Submitted:
19 May 2025
Posted:
20 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Works and Our Contributions
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Consistency-Based Feature Selection
| Algorithm 1 CWC [7] over plaintexts |
|
3.2. Computation on FHE
4. Method
4.1. Sorting Network on FHE
4.2. A Naive Algorithm for Private CWC
| Algorithm 2 Naive pCWC for ciphertexts |
|
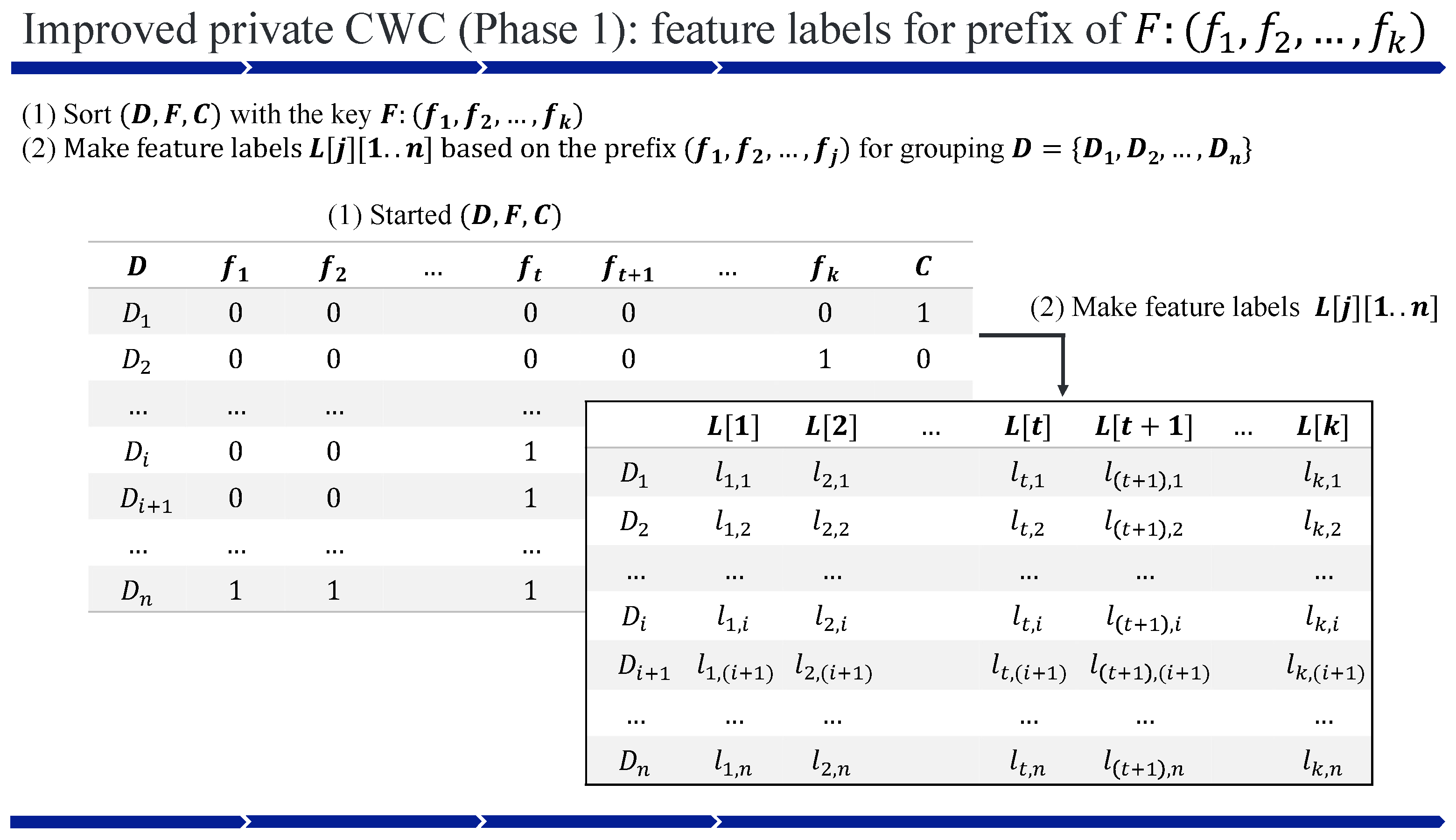
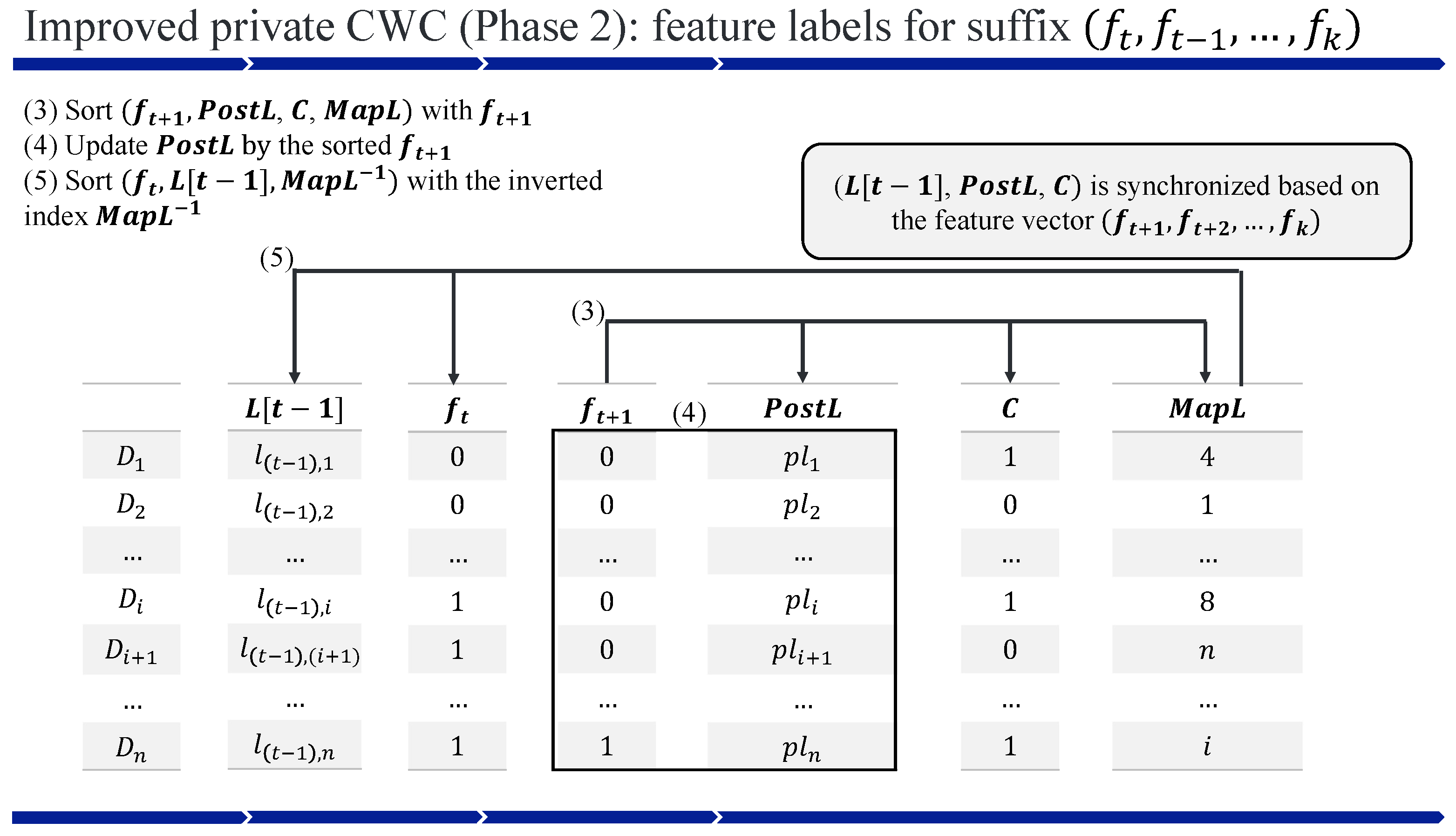
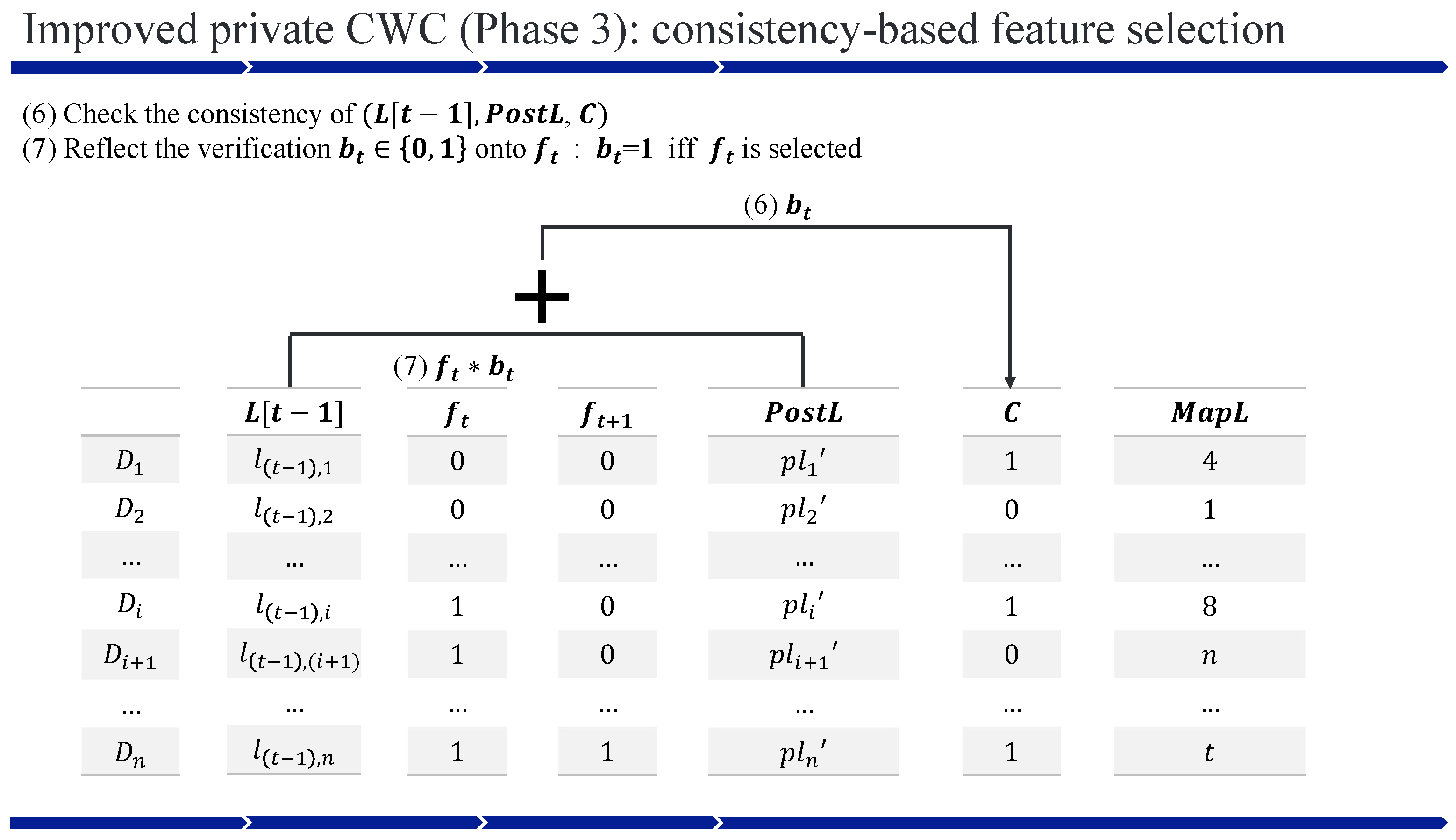
4.3. Improved Private CWC
| Algorithm 3 Improved pCWC for ciphertexts |
|
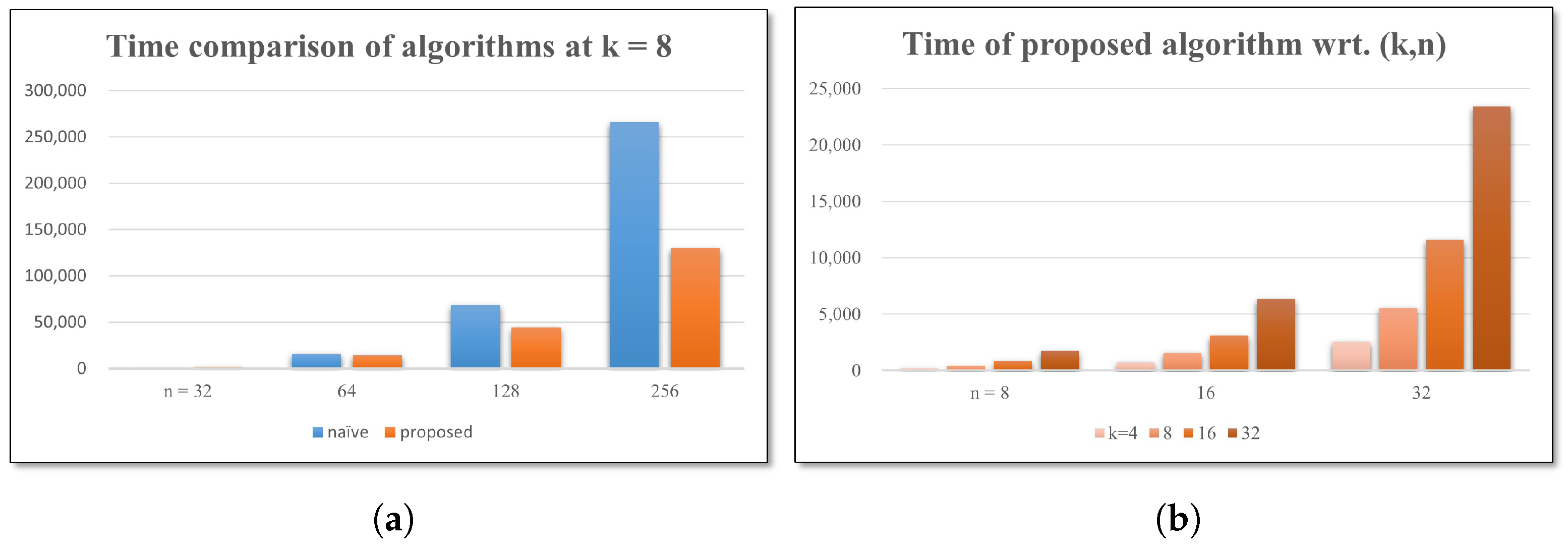
5. Experimental Results
