Submitted:
24 May 2025
Posted:
26 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Financial Shared Service Centers
2.1. Definition and Development of FSSCs
2.2. Operational Model and Core Functions of FSSCs
2.3. Current Status and Challenges of FSSCs
3. Basic Concepts and Application Prospects of Large Language Models
4. Application of Large Language Models in Financial Shared Service Centers
5. Application Cases and Data Analysis
5.1. Application Cases of Large Language Models in Financial Shared Service Centers
5.2. Data Analysis: Comparison of Benefits Before and After the Application of Large Language Models
6. Challenges and Solutions in the Application of Large Language Models
7. Conclusion
References
- Yang, H., Lu, Q., Wang, Y., Liu, S., Zheng, J., & Xiang, A. (2025). User Behavior Analysis in Privacy Protection with Large Language Models: A Study on Privacy Preferences with Limited Data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.06305.
- Tang, Xirui, et al. "Research on heterogeneous computation resource allocation based on data-driven method." 2024 6th International Conference on Data-driven Optimization of Complex Systems (DOCS). IEEE, 2024.
- Yin Z, Hu B, Chen S. Predicting employee turnover in the financial company: A comparative study of catboost and xgboost models. Applied and Computational Engineering, 2024, 100: 86-92.
- Qi, Zhen, et al. "Detecting and Classifying Defective Products in Images Using YOLO." arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.16935 (2024).
- Shi X, Tao Y, Lin S C. Deep Neural Network-Based Prediction of B-Cell Epitopes for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2: Enhancing Vaccine Design through Machine Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.00109, 2024.
- Xiang A, Zhang J, Yang Q, et al. Research on splicing image detection algorithms based on natural image statistical characteristics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.16296, 2024.
- Mo K, Chu L, Zhang X, et al. Dral: Deep reinforcement adaptive learning for multi-uavs navigation in unknown indoor environment. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.03930, 2024.
- Tan, Chaoyi, et al. "Generating Multimodal Images with GAN: Integrating Text, Image, and Style." arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.02167 (2025).
- Tan, Chaoyi, et al. "Real-time Video Target Tracking Algorithm Utilizing Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)." 2024 4th International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer (EIECT). IEEE, 2024.
- Xiang A, Huang B, Guo X, et al. A neural matrix decomposition recommender system model based on the multimodal large language model. Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Machine Learning and Machine Intelligence (MLMI). 2024: 146-150.
- Ge, Ge, et al. "A review of the effect of the ketogenic diet on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes." Precision Nutrition 4.1 (2025): e00100.
- Lv, Guangxin, et al. "Dynamic covalent bonds in vitrimers enable 1.0 W/(m K) intrinsic thermal conductivity." Macromolecules 56.4 (2023): 1554-1561.
- Lin, Xueting, et al. "Enhanced Recommendation Combining Collaborative Filtering and Large Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.18713 (2024).
- Yang, Haowei, et al. "Research on the Design of a Short Video Recommendation System Based on Multimodal Information and Differential Privacy." arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.08751 (2025).
- Guo H, Zhang Y, Chen L, et al. Research on vehicle detection based on improved YOLOv8 network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.00300, 2024.
- Xiang A, Qi Z, Wang H, et al. A multimodal fusion network for student emotion recognition based on transformer and tensor product. 2024 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Sensors, Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICSECE). IEEE, 2024: 1-4.
- Yang, Haowei, et al. "Optimization and Scalability of Collaborative Filtering Algorithms in Large Language Models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.18715 (2024).
- Yu Q, Wang S, Tao Y. Enhancing anti-money laundering detection with self-attention graph neural networks. SHS Web of Conferences. EDP Sciences, 2025, 213: 01016.
- Yang, Haowei, et al. "Analysis of Financial Risk Behavior Prediction Using Deep Learning and Big Data Algorithms." arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.19394 (2024).
- Diao, Su, et al. "Ventilator pressure prediction using recurrent neural network." arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.06552 (2024).
- Wang, H. , Zhang, G., Zhao, Y., Lai, F., Cui, W., Xue, J.,... & Lin, Y. (2024, December). Rpf-eld: Regional prior fusion using early and late distillation for breast cancer recognition in ultrasound images. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) (pp. 2605-2612). IEEE.
- Shih K, Han Y, Tan L. Recommendation System in Advertising and Streaming Media: Unsupervised Data Enhancement Sequence Suggestions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.08740, 2025.
- Wang T, Cai X, Xu Q. Energy Market Price Forecasting and Financial Technology Risk Management Based on Generative AI. Applied and Computational Engineering, 2024, 100: 29-34.
- Huang B, Lu Q, Huang S, et al. Multi-modal clothing recommendation model based on large model and VAE enhancement. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.02219, 2024.
- Yin J, Wu X, Liu X. Multi-class classification of breast cancer gene expression using PCA and XGBoost. Theoretical and Natural Science, 2025, 76: 6-11.
