1. Introduction
Entropic forces are emergent forces that arise from the statistical tendency of a system to increase its entropy (Taylor & Tabachnik, 2013, Wissner-Gross & Freer 2013). Unlike other fundamental forces (like gravity or electromagnetism), entropic forces originate from the system’s tendency to maximize the number of accessible microstates (Sokolov, 2010). Entropic origin of these forces represents the tendency of a system to evolve into a more probable state, rather than simply into one of lower potential energy (Taylor & Tabachnik, 2013). Elasticity of polymers is driven to a much extent by entropy (Gedde, 2001; Rubinstein & Colby, 2003, Graessley, 2004; Kartsovnik & Volchenkov, 2022). Maximizing entropy of a polymer chain implies reducing the distance between its two free ends. Consequently, an entropic elastic force emerges, that tends to collapse the chain. Elasticity of the muscles arises from entropy in a way very similar to the entropy-driven elasticity of polymer chains (Tskhovrebova, 1997). Entropic forces drive contraction of cytoskeletal networks (Braun et al. 2016). Verlinde suggested that gravity is actually the entropic force (Verlinde, 2011). According to Verlinde, gravity emerges from fundamental principles of statistical mechanics and information theory rather than being a fundamental interaction like electromagnetism. His idea is rooted in holographic principle and thermodynamics (Verlinde, 2011). Verlinde showed that if information about matter is stored on a holographic screen (a surface encoding information about space), then the tendency of entropy to maximize leads to an effect that mimics Newton’s law of gravity (Verlinde, 2011). In a similar way the Coulomb interaction was treated as an entropic force (Wang, 2010).
Usually, entropic forces grow with temperature, however, the exceptions to this rule were reported, when the system of elementary magnets supposed to be in the thermal equilibrium with the thermal bath is exposed to external magnetic field (Bormashenko, 2022).
Our paper addresses the situation when the entropic/polymer spring gives rise to the effect of the negative mass). The effect of the negative mass is a resonance effect, emerging in core-shell mechanical systems. This effect occurs when the frequency of the harmonic external force acting on core-shell system connected by a Hookean massless spring, approaches from above to the eigen-frequency of the system (Liu et al., 2000, Chan et al., 2006; Milton & Willis, 2007, Liu et al., 2011, Yang et al. 2013). Negative-inertia converters for both translational and rotational motion were introduced (Lončar, Igrec, & Babić, 2022).
The energy of the vibrated core-shell system is not conserved, due to the fact that it is exposed to the external harmonic force, as it occurs, for example, in the famous Kapitza pendulum, in which the pivot point vibrates in a vertical direction, up and down (Ramachandran & Nosonovsky, 2014; Hasan & Nosonovsky, M. 2020). Unlike the Kapitza pendulum, the effect of “negative effective mass” arises in the linear approximation to the analysis of the motion (Liu et al., 2000, Chan et al., 2006; Milton & Willis, 2007, Bormashenko, 2025). The effect of the negative effective mass/negative effective density may be achieved with the plasma oscillations of the free electron gas in metals (Huang, Sun & Huang, 2009, Bormashenko & Legchenkova, 2020; Bormashenko et al., 2020).
The effects of negative mass and negative density gave rise to the novel mechanic and thermal metamaterials (Kshetrimayum, 2004; Wu et al., 2019; Li et al., 2021; Karami & Ghayesh, 2024; Wang et al., 2024). The negative effective mass materials were manufactured by dispersion of soft silicon rubber coated heavy spheres in epoxy, acting as the mechanical resonators (Liu et al., 2000). The negative density metamaterial was manufactured in an aluminum plate, comprising the resonant structure (Sang, Mhannawee & Wang, 2019). Soft 3D acoustic metamaterials polymer materials demonstrating negative effective density were reported (Brunet et al. 2014). Our paper is devoted to the possibility of realization of negative mass/density metamaterials exploiting entropic elastic forces.
