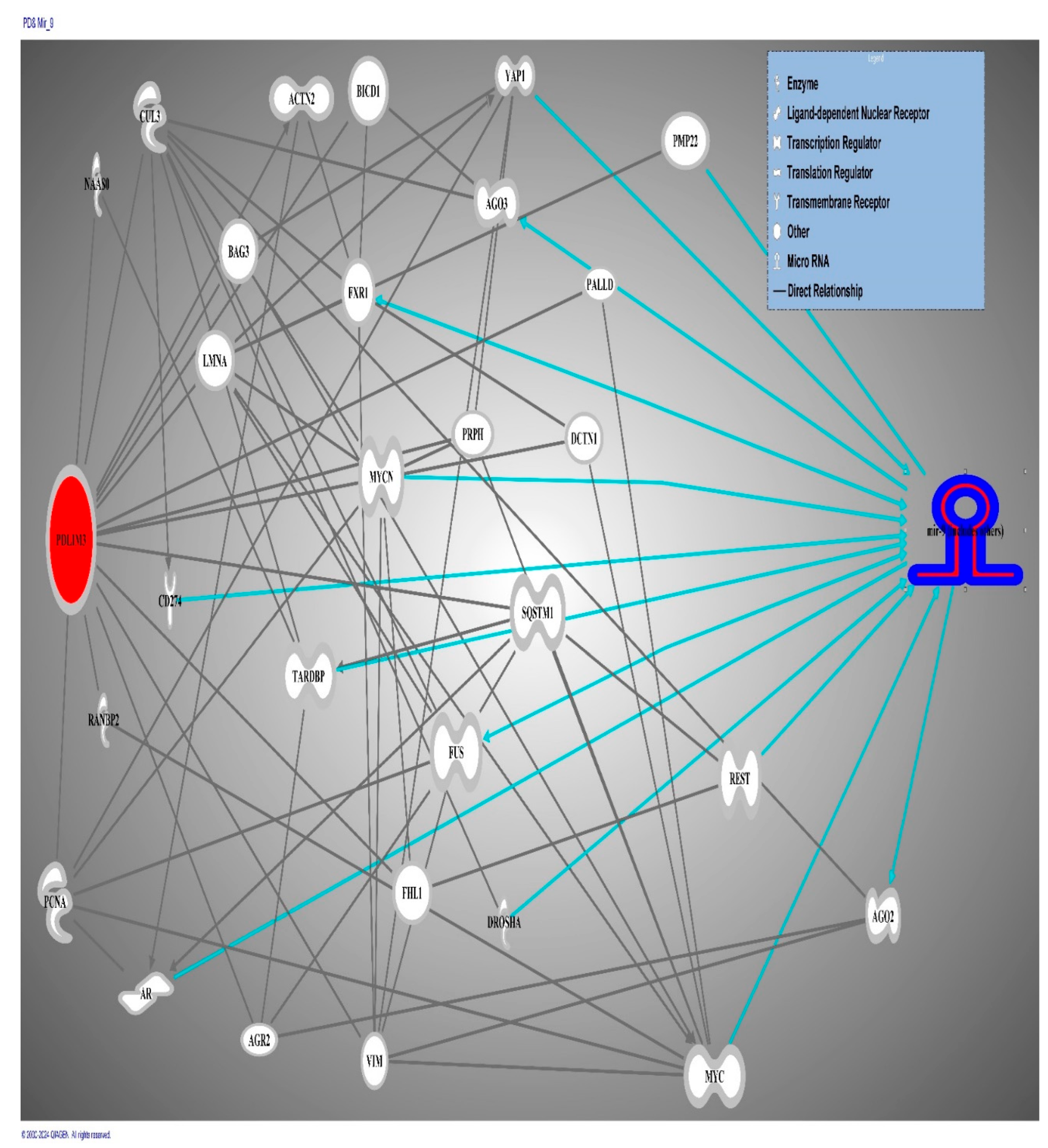
3. Molecular Pathway Analysis of Molecules Mediating the Relationship Between miRNA9 and Directly Affecting Expression of the RUNX-2 Gene
4. Molecular Pathway Analysis of Molecules Mediating the Relationship Between miRNA10 and Directly Affecting Expression of the RUNX-2 Gene
5. Molecular Pathway Analysis of Molecules Mediating the Relationship Between PDLIM-3 and Had Direct Effects on Expression of miRNA9
6. Molecular Pathway Analysis of Molecules Mediating the Relationship Between PDLIM-3 and Had Direct Effects on Expression of miRNA10
7. Identification and Analysis of the Molecule Network Regulated by Estrogen, PDLIM-3, miRNA9, and miRNA10 affects the expression of RUNX-2.
8. Identification and Analysis of the Molecules Network Regulated by Estrogen, PDLIM-3, miR-1896, microRNA6769B affects the expression of RUNX-2.
IV. Discussion and Conclusion
V. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| AKT | Protein kinase B; serine/threonine kinase in the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating survival and metabolism. |
| ALP | Actin-associated LIM protein; structural and signaling protein encoded by PDLIM3, localized in cardiac and skeletal muscle Z-discs. |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1; transcription factor complex (Fos/Jun) regulating proliferation and apoptosis. |
| BAX | Bcl-2–associated X protein; pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. |
| BCL-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2; anti-apoptotic protein that promotes cell survival. |
| CBFα1 | Core-binding factor subunit alpha-1; alternative name for RUNX2 transcription factor. |
| CCD | Cleidocranial dysplasia; hereditary skeletal disorder caused by mutations in RUNX2. |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase; enzyme family that regulates cell-cycle progression. |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4; G1 phase cell-cycle regulator. |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein; transcription factor that regulates metabolism, survival, and plasticity. |
| CV | Coefficient of variation; measure of relative variability in gene expression or stability. |
| DCM | Dilated cardiomyopathy; disorder characterized by dilation and impaired contraction of cardiac chambers. |
| E1 | Estrone; endogenous estrogen. |
| E2 | 17β-estradiol; the most potent and biologically active endogenous estrogen. |
| E3 | Estriol; estrogen predominant during pregnancy. |
| E4 | Estetrol; fetal liver–derived estrogen present during pregnancy. |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix; structural network of proteins and polysaccharides surrounding cells. |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor; receptor tyrosine kinase regulating proliferation and survival. |
| ER | Estrogen receptor; ligand-activated transcription factor mediating estrogen actions. |
| ERα / ERβ | Estrogen receptor alpha / beta; two main nuclear estrogen receptor isoforms. |
| ERGs | Estrogen-responsive genes; genes whose transcription is modulated by estrogen receptor signaling. |
| EREs | Estrogen response elements; DNA sequences bound by ER complexes to regulate transcription. |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK family kinase involved in proliferation and differentiation. |
| ESR1 / ESR2 | Estrogen receptor 1 / 2; gene symbols encoding ERα and ERβ, respectively. |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone; gonadotropin regulating follicle development and spermatogenesis. |
| Fos | Proto-oncogene c-Fos; component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex. |
| GPER1 | G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; membrane-bound estrogen receptor mediating rapid non-genomic signaling. |
| GR | Glucocorticoid receptor; nuclear receptor for glucocorticoid hormones. |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; serine/threonine kinase involved in metabolism and Wnt/MAPK signaling. |
| HRT | Hormone replacement therapy; clinical use of hormones (e.g., estrogens) to treat menopausal or deficiency symptoms. |
| HSPs | Heat shock proteins; molecular chaperones that stabilize and refold proteins, also associated with steroid receptors. |
| ID | Inhibitor of differentiation; family of helix-loop-helix transcriptional regulators. |
| ID3 | Inhibitor of DNA-binding protein 3; an ID family member downregulated by miR-10a-3p during osteogenic differentiation. |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1; peptide growth factor important for growth and metabolism. |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis; QIAGEN bioinformatics software for pathway and network modeling. |
| IRS-1 | Insulin receptor substrate 1; adaptor protein transmitting insulin/IGF-1 receptor signaling. |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase; stress-activated protein kinase within the MAPK family. |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone; gonadotropin regulating ovulation and gonadal steroid production. |
| MAP | Molecule Activity Predictor; Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) tool predicting activation/inhibition effects within networks. |
| MAPK / MAPK-1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase / MAPK-1; serine/threonine kinases mediating downstream signaling (ERK2 often referred to as MAPK-1). |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; immune-suppressive myeloid cell population modulating tumor and inflammatory responses. |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; dual-specificity kinase upstream of ERK in the MAPK cascade. |
| miR / miRNA | MicroRNA; small (~19–25 nt) non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression post-transcriptionally. |
| miR-9 | MicroRNA-9; miRNA regulating neurogenesis, osteogenesis, and immune functions. |
| miR-10 / miRNA10 / miR-10a | MicroRNA-10; family associated with differentiation, apoptosis, and cancer; miR-10a is a specific isoform. |
| miR-1896 | MicroRNA-1896; miRNA implicated in indirect regulation of RUNX2 via shared seed sequences. |
| miR-6769b / microRNA6769B | MicroRNA-6769b; newly implicated epigenetic regulator in RUNX2-related signaling. |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin; central kinase controlling growth and metabolism. |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-B; transcription factor regulating inflammatory and immune responses. |
| OPN | Osteopontin; extracellular matrix phosphoprotein involved in bone remodeling and mineralization. |
| PCNA | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; sliding clamp protein and marker of DNA replication and repair. |
| PDLIM3 | PDZ and LIM domain protein 3; actin-associated structural and signaling protein (ALP), here identified as an estrogen-regulated intermediary upstream of RUNX2. |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; lipid kinase that generates PIP3 and activates AKT signaling. |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog; tumor suppressor and negative regulator of PI3K/AKT signaling. |
| QKB | QIAGEN Knowledge Base; curated database underpinning Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. |
| Ras | Rat sarcoma; small GTP-binding protein family regulating proliferation and survival pathways. |
| RUNX2 / RUNX-2 | Runt-related transcription factor 2; master transcription factor for osteoblast differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis. |
