Submitted:
10 May 2025
Posted:
12 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Background:
Current state of developed AI software for Echocardiographic analysis:
Challenges of Ai in echocardiography of complex congenital heart disease
Key solutions for achieving image-specific diagnosis in complex congenital heart disease.
Standardization of the image protocol and quality:
Segmental analysis
The emergence of Visual large language models as a potential solution:
Conclusion:
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CHD | Congenital Heart Disease |
| CXCHD | Complex Congenital Heart Disease |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| VLM/VLLM | Vision Language Model/Large Language Model |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| STE | Speckle Tracking Echocardiography |
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tworetzky W, McElhinney DB, Brook MM, Mohan Reddy V, Hanley FL, Silverman NH (1999) Echocardiographic diagnosis alone for the complete repair of major congenital heart defects. J Am Coll Cardiol 33:228–233. [CrossRef]
- Mcleod G, Shum K, Gupta T, Chakravorty S, Kachur S, Bienvenu L, White M, Shah SB (2018) Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 61:468–475. [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz RA, Caldwell RL (1998) Should Pediatric Echocardiography Be Performed in Adult Laboratories? Pediatrics 102:e15–e15. [CrossRef]
- Koestenberger M (2012) Transthoracic echocardiography in children and young adults with congenital heart disease. ISRN Pediatr 2012:753481. [CrossRef]
- White BR, Ho DY, Rogers LS, Natarajan SS (2019) A standardized imaging protocol improves quality and reduces practice variability in echocardiographic assessment of ventricular function by first-year pediatric cardiology fellows. Echocardiography 36:1515–1523. [CrossRef]
- Samyn MM, Yan K, Masterson C, Goot BH, Saudek D, Lavoie J, Kinney A, Krolikowski M, Hor K, Cohen S (2019) Echocardiography vs cardiac magnetic resonance imaging assessment of the systemic right ventricle for patients with d-transposition of the great arteries status post atrial switch. Congenit Heart Dis 14:1138–1148. [CrossRef]
- Baessato F, Fusini L, Muratori M, Tamborini G, Ghulam Ali S, Mantegazza V, Baggiano A, Mushtaq S, Pepi M, Patti G, Pontone G (2023) Echocardiography vs. CMR in the Quantification of Chronic Mitral Regurgitation: A Happy Marriage or Stormy Divorce? J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 10:150. [CrossRef]
- Kramer CM, Barkhausen J, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Flamm SD, Kim RJ, Nagel E (2020) Standardized cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) protocols: 2020 update. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 22:1–18. [CrossRef]
- Soemantoro R, Kardos A, Tang G, Zhao Y (2023) An AI-powered navigation framework to achieve an automated acquisition of cardiac ultrasound images. Sci Rep 13:1–13. [CrossRef]
- Yang PC, Jha A, Xu W, Song Z, Jamp P, Teuteberg JJ (2024) Cloud-Based Machine Learning Platform to Predict Clinical Outcomes at Home for Patients With Cardiovascular Conditions Discharged From Hospital: Clinical Trial. JMIR Cardio 8:. [CrossRef]
- Anisuzzaman DM, Malins JG, Jackson JI, Lee E, Naser JA, Rostami B, Greason G, Bird JG, Friedman PA, Oh JK, Pellikka PA, Thaden JJ, Lopez-Jimenez F, Attia ZI, Pislaru S V, Kane GC (2025) Leveraging Comprehensive Echo Data to Power Artificial Intelligence Models for Handheld Cardiac Ultrasound. Mayo Clin proceedings Digit Heal 3:100194. [CrossRef]
- Abdelmassih AF, Haidar W, Alabid S, Attallah T, Khraisat B, Khan A, Hafez B (2025) Understanding Why Postpericardiotomy Syndrome is More Common after Surgical Atrial Septal Defect Closure : A Sneak Peek at Atrial Functions by Speckle - tracking Echocardiography. 101–104. [CrossRef]
- Cioccari L, Baur HR, Berger D, Wiegand J, Takala J, Merz TM (2013) Hemodynamic assessment of critically ill patients using a miniaturized transesophageal echocardiography probe. Crit Care 17:. [CrossRef]
- Christensen M, Vukadinovic M, Yuan N, Ouyang D (2024) Vision–language foundation model for echocardiogram interpretation. Nat Med 30:1481–1488. [CrossRef]
- Holste G, Oikonomou EK, Tokodi M, Kovács A, Wang Z, Khera R (2024) PanEcho: Complete AI-enabled echocardiography interpretation with multi-task deep learning.
