Submitted:
25 June 2025
Posted:
25 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
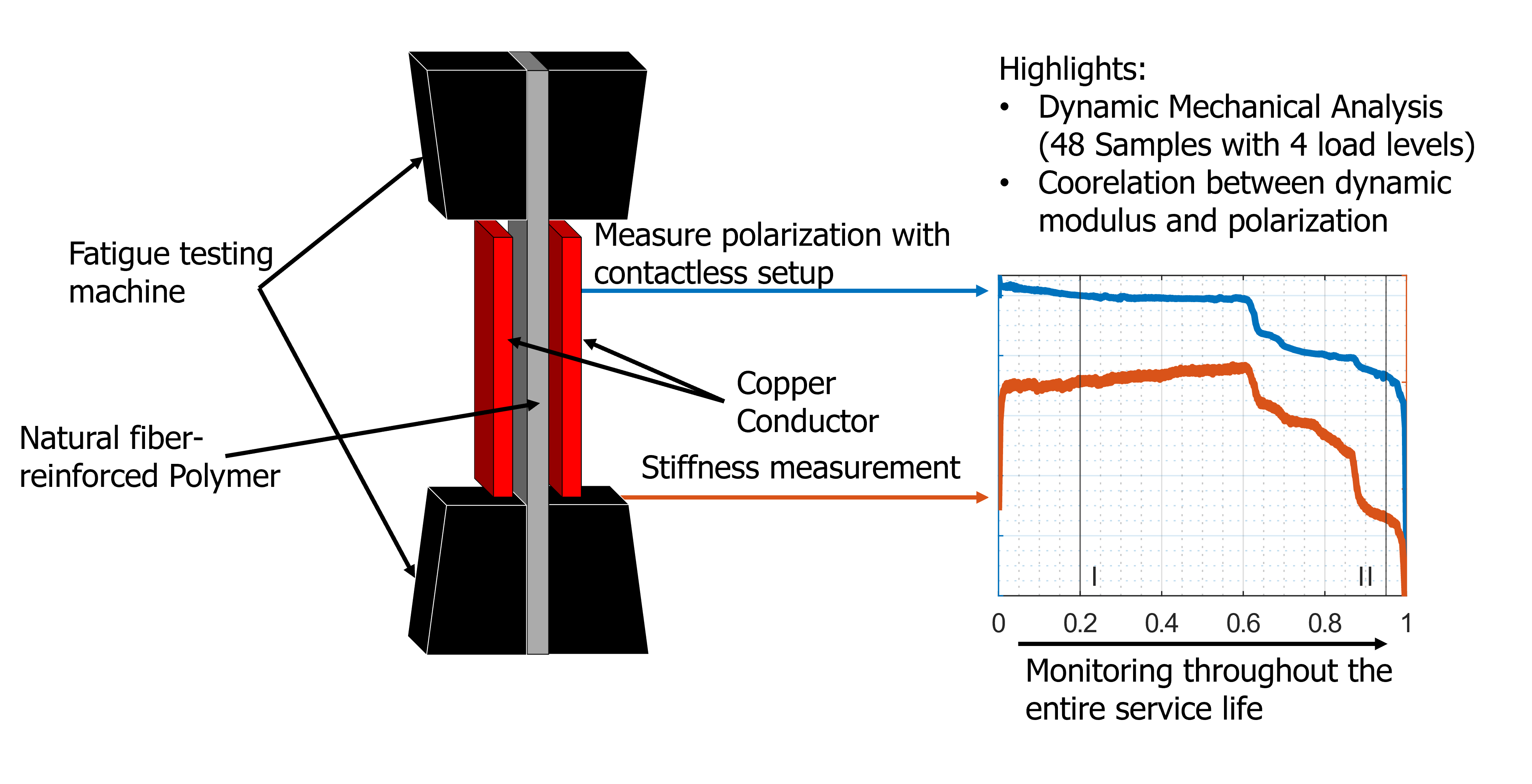
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manufacturing of Flax Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Samples
2.2. Dynamic Investigation of the Composite Material
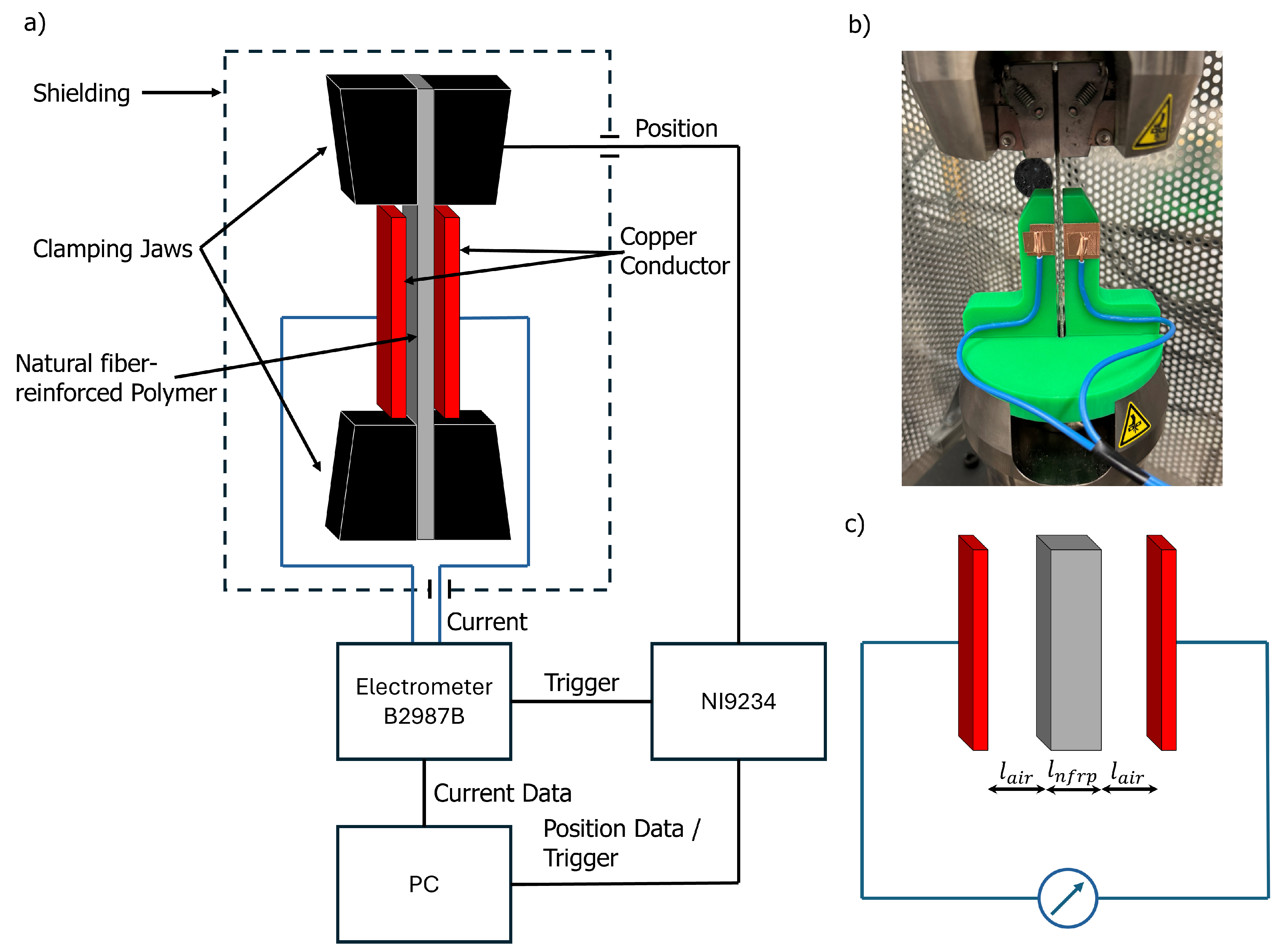
2.3. Electrical Measurement Setup
2.4. Derivation of Composite Material Polarization
