Submitted:
20 May 2025
Posted:
21 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
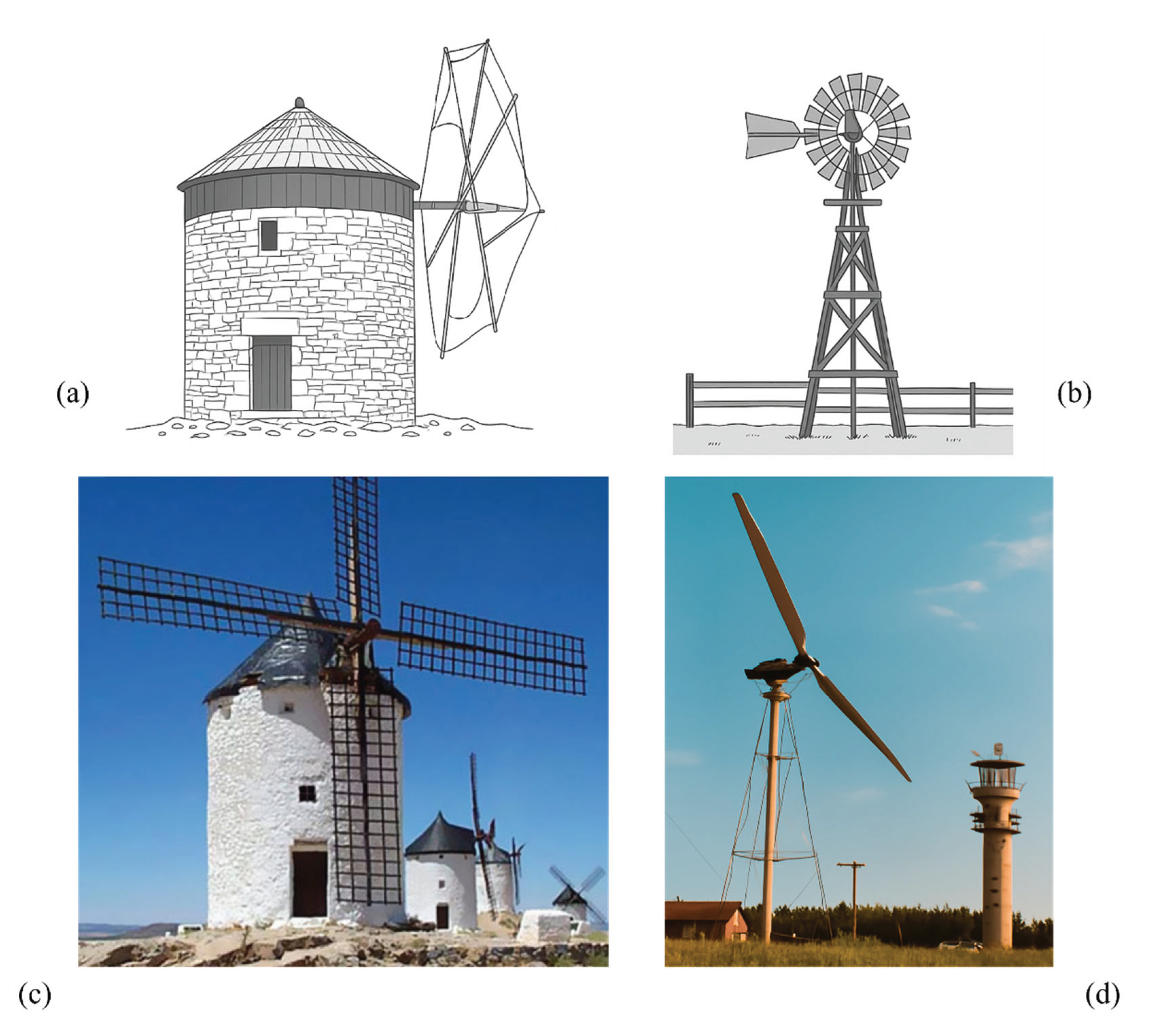
1. Introduction
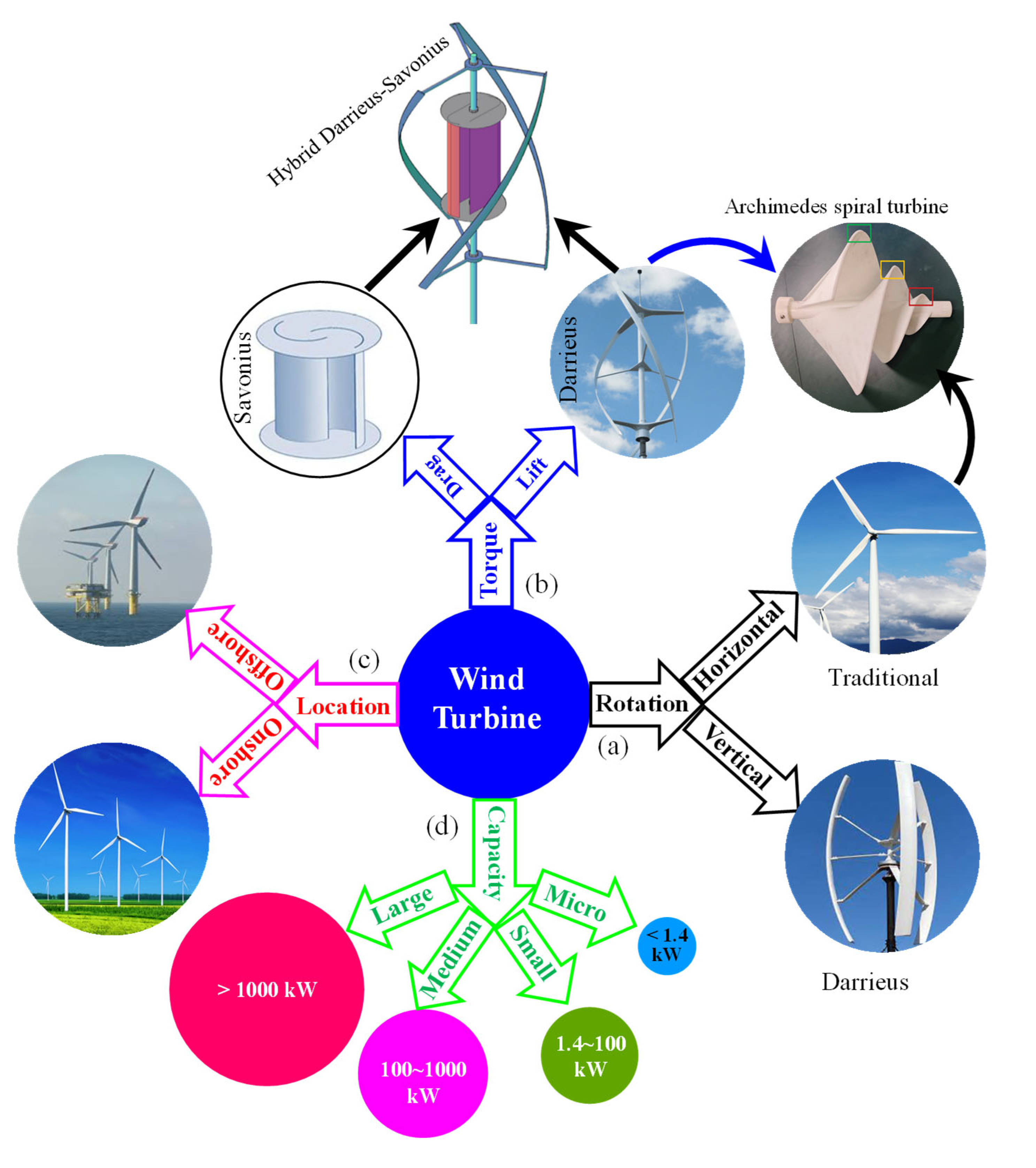
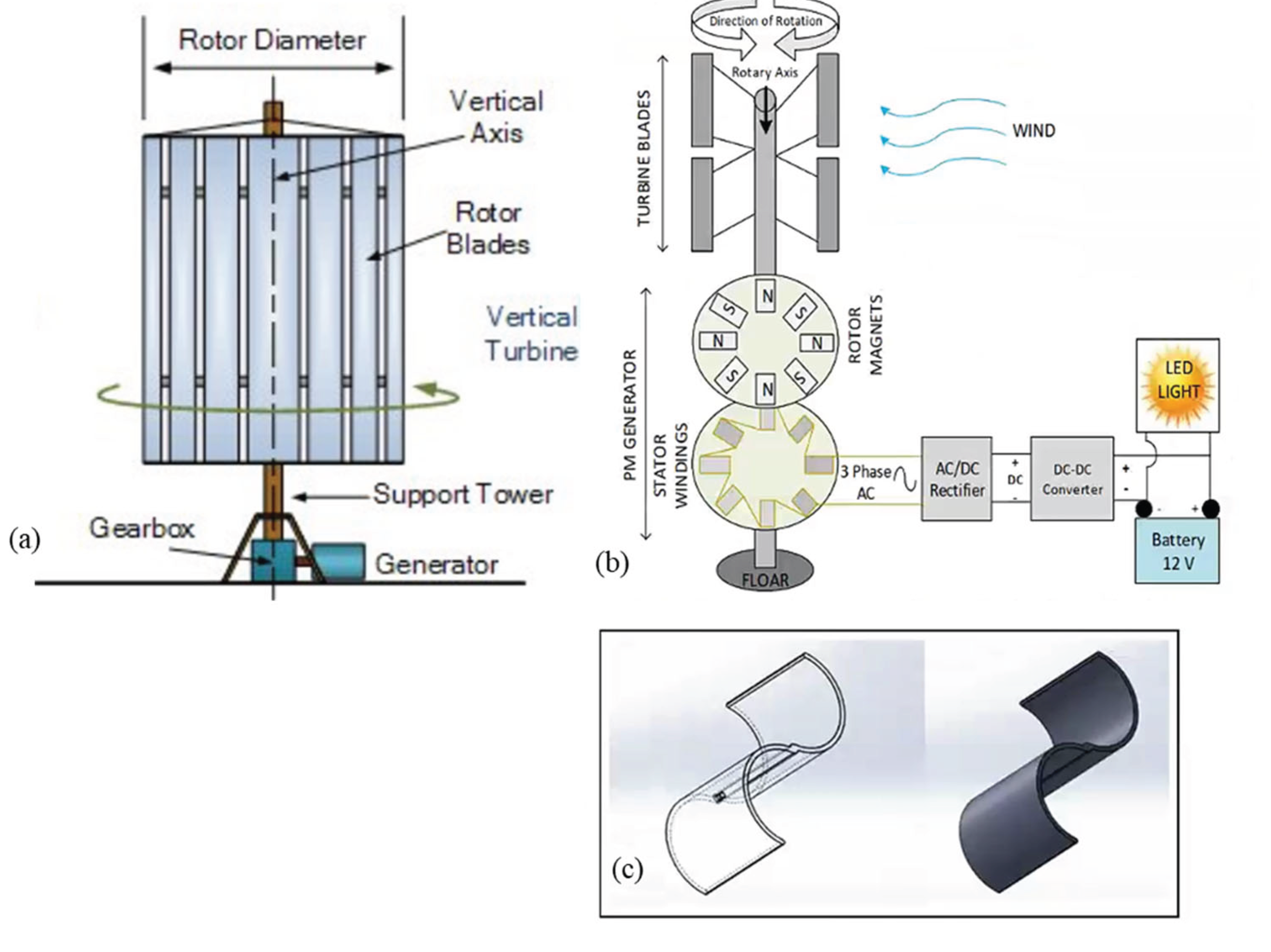
2. Types of Wind Turbines
3. Principle of Wind Turbine Blade
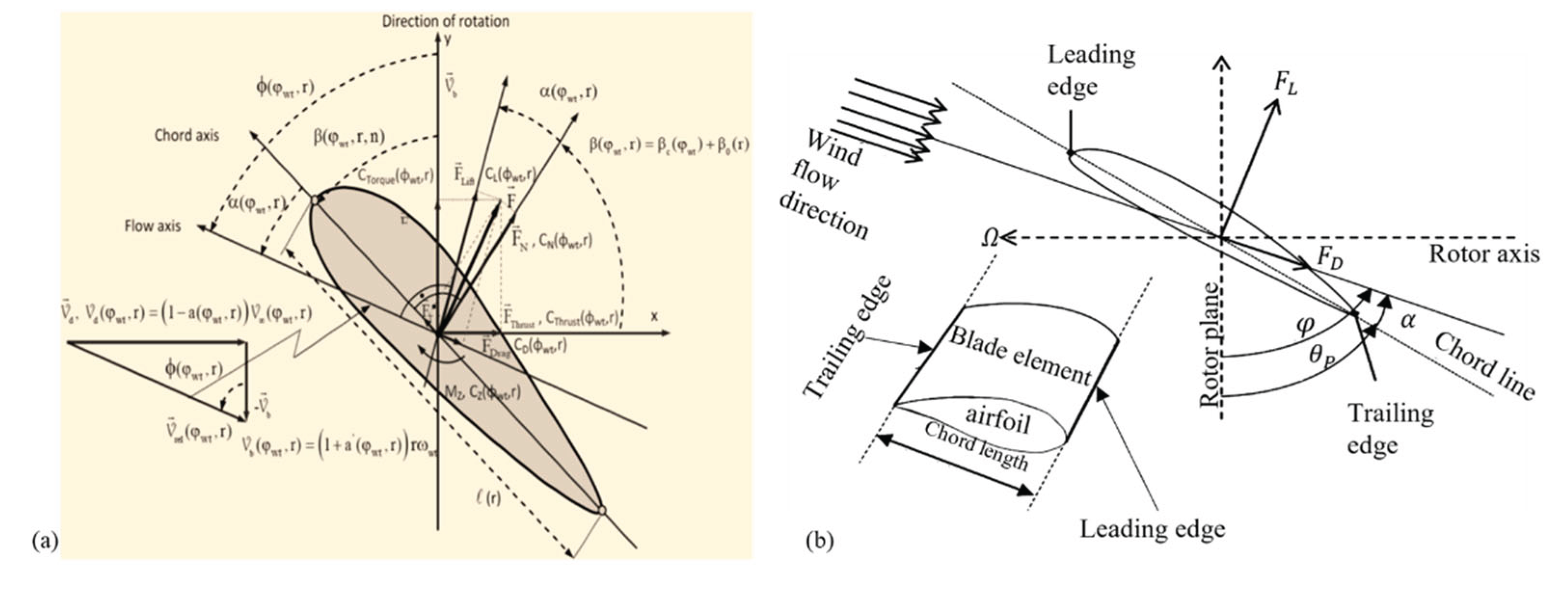
3.1. Aerodynamics
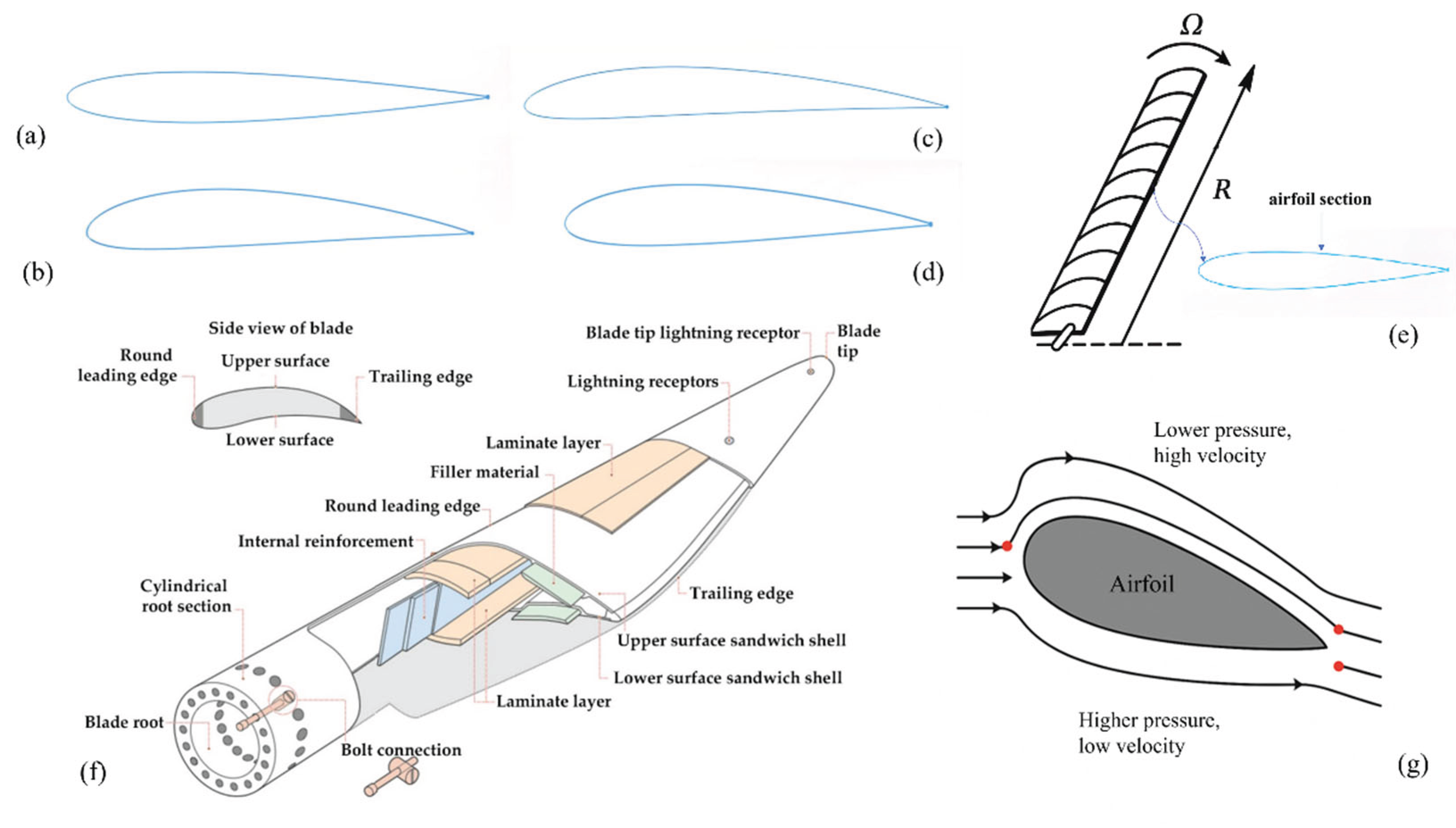
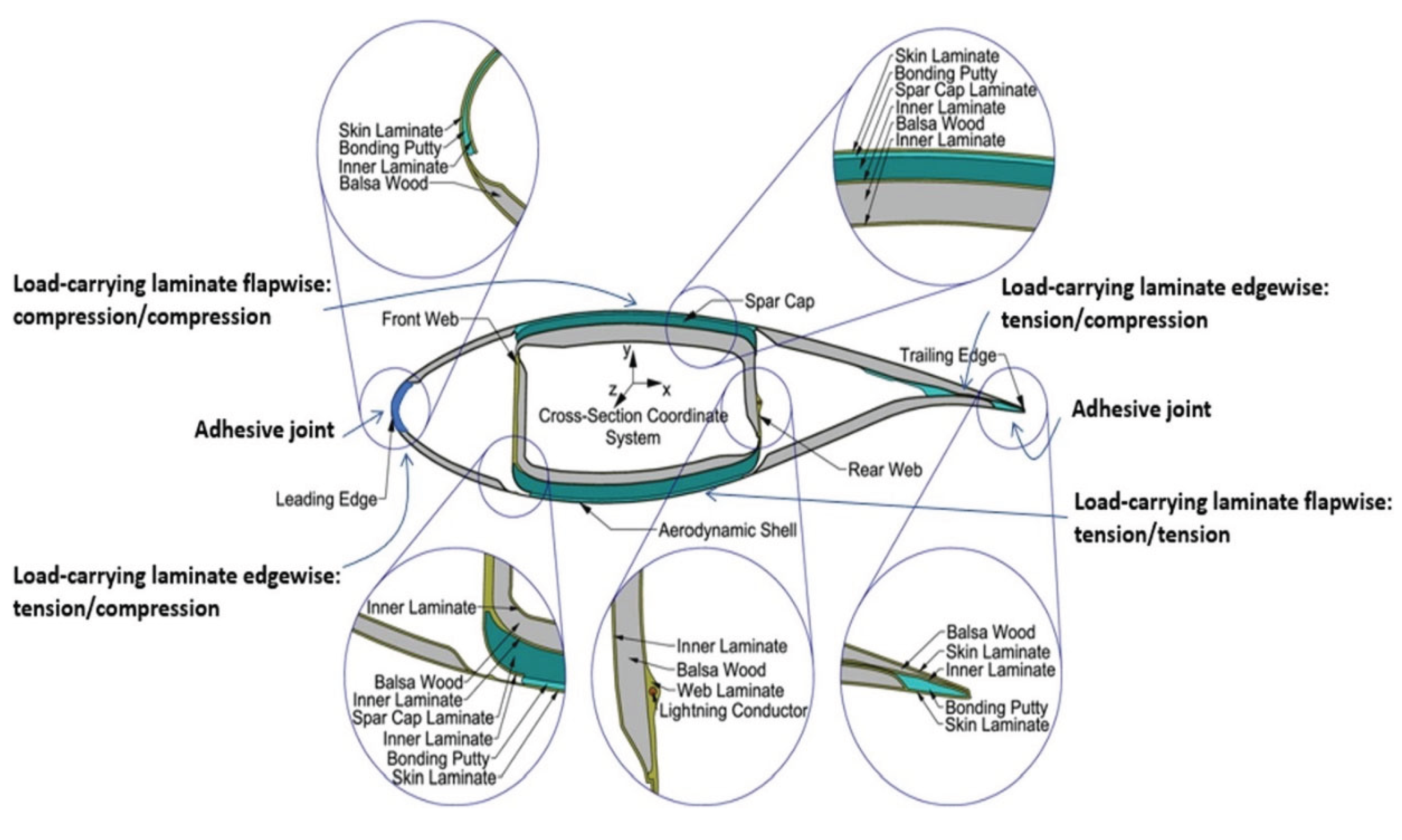
3.2. Design and Geometry
3.3. Materials Used in Blade Construction
| Period | Types | Description | Advantages |
| Early years: 1970 −1980 | Wood | Laminated wood was used in early wind turbine blades, often in small-scale turbines. | Readily available and easy to shape. |
| 1980 − 1990 | Fiberglass | Fiberglass became the most commonly used material due to its light weight and high strength. Composites are often made with epoxy or polyester resins. | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion, and resistance. |
| 1990 −2000 | Wood–epoxy composites | The incorporation of wood fibers and epoxy marked a significant advancement over conventional wood construction, resulting in increased strength and extended lifespan. | Cost-effective, better mechanical properties. |
| 2000 −present | Carbon fiber reinforced plastics; Glass fiber reinforced Plastics |
Carbon fiber composites, combined with resins, offer high performance and low weight. Glass fibers are also used in blade manufacturing due to their low cost and ease of production. | Good mechanical properties, low cost. Environmentally friendly, sustainable. |
| Recent developments: 2010 − present |