2. Results
2.1. Negative Mass in the Core-Shell System Driven by Entropic Elastic Force
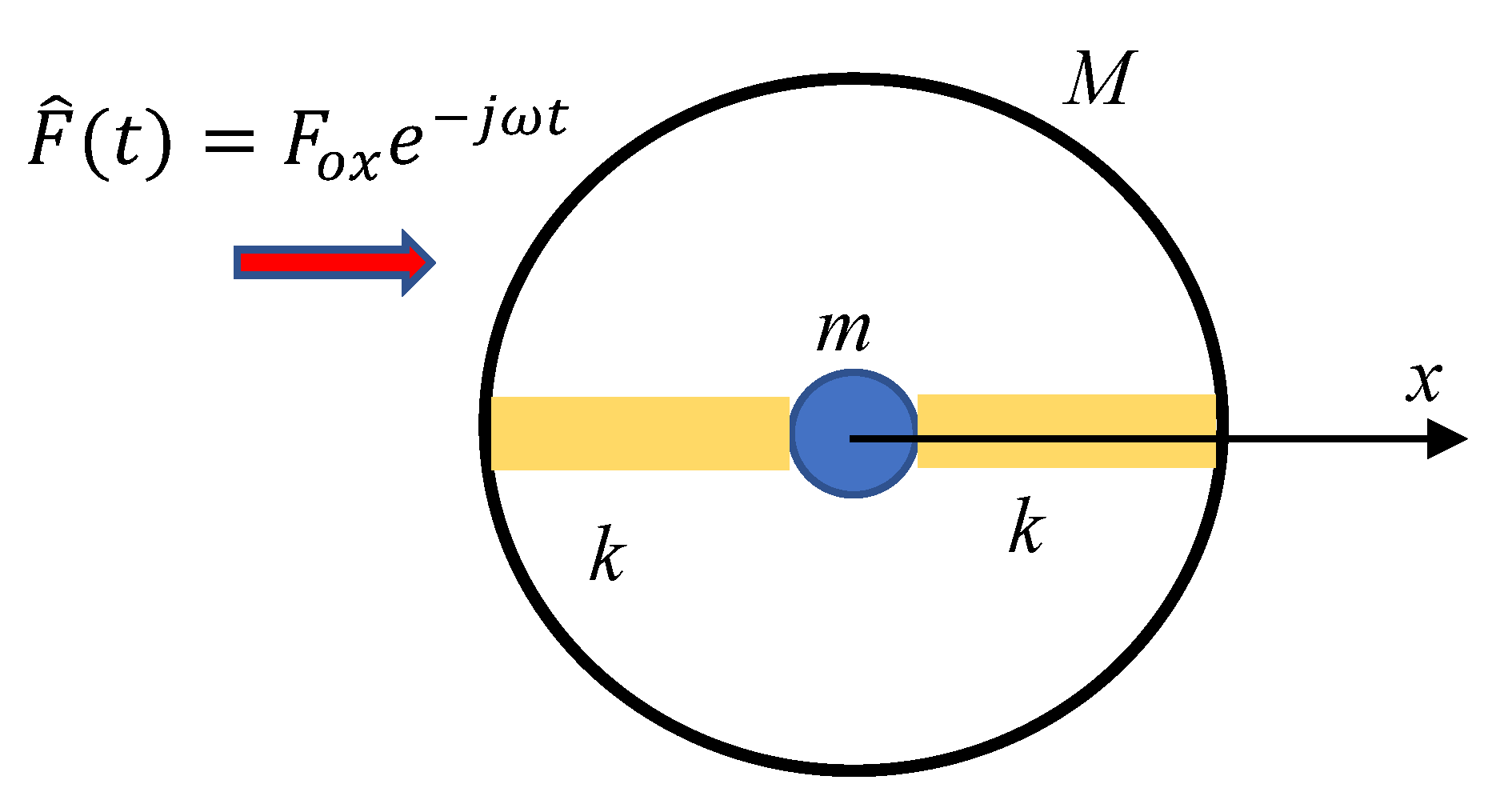
Consider the core-shell mechanical system, depicted in
Figure 1. The core mass
m is connected to the shell
M with two polymer stripes/springs. The entire system is subjected to the external sinusoidal force
, as shown in
Figure 1. We assume that the masses of the polymer stripes are much smaller than both masses of the core and shell; thus, the masses of polymer springs are negligible. The core-shell system may be replaced with a single effective mass
expressed with Eq. 1 (for the rigorous derivation of Eq. 1, see: Chan et al. 2006; Milton & Willis, 2007, Liu et al., 2011; Huang, Sun & Huang, 2009, Bormashenko, 2025).
