Introduction
The organic food industry has witnessed substantial growth in recent years due to increasing consumer awareness of health benefits, environmental sustainability, and ethical sourcing. Consumers are shifting towards organic products as they perceive them to be healthier, environmentally friendly, and free from harmful chemicals ([
1,
10,
19]). However, despite this rising demand, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of organic products, including high prices, limited availability, and consumer skepticism about certification standards ([
2,
7,
9]). These barriers create a gap between organic product suppliers and potential consumers, highlighting the need for technology-driven solutions.
With advancements in e-commerce and digital marketing, online platforms have emerged as effective channels for organic food distribution ([
6,
14,
16]). Village 24x7, an organic e-commerce platform, aims to bridge this gap by providing consumers with a user-friendly interface, transparent product information, and seamless delivery services. Research suggests that social media influence, trust in organic labels, and effective digital marketing strategies significantly impact consumer purchasing behavior ([
5,
6,
14,
17]).
This review paper explores the existing literature on consumer behavior, pricing strategies, and the role of organic stores in promoting sustainability to assess how Village 24x7 can leverage these insights. Additionally, the study examines challenges faced by organic food retailers and the effectiveness of different marketing strategies to enhance consumer engagement ([
3,
7,
8,
14]). The findings provide a comprehensive understanding of the organic food market and highlight how digital platforms like Village 24x7 can revolutionize organic product accessibility.
By synthesizing key insights from 20 research papers, this review aims to present an informed perspective on consumer expectations, industry challenges, and potential strategies for online organic marketplaces. The paper also underscores the importance of transparent labeling, competitive pricing, and efficient supply chain management in building consumer trust and fostering long-term growth in the organic food sector.
Literature Review
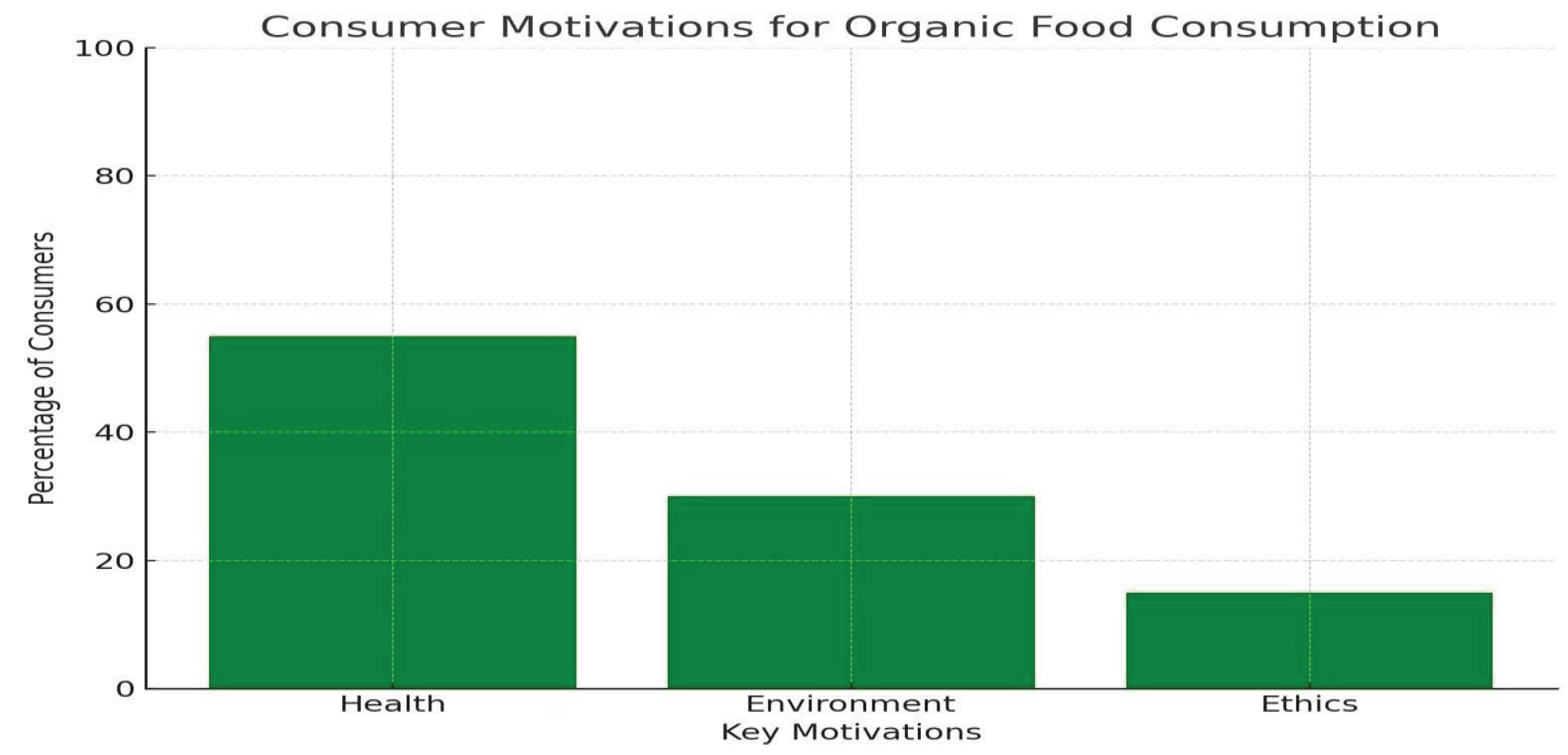
Consumer motivations for purchasing organic food are multifaceted, driven by health benefits, environmental concerns, and ethical considerations. Studies highlight that consumers often choose organic food because they believe it to be healthier, free from pesticides, and more sustainable. Research by Hansen et al. (2018) [
15] and Hughner et al. (2007) [
19] shows that the primary drivers for purchasing organic products include health consciousness and environmental sustainability
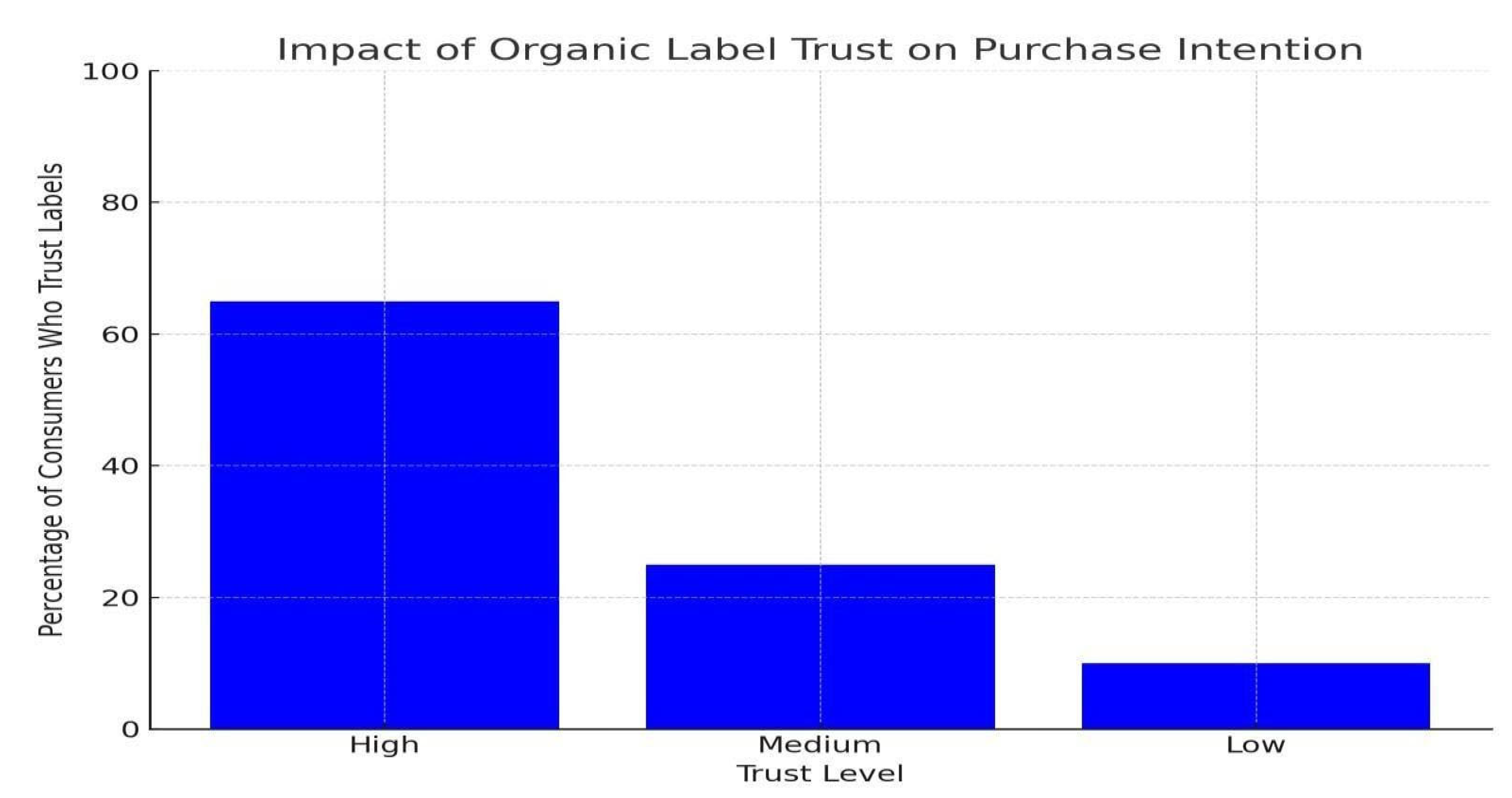