- Wessler BS, Huang Z, Long GM, Pacifici S, Prashar N, Karmiy S, Sandler RA, Sokol JZ, Sokol DB, Dehn MM, Maslon L, Mai E, Patel AR, Hughes MC (2023) Automated Detection of Aortic Stenosis Using Machine Learning. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 36:411–420. [CrossRef]
- Vukadinovic M, Tang X, Yuan N, Cheng P, Li D, Cheng S, He B, Ouyang D (2024) EchoPrime: A Multi-Video View-Informed Vision-Language Model for Comprehensive Echocardiography Interpretation.
- Amadou AA, Zhang Y, Piat S, Klein P, Schmuecking I, Passerini T, Sharma P (2024) EchoApex: A General-Purpose Vision Foundation Model for Echocardiography.
- Sadeghpour A, Jiang Z, Hummel YM, Frost M, Lam CSP, Shah SJ, Lund LH, Stone GW, Swaminathan M, Weissman NJ, Asch FM (2025) An Automated Machine Learning–Based Quantitative Multiparametric Approach for Mitral Regurgitation Severity Grading. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 18:1–12. [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll JM, Hawkes W, Beqiri A, Mumith A, Parker A, Upton R, McCourt A, Woodward W, Dockerill C, Sabharwal N, Kardos A, Augustine DX, Balkhausen K, Chandrasekaran B, Firoozan S, Marciniak A, Heitner S, Yadava M, Kaul S, Sarwar R, Sharma R, Woodward G, Leeson P (2022) Left ventricular assessment with artificial intelligence increases the diagnostic accuracy of stress echocardiography. Eur Hear J Open 2:1–10. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad A, Shigemitsu S, Termachi Y, Windram J, Khoo N, Colen T, Eckersley L (2022) Comparing a knowledge-based 3D reconstruction algorithm to TomTec 3D echocardiogram algorithm in measuring left cardiac chamber volumes in the pediatric population. Echocardiography 39:1180–1189. [CrossRef]
- Haji-Hassan M, Duțu B, Bolboacă SD (2023) Handheld Echocardiography Measurements Concordance and Findings Agreement: An Exploratory Study. Diagnostics 13:1–14. [CrossRef]
- Naghavi M, Reeves AP, Atlas K, Zhang C, Atlas T, Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF, Budoff MJ, Li D, Roy SK, Nasir K, Molloi S, Fayad Z, McConnell M V., Kakadiaris I, Maron DJ, Narula J, Williams K, Shah PK, Levy D, Wong ND (2024) Artificial intelligence applied to coronary artery calcium scans (AI-CAC) significantly improves cardiovascular events prediction. npj Digit Med 7:309. [CrossRef]
- Asch FM, Poilvert N, Abraham T, Jankowski M, Cleve J, Adams M, Romano N, Hong H, Mor-Avi V, Martin RP, Lang RM (2019) Automated Echocardiographic Quantification of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Without Volume Measurements Using a Machine Learning Algorithm Mimicking a Human Expert. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 12:1–9. [CrossRef]
- Muhtaseb R, Yaqub M (2022) EchoCoTr: Estimation of the Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction from Spatiotemporal Echocardiography. arXiv:arXiv:2209.04242v1.
