Submitted:
19 May 2025
Posted:
20 May 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Introduction
1.3. Problem Statement
1.4. Significance and Rationale
1.5. Literature Review
1.6. Theoretical Framework
1.7. Objectives and Research Questions
- What are the most significant legal risks in international player transfer contracts?
- How do new market trends and technologies affect the legal landscape of player transfers?
- What strategies can stakeholders adopt to mitigate legal uncertainties and promote harmonization?
- Hypotheses:
- H1: Regulatory inconsistencies significantly increase the likelihood of contractual disputes in player transfers.
- H2: The adoption of digital contract management tools reduces legal ambiguities and dispute frequency.
2. Theoretical Foundations and Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Foundations
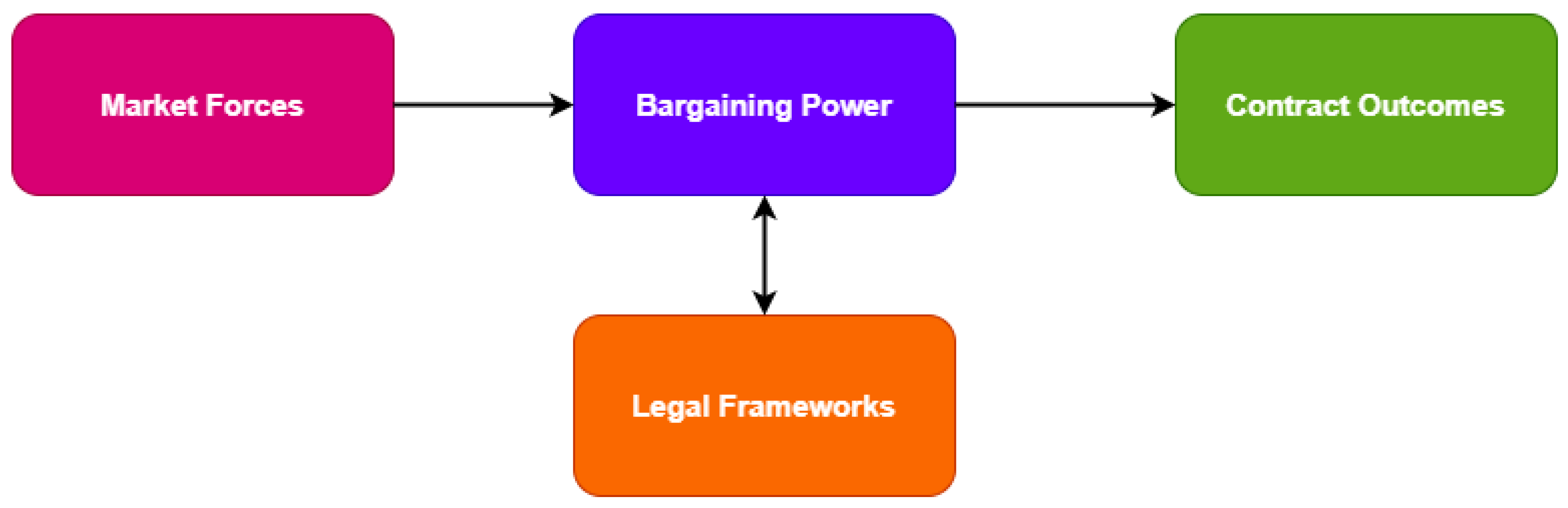
2.2. Review of Related Literature
2.2.1. Economic and Legal Aspects of Transfers
| Determinant | Economic Impact | Legal Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Player performance | Higher transfer fees | Contractual disputes |
| Contract length | Value retention | Early termination issues |
| Regulatory differences | Market segmentation | Compliance challenges |
| Third-party ownership | Investment incentives | Ownership disputes |
2.2.2. Negotiation Dynamics and Bargaining Power
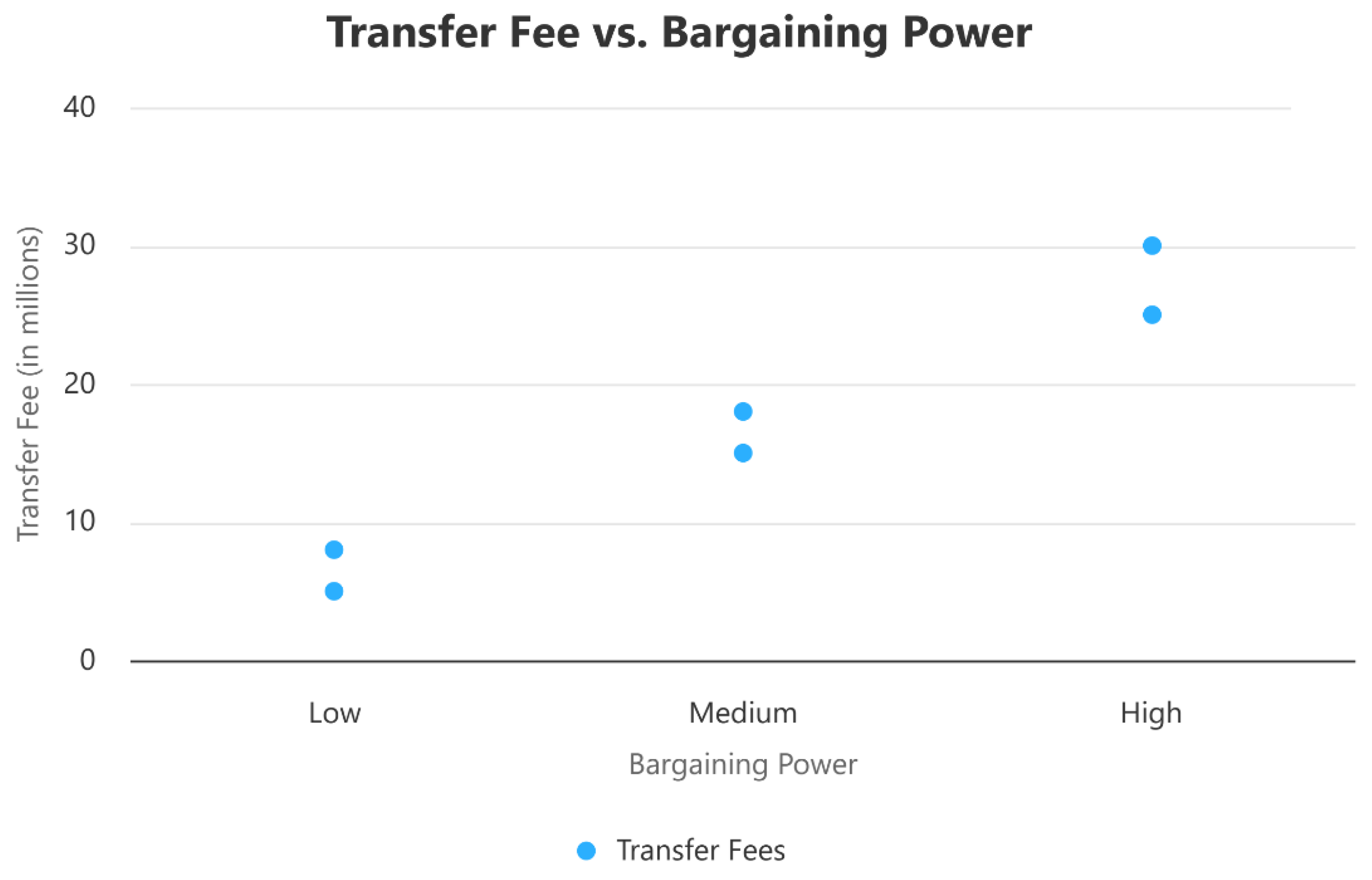