Natural Fiber Composites | Natural fiber composites, such as those made from hemp, flax, and jute, are receiving increasing attention due to their moderate mechanical properties and sustainability benefits. | Environmentally friendly, sustainable. |
| Present & Emerging: 2020 − present |
Biocomposites (natural fibers + bio-based resins); Thermoplastic composites; Bamboo composites |
Biocomposites, which combine natural fibers (like flax and bamboo) with bio-based resins (such as PLA and plant oil epoxy), offer sustainability, recyclability, and lightweight advantages. While thermoplastics like polypropylene (PP) and polyamide (PA) are being explored for recyclable wind turbine blades, bamboo fibers are particularly valued for their resilience. |
High recyclability and faster manufacturing times. Sustainable, low-cost, good mechanical performance. |
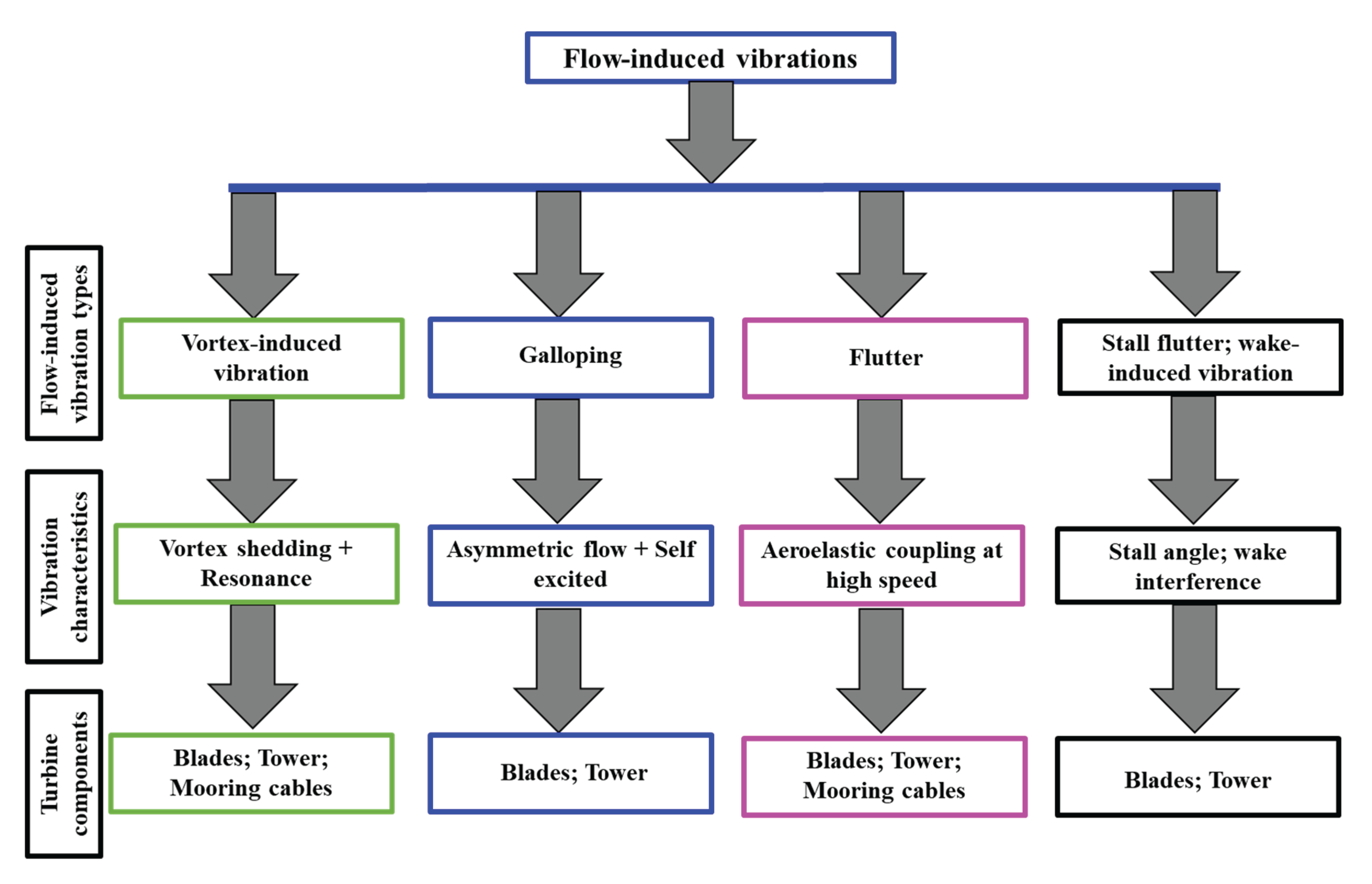
4. Flow-Induced Vibrations
4.1. Basic Principles and Types of Flow-Induced Vibrations
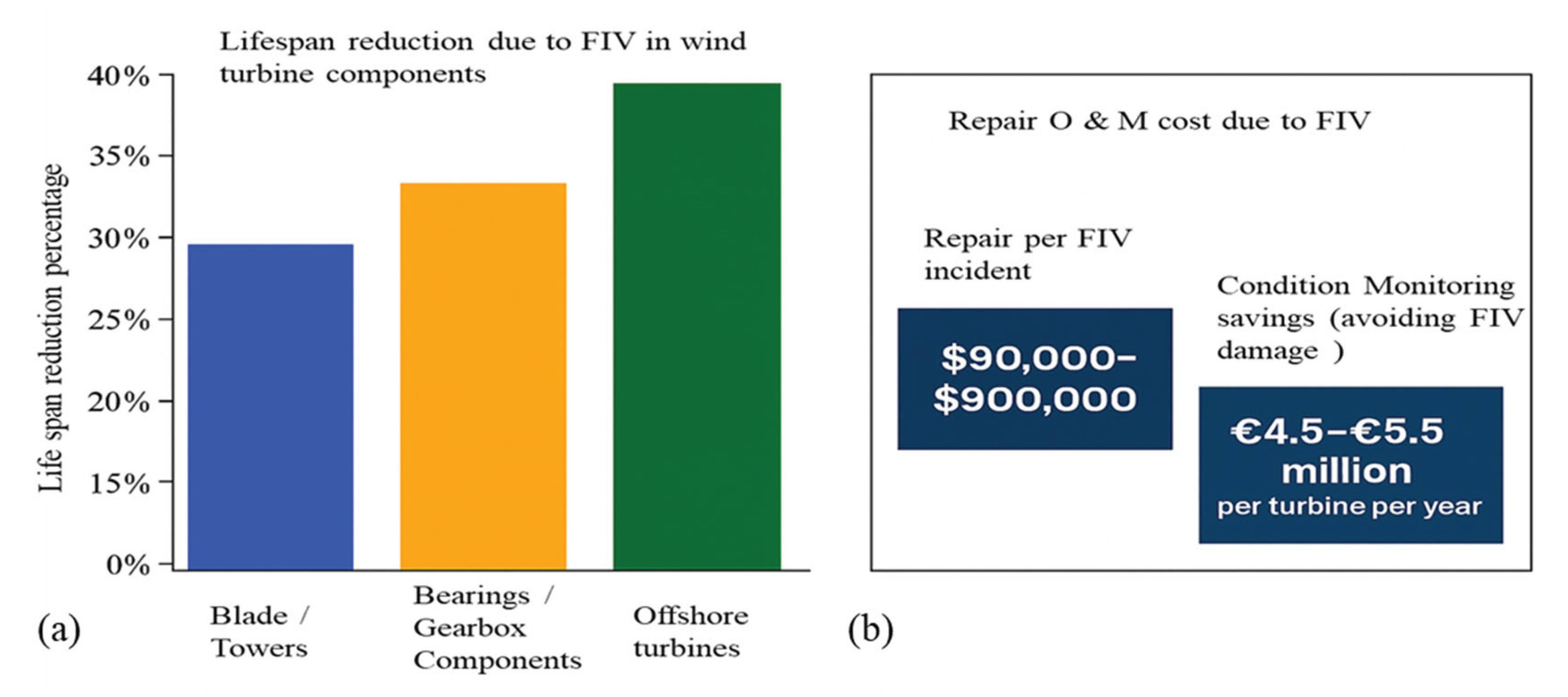
4.2. Impact of Vibrations on Turbine Performance and Longevity
5. Vibration Mitigation Strategies
5.1. Active and Passive Vibration Control Methods
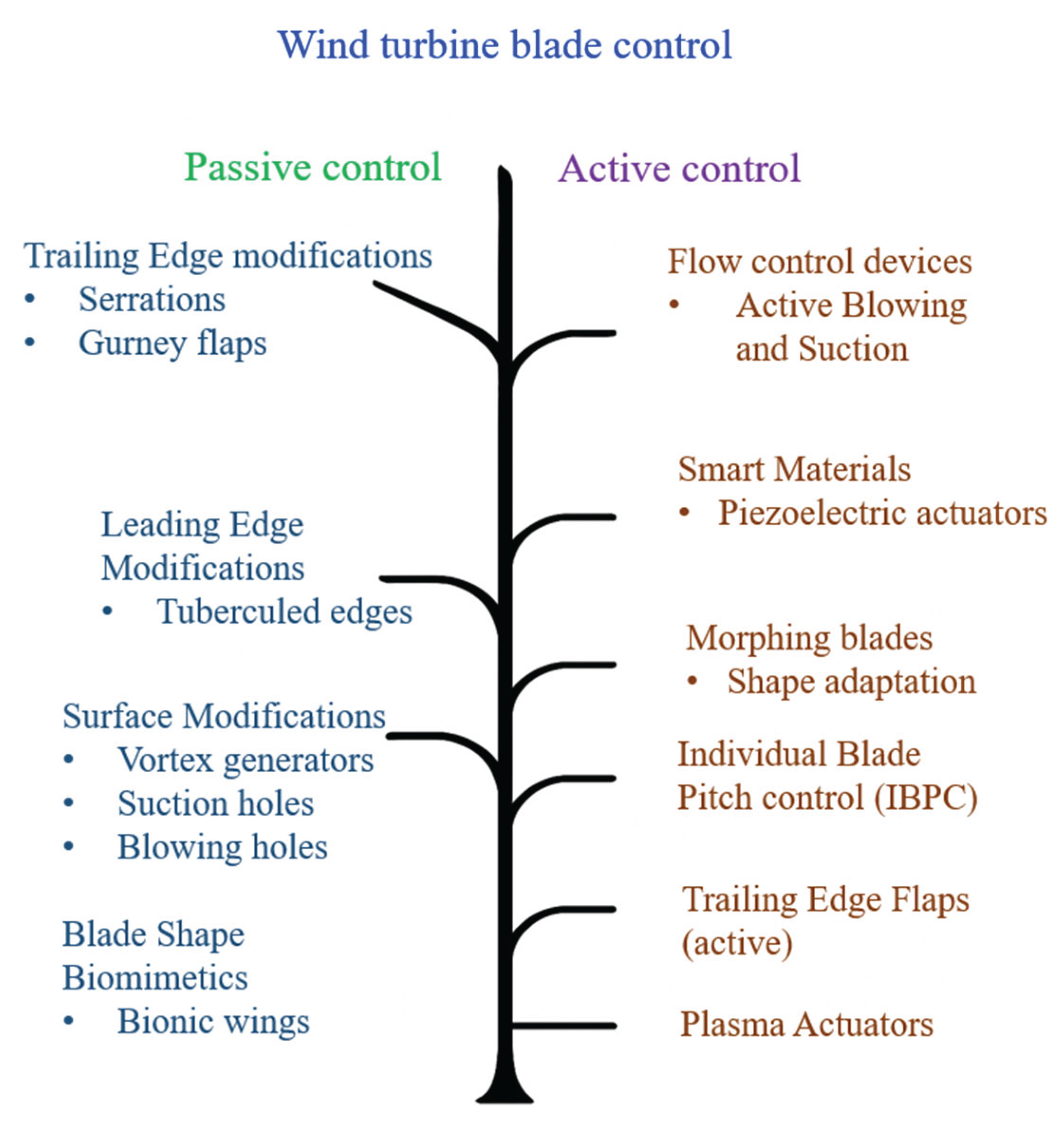
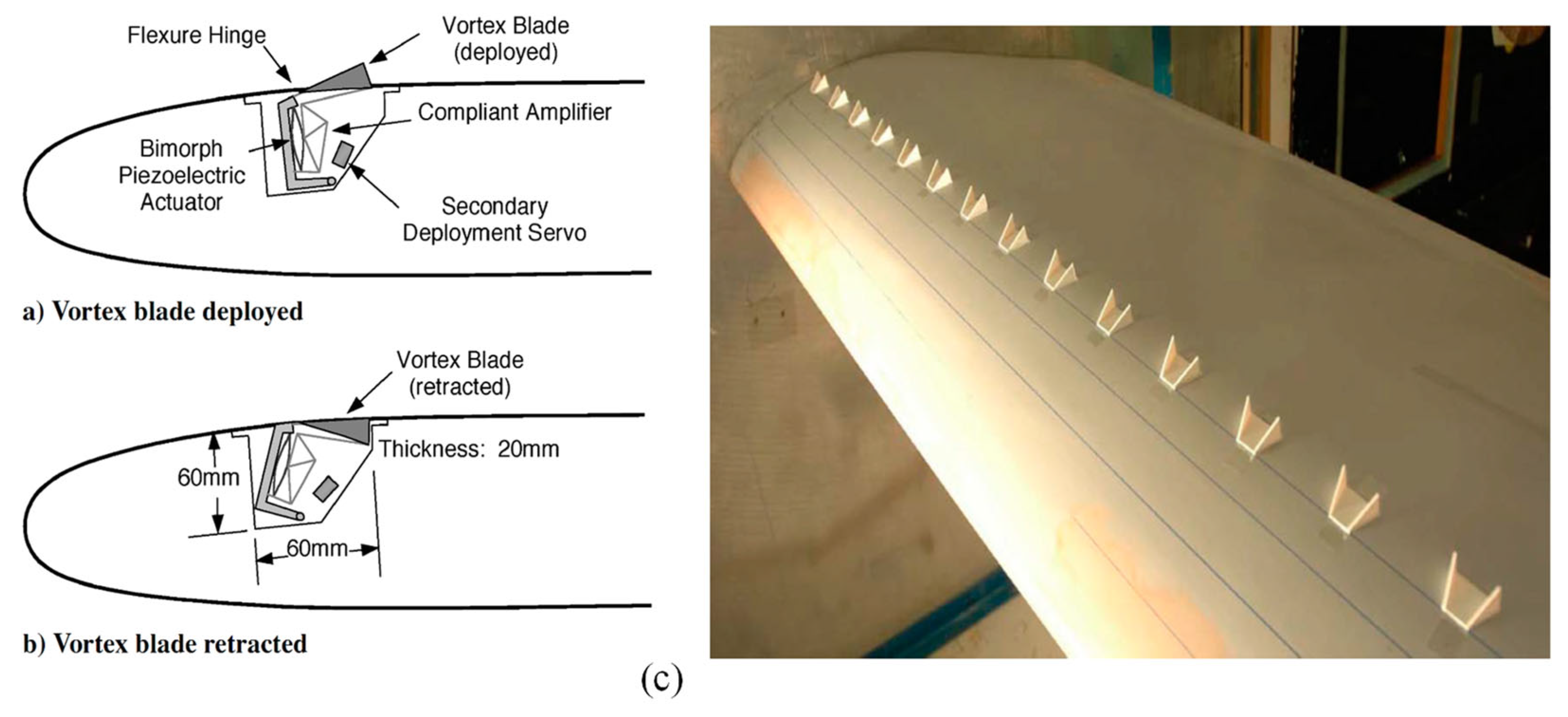
5.2. Design Modifications and Innovative Materials for Vibration Reduction
5.3. Recent Innovations and Research in Vibration Mitigation
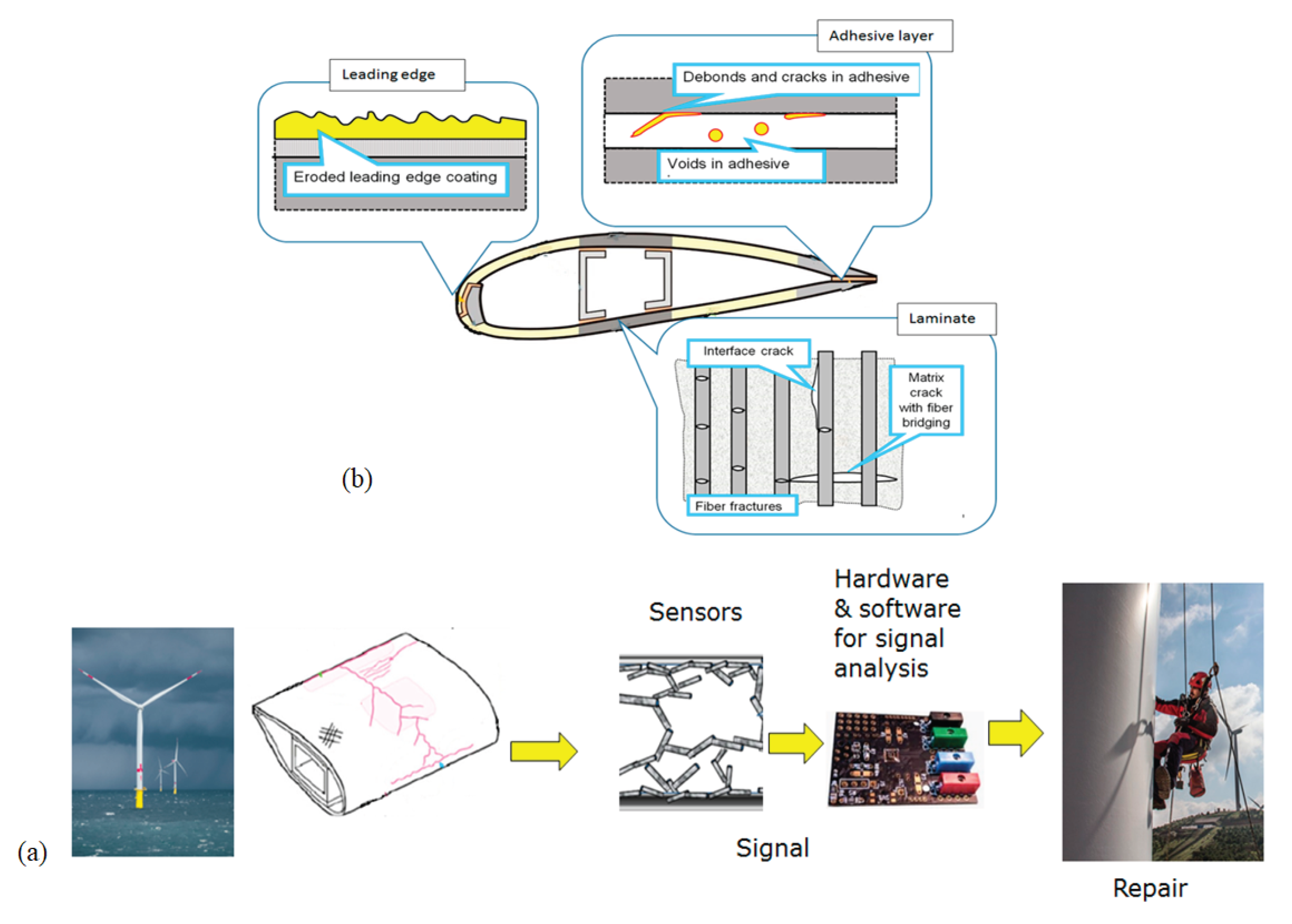
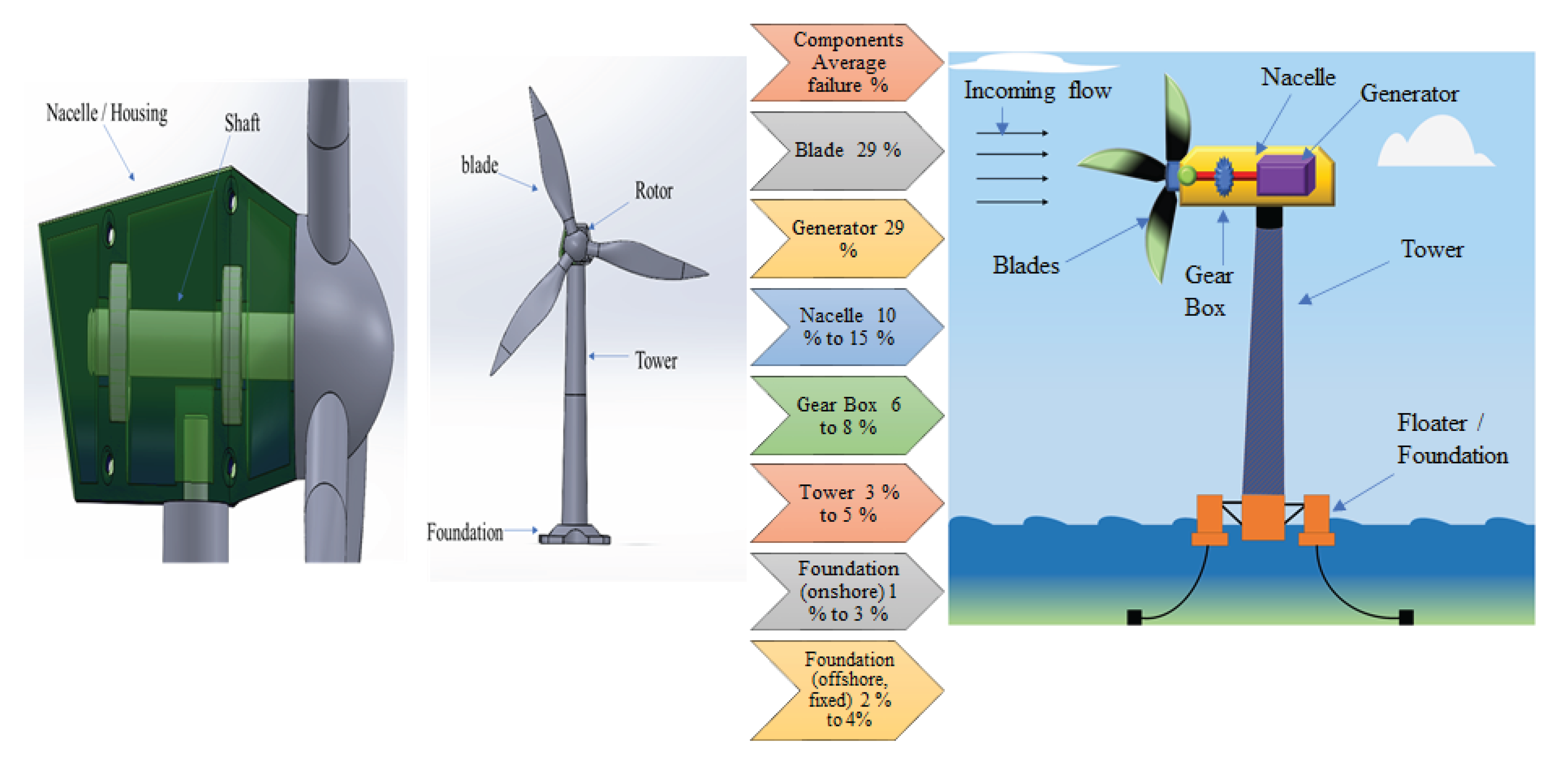
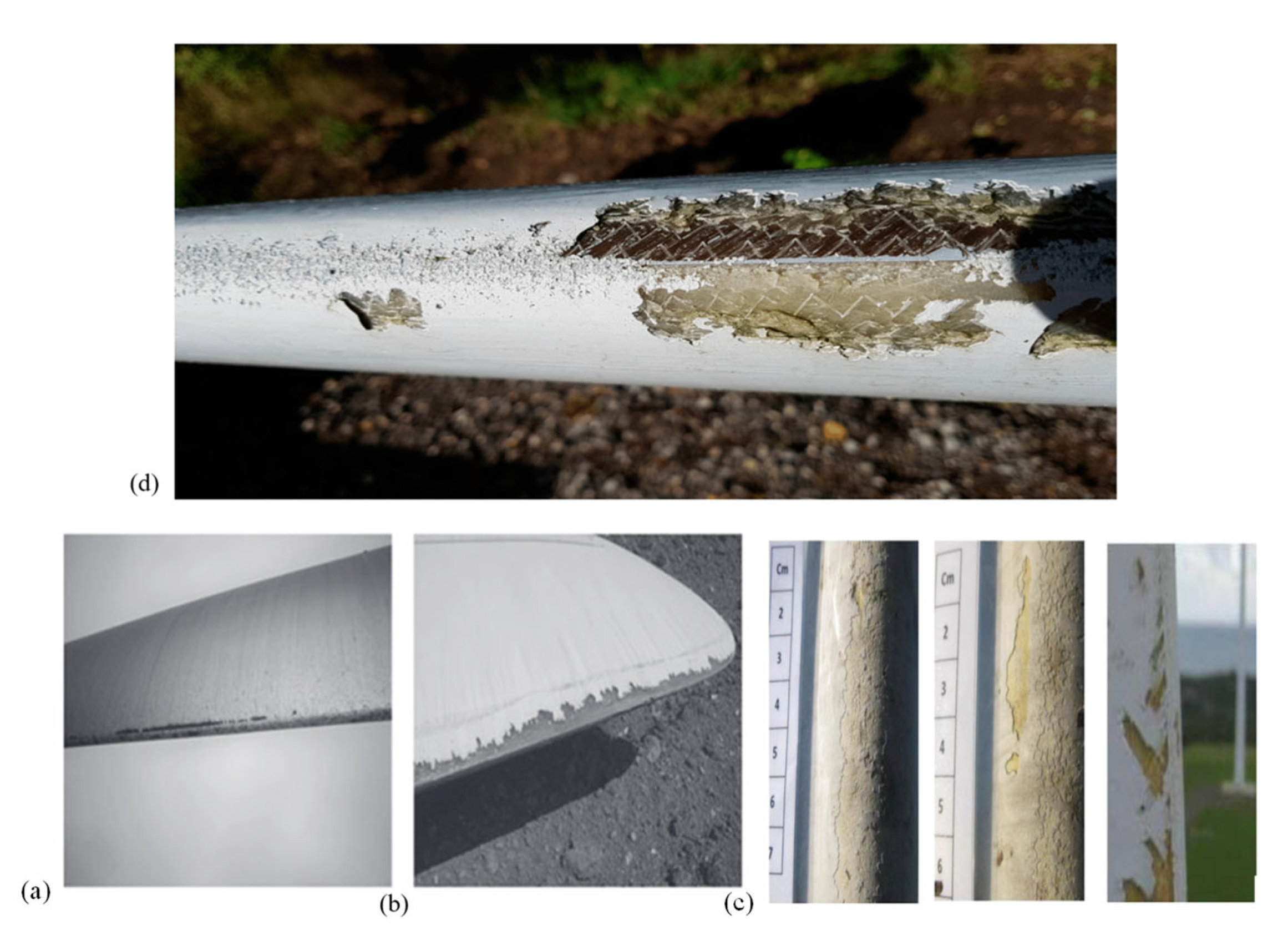
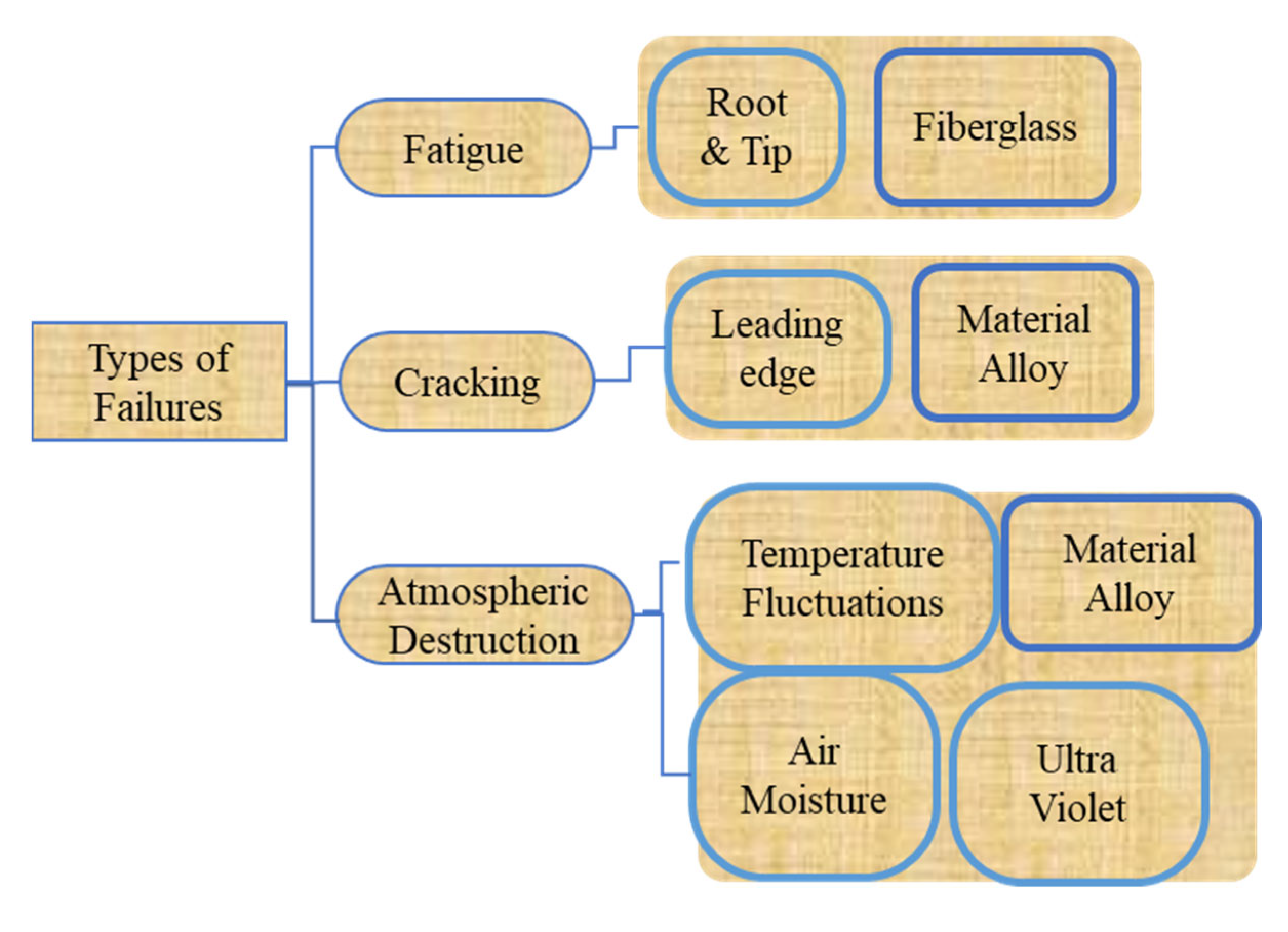
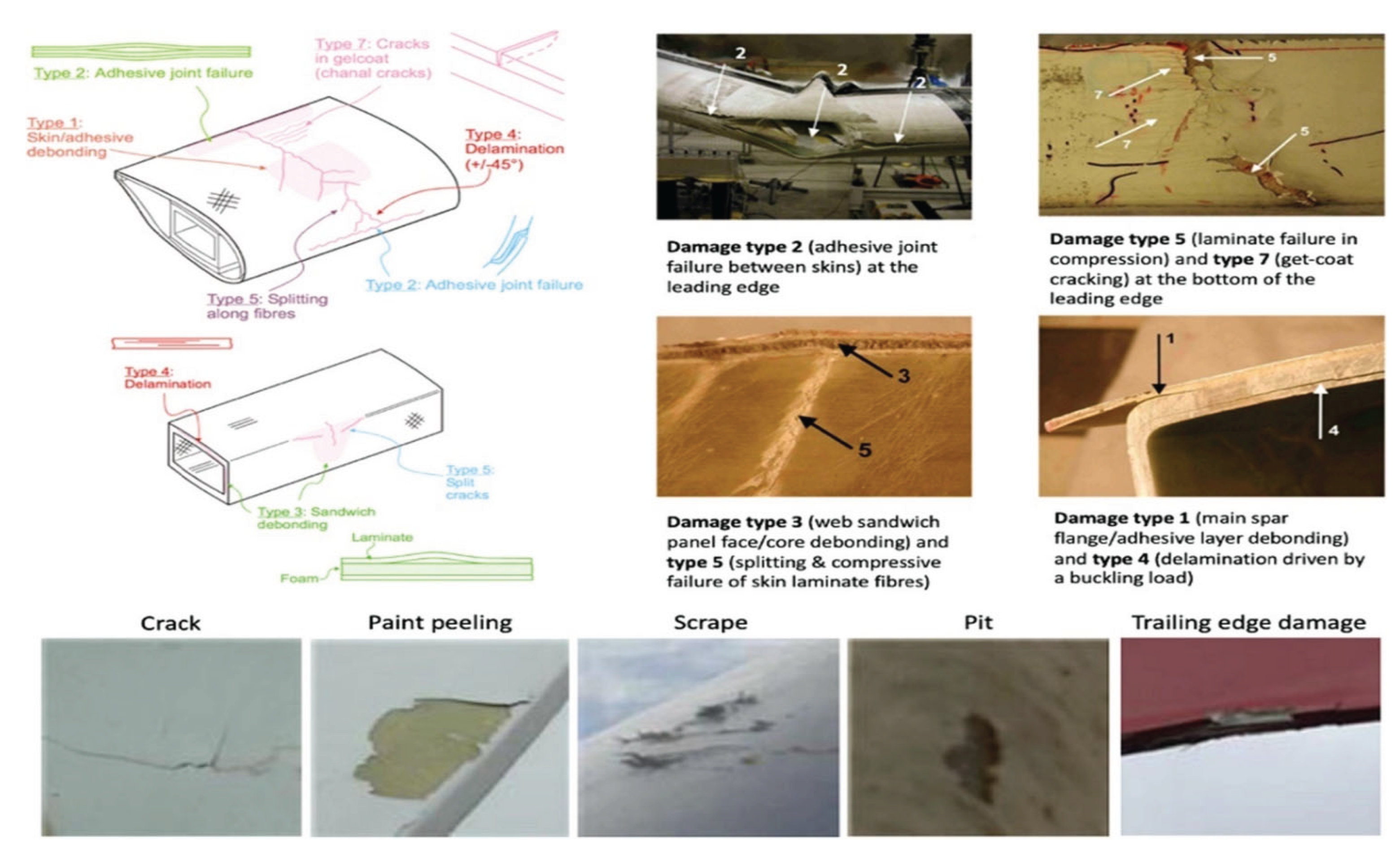
6. Failure Mechanisms in Wind Turbine Blades
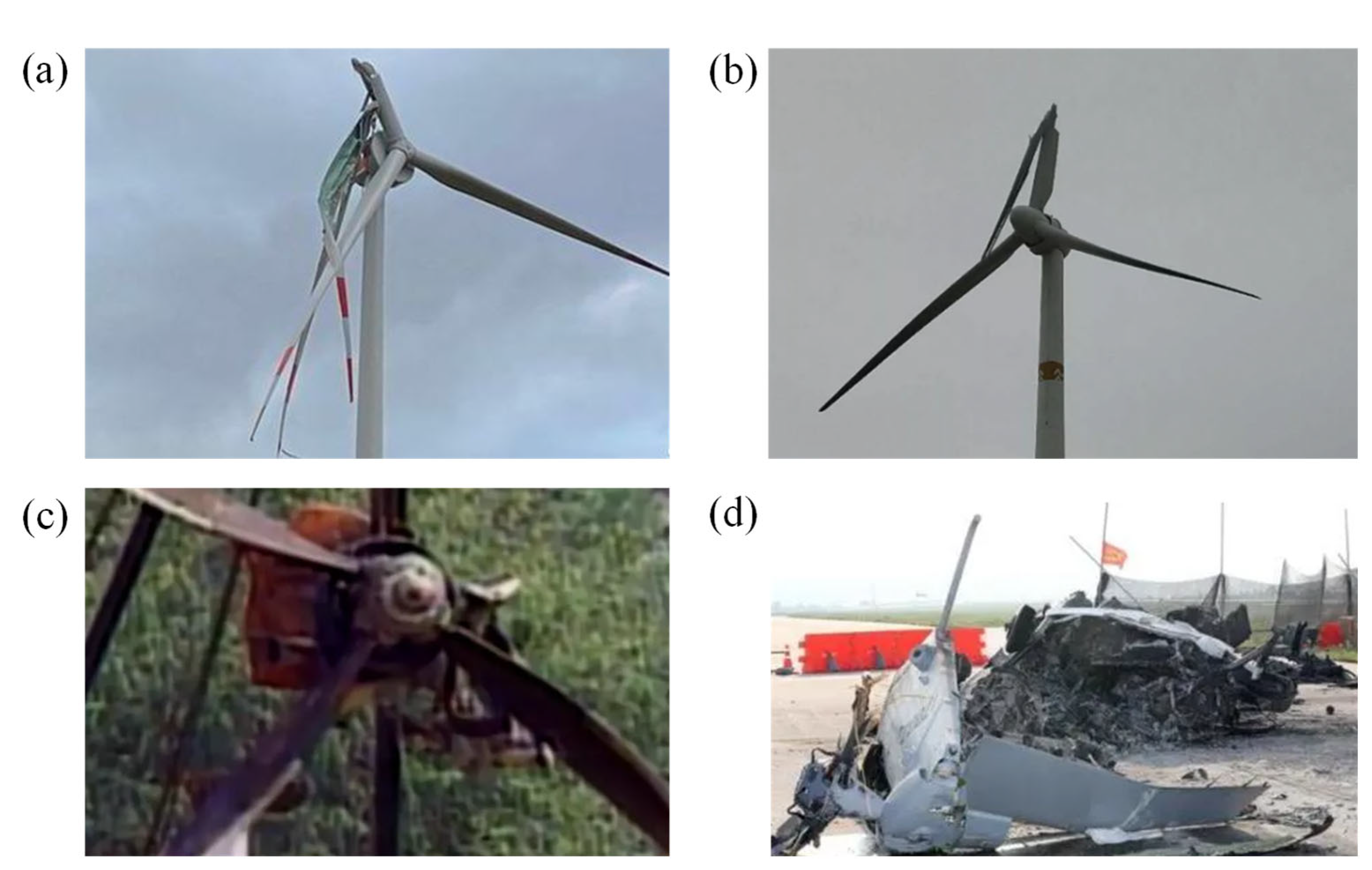
6.1. Types of Failures
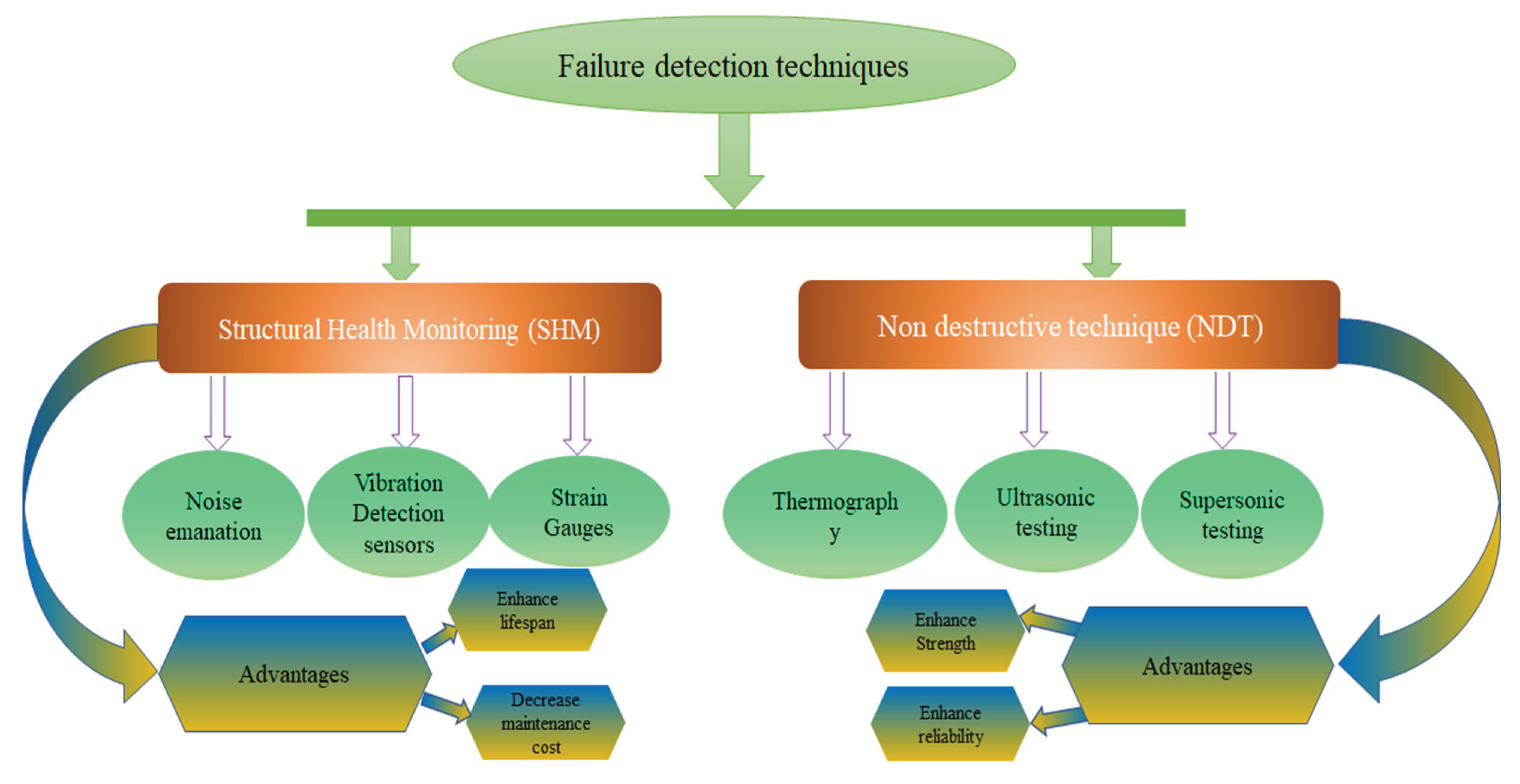
6.2. Failure Detection Method