- Min, Liu, et al. "Financial Prediction Using DeepFM: Loan Repayment with Attention and Hybrid Loss." 2024 5th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computer Application (ICMLCA). IEEE, 2024.
- Ziang H, Zhang J, Li L. Framework for lung CT image segmentation based on UNet++. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.02428, 2025.
- Li, Xiangtian, et al. "Artistic Neural Style Transfer Algorithms with Activation Smoothing." arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.08014 (2024).
- Shen, Jiajiang, Weiyan Wu, and Qianyu Xu. "Accurate prediction of temperature indicators in eastern china using a multi-scale cnn-lstm-attention model." arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.07997 (2024).
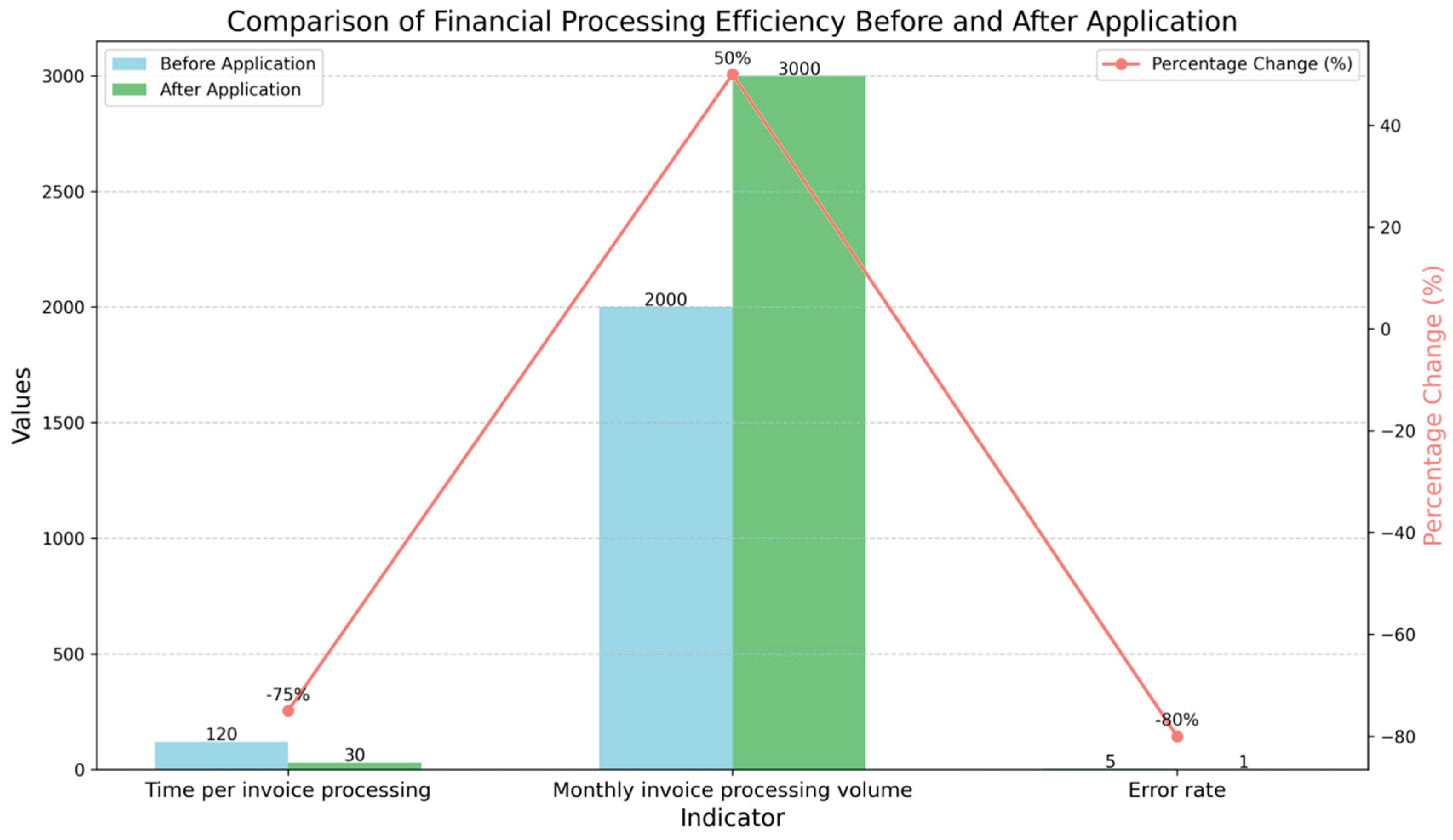
| Indicator | Before Application | After Application | Percentage Change |
| Response time per inquiry | 45 minutes | 10 minutes | -77.78% |
| Accuracy of answering common questions | 85% | 95% | +11.76% |
| Customer satisfaction | 78% | 92% | +17.95% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