2.5. Procedure Before the Experiment
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results & Discussion
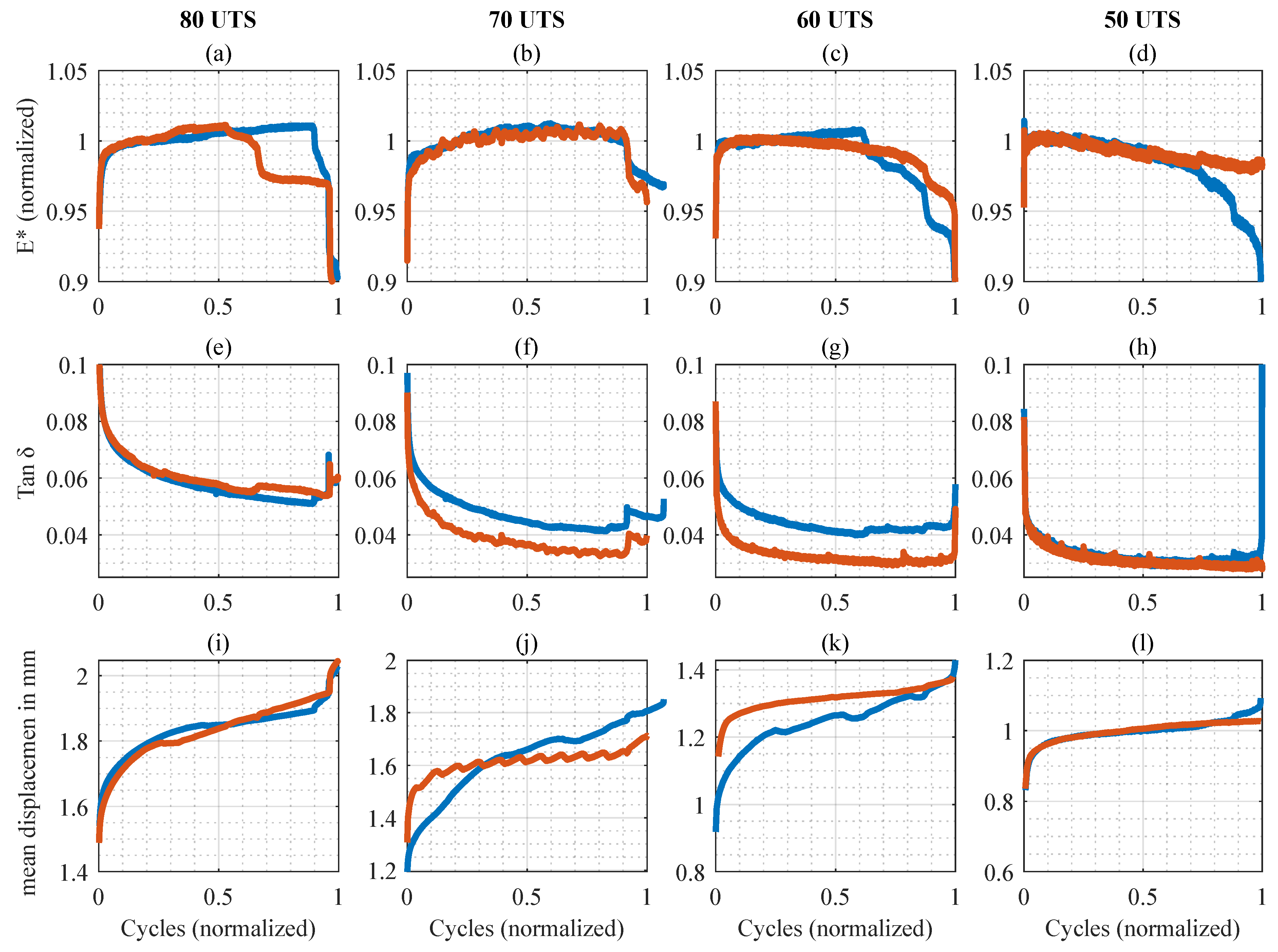
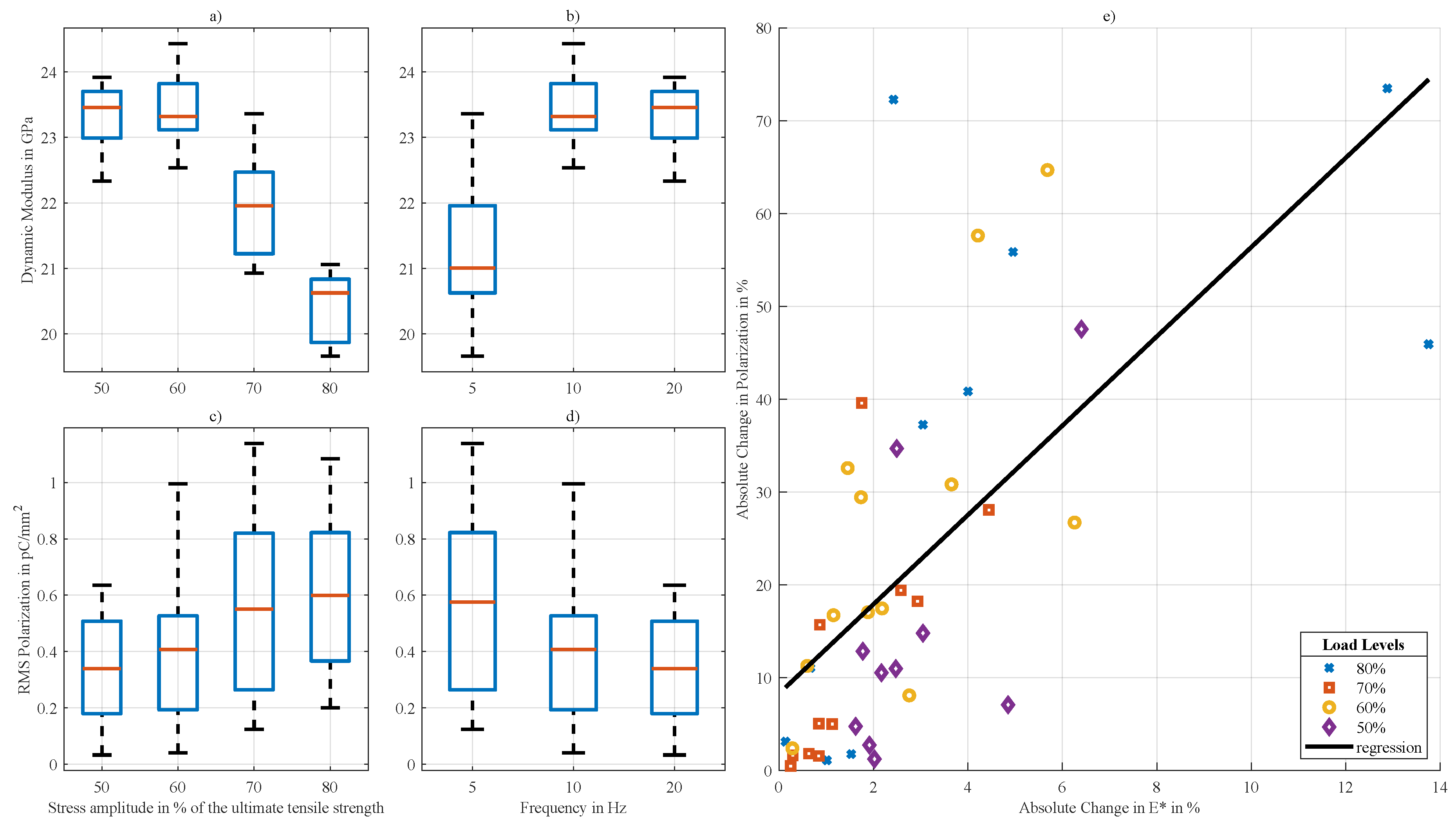
3.1. Mechanical Analysis
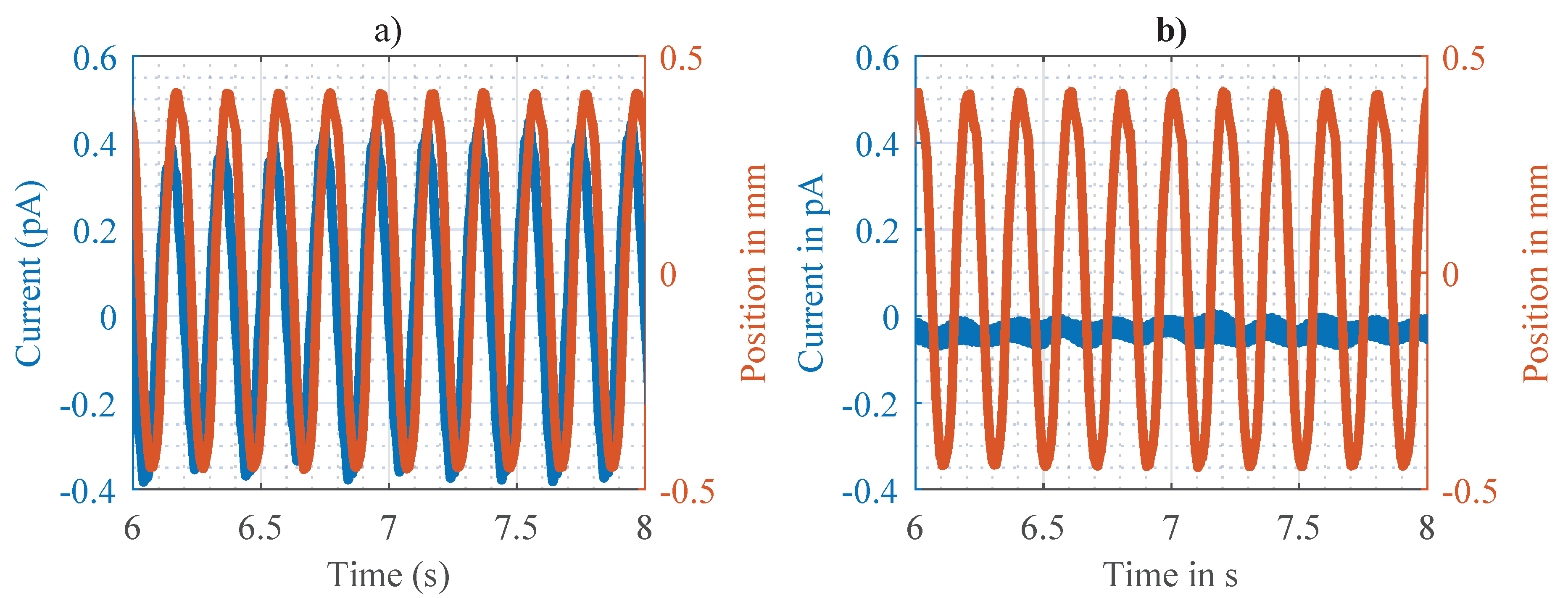
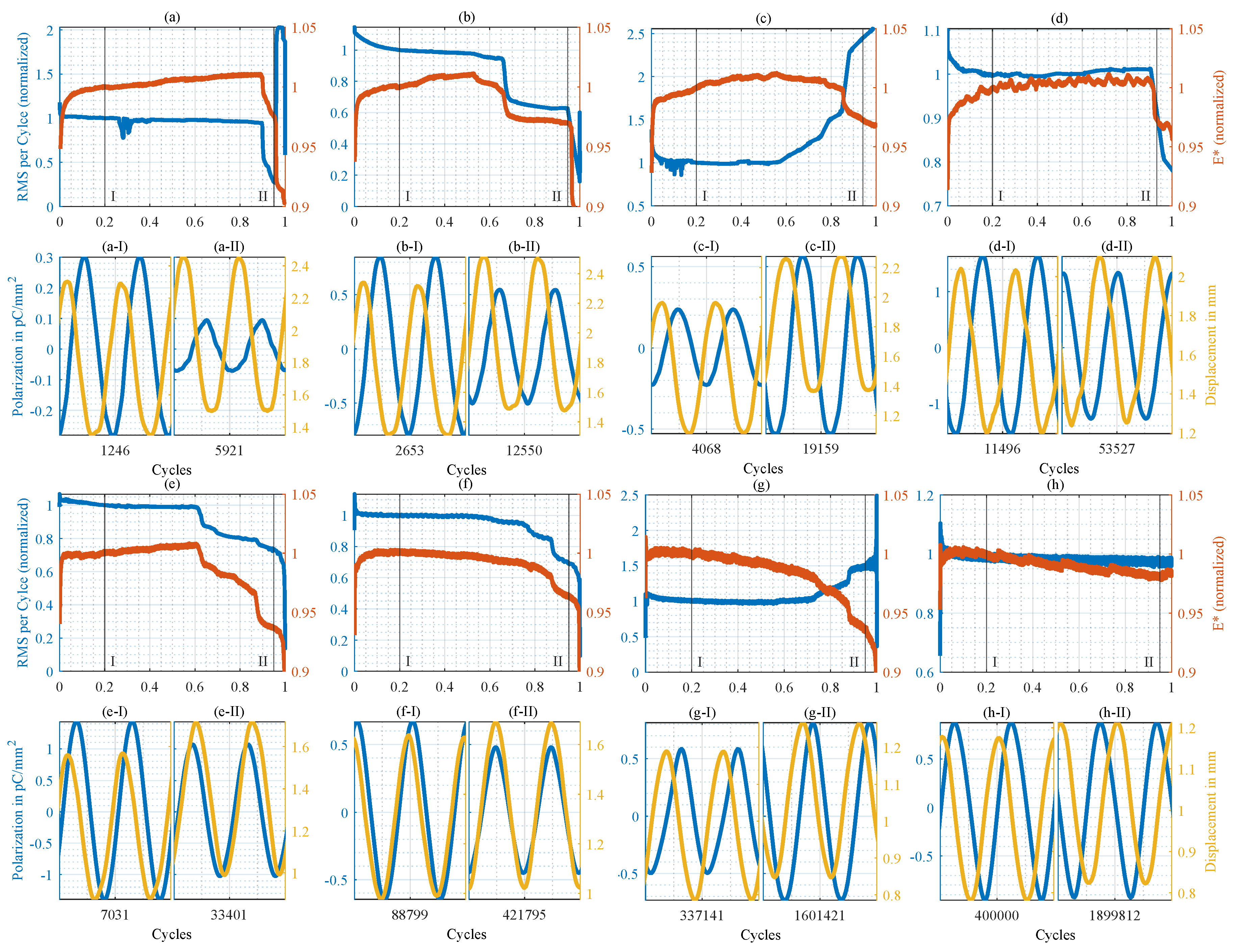
3.2. Mechanoelectrial Analysis
3.3. Cause of the Electrical Effect
3.4. Future Challenges