where
, and
k is the elastic constant of the polymer stripe (the core mass is driven by the pair of polymer springs). It is easily seen from Eq. 1 that, when the frequency
approaches
from above, the effective mass
will be negative (Chan et al. 2006; Milton & Willis, 2007, Liu et al., 2011; Huang, Sun & Huang 2009, Bormashenko, 2025). For the sake of simplicity we assume that the polymer stripe/spring is built of
identical polymer chains, each of which may be represented by the ideal Kuhn equivalent freely jointed chain, built of
N Kuhn monomers, the Kuhn length of the monomer is
b (Rubinstein & Colby, 2003). The elastic constant
k of the polymer spring is given by Eq. 2:
where
is the Boltzmann constant, and
T is the temperature; we assume that the temperature is constant along the addressed core-shell system (Rubinstein & Colby, 2003). Substitution of Eq. 2 into Eq. 1 yields for the effective mass of the entire core-shell system (the masses of the polymer springs are neglected):
Now we fix the frequency of the external force
, and vary the temperature of the core-shell system
T. It is easily seen, that the effective mass
becomes negative when the temperature of the core-shell system approaches the critical temperature
from below, where
is given by Eq. 4:
The dependence
is presented in
Figure 2 (the value of
is fixed). It is instructive to calculate the asymptotic values of
When,
we derive from Eq 3.
which is intuitively clear for an infinitively stiff spring. The low-temperature limit of the effective mass is also easily calculated.
Eq.7 is also intuitively clear; indeed, the influence of the “weak” polymer spring (the temperatures are low) becomes negligible.
2.2. Negative Density of the Chain of Core-Shell Systems Driven by Elastic Forces
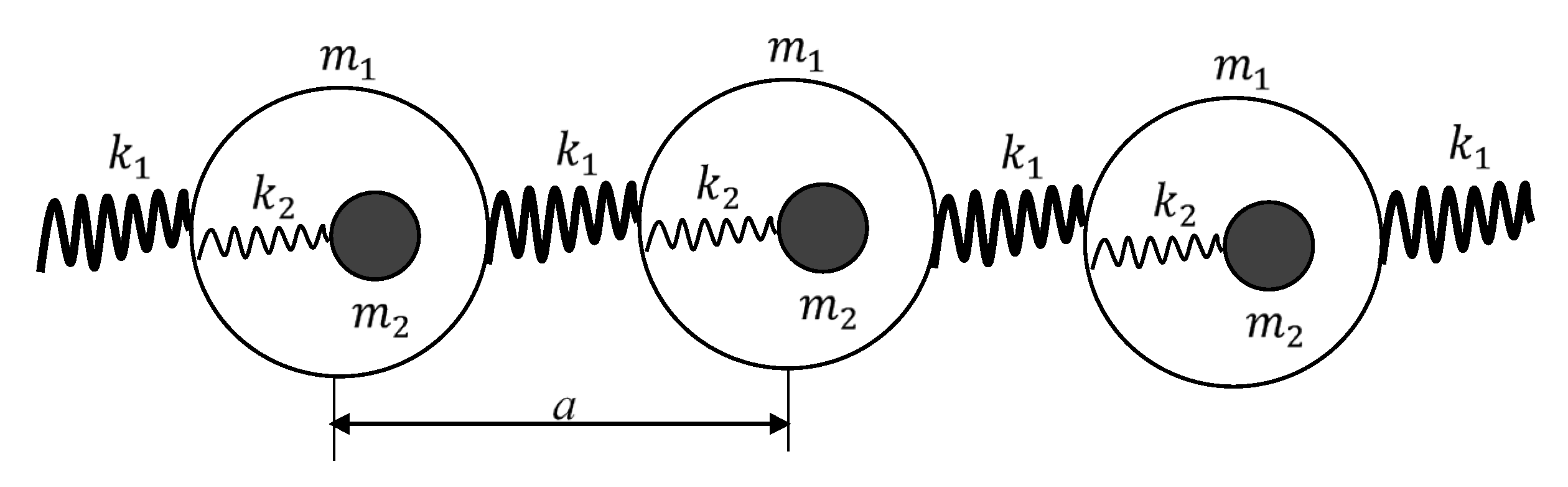
The concept of negative resonant density emerging in the chain of core-shell units, depicted in
Figure 3, was introduced (Huang, Sun, & Huang 2009). The effective density of the chain depicted in
Figure 3 , was calculated (Huang, Sun, & Huang 2009); and it is given by Eq. 8:
where
and
are the masses of the shell and core correspondingly, the static linear density of the chain
is given by:
;
and
a is the lattice constant (see
Figure 3),
. It was demonstrated that the effective density becomes negative, when the frequency of external force
approaches
from above (Huang, Sun, & Huang 2009).