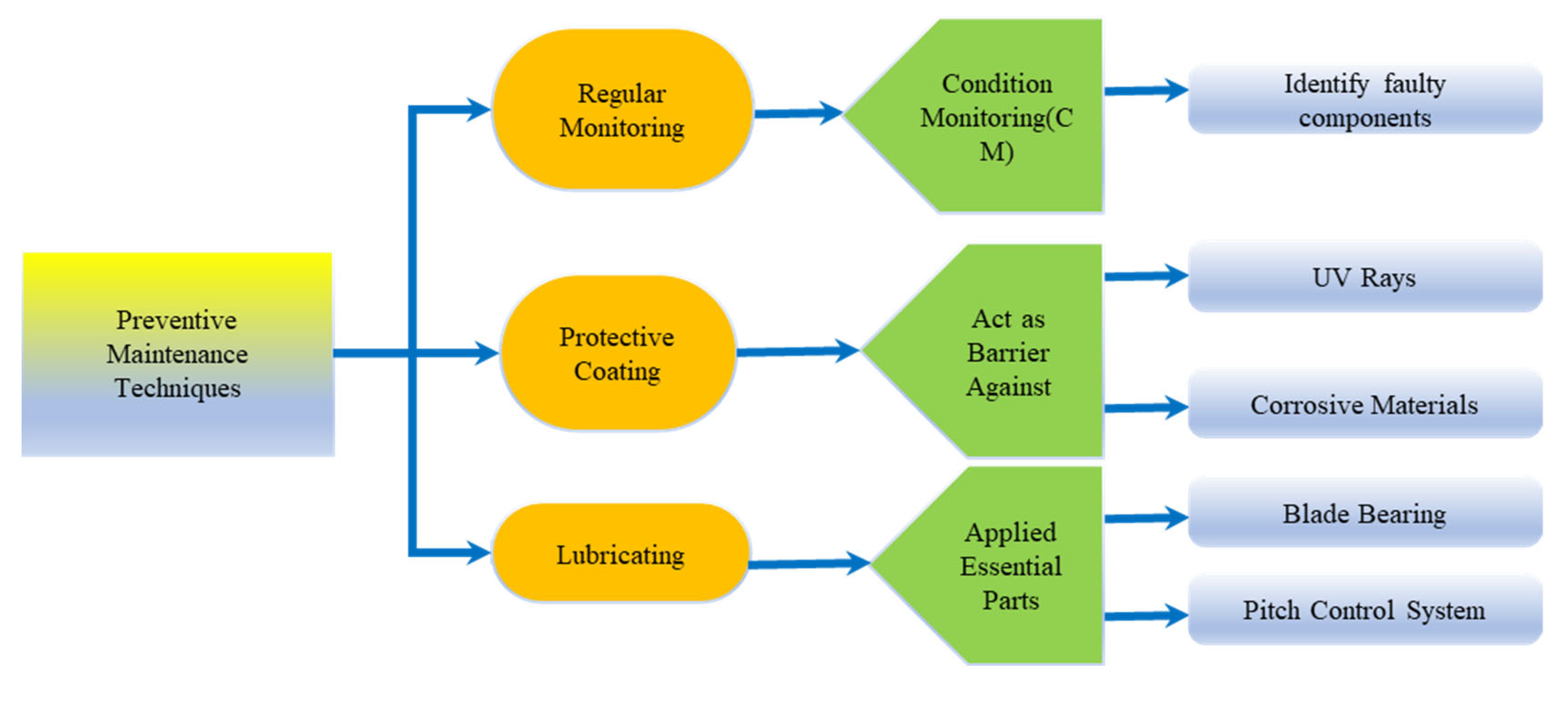
7. Preventive Maintenance Techniques
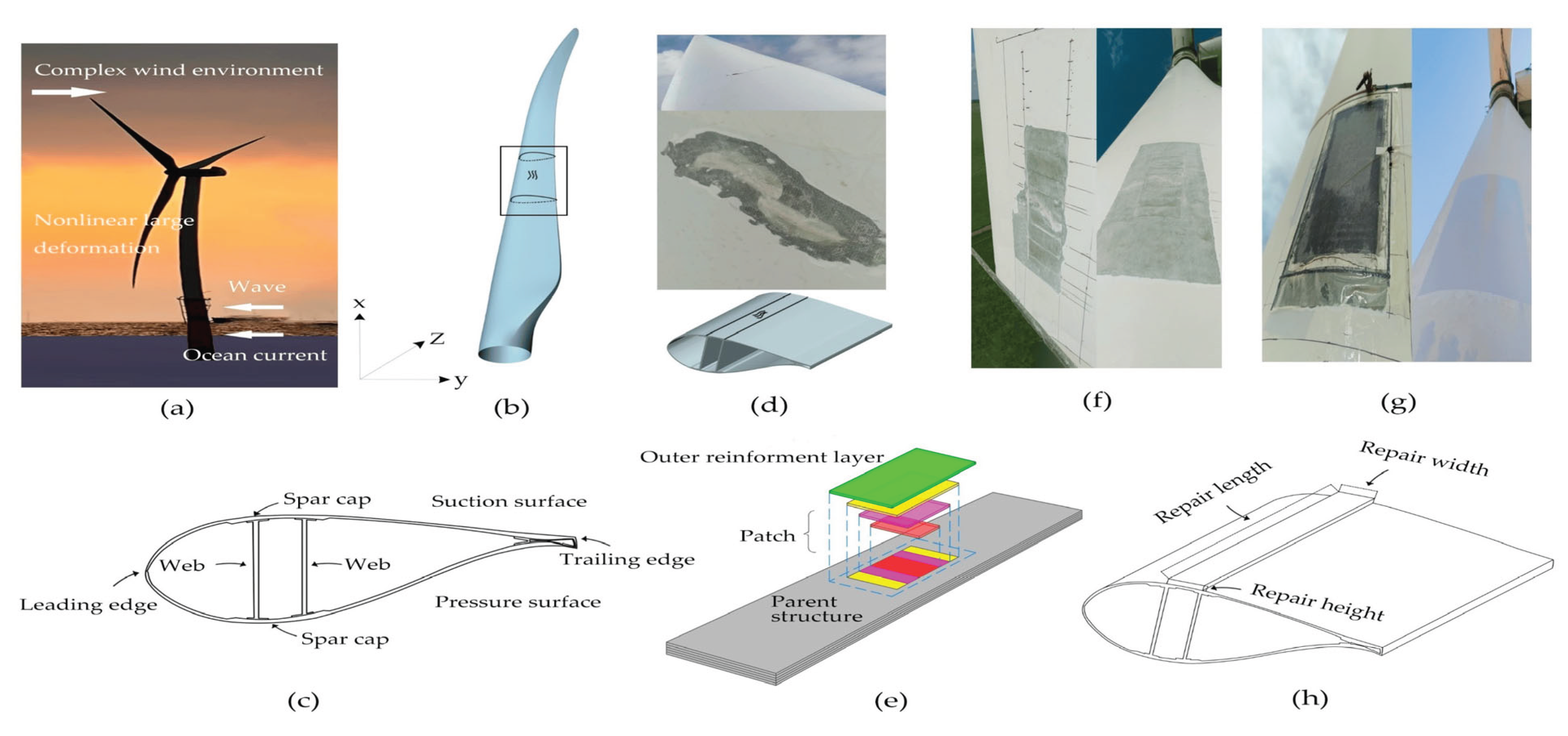
8. Early Damage Detection
9. Inspection and Repair Strategies
10. Challenges and Advancements in Maintenance Technologies
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armaroli, N.; Balzani, V. The future of energy supply: challenges and opportunities. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2007, 46, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dincer, F. The analysis on wind energy electricity generation status, potential and policies in the world. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2011, 15, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Al-Hadhrami, L.M.; Alam, M.M. Pumped hydro energy storage system: A technological review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 44, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, A.V.; Lipman, T. E.; Kammen, D.M. Renewable energy sources. Encyclopedia of life support systems (EOLSS). Forerunner Volume-Perspectives and overview of life support systems and sustainable development 2001, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, H. What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?. Our World in Data. 2020 Feb 10.
- Tummala, A.; Velamati, R.K.; Sinha, D. K.; Indraja, V.; Krishna, V.H. A review on small scale wind turbines. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 56, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Aliyu, K.N.; Alhems, L.M.; Mohandes, M.A.; Himri, Y.; Allouhi, A.; Alam, M.M. A comprehensive global review of building integrated photovoltaic power systems. FME transactions 2021, 49(2), 