| SRC | Steroid receptor coactivator; transcriptional co-regulator that enhances nuclear receptor–mediated gene expression. |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription; transcription factor family that mediates cytokine and growth factor signaling. |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor; central regulator of angiogenesis and vascular permeability. |
References
- Huether, S. E., & McCance, K. L. (2019). Understanding pathophysiology (7th ed., p. 767). Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-0-32-367281-8.
- Delgado, B. J., & Lopez-Ojeda, W. (2023, June 26). Estrogen. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555922/.
- Sier, J. H., Thumser, A. E., & Plant, N. J. (2017). Linking physiologically-based pharmacokinetic and genome-scale metabolic networks to understand estradiol biology. BMC Systems Biology, 11(1), 93. [CrossRef]
- Shaban, N. Z., Talaat, I., Elrashidy, F., Hegazy, A., & Sultan, A. (2017). Therapeutic role of Punica granatum (pomegranate) seed oil extract on bone turnover and resorption induced in ovariectomized rats. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 21(10), 1299–1306. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P. A., & Ambrosone, C. (2000). Molecular epidemiology of genetic polymorphisms in estrogen-metabolizing enzymes in human breast cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute Monographs, 27, 125–134. [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, N., & Silveyra, P. (2019). Estrogen receptor signaling mechanisms. Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 116, 135–170. [CrossRef]
- Le Dily, F., & Beato, M. (2018). Signaling by steroid hormones in the 3D nuclear space. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 306. [CrossRef]
- Komori, T. (2019). RUNX2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation. Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 151(1), 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Lucero, M. J., Vega, O. A., Osorio, M. M., Tapia, J. C., Antonelli, M., Stein, G. S., & Galindo, M. A. (2013). The cancer-related transcription factor RUNX2 modulates cell proliferation in human osteosarcoma cell lines. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 228(4), 714–723. [CrossRef]
- Lin, T. C. (2023). RUNX2 and cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7001. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X., Chen, M., Ruan, Q., Shi, C., Pan, J., & Luo, L. (2022). Comprehensive analysis of PDLIM3 expression profile, prognostic value, and correlations with immune infiltrates in gastric cancer. Journal of Immunology Research, 2022, 2039447. [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K., Fu, W., & Kiyama, R. (2022). Novel estrogen-responsive genes (ERGs) for the evaluation of estrogenic activity. PLoS ONE, 17(8), e0272003. [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, K., & Sivasankar, V. (2014). MicroRNAs: Biology and clinical applications. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology: JOMFP, 18(2), 229–234. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H., Gao, H., Liu, F., & Qiu, B. (2017). Regulation of RUNX2 by microRNA-9 and microRNA-10 modulates the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 39(4), 1046–1052. [CrossRef]
- Tamkovich, S., Borisova, A., Shevela, A., Chernyavskiy, A., & Chernyshovа, A. (2025). Exosomal microRNA: Diagnostic potential and role in breast cancer dissemination. Molecules, 30(19), 3858. [CrossRef]
- Tian, J., Rui, K., Tang, X., Ma, J., Wang, Y., Tian, X., et al. (2015). MicroRNA-9 regulates the differentiation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via targeting Runx1. Journal of Immunology, 195(3), 1301–1311. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M., Zhang, W., Zhang, R., Liu, P., Ye, Y., Yu, W., Guo, X., & Yu, J. (2020). Cancer exosome-derived miR-9 and miR-181a promote the development of early-stage MDSCs via interfering with SOCS3 and PIAS3 respectively in breast cancer. Oncogene, 39(24), 4681–4694. [CrossRef]
- Mu, N., Gu, J., Huang, T., Zhang, C., Shu, Z., Li, M., et al. (2016). A novel NF-κB/YY1/microRNA-10a regulatory circuit in fibroblast-like synoviocytes regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Scientific Reports, 6, 20059. [CrossRef]
- Xu, D., Huang, C. C., Kachaochana, A., Morgan, G. A., Bonaldo, M. F., Soares, M. B., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-10a regulation of proinflammatory mediators: An important component of untreated juvenile dermatomyositis. Journal of Rheumatology, 43(1), 161–168. [CrossRef]
- Stadthagen, G., Tehler, D., Høyland-Kroghsbo, N. M., Wen, J., Krogh, A., Jensen, K. T., et al. (2013). Loss of miR-10a activates lpo and collaborates with activated Wnt signaling in inducing intestinal neoplasia in female mice. PLoS Genetics, 9(10), e1003913. [CrossRef]
- Xu, C., Zhang, H., Gu, W., Wu, H., Chen, Y., Zhou, W., et al. (2018). The microRNA-10a/ID3/RUNX2 axis modulates the development of ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Scientific Reports, 8, 12577. [CrossRef]
- Bishir, M., Rengifo, T., Huang, W., Kim, R. J., Chidambaram, S. B., & Chang, S. L. (2023). Network meta-analysis on alcohol-mediated modulation of Alzheimer’s disease in the diseases of inflammation including COVID-19. NeuroImmune Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 2(3), 267–281. [CrossRef]
- Rengifo, T., Bishir, M., Huang, W., Snyder, M., & Chang, S. L. (2024). Network meta-analysis of the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways underlying alcohol-induced thymic atrophy. Alcohol: Clinical and Experimental Research, 48(5), 795–809. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J., Bishir, M., Barbhuiya, S., & Chang, S. L. (2023). Meta-analysis of the mechanisms underlying COVID-19 modulation of Parkinson’s disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13554. [CrossRef]
- Otto, F., Thornell, A. P., Crompton, T., Denzel, A., Gilmour, K. C., Rosewell, I., et al. (1997). Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Cell, 89(5), 765–771. [CrossRef]
- Krcmery, J., Klaska, V., Cimler, R., & Kocianova, E. (2010). Loss of the cytoskeletal protein α-actinin-2 leads to dilated cardiomyopathy and skeletal muscle dysfunction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(6), 2345–2350. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q., Wu, X., Tao, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., & Li, Y. (2023). Osteoarthritis: Pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 8, 56. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L., Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Li, H., & Sun, Y. (2015). MiR-9 promotes osteoblast differentiation and suppresses osteoclastogenesis via targeting DKK1. Gene, 564(2), 137–144. [CrossRef]
- Wu, D., Chen, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., & Li, H. (2014). MiR-10a promotes osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells. Aging Cell, 13(2), 333–341. [CrossRef]
- Sun, G., Yu, R., Wang, X., & Zhang, X. (2013). miR-9 regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting TLX and REST. Developmental Cell, 20(6), 897–909. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Qiu, X., Zhang, X., Li, F., & Chen, J. (2015). miR-10a regulates T cell activation and promotes immunosuppression in ovarian cancer. Cell Death & Disease, 6, e1915. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Zhang, H., & Li, S. (2022). miR-6769b-5p targets CCND1 to regulate proliferation in cadmium-exposed placental trophoblasts. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 91, 103752. [CrossRef]
- NET Research Team. (2019). Exosome-mediated regulation of bone remodeling by miRNAs including miR-6769b. NET Archives. https://www.netarchives.org/exosome-bone-miRNA.