Now we assume that both of the springs are polymer stripes. The elasticity of the stripes is given by Eqs. 9-10 (Rubinstein & Colby, 2003):
where
are the numbers and parameters of the Kuhn chains, constituting the strings. It is noteworthy that the parameter;
is temperature-independent. Thus, the squared resonant frequency
is given by Eq. 11:
where
. Hence, the effective density of the chain appears as follows:
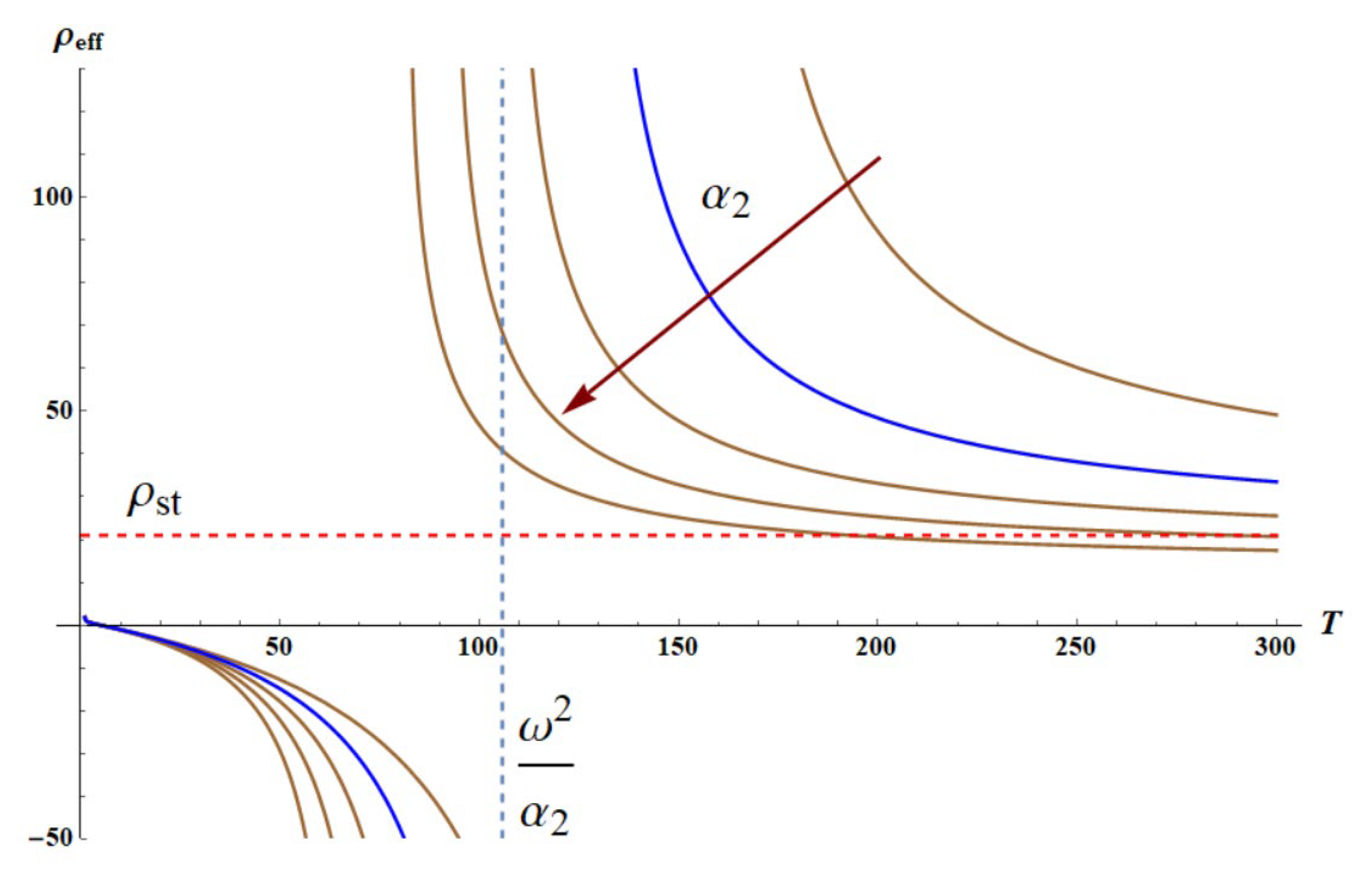
Now we fix the frequency of the external force
The plot
is depicted in
Figure 4. The graph is numerically built with Wolfram Mathematica software. The blue curve depicts the dependence
for the dimensionless parameters:
It is recognized that
becomes negative, when the temperature of the core-shell system approaches to the critical temperature
from below, where
is given by Eq. 13:
where
. Set of the brown curves, appearing in
Figure 4, depicts the temperature dependencies of the effective density
calculated for the different values of
It is easily demonstrated that the high-temperature limit of the effective density is given by Eq. 14:
which is well-expected for the massless, infinitely stiff springs.
3. Discussion
Resonances are ubiquitous in nature and engineering (Feynman, 1964; Ogata, 2005; Manevich & Gendelman 2011). It is well known, that the resonant phenomena may be temperature dependent. The temperature dependence of the resonance frequency of the fundamental and four higher order modes of a silicon dioxide microcantilever was established (Sandberg et al. 2005). Temperature effects in resonant Raman spectroscopy were registered (Fantini et al. 2004). Temperature dependent Raman resonant response in was reported (Livneh, 2022). The temperature dependence of the Fano resonance discovered in infrared spectra of nano-diamonds was discussed (Shiryaev et al. 2022). We address the temperature dependent resonant effects giving rise the phenomenon of the “negative effective mass effect”, exerted to the intensive research in the last decade.