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, M.; Natarajan, N.; Kumar, E.S. Tamizharasu, S., Rehman, S., Alhems, L. M., & Alam, M. M. Environmental and Socio-Economic Aspects of Public Acceptance of Wind Farms in Tamil Nadu, India–Key Observations and a Conceptual Framework for Social Inclusion. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 2023, 32, 3339–3353. [Google Scholar]
- Allamehzadeh, H. Wind energy history, technology and control. In2016 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech) 2016 Oct 9 (pp. 119-126). IEEE.
- Gipe P, Möllerström E. An overview of the history of wind turbine development: Part I—The early wind turbines until the 1960s. Wind Engineering 2022, 46, 1973–2004.
- Ragheb, M. History of harnessing wind power. In Wind Energy Engineering 2017 Jan 1 (pp. 127-143). Academic Press.
- Baker, C. Wind engineering—Past, present and future. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 2007, 95, 843–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, DM. Illustrated history of wind power development. Darell M. Dodge; 2001.
- Alam M.M.; Rehman, S.; Meyer. J.P.; Al-Hadhrami, L,M. Review of 600–2500 kW sized wind turbines and optimization of hub height for maximum wind energy yield realization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2011, 15, 3839–49.
- Ragheb, M. Historical Wind Generators Machines. Historical Wind Generators Machines. pdf. 2009.
- Soter, S.; Wegener, R. Development of induction machines in wind power technology. 2007 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference 2007. 10.1109/IEMDC.2007.383648.
- Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC). Global Wind Report 2024; GWEC: Brussels, Belgium, 2024; Available online: https://gwec.net/global-wind-report-2024/ (accessed on 15 Feb 2025).
- Márquez, F.P.G.; Pérez, J.M.P.; Marugán, A.P.; Papaelias, M. Identification of critical components of wind turbines using FTA over the time. Renewable Energy 2016, 87, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezamand, M.; Kordestani, M.; Carriveau, R.; Ting, D.S.; Orchard, M.E.; Saif, M. Critical wind turbine components prognostics: A comprehensive review. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2020, 69, 9306–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Guo, T.; Alam, M.M. A review of wind energy harvesting technology: Civil engineering resource, theory, optimization, and application. Applied Energy 2025, 389, 125771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söker, H. Loads on wind turbine blades. In Advances in Wind Turbine Blade Design and Materials 2013 (pp. 55-78). Woodhead Publishing.
- Yang, B.; Sun, D. Testing, inspecting and monitoring technologies for wind turbine blades: A survey. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2013, 22, 515–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M. A review of wind turbine blade morphing: power, vibration, and noise. Fluid Dynamics & Material Processing 2025, 21, 657–695. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.; McDonald, A.; McMillan, D. Failure rate, repair time and unscheduled O&M cost analysis of offshore wind turbines. Wind energy 2016, 19, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. Fracture of wind turbine blades in operation—Part I: A comprehensive forensic investigation. Wind energy 2018, 21, 