- ResearchGate. (2025). Network meta-analysis of estrogen's direct and indirect influence on signaling pathways controlling RUNX2 through novel ERG genes. [CrossRef]
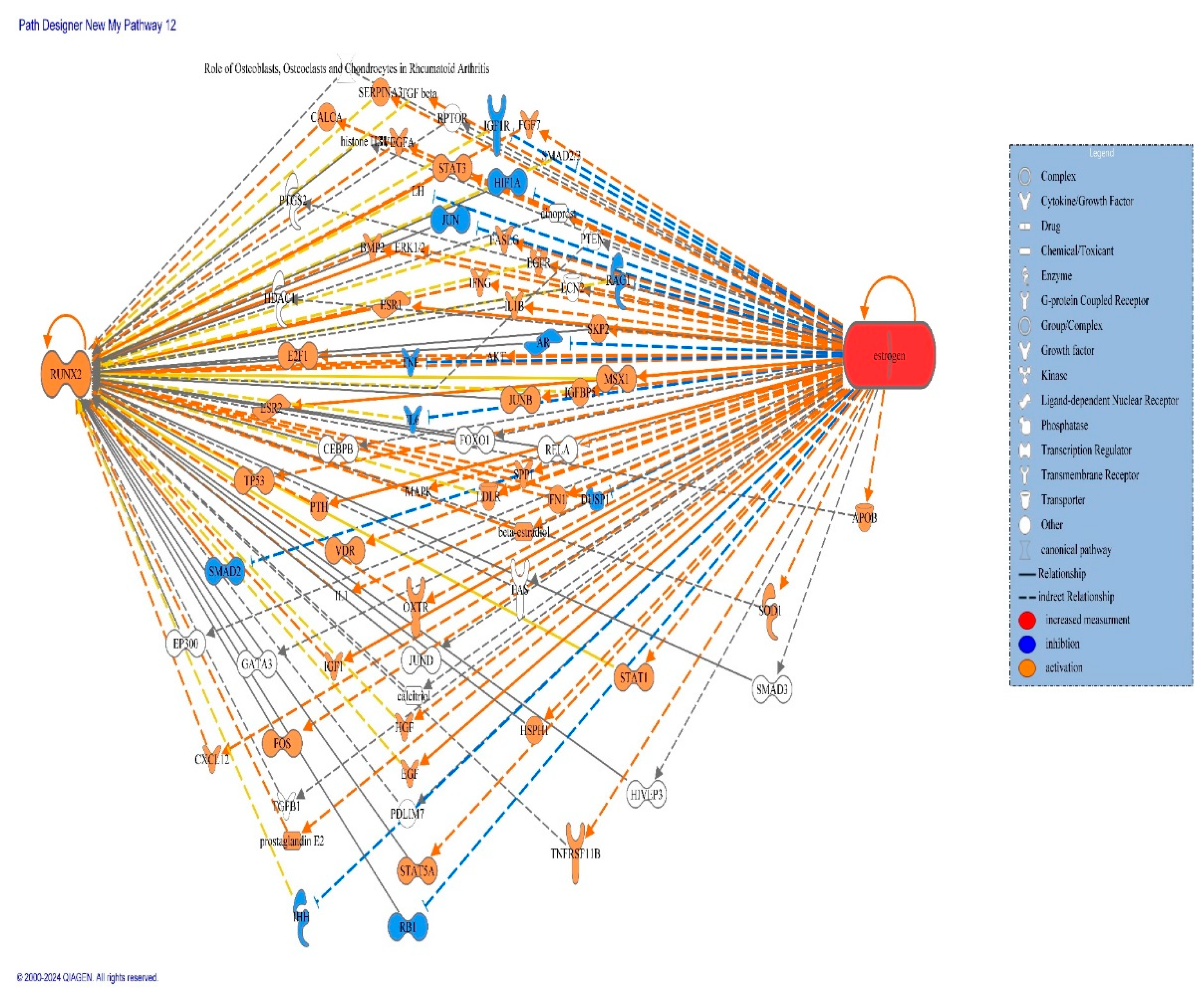
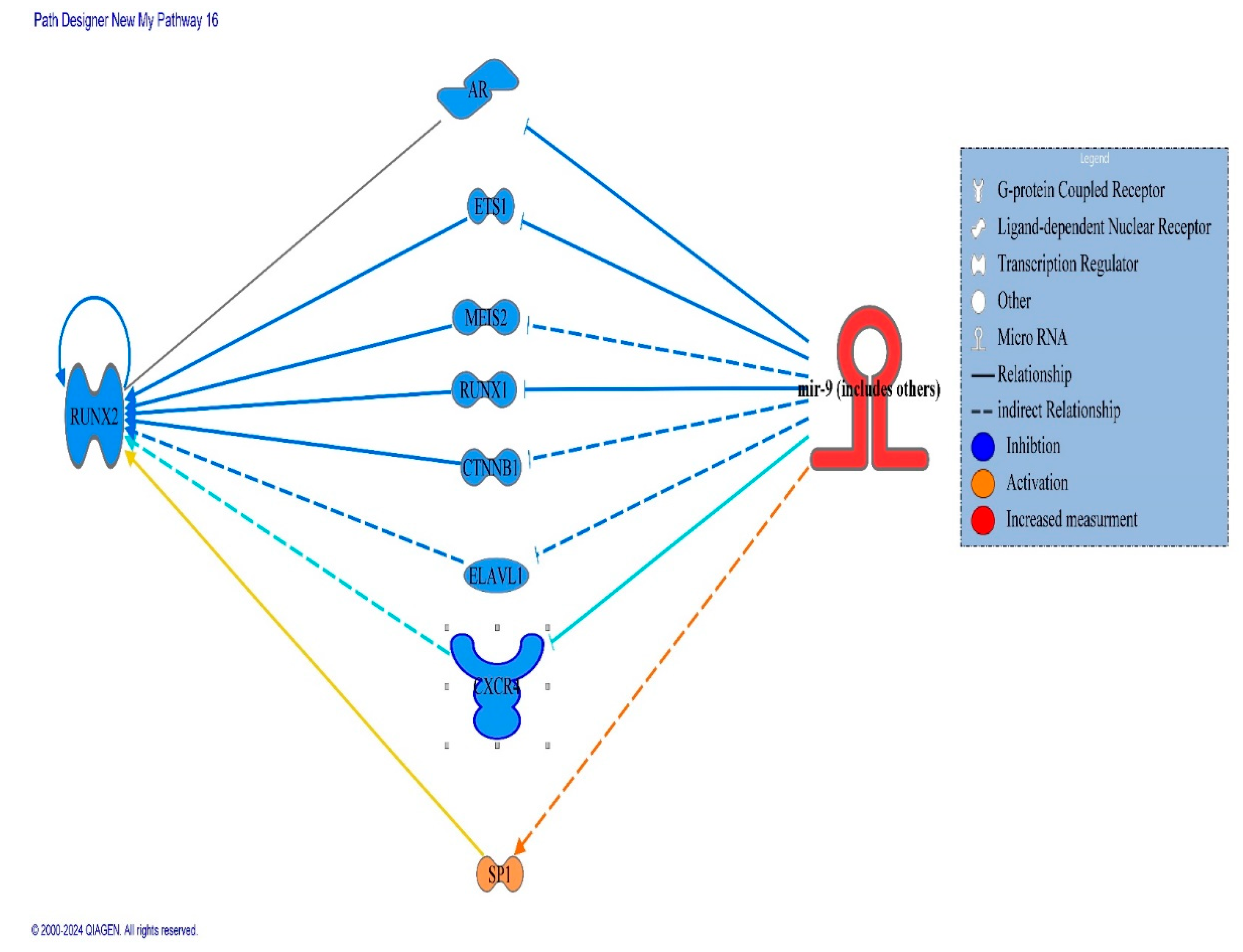
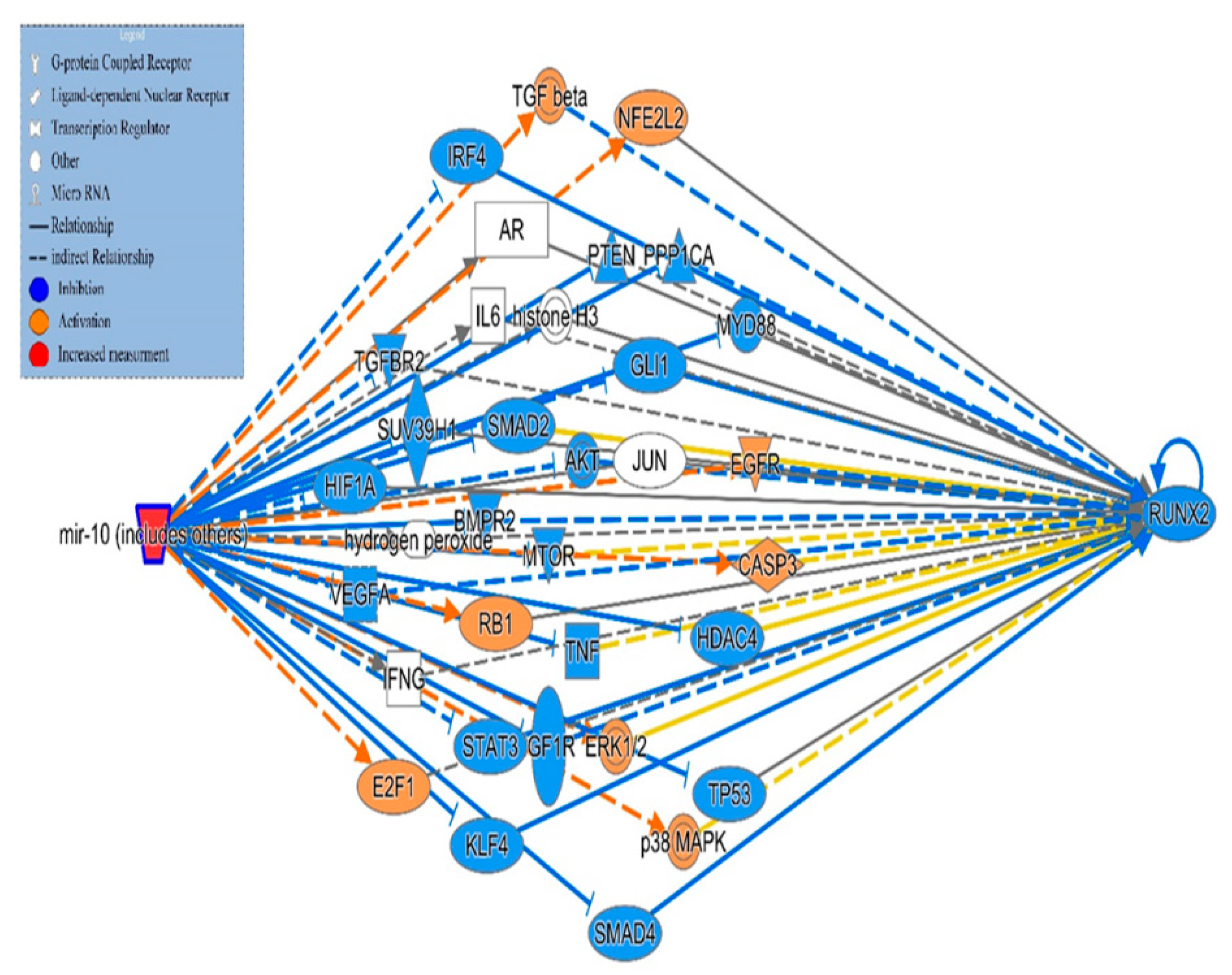

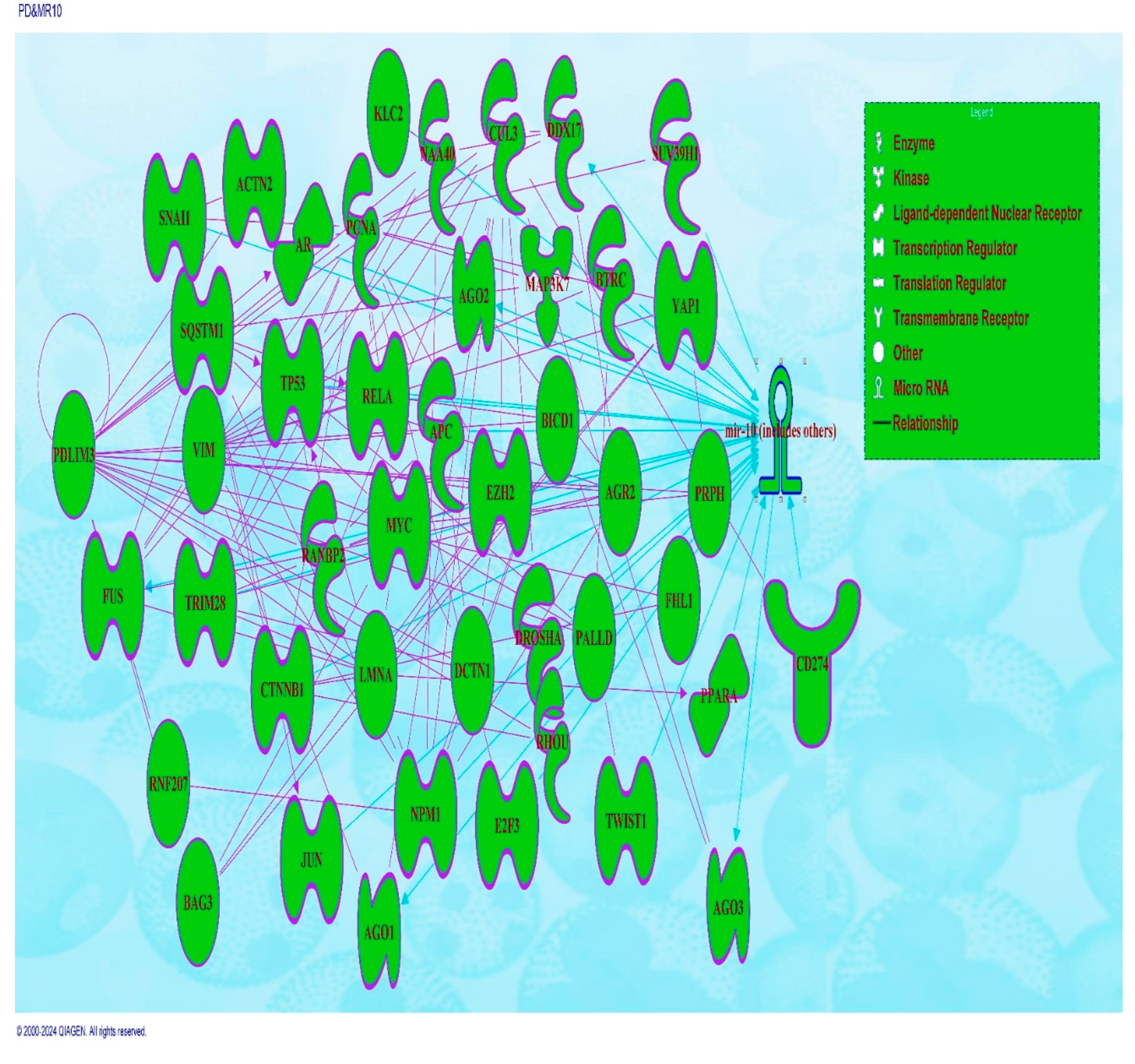
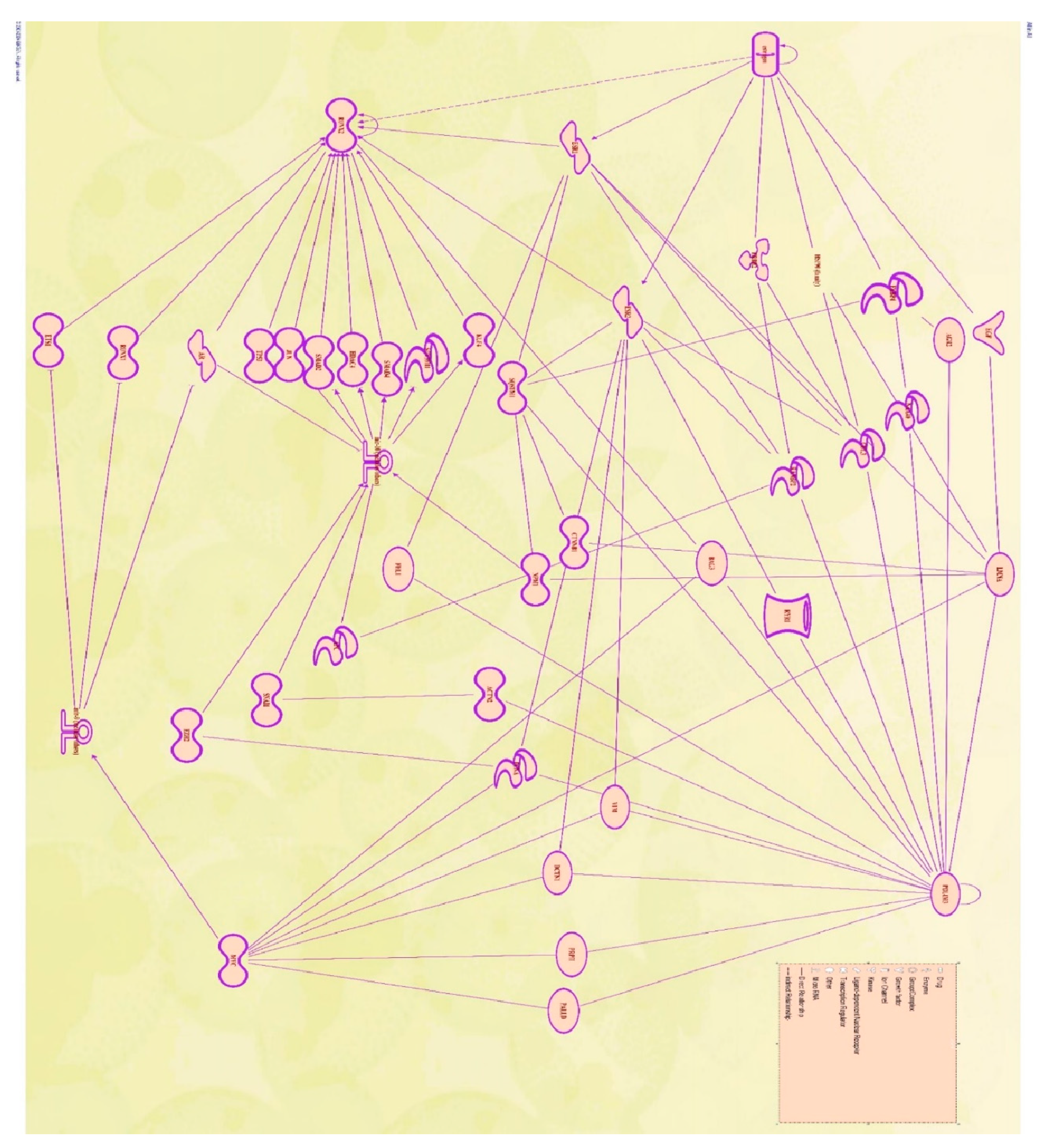
| Symbol | molecule/ Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1. | Cytoplasm | group |
|
apolipoprotein B | Extracellular Space | Transporter |
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
beta-estradiol | Other | chemical - endogenous mammalian |
|
bone morphogenetic protein 2 | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
calcitonin related polypeptide alpha | Plasma Membrane | Other |
|
calcitriol | Other | chemical drug |
|
CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 | Extracellular Space | Cytokine |
|
dinoprost | Other | chemical - endogenous mammalian |
|
dual specificity phosphatase 1 | Nucleus | Phosphatase |
|
E2F transcription factor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
epidermal growth factor | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
epidermal growth factor receptor | Plasma Membrane | Kinase |
|
E1A binding protein p300 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
ERK1/2 | Cytoplasm | Group |
|
estrogen receptor 1 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
estrogen receptor 2 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
estrogen | Other | chemical drug |
|
Fas cell surface death receptor | Plasma Membrane | transmembrane receptor |
|
Fas ligand | Extracellular Space | Cytokine |
|
fibroblast growth factor 7 | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
fibronectin 1 | Extracellular Space | Other |
|
Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
forkhead box O1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
GATA binding protein 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
histone deacetylase 1 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
hepatocyte growth factor | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
histone H3 | Nucleus | group |
|
HIVEP zinc finger 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
heat shock protein family H (Hsp110) member 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
interferon gamma | Extracellular Space | cytokine |
|
insulin like growth factor 1 | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
insulin like growth factor 1 receptor | Plasma Membrane | transmembrane receptor |
|
insulin like growth factor binding protein 5 | Extracellular Space | other |
|
Indian hedgehog signaling molecule | Extracellular Space | enzyme |
|
IL1 | Extracellular Space | group |
|
interleukin 1 beta | Extracellular Space | cytokine |
|
interleukin 6 | Extracellular Space | cytokine |
|
Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
JunB proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
JunD proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
lipocalin 2 | Extracellular Space | transporter |
|
low density lipoprotein receptor | Plasma Membrane | Transporter |
|
LH | Plasma Membrane | Complex |
|
MAPK | Cytoplasm | Group |
|
msh homeobox 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
oxytocin receptor | Plasma Membrane | G-protein coupled receptor |
|
PDZ and LIM domain 7 | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
prostaglandin E2 | Other | chemical - endogenous mammalian |
|
phosphatase and tensin homolog | Cytoplasm | Phosphatase |
|
prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 | Cytoplasm | Enzyme |
|
parathyroid hormone | Extracellular Space | Other |
|
recombination activating 1 | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
RB transcriptional corepressor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
regulatory associated protein of MTOR complex 1 | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
serpin family A member 3 | Extracellular Space | Other |
|
S-phase kinase associated protein 2 | Nucleus | other |
|
SMAD family member 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
SMAD2/3 | Cytoplasm | group |
|
SMAD family member 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
superoxide dismutase 1 | Cytoplasm | Enzyme |
|
secreted phosphoprotein 1 | Extracellular Space | Cytokine |
|
signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
TGF beta | Extracellular Space | Group |
|
transforming growth factor beta 1 | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
tumor necrosis factor | Extracellular Space | Cytokine |
|
TNF receptor superfamily member 11b | Plasma Membrane | transmembrane receptor |
|
tumor protein p53 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vitamin D receptor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vascular endothelial growth factor A | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AFP |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
membership | ESR1 |
|
activation | CTNNB1 |
|
activation | EP300 |
|
activation | ERK1/2 |
|
activation | NOTCH1 |
|
activation | SP1 |
|
activation | STAT1 |
|
activation | STAT3 |
|
activation | histone H3 |
|
inhibition | FOXO3 |
|
inhibition | RB |
|
inhibition | RB1 |
|
phosphorylation | CTNNB1 |
|
phosphorylation | EP300 |
|
phosphorylation | ERK1/2 |
|
phosphorylation | FOXO3 |
|
phosphorylation | RB |
|
phosphorylation | RB1 |
|
phosphorylation | SP1 |
|
phosphorylation | STAT1 |
|
phosphorylation | STAT3 |
|
phosphorylation | histone H3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CBL |
|
protein-protein interactions | CCNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL4A |
|
protein-protein interactions | NOTCH1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT3 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | ESR2 |
|
activation | Ap1 |
|
activation | ESR2 |
|
activation | RELA |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
activation | SMAD3 |
|
activation | SP1 |
|
activation | STAT5A |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | AR |
|
expression | CBL |
|
expression | CCNB1 |
|
expression | CEBPA |
|
expression | CEBPB |
|
expression | CEBPD |
|
expression | CTNNB1 |
|
expression | CUL4B |
|
expression | EHMT2 |
|
expression | EP300 |
|
expression | ESR2 |
|
expression | FOS |
|
expression | FOSB |
|
expression | FOSL1 |
|
expression | FOSL2 |
|
expression | FOXO1 |
|
expression | FOXO4 |
|
expression | GATA3 |
|
expression | GLI2 |
|
expression | GSN |
|
expression | HES1 |
|
expression | HEY1 |
|
expression | HIF1A |
|
expression | HSPD1 |
|
expression | HSPH1 |
|
expression | ID1 |
|
expression | IRF4 |
|
expression | JUN |
|
expression | JUNB |
|
expression | JUND |
|
expression | LIMA1 |
|
expression | NFYB |
|
expression | NOTCH1 |
|
expression | NR0B2 |
|
expression | OSTF1 |
|
expression | PPARD |
|
expression | PPARG |
|
expression | RB1 |
|
expression | RBL2 |
|
expression | RELA |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | SKP2 |
|
expression | SMAD2 |
|
expression | SMAD3 |
|
expression | SMAD5 |
|
expression | SMAD6 |
|
expression | SMURF1 |
|
expression | SMURF2 |
|
expression | SNAI1 |
|
expression | SNAI2 |
|
expression | SOX9 |
|
expression | SP1 |
|
expression | STAT1 |
|
expression | STAT3 |
|
expression | STAT5A |
|
expression | TCF7L2 |
|
expression | THRB |
|
expression | TP53 |
|
expression | TRIB3 |
|
expression | TSC22D3 |
|
expression | VDR |
|
expression | ZBTB7B |
|
inhibition | RELA |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | TP53 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | CREBBP |
|
protein-DNA interactions | ESRRA |
|
