1. Introduction
With the ever-increasing transformation of financial markets, the stock market has turned into a very important part of the world's economy. Uncertainty and volatility of the stock market make the prediction of stock prices a never-ending research problem. Stock prices are influenced by various factors like economic information, policy announcements, and market moods, which make stock price prediction very challenging. The conventional methods of forecasting stock prices rely largely on technical and fundamental analysis [
1]. Such methods, nonetheless, disregard the temporal properties and complex nonlinear dynamics of the data. Therefore, accurate modeling of stock price pattern movements and accuracy in prediction have emerged as critical issues in finance research.
Over the past few years, deep learning technology has made significant progress in various fields, especially in time-series data modeling. Optimized recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for sequence data have become essential tools for predicting stock prices since they can learn temporal relationships between the data. RNNs can accept past stock prices and other attributes as input and provide future stock prices as output. However, traditional RNN models suffer from vanishing and exploding gradients during the processing of long sequences and therefore restrict the ability to capture long-range dependencies [
2]. To overcome this drawback, state-of-the-art RNN models like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) have been developed, and these have been successful in improving stock price prediction precision.
At the same time, the incorporation of attention mechanisms introduces a novel perspective to deep learning models. The attention mechanism enables the model to concentrate on pertinent historical information by assigning weights to various time steps’ information, thereby enhancing its ability to learn long-term dependencies and discern meaningful features. In stock price prediction, the attention mechanism aids the model in identifying the primary factors that influence stock price fluctuations and assigning them higher weights. Not only can this mechanism enable the model to predict more precisely but also enable the model to be more flexible and efficient in handling complex stock market data. The combination of RNNs and attention mechanisms can also further enhance the performance of stock price prediction models to capture the fine-grained signals in market movements [
3]. Accurate stock-price forecasting benefits not only individual investors but also the stability and efficiency of U.S. financial markets. With more than half of American households exposed to equities through 401(k)s, IRAs, and pension funds, better predictions safeguard household wealth and support prudent asset-allocation decisions by institutions, thereby strengthening overall market liquidity. Advancing RNN and attention-based models for this task thus serves a clear national interest while offering rich theoretical and practical value [
4]. With the continuous development of artificial intelligence, deep learning-based stock price prediction models have become a research hotspot in both academia and the financial industry.
2. Background and Fundamentals
Recent developments in deep learning have significantly advanced the modeling of financial time-series data. Among these, the integration of attention mechanisms into neural network architectures has proven particularly effective in capturing critical temporal dependencies and highlighting salient input features. This work draws on such advancements to enhance prediction accuracy in volatile stock market environments.
Attention-enhanced models have demonstrated their utility across various domains. For example, the application of global-local attention mechanisms to classification tasks has showcased how selectively weighting input features improves learning outcomes, which is mirrored in the attention-driven enhancement of recurrent architectures in this study [
5]. Similarly, self-attention modules incorporated into fraud detection frameworks have revealed their strength in isolating significant temporal and contextual information from noisy financial data [
6]. Hybrid architectures that combine BiLSTM and Transformer layers have shown promising results in handling sequential data by leveraging both temporal dynamics and contextual embeddings, a strategy that closely parallels the approach used in this paper [
7]. Furthermore, reinforcement learning approaches adapted for time-series risk control suggest that models capable of learning dynamic decision policies can be effective in financial settings marked by uncertainty and nonlinearity [
8].
Graph-based learning methods, particularly those utilizing graph attention networks, offer another dimension of temporal and relational understanding by modeling complex interdependencies within financial data structures. Such methods illustrate the potential for future enhancements to the current model through graph-based representations [
9]. Robust model training techniques such as ensemble learning, data balancing, and multi-source data fusion have been employed to address issues of class imbalance and data heterogeneity in financial detection systems. These methodologies contribute valuable insights into improving model generalizability and stability, which are essential in stock price prediction tasks [10-11].
Recent explorations into contrastive learning for anomaly detection further underscore the value of unsupervised representation learning, especially in scenarios with limited labeled financial data [
12]. Additionally, combining deep learning with large language models or textual fusion has highlighted the effectiveness of integrating structured and unstructured data sources—a potential future direction for stock forecasting models [
13]. At the architectural level, the intersection of deep learning with neural architecture search has emphasized the importance of automatic model optimization to enhance performance and reduce manual tuning. This aligns with the pursuit of constructing efficient, high-performing models tailored for financial time series analysis [
14].
