Submitted:
13 May 2025
Posted:
15 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure
2.2. Participants
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
2.3.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.3. Dietary Assessment
2.3.4. The Planetary Health Diet Index
2.3.5. Mediterranean Diet Score
2.3.6. Dietary Inflammatory Index
2.3.7. Environment Impact Indicators
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NCDs | Non-communicable diseases |
| PHD | Planetary Health Diet |
| MD | Mediterranean Diet |
| IPAQ-LF | International Physical Activity Questionnaire—Long Form |
| FFQ | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| MET | Metabolic Equivalent of Task |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| PHDI | Planetary Health Diet Index |
| MDS | Mediterranean Diet Score |
| DII | Dietary Inflammatory Index |
References
- Fanzo, J.; Davis, C. Can diets be healthy, sustainable, and equitable? Current Obesity Reports 2019, 8(4), 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. The Lancet 2019, 0170), 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature 2014, 515(7528), 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Pandian, V.; Davidson, P. M.; Song, Y.; Chen, N.; Fong, D. Y. T. Burden and attributable risk factors of non-communicable diseases and subtypes in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. International Journal of Surgery 2025, 111(3), 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Dietary risks – Level 2 risk. Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. 2024. https://www.healthdata.org/research-analysis/diseases-injuries-risks/factsheets/2021-dietary-risks-level-2-risk (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Steel, N.; Bauer-Staeb, C. M. M.; Ford, J. A.; et al. Changing life expectancy in European countries 1990–2021: A subanalysis of causes and risk factors from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet Public Health 2025, 10(3), e172–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD; FAO. Environmental sustainability in agriculture 2023; Rome, Italy, 2023. [CrossRef]
- FAO. Greenhouse gas emissions from agrifood systems – Global, regional and country trends, 2000–2022; FAOSTAT Analytical Brief Series, No. 94; Rome, Italy, 2024. https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cd3167en.
- FAO. Land statistics 2001–2022 – Global, regional and country trends; FAOSTAT Analytical Briefs, No. 88; Rome, Italy, 2024. [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2024 – Value-driven transformation of agrifood systems; Rome, Italy, 2024c. [CrossRef]
- FAO. Sustainable Diets and Biodiversity – Directions and solutions for policy, research and action; Proceedings of the International Scientific Symposium on Biodiversity and Sustainable Diets: United Against Hunger; Rome, Italy, 2012. https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/i3004e.