protein-DNA interactions | FOSL1 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | FOXC1 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | GATA3 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | KAT6B |
|
protein-DNA interactions | NR0B2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | PPARGC1A |
|
protein-DNA interactions | SIRT1 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | SOX9 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | STAT5A |
|
protein-DNA interactions | TP53 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | ZMYND8 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ALYREF |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | Ap1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CBX5 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CEBPA |
|
protein-protein interactions | CEBPB |
|
protein-protein interactions | CIC |
|
protein-protein interactions | CREBBP |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTBP2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL4B |
|
protein-protein interactions | DDX5 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EHMT2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EP300 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESRRA |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOS |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOSL2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOXO1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOXO4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GATA3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GSN |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HIF1A |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPH1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUN |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUNB |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUND |
|
protein-protein interactions | LIMA1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NR0B2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PPARG |
|
protein-protein interactions | PPARGC1A |
|
protein-protein interactions | RELA |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SIRT1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SKP2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMURF1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SP1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT5A |
|
protein-protein interactions | TCF7L2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | TP53 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ZBTB7B |
|
protein-protein interactions | ZMYND8 |
|
transcription | ESRRA |
|
transcription | FOS |
|
transcription | PPARGC1A |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | SIRT1 |
|
transcription | TP53 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | ESR1 |
|
activation | AR |
|
activation | ESR1 |
|
activation | RELA |
|
activation | SP1 |
|
activation | STAT3 |
|
activation | STAT5A |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | AR |
|
expression | CEBPD |
|
expression | CREBBP |
|
expression | CTNNB1 |
|
expression | EHMT2 |
|
expression | ELK1 |
|
expression | EP300 |
|
expression | ESR1 |
|
expression | EZH2 |
|
expression | FOS |
|
expression | FOSL2 |
|
expression | FOXC2 |
|
expression | FOXO1 |
|
expression | FOXO3 |
|
expression | GATA1 |
|
expression | GATA3 |
|
expression | HSPD1 |
|
expression | JAG2 |
|
expression | JUNB |
|
expression | KLF4 |
|
expression | NOTCH1 |
|
expression | RELA |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | SKP2 |
|
expression | SMAD2 |
|
expression | SMAD3 |
|
expression | SMAD4 |
|
expression | SNAI1 |
|
expression | SNAI2 |
|
expression | SP1 |
|
expression | SRF |
|
expression | TWIST1 |
|
expression | YY1 |
|
expression | osteocalcin |
|
inhibition | RELA |
|
protein-DNA interactions | FOS |
|
protein-RNA interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ALYREF |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | ASAH1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CIC |
|
protein-protein interactions | CREBBP |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTBP2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EED |
|
protein-protein interactions | EHMT2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EP300 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOS |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOXO3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SP1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT5A |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
membership | ESR1 |
|
membership | ESR2 |
|
membership | ESR1 |
|
membership | ESR2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
activation | AR |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DET1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EWSR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EZH2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NR3C1 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
membership | GNB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
activation | AR |
|
activation | STAT3 |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EWSR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GATA3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC6 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HIF1A |
|
protein-protein interactions | NR3C1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STAT3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | STUB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | TP53 |
|
protein-protein interactions | histone H4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | ESR1 |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
phosphorylation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | NOTCH1 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
localization | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
molecular cleavage | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ALYREF |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | Ap1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CCNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CEBPB |
|
protein-protein interactions | CEBPD |
|
protein-protein interactions | CIC |
|
protein-protein interactions | CREBBP |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTBP2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL4A |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL4B |
|
protein-protein interactions | DDX5 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DET1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EHMT2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EP300 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERK1/2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ETS1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EWSR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FHL2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOS |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOXO1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GATA3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GLI2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GNB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GSN |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC5 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC6 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC7 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HES1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HEY1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HIF1A |
|
protein-protein interactions | HMGB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPA4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPA4L |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSPH1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | IFI16 |
|