Together, these contributions provide a comprehensive foundation and justification for the proposed integration of RNN and attention mechanisms, informing both the architectural design and methodological orientation of this study.
3. Method
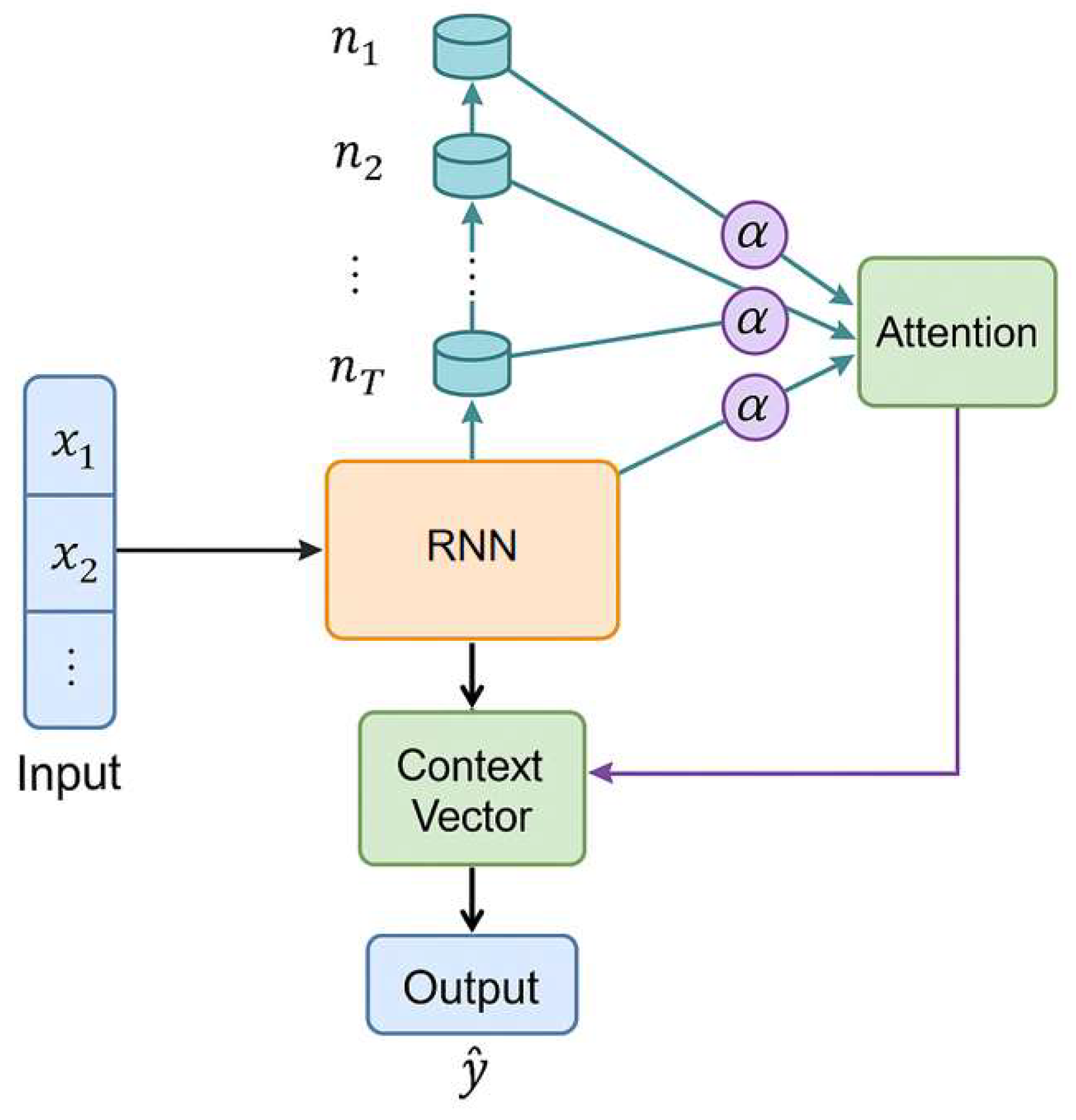
In this stock price prediction model, a hybrid architecture is constructed by combining a recurrent neural network (RNN) with an attention mechanism to effectively capture long-term dependencies in the financial time series while highlighting critical information across different time steps. The RNN component is responsible for processing the sequential input data and learning temporal patterns from historical stock prices. To enhance this process, an attention layer is introduced, which assigns varying weights to different time steps, allowing the model to focus more on those periods that are more relevant to the prediction task. This selective weighting improves the model’s ability to extract meaningful patterns from the data, especially in the context of dynamic and often volatile stock price movements. The design draws inspiration from Liu [
15], who emphasized the importance of enhancing deep learning architectures for financial forecasting by improving their capacity to identify and emphasize key features within historical data. Liu’s work focused on convolutional improvements, the same principle of targeted feature enhancement is applied here through the attention mechanism embedded in the RNN structure. As a result, the model can better respond to subtle fluctuations and dominant trends within the input sequence, leading to improved predictive accuracy. The overall architecture of the proposed RNN-Attention model is illustrated in
Figure 1.