- Cacau, L.T.; De Carli, E.; de Carvalho, A.M.; et al. Development and validation of an index based on EAT-Lancet recommendations: The Planetary Health Diet Index. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrowicz, L.; Green, R.; Joy, E.J.M.; Smith, P.; Haines, A. The impacts of dietary change on greenhouse gas emissions, land use, water use, and health: A systematic review. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0165797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghoebar, S.; Mesch, A.; Gulikers, J.; Winkens, L.H.H.; Wesselink, R.; Haveman-Nies, A. Experts’ perceptions on motivators and barriers of healthy and sustainable dietary behaviors among adolescents: The SWITCH project. Appetite 2024, 194, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Gonzalez, P.; López-Toledo, S.; Bach-Faig, A.; Medina, F.-X. Barriers and enablers of healthy eating among university students in Oaxaca de Juarez: A mixed-methods study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoraie, N.M.; Alothmani, N.M.; Alomari, W.D.; Al-Amoudi, A.H. Addressing nutritional issues and eating behaviours among university students: A narrative review. Nutr Res Rev 2025, 38, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, D.; Rešetar, J.; Šteković, M.; Czlapka-Matyasik, M.; Verbanac, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Diet quality and its association with lifestyle and dietary behaviors among Croatian students during two COVID-19 lockdowns. Foods 2023, 12, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieziene, B.; Burkaite, G.; Emeljanovas, A.; Tilindiene, I.; Novak, D.; Kawachi, I. Adherence to Mediterranean diet among Lithuanian and Croatian students during COVID-19 pandemic and its health behavior correlates. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 1000161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavičić Žeželj, S.; Dragaš Zubalj, N.; Fantina, D.; Krešić, G.; Kenđel Jovanović, G. Adherence to Mediterranean diet in University of Rijeka students. Paediatr Croat 2019, 63, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayhan, F.; Helvacı, G. Evaluation of university students' Mediterranean diet quality and sustainable eating behaviors: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res 2025, 35, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcuoğlu, İ. Z.; Kızıltan, G. Effect of nutrition education on diet quality, sustainable nutrition and eating behaviors among university students. Journal of the American Nutrition Association 2022, 41(7), 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pınarlı Falakacılar, Ç.; Yücecan, S. The impact of sustainability courses: Are they effective in improving diet quality and anthropometric indices? Nutrients 2024, 16(11), 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telleria-Aramburu, N.; Bermúdez-Marín, N.; Rocandio, A. M.; et al. Nutritional quality and carbon footprint of university students' diets: Results from the EHU12/24 study. Public Health Nutrition 2022, 25(1), 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazat, L.; Nicklaus, S.; de Lauzon-Guillain, B.; Marty, L. Behavioural determinants of healthy and environmentally friendly diets in French university students. Appetite 2024, 200, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazat, L.; Nicklaus, S.; de Lauzon-Guillain, B.; Marty, L. Identification of three dietary groups in French university students and their associations with nutritional quality and environmental