1. Introduction
With the acceleration of globalization, the volatility of financial markets is increasing. The occurrence of market turmoil not only has a profound impact on economic development but also poses a huge challenge to the stability of investors, financial institutions, and the entire society [
1]. Market turmoil is usually manifested in stock market crashes, currency depreciation, rising credit risks, and other phenomena, which bring a lot of financial risks. How to predict market turmoil in a complex and dynamic financial environment in a timely manner and effectively control risks has become an important issue to be solved in the field of financial technology [
2]. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, especially the successful application of deep reinforcement learning in many fields, more and more scholars and practitioners have begun to try to apply it to the prediction and risk management of financial markets [
3,
4].
As an advanced deep reinforcement learning algorithm, the A3C (Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic) algorithm has demonstrated its powerful ability in solving high-dimensional and complex problems through its unique parallel training mechanism [
5]. The A3C algorithm merges the policy gradient method and the value function method, enabling the acquisition of more stable and efficient decision-making strategies while processing vast datasets. In the task of market turmoil prediction and risk control, the A3C algorithm can understand the inherent laws of market behavior by learning historical market data, and make optimal decisions in a dynamically changing market environment. Therefore, the research on market turbulence prediction and risk control model based on the A3C algorithm has important theoretical significance and practical value [
6].
The prediction of market turbulence is not only the modeling of financial data but also a deep insight into the potential risks of the market. Traditional financial market prediction methods mostly rely on statistical models and machine learning algorithms, which usually cannot fully consider the complexity and nonlinear characteristics of the market. Especially when the market environment changes, traditional methods often cannot respond flexibly. The introduction of the A3C algorithm can gradually optimize the strategy in the process of interaction with the market through its reinforcement learning characteristics, and adjust the decision according to the real-time feedback of the market, which has stronger adaptability and flexibility [
7]. In this context, A3C algorithm provides a new idea for financial risk management.
In addition to predicting market turbulence, risk control remains crucial in finance. Traditional approaches that rely on historical data and risk metrics often struggle with sudden market swings and rare events. An A3C-based risk strategy can dynamically adjust portfolios and exposures, mitigating losses through rapid responses. By simulating multiple market scenarios, A3C learns optimal strategies that boost system stability. Optimizing the A3C architecture for financial contexts thus stands as a key focus in advancing market resilience.
2. Related Work
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has shown strong potential for financial market prediction and risk control due to its ability to continuously learn and adapt in complex, dynamic environments. The A3C algorithm, as an advanced actor-critic framework, combines value estimation and policy optimization, making it particularly effective for high-dimensional financial data and non-stationary markets. Yao [
8] applied nested reinforcement learning to dynamic risk control tasks, demonstrating the value of multi-level decision-making strategies that improve adaptability in rapidly changing financial markets. This hierarchical approach offers important insights for enhancing turbulence prediction and risk control models.
To further improve model adaptability, Wu et al. [
9] proposed an improved BERT model that integrates adaptive attention mechanisms and feature embeddings to better capture key information in high-dimensional environments. These techniques are highly valuable for financial market prediction, where the ability to focus on critical signals—such as volatility surges or economic shocks—can significantly enhance prediction accuracy. Hybrid modeling strategies also contribute to improving forecasting precision in complex environments. Deng [
10] combined association rules with LSTM networks to improve spatiotemporal forecasting, illustrating how integrating statistical pattern mining with deep sequence learning can improve both interpretability and performance. This hybrid approach is particularly relevant when designing turbulence prediction models capable of capturing both historical trends and real-time anomalies.
Handling sparse or unbalanced data is another critical challenge in financial risk control, especially when predicting rare turbulence events. Gao et al. [
11] applied transfer learning and meta-learning techniques to few-shot text classification, offering valuable strategies for enhancing model generalization with limited labeled data—a problem highly relevant for rare market disruptions. Similarly, Du et al. [
12] proposed a structured reasoning framework that leverages probabilistic modeling to improve classification under imbalance, providing a methodological foundation for improving how reinforcement learning agents weigh rare but high-impact market events. Adaptive learning frameworks have also proven effective in dynamic financial contexts. Long et al. [
13] introduced an adaptive sequence network for evolving transaction patterns, showing the benefits of continuously adjusting to new data. Combined with real-time data streams, such adaptability is crucial for reinforcement learning agents tasked with market risk control.