protein-protein interactions | IMPDH1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | JAG2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUN |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUNB |
|
protein-protein interactions | KAT2B |
|
protein-protein interactions | KAT6A |
|
protein-protein interactions | KAT6B |
|
protein-protein interactions | KLF4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LEF1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LIMA1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MATK |
|
protein-protein interactions | MEN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MSX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NFYB |
|
protein-protein interactions | NOTCH1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NR0B2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PIN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PML |
|
protein-protein interactions | PPARG |
|
protein-protein interactions | RB |
|
protein-protein interactions | RB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RBL2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RBM14 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RBM28 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD5 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SNAI1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | osteocalcin |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AFP |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | PTH |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
activation | ERBB2 |
|
activation | ESR1 |
|
activation | ESR2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
activation | estrogen receptor |
|
chemical-protein interactions | AFP |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen receptor |
|
inhibition | ERBB2 |
|
reaction | ER/estrogen |
|
reaction | ESTG:ESR1:chaperone |
|
reaction | ESTG:ESR2:chaperone |
|
reaction | ESTG:Me-PalmS-ESR dimers |
|
translocation | estrogen |
|
activation | FOS |
|
activation | JUN |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
inhibition | DDX5 |
|
membership | ESR1 |
|
membership | ESR2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | FOS |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | CREBBP |
|
protein-protein interactions | DDX5 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EP300 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FOS |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUN |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
| Symbol | Molecule/ Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
catenin beta 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 | Plasma Membrane | G-protein coupled receptor |
|
ELAV like RNA binding protein 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
ETS proto-oncogene 1, transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Meis homeobox 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
relatives of microRNA 9 | Cytoplasm | microRNA |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Sp1 transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
localization | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
molecular cleavage | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ETS1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX1 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | AR |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | CXCR4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | ETS1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | RUNX1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | AR |
|
expression | AR |
|
expression | CTNNB1 |
|
expression | CXCR4 |
|
expression | ETS1 |
|
expression | MEIS2 |
|
expression | RUNX1 |
|
expression | SP1 |
|
inhibition | ELAVL1 |
| Symbol | Molecule/ Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cytoplasm | group | |
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 | Plasma Membrane | kinase |
|
caspase 3 | Cytoplasm | peptidase |
|
E2F transcription factor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
epidermal growth factor receptor | Plasma Membrane | kinase |
|
Cytoplasm | group | |
|
GLI family zinc finger 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
histone deacetylase 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Nucleus | Group | |
|
Other | chemical - endogenous mammalian | |
|
interferon gamma | Extracellular Space | Cytokine |
|
insulin like growth factor 1 receptor | Plasma Membrane | transmembrane receptor |
|
interleukin 6 | Extracellular Space | Cytokine |
|
interferon regulatory factor 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
KLF transcription factor 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
relatives of microRNA 10 | Cytoplasm | microRNA |
|
mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase | Nucleus | Kinase |
|
MYD88 innate immune signal transduction adaptor | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
NFE2 like bZIP transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Cytoplasm | group | |
|
protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit alpha | Cytoplasm | phosphatase |
|
phosphatase and tensin homolog | Cytoplasm | phosphatase |
|
RB transcriptional corepressor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
SMAD family member 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
SMAD family member 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
Extracellular Space | group | |
|
transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 | Plasma Membrane | kinase |
|
tumor necrosis factor | Extracellular Space | cytokine |
|
tumor protein p53 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vascular endothelial growth factor A | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
phosphorylation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
phosphorylation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
localization | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
molecular cleavage | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERK1/2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | GLI1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HIF1A |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUN |
|
protein-protein interactions | KLF4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NFE2L2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD4 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
localization | RUNX2 |
|
molecular cleavage | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | AR |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | BMPR2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | HDAC4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | IGF1R |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | KLF4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | MTOR |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | MYD88 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | PPP1CA |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | PTEN |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SMAD2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SMAD4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SUV39H1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | TNF |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | TP53 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | JUN |
|
activation | AKT |
|
activation | CASP3 |
|
activation | EGFR |
|
activation | ERK1/2 |
|
activation | STAT3 |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
expression | AKT |
|
expression | AR |
|
expression | BMPR2 |
|
expression | E2F1 |
|
expression | GLI1 |
|
expression | HDAC4 |
|
expression | HIF1A |
|
expression | IGF1R |
|
expression | IL6 |
|