impact. Frontiers in Nutrition 2023, 10, 1323648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaş, H.; Navruz-Varlı, S.; Bilici, S. Adherence to the Planetary Health Diet and its association with diet quality in the young adult population of Türkiye: A large cross-sectional study. Nutrients 2024, 16(6), 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.; Mooney, E.; McCloat, A. The relationship between nutrition knowledge and dietary intake of university students: A scoping review. Dietetics 2025, 4(2), 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C. L.; Marshall, A. L.; Sjöström, M.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2003, 35(8), 1381–1395. [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Sampson, L.; Stampfer, M. J.; et al. Reproducibility and validity of a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. American Journal of Epidemiology 1985, 122(1), 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaić-Rak, A.; Antonić, K. Tablice o sastavu namirnica i pića. Zavod za Zaštitu Zdravlja SR Hrvatske. 1990.
- National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark. Food data (Version 4.2). Technical University of Denmark. 2022. Available online: https://frida.fooddata.dk/index.php?lang=en (accessed on day month year).
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. FoodData Central. U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2019. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on day month year).
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G. F.; Casini, A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 337, a1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Román-Viñas, B.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Corella, D.; La Vecchia, C. Benefits of the Mediterranean diet: Epidemiological and molecular aspects. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 2019, 67, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germani, A.; Vitiello, V.; Giusti, A. M.; Pinto, A.; Donini, L. M.; Del Balzo, V. Environmental and economic sustainability of the Mediterranean diet. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 2014, 65(8), 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernini, S., Berry, E. M., Serra-Majem, L., La Vecchia, C., Capone, R., Medina, F. X., Aranceta-Bartrina, J., Belahsen, R., Burlingame, B., Calabrese, G.; Corella, D.; Donini, L. M.; et al. Med Diet 4.0: The Mediterranean diet with four sustainable benefits. Public Health Nutrition 2017, 20(7), 1322–1330. [CrossRef]
- Marx, W; Veronese, N.; Kelly, J. T.; et al. The dietary inflammatory index and human health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. Advances in Nutrition 2021, 12(5), 1681–1690. [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S. E.; Hurley, T. G.; Hussey, J. R.; Hébert, J. R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutrition 2014, 17(8), 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, E.; Kaptijn, G.; Kuijsten, A.; van Zanten, H. H. E.; Geleijnse, J. M.; van 't Veer, P. SHARP Indicators Database (Version 2) [Dataset]. DANS Data Station Life Sciences. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Petersson, T.; Secondi, L., Magnani, A.; Antonelli, M.; Dembska, K.; Valentini, R.; Varotto, A.; Castaldi, S. SU-EATABLE LIFE: A comprehensive database of carbon and water footprints of food commodities [Dataset]. figshare. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. C. , Howe, G. R.; Kushi, L. H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1997, 65(4 Suppl), 1220S–1231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, E.; Kuijsten, A. , Feskens, E. J. M. Gender differences in diet quality and nutrient intake in European adults. European Journal of Nutrition 2020, 59(3), 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkazemi, D. Gender differences in weight status, dietary habits, and health attitudes among college students in Kuwait: A cross-sectional study. Nutrition and Health 2019, 25(2), 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Rudy, M.; Stanisławczyk, R.; Duma-Kocan, P.; Żurek, J. Gender differences in eating habits of Polish young adults aged 20–26. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19(22), 15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprake, E. F., Russell, J. M., Cecil, J. E., et al. Dietary patterns of university students in the UK: A cross-sectional study. Nutrition Journal 2018, 17(1), 90. [CrossRef]
- Valli, C.; D’Addezio, L., Rosi, A. Educational level and diet quality: A systematic review. Nutrients 2022, 14(5), 1035. [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, A.; King, J. A.; Deighton, K.; et al. The association of smoking with different eating and dietary behaviours: A cross-sectional analysis of 80,296 United Kingdom adults. Addiction 2024, 119(10), 1737–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S. A.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Associations between smoking status and diet quality among Korean adults. Nutrition Research and Practice 2019, 13(3), 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Silva, A.; Lopes, C. Physical activity and diet quality in university students: A cross-sectional study. Public Health Nutrition 2021, 24(15), 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macit-Çelebi, M. S.; Bozkurt, O.; Kocaadam-Bozkurt, B.; Köksal, E. Evaluation of sustainable and healthy eating behaviors and adherence to the Planetary Health Diet Index in Turkish adults: A cross-sectional study. Frontiers in Nutrition 2023, 10, 1180880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacau, L. T.; Benseñor, I. M.; Goulart, A. C.; Cardoso, L. O.; Lotufo, P. A.; Moreno, L. A.; Marchioni, D. M. Adherence to the Planetary Health Diet Index and obesity indicators in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Nutrients 2021, 13, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaadam-Bozkurt, B.; Bozkurt, O. Relationship between adherence to the Mediterranean diet, sustainable and healthy eating behaviors, and awareness of reducing the ecological footprint. International Journal of Environmental Health Research 2023, 33, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seconda, L.; Egnell, M.; Julia, C.; et al. Association between sustainable dietary patterns and body weight, overweight, and obesity risk in the NutriNet-Santé prospective cohort. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2020, 112(1), 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioni, D. M.; Cacau, L. T.; De Carli, E.; Carvalho, A. M.; Rulli, M. C. Low adherence to the EAT-Lancet sustainable reference diet in the Brazilian population: Findings from the National Dietary Survey 2017–2018. Nutrients 2022, 14(6), 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Jacob, L.; Firth, J. Dietary patterns and obesity in young adults: A systematic review. Obesity Reviews 2023, 24(1), e13456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, G.; Mirmiran, P.; Yuzbashian, E.; Azizi, F. A systematic review of diet quality indices in relation to obesity. British Journal of Nutrition 2017, 117(8), 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camprodon-Boadas, P.; Gil-Dominguez, A.; De la Serna, E.; Sugranyes, G.; Lázaro, I.; Baeza, I. Mediterranean diet and mental health in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Nutrition Reviews 2025, 83(2), e343–e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z. Dietary inflammatory potential and the incidence of depression and anxiety: A meta-analysis. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition 2022, 41(1), 24. [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G.; Lampousi, A. M. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9(10), 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Luo, N.; et al. Temporal trends in the Planetary Health Diet Index and its association with cardiovascular, kidney, and metabolic diseases: A comprehensive analysis from global and individual perspectives. Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging 2025, 29(5), 100520. [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Springmann, M.; Hill, J.; Tilman, D. Multiple health and environmental impacts of foods. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2020, 117(24), 13857–13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springmann, M.; Godfray, H. C. J.; Rayner, M.; Scarborough, P. Analysis and valuation of the health and climate change co-benefits of dietary change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 113(15), 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y. X.; Geng, T. T.; Zhou, Y. F.; et al. Adherence to a Planetary Health Diet, environmental impacts, and mortality in Chinese adults. JAMA Network Open 2023, 6(10), e2339468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, A.; Howse, E.; Boylan, S. A scoping review of policies promoting and supporting sustainable food systems in the university setting. Nutrition Journal 2020; 19, 97. [CrossRef]
- Franchini, C.; Biasini, B. , Rosi, A.; Scazzina, F. Best practices for making the university campus a supportive environment for healthy and sustainable diets. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health 2023, 32, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, J.; Campos, L.; Guedes, D.; Roque, L.; Brazão, V.; Truninger, M.; Godinho, C. How to enable healthier and more sustainable food practices in collective meal contexts: A scoping review. Appetite 2023, 187, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.; Herrmann, A.; Quitmann, C.; Stieglbauer, G.; Zeitz, C.; Franke, B.; Danquah, I. Effects of a cafeteria-based sustainable diet intervention on the adherence to the EAT-Lancet planetary health diet and greenhouse gas emissions of consumers: A quasi-experimental study at a large German hospital. Nutrition Journal 2024, 23(1), 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilos, M.; Leggett, Z.; Jeffries, S.; Lupek, M.; Ardon, M. University students’ ecological footprint and lifestyle changes: Awareness vs. action. Education Sciences 2025, 15(4), 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springmann, M.; Wiebe, K.; Mason-D' Croz, D.; Sulser, T. B.; Rayner, M.; Scarborough, P. Health and nutritional aspects of sustainable diet strategies and their association with environmental impacts: A global modelling analysis with country-level detail. The Lancet Planetary Health 2018, 2(10), e451–e461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
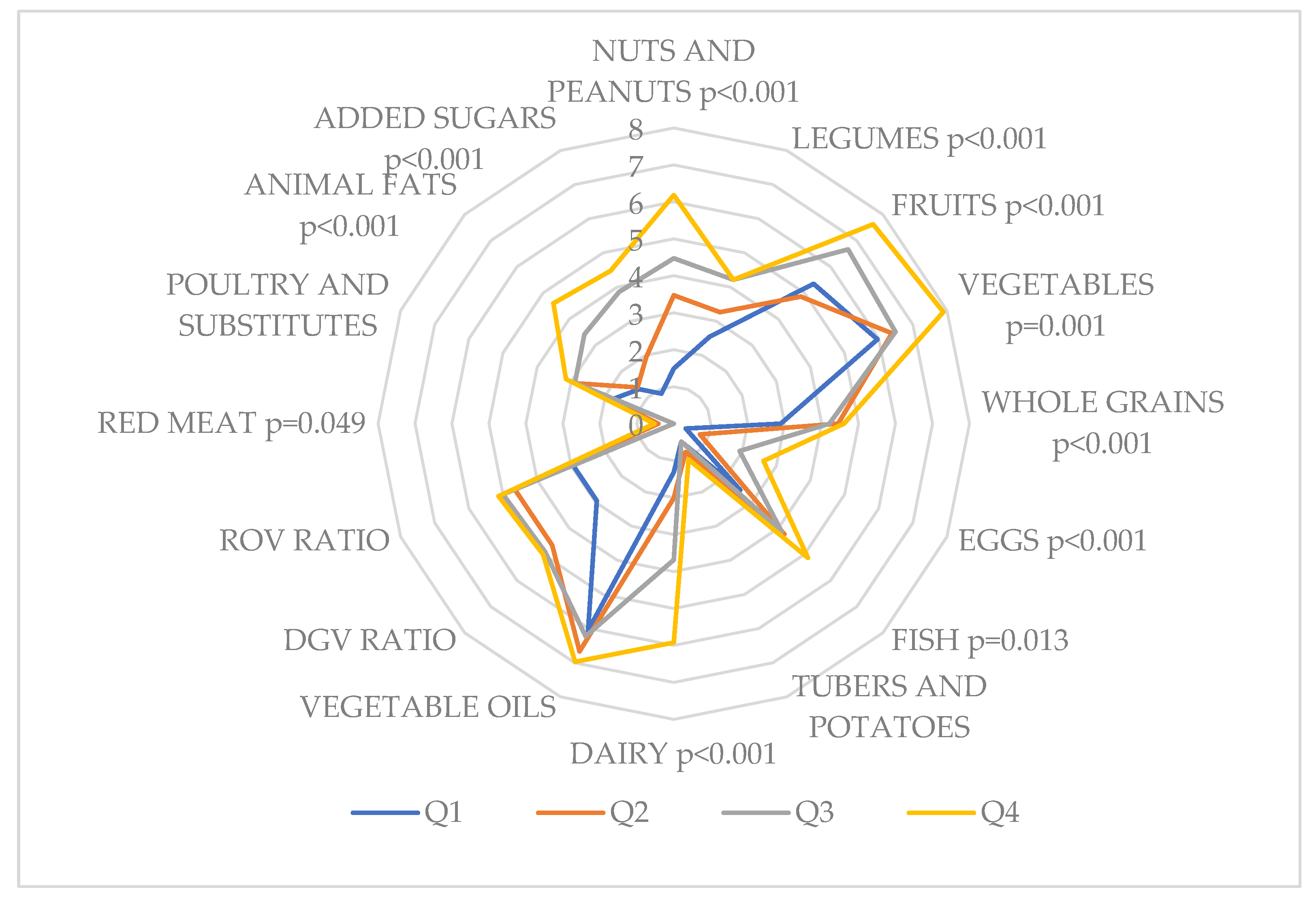
| Variables | N (%) | p-value | Planetary Health Diet Index | p-value | Quartile 1 (20-45) |
Quartile 2 (46-55) |
Quartile 3 (56-65) |
Quartile 4 (66-100) |
p-value |
| N | 224 (100) | 55.54 ± 13.30 | 57 (25) | 72 (32) | 57 (25) | 38 (17) | 0.019 | ||
| Men | 121 (54) | 0.229 | 56.96 ± 11.10 | 0.086 | 23 (40) | 41 (57) | 38 (67) | 19 (50) | 0.038 |
| Women | 103 (46) | 53.87 ± 15.48 | 34 (60) | 31 (43) | 19 (33) | 19 (50) | |||
| Age (years) | 22.67 ± 2.19 | 22.44 ± 1.97 | 22.89 ± 2.33 | 22.67 ± 2.25 | 22.58 ± 2.18 | 0.704 | |||
| Level of study | |||||||||
| Undergraduate | 118 (53) | 0.423 | 54.87 ± 12.50 | 0.188 | 45 (79) | 37 (51) | 27 (47) | 20 (53) | 0.004 |
| Graduate | 106 (47) | 56.27 ± 14.16 | 12 (21) | 35 (49) | 30 (53) | 18 (47) | |||
| Nonsmokers | 168 (75) | <0.001 | 55.83 ± 13.62 | 0.563 | 46 (81) | 51 (71) | 41 (72) | 30 (79) | 0.521 |
| Smokers | 56 (25) | 54.64 ± 12.35 | 11 (19) | 21 (29) | 16 (28) | 8 (21) | |||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.11 ± 3.50 | 23.29 ± 2.93 | 24.55 ± 3.86 | 24.08 ± 3.50 | 24.65 ± 3.50 | 0.181 | |||
| Underweight | 6 (3) | <0.001 | 53.33 ± 10.33 | 0.750 | 3 (5) | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 0.653 |
| Normal weight | 139 (62) | 54.93 ± 13.12 | 37 (65) | 43 (60) | 39 (68) | 20 (53) | |||
| Overweight | 64 (28) | 56.56 ± 13.74 | 15 (26) | 23 (32) | 12 (21) | 14 (37) | |||
| Obesity | 15 (7) | 57.67 ± 14.74 | 2 (4) | 5 (7) | 5 (9) | 3 (8) | |||
| Physical activity level | |||||||||
| Low | 45 (20) | <0.001 | 57.13 ± 11.32 | 0.101 | 11 (19) | 15 (21) | 12 (21) | 7 (18) | 0.001 |
| Moderate | 99 (44) | 53.98 ± 13.98 | 35 (62) | 37 (51) | 16 (28) | 11 (29) | |||
| Vigorous | 80 (36) | 58.27 ± 12.56 | 11 (19) | 20 (28) | 29 (51) | 20 (53) | |||
| Energy intake (kcal/day) | 2397.59 ± 1197.53 | 1951.67 ± 1233.90 | 2465.86 ± 1164.32 | 2692.25 ± 1135.83 | 2495.12 ± 1151.53 | 0.007 | |||
| Mediterranean Diet Score (MDS) | 4.00 ± 1.47 | 3.04 ± 1.27 | 3.96 ± 1.41 | 4.46 ± 1.39 | 4.82 ± 1.20 | <0.001 | |||
| Low adherence (MDS≤4) | 141 (63) | <0.001 | 51.63 ± 12.78 | <0.001 | 49 (86) | 49 (68) | 29 (51) | 14 (37) | <0.001 |
| High adherence (MDS ≥5) | 83 (37) | 62.17 ± 11.45 | 8 (14) | 23 (32) | 28 (49) | 24 (63) | |||
| Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) |