In addition to these core techniques, data fusion and representation learning are becoming increasingly important for improving financial modeling. Hu et al. [
14] applied contrastive learning to enhance cold-start recommendations through adaptive feature fusion, a strategy that can be extended to financial data by combining price, sentiment, and macroeconomic indicators into richer state representations. Similarly, Liao et al. [
15] explored fine-tuning strategies with knowledge graphs to incorporate domain-specific knowledge into pre-trained models, which can enhance the contextual awareness of reinforcement learning agents in financial environments. While some works focus on other application areas, the underlying methods contribute useful techniques. Wang et al. [
16] demonstrated how deep learning can effectively handle complex feature spaces in quality assessment tasks, while Du [
17] applied convolutional networks to anomaly detection in financial statements, highlighting the broader value of deep feature extraction techniques. These foundational methods support the development of more robust financial market prediction and risk control systems.
Collectively, these works provide important methodological building blocks that contribute to the development of the proposed improved A3C-based model, supporting its enhanced ability to predict turbulence, dynamically control risk, and adapt to evolving financial conditions.
3. Method
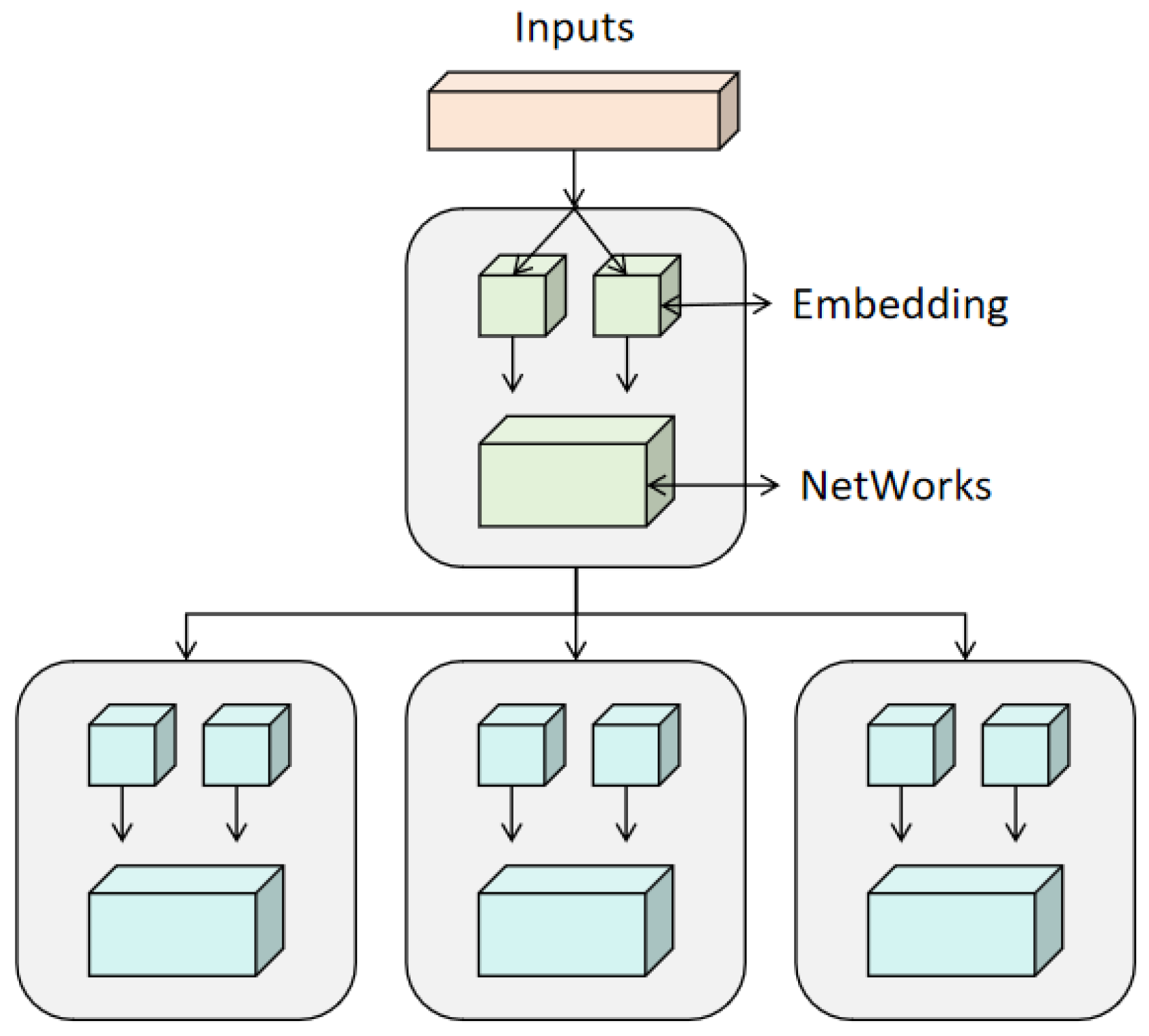
In this study, the A3C (Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic) algorithm is used to build a market turbulence prediction and risk control model. The A3C algorithm is an algorithm based on reinforcement learning, which combines the policy gradient method and the value function method. It uses multiple parallel agents to independently learn in different environments and finally converge the results, solving the stability problem in traditional reinforcement learning methods [
18]. Specifically, the A3C algorithm continuously updates the strategy and value function to learn the optimal control strategy to achieve the goal of predicting market turbulence and controlling risks. Its specific architecture is shown in
Figure 1.
First of all, the basic framework of reinforcement learning is to learn through the interaction between the agent and the environment. The goal of the agent is to learn the optimal strategy by maximizing the accumulated returns. In the problem of market turbulence prediction and risk control, the agent can be regarded as an investor or trading system, and the environment is the market itself. The market state can be described by a set of historical data, such as stock prices, trading volumes, volatility, interest rates, etc. The agent observes these market states, takes a series of actions, and obtains reward signals based on market feedback.