expression | IRF4 |
|
expression | KLF4 |
|
expression | MTOR |
|
expression | MYD88 |
|
expression | NFE2L2 |
|
expression | PPP1CA |
|
expression | PTEN |
|
expression | RB1 |
|
expression | SMAD2 |
|
expression | SMAD4 |
|
expression | SUV39H1 |
|
expression | TGF beta |
|
expression | TGFBR2 |
|
expression | TNF |
|
expression | TP53 |
|
expression | VEGFA |
|
expression | p38 MAPK |
|
localization | IFNG |
|
localization | hydrogen peroxide |
|
molecular cleavage | CASP3 |
|
phosphorylation | AKT |
|
phosphorylation | EGFR |
|
phosphorylation | ERK1/2 |
|
phosphorylation | STAT3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SUV39H1 |
|
regulation of binding | IL6 |
|
regulation of binding | histone H3 |
|
translocation | STAT3 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
| Symbol | Molecule/ Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
actinin alpha 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
argonaute RISC catalytic component 2 | Cytoplasm | translation regulator |
|
argonaute RISC catalytic component 3 | Cytoplasm | translation regulator |
|
anterior gradient 2, protein disulphide isomerase family member | Extracellular Space | other |
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
BAG cochaperone 3 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
BICD cargo adaptor 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
CD274 molecule | Plasma Membrane | transmembrane receptor |
|
cullin 3 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
dynactin subunit 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
drosha ribonuclease III | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
four and a half LIM domains 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
FUS RNA binding protein | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
FMR1 autosomal homolog 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
lamin A/C | Nucleus | other |
|
relatives of microRNA 9 | Cytoplasm | microRNA |
|
MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
MYCN proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
N-alpha-acetyltransferase 40, NatD catalytic subunit | Cytoplasm | enzyme |
|
palladin, cytoskeletal associated protein | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
proliferating cell nuclear antigen | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
PDZ and LIM domain 3 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
peripheral myelin protein 22 | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
peripherin | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
RAN binding protein 2 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
RE1 silencing transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
sequestosome 1 | Cytoplasm | transcription regulator |
|
TAR DNA binding protein | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vimentin | Cytoplasm | other |
|
Yes1 associated transcriptional regulator | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
activation | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
expression | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO3 |
|
expression | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
expression | CD274 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CD274 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
regulation of binding | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
expression | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
molecular cleavage | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-RNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BICD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
expression | MYC |
|
inhibition | YAP1 |
|
localization | YAP1 |
|
phosphorylation | YAP1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | FXR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | YAP1 |
|
transcription | YAP1 |
|
expression | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
transcription | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FHL1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYCN |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BICD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FHL1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PALLD |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
regulation of binding | ACTN2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYCN |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | FHL1 |
|
activation | AR |
|
localization | AR |
|
molecular cleavage | TARDBP |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | REST |
|
protein-protein interactions | TARDBP |
|
expression | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SQSTM1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | FXR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYCN |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PRPH |
|
protein-protein interactions | VIM |
|
transcription | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | AR |
|
protein-RNA interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | AGO3 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | FUS |
|
protein-RNA interactions | FXR1 |
| Symbol | Entrez Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
actinin alpha 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
argonaute RISC component 1 | Cytoplasm | translation regulator |
|
argonaute RISC catalytic component 2 | Cytoplasm | translation regulator |
|
argonaute RISC catalytic component 3 | Cytoplasm | translation regulator |
|
anterior gradient 2, protein disulphide isomerase family member | Extracellular Space | other |
|
APC regulator of WNT signaling pathway | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
BAG cochaperone 3 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
BICD cargo adaptor 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
beta-transducin repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase | Cytoplasm | enzyme |
|
CD274 molecule | Plasma Membrane | transmembrane receptor |
|
catenin beta 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
cullin 3 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
dynactin subunit 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
DEAD-box helicase 17 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
drosha ribonuclease III | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
E2F transcription factor 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
four and a half LIM domains 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
FUS RNA binding protein | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
kinesin light chain 2 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
lamin A/C | Nucleus | other |
|
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 | Cytoplasm | kinase |
|
relatives of microRNA 10 | Cytoplasm | microRNA |
|
MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
N-alpha-acetyltransferase 40, NatD catalytic subunit | Cytoplasm | enzyme |
|
nucleophosmin 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
palladin, cytoskeletal associated protein | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
proliferating cell nuclear antigen | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
PDZ and LIM domain 3 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
peripherin | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
RAN binding protein 2 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
ras homolog family member U | Cytoplasm | enzyme |
|
ring finger protein 207 | Other | other |
|
snail family transcriptional repressor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
sequestosome 1 | Cytoplasm | transcription regulator |
|
SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