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Measurement of the Permittivity of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Polymers at Low Frequencies
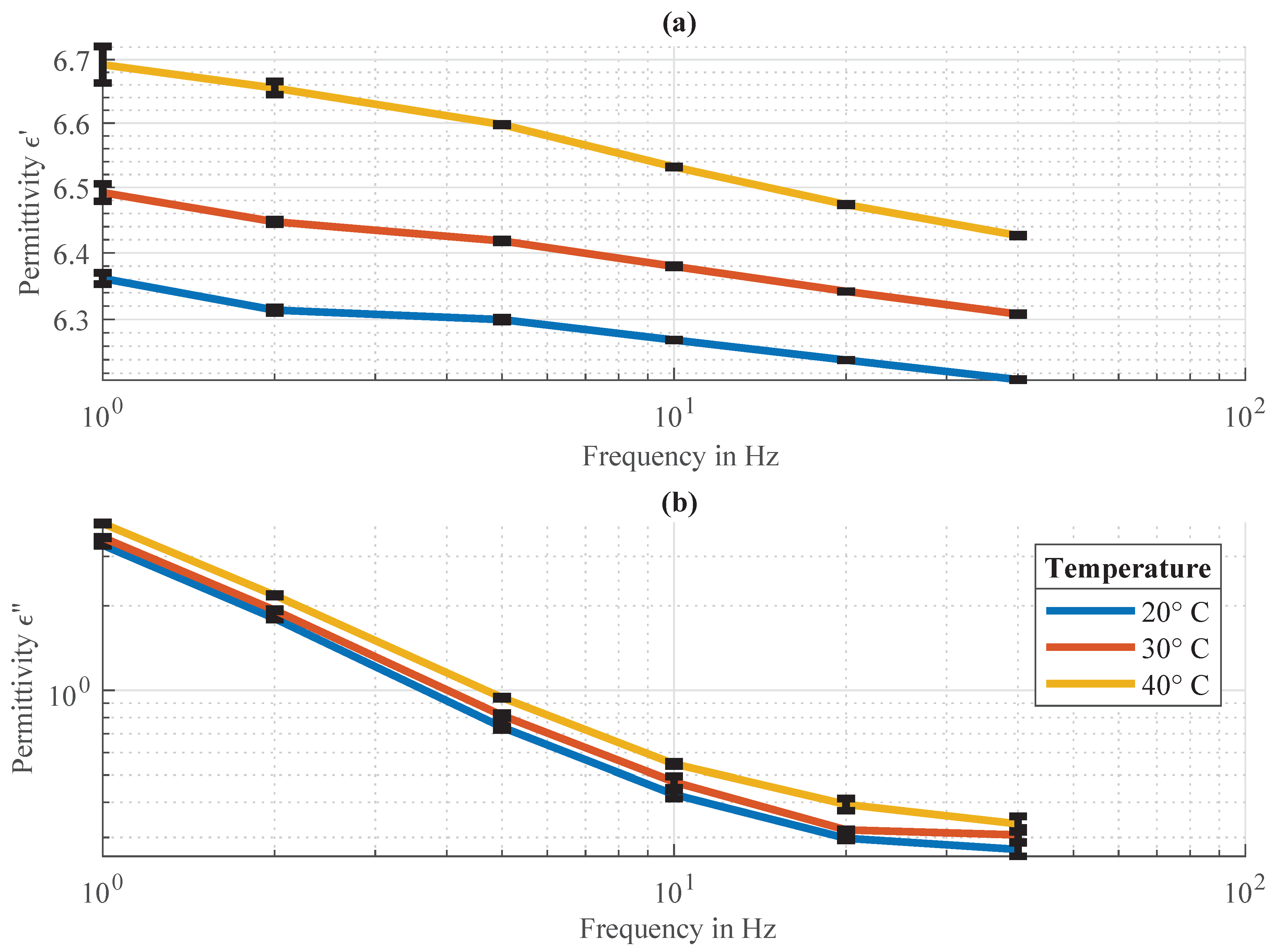
| UTS in % | Excitation Frequency (Hz) | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 5 | 40 | 6.6 | 0.94 |
| 70 | 5 | 40 | 6.6 | 0.94 |
| 60 | 10 | 40 | 6.53 | 0.55 |
| 50 | 20 | 40 | 6.47 | 0.39 |