The core idea of the A3C algorithm is to simultaneously learn the policy function (Actor) [
19] and the value function (Critic) through the "Actor-Critic" architecture [
20]. Specifically, assuming that at a certain moment, the state of the environment is
, the agent selects action
according to the current strategy, and obtains reward
and a new state
after executing the action in the environment. Through this process, the goal of the agent is to maximize the total reward it obtains. The total reward can be represented by the cumulative discounted reward, recorded as:
Among them, is the discount factor, which controls the degree of attenuation of future rewards.
In the A3C algorithm, the role of the Critic is to guide the Actor's strategy optimization by estimating the value function
in the current state. The value function
refers to the expected total reward that can be obtained by executing the current strategy in state
. The Critic updates the value function through the following error:
Among them, is called TD error, which represents the deviation of the current value function estimate. The goal of Critic is to minimize this error, so as to make the value function more accurate.
On the other hand, the goal of the Actor is to adjust the strategy
so that the agent can choose the best action in each state. The Actor updates the strategy by maximizing the expected return, which can be achieved through the policy gradient method. The calculation of the policy gradient can be expressed as:
Among them, represents the probability distribution of selecting action given state , is the parameter of the policy network, and is the TD error calculated by the Critic. Through this gradient update, the Actor can gradually adjust the strategy so that the agent can learn the optimal behavior in long-term interaction.
In order to improve the training efficiency and stability of the A3C algorithm, A3C adopts a parallel training mechanism. Multiple agents are trained independently in different copies of the environment, sharing global parameters with each other. This parallel training method can significantly accelerate the convergence of the algorithm and avoid the problem of falling into local optimality that a single agent may encounter during training. Specifically, multiple agents update parameters through local networks and synchronize the updated results to the global network, thereby accelerating the learning process of the model.