tumor protein p53 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
tripartite motif containing 28 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
twist family bHLH transcription factor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vimentin | Cytoplasm | other |
|
Yes1 associated transcriptional regulator | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
activation | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
inhibition | TP53 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | TP53 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BICD1 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CD274 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | APC |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | PPARA |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EZH2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | TP53 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | DDX17 |
|
protein-protein interactions | KLC2 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BICD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BTRC |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | APC |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DDX17 |
|
protein-protein interactions | E2F3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EZH2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | MAP3K7 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BICD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FHL1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PALLD |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | APC |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EZH2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NPM1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
transcription | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
activation | AR |
|
activation | TP53 |
|
expression | RELA |
|
expression | SNAI1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUN |
|
protein-protein interactions | MAP3K7 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | NPM1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RELA |
|
protein-protein interactions | SNAI1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | TP53 |
|
transcription | JUN |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | mir-10 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BICD1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PALLD |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | RANBP2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SQSTM1 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | RANBP2 |
|
expression | mir-10 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PALLD |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | APC |
|
protein-protein interactions | BTRC |
|
protein-protein interactions | EZH2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | NPM1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RELA |
|
protein-protein interactions | TP53 |
|
protein-protein interactions | TRIM28 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PRPH |
|
protein-protein interactions | VIM |
|
transcription | mir-10 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | APC |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | BTRC |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | JUN |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | MAP3K7 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | AGO1 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | AGO2 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | AGO3 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | DDX17 |
|
protein-RNA interactions | FUS |
|
protein-protein interactions | KLC2 |
| Symbol | Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
actinin alpha 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
anterior gradient 2, protein disulphide isomerase family member | Extracellular Space | other |
|
APC regulator of WNT signaling pathway | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
BAG cochaperone 3 | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
catenin beta 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
cullin 3 | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
dynactin subunit 1 | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
epidermal growth factor | Extracellular Space | growth factor |
|
erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 | Plasma Membrane | Kinase |
|
estrogen receptor 1 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
estrogen receptor 2 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
ETS proto-oncogene 1, transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
four and a half LIM domains 1 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
FKBP prolyl isomerase 4 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
histone deacetylase 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Cytoplasm | group | |
|
Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
KLF transcription factor 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
lamin A/C | Nucleus | other |
|
relatives of microRNA 10 | Cytoplasm | microRNA |
|
relatives of microRNA 9 | Cytoplasm | microRNA |
|
MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
N-alpha-acetyltransferase 40, NatD catalytic subunit | Cytoplasm | enzyme |
|
nucleophosmin 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
palladin, cytoskeletal associated protein | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
proliferating cell nuclear antigen | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
PDZ and LIM domain 3 | Cytoplasm | other |
|
peripherin | Plasma Membrane | other |
|
RAN binding protein 2 | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
ryanodine receptor 1 | Cytoplasm | ion channel |
|
SMAD family member 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
SMAD family member 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
snail family transcriptional repressor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
sequestosome 1 | Cytoplasm | transcription regulator |
|
SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase | Nucleus | enzyme |
|
tumor protein p53 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vimentin | Cytoplasm | other |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EGF |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HSP90 (family) |
|
expression | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-DNA interactions | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
transcription | mir-9 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | EZH2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AGR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FHL1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PALLD |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | APC |
|
protein-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
localization | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
molecular cleavage | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | BAG3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ETS1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | JUN |
|
protein-protein interactions | KLF4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | SMAD4 |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | ACTN2 |
|
transcription | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
protein-protein interactions | CTNNB1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | FKBP4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NPM1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | mir-10 (includes others) |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | MYC |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