2.2.3. Regulatory and Jurisdictional Challenges
2.2.4. Emerging Trends and Gaps
| Study (Year) | Focus Area | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Memari et al. (2023) | Nash bargaining in transfers | Bargaining power is central to transfer terms |
| Budzinski & Feddersen (2024) | Contest theory in transfers | Competition drives effort and transfer value |
| Ech-choayby (2024) | Digitalization, new markets | New entrants reshape legal frameworks |
| Duval & Rigozzi (2023) | International regulation | Need for harmonized legal standards |
2.3. Synthesis
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Type
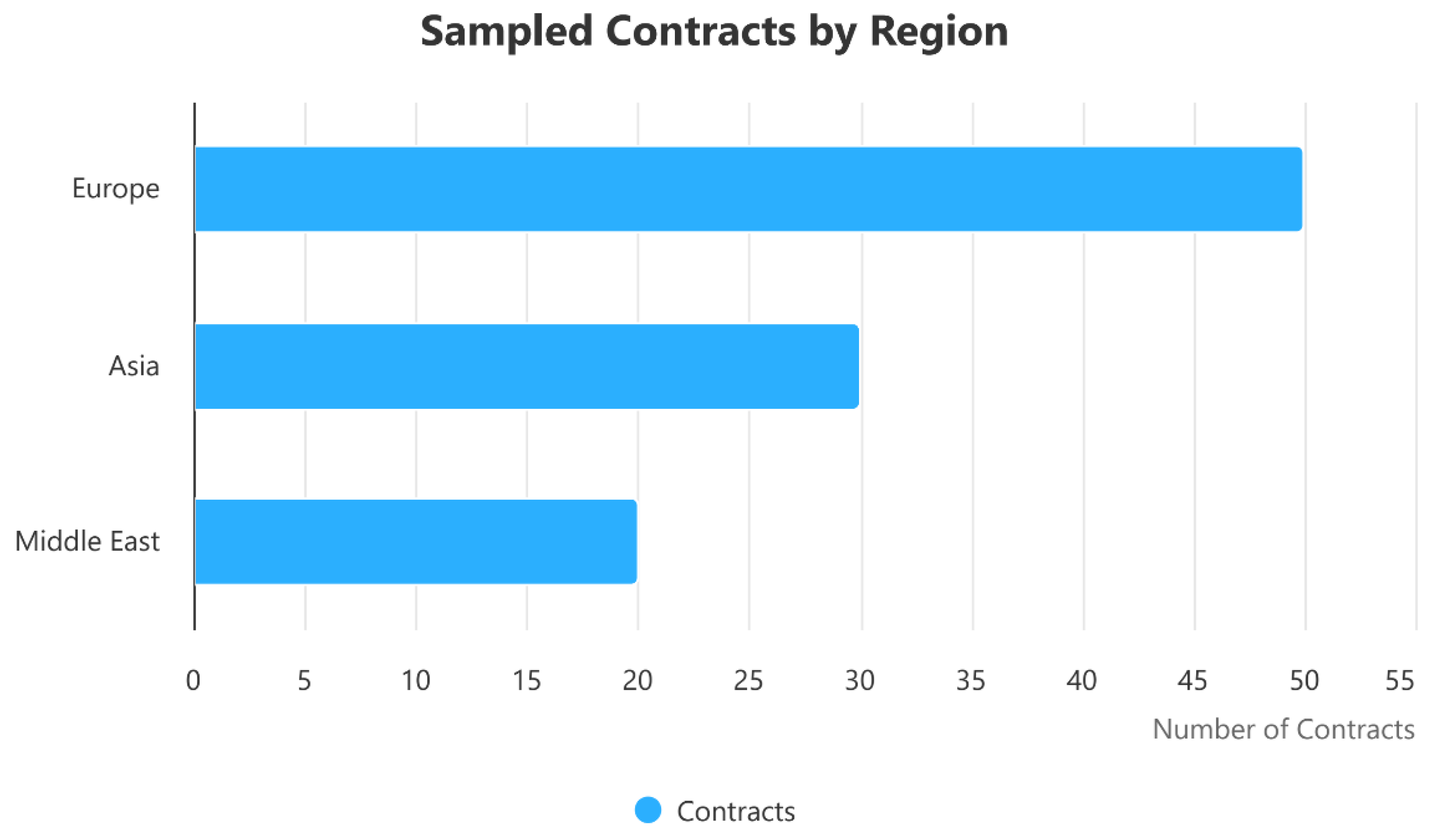
3.2. Statistical Population