The model structure diagram shows a time series prediction network based on the fusion of RNN and attention mechanism, which is mainly used to capture the temporal dependencies and key features in the stock price series. The input historical stock price series is first extracted through RNN to extract the hidden state of each time step, and then the weight coefficient is calculated by the attention mechanism to sum it up to obtain the context vector representing the global information. Finally, the context vector outputs a single stock price prediction value through the fully connected layer to achieve modeling of future trends.
First, the traditional RNN model combines the current input with the previous hidden state through a recursive structure to calculate the hidden state at the next moment. Specifically, the update formula of RNN is as follows:
Among them, is the hidden state at the current moment, is the input data at the current moment, and are the weight matrices of the input and hidden states respectively, is the bias term, and is the activation function.
To address the inherent limitation of standard recurrent neural networks (RNNs) in modeling long sequences—specifically the vanishing gradient problem—this study employs improved RNN variants such as long short-term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent units (GRUs). These architectures are specifically designed to preserve information over extended time horizons by regulating memory updates. LSTM networks, in particular, mitigate the degradation of gradients during backpropagation by incorporating dedicated gating mechanisms—namely the input gate, forget gate, and output gate—that modulate the flow and retention of temporal information. This gating mechanism enables the model to dynamically learn long-term dependencies in financial time series data, which is essential for capturing the temporal patterns in stock price fluctuations. This approach aligns with previous works that highlight the superiority of LSTM-based architectures in financial prediction contexts, where long-range dependencies and nonlinear temporal features are prevalent. In particular, studies leveraging deep neural designs for anomaly detection and financial risk assessment have demonstrated the robustness of LSTM in capturing meaningful sequential dependencies under volatile market conditions [
16]. Furthermore, time-series forecasting strategies integrating advanced architectures such as bidirectional attention-based models reinforce the notion that augmenting traditional RNN structures enhances model convergence and predictive accuracy in stock-related tasks [
17]. The underlying mechanism of the LSTM architecture can be formalized as follows:
Among them, is the output of the forget gate, is the output of the input gate, is the candidate memory state, and is the current cell state.
In the process of incorporating the attention mechanism, we apply attention weights to the output of the RNN or LSTM to weight the hidden states at different time steps. This process is achieved by calculating the weight coefficient for each time step and taking a weighted average. Specifically, given an input sequence
, the weight calculation formula of the attention mechanism is:
Among them,
is the score of the hidden state at each time step,
is a learnable weight vector, and
and
are parameters. Then, the model obtains the final context representation by weighted averaging the hidden states of each time step:
Finally, based on the weighted average context representation c, the model predicts the stock price and outputs the predicted value through a fully connected layer. By introducing the attention mechanism, the model can automatically select important time steps, thereby effectively improving the accuracy of the prediction.
4. Experimental Results
A. Dataset
The dataset used in this study consists of historical stock trading data of Apple Inc. The time span ranges from January 1, 2024, to January 1, 2025. It includes the company's daily stock price movements during this period. The data is sourced from publicly available financial platforms. Key indicators include opening price, highest price, lowest price, closing price, and trading volume. These metrics comprehensively reflect Apple's market performance over the year.
