Submitted:
23 May 2025
Posted:
26 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Recent Advances and the Rise of Foundational Models
1.2. The Case for Domain-Specific Benchmarks
1.2.1. Main Contributions
- Presents a pioneering and comprehensive survey of domain-specific benchmarks for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) across a wide array of disciplines.
- Highlights the critical role of developing MLLMs tailored for diverse domains as essential for addressing the `last mile problem’ and achieving practical efficacy in real-world applications.
- Argues that such specialized advancements not only ensure domain-specific efficacy but also supplementally contribute to the broader development and refinement of large foundational models.
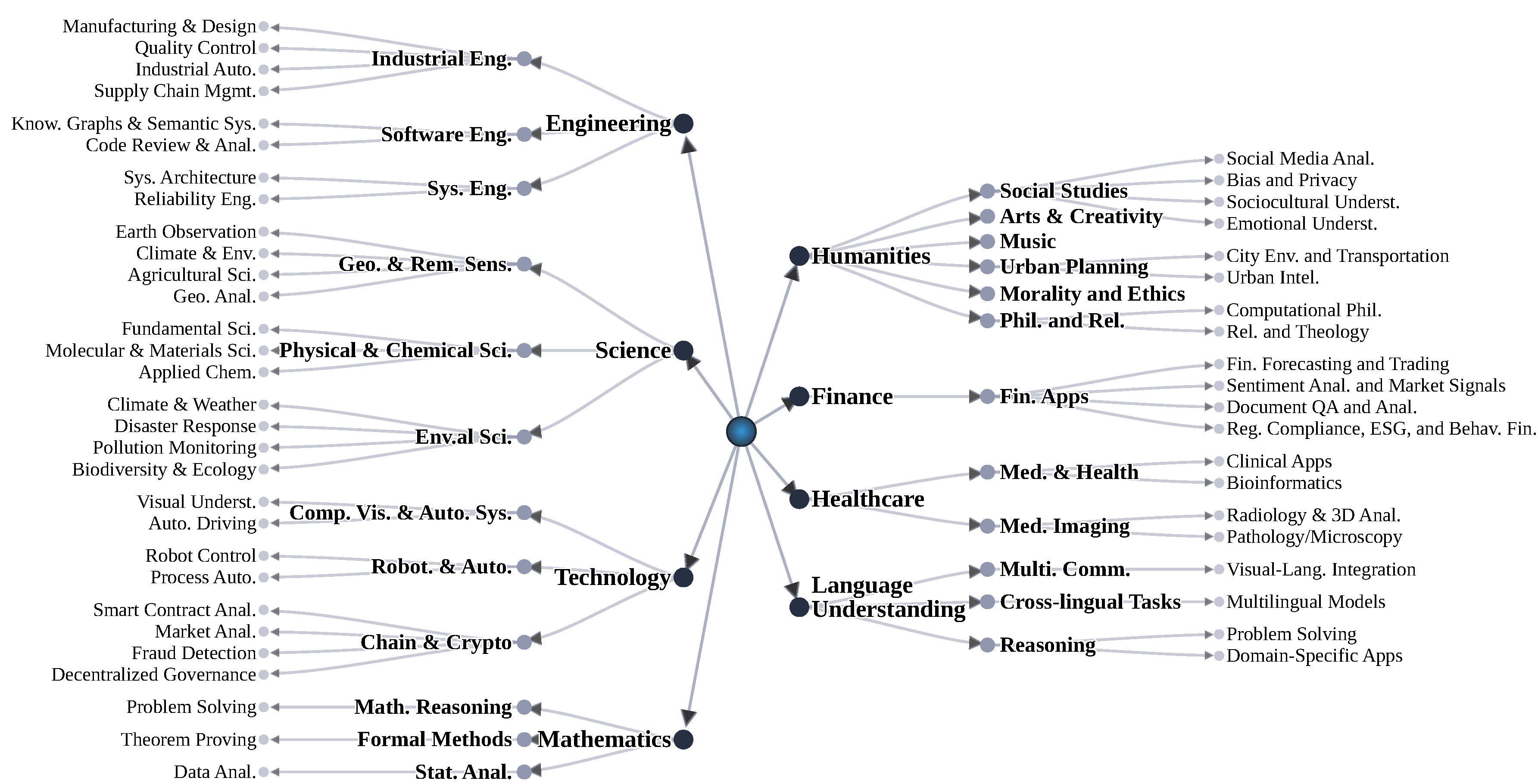
2. Review Methodology & Framework
- Engineering (Section 3) - Including industrial engineering, software engineering, and systems engineering
- Science (Section 4) - Covering geography & remote sensing, physics & chemistry, and environmental science
- Technology (Section 5) - Encompassing computer vision & autonomous systems, robotics & automation, and blockchain & cryptocurrency
- Mathematics (Section 6) - Addressing mathematical reasoning, formal methods, and statistical analysis
- Humanities (Section 7) - Examining social studies, arts & creativity, music, urban planning, morality & ethics, and philosophy & religion
- Finance (Section 8) - Covering financial forecasting, sentiment analysis, document QA, and regulatory compliance
- Healthcare (Section 9) - Focusing on medicine & healthcare and medical imaging
- Language Understanding (Section 10) - Including multimodal communication, cross-lingual tasks, and reasoning
- Scale: Dataset size and diversity, color-coded to indicate precise quantities (blue), collection descriptors (green), or unspecified amounts (gray)
- Task Type: Nature and complexity of the evaluation task
- Input Modality: Input types utilized (text, image, audio, video)
- Model: Models evaluated in the benchmark
- Performance: Quantitative or qualitative results reported
- Key Focus: Core objectives and applications of the benchmark
3. Engineering
3.1. Industrial Engineering
3.1.1. Manufacturing & Design
3.1.2. Quality Control
3.1.3. Industrial Automation
3.1.4. Supply Chain Management
3.2. Software Engineering
3.2.1. Knowledge Graphs & Semantic Systems
3.2.2. Code Review & Analysis
3.3. Systems Engineering
3.3.1. Systems Architecture
3.3.2. Reliability Engineering
4. Science
4.1. Geography & Remote Sensing
4.1.1. Earth Observation
4.1.2. Climate & Environment
4.1.3. Agricultural Science
4.1.4. Geospatial Analysis
4.2. Physical & Chemical Sciences
4.2.1. Fundamental Science
4.2.2. Molecular & Materials Science
4.2.3. Applied Chemistry
4.3. Environmental Science
4.3.1. Climate & Weather
4.3.2. Disaster Response
4.3.3. Pollution Monitoring
4.3.4. Biodiversity & Ecology
5. Technology
5.1. Computer Vision & Autonomous Systems
5.1.1. Visual Understanding
5.1.2. Autonomous Driving
5.2. Robotics & Automation
5.2.1. Robot Control
5.2.2. Process Automation
5.3. Blockchain & Cryptocurrency
5.3.1. Brief Introduction
5.3.2. Smart Contract Analysis and Auditing
5.3.3. Market Analysis and Sentiment Forecasting
5.3.4. Fraud Detection and Anomaly Detection
5.3.5. Decentralized Governance and Decision-Making
5.3.6. Section Conclusion
6. Mathematics
6.1. Mathematical Reasoning – Problem Solving
6.2. Formal Methods – Theorem Proving
6.3. Statistical Analysis – Data Analysis
7. Humanities
7.1. Social Studies
7.1.1. Social Media Analysis
7.1.2. Bias and Privacy
7.1.3. Sociocultural Understanding
7.1.4. Emotional Understanding
7.2. Arts & Creativity
7.3. Music
7.4. Urban Planning
7.4.1. City Environment and Transportation
7.4.2. Urban Intelligence
7.5. Morality and Ethics
7.6. Philosophy and Religion
7.7. Section Conclusion
8. Finance
8.1. Introduction
8.2. LLM Applications and Benchmarks in Finance
8.2.1. Financial Forecasting and Trading
8.2.2. Sentiment Analysis and Market Signals
8.2.3. Document Question Answering and Analysis
8.2.4. Regulatory Compliance, ESG and Behavioural Finance
8.3. Section Conclusion
9. Healthcare
9.1. Medicine & Healthcare
9.1.1. Clinical Applications
9.1.2. Bioinformatics
9.2. Medical Imaging
9.2.1. Radiology & 3D Analysis
9.2.2. Pathology/Microscopy
10. Language Understanding
10.1. Multimodal Communication
10.2. Cross-lingual Tasks
10.3. Reasoning
10.4. Domain-Specific Applications
11. Conclusions and Future Work
References
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774, arXiv:2303.08774 2023.