It is unnecessary to say that actually there is no negative mass (Yao, Zhou & Hu, 2008; Huang, Sun & Huang 2009). The phenomenon of the “negative effective mass” arises when we substitute the core-shell mechanical systems comprising a pair of masses (M and m) and the massless Hookean spring k by a single effective mass , that is to say that the internal mass m is hidden and its influence is expressed by the introduction of the mass (Chan et al. 2006; Milton & Willis, 2007, Liu et al., 2011; Yao, Zhou & Hu, 2008; Huang, Sun & Huang, 2009). The negative effective mass represents the contra-intuitive situation of “anti-vibrations”, when the harmonic acceleration of the system is in an opposite direction to the sinusoidal applied force (Chan et al. 2006; Milton & Willis, 2007; Liu et al., 2011; Huang, Sun & Huang, 2009, Bormashenko, 2025). We considered the situation when the vibrations are driven by temperature-dependent entropic forces, inherent for polymer systems. The stiffness of the polymer spring is temperature-dependent, and the physical situation resembling the parametric resonance emerges, when the temperature is varied (Landau & Lifshitz, 2000). Thus, the temperature-dependent effective mass emerges. The effect may be exemplified with polymer acoustic meta-materials (Brunet et al., 2015; Fok & Zhang, 2011).
4. Conclusions
We conclude that the effect of the temperature-dependent effective mass becomes possible in the core-shell systems in which the spring connecting the core mass to the shell is driven by the temperature-dependent entropic elasticity, such as that inherent for polymer materials. The core-shell system may be replaced with a single effective mass exposed to the external harmonic force. When the frequency of the external force is fixed and the temperature of the core-shell system T is varied, the resonance becomes possible, and the harmonic acceleration of the shell may move in an opposite direction to the applied force. We demonstrate that the effective mass becomes negative when the temperature of the core-shell system approaches to the critical temperature from below.