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandrashekar, G.; Sahin, F. A survey on feature selection methods. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2014 40, 16–28. [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough Sets, Theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1991. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Motoda, H.; Dash, M. A monotonic measure for optimal feature selection. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Machine Learning, Chemnitz, Germany, 21–23 April 1998; pp. 101–106. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, H. Searching for interacting features. In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hyderabad, India, 6–12 January 2007; pp. 1156–1161. http://ijcai.org/Proceedings/07/Papers/187.pdf.
- Dash, M.; Liu, H. Consistency-based search in feature selection. Artificial Intell. 2003, 151, 155–176. doi:10.1016/S0004-3702(03)00079-1.
- Arauzo-Azofra, A.; Benitez, J.M.; Castro, J.L. Consistency measures for feature selection. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2008, 30, 273–292. [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Fernandes, D.; Miyazaki, D. Consistency measures for feature selection: A formal definition, relative sensitivity comparison, and a fast algorithm. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Barcelona, Spain, 16–22 July 2011; pp.1491–1497. https://www.ijcai.org/Proceedings/11/Papers/251.pdf.
- Shin, K.; Kuboyama, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Shepard, D. SCWC/SLCC: Highly scalable feature selection algorithms. Information 2017, 8, 159. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Boyle, E.; Chandran, N.; Gilboa, N.; Gupta, D.; Ishai, Y.; Kelkar, M.; Ma, Y. Secure sorting and selection via function secret sharing. Proc. 2024 ACM SIGSAC Conf. Comput. Commun. Secur. (CCS’24), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, Oct 14–18, 2024; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp 3023–3030. [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.; Gillenwater, J.; Joseph, M. Better private linear regression through better private feature selection. In Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), New Orleans, LA, USA, Dec 2023. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3666122.3668448.