To facilitate model training and validation, the raw data was preprocessed. First, missing and abnormal values were handled to ensure data integrity and reliability. Then, Min-Max normalization was applied to scale all features to the [0, 1] range. This improves the training efficiency and stability of neural networks. In addition, to enhance model generalization, the dataset was divided into training, validation, and test sets. These sets were used for model learning, parameter tuning, and performance evaluation, respectively.
This dataset is highly representative. It captures Apple's daily stock fluctuations within a specific timeframe. It also reflects performance characteristics under various market conditions. By leveraging this high-quality real-world data, this study can effectively assess the applicability and accuracy of RNN and attention-based prediction models in real financial scenarios.
B. Experimental Results
First, this paper gives the comparative experimental results of different algorithms, as shown in
Table 1.
Experimental results demonstrate that the RNN+Attention model outperforms other methods across all metrics in stock price prediction. It achieved a notably low MSE of 0.0003 and an MAE of 0.021, indicating high prediction accuracy. Its R² score of 0.857 reflects strong model fit and trend-capturing ability.
Compared to RNN and LSTM, the RNN+Attention model yields significantly lower errors and better fit, benefiting from the attention mechanism’s ability to highlight key time steps—an advantage lacking in traditional sequence models. While LSTM improves on RNN, it still underperforms in accuracy and adaptability.Against Transformer and MLP models, RNN+Attention also leads. Though Transformer handles long dependencies well, its complexity may hinder fine-grained prediction. MLP lacks temporal modeling, limiting its effectiveness. In contrast, RNN+Attention balances sequential learning and attention weighting for optimal results.
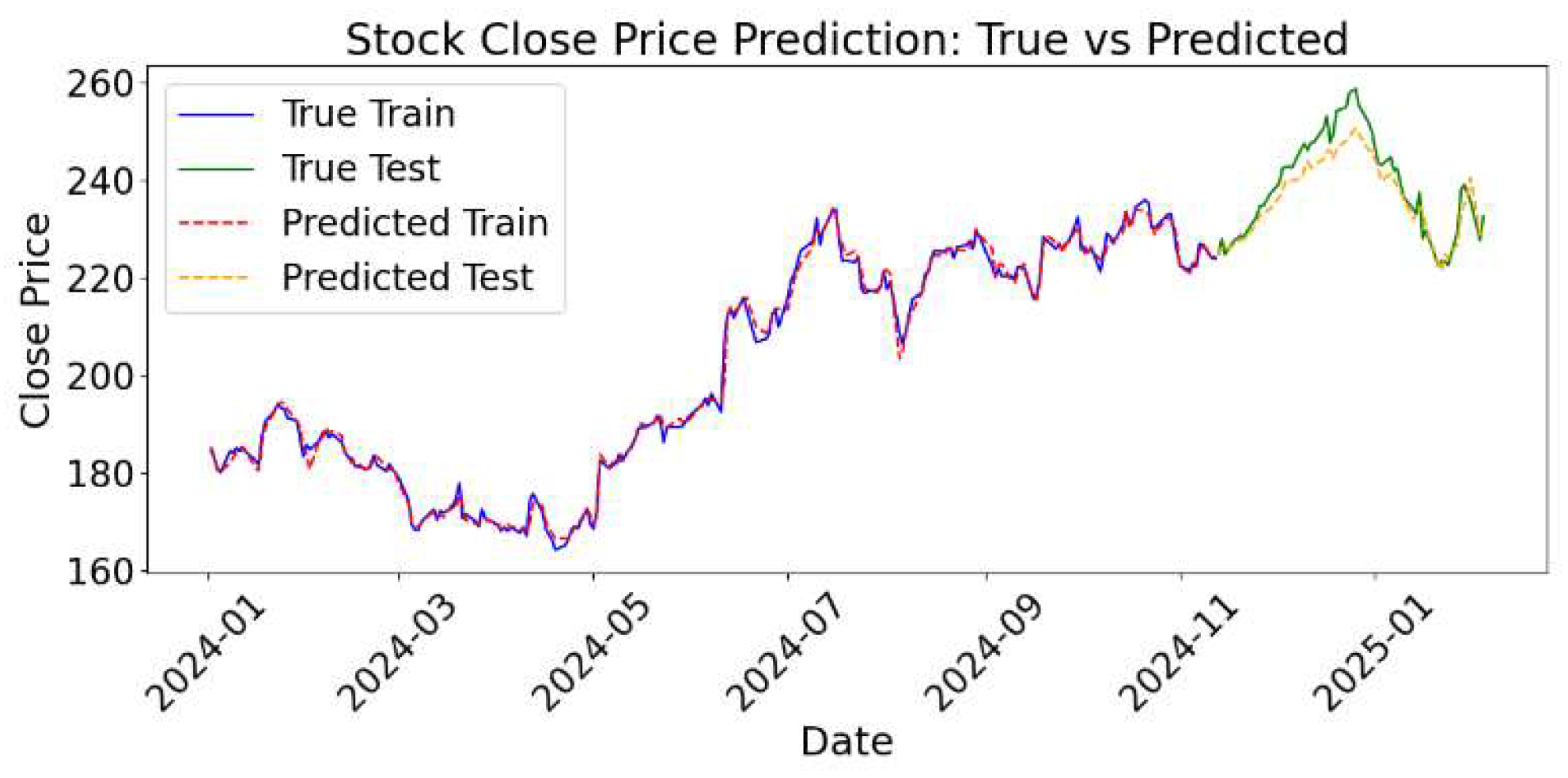
Figure 2 illustrates the model’s predictive accuracy, with predicted values closely tracking actual stock prices, visually confirming its ability to capture temporal patterns in financial data.