We also considered the chain built of core-shell units, in which entropic forces are acting. In this case, the effect of “negative density” is attainable under variation the temperature of the system. Again, the negative density becomes negative when the temperature of the core-shell system approaches the critical temperature from below. The critical temperature is defined by the parameters of polymer chain and frequency of the external force The effect may be demonstrated experimentally with polymer meta-materials.
Author Contributions
Edward Bormashenko: Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation. Artem Gilevich: Formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation. Shraga Shoval: Conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, writing—original draft preparation.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
This paper is a part of an ongoing research and hence the data cannot be shared at this stage.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Brunet, T. , Merlin, A., Mascaro, B. Zimny, K.m Leng, J., Poncelet, O., Aristégui, Ch. & Mondain-Monval, O. (2014) Soft 3D acoustic metamaterial with negative index. ( 2014) Soft 3D acoustic metamaterial with negative index. Nature Mater. 14, 384–388.
- Bormashenko (Ed.) & Legchenkova, I. (2020) Negative effective mass in plasmonic systems. ( 13(8), 1890.
- Bormashenko (Ed.) , Legchenkova, I. & Frenkel, M. (2020) Negative Effective Mass in Plasmonic Systems II: Elucidating the Optical and Acoustical Branches of Vibrations and the Possibility of Anti-Resonance Propagation. Materials 13. [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko (2022) Magnetic Entropic Forces Emerging in the System of Elementary Magnets Exposed to the Magnetic Field, Entropy, 24(2), 299.
- Bormashenko (Ed.) (2025) Bioinspired Materials and Metamaterials, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl., USA.
- Braun, M. , Lansky, Z., Hilitski, F., Dogic, Z. & Diez, S. (2016) Entropic forces drive contraction of cytoskeletal networks. ( 2016) Entropic forces drive contraction of cytoskeletal networks. BioEssays 38, 474–481. [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. T. , Li, J. & Fung, K. H. (2006) On extending the concept of double negativity to acoustic waves. H. ( 7, 24–28. [CrossRef]
- Fantini, C. , Jorio, A., Souza, M., Strano, M.S., Dresselhaus, M.S. Pimenta, M.A. (2004) Optical Transition Energies for Carbon Nanotubes from Resonant Raman Spectroscopy: Environment and Temperature Effects, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 147406. [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R. (1964) The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Addison Wesley Publishinng Co. Reading, Massachusetts, Palo Alto.
- Fok, L. , & Zhang X. ( Phys. Rev. B 83, 214304. [CrossRef]
- Gedde U., W. (2001) Polymer Physics, Kluwer, Dedrecht, Netherlands.
- Graessley, W.W. Polymeric Liquids and Networks: Structure and Properties; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.S. & Nosonovsky, M. ( Phys. Rev. Fluids 5, 054201.
- Huang, H. H. , Sun, C. T. & Huang, G. L. (2009) On the negative effective mass density in acoustic metamaterials. L. ( 2009) On the negative effective mass density in acoustic metamaterials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 47, 610–617. [CrossRef]
- Karami, B. & Ghayesh, M. H. (2024) Dynamics of graphene origami-enabled auxetic metamaterial beams via various shear deformation theories Int. J. Eng. Sci. 203, 104123. [CrossRef]
- Kartsovnik, VI & Volchenkov, D. ( 24(9), 1260. [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D. & Lifshitz, E.M. (2000) Mechanics, vol.1, Course of Theoretical Physics, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK.
- Lim, C.W. From Photonic Crystals to Seismic Metamaterials: A Review via Phononic Crystals and Acoustic Metamaterials. (2022) Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. ( 2022) Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 29, 1137–1198.
- Liu, X.N. , Hu, G. K., Huang, G. L. & Sun, C. T. (2011) An elastic metamaterial with simultaneously negative mass density and bulk modulus. T. ( 2011) An elastic metamaterial with simultaneously negative mass density and bulk modulus. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 251907.