Appendix B. Simulation of Mechanoelectrical Effects with Variable Stiffness
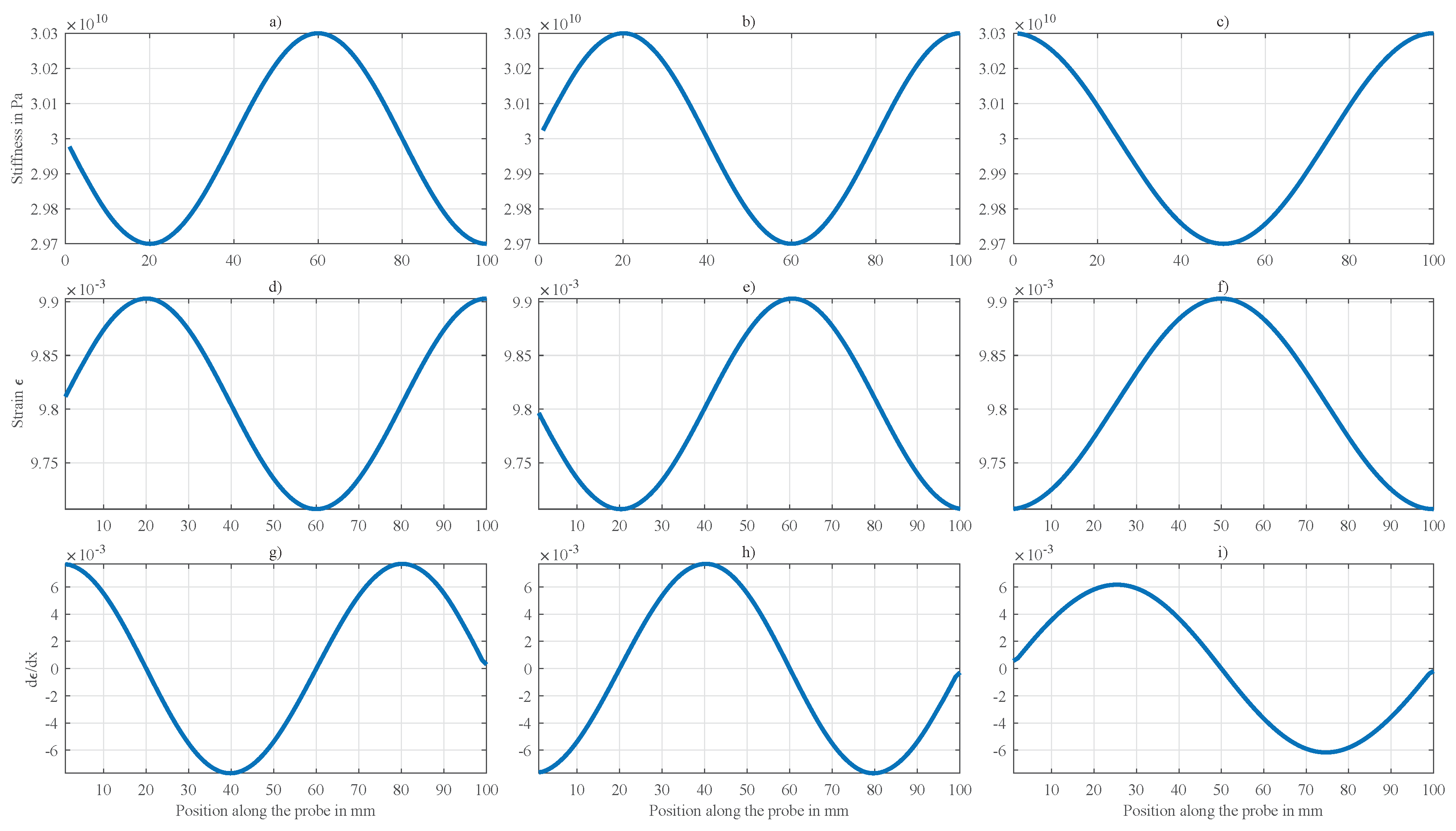
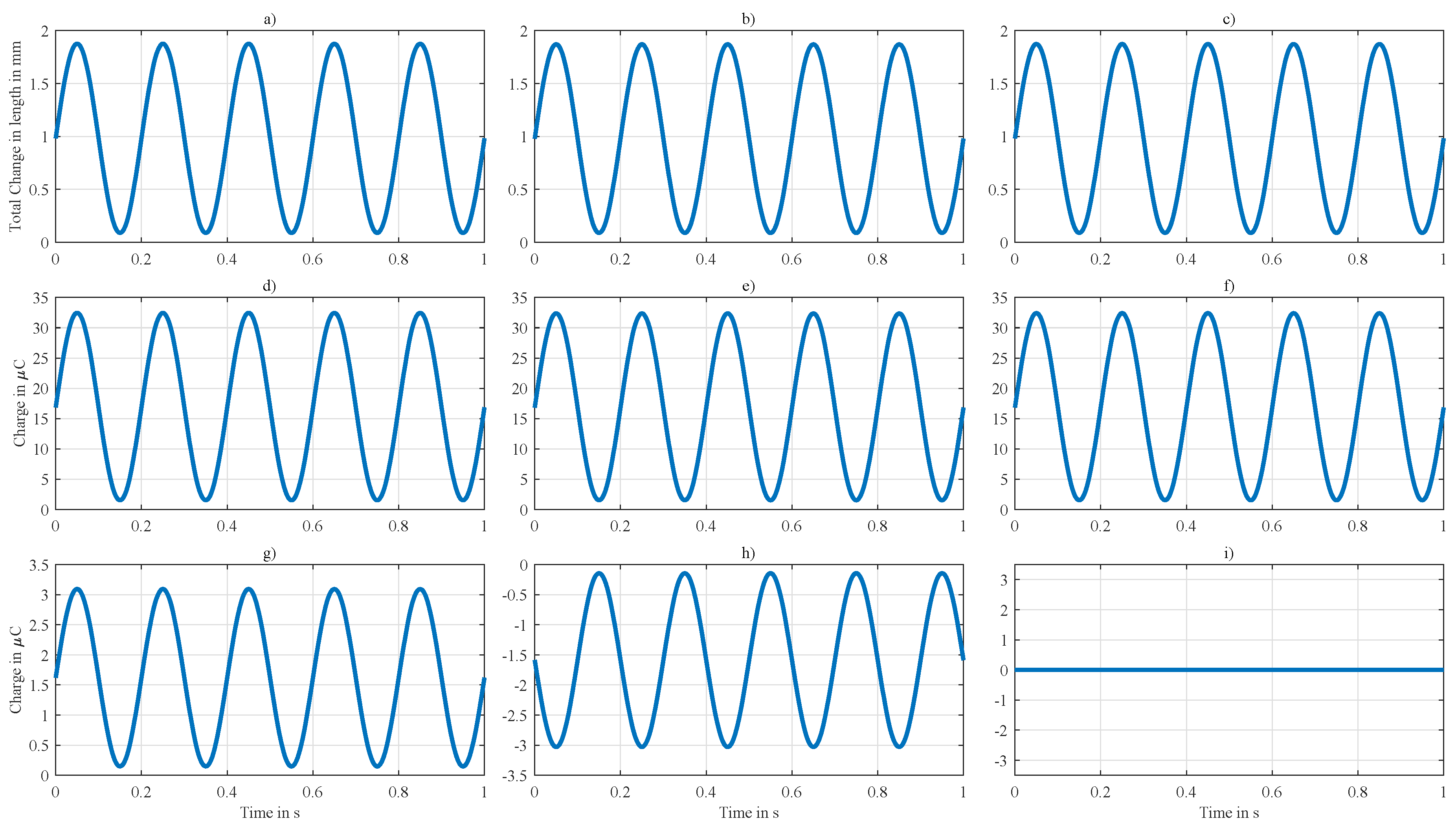
Appendix C. Values Used for Normalization
| Specimen | E* in MPa | RMS Polarization | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| P04 P1 | 20.644,69 | 0,2073 | 6.233 |
| P04 P2 | 21.061,19 | 0,5786 | 13.268 |
| P06 P1 | 20.927,75 | 0,1669 | 20.344 |
| P07 P5 | 21.819,09 | 1,1318 | 57.482 |
| P09 P4 | 23.372,05 | 0,9952 | 35.159 |
| P09 P5 | 23.903,58 | 0,4608 | 443.995 |
| P10 P6 | 22.948,86 | 0,3654 | 1.685.707 |
| P11 P3 | 23.072,00 | 0,6357 | 2.000.000 |
References
- Niels de Beus.; Michael Carus.; Martha Barth. Carbon Footprint and Sustainability of Different Natural Fibres for Biocomposites and Insulation Material: Study providing data for the automotive and insulation industry.