1046–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishnaevsky, J.L. Repair of wind turbine blades: Review of methods and related computational mechanics problems. Renewable energy 2019, 140, 828–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishnaevsky, L. Root causes and mechanisms of failure of wind turbine blades: Overview. Materials 15, 2959.
- Katsaprakakis, D.A.; Papadakis, N.; Ntintakis, I. A comprehensive analysis of wind turbine blade damage. Energies 2021, 14, 5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söker, H. Loads on wind turbine blades. In Advances in Wind Turbine Blade Design and Materials 2013, (pp. 55-78). Woodhead Publishing.
- Muheisen, A.H.; Yass, M.A. Irthiea IK. Enhancement of horizontal wind turbine blade performance using multiple airfoils sections and fences. Journal of King Saud University-Engineering Sciences. 2023, 35, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabhani, A.; Tousi, N.M.; Coma, M.; Bugeda, G. Bergadà, J.M. Large-scale horizontal axis wind turbine aerodynamic efficiency optimization using active flow control and synthetic jets. Energy 2025, 319, 134940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, K.A.; Ijumba, N.; Colton; J. The effect of the number of blades on the efficiency of a wind turbine. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 801, 012020, IOP Publishing.
- Zhang, L.A.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, W. Structural failure test of a 52.5 m wind turbine blade under combined loading. Engineering failure analysis 2019, 103, 286–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts D. These huge new wind turbines are a marvel. They’re also the future. vox. com. 2019 May 20.