- Team, G.; Anil, R.; Borgeaud, S.; Alayrac, J.B.; Yu, J.; Soricut, R.; Schalkwyk, J.; Dai, A.M.; Hauth, A.; Millican, K.; et al. Gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.11805, arXiv:2312.11805 2023.
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07258, arXiv:2108.07258 2021.
- Grattafiori, A.; Dubey, A.; Jauhri, A.; Pandey, A.; Kadian, A.; Al-Dahle, A.; Letman, A.; Mathur, A.; Schelten, A.; Vaughan, A.; et al. The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.21783, arXiv:2407.21783 2024.
- Abdin, M.; Aneja, J.; Behl, H.; Bubeck, S.; Eldan, R.; Gunasekar, S.; Harrison, M.; Hewett, R.J.; Javaheripi, M.; Kauffmann, P.; et al. Phi-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.08905, arXiv:2412.08905 2024.
- Islam, P.; Kannappan, A.; Kiela, D.; Qian, R.; Scherrer, N.; Vidgen, B. FinanceBench: A new benchmark for financial question answering, [2311.11944]. arXiv preprint.
- Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Shi, E.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z. Top General Performance = Top Domain Performance? A: DomainCodeBench, 2025; arXiv:cs.SE/2412.18573]. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, N.; Peng, Y.; Feng, F.; Tang, J. Mmro: Are multimodal llms eligible as the brain for in-home robotics? arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.19693, arXiv:2406.19693 2024.
- Doris, A.C.; Grandi, D.; Tomich, R.; Alam, M.F.; Ataei, M.; Cheong, H.; Ahmed, F. DesignQA: A Multimodal Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models’ Understanding of Engineering Documentation. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2024, 25, 021009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernan Freire, S.; Wang, C.; Foosherian, M.; Wellsandt, S.; Ruiz-Arenas, S.; Niforatos, E. Knowledge sharing in manufacturing using LLM-powered tools: user study and model benchmarking. Frontiers in Artificial intelligence 2024, 7, 1293084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Dong, X.; Rong, H.; Fu, B. Manu-Eval: A Chinese Language Understanding Benchmark for Manufacturing Industry. In Proceedings of the China Conference on Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing. Springer; 2024; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Eslaminia, A.; Jackson, A.; Tian, B.; Stern, A.; Gordon, H.; Malhotra, R.; Nahrstedt, K.; Shao, C. FDM-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models in Additive Manufacturing Tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.09819, arXiv:2412.09819 2024.
- Fakih, M.; Dharmaji, R.; Moghaddas, Y.; Quiros, G.; Ogundare, O.; Al Faruque, M.A. LLM4PLC: Harnessing Large Language Models for Verifiable Programming of PLCs in Industrial Control Systems. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 46th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Practice, New York, NY, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Tizaoui, T.; Tan, R. Towards a benchmark dataset for large language models in the context of process automation. Digital Chemical Engineering, 1001. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jazdi, N.; Weyrich, M. Incorporating Large Language Models into Production Systems for Enhanced Task Automation and Flexibility. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.08550, arXiv:2407.08550 2024.
- Ogundare, O.; Madasu, S.; Wiggins, N. Industrial Engineering with Large Language Models: A case study of ChatGPT’s performance on Oil & Gas problems. In Proceedings of the 2023 11th International Conference on Control, Mechatronics and Automation (ICCMA). IEEE; 2023; pp. 458–461. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.A.; Chawla, S.; Yaqot, M.; Menezes, B. Leveraging Large Language Models for Supply Chain Management Optimization: A Case Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Intelligent Industrial Production and Logistics. Springer; 2024; pp. 175–197. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Mellou, K.; Zhang, B.; Pathuri, J.; Menache, I. Large language models for supply chain optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.03875, arXiv:2307.03875 2023.
- Raman, R.; Sreenivasan, A.; Suresh, M.; Gunasekaran, A.; Nedungadi, P. AI-driven education: a comparative study on ChatGPT and Bard in supply chain management contexts. Cogent Business & Management 2024, 11, 2412742. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, L.P.; Frey, J.; Junghanns, K.; Brei, F.; Bulert, K.; Gründer-Fahrer, S.; Martin, M. 2023; arXiv:cs.AI/2308.16622].
- bench authors, B. Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models. Transactions on Machine Learning Research 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Azanza, M.; Lamancha, B.P.; Pizarro, E. A: the Moving Target, 2025; arXiv:cs.SE/2504.18985].
- Shah, N.; Genc, Z.; Araci, D. StackEval: Benchmarking LLMs in Coding Assistance. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 37, 36976–36994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Fang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z. 2024; arXiv:cs.SE/2312.15223].
- Bell, R.; Longshore, R.; Madachy, R. Introducing SysEngBench: A novel benchmark for assessing large language models in systems engineering. Technical report, Acquisition Research Program, 2024.
- Hu, Y.; Goktas, Y.; Yellamati, D.D.; De Tassigny, C. The use and misuse of pre-trained generative large language models in reliability engineering. In Proceedings of the 2024 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium (RAMS). IEEE; 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vendrow, J.; Vendrow, E.; Beery, S.; Madry, A. Do Large Language Model Benchmarks Test Reliability? arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.03461, arXiv:2502.03461 2025.
- Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ton, J.F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, R.; Cheng, H.; Klochkov, Y.; Taufiq, M.F.; Li, H. a: LLMs, 2024; arXiv:cs.AI/2308.05374].
- Irvin, J.A.; Liu, E.R.; Chen, J.C.; Dormoy, I.; Kim, J.; Khanna, S.; Zheng, Z.; Ermon, S. TEOChat: A Large Vision-Language Assistant for Temporal Earth Observation Data, 2024. _eprint: 2410.06234.
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X.X. EarthNets: Empowering artificial intelligence for Earth observation. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Good at captioning, bad at counting: Benchmarking gpt-4v on earth observation data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.17600, arXiv:2401.17600 2024.
- Li, W.; Yao, D.; Zhao, R.; Chen, W.; Xu, Z.; Luo, C.; Gong, C.; Jing, Q.; Tan, H.; Bi, J. STBench: Assessing the Ability of Large Language Models in Spatio-Temporal Analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.19065, arXiv:2406.19065 2024.
- Sapkota, R.; Qureshi, R.; Hassan, S.Z.; Shutske, J.; Shoman, M.; Sajjad, M.; Dharejo, F.A.; Paudel, A.; Li, J.; Meng, Z.; et al. Multi-modal LLMs in agriculture: A comprehensive review. Authorea Preprints.
- Danish, M.S.; Munir, M.A.; Shah, S.R.A.; Kuckreja, K.; Khan, F.S.; Fraccaro, P.; Lacoste, A.; Khan, S. GEOBench-VLM: Benchmarking Vision-Language Models for Geospatial Tasks, 2024. _eprint: 2411.19325.
- Roberts, J.; Lüddecke, T.; Sheikh, R.; Han, K.; Albanie, S. Charting new territories: Exploring the geographic and geospatial capabilities of multimodal llms. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp.
- Liu, X.; Lian, Z. RSUniVLM: A Unified Vision Language Model for Remote Sensing via Granularity-oriented Mixture of Experts, 2024. _eprint: 2412.05679.
- Lin, C.; Lyu, H.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. INS-MMBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating LVLMs’ Performance in Insurance. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.09105, arXiv:2406.09105 2024.
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Basart, S.; Zou, A.; Mazeika, M.; Song, D.; Steinhardt, J. Measuring massive multitask language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.03300, arXiv:2009.03300 2020.
- Lu, P.; Mishra, S.; Xia, T.; Qiu, L.; Chang, K.W.; Zhu, S.C.; Tafjord, O.; Clark, P.; Kalyan, A. Learn to explain: Multimodal reasoning via thought chains for science question answering. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 2507–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.; Guo, R.; Khalighinejad, G.; Liu, O.; Dhingra, B.; Yogatama, D.; Jia, R.; Neiswanger, W. Isobench: Benchmarking multimodal foundation models on isomorphic representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.01266, arXiv:2404.01266 2024.
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, B.; Tang, J. VisScience: An Extensive Benchmark for Evaluating K12 Educational Multi-modal Scientific Reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.13730, arXiv:2409.13730 2024.