3.3. Sample and Sampling Method
3.4. Data Collection Tools
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Document analysis | Extract legal and contractual variables |
| Questionnaire | Quantify perceptions of legal risks |
| Expert interviews | Qualitative insight and validation |
3.5. Validity and Reliability of Tools
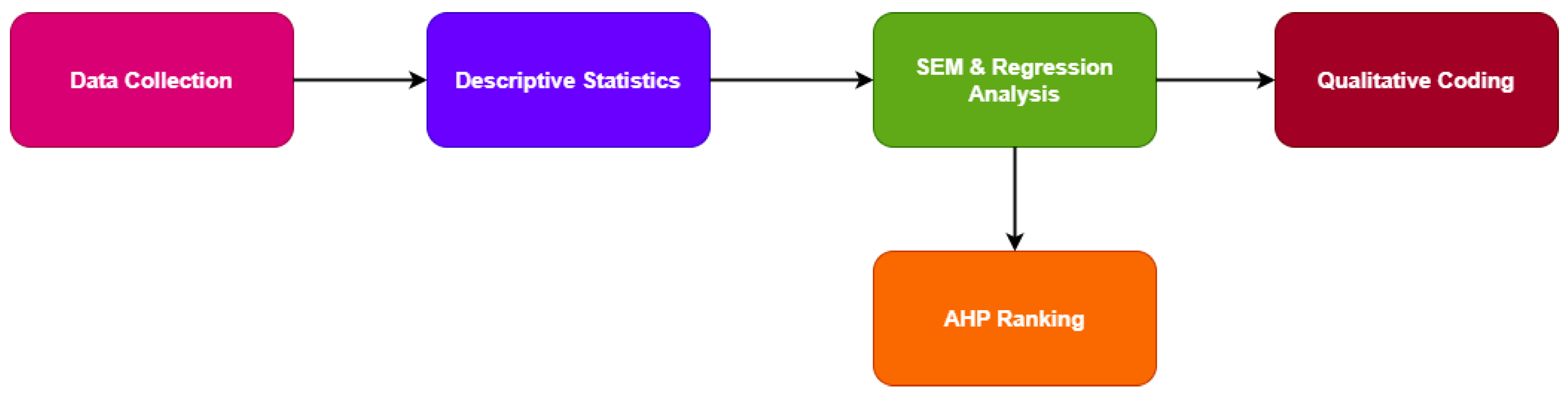
3.6. Data Analysis Methods
- Descriptive statistics (mean, standard deviation)
- Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to examine relationships among legal risk factors
- Multivariate regression analysis to assess the impact of market variables on legal outcomes
- The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) for expert-based ranking of legal challenges