1.07 ± 2.62 | 3.03 ± 2.13 | 1.25 ± 2.49 | -0.19 ± 2.13 | -0.31 ± 2.29 | <0.001 | |||
| Proinflammatory diet (DII > 0) | 139 (62) | <0.001 | 51.12 ± 13.28 | <0.001 | 53 (93) | 47 (65) | 25 (44) | 14 (37) | <0.001 |
| Anti-inflammatory diet (DII < 0) | 85 (38) | 62.76 ± 9.71 | 4 (7) | 25 (35) | 32 (14) | 24 (63) | |||
| Variables | Carbon footprint (kg CO2 eqv.)/1000 kcal |
Water footprint (m3)/1000 kcal |
Ecological footprint (m2*year)/1000 kcal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 2.22 ± 0.53 | 1.90 ± 0.34 | 4.83 ± 1.37 |
| Men | 2.33 ± 0.53 | 1.95 ± 0.34 | 5.13 ± 1.33 |
| Women | 2.11 ± 0.50 | 1.74 ± 0.34 | 4.47 ± 1.33 |
| p-value | 0.002 | 0.017 | <0.001 |
| Level of study | |||
| Undergraduate | 2.27 ± 0.43 | 1.93 ± 0.31 | 4.98 ± 1.22 |
| Graduate | 2.17 ± 0.57 | 1.87 ± 0.37 | 4.65 ± 1.50 |
| p-value | 0.137 | 0.186 | 0.077 |
| Smoking status | |||
| Smokers | 2.25 ± 0.55 | 1.89 ± 0.34 | 4.81 ± 1.34 |
| Nonsmokers | 2.21 ± 0.53 | 1.90 ± 0.34 | 4.83 ± 1.38 |
| p-value | 0.643 | 0.812 | 0.920 |
| BMI category | |||
| Underweight | 2.26 ± 0.29 | 1.86 ± 0.12 | 4.76 ± 0.66 |
| Normal weight | 2.22 ± 0.57 | 1.91 ± 0.37 | 4.83 ± 1.48 |
| Overweight | 2.15 ± 0.48 | 1.85 ± 0.30 | 4.67 ± 1.23 |
| Obesity | 2.49 ± 0.32 | 2.05 ± 0.21 | 5.43 ± 0.78 |
| p-value | 0.176 | 0.242 | 0.278 |
| Physical activity level | |||
| Low | 2.18 ± 0.52 | 1.86 ± 0.34 | 4.72 ± 1.31 |
| Moderate | 2.27 ± 0.54 | 1.92 ± 0.35 | 4.90 ± 1.41 |
| Vigorous | 2.13 ± 0.51 | 1.88 ± 0.32 | 4.71 ± 1.32 |
| p-value | 0.216 | 0.632 | 0.587 |
| Mediterranean Diet Score | |||
| Low adherence (MDS ≤4) | 2.24 ± 0.57 | 1.93 ± 0.37 | 4.87 ± 1.44 |
| High adherence (MDS ≥5) | 2.19 ± 0.45 | 1.85 ± 0.27 | 4.75 ± 1.24 |
| p-value | 0.462 | 0.052 | 0.535 |
| Dietary Inflammatory Index | |||
| Pro-inflammatory diet (DII >0) | 2.20 ± 0.60 | 1.91 ± 0.39 | 4.76 ± 1.48 |
| Anti-inflammatory diet (DII <0) | 2.25 ± 0.41 | 1.88 ± 0.24 | 4.93 ± 1.11 |
| p-value | 0.492 | 0.448 | 0.333 |
| Planetary Health Diet Index | |||
| Quartile 1 | 2.46 ± 0.53 | 2.07 ± 0.36 | 5.43 ± 1.30 |
| Quartile 2 | 2.20 ± 0.50 | 1.89 ± 0.28 | 4.73 ± 1.27 |
| Quartile 3 | 2.15 ± 0.57 | 1.83 ± 00.39 | 4.66 ± 1.45 |
| Quartile 4 | 2.01 ± 0.41 | 1.77 ± 0.25 | 4.35 ± 1.26 |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Environmental impact indicators | PDHI (z-score) | |||
| β | 95 % CI | p-value | ||
| Carbon footprint (kg CO2 equivalent)/1000kcal | ||||
| Model crude | -7.24 | -10.41 | -4.06 | <0.001 |
| Model adjusted | -7.94 | -11.17 | -4.72 | <0.001 |
| Water footprint (m3)/1000kcal | ||||
| Model crude | -12.96 | -17.81 | -8.11 | <0.001 |
| Model adjusted | -13.88 | -18.76 | -8.99 | <0.001 |
| Ecological footprint (m2*year) /1000kcal | ||||
| Model crude | -2.80 | -4.03 | -1.56 | <0.001 |
| Model adjusted | -3.15 | -4.41 | -1.89 | <0.001 |
| PDHI (z-score) | ||||
| β | 95 % CI | p-value | ||
| Energy (kcal/d) | 2.15 | 0.59 | 3.70 | 0.007 |
| Protein (g/d) | -0.38 | -0.69 | -0.07 | 0.017 |
| Animal protein (g/d) | -0.46 | -0.71 | -0.22 | <0.001 |
| Vegetable protein (g/d) | 1.94 | 1.24 | 2.64 | <0.001 |
| Total fat (g/d) | 0.14 | -0.14 | 0.32 | 0.324 |
| Saturated fat (g/d) | -1.67 | -2.24 | -1.10 | <0.001 |