- Strom JB, Playford D, Stewart S, Strange G (2024) An Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Detection of Severe Aortic Stenosis: A Clinical Cohort Study. JACC Adv 3:1–12. [CrossRef]
- Edwards LA, Feng F, Iqbal M, Fu Y, Sanyahumbi A, Hao S, McElhinney DB, Ling XB, Sable C, Luo J (2023) Machine Learning for Pediatric Echocardiographic Mitral Regurgitation Detection. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 36:96-104.e4. [CrossRef]
- Karužas A, Balčiūnas J, Fukson M, Verikas D, Matuliauskas D, Platūkis T, Vaičiulienė D, Jurgaitytė J, Kupstytė-Krištaponė N, Dirsienė R, Jaruševičius G, Šakalytė G, Plisienė J, Lesauskaitė V (2022) Artificial intelligence for automated evaluation of aortic measurements in 2D echocardiography: Feasibility, accuracy, and reproducibility. Echocardiography 39:1439–1445. [CrossRef]
- Selmeryd J, Henriksen E, Leppert J, Hedberg P (2016) Interstudy heterogeneity of definitions of diastolic dysfunction severely affects reported prevalence. Eur Hear J – Cardiovasc Imaging 17:892–899. [CrossRef]
- Waisberg E, Ong J, Kamran SA, Paladugu P, Zaman N, Lee AG, Tavakkoli A (2023) Transfer learning as an AI-based solution to address limited datasets in space medicine. Life Sci Sp Res 36:36–38. [CrossRef]
- Ramlogan S, Aly D, France R, Schmidt S, Hinzman J, Sherman A, Goudar SP, Forsha D (2020) Reproducibility and Intervendor Agreement of Left Ventricular Global Systolic Strain in Children Using a Layer-Specific Analysis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 33:110–119. [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara A, Fujita S, Ohno Y, Aoki S (2020) Variability and Standardization of Quantitative Imaging. Invest Radiol 55:601–616. [CrossRef]
- Li XT, Huang RY (2020) Standardization of imaging methods for machine learning in neuro-oncology. Neuro-oncology Adv 2:iv49–iv55. [CrossRef]