Trust in organic food labels is a significant factor influencing consumer decisions. Bunte and van der Lans (2011) [
2] emphasized that consumers rely on organic labels as a sign of quality and authenticity. However, the effectiveness of these labels is influenced by factors like the transparency of certification organizations and consumers' prior experiences with organic products
.
Consumers who trust the certification system are more likely to purchase organic food.
Labels that include information about sustainability and production practices are highly valued by informed consumers.
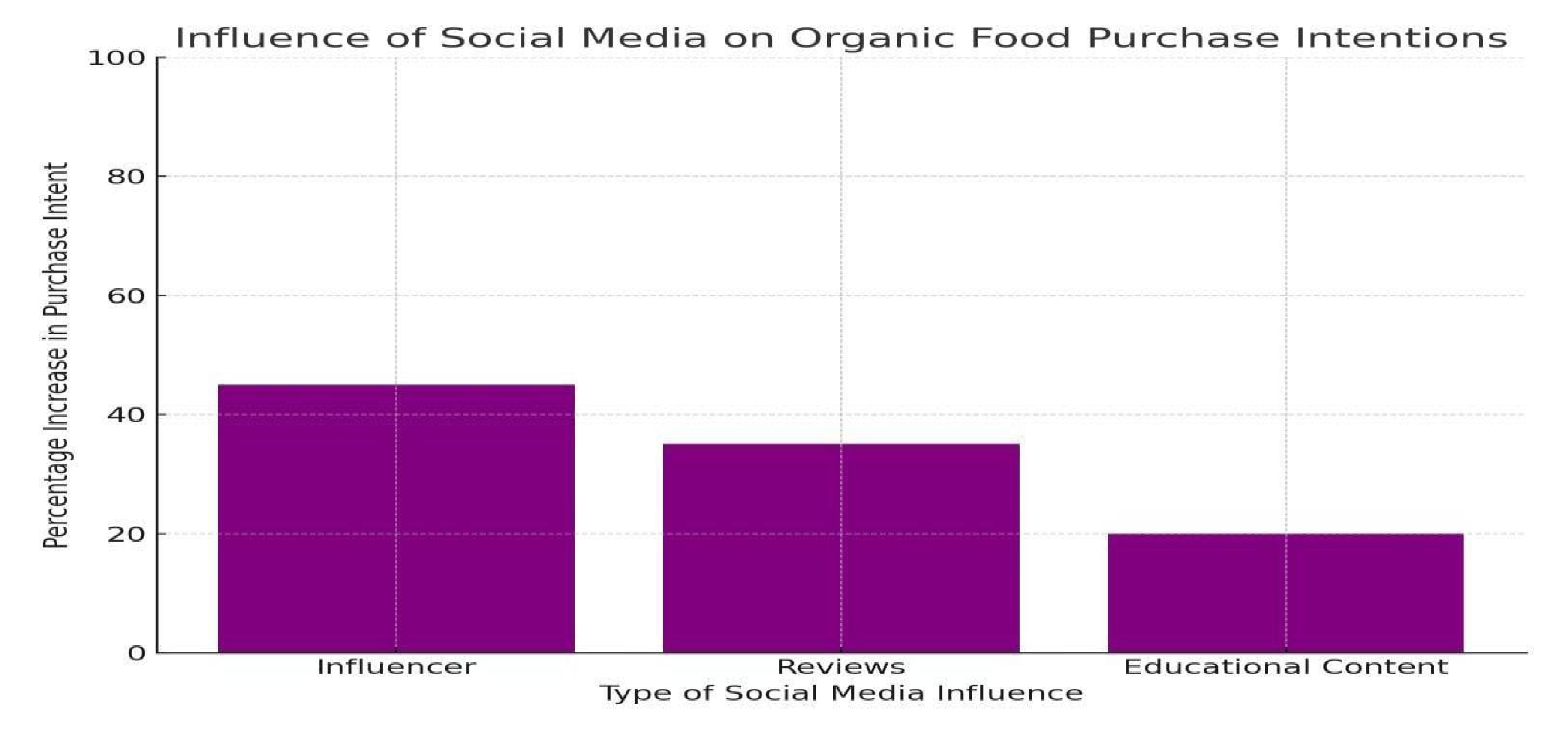
Social Media Influence:
Social media is playing an increasingly prominent role in shaping consumer perceptions of organic food. Lim and Ting (2019) [
6] and Choudhury and Kaur (2020) [
14] highlight how platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube help brands engage with consumers through influencers, product reviews, and educational content.
Younger Consumers: Social media is particularly influential among younger consumers who are more likely to share experiences and interact with organic food brands online.
Influencer Endorsements: Social media influencers significantly impact the purchase intentions of organic food products.
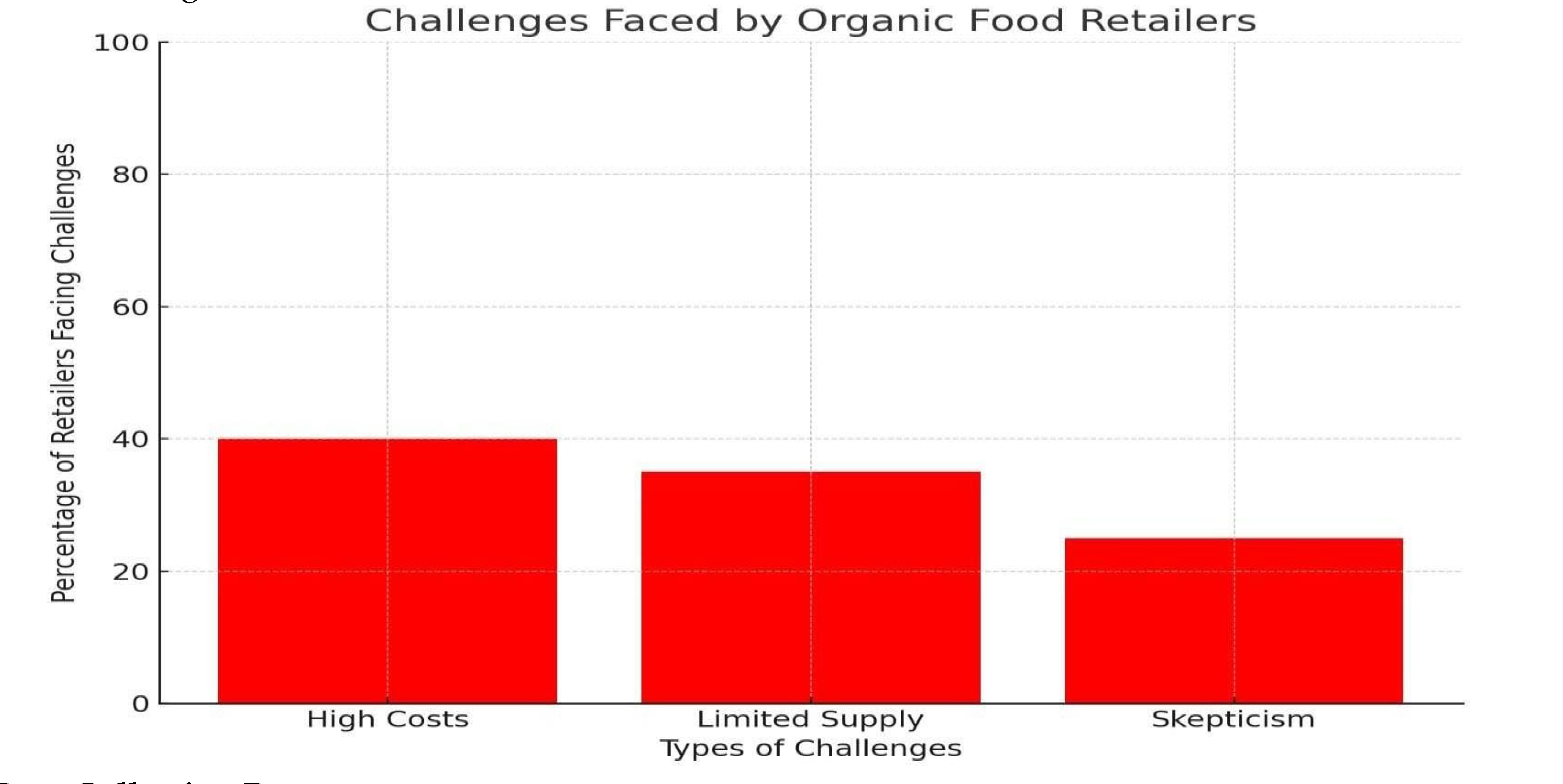
- 2.
Challenges for Organic Food Retailers:
Despite the growing demand for organic food, retailers face several challenges that hinder market expansion. McEachern & McClean (2016) [
7] and Padel & Foster (2005) [
8] pointed out key issues such as high production costs, limited availability, and consumer skepticism about the authenticity of organic claims.
High Production Costs: Organic products typically cost more to produce, making them less competitive in price-sensitive markets. Supply Chain Issues: Ensuring a consistent supply of organic products can be difficult due to certification and regulatory hurdles.
Methodologies
The research papers included in this review were selected based on the following criteria:
- ➢
Relevance: Studies focusing on consumer perceptions, organic food marketing, pricing strategies, e-commerce adoption, and sustainability ([
1,
20]).
- ➢
Publication Quality: Only peer-reviewed journals such as the Journal of Consumer Affairs, Food Quality and Preference, and British Food Journal were considered ([
8,
14,
17]).
- ➢
Time Frame: Research spanning from 2005 to 2020, ensuring coverage of both traditional and modern trends in organic food retail ([
8,
14,
17]).
- 2.
Data Analysis Approach
A qualitative content analysis method was used to categorize insights into the following key themes:
Identifying primary motivations for organic food purchases, such as health benefits, environmental concerns, and ethical considerations ([
1], [
5,
6,
11,
19]).
Understanding how social media influences consumer choices ([
6,
14,
17]).
Analyzing consumer skepticism regarding organic certifications and how transparent labeling and branding strategies can address these concerns ([
2,
7,
9]).
Reviewing pricing strategies that influence consumer decisions and exploring how affordability can be balanced with profitability ([
4,
16]).
Examining how pricing affects demand for organic food in developing nations ([
16]).
Evaluating the effectiveness of digital marketing strategies, social media, and influencer marketing in driving organic product sales ([
6,
14,
17]).
Understanding how e-commerce platforms enhance consumer convenience and market reach ([
3,
13,
14]).
Identifying logistical challenges, high operational costs, and supply chain inefficiencies faced by organic food retailers ([
3,
7,
8]).
Exploring how Village 24x7 can mitigate these challenges by leveraging efficient inventory management and tech-driven solutions ([
3,
8,
13]).
- 3.
Application to Village 24x7
The insights from these studies were mapped to the business model of Village 24x7, focusing on:
Implementation
-
Front-End Development
Village 24x7 uses React.js for dynamic and interactive user interfaces, paired with Tailwind CSS for a responsive, clean design. This combination ensures a seamless and visually appealing shopping experience across devices.
