Submitted:
18 June 2025
Posted:
20 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Foundations of Functions in Education
2.1. Modeling Factors Influencing Teaching Quality
- -
- : Teacher competence
- -
- : Student engagement
- -
- : Resources available
- -
- : Institutional policies
- -
- : Educational environment
2.2. Optimizing Teaching Quality through Functional Analysis
2.3. Empirical Evidence and Model Validation
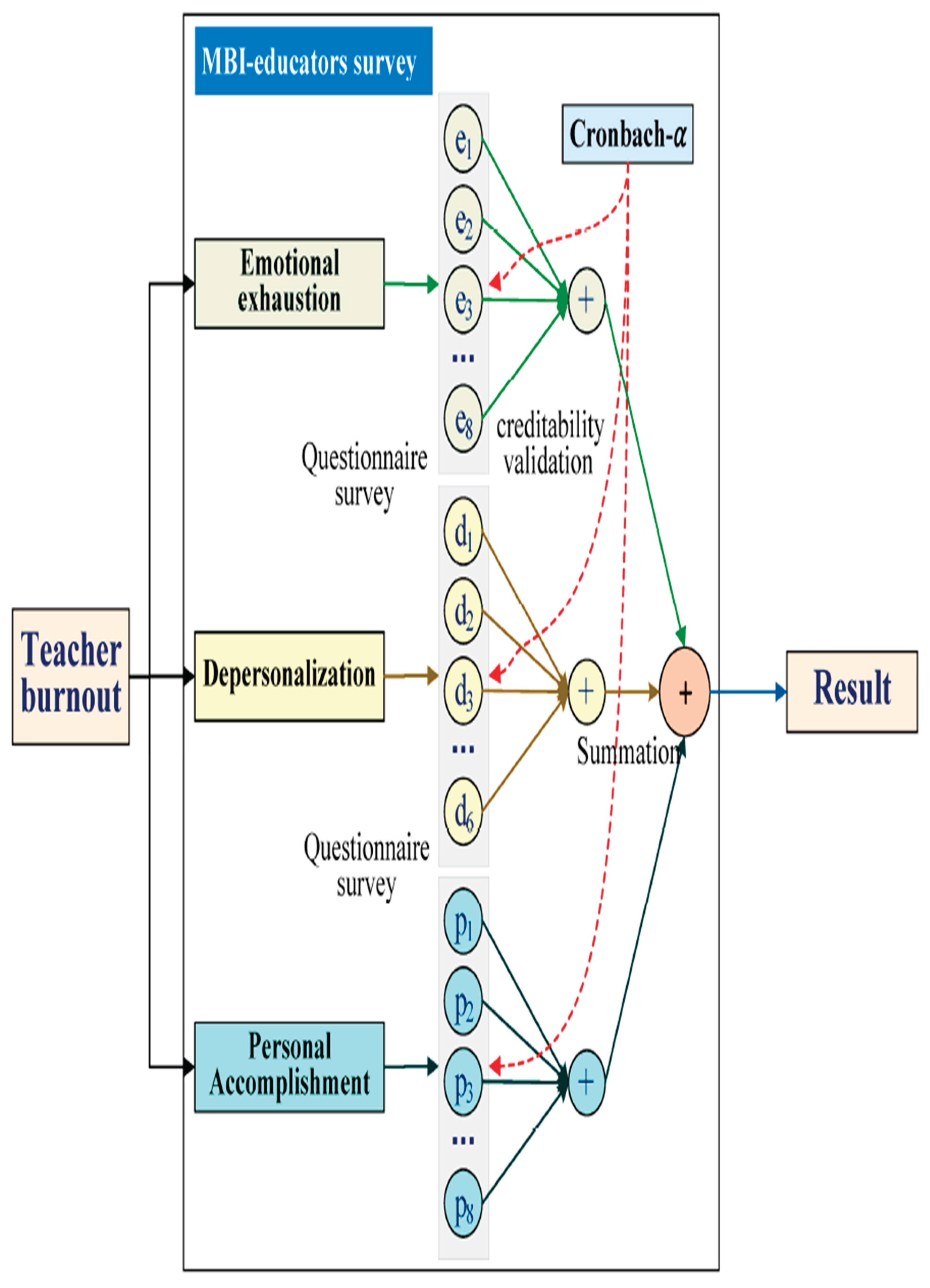
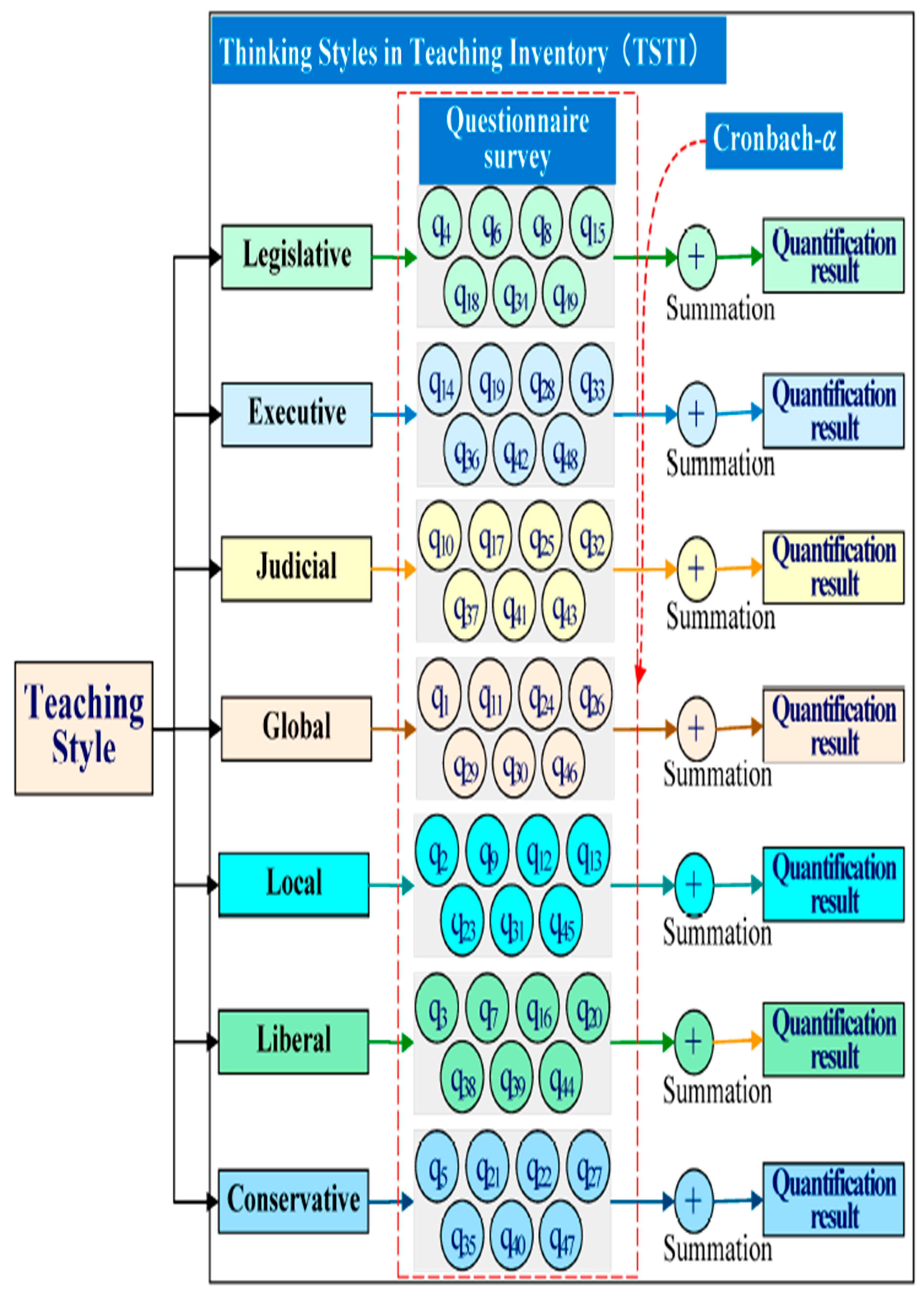
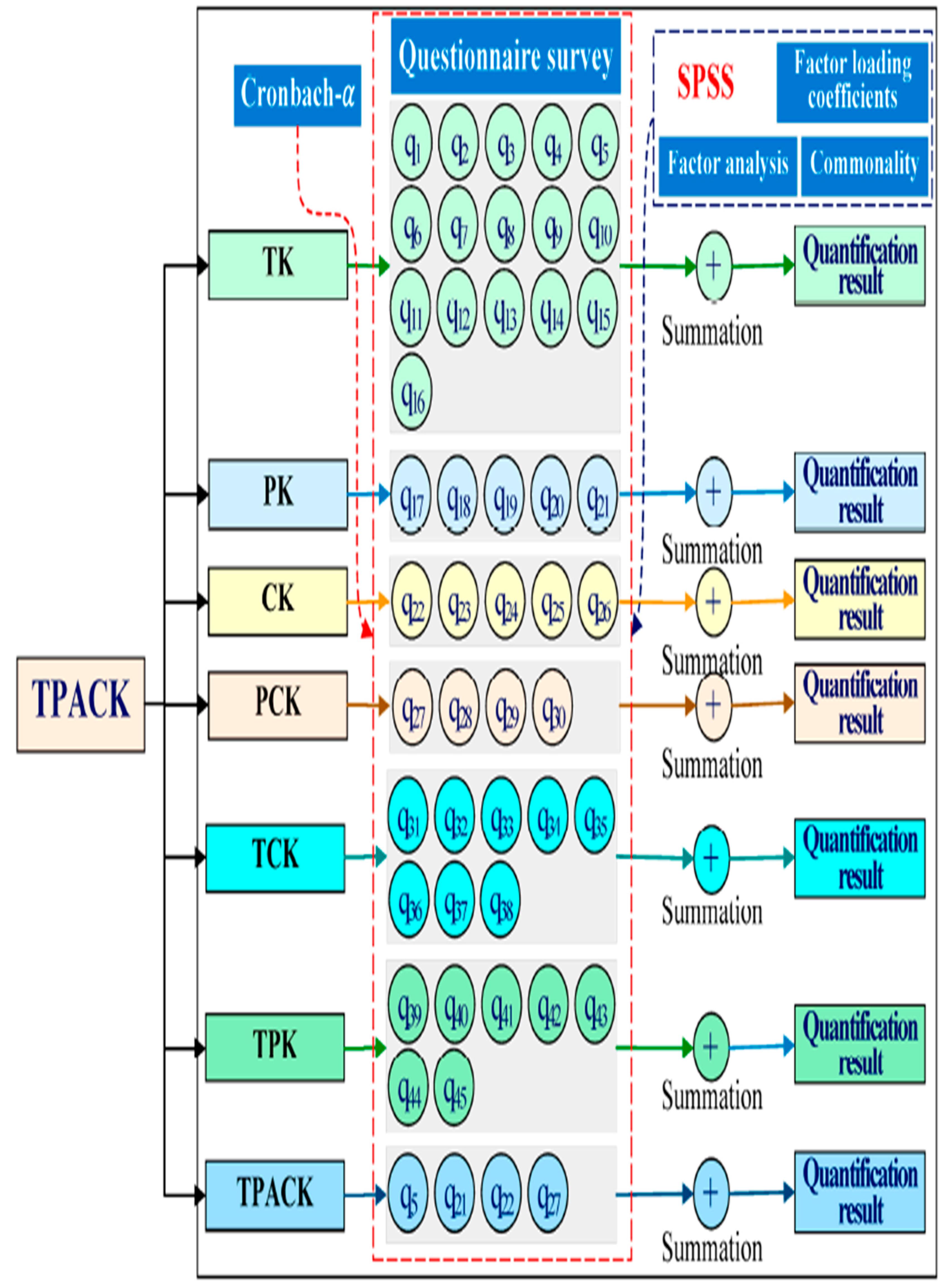
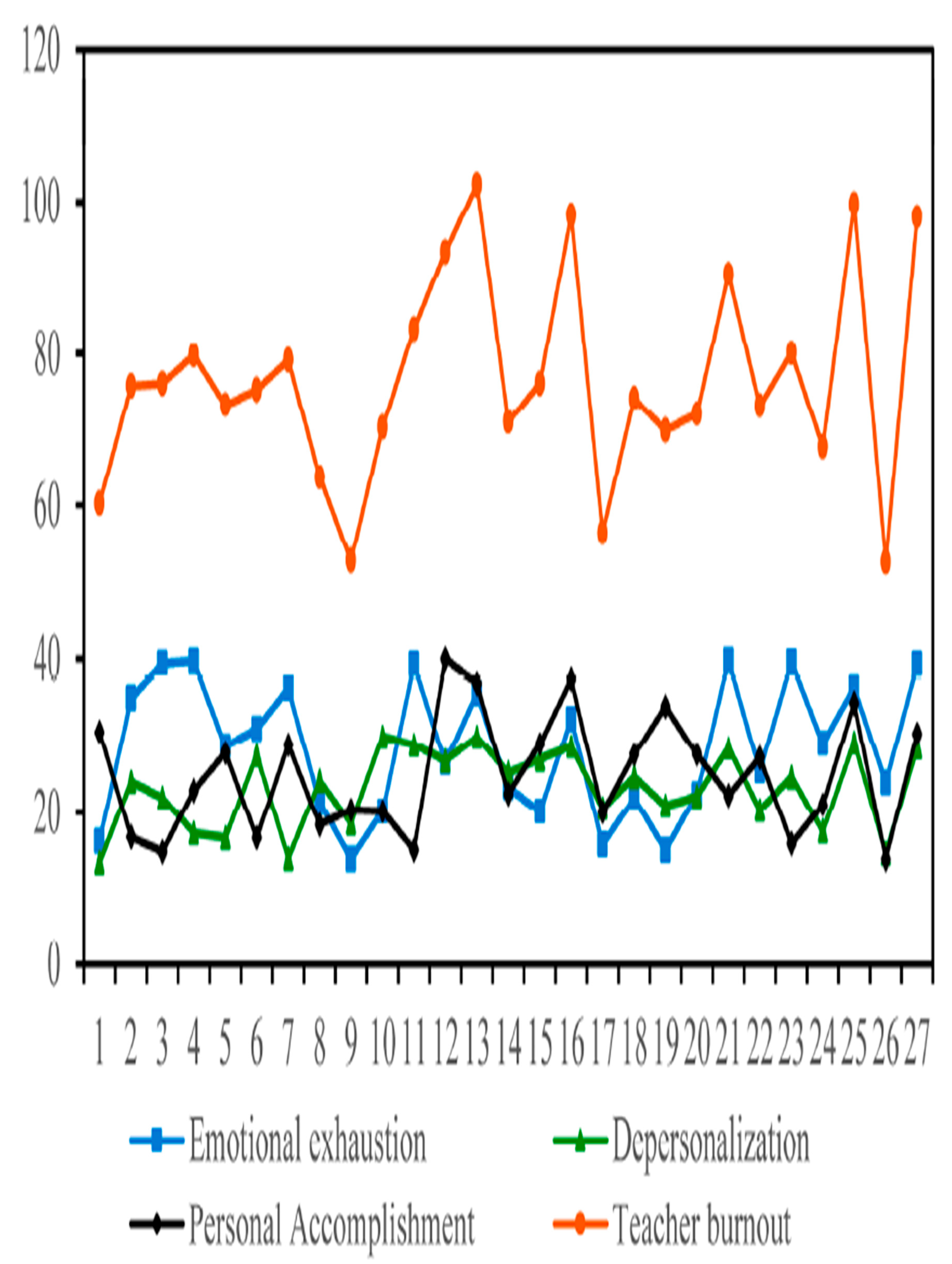
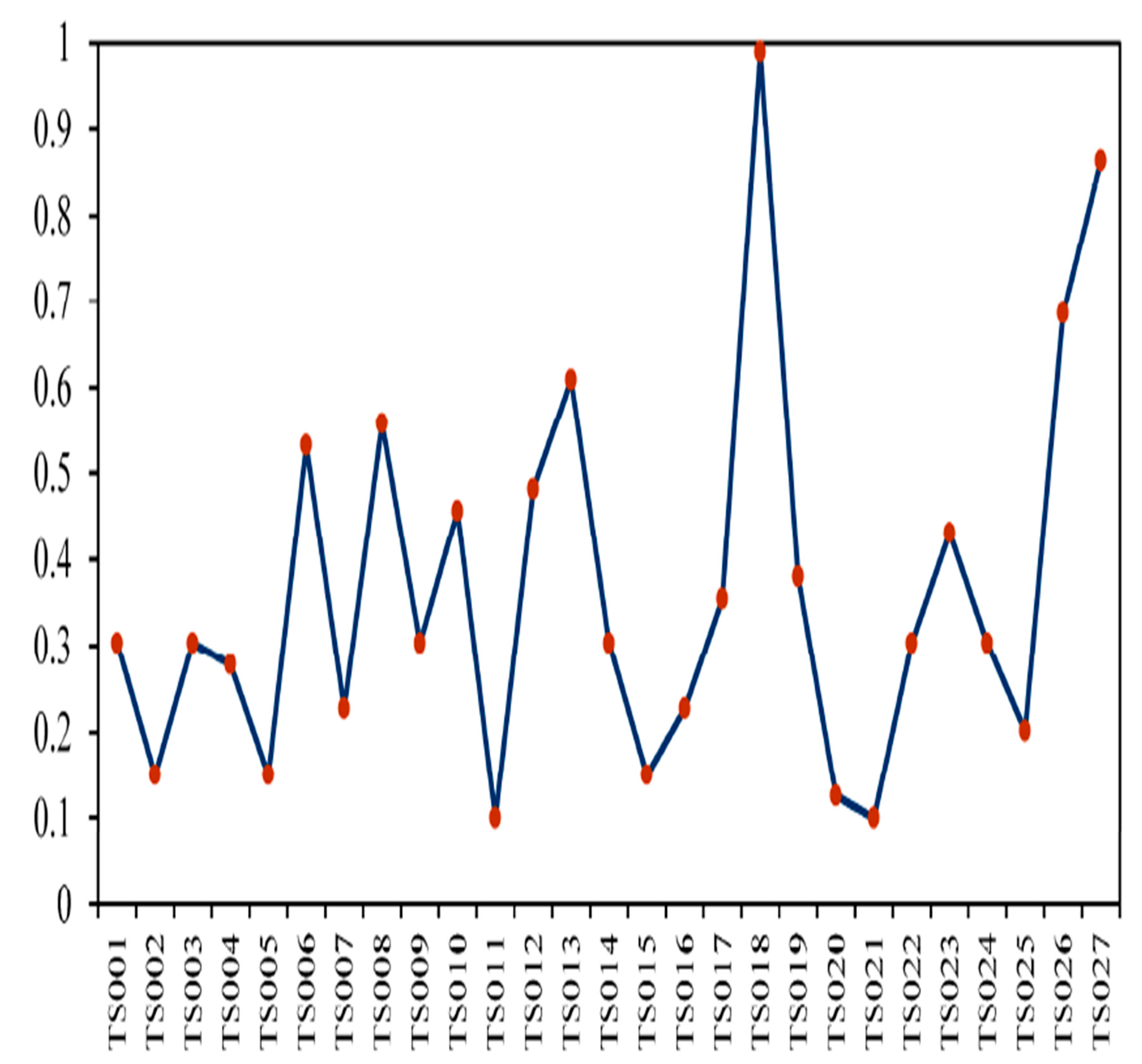
2.4. Discussion
- Predictive Power: Based on variable changes, models can project results (Almalawi et al., 2024).
- Strategically planning locating main leverage points for resource distribution (Jafari et al., 2024).
- Ongoing improvement: Tracking developments over time to improve approaches (Yorkofsky et al., 2020). Data quality, the complexity of human variables, and contextual variation across educational environments, nevertheless, present issues (Lee et al., 2024).
3. Open Problems
- Looking at Eqs (1)-(6), it is needed to explore further investigations to find the exact expressions of in terms of Institutional policies () and Educational environment ().
- Having done that, exploratory research needs to be undertaken to closely analyse and examine the equational relations between and
- The third phase ahead is to examine other undisclosed factors, shown as , referring for error or unmodeled variability, and how to mathematically configure such an .
- The fourth phase is to redefine Eqs (1) - (6) and solve the whole system of the newly generated (1)-(6).
Conclusion
References
- Almalawi, A., Soh, B., Li, A. and Samra, H., 2024. Predictive Models for Educational Purposes: A. [CrossRef]
- Amtu, O., Makulua, K., Matital, J. and Pattiruhu, C.M., 2020. Improving student learning outcomes through school culture, work motivation and teacher performance. International Journal of Instruction, 13(4), pp.885-902. [CrossRef]
- and Five. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Curriculars: Innovative Next-Generation Teaching of Mathematics Across Key Stages Three, Four,.