- Summerscales, J.; Dissanayake, N.P.; Virk, A.S.; Hall, W. A review of bast fibres and their composites. Part 1 – Fibres as reinforcements. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2010, 41, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, P.; Ivens, J.; Verpoest, I. Natural fibres: can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics? Composites Science and Technology 2003, 63, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Drzal, L.; Mohanty, A.; Arora, S. Are natural fiber composites environmentally superior to glass fiber reinforced composites? Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2004, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANDERSONS, J.; SPARNINS, E.; JOFFE, R.; WALLSTROM, L. Strength distribution of elementary flax fibres. Composites Science and Technology 2005, 65, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Mizue, T.; Goda, K.; Noda, J. Effects of fluctuation of fibre orientation on tensile properties of flax sliver-reinforced green composites. Composite Structures 2012, 94, 3457–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Worden, K. An introduction to structural health monitoring. Philosophical transactions. Series A, Mathematical, physical, and engineering sciences 2007, 365, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Koch, K.P.; Fischer, G. Measuring Deformation in Natural Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Using Mechanoelectrical Effect. IEEE Sensors Letters 2024, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Mousavi, M.; Gandomi, A.H. Structural Health Monitoring in Composite Structures: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, P.; Lenz, P.; Wittmann, A.; Fischer, G. Integrity-Sensing Based on Surface Roughness of Copper Conductors for Future Use in Natural Fiber Composites. IEEE Sensors Letters 2021, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, P. Entwicklung eines mechano-elektrischen Sensorelements zur strukturellen Bauteilüberwachung von Naturfaserverbundwerkstoffen mittels hochfrequenter Wechselströme; Vol. 46, FAU Forschungen Reihe B, FAU University Press: Erlangen, 2024.
- Wen, J.; Xia, Z.; Choy, F. Damage detection of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites via electrical resistance measurement. Composites Part B: Engineering 2011, 42, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.C.; Robert, C.; Koutsos, V.; Ray, D. Methods of modifying through-thickness electrical conductivity of CFRP for use in structural health monitoring, and its effect on mechanical properties – A review. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2020, 133, 105885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkov, M.; Eremin, A. Hybrid CFRP/SWCNT Composites with Enhanced Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 2018, 27, 5984–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Wang, H.; Bi, Y. Using acoustic emission technique for structural health monitoring of laminate composite: A novel CNN-LSTM framework. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 2024, 309, 110447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadarah, N.; Ayre, D. A Review on Acoustic Emission Testing for Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer-Based Composites. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, S.; El Mahi, A.; Turki, S. Fatigue behaviour and structural health monitoring by acoustic emission of E-glass/epoxy laminates with piezoelectric implant. Applied Acoustics 2016, 108, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzo, F.; Huang, Y.; Nemat-Nasser, S. Onset of Resin Micro-Cracks in Unidirectional Glass Fiber Laminates with Integrated SHM Sensors: Experimental Results. Structural Health Monitoring 2009, 8, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuloup, C.; Harizi, W.; Aboura, Z.; Meyer, Y. Integration of piezoelectric transducers (PZT and PVDF) within polymer-matrix composites for structural health monitoring applications: new success and challenges. International Journal of Smart and Nano Materials 2020, 11, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niezrecki, C.; Baqersad, J.; Sabato, A. Digital Image Correlation Techniques for NDE and SHM. Mechanical Engineering Publications 2018, 111, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Blanc, R.; Soutis, C.; Withers, P.J. Evolution of damage during the fatigue of 3D woven glass-fibre reinforced composites subjected to tension–tension loading observed by time-lapse X-ray tomography. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2016, 82, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.Y.; Yang, L.X.; Huang, Y.H., Eds. Non-destructive evaluation (NDE) of composites: digital shearography; Elsevier, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Dong, C.Z.; Liu, T. A Review of Machine Vision-Based Structural Health Monitoring: Methodologies and Applications. Journal of Sensors 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payawal, J.M.G.; Kim, D.K. Image-Based Structural Health Monitoring: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.U. Developing plant fibre composites for structural applications by optimising composite parameters: a critical review. Journal of Materials Science 2013, 48, 6083–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, A.; Li, H.; Dao, D.V.; Prusty, G. Natural fiber–reinforced composites: A review on material, manufacturing, and machinability. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials 2021, 34, 238–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BComp Ltd. ampliTex TM, 2021.
- Rask, M.; Madsen, B. Twisting of fibres in yarns for natural fibre composites. 2011. 18th International Conference on Composite Materials, ICCM18 ; Conference date: 21-08-2011 Through 26-08-2011.
- Baley, C.; Gomina, M.; Breard, J.; Bourmaud, A.; Drapier, S.; Ferreira, M.; Le Duigou, A.; Liotier, P.J.; Ouagne, P.; Soulat, D.; et al. Specific features of flax fibres used to manufacture composite materials. International Journal of Material Forming 2019, 12, 1023–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entropy Resins. 305 - Compression Moulding Epoxy, 2024.