4. Findings
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
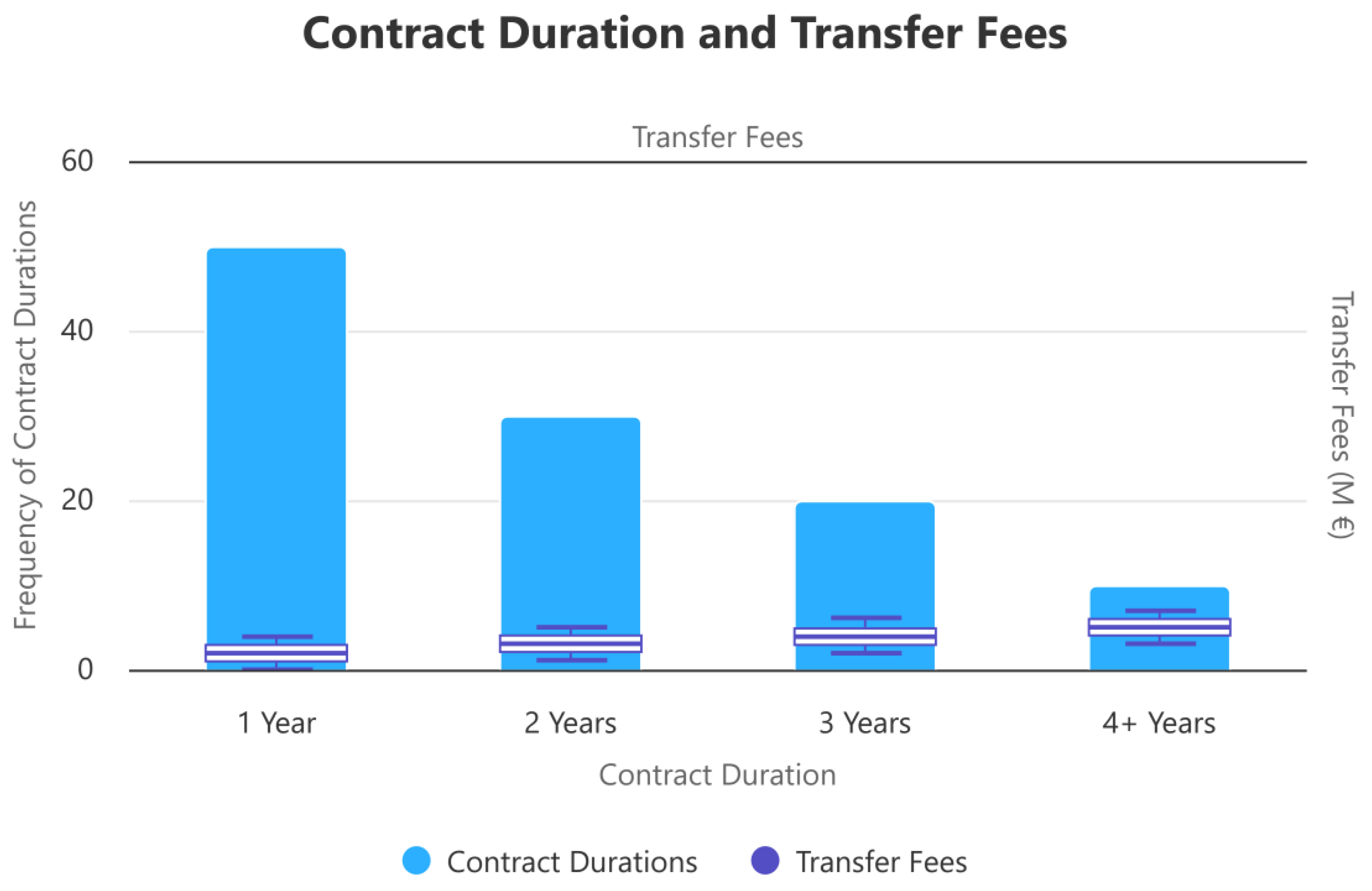
4.2. Statistical Test Results
| Predictor | Beta (β) | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory inconsistency | 0.34 | 0.001 |
| Third-party ownership | 0.27 | 0.019 |
| Dispute resolution | 0.22 | 0.031 |
4.3. Hypotheses and Research Questions
- H1: Regulatory inconsistencies significantly increase the likelihood of contractual disputes in player transfers.Supported: SEM and regression results confirm a strong positive relationship (β = 0.34, p < 0.01).
- H2: The adoption of digital contract management tools reduces legal ambiguities and dispute frequency.