- Seetharam K, Thyagaturu H, Ferreira GL, Patel A, Patel C, Elahi A, Pachulski R, Shah J, Mir P, Thodimela A, Pala M, Thet Z, Hamirani Y (2024) Broadening Perspectives of Artificial Intelligence in Echocardiography. Cardiol Ther 13:267–279. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Li L, Jiang Y, Wang H, Qiao X, Feng T, Luo H, Zhao Y (2025) Vision-Language Models in medical image analysis: From simple fusion to general large models. Inf Fusion 118:102995. [CrossRef]
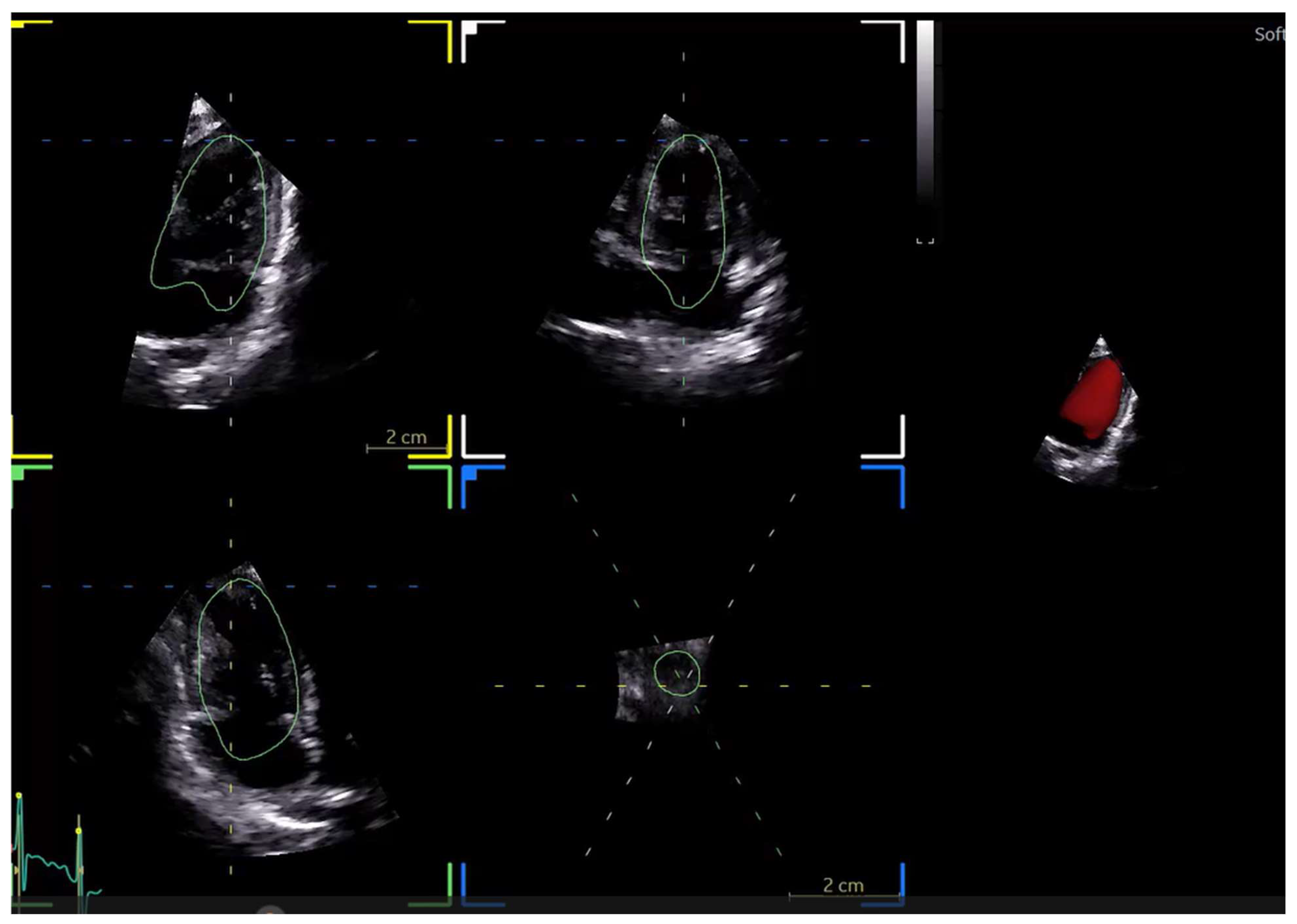
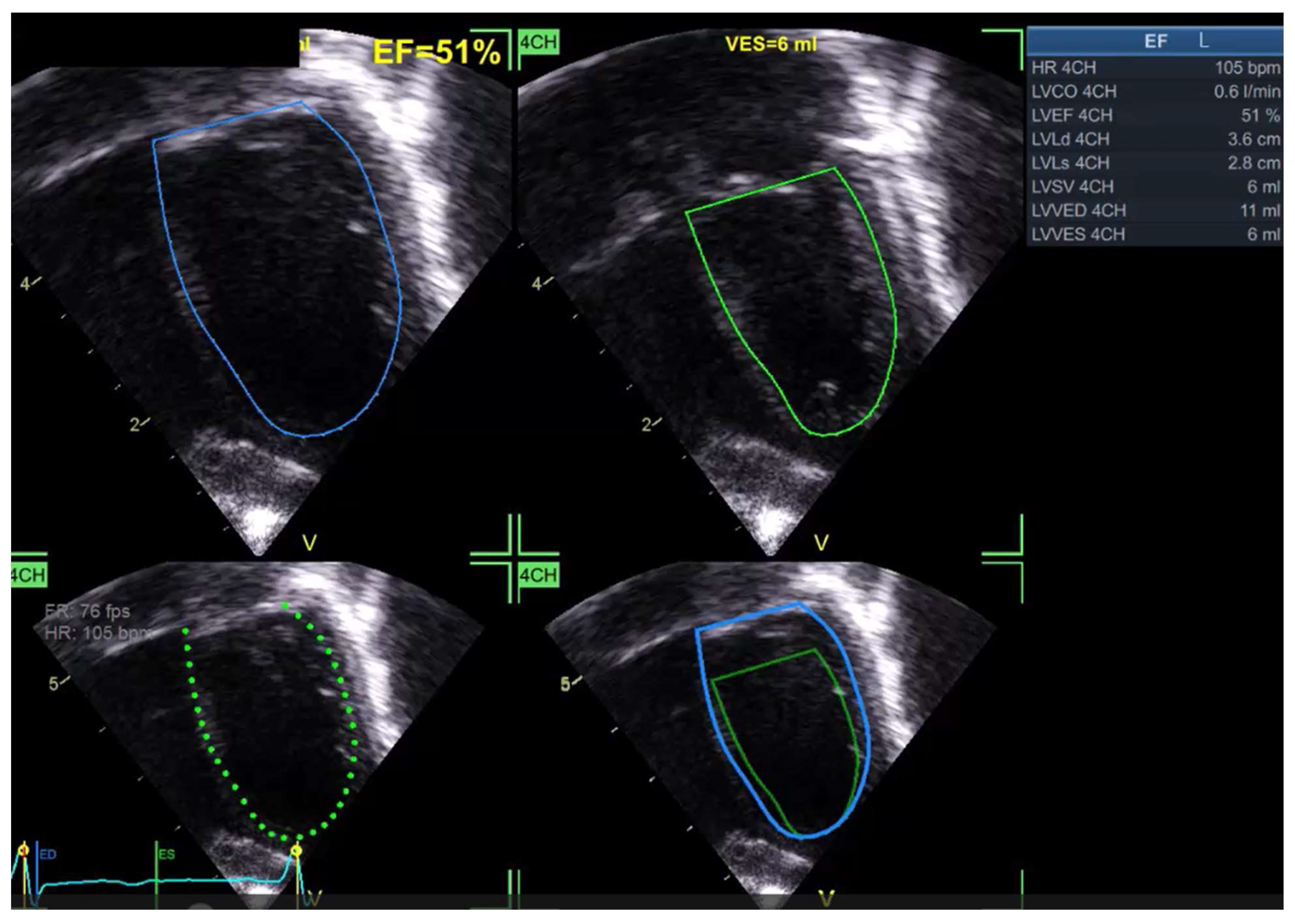
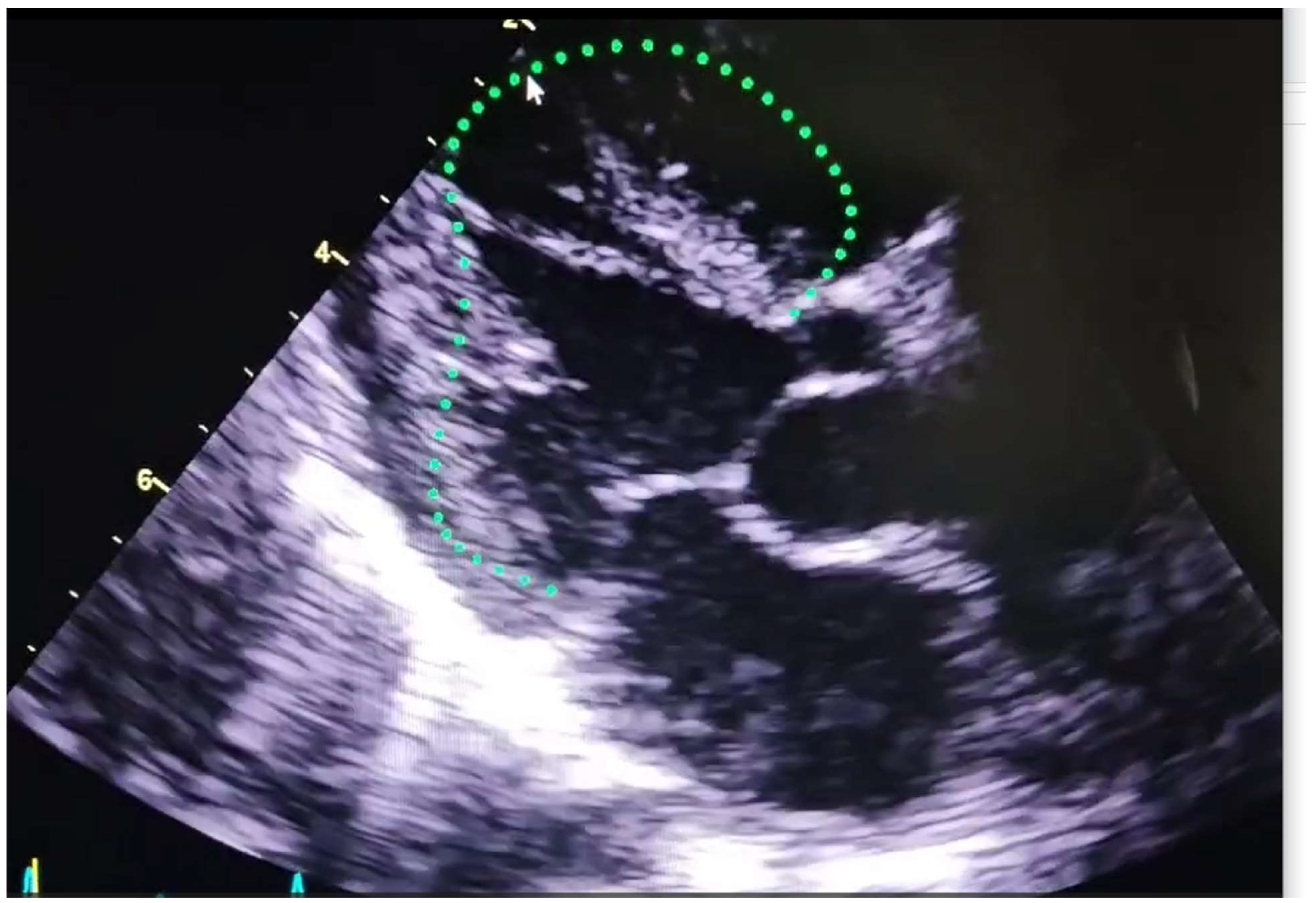

| Software | Main Tools for Echocardiographic Analysis | Developing Company/Institute | Auto EF | Standardizing image acquisition | STE Analysis | Valve function | Image specific diagnosis | Ai model applied | ||
| Standardizing image acquisition | ||||||||||
| Vscan Air SL with Caption AI [9] | Step by step instructions, auto capture images, quality meter “real time feedback on image quality | GE | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | CNN | ||
| Kitware's AI-Powered Ultrasound(No available citations) | Assistance in probe placement, autonomous scanning, CHD identification in newborns. | Kitware | No | Yes | No | No | CNN | |||
| Cloud-based solutions | ||||||||||
| CardioCloud by Cardio-Care [10] | Remote access to studies, echocardiographic analysis | CardioCare | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | CNN | ||
| Main focus: Functional assessment | ||||||||||
| Philips Intellispace Cardiovascular and Tomtec [11] | Advanced echocardiography analysis, 3D reconstruction, integration with other imaging modalities | Philips Healthcare | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | CNN | ||
| GE Healthcare EchoPAC/Verisound [12] | Automated measurements, advanced reporting, comprehensive analysis | GE Healthcare | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | CNN | ||
| Imacor [13] | Myocardial strain assessment, 3D echocardiographic evaluation, hemodynamic ultrasound using TEE in critical care | Imacor | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | CNN | ||