- Entropy Resins. CPF Fast, 2024.
- Kern-sohn. Kern Digitalscale EMB 1000-2, 2024.
- Muthuvel, B.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Bickerton, S. Development of innovative flow visualisation methods to investigate the stages of Wet Compression Moulding (WCM) process. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2020, 912, 052013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 527-4: Plastics - Determination of tensile properties, Part 4: Test conditions for isotropic and orthotropic fibre-reinforced plastic composites, 2023-07-00.
- BS ISO 13003: Fibre-reinforced plastics. Determination of fatigue properties under cyclic loading conditions, 2004-02-03.
- ASTM D 3039: Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials, 2017-00-00.
- ASTM D 3479: Standard Test Method for Tension-Tension Fatigue of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials, 2019-00-00.
- Roe, P.J.; Ansell, M.P. Jute-reinforced polyester composites. Journal of Materials Science 1985, 20, 4015–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Anisotropic behaviors of moisture absorption and hygroscopic swelling of unidirectional flax fiber reinforced composites. Composite Structures 2022, 297, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Gning, P.B.; Guillaumat, L. A comparative study of fatigue behaviour of flax/epoxy and glass/epoxy composites. Composites Science and Technology 2012, 72, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, T.; Gabrion, X.; Ramasso, E.; Placet, V. About the fatigue endurance of unidirectional flax-epoxy composite laminates. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 165, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sawi, I.; Fawaz, Z.; Zitoune, R.; Bougherara, H. An investigation of the damage mechanisms and fatigue life diagrams of flax fiber-reinforced polymer laminates. Journal of Materials Science 2014, 49, 2338–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katunin, A.; Wachla, D.; Santos, P.; Reis, P.N. Fatigue life assessment of hybrid bio-composites based on self-heating temperature. Composite Structures 2023, 304, 116456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouenne, J.B.; Barbier, D.; Hounkpati, V.; Cauret, L.; Vivet, A. Influence of flax fibers on the curing kinetics of bio-based epoxy resin. Journal of Materials Science 2024, 59, 12418–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S. Isoconversional Kinetics of Polymers: The Decade Past. Macromolecular rapid communications 2017, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahboob, Z.; Bougherara, H. Fatigue of flax-epoxy and other plant fibre composites: Critical review and analysis. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2018, 109, 440–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannin, T.; Berges, M.; Gabrion, X.; Léger, R.; Person, V.; Corn, S.; Piezel, B.; Ienny, P.; Fontaine, S.; Placet, V. Influence of hydrothermal ageing on the fatigue behaviour of a unidirectional flax-epoxy laminate. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 174, 107056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Gning, P.B.; Guillaumat, L. Properties evolution of flax/epoxy composites under fatigue loading. International Journal of Fatigue 2014, 63, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.B.; Canevarolo, S.; de Sousa, J.A. Correlation of fatigue behavior and dynamic mechanical properties of hybrid composites of polypropylene/short glass fibers/hollow glass beads. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials 2023, 36, 2233–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Archi, Y.; Lahellec, N.; Lejeunes, S.; Jouan, A.; Tranquart, B. Multiscale simulation and experimental analysis of damping in CFRP structures containing rubber. Composite Structures 2022, 289, 115456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Paridah, M.T. A review on dynamic mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced polymer composites. Construction and Building Materials 2016, 106, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya Nagendra, P.; Prasad, V.; Ramji, K. A Study on Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Natural Nano Banana Particle Filled Polymer Matrix Composites. Materials Today: Proceedings 2017, 4, 9081–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idicula, M.; Malhotra, S.K.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical analysis of randomly oriented intimately mixed short banana/sisal hybrid fibre reinforced polyester composites. Composites Science and Technology 2005, 65, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.L.; Palmer, K.I. Cable transient voltages due to microphonics. Journal of Electrostatics 2007, 65, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Jeong, D.Y.; Fu, Z.; Chu, B. Flexoelectric Effect of Ferroelectric Materials and Its Applications. Actuators 2023, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Adamski, N.; Mu, S.; van de Walle, C.G. Piezoelectric effect and polarization switching in Al1- x Sc x N. Journal of Applied Physics 2021, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, P.F.; Yao, C.G.; Chen, S.P.; Cai, K.D.; Shi, F.N. Recent advances of ferro-/piezoelectric polarization effect for dendrite-free metal anodes. Rare Metals 2023, 42, 2516–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.J. Introduction to Electrodynamics, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kersani, M.; Lomov, S.V.; van Vuure, A.W.; Bouabdallah, A.; Verpoest, I. Damage in flax/epoxy quasi-unidirectional woven laminates under quasi-static tension. Journal of Composite Materials 2015, 49, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, Y.; Lebrun, G.; Chatelain, J.F.; Beauchamp, Y. Experimental investigation of failure mechanisms and evaluation of physical/mechanical properties of unidirectional flax–epoxy composites. Journal of Composite Materials 2020, 54, 2781–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karray, M.; Triki, A.; Poilâne, C.; Picart, P.; Gargouri, M. Dielectric relaxation phenomena in flax fibers composite. Fibers and Polymers 2016, 17, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triki, A.; Karray, M.; Poilâne, C.; Picart, P.; Gargouri, M. Dielectric analysis of the interfacial polarization of alkali treated woven flax fibers reinforced epoxy composites. Journal of Electrostatics 2015, 76, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Z. Effect of physiochemical structure on energy absorption properties of plant fibers reinforced composites: Dielectric, thermal insulation, and sound absorption properties. Composites Communications 2018, 10, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, P.; Lenz, P.; Koch, K.P.; Wittmann, A.; Fischer, G. Dielectric properties of unidirectional and biaxial flax/epoxy composites at frequencies up to 1 GHz. Materials Today Communications 2023, 36, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, Y.; Lilholt, H.; Madsen, B. Stiffening effect of fatigue and creep loading in unidirectional flax fibre/epoxy composites. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2018, 388, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kek, T.; Potočnik, P.; Misson, M.; Bergant, Z.; Sorgente, M.; Govekar, E.; Šturm, R. Characterization of Biocomposites and Glass Fiber Epoxy Composites Based on Acoustic Emission Signals, Deep Feature Extraction, and Machine Learning. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggui, M.; El Mahi, A.; Jendli, Z.; Akrout, A.; Haddar, M. Static and fatigue characterization of flax fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites by acoustic emission. Applied Acoustics 2019, 147, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosuke Ueki.; Hans Lilholt.; Bo Madsen. Fatigue behaviour of uni-directional flax fibre/epoxy composites. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Composite Materials 2015.