- Partially Supported: Qualitative analysis of expert interviews indicated that clubs using digital tools reported fewer ambiguities, but quantitative effects were not statistically significant at the 0.05 level.
4.3.1. Research Questions:
- The most significant legal risks are regulatory inconsistencies, third-party ownership, and dispute resolution complexity.
- New market trends and digitalization are reshaping the legal landscape, with regulations struggling to keep pace.
- Stakeholders can mitigate legal uncertainties by advocating for harmonized regulations and adopting transparent digital management systems.
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Interpretation of Findings
5.2. Comparison with Previous Research
5.3. Overall Conclusion
6. Recommendations
6.1. Practical Recommendations
- Drafting Clear and Comprehensive Contracts: Clubs and players should ensure that all contracts specify the identities and qualifications of both parties, the duration, payment terms, and detailed obligations, including training attendance and compliance with club regulations. All terms, including dispute resolution mechanisms and grounds for contract termination, must be explicitly stated to minimize ambiguity and potential legal disputes.
- Utilizing Expert Legal Counsel: Engaging specialized sports law attorneys in drafting and reviewing contracts can significantly reduce legal risks and ensure that all regulatory and compliance requirements are met, especially when dealing with cross-border transfers or third-party ownership.
- Adopting Digital Contract Management Tools: Implementation of digital platforms for contract drafting, storage, and monitoring can enhance transparency, facilitate compliance checks, and reduce the likelihood of disputes arising from lost or altered documents.
- Establishing Internal Legal Teams: Sports organizations should develop or strengthen their in-house legal teams to regularly review contracts, monitor regulatory updates, and proactively manage potential disputes, as recommended for effective post-pandemic sports dispute management.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Clubs must verify that all parties hold the necessary licenses and are free from disqualifying conditions (such as doping bans or unresolved suspensions) before finalizing contracts.
- Transparent Dispute Resolution: All contracts should include clear provisions for arbitration or other dispute resolution mechanisms, specifying the competent authority and procedures for resolving conflicts.
6.2. Recommendations for Future Research
- Comparative Legal Analysis: Future studies should compare the effectiveness of different national and international legal frameworks in managing player transfers, focusing on best practices for harmonization and dispute resolution.
- Impact of Digitalization: Researchers are encouraged to investigate the long-term effects of digital contract management tools on reducing legal ambiguities and improving compliance in sports transfers.
- Third-Party Ownership and New Market Dynamics: Further research should analyze how emerging market trends-such as increased investment from new regions and the evolving role of third-party ownership-affect legal risks and contract stability.
- Behavioral and Economic Modelling: Expanding the use of advanced statistical and game theory models can provide deeper insights into negotiation dynamics and the allocation of bargaining power among stakeholders.
- Longitudinal Studies: Conducting longitudinal analyses of legal disputes in player transfers will help identify persistent challenges and the effectiveness of implemented reforms over time.
References
- Alcántara, A., & Ruiz, C. (2022, January 1). Optimal day-ahead offering strategy for large producers based on market price response learning. arXiv (Cornell University). https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.11672.
- AllahRakha, N. (2023, December 19). Legal challenges for international fintech startups. International Journal of Law and Policy, 1(8). [CrossRef]
- Aroyssi, J. A. W., Fathin, M. R., & Priabas, Y. I. (2022). Marketing innovation in the digital communication era. International Journal of Research and Applied Technology, 2(1). [CrossRef]
- Cho, S., Conrad, M., Holden, J. T., & Dodds, M. (2023, August 24). Regulatory schemes and legal aspects of sport governance: Theoretical perspectives and conceptual framework. Journal of Global Sport Management, 9(2), 269. [CrossRef]
- Domizio, D. M., Caruso, R., & Frick, B. (2024, February 1). The appraisal of players’ transfer market values: Empirical evidence from Italian Serie A. International Journal of Sport Finance, 19(1), 39. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z., Li, F., & Tan, C. (2023). Alternating-offers bargaining with Nash bargaining fairness concerns. Behavioral Sciences, 13(2), 124. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-328X/13/2/124/pdf?version=1675260884.