| Automated decision-making regarding fluid therapy in ICU | ||||||||||
| EchoCLIP | Generates full echocardiographic reports, being trained not on individual data sets but on series of full exams and their corresponding expert reports | Researchers at Cedars Sinai Medical Center’s Smidt Heart Institute | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Vision large V/LLM) | ||
| [14] | ||||||||||
| PanEcho [15] | Uses View-agnostic, multi-task deep learning architecture to process Echo videos. It can detect valvular diseases and chamber sizes. Can also accurately estimate LVEF and detect systolic dysfunction | Researchers at Yale School of Medicine and University of Texas at Austin | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | CNN | ||
| EchoMeasure [16] | Uses automated view classification and quality assessment. Provides comprehensive cardiac measurements including Left ventricular volumes, right ventricular diameter, posterior wall thickness, aortic annulus diameter. | iCardio.ai, a Los Angeles- based artificial intelligence company. | Yes | No | No | Yes (AS) | Yes | CNN | ||
| EchoPrime [17] | Consists of multiple modules integral for the interpretation of echocardiography, including video encoder, text encoder, view classifier, and anatomical attention module | Multi-disciplinary team at Cedars-Sinai Medical center | Yes | No | No | Yes | yes | V/LLM | ||
| EchoApex [18] | Uses task specific decoders for view classification, structure segmentation, left ventricular measurement and ejection fracture estimation. | Siemen Healthineers | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | CNN | ||
| Us2.ai[19] | Automated measures (45 echo parameters), disease detection like amyloidosis, generating real time report, POCUS AI guided HF screen | US2.ai Ltd. | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | CNN | ||
| Ultromics EchoGo [20] | Process ECHO data and provide detailed report. HF detection with preserve EF | Ultromics | Yes | No | Yes (including global longitudinal strain (GLS)) | Yes | Yes | CNN | ||