- Asgarinia, S.; Viriyasuthee, C.; Phillips, S.; Dubé, M.; Baets, J.; van Vuure, A.; Verpoest, I.; Lessard, L. Tension–tension fatigue behaviour of woven flax/epoxy composites. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites 2015, 34, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.U. Damage in biocomposites: Stiffness evolution of aligned plant fibre composites during monotonic and cyclic fatigue loading. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2016, 83, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Lampke, T.; Utschick, H.; Soergel, F. Processing of natural-fibre reinforced polymers and the resulting dynamic–mechanical properties. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2003, 139, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tan, J.; Fernandes, L.; Qu, Z.; Li, Y. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis on Delaminated Flax Fiber Reinforced Composites. Materials (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Membrane–Based Self–Powered Triboelectric Sensors for Pressure Change Detection and Its Uses in Security Surveillance and Healthcare Monitoring. Advanced functional materials 2014, 24, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Quan, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Dong, S.; Lü, C.; Luo, J. A general optimization approach for contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perls, T.A. Electrical Noise from Instrument Cables Subjected to Shock and Vibration. Journal of Applied Physics 1952, 23, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Kervoelen, A.; Le Grand, A.; Nardin, M.; Baley, C. Interfacial properties of flax fibre–epoxy resin systems: Existence of a complex interphase. Composites Science and Technology 2014, 100, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Beckmann, A.; Wittmann, A.; Koch, K.P.; Fischer, G. Investigation of the Discrepancy Between Optically and Gravimetrically Calculated Fiber Volume Fraction in Flax-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer. Journal of Composites Science 2025, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, V.; Newnham, R.E. Converse method measurements of electrostriction coefficients in low-K dielectrics. Materials Research Bulletin 1996, 31, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Janolin, P.E. Defining “giant” electrostriction. Journal of Applied Physics 2022, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagantsev, A.K.; Yudin, P.V. Flexoelectricity in Solids 2016. [CrossRef]
- Jianfeng Lu.; Xu Liang.; Shuling Hu. Flexoelectricity in Solid Dielectrics: From Theory to Applications. Computers, Materials & Continua 2015, 45, 145–162. [CrossRef]
- Trellu, H.; Le Scornec, J.; Leray, N.; Moreau, C.; Villares, A.; Cathala, B.; Guiffard, B. Flexoelectric and piezoelectric effects in micro- and nanocellulose films. Carbohydrate polymers 2023, 321, 121305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubko, P.; Catalan, G.; Buckley, A.; Welche, P.R.L.; Scott, J.F. Strain-gradient-induced polarization in SrTiO3 single crystals. Physical review letters 2007, 99, 167601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S. Flexoelectric nano-generator: Materials, structures and devices. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefeuvre, A.; Bourmaud, A.; Morvan, C.; Baley, C. Elementary flax fibre tensile properties: Correlation between stress–strain behaviour and fibre composition. Industrial Crops and Products 2014, 52, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baley, C.; Gomina, M.; Breard, J.; Bourmaud, A.; Davies, P. Variability of mechanical properties of flax fibres for composite reinforcement. A review. Industrial Crops and Products 2020, 145, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.; Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Sørensen, B.F.; Madsen, B. Strength variability of single flax fibres. Journal of Materials Science 2011, 46, 6344–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneto, A.G.; Vila, C.; Ariza, J.; Vidal, T. Thermogravimetric measurement of amorphous cellulose content in flax fibre and flax pulp. Cellulose 2011, 18, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, S.; Foreman, K.; Adenwalla, S.; Ducharme, S. Finite-size scaling of flexoelectricity in Langmuir-Blodgett polymer thin films. Applied Physics Letters 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiffard, B.; Saadeh, M.; Frère, P.; Seveno, R.; El-Gibari, M.; Sghaier, T.; Merupo, V.I.; Kassiba, A. Potentialities of flexoelectric effect in soft polymer films for electromechanical applications. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2019, 1322, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolier-McKinstry, S., Crystal Chemistry of Piezoelectric Materials. In Piezoelectric and Acoustic Materials for Transducer Applications; Safari, A.; Akdoğan, E.K., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2008; pp. 39–56. [CrossRef]
- Fukada, E. Piezoelectricity as a fundamental property of wood. Wood Science and Technology 1968, 2, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werling, K.A.; Hutchison, G.R.; Lambrecht, D.S. Piezoelectric Effects of Applied Electric Fields on Hydrogen-Bond Interactions: First-Principles Electronic Structure Investigation of Weak Electrostatic Interactions. The journal of physical chemistry letters 2013, 4, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werling, K.A.; Griffin, M.; Hutchison, G.R.; Lambrecht, D.S. Piezoelectric hydrogen bonding: computational screening for a design rationale. The journal of physical chemistry. A 2014, 118, 7404–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Y.; Ruiz-Blanco, Y.B.; Marrero-Ponce, Y.; Sotomayor-Torres, C.M. Orthotropic Piezoelectricity in 2D Nanocellulose. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 34616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T.; Hamatake, M.; Nakao, T. Relationship between piezoelectric behavior and the stress – strain curve of wood under combined compression and vibration stresses. Journal of Wood Science 2004, 50, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindl, W.; Emsenhuber, G.; Plackner, J.; Konnerth, J.; Keckes, J. Converse piezoelectric effect in cellulose I revealed by wide-angle X-ray diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, I.; Jeong, C.K.; Ounaies, Z.; Kim, S.H. Review on Electromechanical Coupling Properties of Biomaterials. ACS applied bio materials 2018, 1, 936–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-karim, A.M.; Salama, A.H.; Hassan, M.L. Electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of nanofibrillated cellulose thin films from bagasse. Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuffel, W.; Pizzi, A. The Piezoelectric Effect in Structural Timber. Holzforschung 1986, 40, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnau, A.; Soares, D. Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity. In Piezoelectric Transducers and Applications; Vives, A.A., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN IEC 62631-2-1 Dielectric and resistive properties of solid insulating materials – Part 2-1: Relative permittivity and dissipation factor – Technical frequencies (0,1 Hz to 10 MHz) – AC Methods, 2018-12-00.
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, Y.D. The Effects of Filler Content and Size on the Properties of PTFE/SiO 2 Composites. Journal of Polymer Research 2003, 10, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subodh, G.; Joseph, M.; Mohanan, P.; Sebastian, M.T. Low Dielectric Loss Polytetrafluoroethylene/TeO 2 Polymer Ceramic Composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2007, 90, 3507–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amor, I.; Rekik, H.; Kaddami, H.; Raihane, M.; Arous, M.; Kallel, A. Effect of Palm Tree Fiber Orientation on Electrical Properties of Palm Tree Fiber-reinforced Polyester Composites. Journal of Composite Materials 2010, 44, 1553–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataroglu, A.; Durmuş, H.; Vahid, A.F.; Avar, B.; Altındal, Ş. High-temperature sensitivity complex dielectric/electric modulus, loss tangent, and AC conductivity in Au/(S:DLC)/p-Si (MIS) structures. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2024, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