- Liu, Z. Y. Liu, Z. Y., Zhang, X. X., Mao, Y. W., Zhu, Y.Y., Yang, Z. Y. Chan, C. N. & Sheng, P. (2000) Locally resonant sonic materials, Science 289 (5485), 1734-1736. ( 289(5485), 1734–1736. [PubMed]
- Livneh, T. (2022) Resonant Raman scattering in UO2 revisited, Phys. Rev. B 105, 045115.
- Lončar, J. , Igrec, B. & Babić, D. (2022) Negative-Inertia Converters: Devices Manifesting Negative Mass and Negative Moment of Inertia, Symmetry 14(3), 529.
- Manevich, L.I. & Gendelman, O. (2011) Tractable models of solid mechanics: Formulation, analysis and interpretation, Springer, Berlin, Ge.
- Milton, G. W. & Willis, J. R. (2007) On modifications of Newton’s second law and linear continuum elastodynamics. Proc. R. Soc. A, 463.
- Ogata, K (2005). System Dynamics (4th ed.). Harlow, Pearson, NJ. USA.
- Peralta, I. , Fachinotti, V. D. & Álvarez Hostos, J. C. (2020) A Brief Review on Thermal Metamaterials for Cloaking and Heat Flux Manipulation, Adv. Eng. Mater. 22.
- Ramachandran, R. , & Nosonovsky, M. (2014) Vibro-levitation and inverted pendulum: parametric resonance in vibrating droplets and soft materials, Soft Matter 10, 4633-4639.
- Rubinstein, M. & Colby R. H. Polymer Physics, Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 2003.
- Sandberg, R. , Svendsen, W., Mølhave, K. & Boisen, A. (2005) Temperature and pressure dependence of resonance in multi-layer microcantilevers, J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 1454. [CrossRef]
- Sang, S. , Mhannawee, A. & Wang, Z. (2019) A design of active elastic metamaterials with negative mass density and tunable bulk modulus. Acta Mech. 230, 1003–1008.
- Shiryaev, A.A. , Ekimov, E.A., Prokof’ev, V.Y. et al. (2022) Temperature Dependence of the Fano Resonance in Nanodiamonds Synthesized at High Static Pressures. Y. et al. ( 2022) Temperature Dependence of the Fano Resonance in Nanodiamonds Synthesized at High Static Pressures. Jetp. Lett. 115, 651–656. [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, I. M. (2010) Statistical mechanics of entropic forces: disassembling a toy. Eur. J. Phys. 31,.
- Taylor, P. L & Tabachnik, J. (2013) Entropic forces—making the connection between mechanics and thermodynamics in an exactly soluble model. Eur. J. Phys. 34,.
- Tskhovrebova, L. , Trinick, J., Sleep, J.A. & Simmons, R.M. (1997) Elasticity and unfolding of single molecules of the giant muscle protein titin. M. ( 387, 308–312.
- Valipour, A. , Kargozarfard, M. H., Rakhshi, M., Yaghootian, A. & Sedighi, H. M. (2021) Metamaterials and their applications: An overview, Proceedings Institution Mechanical Engineers, Part L 2021, 1-40.
- Verlinde, E. (2011) On the origin of gravity and the laws of Newton. J. High Energ. Phys. 2011, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. (2010) Coulomb force as an entropic force, Phys. Rev. 1040; 81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. , Qin, Y., Luo, K., Tian, Q. & Hu H. (2024) Dynamic modeling and simulation of hard-magnetic soft beams interacting with environment via high-order finite elements of ANCF, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 202. [CrossRef]
- Wissner-Gross, A. D & Freer, C. E. (2013) Causal Entropic Forces, Phys. Rev. Lett. E. ( Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 168702.
- Yang, M. , Ma, G., Yang, Z., & Sheng, P. (2013) Coupled Membranes with Doubly Negative Mass Density and Bulk Modulus, Phys. Rev. Lett. ( Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 134301. [CrossRef]
- Yao, S. , Zhou, X. & Hu, G. (2008) Experimental study on negative effective mass in a 1D mass–spring system, New J. Phys. 10.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).