- Rehman, S.; Al-Hadhrami, L.M.; Alam, M.M. Pumped hydro energy storage system: A technological review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 44, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Crespo, B. Damage Sensing in Blades. In MARE-WINT: New Materials and Reliability in Offshore Wind Turbine Technology; Ostachowicz, W., McGugan, M., Schröder-Hinrichs, J.-U., Luczak, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, S. Giant Turbines Poised to Claim Offshore Wind. Engineering 2021, 7, 894–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S., Alhems, L.M., Alam, M. M., Wang, L., and Toor, J. A review of energy extraction from wind and ocean: technologies, merits, efficiencies, and cost. Ocean Engineering 2023, 267, 113192. [CrossRef]
- Holierhoek, J. An overview of possible aeroelastic instabilities for wind turbine blades. Wind Engineering 2013, 37, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang Z, Karimirad M, Moan T. Dynamic response analysis of wind turbines under blade pitch system fault, grid loss, and shutdown events. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 1385–409. [CrossRef]
- Gharbia, Y., Derakhshandeh, J.F., Alam, M. M., and Amer, A.M.F. Developments in wingtip vorticity mitigation techniques: a comprehensive review. Aerospace 2024, 11, 36. [CrossRef]
- Thapa, M.; Missoum, S. Surrogate-Based Stochastic Optimization of Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbine Composite Blades. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2022, 65, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna R, vd Leye PO, Fichtner W. Key challenges and prospects for large wind turbines. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 53, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed ET, Olabi AG, Alami AH, Radwan A, Mdallal A, Rezk A, Abdelkareem MA. Renewable energy and energy storage systems. Energies 2023, 16, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztaş A, Demirbaş O, Şahin ME. Investigation of vertical axis wind turbines and the design of their components. Turkish Journal of Electromechanics and Energy 2021, 6, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gohar GA, Manzoor T, Ahmad A, Hameed Z, Saleem F, Ahmad I, Sattar A, Arshad A. Design and comparative analysis of an INVELOX wind power generation system for multiple wind turbines through computational fluid dynamics. Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2019, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, I.R.; Hodzic, M.; Crossan, A.N.; Crossan, N.; Acharige, N.; Runcie, J.W. Estimating Maximum Power from Wind Turbines with a Simple Newtonian Approach. Archives of Advanced Engineering Science 2023, 1, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arini, N.R.; Muhammad, G.; Pratilastiarso, J.; Tridianto, E.; Sumantri, B.; Nugroho, S. Prediction on the Maximum Lift Force of Twisted Clark Y Wind Turbine Blade with 30° Winglet Tip in Various Pitch Angles Using CFD Method. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Bristol, UK 2022, 1121, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.H.; Hemal, M.F.; Ahmed, M.M.; Taki, M.F.; Himel, M.H.; Ananno, A.A.; Dabnichki, P. Effect of Aerodynamics on Wind Turbine Design. In Wind Energy Storage and Conversion: From Basics to Utilities; Inamuddin, Altalhi, T., Luqman, M., Eds.; Wiley-Scrivener: Beverly, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 207–245. [Google Scholar]
- Belfkira, Z.; Mounir, H.; El Marjani, A. New Investigation of Mechanical Properties of a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine Blade Based on a Hybrid Composites with Kenaf Fibers. SN Applied Sciences 2020, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genov, J. Some Aspects of the Influence of the Vertical Wind Speed Gradient on the Blade Aerodynamics Loads in High Class Wind Generators. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences 2018, 234, 04006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almukhtar, A.H. Effect of Drag on the Performance for an Efficient Wind Turbine Blade Design. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastlake, C.N. An Aerodynamicist's View of Lift, Bernoulli, and Newton. The Physics Teacher 2002, 40, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, U.; Hussain, J. Enhancing the Efficiency of Wind Energy Conversion Systems Using Novel Airfoil-Based Small Scale Wind Turbine. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro) 2025, 30, e20240827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Evolutionary Understanding of Airfoil Lift. Advances in Aerodynamics 2021, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbache, M.; Hazmoune, M.; Derfouf, S.; Ciupageanu, D.A.; Lazaroiu, G. Wind Blade Twist Correction for Enhanced Annual Energy Production of Wind Turbines. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Alam, M.M.; Yang, H.X.; Guo, H.; Wood, D.H. Fluid Forces on a Very Low Reynolds Number Airfoil and Their Prediction. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow 2011, 32, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Alam, M.M.; Yang, H. Turbulent Intensity and Reynolds Number Effects on an Airfoil at Low Reynolds Numbers. Physics of Fluids 2014, 26, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.X.; Guo, H.; Mi, J. The Ultra-Low Reynolds Number Airfoil Wake. Experiments in Fluids 2010, 48, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Alam, M.M.; Zhou, Y. Experimental Study of a Passive Control of Airfoil Lift Using Bioinspired Feather Flap. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics 2019, 14, 066005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Alam, M.M.; Rehman, S.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Blowing and Suction Jets on the Aerodynamic Performance of Wind Turbine Airfoil. Renewable Energy 2022, 196, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, U.; Hussain, J. Enhancing the Efficiency of Wind Energy Conversion Systems Using Novel Airfoil-Based Small Scale Wind Turbine. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro) 2025, 30, e20240827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Shen, W.Z.; Wang, T.G.; Zhu, W.J. A New Method of Determination of the Angle of Attack on Rotating Wind Turbine Blades. Energies 2019, 12, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeiha, A.; Pereira, R.; Kotsonis, M. Fluctuations of Angle of Attack and Lift Coefficient and the Resultant Fatigue Loads for a Large Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine. Renewable Energy 2017, 114, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumthae, C., & Chitsomboon, T. Optimal angle of attack for untwisted blade wind turbine. Renewable energy 2009, 34, 1279–1284.
- Bakırcı, M., & Yılmaz, S.. Theoretical and computational investigations of the optimal tip-speed ratio of horizontal-axis wind turbines. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal 2018, 21, 1128–1142.
- Yurdusev, M., Ata, R., & Çetin, N. Assessment of optimum tip speed ratio in wind turbines using artificial neural networks. Energy 2006, 31, 2153–2161.
- Jasa, J.; Glaws, A.; Bortolotti, P.; Vijayakumar, G.; Barter, G. Wind Turbine Blade Design with Airfoil Shape Control Using Invertible Neural Networks. IOP Conference Series: Physics and Engineering 2022, 2265, 042052, IOP Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W. J., Shen, W. Z., & Sørensen, J. N. Integrated airfoil and blade design method for large wind turbines. Renewable energy 2014, 70, 172–183.
- Lucena, J. d. A. Y. Recent advances and technology trends of wind turbines. Recent Advances in Renewable Energy Technologies 2021, 177–210. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, N.; Anand, R.; Suthakar, T.; Barhate, S. Materials, Innovations and Future Research Opportunities on Wind Turbine Blades—Insight Review. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy 2019, 38, e13046. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyeye, K.A.; Ijumba, N.; Colton, J. The Effect of the Number of Blades on the Efficiency of a Wind Turbine. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 801, 012020, IOP Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K., Dyer, K., Payne, C., Hamerton, I., & Weaver, P. M. Progress and trends in damage detection methods, maintenance, and data-driven monitoring of wind turbine blades–A review. Renewable Energy Focus 2023, 44, 390–412.
- Gambier, A. Pitch Control of Three Bladed Large Wind Energy Converters—A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namik, H., & Stol, K. Individual blade pitch control of floating offshore wind turbines. Wind Energy: An International Journal for Progress and Applications in Wind Power Conversion Technology 2010, 13, 74–85.
- Schubel, P.J.; Crossley, R.J. Wind Turbine Blade Design. Energies 2012, 5, 3425–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Ramachandra, M. Advanced Materials for Wind Turbine Blade—A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2018, 5, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Thomas, T.T.; Warudkar, V. Structural Design of a Wind Turbine Blade: A Review. International Journal of ChemTech Research 2013, 5, 2443–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Brøndsted, P.; Holmes, J.W.; Sørensen, B.F.; Sun, Z. Bamboo Based Composites for Wind Turbine Blades. Materials Research Division, Risø DTU, The Technical University of Denmark, 2009.
- Wibawa, Y.M.; Irawan, A.P.; Djamil, S.; Abdullah, M.Z. Development of Wind Turbine Blade Using Bamboo Fiber Composite Material. AIP Conference Proceedings 2023, 2680. AIP Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Qin Y, Xu J, Zhang Y. Bamboo as a potential material used for wind turbine bladesTechnological and socio-Economic Planning-Technical Report, Roskilde University, 2009, 1-55.
- Rashedi, A.; Sridhar, I.; Tseng, K.J. Multi-Objective Material Selection for Wind Turbine Blade and Tower: Ashby’s Approach. Materials & Design 2012, 37, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Dathu, K.P.; Hariharan, R. Design of Wind Turbine Blade Material for Higher Efficiency. Materials Today: Proceedings 2020, 33, 565–569. [Google Scholar]
- Firoozi, A.A.; Firoozi, A.A.; Hejazi, F. Innovations in Wind Turbine Blade Engineering: Exploring Materials, Sustainability, and Market Dynamics. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veers, P.S.; Ashwill, T.D.; Sutherland, H.J.; Laird, D.L.; Lobitz, D.W.; Griffin, D.A.; Mandell, J.F.; Musial, W.D.; Jackson, K.; Zuteck, M.; Miravete, A. Trends in the Design, Manufacture and Evaluation of Wind Turbine Blades. Wind Energy: An International Journal for Progress and Applications in Wind Power Conversion Technology 2003, 6, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.; Alam, M.M. Vibration of a Square Cylinder Submerged in a Wake. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2018, 853, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M. A Note on Flow-Induced Force Measurement of Oscillating Cylinder by Loadcell. Ocean Engineering 2022a, 245, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M. New Scaling of Critical Damping and Reduced Frequency for Mechanically Excited Systems. Sound & Vibration, 2025b; 59, 2600. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.M. Flow-Induced Vibrations of Various Bluff Bodies: A Review of Blockage and Wall Effects. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2025c, 136, 104328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Kaneko, S.; Inada, F.; Kato, M.; Ishihara, K.; Nishihara, T.; Mureithi, N.W.; Langthjem, M.A. (Eds.) Flow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical Experiences; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.M.; Meyer, J.P. Global Aerodynamic Instability of Twin Cylinders in Cross Flow. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2013, 41, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Rajendran, P.; Khan, S.A. Energy Harvesting from Aerodynamic Instabilities: Current Prospect and Future Trends. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2018, 290, 012054, IOP Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.C.; Hourigan, K.; Thompson, M.C.; Zhao, J. The Effect of Structural Damping on Flow-Induced Vibration of a Thin Elliptical Cylinder. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2023, 974, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.B.; Armandei, M. Renewable Energy Harvesting by Vortex-Induced Motions: Review and Benchmarking of Technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 70, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jo, S.; Seok, J. Development of the Optimal Bluff Body for Wind Energy Harvesting Using the Synergetic Effect of Coupled Vortex Induced Vibration and Galloping Phenomena. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences 2019, 156, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; McConkey, R.; Lien, F.S.; Yee, E. Modelling of Flow-Induced Vibration of Bluff Bodies: A Comprehensive Survey and Future Prospects. Energies 2022, 15, 8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M. Effects of Mass and Damping on Flow-Induced Vibration of a Cylinder Interacting with the Wake of Another Cylinder at High Reduced Velocities. Energies 2021, 14, 5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Alam, M.M.; Zhou, Y. Two Tandem Cylinders of Different Diameters in Crossflow: Flow-Induced Vibration. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2017, 829, 621–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Alam, M.M.; Ji, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S. Flow-Induced Vibration of Two Cylinders of Different Natural Frequencies. Ocean Engineering 2018, 155, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Alam, M.M.; Zhou, Y. Free Vibrations of Two Tandem Elastically Mounted Cylinders in Cross-Flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2019, 861, 349–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Alam, M.M.; Sakamoto, H.; Zhou, Y. Flow-Induced Vibration of Two Circular Cylinders in Tandem Arrangement. Part 2: Suppression of Vibrations. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 2009, 97, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ji, C.; Alam, M.M.; Xu, D.; An, H.; Tong, F.; Zhao, Y. Flow-Induced Vibrations of a D-Section Prism at a Low Reynolds Number. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2022, 941, A52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Alam, M.M.; Li, Y.; Ji, C. Two-Degree-of-Freedom Flow-Induced Vibrations of a D-Section Prism. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2023, 971, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Alam, M.M.; Zhu, H.; Islam, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zeinoddini, M. Flow-Induced Vibrations of a Wake Cylinder at a Low Mass-Damping Ratio. Ocean Engineering 2025, 322, 120530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu H, Zhong J, Shao Z, Zhou T, Alam MM. Fluid-structure interaction among three tandem circular cylinders oscillating transversely at a low Reynolds number of 150. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2024, 130, 104204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou Q, Cao S, Alam MM, Han B. Aerodynamics of a 5: 1 rectangular cylinder under transient accelerated and decelerated winds. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 2025, 258, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejadali, J. Design Improvement of the Small-Scale Vortex-Induced Bladeless Wind Turbine Considering the Characteristic Length of the Oscillating Structure. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering 2024, 48, 1839–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdravkovich, M.M. Flow around Circular Cylinders: Volume 2: Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.M. Fluid Force, Moment, and Torque Measurements of Oscillating Prism and Cylinder Using Loadcell. Physics of Fluids 2022, 34, 127108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson CH, Roshko A. Vortex formation in the wake of an oscillating cylinder. Journal of fluids and structures 1988, 2, 355–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Huang Y, Zhao J. In-line flow-induced vibration of rotating elliptical cylinders. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2024, 130, 104186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U. Study of Heat Transfer and Flow-Induced Vibrations of Circular Cylinders in Cross Flow. Doctoral Dissertation, Khalifa University of Science, 2024.
- Heinz JC, Sørensen NN, Zahle F, Skrzypiński W. Vortex-induced vibrations on a modern wind turbine blade. Wind Energy 2016, 19, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson CH, Govardhan R. Vortex-induced vibrations. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 2004, 36, 413–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li X, Lyu Z, Kou J, Zhang W. Mode competition in galloping of a square cylinder at low Reynolds number. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2019, 867, 516–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin C, Alam MM. Intrinsic features of flow-induced stability of a square cylinder. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2024, 988, A50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simiu E, Scanlan RH. Wind effects on structures: fundamentals and applications to design. New York: John Wiley; 1996.
- Wang J, Geng L, Ding L, Zhu H, Yurchenko D. The state-of-the-art review on energy harvesting from flow-induced vibrations. Applied Energy 2020, 267, 114902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen MO, Sørensen JN, Voutsinas S, Sørensen N, Madsen HA. State of the art in wind turbine aerodynamics and aeroelasticity. Progress in Aerospace Sciences 2006, 42, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourazarm P, Caracoglia L, Lackner M, Modarres-Sadeghi Y. Stochastic analysis of flow-induced dynamic instabilities of wind turbine blades. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 2015, 137, 37-45.
- Zheng Q, Gao Z, Zhao B, Bai Y, Su R, Han X, Zhao F, Dong X, Wang J. Experimental study on the influence of centroid position of wind turbine section on flutter. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath MT, Lee AK, Prusty BG. Design of shape-adaptive wind turbine blades using Differential Stiffness Bend–Twist coupling. Ocean Engineering 2015, 95, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, MH. Improved modal dynamics of wind turbines to avoid stall-induced vibrations. Wind Energy 2003, 6, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, MH. Aeroelastic instability problems for wind turbines. Wind Energy 2007, 10, 551–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer E, Willden RH. Blade–wake interactions in cross-flow turbines. International Journal of Marine Energy 2015, 11, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiso, M. The tower shadow effect in downwind wind turbines. Doctoral dissertation, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Trondheim, Norway, 2013.