- Demidovich, B. and Yankovskv, G., 2020. Problems in mathematical analysis. Mir Publishers.
- Educational Resources. Journal of Resource Management and Decision Engineering, 3(2), pp.41-48.
- Guo, Z., Park, B., Huang, X. and Choi, S., 2023. [Retracted] Evaluation Model of Physical Education Teaching Effect Based on AHP Algorithm. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2023(1), p.9363403.
- . [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S., Naeeni, S.K. and Nouhi, N., 2024. Decision-Making Strategies in the Allocation of.
- Johnson, C.C., Walton, J.B., Strickler, L. and Elliott, J.B., 2023. Online teaching in K-12 education in the United States: A systematic review. Review of Educational Research, 93(3), pp.353-411. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S., Li, N. and Kim, J., 2024. Conceptual model for Mexican teachers' adoption of learning analytics systems: The integration of the information system success model and the technology acceptance model. Education and Information Technologies, 29(11), pp.13387-13412. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., 2022. A Model for analyzing teaching quality data of sports faculties based on particle swarm optimization neural network. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022(1), p.6776603. [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.C., Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A., Zhu, M., Jantaraweragul, K., Christie, L., Krothe, K. and Sparks, K., 2021. How can we support online learning for elementary students? Perceptions and experiences of award-winning K-6 teachers. TechTrends, 65(6), pp.939-951. [CrossRef]
- Madukala, J. and Bai, M., 2025. Over-education, wage gap and job satisfaction of tertiary Education: Evidence from OECD economies. Available at SSRN 5112505.
- Mageed, I. A., 2025a. The Hidden Poetry & Music of Mathematics for Teaching Professionals: Inspiring Students through the Art of Mathematics: A Guide for Educators. Eliva Press. https://www.elivabooks.com/en/book/book-1450104825.
- Mageed, I. A., 2025d. A Fractal Geometric Approach to Teaching Fractions for Mastery in Key.
- Mageed, I., 2025c. Teaching Statistics for Mastery Using Music and Other Phenomenal Extra-.
- Mageed, I.A. 2025b. The Hidden Dancing & Physical Education of Mathematics for Teaching Professionals. Eliva Press. https://www.elivabooks.com/en/book/book-7724827898.
- Mageed, I.A. and Nazir, A.R., 2024. AI-Generated Abstract Expressionism Inspiring Creativity through Ismail A Mageed's Internal Monologues in Poetic Form. Annals of Process Engineering and Management, 1(1), pp.33-85.
- Mageed, I.A., 2024a. Do You Speak The Mighty Triad?(Poetry, Mathematics and Music) Innovative Teaching of Mathematics. MDPI Preprints. [CrossRef].
- Mageed, I.A., 2024b. The Mathematization of Puzzles or Puzzling Mathematics Innovative Teaching of Mathematics. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Mageed, I.A., 2024c. Let’s All Dance and Play Mathematics Innovative Teaching of Mathematics. Preprints.. [CrossRef]
- Mageed, I.A., 2024d. AI-Generated Abstract Expressionism Inspiring Creativity Through Ismail A Mageed's Internal Monologues in Poetic Form. Preprints.
- Mougiakou, S., Vinatsella, D., Sampson, D., Papamitsiou, Z., Giannakos, M. and Ifenthaler, D., 2023. Educational data analytics for teachers and school leaders (p. 238). Springer Nature.
- Poulose, J., Sharma, V. and Maheshkar, C. eds., 2024. Data-Driven Decision Making. Palgrave Macmillan.
- Practice. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Singh, J., Goyal, S.B., Kaushal, R.K., Kumar, N. and Sehra, S.S., 2024. Applied Data Science and Smart Systems. Taylor & Francis Group.
- Stages Two and Three: Open Problems and a Combined Theoretical Framework with Intelligent.
- Systematic Review. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 8(12), p.187.
- Yao, D. and Lin, J., 2023. Identifying key factors influencing teaching quality: A computational pedagogy approach. Systems, 11(9), p.455. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J., 2024. Evaluation of influencing factors of China university teaching quality based on fuzzy logic and deep learning technology. PloS one, 19(9), p.e0303613. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