| Monounsaturated fat (g/d) | 0.80 | 0.36 | 1.23 | <0.001 |
| Polyunsaturated fat (g/d) | 12.47 | 4.18 | 20.77 | 0.003 |
| Omega-3 fatty acids (g/d) | 19.26 | 13.92 | 24.61 | <0.001 |
| Omega-6 fatty acids (g/d) | -39.76 | -55.4 | -24.11 | <0.001 |
| Trans fatty acids (g/d) | -14.50 | -20.70 | -8.31 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/d) | 0.01 | -0.01 | 0.03 | 0.211 |
| Carbohydrates (g/d) | -0.10 | -0.21 | 0.02 | 0.105 |
| Dietary fibres (g/d) | 2.59 | 1.99 | 3.19 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol (g/d) | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.66 | 0.020 |
| Thiamine (mg/d) | 7.67 | -3.76 | 19.09 | 0.187 |
| Riboflavin (mg/d) | 4.34 | -1.18 | 11.05 | 0.113 |
| Niacin (mg/d) | 0.49 | -0.46 | 1.44 | 0.312 |
| Folate (μg/d) | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.16 | <0.001 |
| Pyridoxine (mg/d) | 1.17 | -2.59 | 4.94 | 0.539 |
| Cobalamin (μg/d) | -0.51 | -2.53 | 1.51 | 0.622 |
| Vitamin C (mg/d) | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Beta-carotene (mg/d) | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Retinol (RE/d) | -0.01 | -0.02 | 0.07 | 0.518 |
| Vitamin D (μg/d) | 1.31 | -1.22 | 3.84 | 0.308 |
| Vitamin E (mg/d) | 1.57 | 1.20 | 1.94 | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mg/d) | -0.01 | -0.03 | -1.96 | 0.027 |
| Potassium (mg/d) | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mg/d) | -0.03 | -0.02 | 0.11 | 0.684 |
| Phosphorus (mg/d) | -0.02 | -0.00 | -0.15 | 0.815 |
| Magnesium (mg/d) | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.22 | <0.001 |
| Iron (mg/d) | 2.68 | 1.71 | 3.64 | <0.001 |
| Zinc (mg/d) | 0.88 | -1.00 | 2.77 | 0.357 |
| Selenium (mg/d) | 0.21 | -0.11 | 0.52 | 0.206 |
| Iodine (μg/d) | -0.19 | -0.42 | 0.04 | 0.109 |
| Caffeine (mg/d) | -0.10 | -0.21 | 0.01 | 0.084 |
| Flavan 3-ol (mg/d) | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.010 |
| Flavones (mg/d) | 7.16 | 5.20 | 9.13 | <0.001 |
| Flavanols (mg/d) | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.21 | <0.001 |
| Flavonones (mg/d) | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.008 |
| Anthocyanidins (mg/d) | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.38 | 0.004 |
| PDHI (z-score) | ||||
| β | 95 % CI | p-value | ||
| Nuts and peanuts | 1.38 | 1.03 | 1.74 | <0.001 |
| Legumes | 1.41 | 1.43 | 2.40 | 0.005 |
| Fruits | 1.40 | 0.86 | 1.94 | <0.001 |
| Vegetables | 3.56 | 2.34 | 4.78 | <0.001 |
| Whole grains | 0.18 | -0.31 | 0.67 | 0.465 |
| Eggs | 0.44 | -0.19 | 1.07 | 0.167 |
| Fish | 0.90 | 0.41 | 1.40 | <0.001 |
| Tubers and potatoes | -0.03 | -0.44 | 0.38 | 0.876 |
| Dairy | -0.46 | -0.69 | -0.23 | <0.001 |
| Vegetable oils | 0.90 | 0.43 | 1.37 | <0.001 |
| Dark green vegetables ratio | -0.02 | -0.11 | 0.06 | 0.577 |
| Red to orange vegetables ratio | 0.06 | -0.02 | 0.10 | 0.158 |
| Red meat | -0.21 | -0.56 | 0.14 | 0.234 |
| Poultry and substitutes | -0.90 | -1.42 | -0.38 | <0.001 |
| Animal fats | -18.11 | -24.47 | -11.77 | <0.001 |
| Added sugars | -0.57 | -0.84 | -0.27 | <0.001 |
| Mediterranean Diet Score | 4.29 | 3.22 | 5.36 | <0.001 |
| Dietary Inflammatory Index | -2.91 | -3.51 | -2.32 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