- Ghorbani Asiabar, M., Ghorbani Asiabar, M., & Ghorbani Asiabar, A. (2024, October 9). Legal challenges of big data in judicial proceedings. SSRN. https://ssrn.com/abstract=5247944. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Asiabar, M., Ghorbani Asiabar, M., & Ghorbani Asiabar, A. (2024, June 18). Legal analysis of the role of artificial intelligence in judicial decision-making. SSRN. https://ssrn.com/abstract=5247938. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Asiabar, M. G. A., Ghorbani Asiabar, M., & Ghorbani Asiabar, A. (2025). Legal dimensions of AI contracts in sports talent management: Challenges and solutions [Preprint]. ScienceOpen Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Asiabar, M. G. A., Ghorbani Asiabar, M., & Ghorbani Asiabar, A. (2025). Legal analysis of sports clubs' civil liability for athletes' psychological injuries: Focusing on media and social network pressures [Preprint]. Preprints. [CrossRef]
- Global report on corruption in sport. (2024). [CrossRef]
- The globalization of professional basketball: Context and competition matters in the NBA, WNBA, and Olympics. (2024). The Sport Journal. https://thesportjournal.org/article/the-globalization-of-professional-basketball-context-and-competition-matters-in-the-nba-wnba-and-olympics/.
- Gyamera, E., Atuilik, W. A., Eklemet, I., Adu-Twumwaah, D., Issah, A. B., Tetteh, L. A., et al. (2023, May 4). Examining the effect of financial accounting services on the financial performance of SME: The function of information technology as a moderator. Cogent Business & Management, 10(2). [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T. A., & Bhatti, S. H. (2023, March 22). International business law and regulations. Journal of Social Sciences Review, 3(1), 422. [CrossRef]
- Jurnal Akuntansi dan Pendidikan. (2022). https://e-journal.unipma.ac.id/index.php/assets/article/viewFile/8422/4123.
- Lee, T., White, N. S., & Case. (2023). The Sports Law Review: USA. https://thelawreviews.co.uk/title/the-sports-law-review/usa.
- Mourão, P. R., & Barandela, J. S. (2024, April 9). Exploring soccer transfers in Spanish League–The hidden role of strategic differences among teams. PLoS ONE, 19(4). [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, N. (2022, October 30). Financial transfer in cyber currency and the private international law. Journal Economic & Business Law Review, 2(2), 90. [CrossRef]
- Overcoming regulatory frictions in cross-border payments. (2023). World Economic Forum. https://www.weforum.org/publications/unlocking-interoperability-overcoming-regulatory-frictions-in-cross-border-payments/.