As shown in the figure, the predicted results on both the training and test sets align closely with the actual stock price trends. This indicates strong fitting ability and high prediction accuracy. During training, the predicted curve almost overlaps with the true curve. This demonstrates that the model effectively learns historical price patterns and captures key features in the time series.
In the testing phase, despite the complex and often unpredictable fluctuations in stock prices, the model consistently demonstrates a high level of accuracy in tracking the actual trend. This is particularly evident during periods characterized by large price swings, where the predicted curve maintains close alignment with the real stock price curve. The ability of the model to mirror such volatile movements highlights its robustness and reliability. This strong consistency between predicted and actual values suggests that the model possesses excellent generalization ability, enabling it to effectively adapt to the prediction of future, unseen data in real-world financial scenarios.
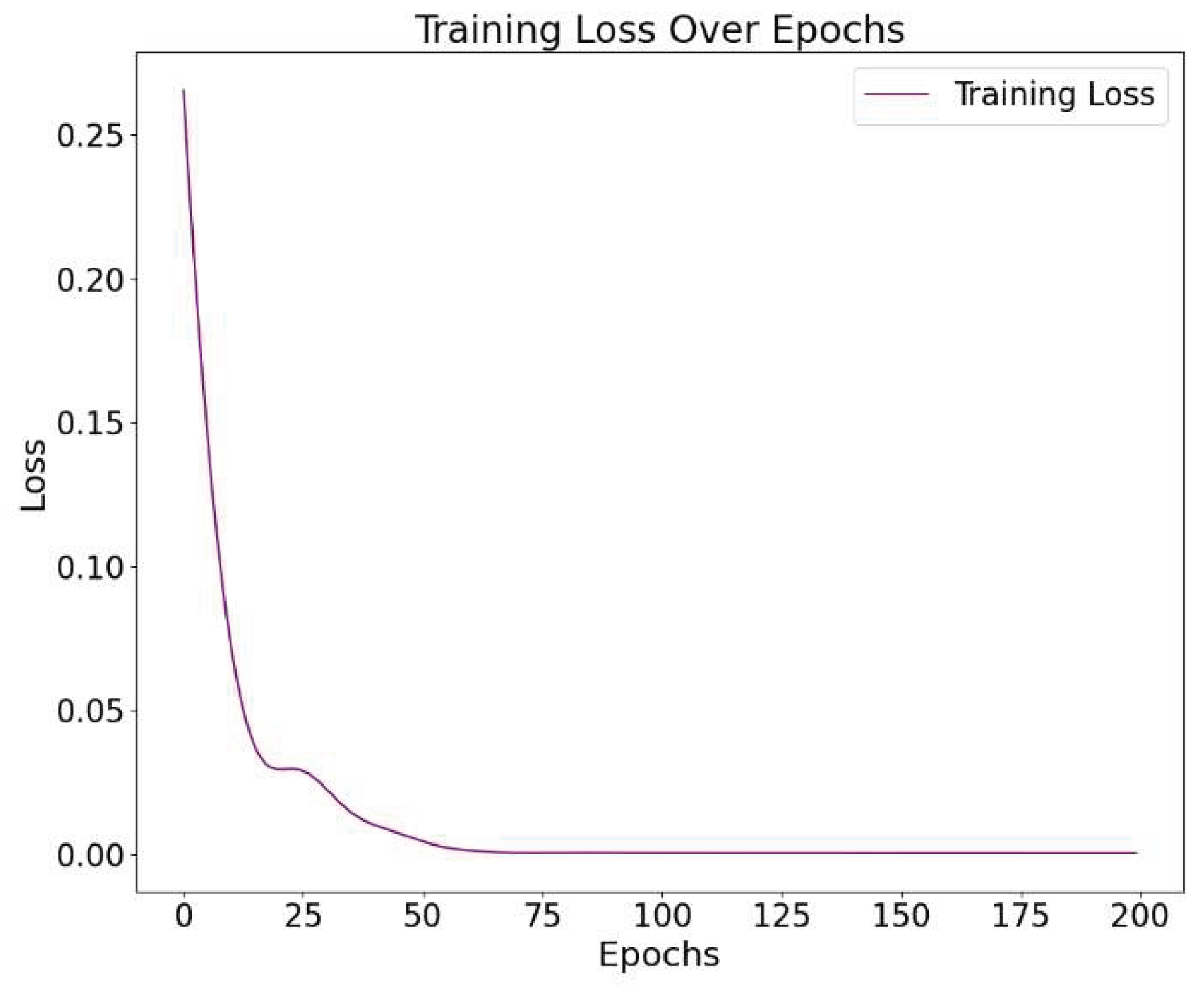
Overall, this comparison chart further supports the validity of the evaluation metrics presented earlier. The consistency between the visual results and the performance indicators-such as MSE, MAE, and R2-confirms the potential and feasibility of applying the RNN with attention mechanism to real-world stock price forecasting. Finally, the loss function drop graph is presented, as shown in
Figure 3. This figure visually demonstrates the training process of the model, showing a steady and continuous decline in the loss value over time. The smooth downward trend indicates effective learning and stable convergence without signs of overfitting or instability. It provides further evidence that the model's parameters were optimized efficiently, supporting the reliability of the training procedure and the robustness of the proposed approach.
From the loss function curve, it can be observed that the model started with a high loss in the early training phase. However, the loss dropped rapidly within the first 30 epochs. This indicates that the model quickly learned effective features and began fitting the training data. The steep decline during this period reflects significant performance improvements driven by weight updates.