activation | ESR1 |
|
activation | ESR2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | EGF |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ERBB2 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
translocation | estrogen |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | AR |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | HDAC4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | KLF4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SMAD2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SMAD4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SUV39H1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | APC |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | JUN |
|
expression | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | SUV39H1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | AR |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | ETS1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | RUNX1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: non-targeting interactions | AR |
|
expression | AR |
|
expression | ETS1 |
|
expression | RUNX1 |
| Symbol | Molecule/ Gene Name | Location | Family |
|---|---|---|---|
|
androgen receptor | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
chromobox 5 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
cyclin D1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
cyclin dependent kinase 4 | Nucleus | kinase |
|
cullin 3 | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
dynactin subunit 1 | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
E74 like ETS transcription factor 4 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
estrogen receptor 1 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
estrogen receptor 2 | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
Other | chemical drug | |
|
FosB proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
FOS like 1, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
FOS like 2, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Plasma Membrane | Complex | |
|
histone deacetylase 7 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
hes family bHLH transcription factor 1 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
HIVEP zinc finger 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
homeobox A11 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
Plasma Membrane | Complex | |
|
lamin A/C | Nucleus | Other |
|
mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | Cytoplasm | Kinase |
|
Meis homeobox 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
methyltransferase 14, N6-adenosine-methyltransferase subunit | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
Cytoplasm | mature microRNA | |
|
microRNA 6769b | Other | microRNA |
|
N-alpha-acetyltransferase 40, NatD catalytic subunit | Cytoplasm | Enzyme |
|
nuclear factor I A | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
PBX homeobox 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
proliferating cell nuclear antigen | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
PDZ and LIM domain 3 | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor delta | Nucleus | ligand-dependent nuclear receptor |
|
PPARG coactivator 1 beta | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
RUNX family transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
tafazzin, phospholipid-lysophospholipid transacylase | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 3 | Nucleus | Enzyme |
|
thyroid hormone receptor associated protein 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
TSC22 domain family member 3 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
twist family bHLH transcription factor 2 | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
upstream binding transcription factor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vitamin D receptor | Nucleus | transcription regulator |
|
vimentin | Cytoplasm | Other |
|
YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein F2 | Cytoplasm | Other |
| From Molecule(s) | Relationship Type | To Molecule(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
regulation of binding | estrogen |
|
chemical-protein interactions | estrogen |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | YTHDF2 |
|
expression | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | MIR6769B |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
processing yields | miR-1896 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | LMNA |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PCNA |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
transcription | RUNX2 |
|
activation | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
inhibition | HIVEP3 |
|
inhibition | RUNX2 |
|
localization | RUNX2 |
|
modification | RUNX2 |
|
molecular cleavage | RUNX2 |
|
protein-DNA interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | AR |
|
protein-protein interactions | ELF4 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HDAC7 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HES1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HIVEP3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | HOXA11 |
|
protein-protein interactions | TAFAZZIN |
|
regulation of binding | RUNX2 |
|
ubiquitination | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | RUNX2 |
|
protein-protein interactions | METTL14 |
|
protein-protein interactions | PDLIM3 |
|
expression | MIR6769B |
|
protein-protein interactions | CUL3 |
|
protein-protein interactions | DCTN1 |
|
protein-protein interactions | NAA40 |
|
activation | CDK4 |
|
activation | ESR1 |
|
activation | ESR2 |
|
activation | MAPK1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR1 |
|
chemical-protein interactions | ESR2 |
|
expression | CCND1 |
|
expression | ESR1 |
|
expression | ESR2 |
|
expression | FSH |
|
expression | LH |
|
expression | PCNA |
|
localization | FSH |
|
localization | LH |
|
molecular cleavage | ESR1 |
|
phosphorylation | ESR1 |
|
phosphorylation | ESR2 |
|
phosphorylation | MAPK1 |
|
regulation of binding | CCND1 |
|
regulation of binding | CDK4 |
|
regulation of binding | ESR1 |
|
regulation of binding | ESR2 |
|
transcription | CCND1 |
|
translocation | ESR1 |
|
translocation | ESR2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | AR |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | CBX5 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | ELF4 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | FOSB |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | FOSL1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | FOSL2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | HDAC7 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | HES1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | HIVEP3 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | HOXA11 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | MEIS2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | NFIA |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | PBX3 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | PPARD |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | PPARGC1B |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | RUNX2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | SUV39H1 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | TAFAZZIN |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | TET3 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | THRAP3 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | TSC22D3 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | TWIST2 |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | UBTF |
|
RNA-RNA interactions: microRNA targeting | VDR |
|
expression | RUNX2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