| Ventripoint VMS [21] | The Ventripoint point of care solution, KBR (Knowledge Based Reconstruction) artificial intelligence software algorithm and accurate sensor positioning allows to accurately reconstruct 2D and 3D echo images into accurate 3D models and precision metrics measurements including Heart structure sizes and ejection fraction. | Ventripoint Diagnostic Ltd. A Toronto based medical technology company | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | CNN/VLLM | ||
| First echocardiographic software for diagnosis of Single ventricle (study announced this year) | ||||||||||
| Full report | ||||||||||
| EchoConfidence by MyCardium Ai (no available citations) | Developed for highly accurate automated measurements. Utilizes fixed convolutional neural networks (CNN) trained on over 100,00 images. Comprehensive assessment of chambers, valves, vessles and Pericardium. | MyCardium Ai Ltd, a medical technology company in Liverpool | Yes | No | No (No information that confirms that it performs STE analysis on its website) | Yes | No | CNN | ||
| EchoNous Kosmos [22] | Real time anatomical labeling (fast exam), auto doppler images and auto present real time images quality optimization | EchoNous | Yes | No | No | No | CNN | |||
| Arterys Cardio Ai [23] | Automates the segmentation of cardiac ventricles, assess myocardial scarring and delay enhancement for conditions like hypertrophic myocardiopathy | Arterys | Yes | Yes (advanced tools for strain imaging similar to STE) | No | No | CNN | |||
| Bay Labs EchoMD [24] | Simplifies the process of ECHO analysis to make it accessible for varying expertise levels, integrates IT system for efficient data sharing and reporting | Bay Labs | Yes | No | No | No | No | CNN | ||
| EchoCoTr[25] | Deep learning-based LVEF estimation using spatiotemporal echocardiographic video analysis (CNN + Transformer) | Mohamed Bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI) | Yes | No | No (not designed for speckle tracking) | No | No | CNN | ||