-
Back-End Development
The platform's back-end is powered by Node.js for fast and scalable server-side operations and MongoDB for flexible, efficient database management. This allows for smooth product data handling and scalability as the platform grows.
-
Payment Integration
RazorPay is integrated for secure, multi-method payment processing, supporting credit/debit cards, net banking, and digital wallets to ensure a smooth transaction experience.
-
User Profiles and Personalization
Personalized recommendations are generated based on detailed user profiles built from past purchases and browsing behavior. This enables a customized shopping experience that evolves with user preferences.
-
Admin Panel
The Admin Panel allows easy management of products, orders, inventory, and user accounts. It provides tools for monitoring platform performance and ensuring efficient order fulfillment.
-
Scalability and Future Enhancements
Village 24x7 is built to scale, with plans for advanced features like AI-powered chatbots, real- time inventory tracking, to further enhance user experiences.Expected Outcomes
The Village 24x7 e-commerce platform for organic products is expected to achieve the following outcomes:
Enhanced Consumer Engagement – By leveraging insights on digital marketing, social media influence, and trust-building strategies, Village 24x7 can effectively attract and retain consumers interested in organic products ([
6,
14,
17]).
Improved Trust and Transparency – Findings suggest that clear labeling, verified organic certifications, and transparent product descriptions significantly boost consumer confidence in organic products, which will be integrated into the Village 24x7 platform ([
2,
7,
9]).
Optimized Pricing Strategy – Research indicates that affordable pricing models combined with perceived health and environmental benefits encourage higher consumer adoption. Village 24x7 will implement a competitive yet sustainable pricing strategy to attract cost- sensitive customers ([
4,
16]).
Efficient Supply Chain Management – By identifying key logistical challenges and retail inefficiencies, Village 24x7 can adopt technology-driven solutions for inventory tracking, supplier coordination, and faster delivery systems ([
3,
8,
13]).
Sustainable Growth of the Organic Food Market – The findings highlight the increasing demand for organic products in developing nations and how e-commerce platforms like Village 24x7 can bridge the gap between suppliers and consumers by offering a seamless online shopping experience ([
16,
19]).
Discussion
Consumer Behavior and Purchase Intentions: Studies indicate that health consciousness, environmental concerns, and ethical motivations are the primary drivers behind organic food purchases ([
1,
11,
19]). Younger consumers, particularly in developing nations, exhibit a strong inclination toward organic products due to their perceived health benefits ([
16]).
Trust and Transparency in Organic Certifications: A major challenge in the organic food market is consumer distrust of labels and certifications ([
2,
7]). Research shows that consumers are more likely to purchase organic products when they have access to transparent supply chain information and reliable third-party certifications ([
9]).
Pricing and Market Accessibility: High prices remain a significant barrier to organic food adoption, especially in price-sensitive markets ([
4,
16]). Studies suggest that competitive pricing, discount strategies, and subscription models can encourage more frequent purchases ([
16]).
Role of E-commerce and Digital Marketing: With the increasing reliance on digital platforms for shopping, e-commerce has become a critical channel for organic food sales ([
6,
14,
17]).
Supply Chain Challenges and Retail Barriers: One of the biggest obstacles faced by organic food retailers is supply chain inefficiencies, including high operational costs, inconsistent product availability, and logistical challenges ([
3,
7,
8]).
Limitations
Limited Product Range: As a newer platform, the product selection may be smaller compared to established competitors, limiting consumer choice.
Supply Chain Challenges: Unpredictable organic farming conditions and supply chain inefficiencies may lead to delays or stock shortages.
User Engagement: Gamification features may not engage all users equally, as their effectiveness varies based on individual preferences.
Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting personal data may raise privacy and security concerns, affecting user trust and engagement.
Conclusions
Village 24x7 is an innovative e-commerce platform that addresses the growing demand for organic products by offering a user-centric and efficient shopping experience. Through the integration of advanced technologies like React.js, Node.js, and MongoDB, the platform provides a seamless and scalable solution for both consumers and producers. Its hybrid recommendation system, powered by collaborative filtering and predictive analytics, ensures personalized product suggestions that enhance the overall shopping experience.
By incorporating gamification elements and fostering social connectivity, Village 24x7 further
engages its users, encouraging repeat interactions and creating a community-driven environment. Real- time data processing and continuous feedback collection enable the platform to adapt and refine its offerings, ensuring that it remains aligned with user preferences and market trends.