In practical applications, the prediction and risk control of market turbulence not only rely on historical market data but also need to account for the nonlinear characteristics and complex dynamic changes of the market. Therefore, during the training process, in addition to traditional basic information such as stock market prices and trading volumes, some derivative indicators such as the volatility index, macroeconomic data, policy changes, etc., can also be introduced to enhance the model’s ability to capture market sentiment and risks. At the same time, when faced with a variety of risk control strategies, the A3C algorithm can effectively process large-scale data and self-regulate in complex environments, broadening its application prospects in financial risk management.
Finally, when predicting market turmoil and controlling risks, the A3C algorithm needs to be trained with a large amount of historical data so that the agent can identify the pattern of market fluctuations and take effective risk-hedging measures. During the training process, the agent adjusts its strategy through continuous interaction and feedback so that it can perform efficient risk control in a real market environment. Through the A3C algorithm, financial institutions can obtain more accurate market forecasts and then take flexible risk control measures to reduce the impact of market turmoil on investment portfolios and improve the robustness and return level of overall assets.
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
The financial market dataset used in this study is "Yahoo Finance Stock Market Data", which contains historical trading data of multiple stock markets, including daily opening price, closing price, highest price, lowest price, trading volume, and other information. The dataset covers multiple financial markets and provides long-term historical data, which is suitable for tasks such as market trend analysis and volatility prediction. The source of the dataset is Yahoo Finance, which is widely used in research and model testing in the financial field and has good openness and credibility. In this study, the stock market price, trading volume and other technical indicators in the dataset are mainly used as input features, combined with the occurrence of market turmoil, to train the prediction and risk control model based on the A3C algorithm. This dataset can provide us with enough historical data to support deep learning and analysis of market dynamics, and has strong representativeness and practicality.
4.2. Experimental Results
In this study, we conducted comparative experiments to validate the effectiveness of the market turbulence prediction and risk control model based on the enhanced A3C algorithm. Specifically, we selected Q-learning, Deep Q-Network (DQN), and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) as comparison models. These algorithms are fundamental reinforcement learning techniques and are widely utilized in diverse tasks. Q-learning is a discrete state space reinforcement learning algorithm based on the value function, suitable for relatively simple environments. DQN addresses the challenges encountered by Q-learning in high-dimensional spaces by incorporating deep neural networks, enabling it to handle more complex tasks. PPO is an algorithm based on policy gradients that enhances learning stability by limiting the magnitude of policy updates. By comparing these models with the A3C algorithm, we can comprehensively assess its performance in market turbulence prediction and risk control, thereby verifying its advantages and potential in practical applications. The experimental results are presented in
Table 1.
From the experimental results, it is evident that the model proposed in this paper outperforms all other compared models, particularly in critical indicators such as average return, convergence speed, and optimal risk control accuracy. Notably, the average return of the proposed model achieved 45.23, which is substantially higher than that of DQN (40.18), PPO (42.31), and Q-learning (35.12). This demonstrates that the model exhibits superior capabilities in acquiring high-quality returns and demonstrating enhanced learning capabilities and strategy optimization effects.
In terms of convergence speed, the training steps of the proposed model are 350,000 steps, which is significantly lower than other models, especially the 500,000 steps of Q-learning. This shows that the model proposed in this paper can learn the optimal strategy faster, reduce training time, and improve training efficiency. This is very important in practical applications because the dynamic changes in the financial market require the model to be able to make effective decisions in a shorter period of time to avoid missing market opportunities due to too long training.
In addition, in terms of risk control accuracy, the model proposed in this paper achieved an optimal accuracy of 92.5%, which is also a significant advantage over other models. DQN and PPO achieved 89.2% and 91.1% accuracy respectively, while Q-learning achieved the lowest accuracy of 85.6%. This shows that the model proposed in this paper can respond to market fluctuations more accurately and effectively reduce potential risks when dynamically adjusting risk control strategies, further verifying its superiority in a complex financial environment. In summary, the model proposed in this paper shows strong capabilities in market turbulence prediction and risk control tasks and has higher practical value and application potential.