| Main Focus: Valvular Function | ||||||||||
| Echo iq [26] | A software developed to detect aortic stenosis | Boston, Massachusetts, USA | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Stanford University research model [27] | Automated view recognition and mitral regurge classification | Stanford | No | No | No | Yes | No | CNN | ||
| Ligence Heart version 2[28] | Artificial intelligence for automated evaluation of aortic measurements in 2D echocardiography: Feasibility, accuracy, and reproducibility | Ligence | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | CNN | ||
| Main Focus: Fetal echocardiography classification | ||||||||||
| Komatsu et al | Classification of normal and abnormal fetal heart echocardiograms | University School of Medicine-Tokyo | No | No | No | No | No | CNN | ||
| Bridge et al | Classification of normal and abnormal fetal heart echocardiograms | Oxford University | No | No | No | No | No | Feed forward networks | ||
| Abbreviations:Ai: Artificial intelligence, CNN: Convoluted Neural Networks, EF: Ejection fraction, GE: General Electric, HF: Heart failure, LV: Left Ventricle, VLM: Vision Language models, IT: Information technology, MBZUAI: Mohamed Bin Zayed University for Artificial intelligence, USA: United states of America | ||||||||||
| Aspect | Feedforward Networks | Convolutional Neural Networks | Visual Language Models |
| Strengths | Capturing temporal dynamics, motion patterns, fetal ECG analysis | Recognizing patterns from pixel data, structural analysis | Combining imaging with clinical notes, reports, enhancing interpretability |
| Application in Echocardiography | Classification of normal vs. abnormal fetal echocardiograms | Myocardial and Valvular functions | Providing full reports and thus allowing image specific diagnosis |
| Standardization barrier | Standard sequence of images required | Not necessarily required | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