Ultimately, Village 24x7 aims to revolutionize the organic food retail market by overcoming barriers such as high prices, limited accessibility, and trust concerns. Its focus on transparency, secure payment processing, and personalized service positions it as a valuable player in the organic e-commerce space, contributing to the growth of a sustainable and ethical marketplace for organic products. Through continuous improvement and innovation, Village 24x7 is set to play a significant role in reshaping the future of organic shopping.
References
- Aschemann-Witzel, J. , & Zielke, S. (2017). Can "t buy me love"? A comprehensive overview of existing literature exploring consumer behavior in relation to organic food has been detailed in the Journal of Consumer Affairs (51(1), pp. 1–24). [CrossRef]
- Bunte, F. H. J. , & van der Lans, I. A. (2011). Consumer trust in organic food labels: The role of information and experience. Food Quality and Preference, 22(5), 455-463. [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K. G., & Juhl, H. J. (2018). Organic retail outlets play a crucial role in encouraging sustainable consumer habits through increased accessibility and awareness. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 45, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Haghiri, M. , & Haghiri, S. (2016). Various pricing models have been analyzed in the context of the organic food sector, highlighting key strategies adopted by businesses to attract eco-conscious consumers. Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics, 41(1), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P., & Singh, R. (2019). A study conducted in the Indian market investigates how consumers perceive organic food products and the factors influencing their purchasing decisions. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 50, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Lim, W. M., & Ting, D. H. (2019). Social media platforms have been found to significantly impact the buying behavior of individuals when it comes to organic food, primarily through awareness and influencer marketing. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 50, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- McEachern, M. G. , & McClean, P. (2016). Challenges faced by organic food retailers: A qualitative study. British Food Journal, 118(2), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Padel, S. , & Foster, C. (2005). Marketing strategies for organic food products: A review. British Food Journal, 107(8), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Sangkumchaliang, P. , & Huang, W.-C. (2012). The organic food market: Opportunities and challenges. The journal Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems (27(1), pp. 1–10) offers insights into sustainable practices and their relationship with organic food systems. [CrossRef]
- Smith-Spangler, C. , et al. (2012). The impact of organic food on health and environment: A systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine, 157(5), 348-366. [CrossRef]
- Thogersen, J. , & Zhou, Y. (2012). Consumer preferences for organic food: A review. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 29(6), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Zepeda, L. , & Deal, D. (2009). Sustainability and organic food: Consumer perspectives. A marketing-focused exploration of organic food products is presented in the Journal of Food Products Marketing (15(3), pp. 1–15). [CrossRef]
- Allen, P., & Wilson, A. (2008). The role of organic stores in local food systems. Journal of Agriculture, Food Systems, and Community Development, 4(1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S. , & Kaur, R. (2020). Digital marketing strategies for organic food retailers. Research published in the Journal of Business Research (116, pp. 1–10) examines consumer trends and decision-making processes in the organic market. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T. , Sørensen, M. I., & Eriksen, M.-L. R. (2018). The interaction between individual motivations and personal values plays a pivotal role in shaping organic food choices, as discussed in Food Policy (74, pp. 39–52). [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R. , & Pathak, G. S. (2016). "Intention to purchase organic food among young consumers: Evidences from a developing nation." Appetite, 96, 122-128. [CrossRef]
- Paul, J. , & Rana, J. (2012). "Consumer behavior and purchase intention for organic food." Journal of Consumer Marketing, 29(6), 412-422. [CrossRef]
- Aertsens, J. , Verbeke, W., Mondelaers, K., & Van Huylenbroeck, G. (2009). A detailed review in theBritish Food Journal (111(10), pp. 1140–1167) examines the key personal factors influencing the consumption of organic food. [CrossRef]
- Hughner, R. S., McDonagh, P., Prothero, A., Shultz, C. J., & Stanton, J. (2007).
- "Who are organic food consumers? A compilation and review of why people purchase organic food." Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 6(2-3), 94-110. [CrossRef]
- Schleenbecker, R. , & Hamm, U. (2013). "Consumers’ perception of organic product characteristics. A review." Appetite, 71, 420-429. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).