- Rein, D.; Hou, B.L.; Stickland, A.C.; Petty, J.; Pang, R.Y.; Dirani, J.; Michael, J.; Bowman, S.R. Gpqa: A graduate-level google-proof q&a benchmark. In Proceedings of the First Conference on Language Modeling; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, A.; Kapuriya, J.; Singh, A.; Saraf, J.; Lal, N.; Verma, A.; Gupta, R.; Shah, R. Mm-phyqa: Multimodal physics question-answering with multi-image cot prompting. In Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Springer; 2024; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, A.; Alampara, N.; Kunchapu, S.; Ríos-García, M.; Emoekabu, B.; Krishnan, A.; Gupta, T.; Schilling-Wilhelmi, M.; Okereke, M.; Aneesh, A.; et al. Are large language models superhuman chemists? arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.01475, arXiv:2404.01475 2024.
- Zhu, S.; Liu, X.; Khalighinejad, G. ChemQA: a Multimodal Question-and-Answering Dataset on Chemistry Reasoning. https://huggingface.co/datasets/shangzhu/ChemQA, 2024.
- Guo, T.; Nan, B.; Liang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chawla, N.; Wiest, O.; Zhang, X.; et al. What can large language models do in chemistry? a comprehensive benchmark on eight tasks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2023, 36, 59662–59688. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Baker, F.N.; Chen, Z.; Ning, X.; Sun, H. Llasmol: Advancing large language models for chemistry with a large-scale, comprehensive, high-quality instruction tuning dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09391, arXiv:2402.09391 2024.
- Zaki, M.; Krishnan, N.; et al. Mascqa: A question answering dataset for investigating materials science knowledge of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09115, arXiv:2308.09115 2023.
- Rubungo, A.N.; Li, K.; Hattrick-Simpers, J.; Dieng, A.B. LLM4Mat-bench: benchmarking large language models for materials property prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.00177, arXiv:2411.00177 2024.
- Cao, H.; Shao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y. Presto: progressive pretraining enhances synthetic chemistry outcomes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.13193, arXiv:2406.13193 2024.
- Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Ke, B.; Lv, J. DrugLLM: Open Large Language Model for Few-shot Molecule Generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.06690, arXiv:2405.06690 2024.
- Rasp, S.; Hoyer, S.; Merose, A.; Langmore, I.; Battaglia, P.; Russell, T.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Yang, V.; Carver, R.; Agrawal, S.; et al. Weatherbench 2: A benchmark for the next generation of data-driven global weather models. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2024, 16, e2023MS004019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, P.; Hua, Y.; Chong, D.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, B.; Liang, J. Vision-language models meet meteorology: Developing models for extreme weather events detection with heatmaps. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.09838, arXiv:2406.09838 2024.
- Ma, C.; Hua, Z.; Anderson-Frey, A.; Iyer, V.; Liu, X.; Qin, L. WeatherQA: Can Multimodal Language Models Reason about Severe Weather? arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11217, arXiv:2406.11217 2024.
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lau, A.K.H.; Qu, H. Cllmate: A multimodal llm for weather and climate events forecasting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.19058, arXiv:2409.19058 2024.
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Peng, Y. Unleashing the potential of large language model: Zero-shot vqa for flood disaster scenario. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering, 2023, pp.
- Rawat, R. Disasterqa: A benchmark for assessing the performance of llms in disaster response. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.20707, arXiv:2410.20707 2024.
- Patel, Z.B.; Bachwana, Y.; Sharma, N.; Guttikunda, S.; Batra, N. VayuBuddy: an LLM-Powered Chatbot to Democratize Air Quality Insights. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.12760, arXiv:2411.12760 2024.
- Pafilis, E.; Frankild, S.P.; Fanini, L.; Faulwetter, S.; Pavloudi, C.; Vasileiadou, A.; Arvanitidis, C.; Jensen, L.J. The SPECIES and ORGANISMS resources for fast and accurate identification of taxonomic names in text. PloS one 2013, 8, e65390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmageed, N.; Löffler, F.; Feddoul, L.; Algergawy, A.; Samuel, S.; Gaikwad, J.; Kazem, A.; König-Ries, B. BiodivNERE: Gold standard corpora for named entity recognition and relation extraction in the biodiversity domain. Biodiversity Data Journal 2022, 10, e89481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gema, A.P.; Leang, J.O.J.; Hong, G.; Devoto, A.; Mancino, A.C.M.; Saxena, R.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Du, X.; Madani, M.R.G.; et al. Are We Done with MMLU? arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.04127, arXiv:2406.04127 2024.
- Richard, A.M.; Huang, R.; Waidyanatha, S.; Shinn, P.; Collins, B.J.; Thillainadarajah, I.; Grulke, C.M.; Williams, A.J.; Lougee, R.R.; Judson, R.S.; et al. The Tox21 10K compound library: collaborative chemistry advancing toxicology. Chemical Research in Toxicology 2020, 34, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic acids research 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Coley, C.; Barzilay, R.; Jaakkola, T. Predicting organic reaction outcomes with weisfeiler-lehman network. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.; Zhai, C.; Ji, H. Text2mol: Cross-modal molecule retrieval with natural language queries. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2021, pp.
- Irwin, J.J.; Tang, K.G.; Young, J.; Dandarchuluun, C.; Wong, B.R.; Khurelbaatar, M.; Moroz, Y.S.; Mayfield, J.; Sayle, R.A. ZINC20—a free ultralarge-scale chemical database for ligand discovery. Journal of chemical information and modeling 2020, 60, 6065–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Nowotka, M.; Papadatos, G.; Dedman, N.; Gaulton, A.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.; Overington, J.P. ChEMBL web services: streamlining access to drug discovery data and utilities. Nucleic acids research 2015, 43, W612–W620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; Dueben, P.D.; Scher, S.; Weyn, J.A.; Mouatadid, S.; Thuerey, N. WeatherBench: a benchmark data set for data-driven weather forecasting. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2020, 12, e2020MS002203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, W.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, X.; Cao, D.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bogdan, P. ClimateLLM: Efficient Weather Forecasting via Frequency-Aware Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.11059, arXiv:2502.11059 2025.
- Sachdeva, E.; Agarwal, N.; Chundi, S.; Roelofs, S.; Li, J.; Kochenderfer, M.; Choi, C.; Dariush, B. Rank2tell: A multimodal driving dataset for joint importance ranking and reasoning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, 2024, pp.
- Ding, X.; Han, J.; Xu, H.; Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Holistic autonomous driving understanding by bird’s-eye-view injected multi-modal large models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp.
- Qian, T.; Chen, J.; Zhuo, L.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.G. NuScenes-QA: A Multi-Modal Visual Question Answering Benchmark for Autonomous Driving Scenario. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2024, 38, 4542–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Brown, E.; Wu, P.; Woo, S.; Middepogu, M.; Akula, S.C.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Iyer, A.; Pan, X.; et al. Cambrian-1: A fully open, vision-centric exploration of multimodal llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.16860, arXiv:2406.16860 2024.
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Du, W.; Zhang, H.; Du, Y.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Gan, C. HAZARD Challenge: Embodied Decision Making in Dynamically Changing Environments. Arxiv.
- Yang, Z.; Jia, X.; Li, H.; Yan, J. LLM4Drive: A Survey of Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving. Arxiv.
- Kong, Q.; Kawana, Y.; Saini, R.; Kumar, A.; Pan, J.; Gu, T.; Ozao, Y.; Opra, B.; Sato, Y.; Kobori, N. WTS: A Pedestrian-Centric Traffic Video Dataset for Fine-Grained Spatial-Temporal Understanding. 2025, Vol. 15134, pp. 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Malla, S.; Choi, C.; Dwivedi, I.; Choi, J.H.; Li, J. Drama: Joint risk localization and captioning in driving. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, 2023, pp.
- Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, T.; Dai, B.; Chitta, K.; Wu, P.; Zeng, J.; Luo, P.; et al. Generalized Predictive Model for Autonomous Driving. 2024, pp. 14662–14672.
- Nie, M.; Peng, R.; Wang, C.; Cai, X.; Han, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L. Reason2Drive: Towards Interpretable and Chain-Based Reasoning for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A.; Ricci, E.; Roth, S.; Russakovsky, O.; Sattler, T.; Varol, G., Eds., Cham; 2025; pp. 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, C.; Renz, K.; Chitta, K.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, C.; Beißwenger, J.; Luo, P.; Geiger, A.; Li, H. DriveLM: Driving with Graph Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A.; Ricci, E.; Roth, S.; Russakovsky, O.; Sattler, T.; Varol, G., Eds., Cham; 2025; pp. 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Han, W.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J. Language Prompt for Autonomous Driving, 2023. arXiv:2309. 0437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Pearce, H.; Chen, S. L: Meets Magic, 2025; arXiv:cs.CR/2501.07058].
- Wei, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Hou, Z. 2024; arXiv:cs.CR/2410.09381].
- Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Sun, K.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y. 2024; arXiv:cs.SE/2403.06838].
- Roumeliotis, K.I.; Tselikas, N.D.; Nasiopoulos, D.K. LLMs and NLP Models in Cryptocurrency Sentiment Analysis: A Comparative Classification Study. Big Data and Cognitive Computing 2024, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, E.; Palaiokrassas, G.; Bouraga, S.; Polychroniadou, A.; Tassiulas, L. 2025; arXiv:cs.AI/2503.23190].
- Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Luo, B.; Chen, N.; He, B. 2025; arXiv:cs.MA/2410.12464].
- He, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Ye, H.; Qiao, A.; Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Chen, T. A: Language Models for Blockchain Security, 2025; arXiv:cs.CR/2403.14280].
- Trozze, A.; Davies, T.; Kleinberg, B. Large Language Models in Cryptocurrency Securities Cases: Can a GPT Model Meaningfully Assist Lawyers? 2024; arXiv:cs.AI/2308.06032]. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Ma, Y.; Cao, X.; Ye, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, K.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liao, K.D.; et al. A survey on multimodal large language models for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2024, pp.
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, K.; Li, J.; Qian, Z.; Wen, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, D. Grid-centric traffic scenario perception for autonomous driving: A comprehensive review. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, P.; Brown, E.; Wu, P.; Woo, S.; IYER, A.J.V.; Akula, S.C.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Middepogu, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Cambrian-1: A fully open, vision-centric exploration of multimodal llms. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 37, 87310–87356. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, T.; Dai, B.; Chitta, K.; Wu, P.; Zeng, J.; Luo, P.; et al. Generalized predictive model for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024, pp.
- Shah, R.S.; Chawla, K.; Eidnani, D.; Shah, A.; Du, W.; Chava, S.; Raman, N.; Smiley, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, D. When flue meets flang: Benchmarks and large pre-trained language model for financial domain, [2211.00083]. arXiv preprint.
- Guan, W.; Cao, J.; Qian, S.; Gao, J.; Ouyang, C. 2025; arXiv:cs.SE/2411.08561].
- Sinha, R.; Elhafsi, A.; Agia, C.; Foutter, M.; Schmerling, E.; Pavone, M. 2024; arXiv:cs.RO/2407.08735].
- Zhang, R.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Guo, Z.; Qiu, P.; Zhou, A.; Lu, P.; Chang, K.W.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Mathverse: Does your multi-modal llm truly see the diagrams in visual math problems? In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer; 2024; pp. 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Martinson, S.; Wang, E.Y.; Hausknecht, K.; Brenner, J.; Liu, D.; Peng, N.; Wang, C.; Brenner, M. HARDMATH: A Benchmark Dataset for Challenging Problems in Applied Mathematics. In Proceedings of the The 4th Workshop on Mathematical Reasoning and AI at NeurIPS’24; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yao, A.C.C. Augmenting Math Word Problems via Iterative Question Composing. Arxiv.
- Liang, Z.; Yu, D.; Yu, W.; Yao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, D. Mathchat: Benchmarking mathematical reasoning and instruction following in multi-turn interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.19444, arXiv:2405.19444 2024.
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Hao, H.; Wang, R. Multiple-choice questions are efficient and robust llm evaluators. 2024d. URL https://doi. org/10.48550/arXiv.
- Anantheswaran, U.; Gupta, H.; Scaria, K.; Verma, S.; Baral, C.; Mishra, S. Cutting Through the Noise: Boosting LLM Performance on Math Word Problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.15444, arXiv:2406.15444 2024.
- Yang, K.; Swope, A.; Gu, A.; Chalamala, R.; Song, P.; Yu, S.; Godil, S.; Prenger, R.J.; Anandkumar, A. Leandojo: Theorem proving with retrieval-augmented language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2023, 36, 21573–21612. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Long, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C.; Cohan, A. FinanceMATH: Knowledge-Intensive Math Reasoning in Finance Domains. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), 2024, pp.
- Pezeshkpour, P.; Hruschka, E. Large Language Models Sensitivity to The Order of Options in Multiple-Choice Questions. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2024; Duh, K.; Gomez, H.; Bethard, S., Eds., Mexico City, Mexico; 2024; pp. 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBelle, E. Monte Carlo Tree Search Applications to Neural Theorem Proving. PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2024.
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, W. Finllms: A framework for financial reasoning dataset generation with large language models. IEEE Transactions on Big Data 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Choi, M.; Verma, G.; Wang, J.; Kumar, S. Mm-soc: Benchmarking multimodal large language models in social media platforms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.14154, arXiv:2402.14154 2024.
- Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; Guo, Q.; Jia, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y. HOTVCOM: Generating Buzzworthy Comments for Videos. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024; Ku, L.W.; Martins, A.; Srikumar, V., Eds., Bangkok, Thailand; 2024; pp. 2198–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y. XMeCap: Meme Caption Generation with Sub-Image Adaptability. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Dara, R. Priv-IQ: A Benchmark and Comparative Evaluation of Large Multimodal Models on Privacy Competencies. AI 2025, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, I.O.; et al. Bias and Fairness in Large Language Models: A Survey. Comput. Linguist. 2024, 50, 1097–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; et al. CultureVLM: Characterizing and Improving Cultural Understanding of Vision-Language Models for over 100 Countries. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.01282]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaboura, S.; et al. Time Travel: A Comprehensive Benchmark to Evaluate LMMs on Historical and Cultural Artifacts. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.14865]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; et al. EmoBench-M: Benchmarking Emotional Intelligence for Multimodal Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.04424]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, S.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y. EmotionQueen: A Benchmark for Evaluating Empathy of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024; Ku, L.W.; Martins, A.; Srikumar, V., Eds., Bangkok, Thailand; 2024; pp. 2149–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; et al. EditWorld: Simulating World Dynamics for Instruction-Following Image Editing. CoRR, 2025; 24. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; et al. LLMs Meet Multimodal Generation and Editing: A Survey. CoRR, 2025; 25. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Ding, K.; Jin, L. WenMind: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models in Chinese Classical Literature and Language Arts. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2025, 37, 51358–51410. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; et al. The Music Maestro or The Musically Challenged, A Massive Music Evaluation Benchmark for Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024; Ku, L.W.; Martins, A.; Srikumar, V., Eds., Bangkok, Thailand; 2024; pp. 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weck, B.; Manco, I.; Benetos, E.; Quinton, E.; Fazekas, G.; Bogdanov, D. MuChoMusic: Evaluating Music Understanding in Multimodal Audio-Language Models. CoRR, 2025; 25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; et al. Can LLMs ’Reason’ in Music? An Evaluation of LLMs’ Capability of Music Understanding and Generation. CoRR, 2025; 25. [Google Scholar]
- Hachmeier, S.; Jäschke, R. A Benchmark and Robustness Study of In-Context-Learning with Large Language Models in Music Entity Detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics; Rambow, O.; Wanner, L.; Apidianaki, M.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Eugenio, B.D.; Schockaert, S., Eds., Abu Dhabi, UAE; 2025; pp. 9845–9859. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; et al. MuChin: a chinese colloquial description benchmark for evaluating language models in the field of music. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Thirty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Jeju, Korea, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; et al. CityEQA: A Hierarchical LLM Agent on Embodied Question Answering Benchmark in City Space. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12532]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; et al. TransportationGames: Benchmarking Transportation Knowledge of (Multimodal) Large Language Models. CoRR, 2025; 24. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, T.; Sun, J.; Ma, W. Exploring the Roles of Large Language Models in Reshaping Transportation Systems: A Survey, Framework, and Roadmap. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.21411]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H.; Liu, H.; Xiong, H. Urban Foundation Models: A Survey. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; et al. UrbanPlanBench: A Comprehensive Assessment of Urban Planning Abilities in Large Language Models 2024. Accessed: Feb. 25, 2025.
- Feng, J.; et al. CityBench: Evaluating the Capabilities of Large Language Model as World Model. CoRR, 2025; 25. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Chen, Y.; Jin, M.; Xu, W.; Hua, W.; Zhang, Y. MoralBench: Moral Evaluation of LLMs. CoRR, 2025; 27. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. M3oralBench: A MultiModal Moral Benchmark for LVLMs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.20718]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marraffini, G.F.G.; Cotton, A.; Hsueh, N.F.; Fridman, A.; Wisznia, J.; Corro, L.D. The Greatest Good Benchmark: Measuring LLMs’ Alignment with Utilitarian Moral Dilemmas. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; et al. Value Compass Leaderboard: A Platform for Fundamental and Validated Evaluation of LLMs Values. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.07071]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, S.; Wan, Y.; Sun, L. I Think, Therefore I am: Benchmarking Awareness of Large Language Models Using AwareBench. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.17882]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C.; Jurgensen, J.; Hu, H. InterIDEAS: An LLM and Expert-Enhanced Dataset for Philosophical Intertextuality 2024. Accessed: Feb. 27, 2025.