- Qu, R., & Wu, H. (2024, January 4). Research on the influence of football transfer behavior on major leagues in the 21st century. Advances in Economics Management and Political Sciences, 57(1), 122. [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, H., Martinho, D. V., Gouveia, É. R., Afonso, J., Chmura, P., Field, A., et al. (2024, September 11). The influence of playing position on physical, physiological, and technical demands in adult male soccer matches: A systematic scoping review with evidence gap map. Sports Medicine, 54(11), 2841. [CrossRef]
- Thai, Q. H., Khuong, M. N., & Tung, T. (2023). An evolution of entrepreneurial ecosystem studies: A systematic literature review and future research agenda. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. (2023, January 1). Customer perceived value of blind box to customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. SHS Web of Conferences, 165, 1002. [CrossRef]
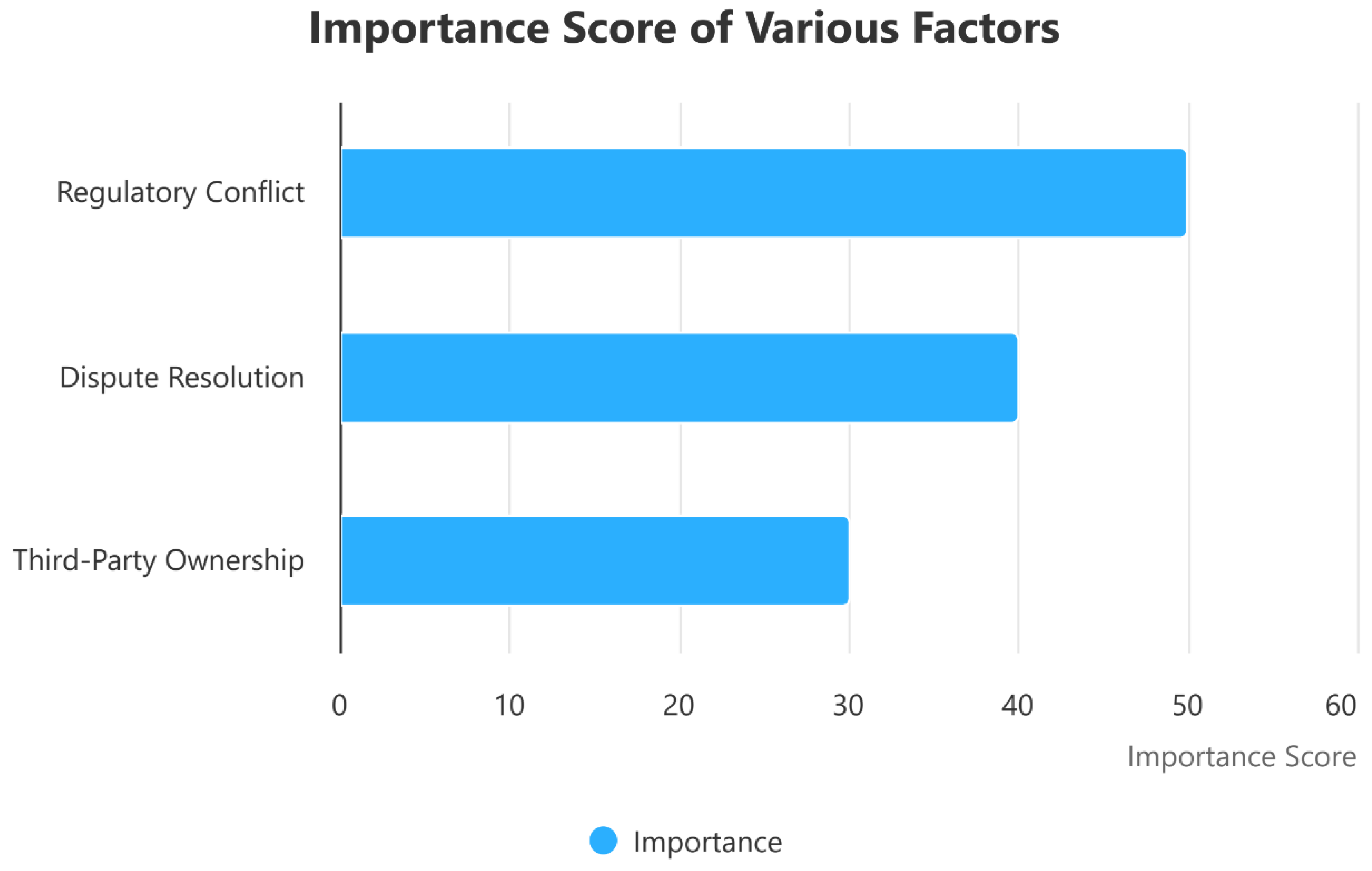
| Legal Risk | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory conflict | Contract invalidation, fines |
| Third-party ownership | Loss of control, sanctions |
| Dispute resolution | Delays, increased costs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