- Alam, M. M., Chen, G., Zhou, Y., Wang, L., Wang, J., Islam, M. Flow-induced vibration of a cantilevered cylinder in the wake of another. Journal of Fluids and Structures 2023, 120, 103901. [CrossRef]
- Asghar, U.; Aziz, I.; Sher, F. Modelling and simulation of flow induced vibrations in vertical axis wind turbine blade. In Proceedings of the 14th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 10 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Struggl S, Berbyuk V, Johansson H. Review on wind turbines with focus on drive train system dynamics. Wind Energy 2015, 18, 567–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu Z, Wei J, Zhang S, Liu Z, Chen X, Yan Q, Guo J. A state-of-the-art review of the vibration and noise of wind turbine drivetrains. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2021, 48, 101629.
- Burton, T.; Jenkins, N.; Sharpe, D.; Bossanyi, E. Wind Energy Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B., Alam, M. M., Ji, C., Liu, Y. and Xu, S. Flow-induced vibration of two cylinders of different natural frequencies. Ocean Engineering 2018, 155, 189–200. [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, H. J. On the fatigue analysis of wind turbines; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1999; Report No. SAND99-0089. [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman, J. M. Dynamics modeling and loads analysis of an offshore floating wind turbine; University of Colorado at Boulder: Boulder, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kuik, G. A.; Peinke, J.; Nijssen, R.; Lekou, D.; Mann, J.; Sørensen, J. N.; Ferreira, C.; van Wingerden, J. W.; Schlipf, D.; Gebraad, P.; Polinder, H. Long-term research challenges in wind energy – a research agenda by the European Academy of Wind Energy. Wind Energy Science 2016, 1, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman M, Ong ZC, Chong WT, Julai S, Khoo SY. Performance enhancement of wind turbine systems with vibration control: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 51, 43-54.
- Cano Bravo, R.A. Vortex-Induced Motions of a Semi-Submersible Floating Offshore Wind Turbine. Master's Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Trondheim, Norway, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Cui, Q.; Xu, D. Wind Turbine Composite Blades: A Critical Review of Aeroelastic Modeling and Vibration Control. Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2025, 21, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Xie F, Aly AM. Structural control and vibration issues in wind turbines: A review. Engineering Structures 2020, 210, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald B, Basu B. Vibration control of wind turbines: recent advances and emerging trends. International Journal of Sustainable Materials and Structural Systems 2020, 4, 347–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada A, Younes R, Ilinca A. Review of vibration control methods for wind turbines. Energies 2021, 14, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staino A, Basu B. Emerging trends in vibration control of wind turbines: a focus on a dual control strategy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2015, 373, 20140069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou XQ, Yu DY, Shao XY, Zhang SQ, Wang S. Research and applications of viscoelastic vibration damping materials: A review. Composite Structures 2016, 136, 460–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang JH, Shieh WL. The influence of a variable friction coefficient on the dynamic behavior of a blade with a friction damper. Journal of Sound and Vibration 1991, 149, 137–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak SM, Kumar VP, Bonu V, Mishnaevsky Jr L, Lakshmi RV, Bera P, Barshilia HC. Development of cellulose-reinforced polyurethane coatings: A novel eco-friendly approach for wind turbine blade protection. Energies 2023, 16, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajiga OK, Obiuto NC, Adebayo RA, Festus-Ikhuoria IC. Advanced Materials for Wind Energy: Reviewing Innovations and Challenges in the USA. International Journal of Advances in Engineering and Management 2024, 6, 454-65.
- Jahangiri V, Sun C, Babaei H. Application of a new two dimensional nonlinear tuned mass damper in bi-directional vibration mitigation of wind turbine blades. Engineering Structures 2024, 302, 117371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Høeg C. Inerter-enhanced tuned mass damper for vibration damping of floating offshore wind turbines. Ocean Engineering 2021, 223, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, V.; Sun, C. A novel two-dimensional nonlinear tuned mass damper inerter and its application in vibration mitigation of wind turbine blade. arXiv 2022, arXiv, 2206.14328.
- Li, W.; Qiao, L.; Li, G.; Du, Y. Vibration control of large wind turbine blades with unidirectional cable pendulum damper. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics 2023, 23, 2350082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglari, H.; Fakhari, V. Edgewise vibration reduction of small size wind turbine blades using shunt damping. J. Vib. Control 2020, 26, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, A.; Sapre, C.A.; Selig, M.S. Effects of leading edge erosion on wind turbine blade performance. Wind Energy 2014, 17, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudern, N. A practical study of the aerodynamic impact of wind turbine blade leading edge erosion. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2014, 524, 012031, IOP Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGugan, M.; Mishnaevsky Jr, L. Damage mechanism based approach to the structural health monitoring of wind turbine blades. Coatings 2020, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangaru, A.K. Early stage fatigue damage mechanisms in composite material used for wind turbine rotor blades. Doctoral Thesis, Technical University of Denmark (DTU), 2021.
- Zhang, Z. – Shu, Z. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)–assisted damage detection of wind turbine blades: A review. Energies 2024, 17, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.Y. – Chen, X. Structural transverse cracking mechanisms of trailing edge regions in composite wind turbine blades. Composite Structures 2023, 308, 116680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai K, Bergot A, Liang C, Xiang WN, Huang Z. Environmental issues associated with wind energy–A review. Renewable Energy 2015, 75, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Temperature and moisture effects on composite materials for wind turbine blades. Doctoral dissertation, Montana State University–Bozeman, College of Engineering, 2000.
- Olabi, A. G., Wilberforce, T., Elsaid, K., Sayed, E. T., Salameh, T., Abdelkareem, M. A., Baroutaji, A. A review on failure modes of wind turbine components. Energies 2021, 14, 5241. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z. Overview of wind turbines and the effects of aging on performance. Bachelor’s Dissertation, Luleå University of Technology, 2024.
- Hossain ML, Abu-Siada A, Muyeen SM. Methods for advanced wind turbine condition monitoring and early diagnosis: A literature review. Energies 2018, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin RW, Sabato A, Schoenberg A, Giles RH, Niezrecki C. Comparison of nondestructive testing techniques for the inspection of wind turbine blades' spar caps. Wind Energy 2018, 21, 980–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raišutis R, Jasiūnienė E, Šliteris R, Vladišauskas A. The review of non-destructive testing techniques suitable for inspection of the wind turbine blades. Ultragarsas/Ultrasound 2008, 63, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- McGugan M, Mishnaevsky Jr L. Damage mechanism based approach to the structural health monitoring of wind turbine blades. Coatings 2020, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez FP, Tobias AM, Pérez JM, Papaelias M. Condition monitoring of wind turbines: Techniques and methods. Renewable energy 2012, 46, 169-78.
- Sareen A, Sapre CA, Selig MS. Effects of leading edge erosion on wind turbine blade performance. Wind energy 2014, 17, 1531–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalili N, Edrisy A, Carriveau R. A review of surface engineering issues critical to wind turbine performance. Renewable and Sustainable energy reviews 2009, 13, 428–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng H, Zhang H, Shangguan L, Fan Y. Review of tribological failure analysis and lubrication technology research of wind power bearings. Polymers 2022, 14, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashtkar A, Hadavinia H, Sahinkaya MN, Williams NA, Vahid S, Ismail F, Turner M. Rain erosion-resistant coatings for wind turbine blades: A review. Polymers and Polymer Composites 2019, 27, 443–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak SM, Kumar VP, Bonu V, Mishnaevsky Jr L, Lakshmi RV, Bera P, Barshilia HC. Enhancing wind turbine blade protection: Solid particle erosion resistant ceramic oxides-reinforced epoxy coatings. Renewable Energy 2025, 238, 121681.
- Keegan MH, Nash DH, Stack MM. On erosion issues associated with the leading edge of wind turbine blades. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 2013, 46, 383001.
- Mishnaevsky Jr L, Branner K, Petersen HN, Beauson J, McGugan M, Sørensen BF. Materials for wind turbine blades: An overview. Materials 2017, 10, 1285.
- Minoofar G, Kandeloos AJ, Koochaki MS, Momen G. Progress in icephobic coatings for wind turbine protection: Merging chemical innovation with practical implementation. Crystals 2025, 15, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li H, Lu X, Xin W, Guo Z, Zhou B, Ning B, Bao H. Repair parameter design of outer reinforcement layers of offshore wind turbine blade spar cap based on structural and aerodynamic analysis. Energies 2023, 16, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li H, Zhou W, Xu J. Structural health monitoring of wind turbine blades. In Wind Turbine Control and Monitoring: Bianchini A, Santos T, editors.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2014; pp. 231–265. [Google Scholar]
- Du Y, Zhou S, Jing X, Peng Y, Wu H, Kwok N. Damage detection techniques for wind turbine blades: A review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2020, 141, 106445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Civera, M. Review of vibration-based damage assessment in wind turbines. Master's thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Italy, 2024.
- Al-Hinai AH, Varaprasad KC, Kumar VV. Comprehensive review of vibration-based analysis for wind turbine condition monitoring. Mechanical Engineering for Society and Industry 2024, 4, 12466.
- Ciang CC, Lee JR, Bang HJ. Structural health monitoring for a wind turbine system: a review of damage detection methods. Measurement science and technology 2008, 19, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
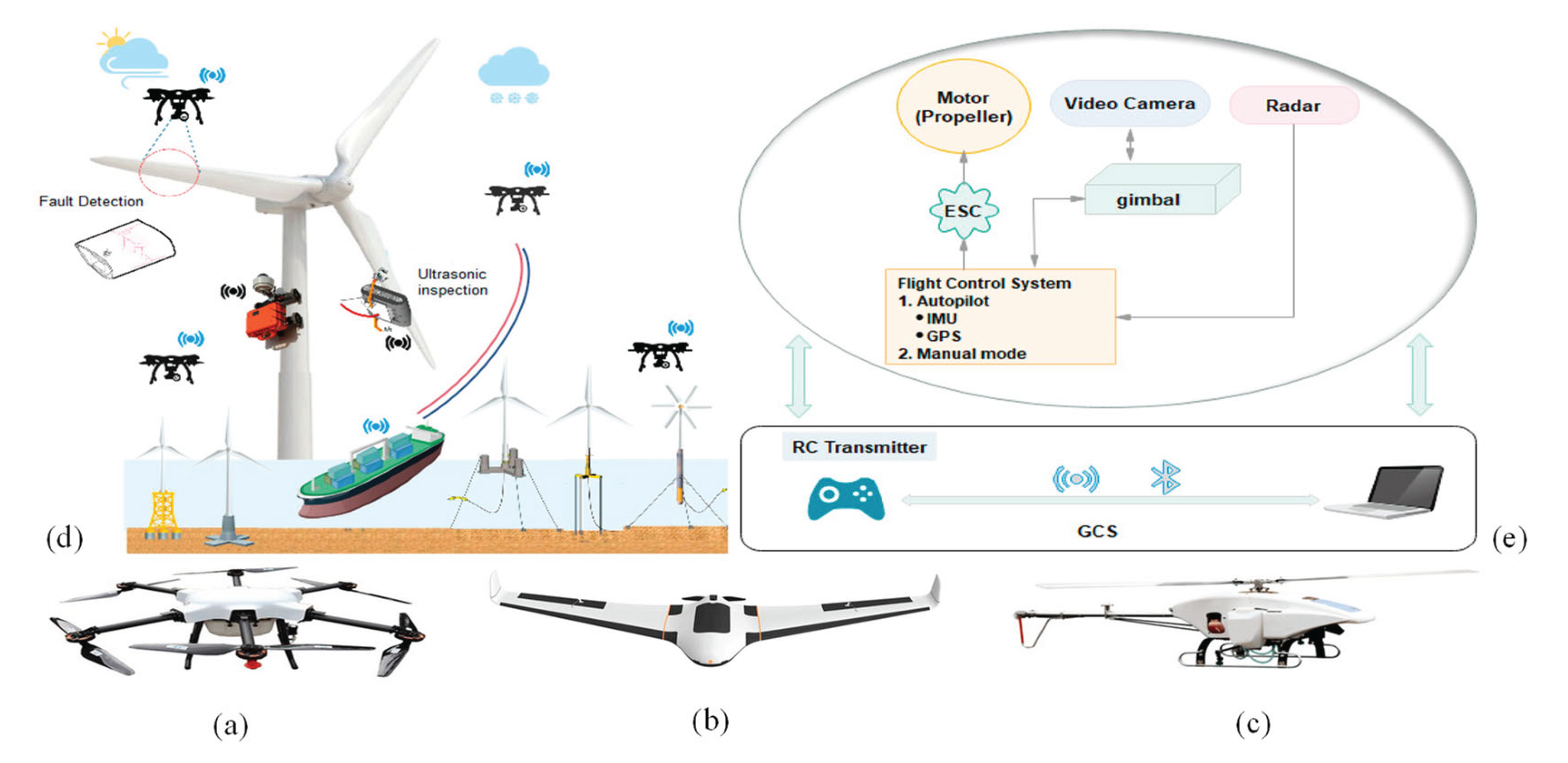
- Heo SJ, Na WS. Review of Drone-Based Technologies for Wind Turbine Blade Inspection. Electronics 2025, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee M, Zhou Z, Mei L, Dinmohammadi F, Karama J, Flynn D. Unmanned aerial drones for inspection of offshore wind turbines: A mission-critical failure analysis. Robotics 2021, 10, 26.
- Memari M, Shakya P, Shekaramiz M, Seibi AC, Masoum MA. Review on the advancements in wind turbine blade inspection: Integrating drone and deep learning technologies for enhanced defect detection. IEEE 2024, 12, 33236-33282.
- Barbosa NB, Nunes DD, Santos AÁ, Machado BA. Technological advances on fault diagnosis in wind turbines. A patent analysis. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 1721.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).