- Trepczyński, M. Religion, Theology, and Philosophical Skills of LLM–Powered Chatbots. Disput. Philos. Int. J. Philos. Relig. 2023, 25, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; et al. Deconstructing The Ethics of Large Language Models from Long-standing Issues to New-emerging Dilemmas. CoRR, 2025; 24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; et al. Piecing It All Together: Verifying Multi-Hop Multimodal Claims. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics; Rambow, O.; Wanner, L.; Apidianaki, M.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Eugenio, B.D.; Schockaert, S., Eds., Abu Dhabi, UAE; 2025; pp. 7453–7469. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; et al. AgentReview: Exploring Peer Review Dynamics with LLM Agents. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; et al. MOSABench: Multi-Object Sentiment Analysis Benchmark for Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models Understanding of Complex Image. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.00060]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilazuarda, M.F.; et al. Towards Measuring and Modeling ’Culture’ in LLMs: A Survey. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y. Recent Advancement of Emotion Cognition in Large Language Models. CoRR, 2025; 24. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty, T.; Laban, P.; Agarwal, D.; Muresan, S.; Wu, C.S. Art or Artifice? Large Language Models and the False Promise of Creativity. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New York, NY, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.l.; Hale, S.A. Beyond English: Evaluating Automated Measurement of Moral Foundations in Non-English Discourse with a Chinese Case Study. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.02451]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulla, L.; De Giorgis, S.; Mongiovì, M.; Gangemi, A. Large Language Models meet moral values: A comprehensive assessment of moral abilities. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 2025, 17, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Lai, Y.; Peng, M.; Lopez-Lira, A.; Huang, J. Pixiu: A large language model, instruction data and evaluation benchmark for finance, [2306.05443]. arXiv preprint.
- Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Smiley, C.; Shah, S.; Borova, I.; Langdon, D.; Moussa, R.; Beane, M.; Huang, T.H.; Routledge, B.; et al. FinQA: A dataset of numerical reasoning over financial data, [2109.00122]. arXiv preprint.
- Reddy, V.; Koncel-Kedziorski, R.; Lai, V.D.; Krumdick, M.; Lovering, C.; Tanner, C. DocFinQA: A long-context financial reasoning dataset, [2401.06915]. arXiv preprint.
- Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Smiley, C.; Ma, Z.; Shah, S.; Wang, W.Y. ConvFinQA: Exploring the chain of numerical reasoning in conversational finance question answering, [2210.03849]. arXiv preprint.
- Webersinke, N.; Kraus, M.; Bingler, J.A.; Leippold, M. Climatebert: A pretrained language model for climate-related text, [2110.12010]. arXiv preprint.
- Sharma, S.; Nayak, T.; Bose, A.; Meena, A.K.; Dasgupta, K.; Ganguly, N.; Goyal, P. FinRED: A dataset for relation extraction in financial domain. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2022, 2022, pp. 595–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Su, H.; Lin, Z.; Qi, Y.; Xu, C.; Su, J.; Zhong, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; et al. Golden Touchstone: A Comprehensive Bilingual Benchmark for Evaluating Financial Large Language Models, [2411.06272]. arXiv preprint.
- Subrahmanyam, A. Behavioural finance: A review and synthesis. European Financial Management 2008, 14, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbaniy, G.; Khalid, A.A.; Syriopoulos, K.; Polyzos, E. Dynamic returns connectedness: Portfolio hedging implications during the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia–Ukraine war. Journal of Futures Markets 2024, 44, 1613–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hoque, H.; Liu, J. Investor sentiment and firm capital structure. Journal of Corporate Finance 2023, 80, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadima, M.; Louri, H. Economic policy uncertainty and non-performing loans: The moderating role of bank concentration. Finance Research Letters 2021, 38, 101458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodbod, A.; Huber, S.; Vasilev, K. Sectoral risk-weights and macroprudential policy. Journal of Banking and Finance 2020, 112, 105336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, J.; James, K.R.; Valenzuela, M.; Zer, I. Model risk of risk models. Journal of Financial Stability 2016, 23, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, A.; Horn, M. Does ChatGPT provide better advice than robo-advisors? Finance Research Letters 2024, 60, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, M.; Lucey, B. ChatGPT for (finance) research: The Bananarama conjecture. Finance Research Letters 2023, 53, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, E.; Fotiadis, A.; Huan, T.C. The asymmetric impact of Twitter sentiment and emotions: Impulse response analysis on European tourism firms using micro-data. Tourism Management 2024, 104, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamara, E.; Turrell, A.; Redl, C.; Kapetanios, G.; Kapadia, S. Making text count: economic forecasting using newspaper text. Journal of Applied Econometrics 2022, 37, 896–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.P.; Constantino, M.; Su, J.J.; Naranpanawa, A. Renewable energy stocks forecast using Twitter investor sentiment and deep learning. Energy Economics 2022, 114, 106285. [Google Scholar]
- Dicks, D.; Fulghieri, P. Uncertainty, investor sentiment, and innovation. The Review of Financial Studies 2021, 34, 1236–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, H.; Zha, D. Fingpt: Democratizing internet-scale data for financial large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10485, arXiv:2307.10485 2023.
- Wu, S.; Irsoy, O.; Lu, S.; Dabravolski, V.; Dredze, M.; Gehrmann, S.; Kambadur, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Mann, G. BloombergGPT: A large language model for finance, [2303.17564]. arXiv preprint.
- Liu, Y.; Bu, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z. AT-FinGPT: Financial risk prediction via an audio-text large language model. Finance Research Letters, 1069. [Google Scholar]
- Polyzos, E. Inflation and the war in Ukraine: Evidence using impulse response functions on economic indicators and Twitter sentiment. Research in International Business and Finance 2023, 66, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Lucey, B.; Xie, Y.; Yarovaya, L. I just like the stock. The role of Reddit sentiment in the GameStop share rally. Financial Review 2023, 58, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lyócsa, Š.; Baumöhl, E.; Výrost, T. YOLO trading: Riding with the herd during the GameStop episode. Finance Research Letters 2022, 46, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, E.; Samitas, A.; Kampouris, I. Quantifying market efficiency: Information dissemination through social media. Available at SSRN 2022, 4082899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiou, E. Does the short squeeze lead to market abnormality and antileverage effect? Evidence from the GameStop case. Journal of Economic Studies 2022, 49, 1360–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.H.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. FinBERT: A large language model for extracting information from financial text. Contemporary Accounting Research 2023, 40, 806–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughran, T.; McDonald, B. When is a liability not a liability? Textual analysis, dictionaries, and 10-Ks. The Journal of Finance 2011, 66, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niţoi, M.; Pochea, M.M.; Radu, Ş.C. Unveiling the Sentiment Behind Central Bank Narratives: A Novel Deep Learning Index. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance 2023, 38, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanski, T.; Reding, A.; Reding, N.; Bingler, J.A.; Kraus, M.; Leippold, M. Bridging the gap in ESG measurement: Using NLP to quantify environmental, social, and governance communication. Finance Research Letters 2024, 61, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, E.; Samitas, A.; Katsaiti, M.S. Who is unhappy for Brexit? A machine-learning, agent-based study on financial instability. International Review of Financial Analysis 2020, 72, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, E.; Abdulrahman, K.; Christopoulos, A. Good management or good finances? An agent-based study on the causes of bank failure. Banks & Bank Systems, 3.
- Stevens Institute of Technology. Applying Large Language Models to Financial Decision-Making. https://www.stevens.edu/news/applying-large-language-models-to-financial-decision-making, 2023. [Accessed ]. 3 March.
- Ye, J.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Duan, H.; Huang, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Gmai-mmbench: A comprehensive multimodal evaluation benchmark towards general medical ai. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 37, 94327–94427. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Su, Y.; Huan, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Chang, K.J.; Xin, X.; Shen, L.; et al. A Spectrum Evaluation Benchmark for Medical Multi-Modal Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.11217, arXiv:2402.11217 2024.
- Keat, K.; Venkatesh, R.; Huang, Y.; Kumar, R.; Tuteja, S.; Sangkuhl, K.; Li, B.; Gong, L.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Klein, T.E.; et al. PGxQA: A Resource for Evaluating LLM Performance for Pharmacogenomic QA Tasks. In Proceedings of the Biocomputing 2025: Proceedings of the Pacific Symposium.