At the same time, we also conducted ablation experiments, and the experimental results are shown in
Table 2.
Gradually incorporating additional modules produces notable gains in performance. The baseline A3C model yields an average return of 38.12, converges at 400,000 steps, and achieves 83.7% risk control accuracy—indicating room for improvement. Adding a parallel mechanism raises the average return to 40.50, speeds convergence to 350,000 steps, and boosts accuracy to 85.4%. Introducing the advantage function further increases the average return to 42.13 and risk control accuracy to 88.2%, though convergence remains at 400,000 steps. These results confirm that combining both parallelization and the advantage function provides the most comprehensive performance.
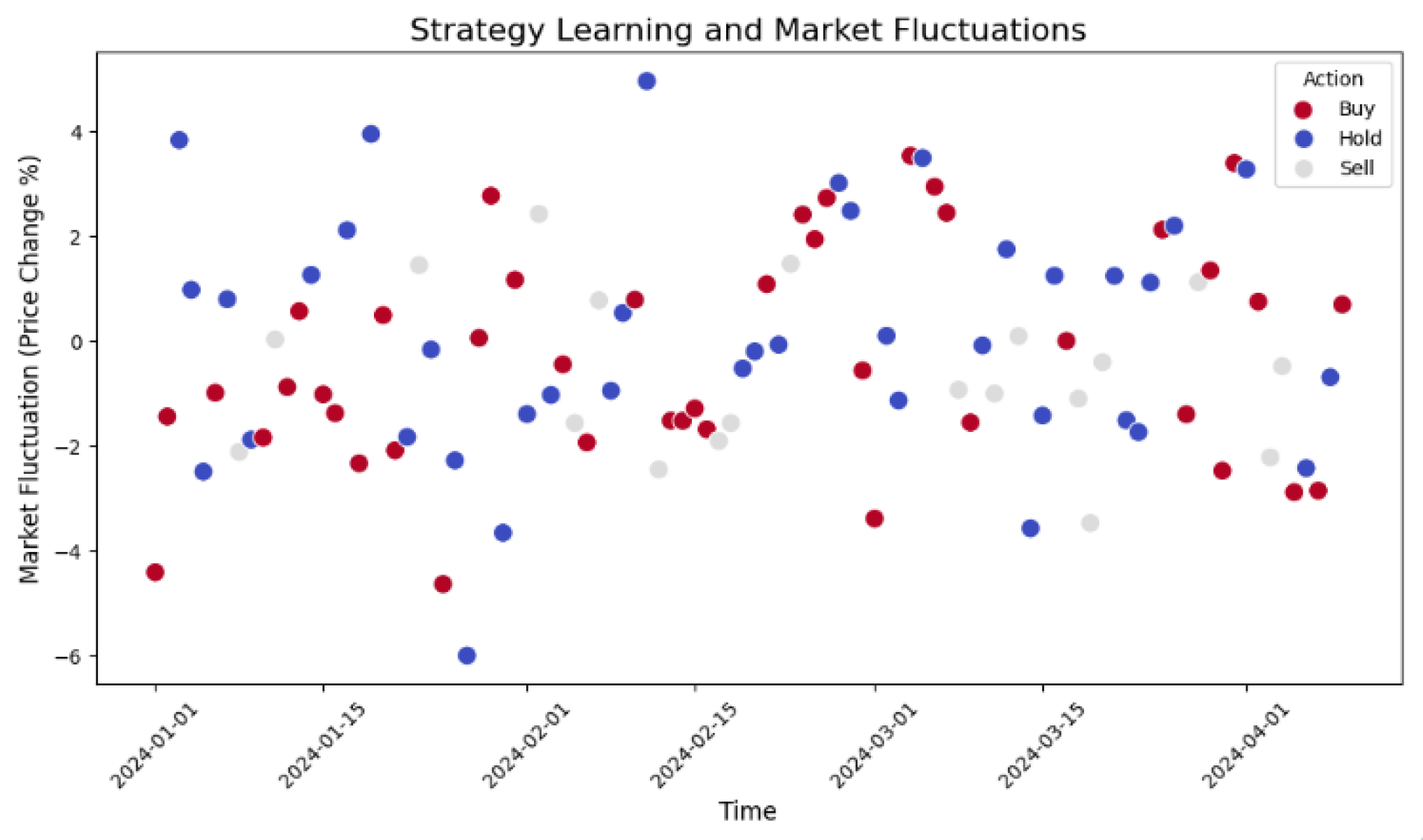
Figure 2 illustrates the relationship between strategy learning and market volatility.