- Gentry, C. Fully homomorphic encryption using ideal lattices. In Proceedings of the 41st ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Bethesda, MD, USA, 31 May–2 June 2009; pp. 169–178. [CrossRef]
- Chillotti, I.; Gama, N.; Georgieva, M.; Izabachène, M. TFHE: Fast fully homomorphic encryption over the torus. J. Cryptol. 2020, 33, 34–91. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dai, W.; Kim, M.; Song, Y. Efficient multi-key homomorphic encryption with packed ciphertexts with application to oblivious neural network inference. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 395–412. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ng, W.K.; Zhang, W. Encrypted SVM for outsourced data mining. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing, New York, NY, USA, 20 August 2015; pp.1085–1092. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Huo, H.; Gui, X.; Dai, H. Privacy-preserving outsourcing scheme for SVM on vertically partitioned data. Secur. Commun. Networks 2022, 2022, 9983463. [CrossRef]
- Saeys, Y.; Inza, I.; Larrañaga, P. A review of feature selection techniques in bioinformatics. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(19), 2507–2517. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm344.
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Machine Learning, 2002, 46(1), 389–422. [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1), 5–32. [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(8), 1226–1238. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Setiono, R. A probabilistic approach to feature selection – a filter solution. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Morgan Kaufmann, Bari, Italy, 1996, pp. 319–327. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:17123515.
- Rivest, R.L.; Shamir, A.; Adleman, L. A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Communications of the ACM, 1978, 21(2), 120–126. [CrossRef]
- Goldwasser, S.; Micali, S. Probabilistic encryption. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1984, 28, 270–299.
- Paillier, P. Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Prague, Czech Republic, 2–6 May 1999; pp. 223–238. [CrossRef]
- Boneh, D.; Goh, E.J.; Nissim, K. Evaluating 2-DNF formulas on ciphertexts. In Proceedings of the Theory of Cryptography Conference, Cambridge, MA, USA, 10–12 February 2005; pp. 325–341. [CrossRef]
- Chillotti, I.; Gama, N.; Georgieva, M.; Izabachène, M. TFHE: Fast fully homomorphic encryption library, August 2016. Available online: https://tfhe.github.io/tfhe (accessed on 28 January 2021).
- Rao, V.; Long, Y.; Eldardiry, H.; Rane, S.; Rossi, R.A.; Torres, F. Secure two-party feature selection. arXiv 2019. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:57375741.
- Li, X.; Dowsley, R.; Cock, M.D. Privacy-preserving feature selection with secure multiparty computation. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 6326–6336. https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/li21e/li21e.pdf.
- Akavia, A.; Galili, B.; Shaul, H.; Weiss, M.; Yakhini, Z. Privacy preserving feature selection for sparse linear regression. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2023, 2023, 1354. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Wu, W.; Zhou, L. Efficient and privacy-preserving feature selection based on multiparty computation. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025, 20, 3505–3518. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2025.3546843.
- Ono, S.; Takata, J.; Kataoka, M.; I, T.; Shin, K.; Sakamoto, H. Privacy-preserving feature selection with fully homomorphic encryption. Algorithms 2022, 15, 229. [CrossRef]
- Garey, M.R.; Johnson, D.S. Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-completeness; Series of Books in the Mathematical Sciences, 1st ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, 1979; p.221–222. [CrossRef]
- Bonnoron, G.; Fontaine, C.; Gogniat, G.; Herbert, V.; Lapôtre, V.; Migliore, V.; Roux-Langlois, A. Somewhat/Fully homomorphic encryption: implementation progresses and challenges. In Codes, Cryptology and Information Security; El Hajji, S., Nitaj, A., Souidi, E. M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp 68–82. [CrossRef]
- Batcher, K.E. Sorting networks and their applications. In Proceedings of the American Federation of Information Processing Societies Spring Joint Computing Conference, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 30 April–2 May 1968; pp. 307–314. [CrossRef]
- Hamada, K.; Chida, K.; Ikarashi, D.; Takahashi, K. Oblivious radix sort: an efficient sorting algorithm for practical secure multi-party computation. IACR Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2014 121. https://eprint.iacr.org/2014/121.