- Liu, H.; Wang, H. GenoTEX: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLM-Based Exploration of Gene Expression Data in Alignment with Bioinformaticians. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.15341, arXiv:2406.15341 2024.
- Bai, F.; Du, Y.; Huang, T.; Meng, M.Q.H.; Zhao, B. M3d: Advancing 3d medical image analysis with multi-modal large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.00578, arXiv:2404.00578 2024.
- Bassi, P.R.A.S.; Yavuz, M.C.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Decherchi, S.; Cavalli, A.; Yang, Y.; Yuille, A.; Zhou, Z. 2025; arXiv:eess.IV/2501.04678].
- Mo, S.; Liang, P.P. MultiMed: Massively Multimodal and Multitask Medical Understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.12682, arXiv:2408.12682 2024.
- Sepehri, M.S.; Fabian, Z.; Soltanolkotabi, M.; Soltanolkotabi, M. MediConfusion: Can you trust your AI radiologist? Probing the reliability of multimodal medical foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.15477, arXiv:2409.15477 2024.
- Neehal, N.; Wang, B.; Debopadhaya, S.; Dan, S.; Murugesan, K.; Anand, V.; Bennett, K.P. Ctbench: A comprehensive benchmark for evaluating language model capabilities in clinical trial design. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.17888, arXiv:2406.17888 2024.
- Khandekar, N.; Jin, Q.; Xiong, G.; Dunn, S.; Applebaum, S.; Anwar, Z.; Sarfo-Gyamfi, M.; Safranek, C.; Anwar, A.; Zhang, A.; et al. Medcalc-bench: Evaluating large language models for medical calculations. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 37, 84730–84745. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; He, D.; Wei, Z.; Hong, L.; Zong, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, Q.; Ma, Z.; et al. Benchmarking Large Language Models on Multiple Tasks in Bioinformatics NLP with Prompting. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.04013, arXiv:2503.04013 2025.
- Chen, L.; Han, X.; Lin, S.; Mai, H.; Ran, H. TriMedLM: Advancing Three-Dimensional Medical Image Analysis with Multi-Modal LLM. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM); 2024; pp. 4505–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.; Nirschl, J.; Burgess, J.; Gupte, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Unell, A.; Yeung, S. Micro-bench: A microscopy benchmark for vision-language understanding. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 37, 30670–30685. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, D.; Lan, X.; Zheng, M.; et al. Pathmmu: A massive multimodal expert-level benchmark for understanding and reasoning in pathology. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer; 2024; pp. 56–73. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, J.; Nirschl, J.J.; Bravo-Sánchez, L.; Lozano, A.; Gupte, S.R.; Galaz-Montoya, J.G.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Bhowmik, D.; Coman, Z.; et al. 2025; arXiv:cs.CV/2503.13399].
- Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Ji, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, T.; Hu, M.; Yu, R.; Qiao, Y.; He, J. 2025; arXiv:cs.CV/2410.11761].
- Lozano, A.; Nirschl, J.; Burgess, J.; Gupte, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Unell, A.; Yeung-Levy, S. 2024; arXiv:cs.CV/2407.01791].
- Wang, X.; Song, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. LongLLaVA: Scaling Multi-modal LLMs to 1000 Images Efficiently via a Hybrid Architecture. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.02889, arXiv:2409.02889 2024.
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Zhang, R.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Llava-onevision: Easy visual task transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.03326, arXiv:2408.03326 2024.
- Huang, S.; Dong, L.; Wang, W.; Hao, Y.; Singhal, S.; Ma, S.; Lv, T.; Cui, L.; Mohammed, O.K.; Patra, B.; et al. A: Is Not All You Need, 2023; arXiv:cs.CL/2302.14045].
- Peng, Z.; Wang, W.; Dong, L.; Hao, Y.; Huang, S.; Ma, S.; Wei, F. 2023; arXiv:cs.CL/2306.14824].
- GLM, T.; Zeng, A.; Xu, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Yin, D.; Zhang, D.; Rojas, D.; Feng, G.; Zhao, H.; et al. Chatglm: A family of large language models from glm-130b to glm-4 all tools. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.12793, arXiv:2406.12793 2024.
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.; Huang, C.; Li, K.; Wan, Z.; Che, W.; Chen, H. Cvlue: A new benchmark dataset for chinese vision-language understanding evaluation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2025, Vol. 39, pp. 8196–8204.
- Yao, S.; Yu, D.; Zhao, J.; Shafran, I.; Griffiths, T.; Cao, Y.; Narasimhan, K. Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, M.A.; Jubery, T.Z.; Roy, T.; Nassiri, R.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.; Hegde, C.; Ganapathysubramanian, B.; Balu, A.; Krishnamurthy, A.; et al. Leveraging Vision Language Models for Specialized Agricultural Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE; 2025; pp. 6320–6329. [Google Scholar]
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Industrial Engineering | Manufacturing & Design | DesignQA [9] | N/A | Rule Comprehension, Extraction | Text + CAD Images | Multiple | 1,449 Qs | Engineering Documentation |
| Freire et al. [10] | Multiple tasks | Knowledge Retrieval | Text | Multiple | 97.5% factuality | Factory Documentation | ||
| Manu-Eval [11] | 22 subcategories | Manufacturing Tasks | Multi-modal | 20 LLMs | N/A | Manufacturing Industry | ||
| FDM-Bench [12] | Multiple tasks | FDM-specific Tasks | Text + G-code | Multiple | 62% accuracy | Additive Manufacturing | ||
| Quality Control | LLM4PLC [13] | Multiple tasks | Code Generation | Text | Multiple | 72% pass rate | PLC Programming | |
| Industrial Automation | Tizaoui et al. [14] | Multiple tasks | Extractive QA | Text | 6 LLMs | N/A | Process Automation | |
| Xia et al. [15] | Multiple tasks | Production Planning | Multi-modal | LLM Agents | N/A | Production Systems | ||
| Ogundare et al. [16] | Multiple tasks | Problem Solving | Text | ChatGPT | N/A | Oil & Gas Engineering | ||
| Supply Chain Management | Rahman et al. [17] | Multiple tasks | Optimization | Text | GPT-4o | 95% correct | Supply Chain Optimization | |
| OptiGuide [18] | Multiple tasks | Query Processing | Text | LLMs | 93% accuracy | Supply Chain Operations | ||
| Raman et al. [19] | 150 questions | Question Answering | Text | ChatGPT, Bard | 4.95/5 accuracy | Supply Chain Management | ||
| Software Engineering | Knowledge Graphs & Semantic Systems |
LLM-KG-Bench [20] | Multiple tasks | Knowledge Graph Engineering | Text | Multiple | N/A | Knowledge Graph Generation |
| BIG-bench [21] | 204 tasks | Multiple Tasks | Text | Multiple | N/A | General Capabilities | ||
| Code Review & Analysis | Azanza et al. [22] | Multiple tasks | Test Generation | Text | Multiple | 90% (2024) | Software Testing | |
| DomainCodeBench [7] | 2,400 tasks | Code Generation | Text | 10 LLMs | +38% w/ context | Domain-specific Coding | ||
| StackEval [23] | Multiple tasks | Coding Assistance | Text | Multiple | 95.5% (hist.), 83% (unseen) | Code Writing & Review | ||
| Zhang et al. [24] | 947 studies | Multiple Tasks | Text | 62 LLMs | N/A | Software Engineering | ||
| Systems Engineering | System Architecture | SysEngBench [25] | Multiple tasks | Systems Engineering Tasks | Text | Multiple | N/A | Systems Engineering |
| Reliability Engineering | Hu et al. [26] | Multiple tasks | Question Answering | Text | GPT-4, GPT-3.5 | 92% (CRE) | Reliability Engineering | |
| Platinum Benchmarks [27] | 15 benchmarks | Multiple Tasks | Text | Multiple | N/A | Model Reliability | ||
| Liu et al. [28] | 29 categories | Trustworthiness Assessment | Text | Multiple | N/A | LLM Trustworthiness |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Geography | Earth Observation | TEOChat [29] | N/A | Temporal EO | Image sequence | TEOChat | SOTA | Earth observation |