As training progressed, the loss gradually stabilized. After around the 50th epoch, it converged to a value close to zero. This suggests that the model had fully captured the data patterns, and further training yielded limited gains. The convergence trend indicates a stable and effective learning process, without signs of oscillation or overfitting. Throughout the entire training process, the loss curve remained smooth and continuous, with no abnormal fluctuations. This shows that the optimization process was effective, and both the network structure and parameter settings were appropriate. These results further confirm that the RNN with an attention mechanism has good convergence and learning efficiency during training, providing a solid foundation for subsequent prediction tasks.
5. Conclusion
This paper presents a stock price prediction model, which is an integration of the RNN and attention mechanism. The model is empirically evaluated on real-world stock price data of Apple Inc. for the years 2024-2025. By presenting the attention mechanism, the model significantly enhances the ability to learn significant features from previous time series. It also improves modeling long-term dependencies. Experimental results show that the new model outperforms traditional methods in many aspects of evaluation. It is more accurate in its prediction and more effective in fitting, enabling a more accurate modeling of stock price patterns.
The visualization results further support the model's stability and effectiveness. Both the comparison between actual and predicted prices and the loss function curve confirm this. In particular, the performance on the test set shows that the model has strong generalization ability. It adapts well to the complex and volatile nature of financial market data. This deep learning-based modeling approach not only advances stock price prediction technology but also provides a more intelligent and automated solution for financial data analysis.
This study validates the effectiveness of combining RNN with attention mechanisms at the theoretical level. It also demonstrates strong adaptability and feasibility in practical applications. The proposed model can be extended to other financial time series prediction tasks, such as foreign exchange forecasting, fund trend analysis, and cryptocurrency price prediction. It has broad application prospects. Moreover, the method can provide solid data support and technical tools for investment decisions, risk control, and asset management in the field of financial technology. Future research can further explore the model structure and data feature dimensions. For example, introducing multi-dimensional market factors, integrating sentiment from financial news texts, or adopting multi-task learning frameworks. These directions may enhance the model's adaptability to real-world market environments. In addition, improving the model's robustness under extreme market conditions and enhancing the efficiency of real-time prediction are also important. These efforts will help promote the practical application of financial AI in real scenarios.