- Ajtai, M.; Szemerédi, E.; Komlós, J. An O(nlogn) sorting network. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Boston, MA, USA, 25–27 April 1983; pp.1–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/800061.808726.
- Bost, R.; Popa, R.A.; Tu, S.; Goldwasser, S. Machine learning classification over encrypted data. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. https://eprint.iacr.org/2014/331.pdf.
- Paul, J.; Tan, B.H.M.; Veeravalli, B.; Aung, K.M.M. Non-interactive decision trees and applications with multi-bit TFHE. Algorithms 2022, 15, 333. [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkarim, A.; Al-Rodhaan, M.; Ma, T.; Tian, Y. PPSDT. A novel privacy-preserving single decision tree algorithm for clinical decision-support systems using IoT devices. Sensors 2019, 19, 142. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Naas, S.-A.; Sigg, S.; Lyu, X. Privacy-preserving federated learning based on multi-key homomorphic encryption. arXiv preprint 2021, arXiv:2104.06824. [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.H.; Kim, A.; Kim, M.; Song, Y. Efficient multi-key homomorphic encryption with packed ciphertexts for secure neural network inference. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 395–412. [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.H.; Choe, H.; Kim, S.; Yeo, Y. Reusable dynamic multi-party homomorphic encryption. In Proceedings of the ACM CCS 2025, Seoul, Republic of Korea. 2025. https://eprint.iacr.org/2025/581.
- Namazi, M.; Farahpoor, M.; Ayday, E.; Pérez-González, F. Privacy-preserving framework for genomic computations via multi-key homomorphic encryption. Bioinformatics 2025, 41 (3), btae754. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, W.; Shi, J.; Li, Q. Approximate homomorphic encryption based privacy-preserving machine learning: a survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 82. [CrossRef]
- Naresh, V.S.; Reddi, S. Exploring the future of privacy-preserving heart disease prediction: a fully homomorphic encryption-driven logistic regression approach. J. Big Data 2025, 12, 52. [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.M.; Syed, M.; Shaik, S.; Thalari, S.; Macha, U.; Chatakondu, A. Fully homomorphic encryption framework for privacy preserving in healthcare through decentralized machine learning. In Challenges in Information, Communication and Computing Technology, Sharmila, V., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2025; Volume 2, pp 812–819. [CrossRef]
- Kolhar, M.; Aldossary, S.M. Privacy-preserving convolutional Bi-LSTM network for robust analysis of encrypted time-series medical images. AI 2023, 4, 706–720. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wu, T.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X. Privacy-preserved approximate classification based on homomorphic encryption. Math. Comput. Appl. 2019, 24, 92. [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, M.; Larasati, H. T.; Hyune-Rhee, K. Blockchain-based federated learning with homomorphic encryption for privacy-preserving healthcare data sharing. Internet Things 2025, 31, 101579. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R. Poisoning attacks resilient privacy-preserving federated learning scheme based on lightweight homomorphic encryption. Inf. Fusion 2025, 121, 103131. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Peng, X.; Tan, X. Secure and flexible privacy-preserving federated learning based on multi-key fully homomorphic encryption. Electronics 2023, 13 (22), 4478. [CrossRef]
- Walskaar, I.; Tran, M.C.; Catak, F.O. A practical implementation of medical privacy-preserving federated learning using multi-key homomorphic encryption and flower framework. Cryptography 2023, 7 (4), 48. [CrossRef]
| Algorithm | Metric | Time | Space | # Round | Outsourced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rao et al. [26] | partially | ||||
| Ono et al. [30] | consistency | 1 | partially | ||
| Proposed | consistency | 1 | fully |
| D | C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 0.189 | 0.189 | 0.049 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| D | C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| sorted | ||||||
| 0:000 | 1:000 | 0:000 | 0:000 | 1:000 | 0 | |
| 0:000 | 1:000 | 0:000 | 0:000 | 1:000 | 0 | |
| 1:001 | 0:001 | 0:001 | 0:001 | 1:001 | 1 | |
| 1:001 | 0:001 | 1:010 | 0:010 | 0:010 | 1 | |
| 1:001 | 0:001 | 1:010 | 1:011 | 1:011 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