| & Remote | EarthNets [30] | 500+ datasets | Earth obs | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Dataset benchmark | |
| Sensing | VLEO-Bench [31] | N/A | EO analysis | Satellite | GPT-4V | Mixed | Scene understanding | |
| Climate & Environment | STBench [32] | 60K QA pairs | Spatio-temporal | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Data mining | |
| Agricultural Science | AgriLLM [33] | Survey paper | Agriculture | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Farming applications | |
| Geospatial Analysis | GEOBench-VLM [34] | 10K instructions | Geospatial | Multi-modal | GPT-4V | 40% | Remote sensing | |
| Roberts et al. [35] | N/A | Geographic | Multi-modal | GPT-4V | Human-level | Geospatial tasks | ||
| RSUniVLM [36] | 1B params | Multi-granular | Multi-modal | RSUniVLM | SOTA | Remote sensing | ||
| INS-MMBench [37] | 2.2K questions | Insurance | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Domain tasks | ||
| Physical | Fundamental Science | MMLU [38] | Varies by Domain | QA | Text | Multiple | Below Expert-Level | Academic knowledge |
| & Chemical | ScienceQA [39] | Varies by Domain | QA | Text and Images | GPT3 with CoT | 75.17% | High-School QA | |
| Sciences | IsoBench [40] | 75 per domain | Multimodal QA | Text and Images | Multiple | Text better than Image | General Science | |
| VisScience [41] | 1000 per domain | Multi-modal reasoning | Text and Images | Multiple | 38.2% Physics, 47.0% Chemistry | K12 assessment | ||
| GPQA [42] | 448 MCQs | Difficult MCQ | Text | Claude 3 Opus | PhD-level (60%) | Graduate-level reasoning | ||
| MM-PhyQA [43] | 4500 q/a | Q/A | Text and Images | LLaVA-1.5 13b | 71.65% | High-school physics | ||
| ChemBench [44] | 2700+ q/a pairs | Q/A, Reasoning | Text | Multiple | 64% accuracy | General Chemistry | ||
| ChemQA [45] | 85k examples | Chemistry reasoning | Text | N/A | N/A | Multiple chemistry tasks | ||
| ChemLLMBench [46] | Varies by task | Multiple tasks | Text | Multiple | Poor vs Chemformer | Molecular reasoning | ||
| SMol-Instruct [47] | 3M+ pairs | Instruction QA | Text | Multiple | SOTA | Chemical Reaction | ||
| Molecular & | MaScQA [48] | 650 QA | QA | Text | GPT4 | 62% Accuracy | Materials Knowledge | |
| Materials Science | LLM4Mat-Bench [49] | 1.9M pairs | Classification | Multiple | Multiple | N/A | Property Prediction | |
| Applied Chemistry | PRESTO [50] | 3M samples | Multiple tasks | Graphs & Text | Multiple | SOTA | Molecule-text Modeling | |
| DrugLLM [51] | N/A | Generation | GMR | N/A | N/A | Drug design | ||
| Environmental | Climate & Weather | WeatherBench 2 [52] | 1-14 day | Forecasting | Multivariate data | N/A | N/A | Medium-range forecasting |
| Science | ClimateIQA [53] | 254,040 VQA | VQA | Image + Text | Multiple | SOTA | Weather Event Detection | |
| WeatherQA [54] | 8000 VQA | VQA | Image + Text | Multiple | Needs Improvement | Weather Event Detection | ||
| CLLMate [55] | 26,156 QA | Forecast | Multiple | Multiple | Needs Improvement | Event Forecasting | ||
| Disaster Response | FFD-IQA [56] | 22,422 questions | VQA | Image + Text | Multiple | Needs Improvement | Safety assessment | |
| DisasterQA [57] | 707 questions | MCQ | Text | GPT-4o | 85.78% | Damage response | ||
| Pollution Monitoring | VayuBuddy [58] | 7 years data | Code Generation | Text | Multiple | N/A | Sensor Data Analysis | |
| Biodiversity & Ecology | Species-800 [59] | 800 abstracts | Classification | Text | N/A | N/A | NER | |
| BiodivNERE [60] | 2057 sentences | Classification | Text | N/A | N/A | NER |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Computer Vision &Autonomous Systems | Visual Understanding | Rank2Tell [70] | N/A | Importance ranking | Multi-modal | N/A | N/A | Object importance |
| NuInstruct [71] | 91K pairs | Multi-view QA | Video + BEV | BEV-InMLLM | +9% | Holistic understanding | ||
| NuScenes-QA [72] | 460K QA pairs | Multi-modal VQA | Image + LiDAR | Multiple | N/A | Multi-frame VQA | ||
| Cambrian-1 [73] | 20+ encoders | Vision-centric | Multi-modal | Cambrian-1 | SOTA | Visual grounding | ||
| Autonomous Driving | HAZARD [74] | 3 scenarios | Decision making | Multi-modal | LLM agent | N/A | Disaster response | |
| LLM4Drive [75] | Survey paper | System review | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | System architecture | ||
| WTS [76] | 1.2k events | Video analysis | Video + Text | VideoLLM | N/A | Pedestrian safety | ||
| DRAMA [77] | 17,785 scenarios | Risk assessment | Video + Objects | N/A | N/A | Risk localization | ||
| GenAD [78] | 2000+ hours | Video prediction | Video + Text | GenAD | N/A | Generalized prediction | ||
| Reason2Drive [79] | 600K+ pairs | Chain reasoning | Video + Text | VLMs | N/A | Interpretable reasoning | ||
| DriveLM [80] | N/A | Graph VQA | Multi-modal | DriveLM-Agent | N/A | End-to-end driving | ||
| NuPrompt [81] | 35,367 prompts | Object tracking | Multi-view | PromptTrack | N/A | Language prompts | ||
| Robotics & | Robot Control | MMRo [8] | N/A | Manufacturing | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Manufacturing |
| Automation | Process Automation | DesignQA [9] | N/A | Design | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Design |
| Blockchain &Cryptocurrency | Smart Contract Analysis | Web3Bugs [82] | Multiple versions | Security classification | Code (Solidity) | GPT-4 (prompted) | 60% false-positive reduction | Bug detection |
| LLM-SmartAudit [83] | Two datasets | Multi-agent audit | Code + Documentation | LLM-SmartAudit | Outperforms conventional tools | Comprehensive auditing | ||
| ACFIX [84] | 118 contracts | Auto-repair | Code (Solidity) | GPT-4 + RBAC | 94.9% fix rate | Patch generation | ||
| Market Analysis | CryptoNews [85] | 3,200 articles | Sentiment analysis | News text | FT-GPT-4 | 86.7% accuracy | Market sentiment | |
| Ethereum Prices [86] | 5 years daily | Price forecasting | Time-series | GPT-2 (FT) | SOTA MSE | Short-term pred. | ||
| LLM-Trading [87] | Multi-modal | Strategy reasoning | Text + Indicators | GPT-4 agent | ↑PnL in sim. | Fact-subjectivity reasoning | ||
| Fraud Detection | BLOCKGPT [88] | M txns | Anomaly detection | Txn graph | BLOCKGPT | 40% attack detection | Real-time monitoring | |
| Governance | Crypto Legal Cases [89] | SEC files | Legal reasoning | Case text | GPT-3.5 | Mixed | Compliance assistance |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Mathematical Reasoning | Problem Solving | MathVerse [97] | 15K samples | Visual math | Image + Text | GPT-4V | N/A | Diagram interpretation |
| HARDMath [98] | 366 problems | Graduate-level | Text | GPT-4 | 43.8% | Advanced reasoning | ||
| MMIQC [99] | N/A | Competition math | Text | Qwen-72B-MMIQC | 45.0% | Question composition | ||
| MathChat [100] | N/A | Interactive | Text + Dialogue | N/A | N/A | Multi-turn reasoning | ||
| GSM-MC [101] | N/A | Multiple-choice | Text | Multiple | 30x faster | Efficient evaluation | ||
| PROBLEMATHIC [102] | N/A | Robustness | Text | Llama-2 | +8% | Noise handling | ||
| Formal Methods | Theorem Proving | LeanDojo [103] | 98,734 theorems | Theorem proving | Text (code) | GPT-4 | N/A | Formal verification |
| Statistical Analysis | Data Analysis | KnowledgeMath [104] | 1,259 problems | Finance MWPs | Text + Tables | GPT-4 | 45.4% | Domain knowledge |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Social Studies | Social Media Analysis | MM-SOC [108] | Multiple | Social media | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Platform analysis |
| HOTVCOM [109] | 10K videos | Comment generation | Video + Text | Multiple | 0.42 ROUGE-L | User engagement | ||
| XMeCap [110] | 10K memes | Caption generation | Multi-image | Multiple | 0.31 BLEU | Meme creation | ||