From this figure, we can see the relationship between market volatility (percentage change in stock price) and strategy decisions (buy, sell, hold). The red dots in the figure represent buy actions, the blue dots represent sell actions, and the gray dots represent hold. The amplitude of market volatility varies greatly, which means that the risk of the market varies in different time periods. First, we can observe that the severity of market volatility affects the choice of strategy. For example, during periods of large market volatility, there may be more sell-and-buy decisions, while in more stable markets, the proportion of hold actions is higher. The distribution of points in the figure also shows that when the market fluctuates more, the model's decisions become more frequent, especially in time periods with large stock price changes. the model tends to adopt a buy or sell strategy, which may be to cope with sudden market risks.
In addition, the fluctuation of market risk not only affects the frequency of strategy decisions but also affects the execution effect of the strategy. In some periods of large volatility, investors or models may be more inclined to adopt defensive strategies (such as selling or holding) to reduce possible losses. Conversely, when the market volatility is small or the stock price is stable, the model may be more inclined to adopt offensive strategies (such as buying), expecting to gain more benefits in a stable market environment. This risk management strategy is critical in practical financial decision-making, especially when dealing with market uncertainties.
5. Conclusions
Through the market turbulence prediction and risk control model based on the A3C algorithm proposed in this paper, we verified the effectiveness of the model in dealing with complex financial market environments. Experimental results show that the model proposed in this paper outperforms traditional reinforcement learning methods in multiple indicators, especially in prediction accuracy, risk control accuracy and convergence speed. This proves that deep reinforcement learning, especially the A3C algorithm, can effectively cope with the nonlinear characteristics and dynamic changes of the market and become an important tool in financial risk management.
Despite certain successes, there are still some challenges and room for improvement. Future research can further optimize the structure of the model, such as by introducing more market factors and macroeconomic indicators to enhance the model's predictive ability. In addition, with the continuous development of the financial market, the uncertainty and complexity of the market are also increasing. Therefore, the model needs to constantly adapt to the new market environment, especially in the face of extreme market fluctuations, how to improve the robustness and stability of the model is still an urgent problem to be solved.
Looking forward to the future, the market turbulence prediction and risk control model based on the A3C algorithm has broad application prospects. With the continuous advancement of deep learning and reinforcement learning technology, the application scope of the model can be further expanded in the future, such as combining real-time market data for online learning, or combining multiple machine learning algorithms to improve the comprehensive performance of the model. As financial technology continues to develop, using advanced artificial intelligence technology to accurately predict market turmoil and control risks will provide financial institutions and investors with more accurate decision-making support, thereby enhancing the stability and risk resistance of the entire financial system.
References
- J. Gao, et al., “Intelligent decision making and risk management in stock index futures markets under the influence of global geopolitical volatility”, Omega, p. 103272, 2025.
- P. K. Nagula and C. Alexakis, “Forecasting natural gas futures prices using hybrid machine learning models during turbulent market conditions: The case of the Russian–Ukraine crisis”, Journal of Forecasting, 2025.
- X. Du, "Audit Fraud Detection via EfficiencyNet with Separable Convolution and Self-Attention", Proceedings of the 2025 Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 2, 2025.