References
- M. Lu and X. Xu, “TRNN: An efficient time-series recurrent neural network for stock price prediction,” Information Sciences, vol. 657, p. 119951, 2024.
- M. M. Billah et al., “Stock price prediction: comparison of different moving average techniques using deep learning model,” Neural Computing and Applications, vol. 36, no. 11, pp. 5861–5871, 2024.
- X. Fan, C. Tao and J. Zhao, “Advanced stock price prediction with xlstm-based models: Improving long-term forecasting,” Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Soft Computing & Machine Intelligence (ISCMI), 2024.
- Ma’arif, A. A. Firdaus and I. Suwarno, “Capability of Hybrid Long Short-Term Memory in Stock Price Prediction: A Comprehensive Literature Review,” International Journal of Robotics & Control Systems, vol. 4, no. 3, 2024.
- Chen; et al. , “Fine-Grained Imbalanced Leukocyte Classification With Global-Local Attention Transformer,” Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 35, no. 8, Article ID 101661, 2023.
- X. Du, “Audit Fraud Detection via EfficiencyNet with Separable Convolution and Self-Attention,” Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 2, 2025.
- P. Feng, “Hybrid BiLSTM-Transformer Model for Identifying Fraudulent Transactions in Financial Systems,” Journal of Computer Science and Software Applications, vol. 5, no. 3, 2025.
- Y. Yao, “Time-Series Nested Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Risk Control in Nonlinear Financial Markets,” Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 1, 2025.
- Q. Sha et al., “Detecting Credit Card Fraud via Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks with Graph Attention,” arXiv preprint 2025. arXiv:2504.08183.
- Y. Wang, “A Data Balancing and Ensemble Learning Approach for Credit Card Fraud Detection,” arXiv preprint 2025. arXiv:2503.21160.
- J. Wang, “Credit Card Fraud Detection via Hierarchical Multi-Source Data Fusion and Dropout Regularization,” Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 1, 2025.
- X. Li et al., “Unsupervised Detection of Fraudulent Transactions in E-commerce Using Contrastive Learning,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.18841, 2025. arXiv:2503.18841.
- J. Gong, Y. Wang, W. Xu and Y. Zhang, “A Deep Fusion Framework for Financial Fraud Detection and Early Warning Based on Large Language Models,” Journal of Computer Science and Software Applications, vol. 4, no. 8, 2024.
- X. Yan, J. Du, L. Wang, Y. Liang, J. Hu and B. Wang, “The Synergistic Role of Deep Learning and Neural Architecture Search in Advancing Artificial Intelligence,” Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Electronics and Devices, Computational Science (ICEDCS), pp. 452–456, Sep. 2024.
- J. Liu, “Deep Learning for Financial Forecasting: Improved CNNs for Stock Volatility,” Journal of Computer Science and Software Applications, vol. 5, no. 2, 2025.
- Wang, Y. Dong, J. Yao, H. Qin and J. Wang, “Exploring anomaly detection and risk assessment in financial markets using deep neural networks,” International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science and Technology, vol. 12, no. 4, 2024.
- Y. Wang, “Time-Series Premium Risk Prediction via Bidirectional Transformer,” Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 2, 2025.
- S. Chavhan et al., “Deep Learning Approaches for Stock Price Prediction: A Comparative Study of LSTM, RNN, and GRU Models,” Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), 2024.
- M. Diqi and H. Hamzah, “Improving Stock Price Prediction Accuracy with StacBi LSTM,” JISKA (Jurnal Informatika Sunan Kalijaga), vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 10–26, 2024.
- L. Yu, Y. Chen and Y. Zheng, “A Multi-Market Data-Driven Stock Price Prediction System: Model Optimization and Empirical Study,” IEEE Access, 2025.
- K. Karthika et al., “Deep Learning Based Hybrid Transformer Model for Stock Price Prediction,” Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Multi-Agent Systems for Collaborative Intelligence (ICMSCI), 2025.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).