| Bias and Privacy | Priv-IQ [111] | Multiple | Privacy intelligence | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Privacy evaluation | |
| LLM-Bias [112] | Survey paper | Bias analysis | Text | Multiple | N/A | Fairness evaluation | ||
| Sociocultural | CultureVLM [113] | 100K images | Cultural understanding | Image + Text | Multiple | N/A | Cultural diversity | |
| TimeTravel [114] | Multiple | Historical reasoning | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Cultural heritage | ||
| Emotional | EmoBench-M [115] | Multiple | Emotion cognition | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Emotional intelligence | |
| EmotionQueen [116] | 1,000 dialogues | Empathy evaluation | Text | Multiple | N/A | Empathetic response | ||
| Arts & Creativity | Creative Tasks | EditWorld [117] | Multiple | Image editing | Image + Text | Multiple | N/A | World dynamics |
| LLM-Narrative [118] | Survey paper | Storytelling | Text | Multiple | N/A | Narrative generation | ||
| WenMind [119] | Multiple | Creative expression | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Emotional creativity | ||
| Music | Music Intelligence | ZIQI-Eval [120] | 14K items | Music knowledge | Text | GPT-4 | 58.68% F1 | Comprehensive music |
| MuChoMusic [121] | 1,187 questions | Audio-language | Audio + Text | Multiple | N/A | Music comprehension | ||
| Music-LLM [122] | Multiple | Symbolic music | Text | Multiple | N/A | Music reasoning | ||
| MER-Benchmark [123] | Multiple | Entity recognition | Text | Multiple | N/A | Music entities | ||
| MuChin [124] | Multiple | Music description | Text | Multiple | N/A | Chinese music | ||
| Urban Planning | City Environment | CityEQA [125] | Multiple | Embodied QA | 3D + Text | Multiple | 60.7% human | Urban navigation |
| TransGames [126] | Multiple | Transportation | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Traffic analysis | ||
| LLM-Transport [127] | Survey paper | Transportation | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | System integration | ||
| Urban Intelligence | Urban-FM [128] | Survey paper | Urban modeling | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Foundation models | |
| UrbanPlanBench [129] | Multiple | Urban planning | Text | Multiple | N/A | Planning knowledge | ||
| CityBench [130] | 13 cities | Urban simulation | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | City management | ||
| Morality & Ethics | Moral Reasoning | MoralBench [131] | Multiple | Moral evaluation | Text | Multiple | N/A | Ethical reasoning |
| M3oralBench [132] | Multiple | Multimodal ethics | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Visual morality | ||
| Greatest-Good [133] | Multiple | Utilitarian reasoning | Text | Multiple | N/A | Moral dilemmas | ||
| Value-Alignment [134] | Multiple | Value systems | Text | Multiple | N/A | Alignment evaluation | ||
| Self-Awareness [135] | Multiple | Self-knowledge | Text | Multiple | N/A | Model capabilities | ||
| Philosophy and Religion | Computational philosophy | InterIDEAS [136] | 45,000 pages | Intertextual link discovery | Text | Custom pipeline | 85-91% accuracy | NLP-philosophy bridges |
| Religion and Theology | Religion & Chatbots [137] | N/A | Philosophical reasoning | Text | Multiple LLMs | N/A | Theological reasoning |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Finance | Forecasting | FLUE [94] | 5 tasks | Sentiment, NER, classification | Text | FLANG-BERT, FinBERT | +3–5% F1 | Financial text processing |
| FinMA / PIXIU [147] | 9 datasets | Classification, QA | Text + Structured | FinMA | +10–37% F1 | Finance-specific fine-tuning | ||
| FinanceMath [104] | 1,259 items | Math reasoning | Text + Tables | GPT-4 | 60.9% accuracy | Financial numerical reasoning | ||
| QA (Numerical) | FinQA [148] | 8,281 pairs | Multi-step QA | Text + Tables | RoBERTa + executor | 65% exec acc. | Semi-structured math QA | |
| QA (Long-context) | DocFinQA [149] | 123k tokens | Document-level QA | Text + Tables | GPT-4 | 67% accuracy | Long-context computation | |
| QA (Conversational) | ConvFinQA[150] | 3,892 dialogues | Conversational QA | Text + Tables | FinQANet | 68.9% exec acc. | Dialogue reasoning | |
| QA (Factual) | FinanceBench [6] | 10,231 items | Retrieval QA | Text + Retrieval | GPT-4 + retriever | 19% correct | Hallucination resistance | |
| ESG/Climate | ClimateBERT [151] | 2M paras | Text classification | Text | DistilROBERTa | 46–48% entropy loss | ESG and greenwashing | |
| Info Extraction | FinRED [152] | 2,400 articles | Entity/relation extraction | Text | FinBERT, RoBERTa | 87% F1 | Structured knowledge extraction | |
| Multilingual QA | Golden Touchstone [153] | 12 datasets | Multi-task NLP | Text (bilingual) | GPT-4, FinGPT | Strong overall | Robust multilingual benchmarking |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Medicine & Healthcare | Clinical Applications | GMAI-MMBench [181] | 284 datasets | VQA | Multi-modal | GPT-4o | 53.96% | Comprehensive medical AI |
| Asclepius [182] | 15 specialties | Multi-task | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Specialty evaluation | ||
| MultiMed [187] | 2.56M samples | Multi-task | Multi-modal | Multiple | N/A | Cross-modality | ||
| MediConfusion [188] | Paired images | VQA | Multi-modal | Multiple | Below random | Model reliability | ||
| CTBench [189] | 2.5K samples | Multi-task | Text | GPT-4 | 72.3% | Clinical trial design | ||
| Bioinformatics | PGxQA [183] | 110K+ questions | QA | Text | GPT-4o | 68.4% | Pharmacogenomics | |
| GenoTEX [184] | Multiple datasets | Gene analysis | Text + Data | GenoAgent | 65-85% | Gene expression | ||
| MedCalc-Bench [190] | 2K problems | Calculation | Text + Numbers | GPT-4 | 57.8% | Medical calculations | ||
| Bio-Benchmark [191] | 30 tasks | Multi-task | Text | GPT-4o | Varies by task | Bioinformatics NLP | ||
| Medical Imaging | Radiology & 3D Analysis | M3D [185] | 120K img pairs | Multi-task | 3D + Text | M3D-LaMed | SOTA | 3D medical imaging |
| TriMedLM [192] | Multi-modal | Multi-task | Image + Text | TriMedLM | N/A | Trimodal integration | ||
| RadGPT [186] | 9.2K CT scans | Report gen | 3D CT + Text | RadGPT | 80-97% sensitivity | Tumor detection | ||
| Pathology/Microscopy | Micro-Bench [193] | 3.2K images | VQA | Image + Text | GPT-4V | 54.7% | Microscopy understanding | |
| PathMMU [194] | 33K questions | Multiple choice | Image + Text | GPT-4V | 49.8% vs 71.8% human | Pathology expertise | ||
| MicroVQA [195] | 2.8K QA pairs | VQA | Image + Text | GPT-4V | 48.2% | Scientific microscopy | ||
| SlideChat [196] | Large-scale | Dialogue | Image + Text | SlideChat | N/A | Interactive analysis | ||
| -Bench [197] | Multiple tasks | Multi-task | Image + Text | Multiple | Varies by task | Microscopy analysis |
| Domain | Sub-domain | Benchmark | Scale | Task Type | Input Modality | Model | Performance | Key Focus |
| Multimodal Communication | Visual-Language Integration | LongLLaVA [198] | 1000 images | Long-context | Multi-modal | LongLLaVA | N/A | Hybrid architecture |
| LLaVA-OneVision [199] | N/A | Multi-scenario | Multi-modal | LLaVA | N/A | Cross-modal transfer | ||
| KOSMOS-1 [200] | Web-scale | Multi-task | Multi-modal | KOSMOS-1 | N/A | Cross-modal transfer | ||
| KOSMOS-2 [201] | Large-scale | Multi-task | Multi-modal | KOSMOS-2 | N/A | Visual grounding | ||
| Cross-lingual Tasks | Multilingual Models | ChatGLM [202] | 10T tokens | Multi-task | Multi-modal | GLM-4 | Matches GPT-4 | Chinese-English LLM |
| CVLUE [203] | 30K+ samples | Multi-task | Multi-modal | X2VLM | 36-55% | Chinese VL understanding | ||
| Reasoning | Problem Solving | ToT [204] | N/A | Problem solving | Text | GPT-4 | 74% | Deliberate reasoning |
| Domain-Specific Applications | AgEval [205] | 12 tasks | Plant phenotyping | Multi-modal | Multiple | 46-73% F1 | Agricultural tasks |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