- Y. Yao, "Stock Price Prediction Using an Improved Transformer Model: Capturing Temporal Dependencies and Multi-Dimensional Features", Proceedings of the 2024 Journal of Computer Science and Software Applications, vol. 5, no. 2, 2024.
- B. Iannone, P. Duttilo and S. A. Gattone, “Evaluating the resilience of ESG investments in European markets during turmoil periods”, Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Finance and Sustainability, 2025.
- B. Shinde, et al., “Behavioural finance and risk management: Navigating volatility in the Indian stock market with a focus on Bank Nifty”, Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Financial Risk and Behavioral Finance, 2025.
- J. Cao, R. Xu, X. Lin, F. Qin, Y. Peng and Y. Shao, "Adaptive Receptive Field U-Shaped Temporal Convolutional Network for Vulgar Action Segmentation," Neural Computing and Applications, vol. 35, no. 13, pp. 9593-9606, 2023.
- Y. Yao, “Time-Series Nested Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Risk Control in Nonlinear Financial Markets,” Proc. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 1, 2025.
- L. Wu, J. Gao, X. Liao, H. Zheng, J. Hu and R. Bao, “Adaptive Attention and Feature Embedding for Enhanced Entity Extraction Using an Improved Bert Model,” unpublished.
- Y. Deng, “A Hybrid Network Congestion Prediction Method Integrating Association Rules and LSTM for Enhanced Spatiotemporal Forecasting,” Proc. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods, vol. 5, no. 2, 2025.
- J. Gao, S. Lyu, G. Liu, B. Zhu, H. Zheng and X. Liao, “A Hybrid Model for Few-Shot Text Classification Using Transfer and Meta-Learning,” arXiv. arXiv:2502.09086.
- J. Du, S. Dou, B. Yang, J. Hu and T. An, “A Structured Reasoning Framework for Unbalanced Data Classification Using Probabilistic Models,” arXiv 2025. arXiv:2502.03386.
- S. Long, D. Yi, M. Jiang, M. Liu, G. Huang, and J. Du, “Adaptive Transaction Sequence Neural Network for Enhanced Money Laundering Detection,” in Proc. 2024 Int. Conf. Electronics and Devices, Computational Science (ICEDCS), pp. 447-451, 2024.
- J. Hu, T. An, Z. Yu, J. Du, and Y. Luo, “Contrastive Learning for Cold Start Recommendation with Adaptive Feature Fusion,” arXiv 2025. arXiv:2502.03664.
- X. Liao, B. Zhu, J. He, G. Liu, H. Zheng, and J. Gao, “A Fine-Tuning Approach for T5 Using Knowledge Graphs to Address Complex Tasks,” arXiv 2025. arXiv:2502.16484.
- S. Wang, R. Zhang, J. Du, R. Hao, and J. Hu, “A Deep Learning Approach to Interface Color Quality Assessment in HCI,” arXiv 2025. arXiv:2502.09914.
- X. Du, “Optimized Convolutional Neural Network for Intelligent Financial Statement Anomaly Detection,” Proc. Journal of Computer Technology and Software, vol. 3, no. 9, 2024.
- X. Yan, J. Du, L. Wang, Y. Liang, J. Hu and B. Wang, "The Synergistic Role of Deep Learning and Neural Architecture Search in Advancing Artificial Intelligence", Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Electronics and Devices, Computational Science (ICEDCS), pp. 452-456, Sep. 2024.
- Qin, Y. Shao, J. Cao, Y. Peng and R. Ge, "Fine-Grained Imbalanced Leukocyte Classification With Global-Local Attention Transformer," Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 35, no. 8, Article ID 101661, 2023.
- J. Wei, Y. Liu, X. Huang, X. Zhang, W. Liu and X. Yan, "Self-Supervised Graph Neural Networks for Enhanced Feature Extraction in Heterogeneous Information Networks", 2024 5th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computer Application (ICMLCA), pp. 272-276, 2024.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).